Simultaneous Extraction and Emulsification of Food Waste Liquefaction Bio-Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
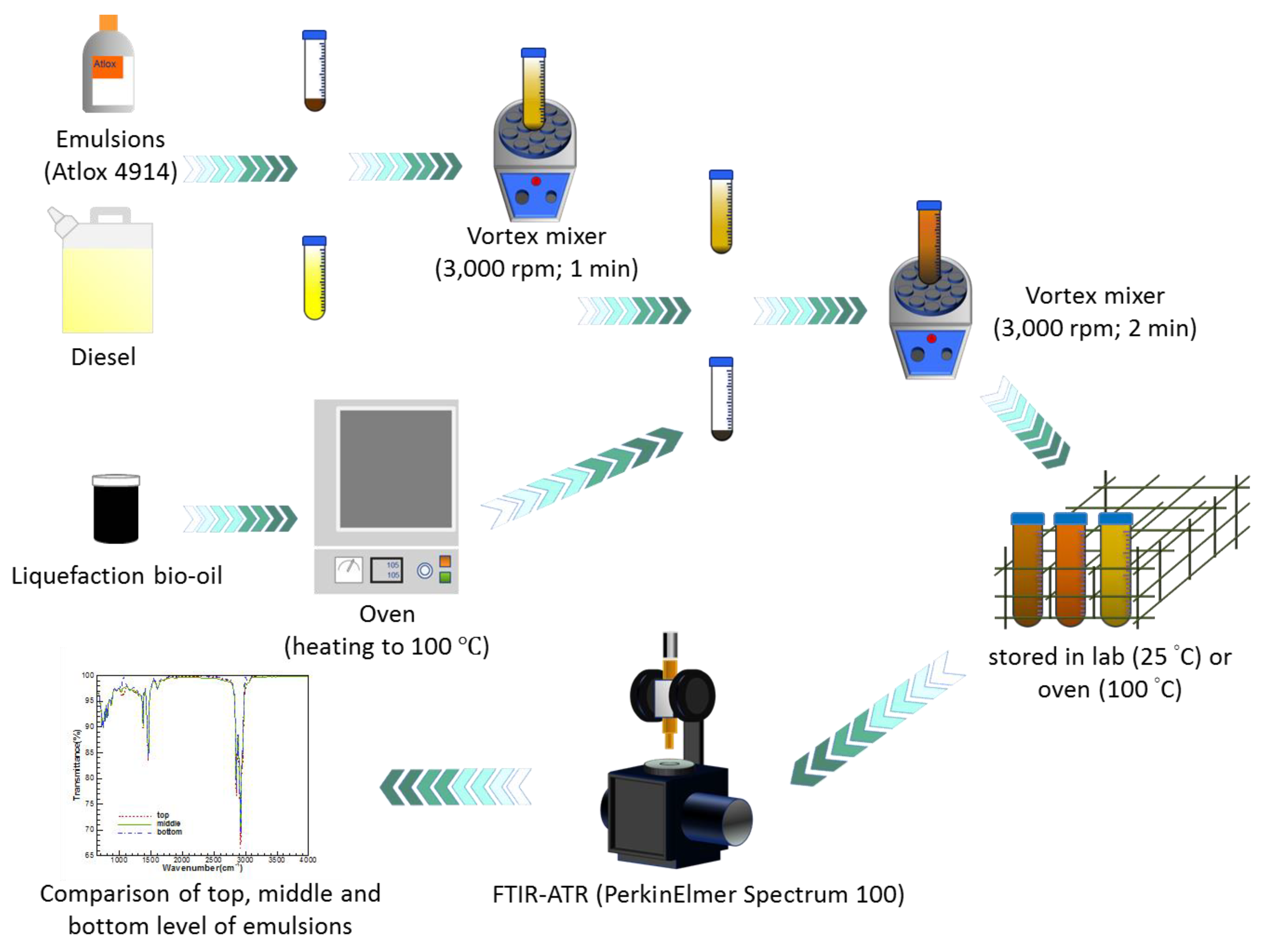
2.2. The Procedure for Preparing the Sample
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
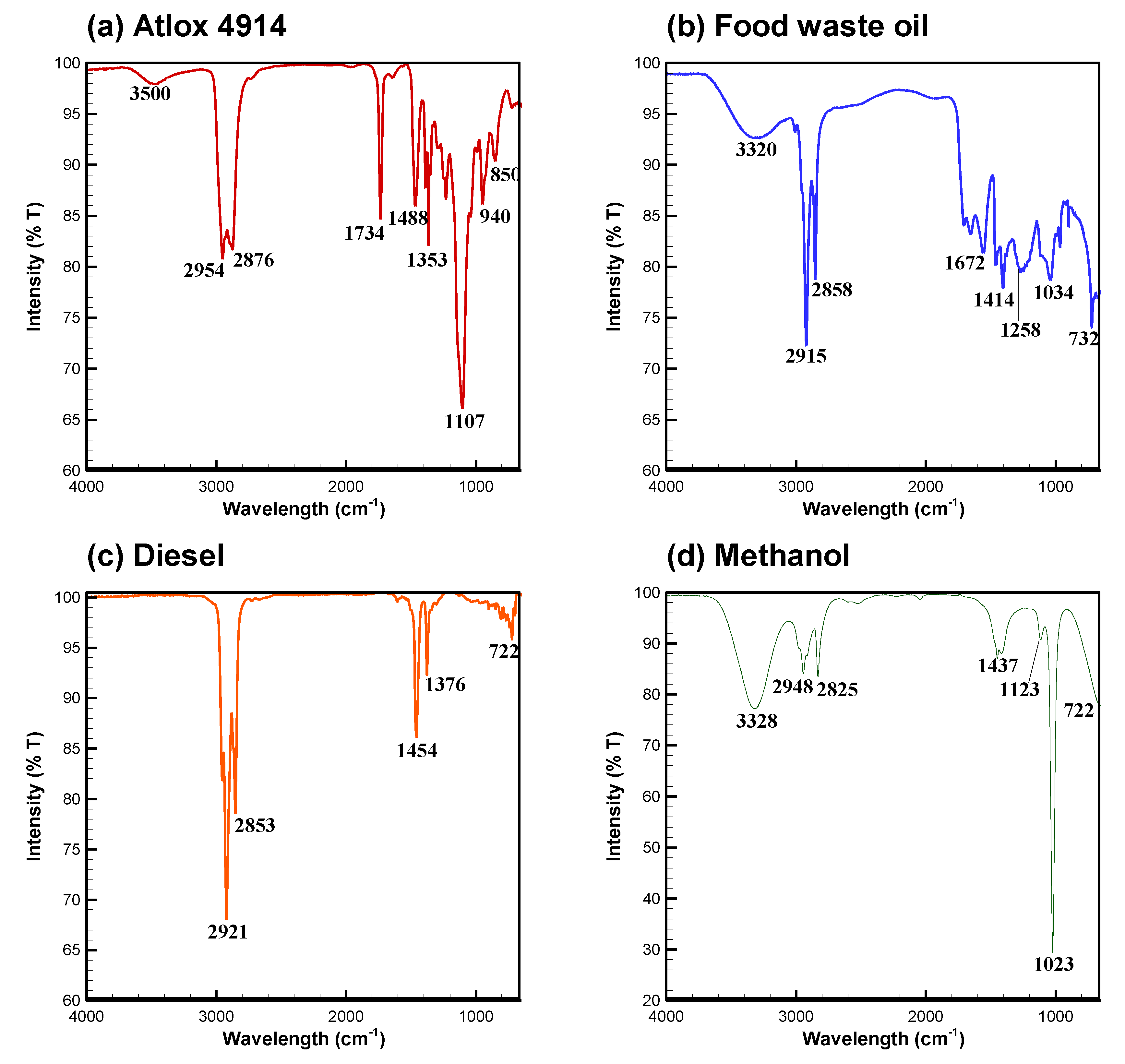
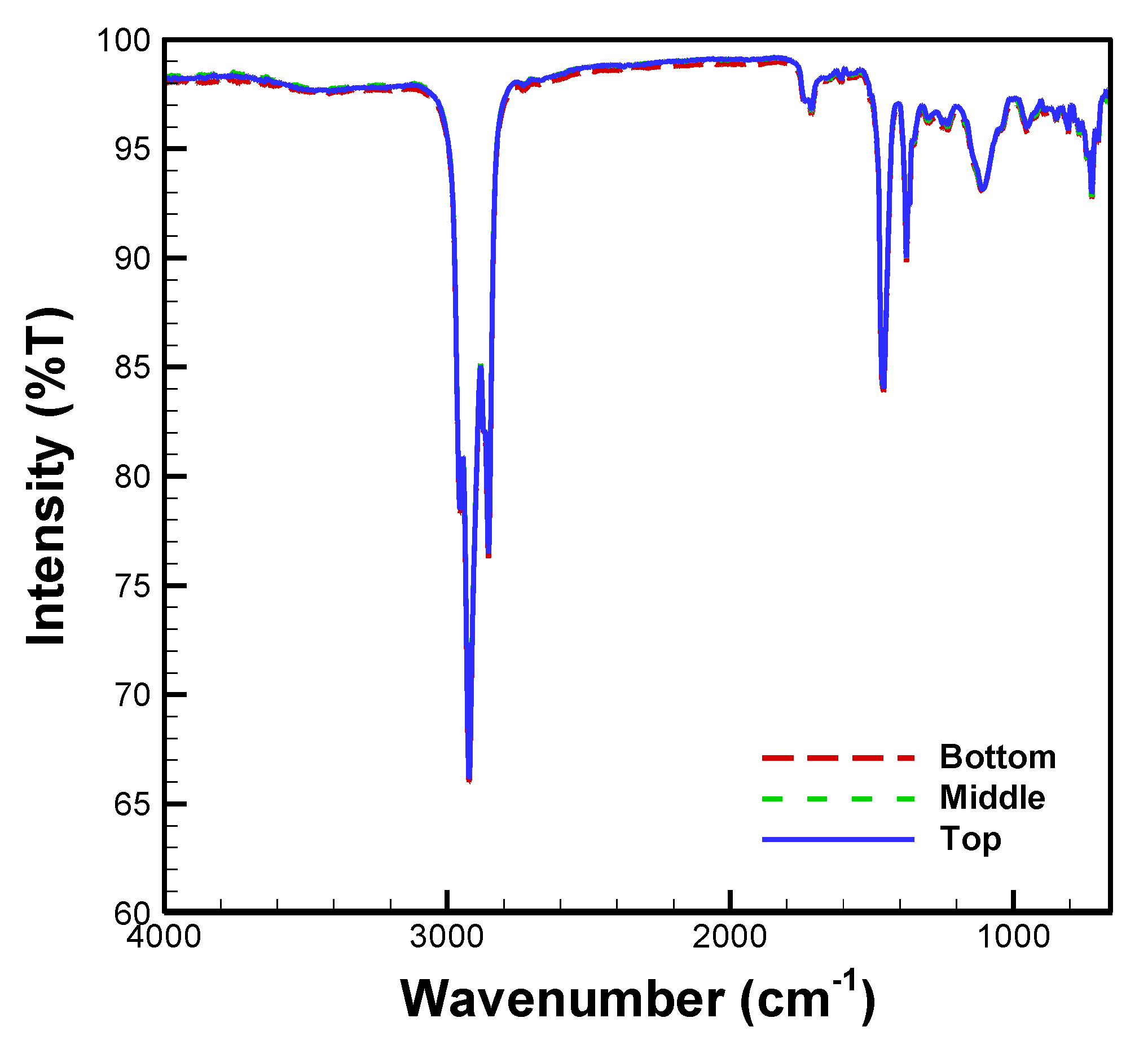
3.1. FTIR Spectra of Atlox, Bio-Oil, Diesel, and Methanol
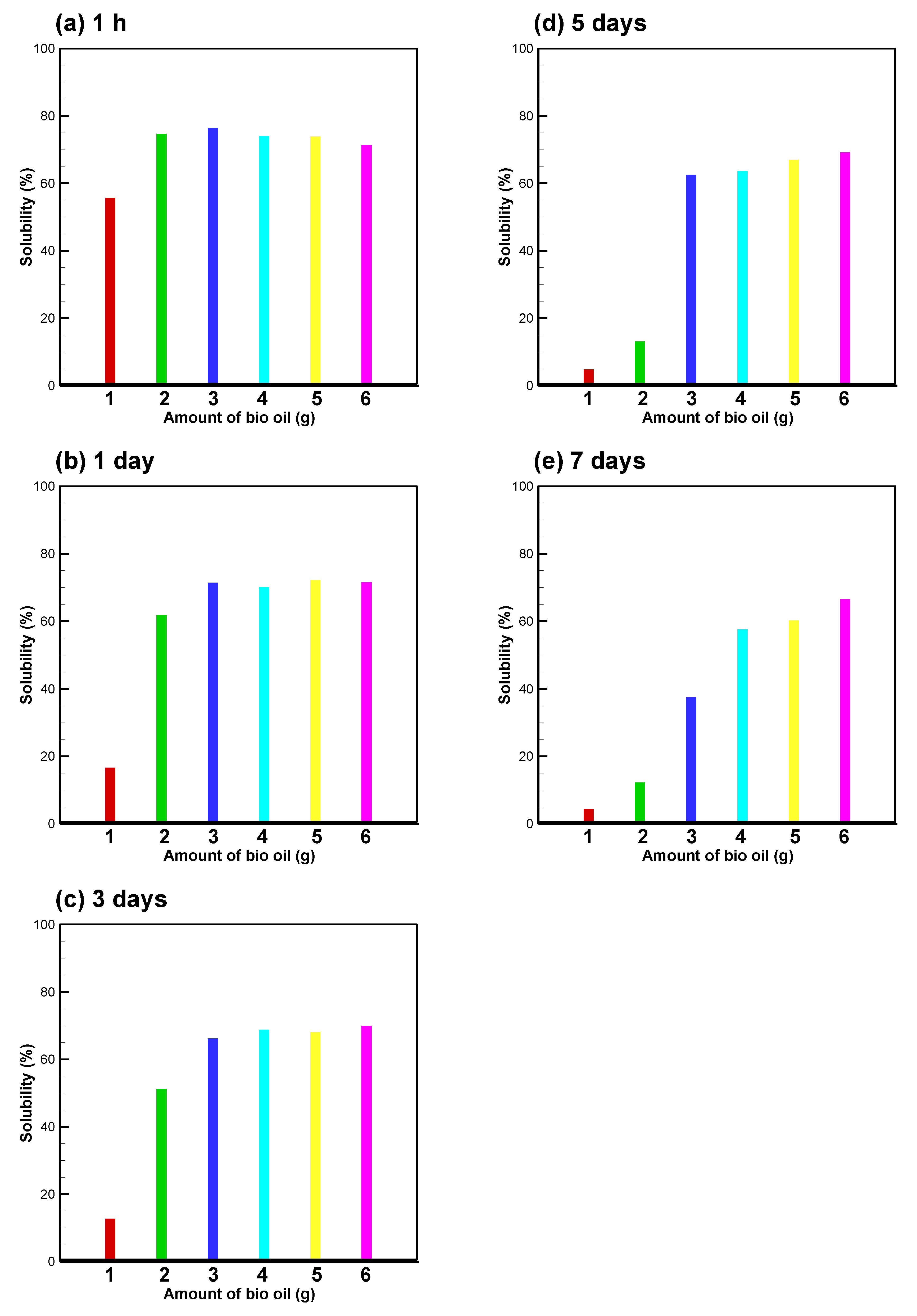
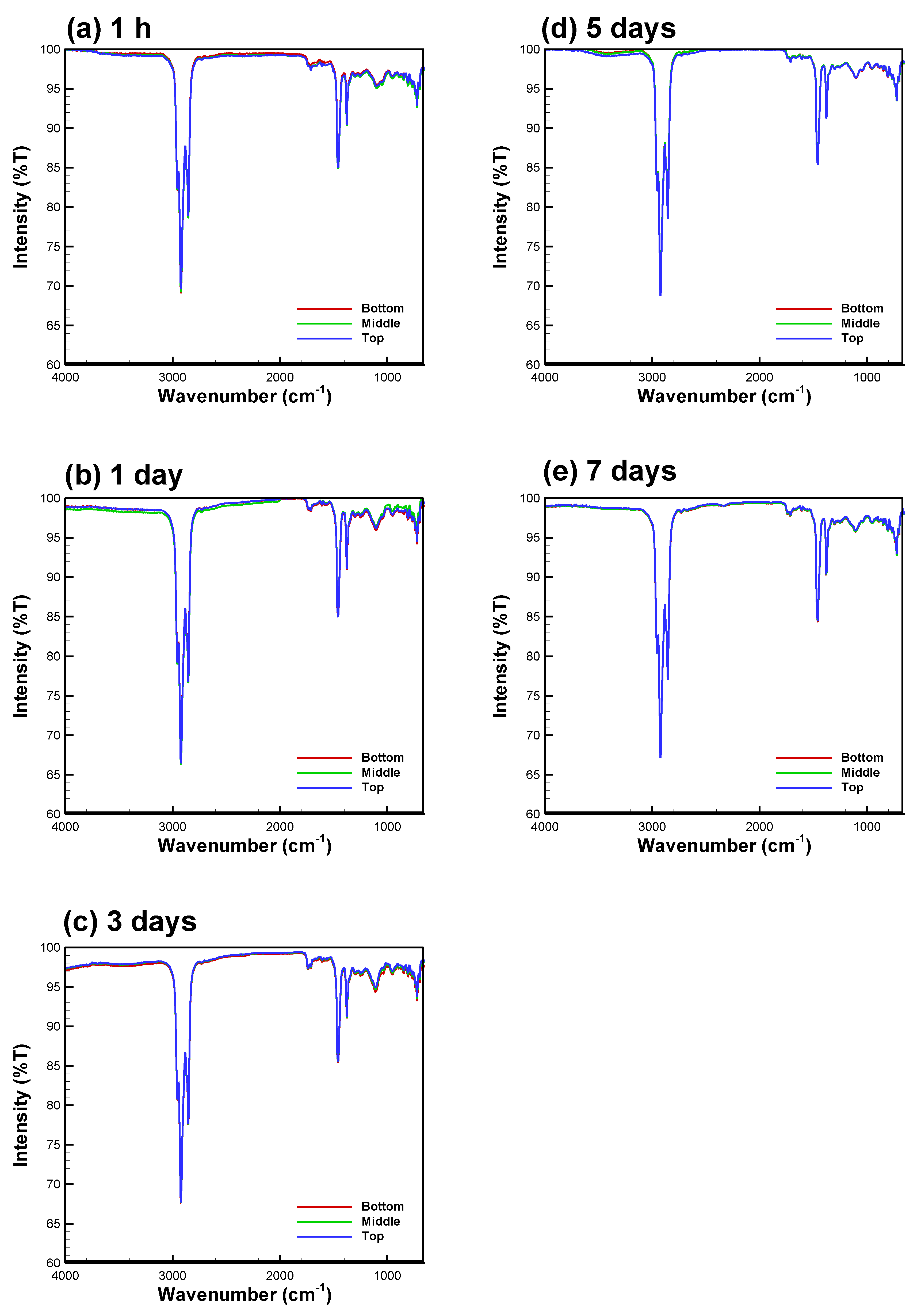
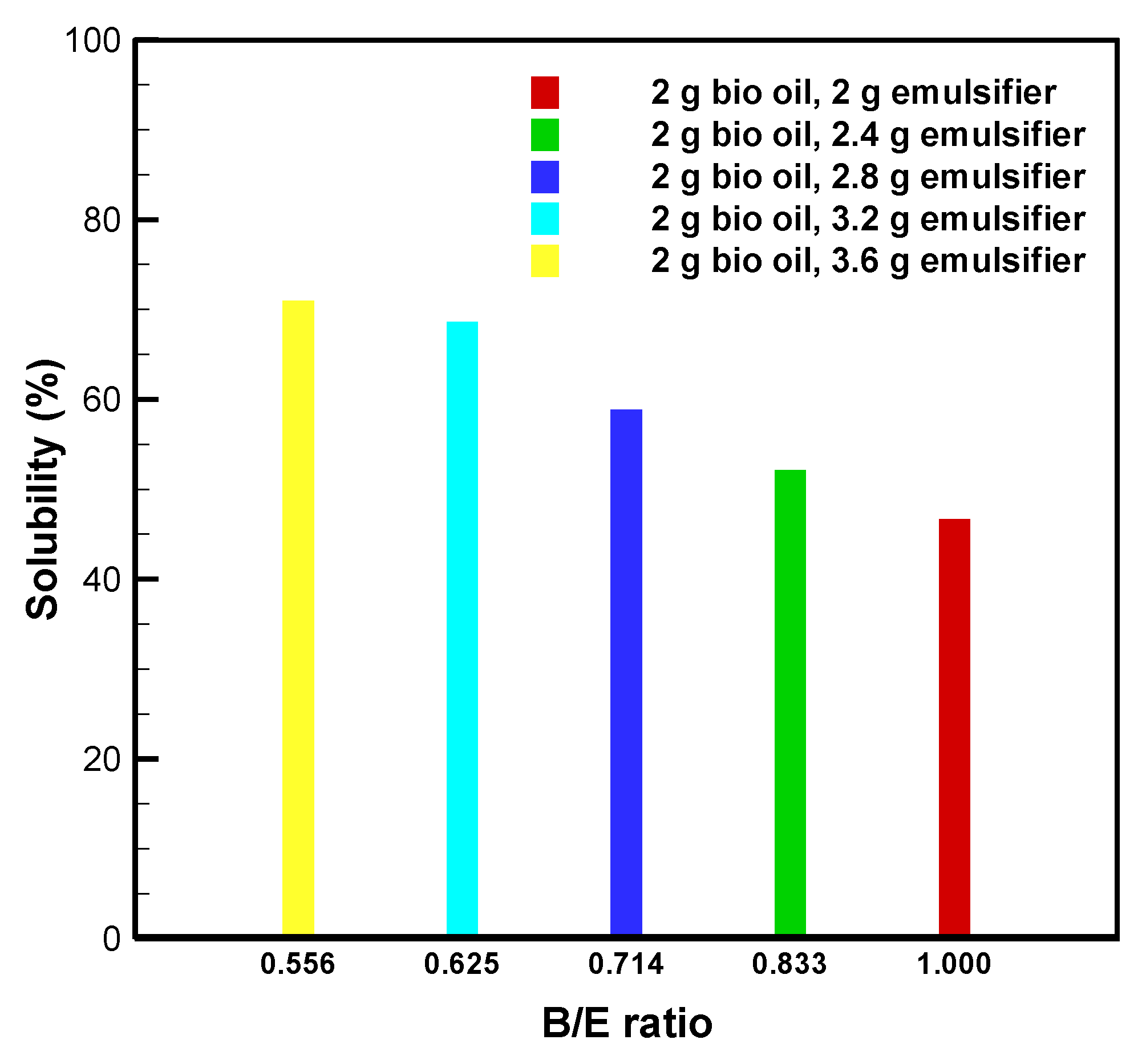
3.2. Bio-Oil Solubility and Emulsion Stability at B/E Ratio = 1
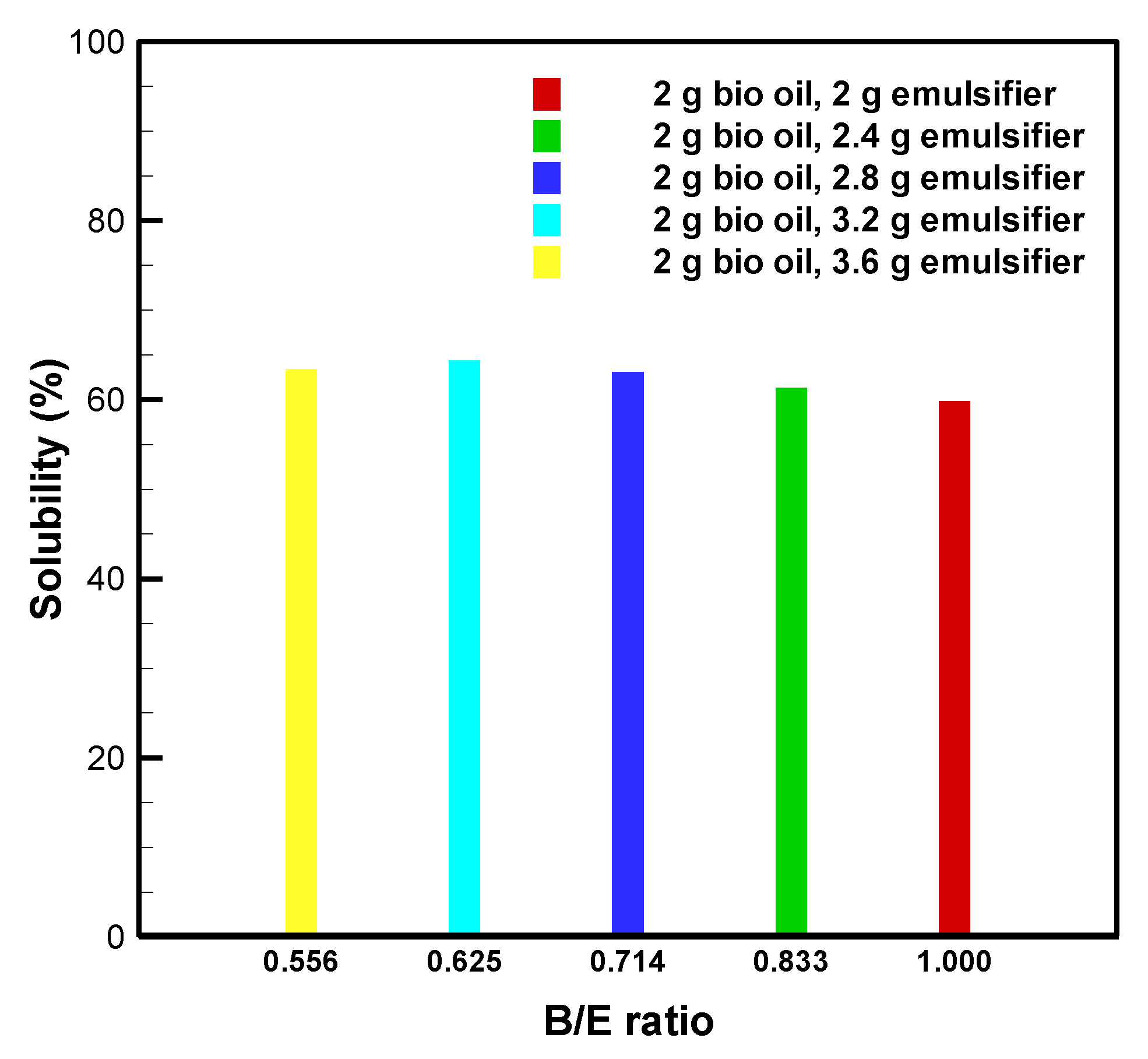
3.3. Bio-Oil Solubility at B/E Ratios between 0.556 and 1
3.4. Temperature Effect
3.5. Co-Surfactant (Methanol) Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kavitha, S.; Banu, J.R.; Priya, A.A.; Uan, D.K.; Yeom, I.T. Liquefaction of food waste and its impacts on anaerobic biodegradability, energy ratio and economic feasibility. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, Q.V.; Chen, W. A comprehensive study on pyrolysis kinetics of microalgal biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 131, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, C.J.; Hung, C.I.; Shen, C.H.; Hsu, H.W. A comparison of gasification phenomena among raw biomass, torrefied biomass and coal in an entrained-flow reactor. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, O.P.; Wong, S.M.J.W.C. Bio-refining of food waste for fuel and value products. In Proceedings of the 4th International conference on Energy and Environment Research (ICEER 2017), Porto, Portugal, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.K.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Mubofu, E.B.; Abderrahim, S. Food waste as a valuable resource for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels. Current situation and global perspective. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 426–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Lin, B.J.; Huang, M.Y.; Chang, J.S. Thermochemical conversion of microalgal biomass into biofuels: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, A.; Bezergianni, S. Hydrothermal liquefaction of various biomass and waste feedstocks for biocrude production: A state of the art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Long, J. Organosolv liquefaction of sugarcane bagasse catalyzed by acidic ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, M.; Golzary, A.; Hosseinpour, M.; Takahashi, F.; Yoshikawa, K. Catalytic hydrothermal liquefaction of microalgae using nanocatalyst. Appl. Energy 2016, 183, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollakota, A.R.K.; Kishore, N.; Gu, S. A review on hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, U.; Das, K.C.; Kastner, J.R. Effect of operating conditions of thermochemical liquefaction on biocrude production from Spirulina platensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6221–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.-J.; Chen, W.-H.; Budzianowski, W.M.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Lin, P.-H. Emulsification analysis of bio-oil and diesel under various combinations of emulsifiers. Appl. Energy 2016, 178, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.D.G.; Cruz, L.A.D.; Chen, W.-H.; Lin, B.-J.; Hsieh, T.-H. Improving the stability of diesel emulsions with high pyrolysis bio-oil content by alcohol co-surfactants and high shear mixing strategies. Energy 2017, 141, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikura, M.; Stanciulescu, M.; Hogan, E. Emulsification of pyrolysis derived bio-oil in diesel fuel. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 24, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonti, D.; Bonini, M.; Fratini, E.; Tondi, G.; Gartner, K.; Bridgwater, A.V.; Grimm, H.P.; Soldaini, I.; Webster, A.; Baglioni, P. Development of emulsions from biomass pyrolysis liquid and diesel and their use in engines—Part 1: Emulsion production. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 25, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Stability mechanism investigation of emulsion fuels from biomass pyrolysis oil and diesel. Energy 2014, 66, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, R.; Li, S.; Zeng, G. Characterization of liquefaction bio-oil from sewage sludge and its solubilization in diesel microemulsion. Energy 2015, 82, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; Hall, F.; Goetz, S.J. Importance of biomass in the global carbon cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114, G00E03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ellis, N. Upgrading Bio-oil through Emulsification with Biodiesel: Mixture Production. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zuo, C.; Tan, J.; He, J. Structural analysis of bio-oils from sub-and supercritical water liquefaction of woody biomass. Energy 2007, 32, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, B.D. A Handbook of Spectroscopic Data Chemistry; Oxford Book Company: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Assanvo, E.F.; Gogoi, P.; Dolui, S.K.; Baruah, S.D. Synthesis, characterization, and performance characteristics of alkyd resins based on Ricinodendron heudelotii oil and their blending with epoxy resins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65 (Suppl. C), 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, M.M.; Gogoi, P.; Deka, D.C.; Kakati, D.K. Synthesis and characterization of yellow oleander (Thevetia peruviana) seed oil-based alkyd resin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52 (Suppl. C), 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, V.; Fullana, A. Torrefaction of olive mill waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 73, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 1Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Firoozabadi, A. Effectiveness of Alcohol Cosurfactants in Hydrate Antiagglomeration. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 5626–5632. [Google Scholar]


| Pyrolysis Bio-Oil Content | Mixing Method | Emulsifier and Co-Surfactant | Stability | Ref. |
| 10–30 wt % | Micro-emulsifier (800–1750 rpm and 5–20 min) | Hypermer B246SF/2234 (Croda International) | 3 to 42 days | [14] |
| 25–75 wt % | Variable speed electrical motor (1100 W) | Polymeric surfactants/short chain additives (n-octanol) | 3 days | [15] |
| 10 wt % | Ultrasonic (20 kHz; 2 min) and Ultrasonic-mechanical (20 kHz; 2 min; and 5000 rpm; 5 min) | Span80 (sorbitan monooleate)/Tween 80 (Polyoxyethylenesorbitan monolaurate)/Span 85 (sorbitan trioleate) | 27 to 31 days | [16] |
| 2–40 wt % | Homogenizer (8800–16,700 rpm) | Span 80 (sorbitan monooleate)/Tween 80 (Polyoxyethylenesorbitan monolaurate) | 5 days | [18] |
| Liquefaction Bio-Oil Content | Mixing Method | Emulsifier or Co-Surfactant | Stability | Ref. |
| 5 wt % | Manual shaking (1 min) and centrifugation (6000 rpm; 20 min) | Span 80 (sorbitan monooleate) | - | [17] |
