Risk-Based Probabilistic Voltage Stability Assessment in Uncertain Power System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Probabilistic Model of Wind Power Generation
3. Security Risk Evaluation of Voltage Stability Issues
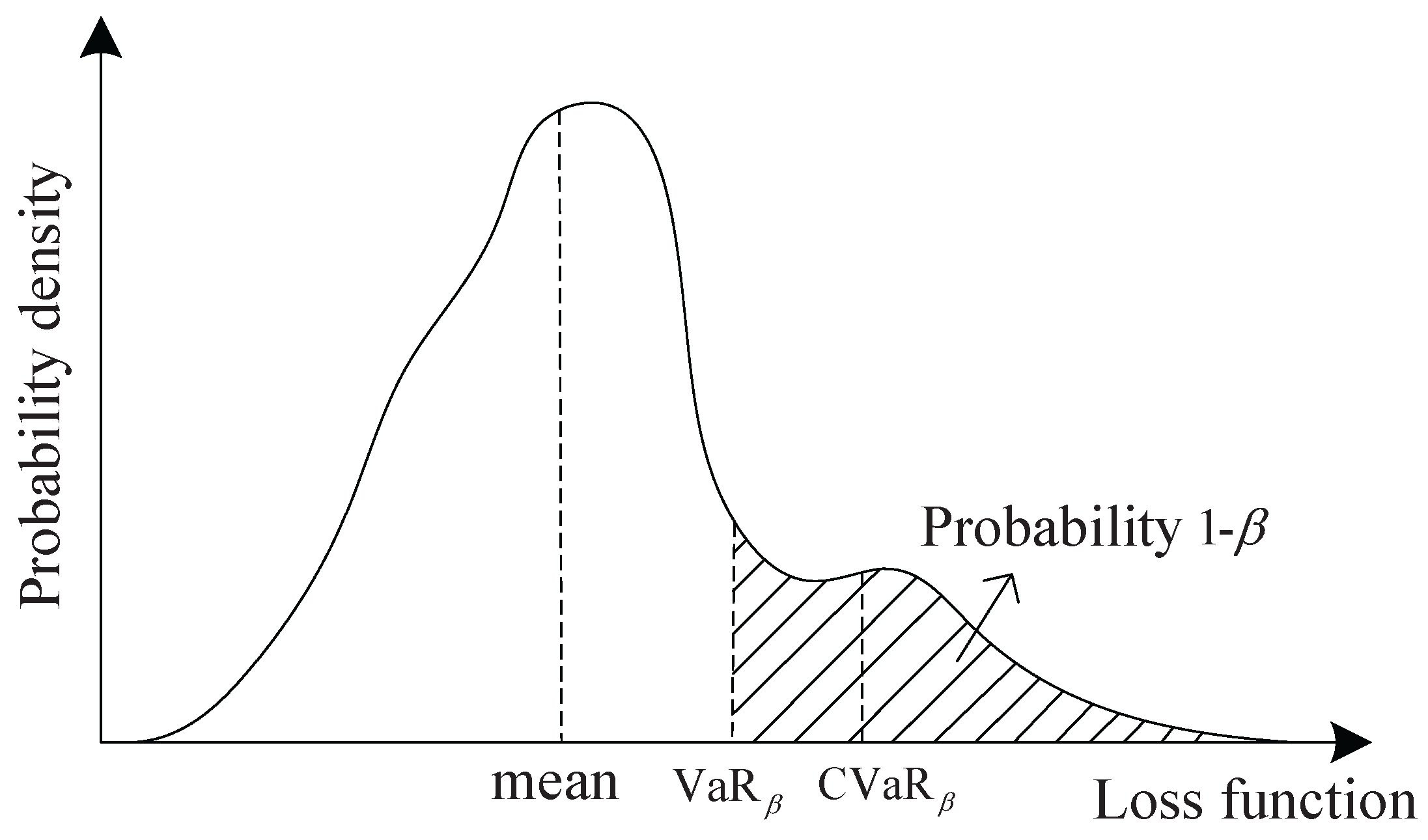
