Combustion Inhibition of Aluminum–Methane–Air Flames by Fine NaCl Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Experimental Apparatus and Procedures
2.2. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.3. Structural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Characterization
3.2. Gas Flames (Validation Test)
3.3. Burning Velocities of the Aluminum/Methane/Air Hybrid Mixtures
3.4. Flame Appearance and Flame Front Formation
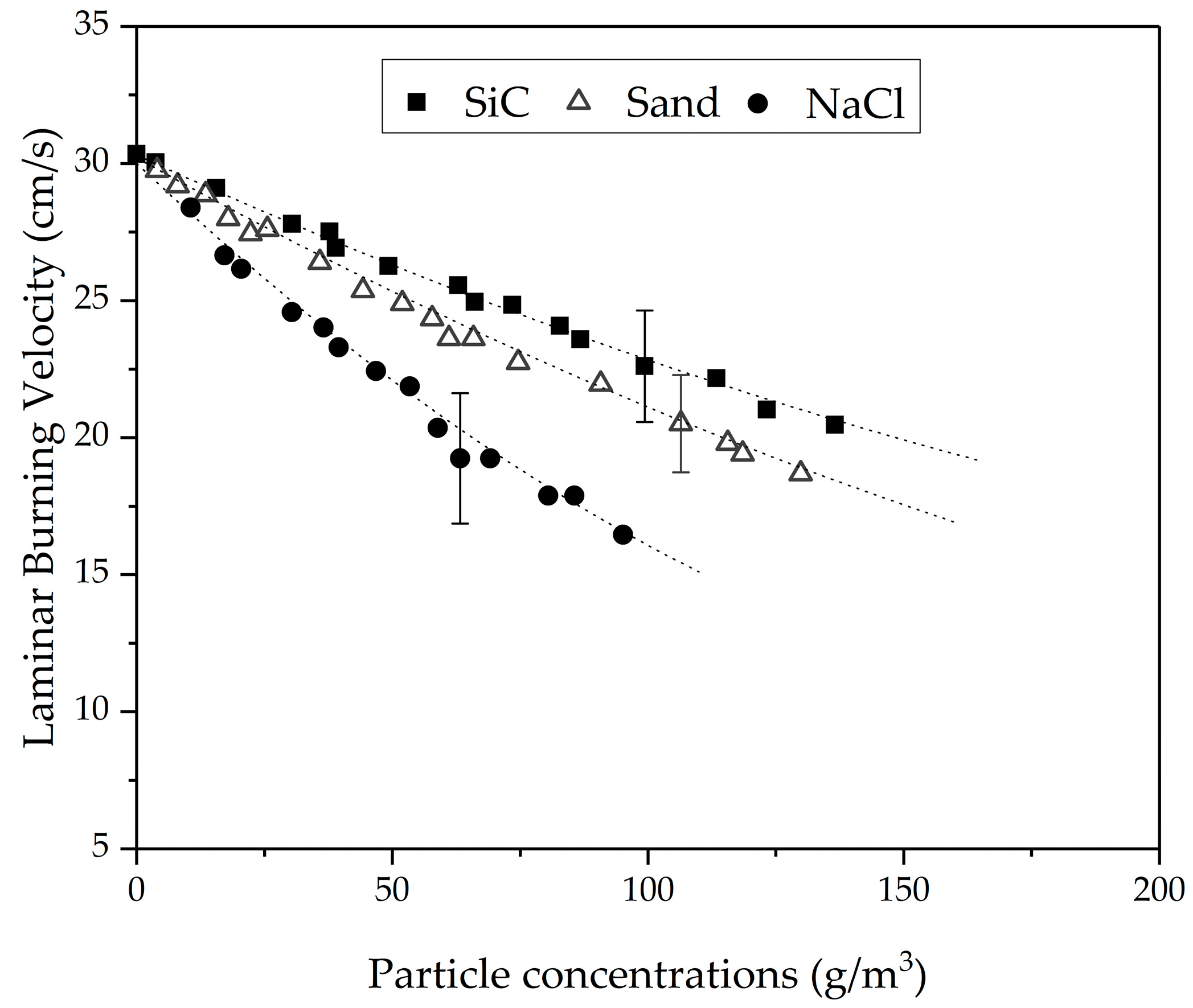
3.5. Burning Velocities of the Aluminum/Methane/Sodium Chloride/Air Hybrid Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouillard, J.; Vignes, A.; Dufaud, O.; Perrin, L.; Thomas, D. Ignition and explosion risks of nanopowders. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Yang, H.X.; Yuan, C.M.; Eckhoff, R.K. A catastrophic aluminium-alloy dust explosion in China. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 39, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Di Benedetto, A.; Sanchirico, R. Theoretical evaluation of the explosion regimes of hybrid mixtures. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2012, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ajrash, M.J.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. Effects of ignition energy on fire and explosion characteristics of dilute hybrid fuel in ventilation air methane. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 40, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Raghavan, V.; Rangwala, A.S. Study of interaction of entrained coal dust particles in lean methane–air premixed flames. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lin, B.; Dai, H.; Zhao, S. Explosion characteristics of H2/CH4/air and CH4/coal dust/air mixtures. Powder Technol. 2012, 229, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greatrix, D. Numerical Evaluation of the Use of Aluminum Particles for Enhancing Solid Rocket Motor Combustion Stability. Energies 2015, 8, 1195–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taveau, J.; Hochgreb, S.; Lemkowitz, S.; Roekaerts, D. Explosion hazards of aluminum finishing operations. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2018, 51, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.K. Combustion Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzi, E.; Frassoldati, A.; Grana, R.; Cuoci, A.; Faravelli, T.; Kelley, A.P.; Law, C.K. Hierarchical and comparative kinetic modeling of laminar flame speeds of hydrocarbon and oxygenated fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 468–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkevits, A.; Hoess, B. Hybrid H2/Al dust explosions in Siwek sphere. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2015, 36, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Bi, M.; Gao, W.; Gan, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q. Inhibition of aluminum dust explosion by NaHCO3 with different particle size distributions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taveau, J.; Vingerhoets, J.; Snoeys, J.; Going, J.; Farrell, T. Suppression of metal dust deflagrations. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2015, 36, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, T.; Mannan, M.S.; Petersen, E.L. Laminar flame speeds of nano-aluminum/methane hybrid mixtures. Combust. Flame 2016, 166, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julien, P.; Whiteley, S.; Soo, M.; Goroshin, S.; Frost, D.L.; Bergthorson, J.M. Flame speed measurements in aluminum suspensions using a counterflow burner. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Dames, E.; Wang, H.; Egolfopoulos, F.N. Propagation and extinction of benzene and alkylated benzene flames. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nativel, D.; Pelucchi, M.; Frassoldati, A.; Comandini, A.; Cuoci, A.; Ranzi, E.; Chaumeix, N.; Faravelli, T. Laminar flame speeds of pentanol isomers: An experimental and modeling study. Combust. Flame 2016, 166, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosschaart, K.J.; De Goey, L.P.H. Detailed analysis of the heat flux method for measuring burning velocities. Combust. Flame 2003, 132, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Lee, M.; Akkerman, V.; Rangwala, A.S. Suppression of premixed flames with inert particles. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2015, 35, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Petrow, D.; Rockwell, S.R.; Rangwala, A.S. Turbulent burning velocity of methane–air–dust premixed flames. Combust. Flame 2018, 188, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwell, S.R.; Rangwala, A.S. Influence of coal dust on premixed turbulent methane–air flames. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, N.; Chauveau, C.; Gökalp, I.; Lee, S.Y.; Santoro, R.J. Characterization of syngas laminar flames using the Bunsen burner configuration. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NPFA 484. In Standard for Combustion Metals; Naional Fire Protection Association: Quincy, MA, USA, 2009.