| 5 to 30 wt % | Vortex mixer (3000 rpm; 2 min) | Atlox4914 (Croda International)/Methanol | 7 days | This study |
| Compound | Density (kg m−3) | Viscosity (mPa s) | HHV (MJ kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bio-oil | 1100.0 | 4916 | 31.41 |
| Diesel | 832.0 | 1.6–5.8 | 44.80 |
| Atlox 4914 | 970.0 | - | 37.64 |
| Methanol | 791.0 | 0.533 | 20.40 |
| Wave Number Range (cm−1) | Functional Group | Mode of Vibration | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3550–3450 | Dimetric O-H | Stretching | [21] |
| 3400–3230 | Polymetric O-H | Stretching | [21] |
| 2949–2915 | Aliphatic C-H | Stretching | [21,22] |
| 2924–2858 | Aliphatic C-H | Stretching | [23] |
| 2835–2815 | CH3-O-CH3 (ethers) | Stretching | [21] |
| 1740–1732 | C=O (ester) | Stretching | [23] |
| 1651–1640 | C=C (aromatic) | Skeletal | [24] |
| 1652–1579 | C-C (ring) | Stretching | [21] |
| 1486–1446 | C-H- (CH3)/(CH2) | Symmetric Asymmetric | [24] |
| 1461–1377 | C-H- (CH3) | Symmetric | [24] |
| 1290–1211 | C-O | Stretching | [21] |
| 1230–1140 | C-O (phenol) | Stretching | [21] |
| 1239–1100 | C-O-C (ester) | Stretching | [22,23] |
| 1090–1049 | C-O | Stretching | [21] |
| 1043–1006 | C-O | Stretching | [24] |
| 970–960 | C=C-H | Bending | [21] |
| 730–710 | C-H-(CH2) | Bending | [21] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Längauer, D.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Wang, C.-W.; Šafář, M.; Čablík, V. Simultaneous Extraction and Emulsification of Food Waste Liquefaction Bio-Oil. Energies 2018, 11, 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113031
Längauer D, Lin Y-Y, Chen W-H, Wang C-W, Šafář M, Čablík V. Simultaneous Extraction and Emulsification of Food Waste Liquefaction Bio-Oil. Energies. 2018; 11(11):3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLängauer, David, Yu-Ying Lin, Wei-Hsin Chen, Chao-Wen Wang, Michal Šafář, and Vladimír Čablík. 2018. "Simultaneous Extraction and Emulsification of Food Waste Liquefaction Bio-Oil" Energies 11, no. 11: 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113031
APA StyleLängauer, D., Lin, Y.-Y., Chen, W.-H., Wang, C.-W., Šafář, M., & Čablík, V. (2018). Simultaneous Extraction and Emulsification of Food Waste Liquefaction Bio-Oil. Energies, 11(11), 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113031