3.1. Definition of Conditional Value at Risk in Security Risk Evaluation
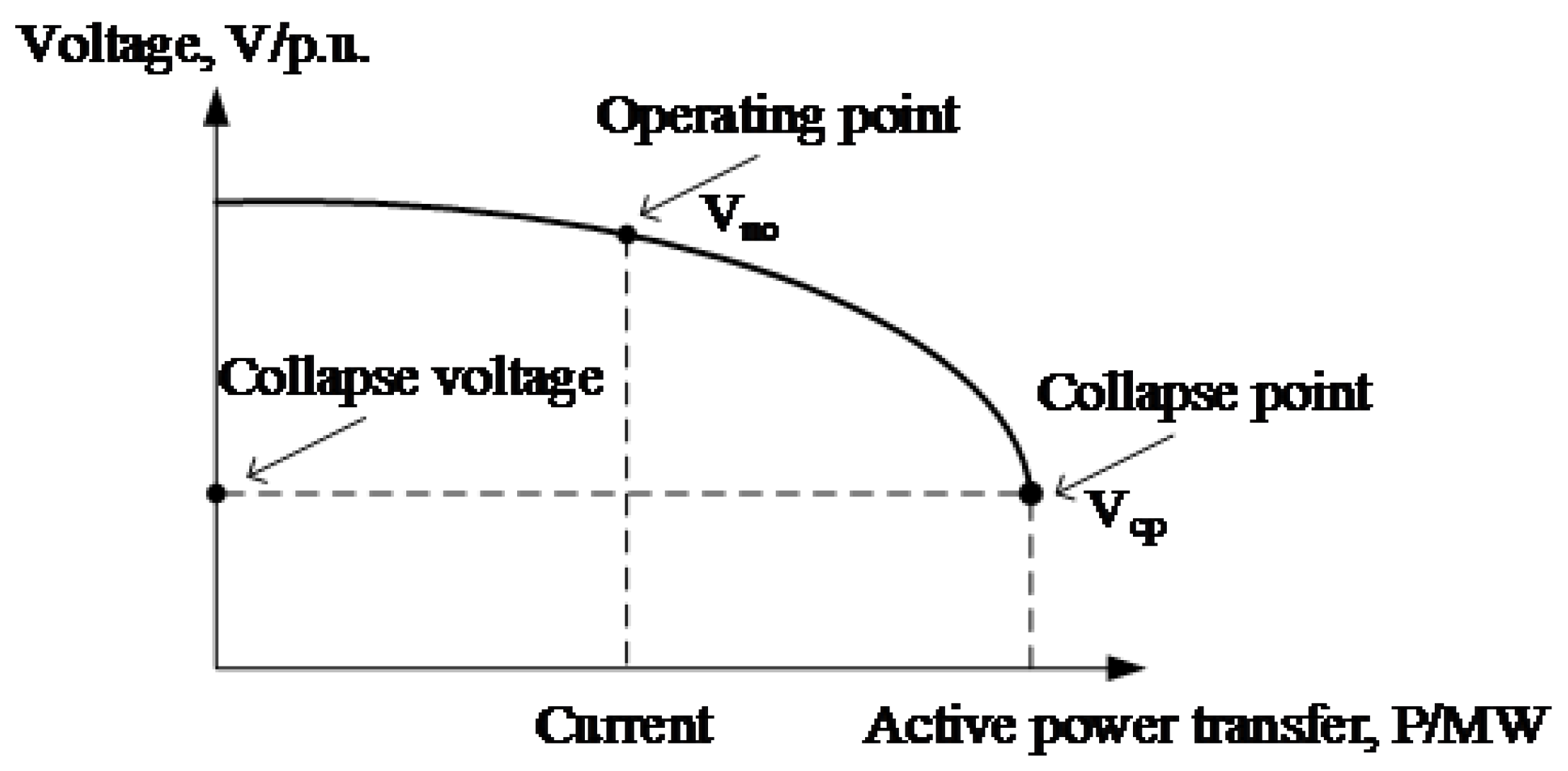
3.2. Index of Voltage Stability Margin Considering the Risk
4. A Quasi-Monte Carlo Simulation for Real-Time Probabilistic Voltage Forecast
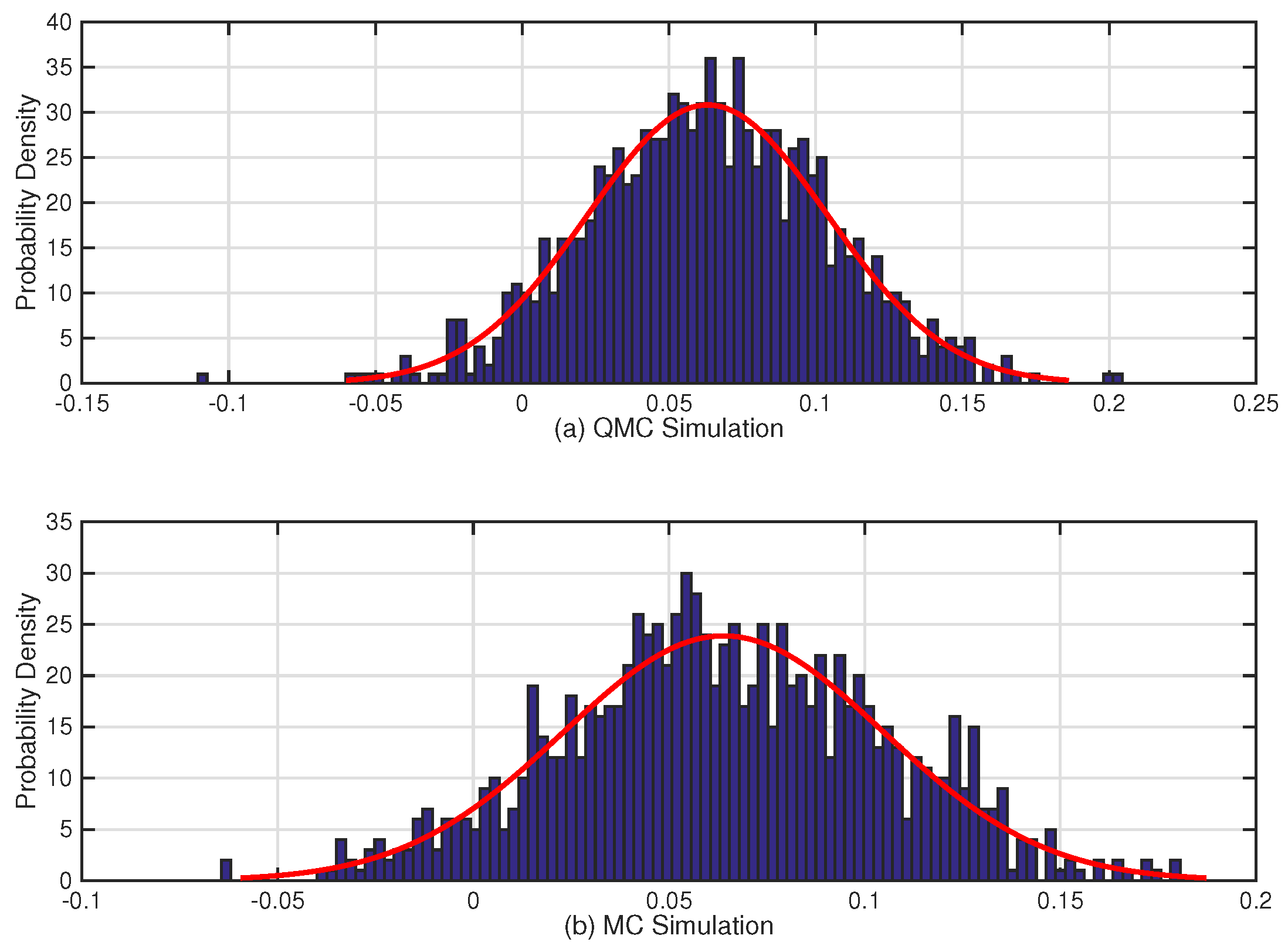