- Roberts, M.; Rogers, W.J.; Sam Mannan, M.; Ostrowski, S.W. Prevention and suppression of metal packing fires. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 104, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalosh, R. Metal hydride fires and fire suppression agents. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2008, 21, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ren, X. Combustion promotion and extinction of premixed counterflow methane/air flames by C6F12O fire suppressant. J. Fire Sci. 2016, 34, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Ren, X. Influence of Halon replacements on laminar flame speed and extinction stretch rate of hydrocarbon flames. Combust. Flame 2017, 182, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, G.J.; Calcote, H.F. Effect of molecular structure on burning velocity. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 1959, 4, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Kobayashi, H.; Niioka, T. Laminar burning velocity of hydrogen–air premixed flames at elevated pressure. Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci. 2000, 21, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagaut, P.; Karsenty, F.; Dayma, G.; Diévart, P.; Hadj-Ali, K.; Mzé-Ahmed, A.; Braun-Unkhoff, M.; Herzler, J.; Kathrotia, T.; Kick, T.; et al. Experimental and detailed kinetic model for the oxidation of a Gas to Liquid (GtL) jet fuel. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pareja, J.; Burbano, H.J.; Ogami, Y. Measurements of the laminar burning velocity of hydrogen–air premixed flames. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, J.; Lieuwen, T.; Seitzman, J. Laminar flame speeds of H2/CO mixtures: Effect of CO2 dilution, preheat temperature, and pressure. Combust. Flame 2007, 151, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapalme, D.; Seers, P. Influence of CO2, CH4, and initial temperature on H2/CO laminar flame speed. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.; Von Elbe, G. Combustions, Flames and Explosions of Gases, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mazas, A.N.; Fiorina, B.; Lacoste, D.A.; Schuller, T. Effects of water vapor addition on the laminar burning velocity of oxygen-enriched methane flames. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 2428–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Hui, S. Experimental study on the laminar flame speed of hydrogen/carbon monoxide/air mixtures. Fuel 2009, 88, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Ranganathan, S.; Rangwala, A.S. Influence of the reactant temperature on particle entrained laminar methane–air premixed flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2015, 35, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Kong, C.; Zong, Y.; Li, S.; Zhuo, J.; Yao, Q. Combustion of aluminum nanoparticle agglomerates: From mild oxidation to microexplosion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.J.; Haq, M.Z.; Lawes, M.; Woolley, R. Laminar burning velocity and markstein lengths of methane-air mixtures. Combust. Flame 2000, 121, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.I.; Aung, K.T.; Faeth, G.M. Measured and predicted properties of laminar premixed methane-air flames at various pressures. Combust. Flame 1998, 115, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenchan, G.; Zhu, D.L.; Law, C.K.; Tse, S.D. Outward propagation, burning velocities, and chemical effects of methane flames up to 60 atm. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2002, 29, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagelopoulos, C.M.; Egolfopoulos, F.N. Direct experimental determination of laminar flame speeds. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1998, 27, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosschaart, K.J.; De Goey, L.P.H. The laminar burning velocity of flames propagating in mixtures of hydrocarbons and air measured with the heat flux method. Combust. Flame 2004, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, M.; Julien, P.; Goroshin, S.; Bergthorson, J.M.; Frost, D.L. Stabilized flames in hybrid aluminum-methane-air mixtures. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Jiang, Y. Combustion Inhibition of Aluminum–Methane–Air Flames by Fine NaCl Particles. Energies 2018, 11, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113147
Xu W, Jiang Y. Combustion Inhibition of Aluminum–Methane–Air Flames by Fine NaCl Particles. Energies. 2018; 11(11):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113147
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wu, and Yong Jiang. 2018. "Combustion Inhibition of Aluminum–Methane–Air Flames by Fine NaCl Particles" Energies 11, no. 11: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113147
APA StyleXu, W., & Jiang, Y. (2018). Combustion Inhibition of Aluminum–Methane–Air Flames by Fine NaCl Particles. Energies, 11(11), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113147