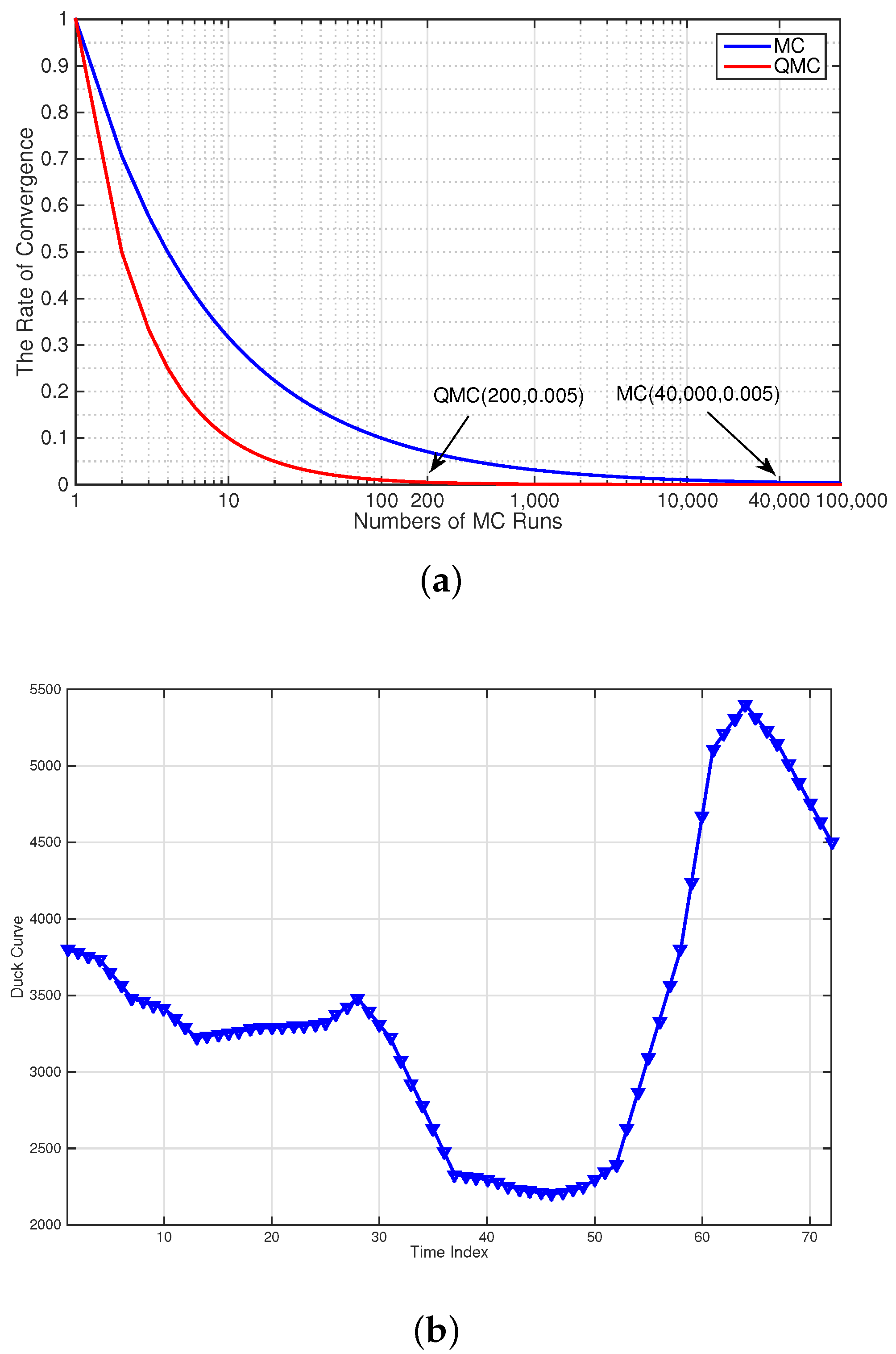
4.1. Quasi Monte Carlo Simulation
4.2. The Formulation of the Real-Time Voltage Forecast Problem
- (1)
- The intervals are disjoint. For all ;
- (2)
- The union of the intervals is a multi-dimensional integration over the entire m-dimensional unit hypercube .
4.3. The Process of the Proposed Algorithm
- (1)
- Obtain the wind power forecast error distribution based on historical data;
- (2)
- Obtain the PV curve and voltage collapse value through continues power flow;
- (3)
- Generate sample sets for the forecast time interval via the QMC algorithm;
- (4)
- Calculate to evaluate the tail risk of the voltage stability loss for each bus;
- (5)
- Calculate to evaluate the voltage stability level for the entire system;
- (6)
- Take the value of the weakest buses for further dispatch adjustment.
5. Results and Discussion
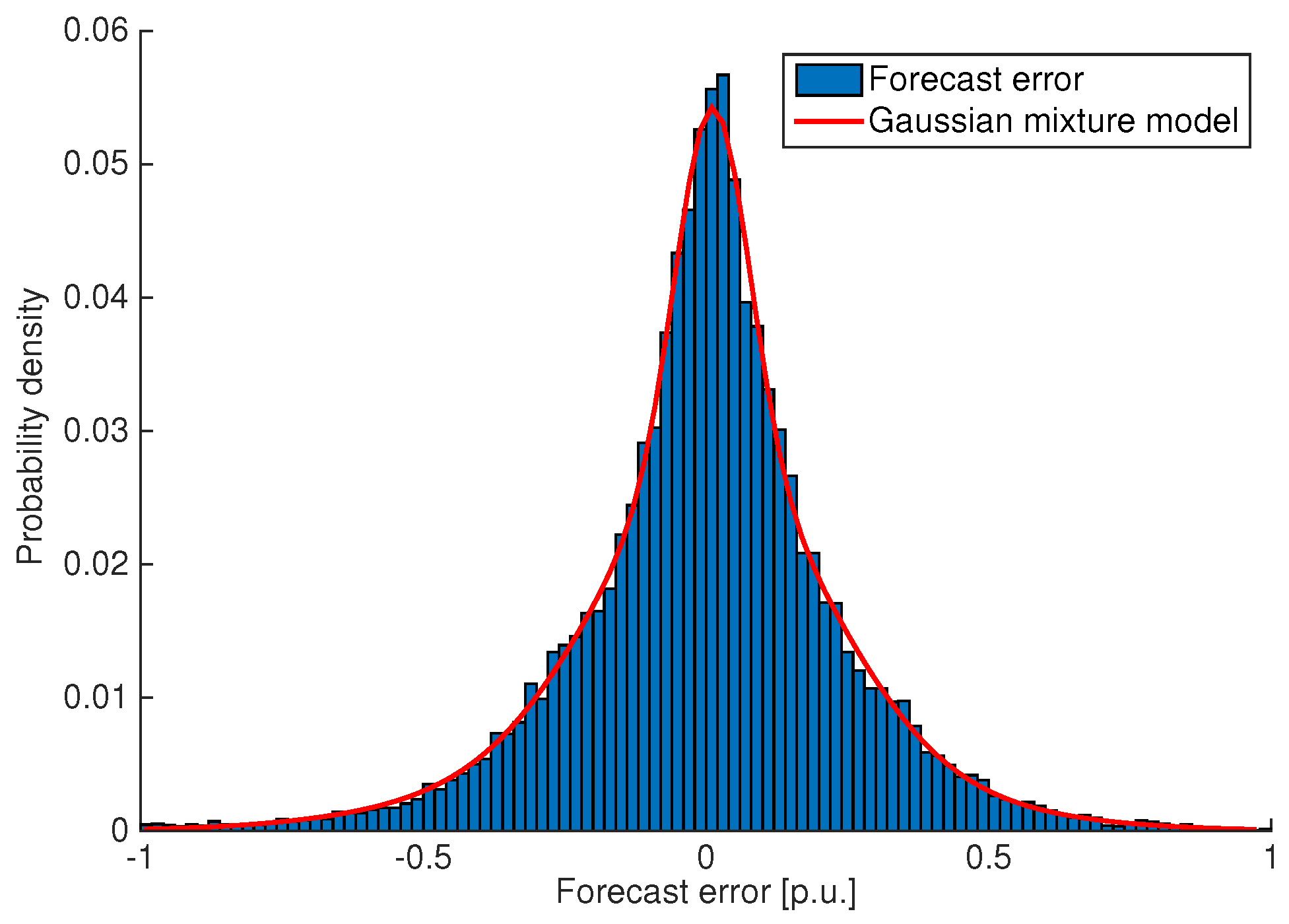
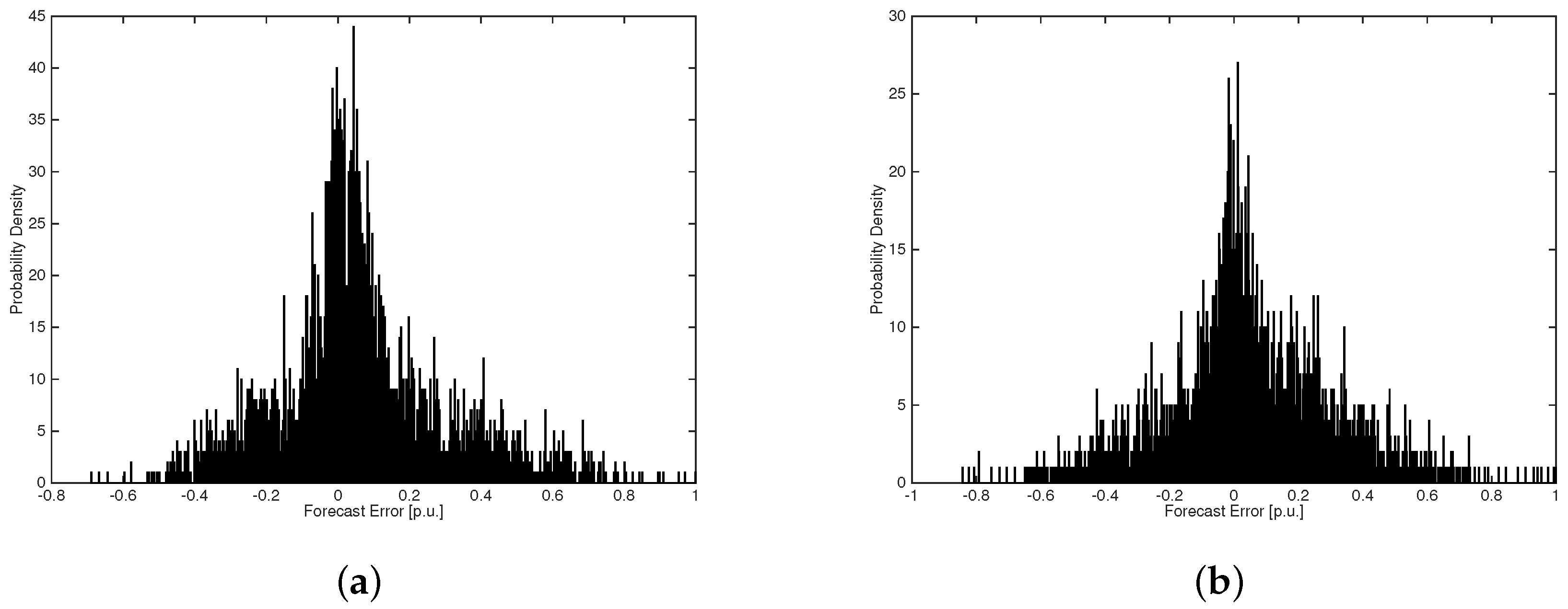
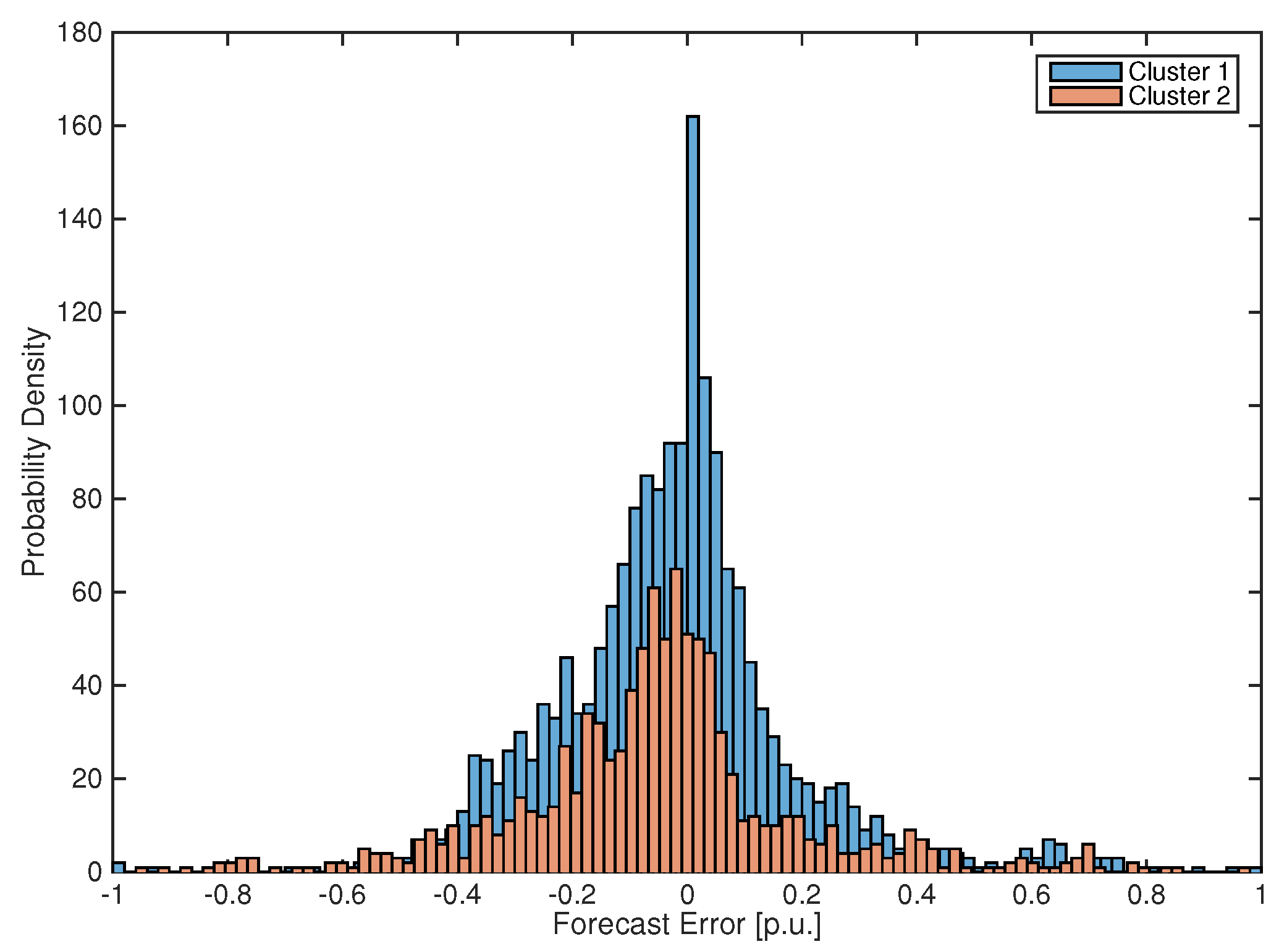
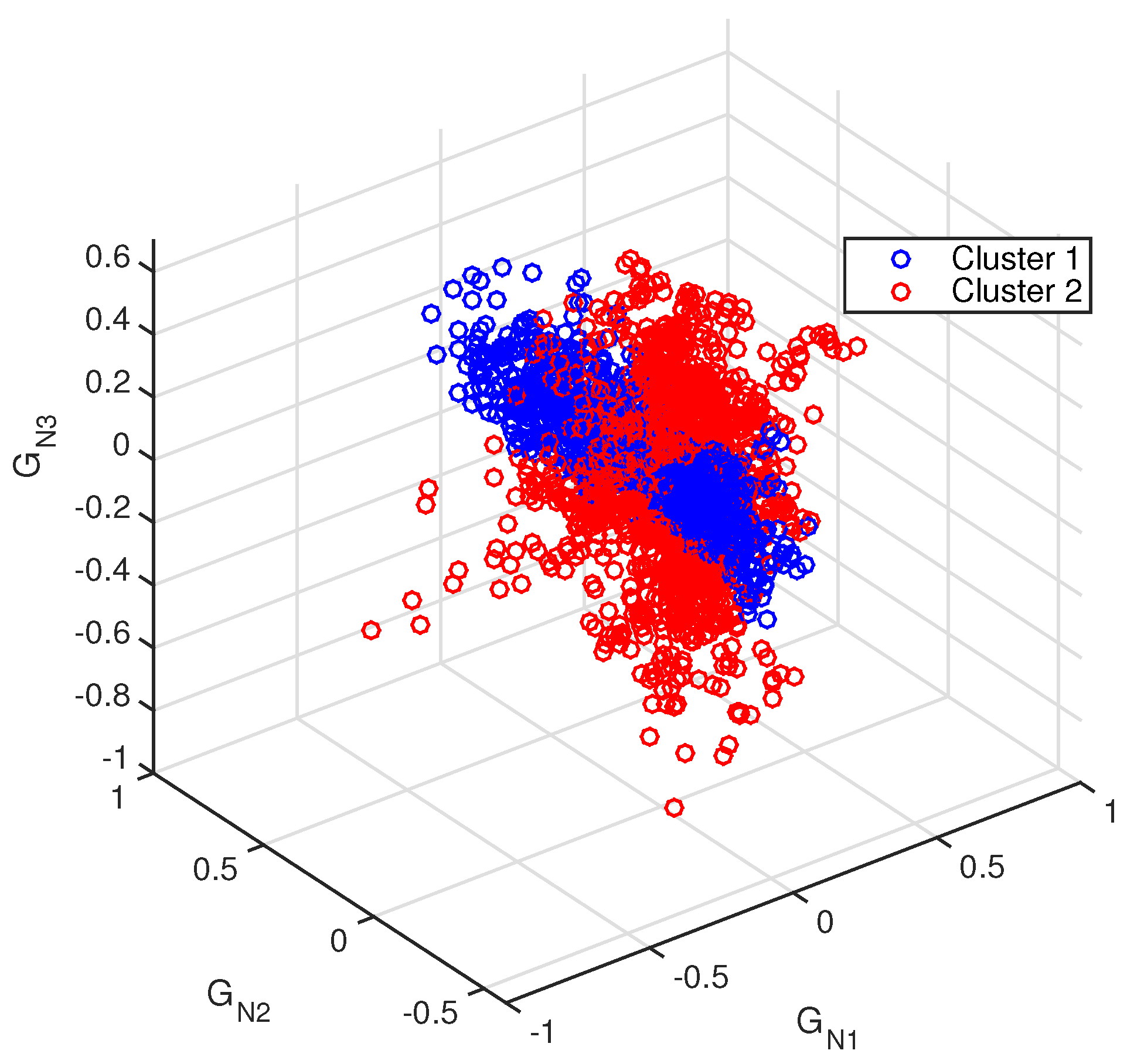
5.1. Statistical Distribution of Wind Power Forecast Error Analysis
5.2. Case Study: IEEE 39-Bus System
5.3. Case Study: IEEE 118-Bus System
- (1)
- Run continuation power flow to obtain the expected value of the loadability;
- (2)
- Compute loadability sensitivities;
- (3)
- Get the PDF for (%margin) ;
- (4)
- Obtain the risk index ;
- (5)
- Store the risk index.
6. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abe, S.; Fukunaga, Y.; Isono, A.; Kondo, B. Power system voltage stability. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1982, PAS-101, 3830–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.B.; De Lorenci, E.V.; Leme, R.C.; De Souza, A.C.Z.; Lopes, B.I.L.; Lo, K. Probabilistic voltage stability assessment considering renewable sources with the help of the PV and QV curves. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2013, 7, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; McCalley, J.D.; Vittal, V. Risk based voltage security assessment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2000, 15, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiraghi, M.; Ranjbar, A. Online voltage security assessment based on wide-area measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, A.; Annakkage, U.D.; Jayasekara, B.; Bagen, B. Risk-based dynamic security assessment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschen, D.; Jayaweera, D. Comparison of risk-based and deterministic security assessments. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2007, 1, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Risk assessment of power systems: Models, methods, and applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ciapessoni, E.; Cirio, D.; Kjølle, G.; Massucco, S.; Pitto, A.; Sforna, M. Probabilistic risk-based security assessment of power systems considering incumbent threats and uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2890–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Lu, P.; Zhang, S. Transmission line overload risk assessment for power systems with wind and load-power generation correlation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, R.; Milanović, J.V. Probabilistic risk assessment of rotor angle instability using fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldeen, M.; Saha, S.; Alpcan, T.; Evans, R. New online voltage stability margins and risk assessment for multi-bus smart power grids. Int. J. Control 2015, 88, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpcan, T.; Saha, S.; Aldeen, M. Assessment of voltage stability risks under intermittent renewable generation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting|Conference & Exposition, Metro Area, Washington, DC, USA, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 1–5.
- Aldeen, M.; Saha, S.; Alpcan, T. Voltage stability margins and risk assessment in smart power grids. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 8188–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.B.; Prada, R.B.; da Guia da Silva, M. Voltage stability probabilistic assessment in composite systems: Modeling unsolvability and controllability loss. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Malbasa, V.; Kezunovic, M. Analysis of voltage stability issues with distributed generation penetration in distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 45th North American Power Symp, Manhattan, NY, USA, 22–24 September 2013; pp. 1–7.
- Yu, J.; Li, W.; Yan, W.; Zhao, X.; Ren, Z. Evaluating risk indices of weak lines and buses causing static voltage instability. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–28 July 2011; pp. 1–7.
- Bienstock, D.; Chertkov, M.; Harnett, S. Chance-constrained optimal power flow: Risk-aware network control under uncertainty. SIAM Rev. 2014, 56, 461–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Giannakis, G.B. Distributed stochastic market clearing with high-penetration wind power. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.; Al-Shakarchi, M.G. Probabilistic techniques in ac load-flow analysis. Electr. Eng. Proc. Inst. 1977, 124, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lee, S.T. Probabilistic load flow computation using the method of combined cumulants and Gram-Charlier expansion. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, X. A probabilistic load flow method considering branch outages. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wu, J. Voltage risk evaluation based on improved probabilistic load flow considering intermittent wind farm. In Proceedings of the 2012 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Shanghai, China, 27–29 March 2012; pp. 1–4.
- Morales, J.M.; Perez-Ruiz, J. Point estimate schemes to solve the probabilistic power flow. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhee, A.; Rutenbar, R.A. Why quasi-monte carlo is better than monte carlo or latin hypercube sampling for statistical circuit analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2010, 29, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Deng, W.; Zhang, K. Application of cost-cvar model in determining optimal spinning reserve for wind power penetrated system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 66, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ding, H.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Bie, P.; Wu, J. Multi-period probabilistic-scenario risk assessment of power system in wind power uncertain environment. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bian, Q.; Xin, H.; Gan, D. A Distributionally Robust Co-Ordinated Reserve Scheduling Model Considering CVaR-Based Wind Power Reserve Requirements. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.T.; Uryasev, S. Optimization of conditional value-at-risk. J. Risk 2000, 2, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uryasev, S. Conditional value-at-risk: Optimization algorithms and applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE/IAFE/INFORMS 2000 Conference on Computational Intelligence for Financial Engineering, New York, NY, USA, 26–28 March 2000; pp. 49–57.
- Sirisena, H.; Brown, E. Representation of non-Gaussian probability distributions in stochastic load-flow studies by the method of Gaussian sum approximations. IEE Proc. C-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1983, 130, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, D.; Chung, C.; Sun, Y. A novel probabilistic optimal power flow model with uncertain wind power generation described by customized Gaussian mixture model. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, G.; Saric, A.; Terzija, V. Probabilistic load flow with non-Gaussian correlated random variables using Gaussian mixture models. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2012, 6, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Pal, B.C.; Jabr, R.A. Statistical representation of distribution system loads using Gaussian mixture model. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilmes, J.A. A Gentle Tutorial of the EM Algorithm and Its Application to Parameter Estimation for Gaussian Mixture and Hidden Markov Models; International Computer Science Institute: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Celeux, G.; Diebolt, J. A stochastic approximation type EM algorithm for the mixture problem. Stochastics 1992, 41, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia. Available online: http://www.elia.be/ (accessed on 23 January 2017).
- Dobson, I.; Van Cutsem, T.; Vournas, C.; DeMarco, C.; Venkatasubramanian, M.; Overbye, T.; Canizares, C. Voltage stability assessment: Concepts, practices and tools. IEEE Power Eng. Soc. Power Syst. Stab. Subcomm. Spec. Publ. 2002, 11, 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, M.; Kewell, B. Risk: A Study of Its Origins, History and Politics; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Palmquist, J.; Uryasev, S.; Krokhmal, P. Portfolio Optimization With Conditional Value-at-Risk Objective and Constraints; Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Veen, R.A.; Abbasy, A.; Hakvoort, R.A. Agent-based analysis of the impact of the imbalance pricing mechanism on market behavior in electricity balancing markets. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, S.R.; Sheikh-El-Eslami, M.K. Risk Assessment of Virtual Power Plants Offering in Energy and Reserve Markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 3572–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Manjrekar, M.; Lin, C.; Tamayo, M.; Jiang, J.N. Voltage stability and sensitivity analysis of grid-connected photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–28 July 2011; pp. 1–7.
- Glasserman, P. Monte Carlo Methods in Financial Engineering; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Niederreiter, H. Quasi-Monte Carlo methods and pseudo-random numbers. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1978, 84, 957–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morokoff, W.J.; Caflisch, R.E. Quasi-random sequences and their discrepancies. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1994, 15, 1251–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.B. Quasi-monte carlo sampling. Monte Carlo Ray Tracing Siggraph 2003, 1, 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Caflisch, R.E. Monte carlo and quasi-monte carlo methods. Acta Numer. 1998, 7, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.L. An estimate concerning the kolmogroff limit distribution. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1949, 67, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chung, C.; Chan, K.W.; Chen, H. Quasi-Monte Carlo based probabilistic small signal stability analysis for power systems with plug-in electric vehicle and wind power integration. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 3335–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date of Wind Projection and Actual Value by TransnetBW. Available online: https://www.transnetbw.com/en/key-figures/renewable-energies/wind-infeed (accessed on 23 January 2017).
- Pai, A. Energy Function Analysis for Power System Stability; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Longatt, F.M. IEEE 118 Bus Test. Available online: http://fglongatt.org/OLD/TestCaseIEEE118. html (accessed on 19 March 2015).
- Ni, M.; McCalley, J.D.; Vittal, V.; Tayyib, T. Online risk-based security assessment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Generation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0374 | 0.0515 | 0.4557 | 0.0853 | 0.0609 | 0.5443 | |
| −0.1042 | 0.0334 | 0.4557 | −0.0534 | 0.0118 | 0.5443 | |
| 0.0331 | 0.0315 | 0.4557 | 0.0072 | 0.0225 | 0.5443 | |
| −0.0679 | 0.0491 | 0.4557 | 0.0215 | 0.0045 | 0.5443 | |
| 0.0096 | 0.0209 | 0.4557 | 0.0215 | 0.0058 | 0.5443 | |
| 0.0096 | 0.0209 | 0.4557 | 0.0257 | 0.0058 | 0.5443 | |
| −0.0322 | 0.0267 | 0.4557 | 0.0257 | 0.0693 | 0.5443 | |
| 0.0741 | 0.0783 | 0.4557 | 0.1068 | 0.0140 | 0.5443 | |
| −0.0427 | 0.0228 | 0.4557 | 0.0518 | 0.0420 | 0.5443 | |
| −0.0191 | 0.0066 | 0.4557 | −0.0211 | 0.0203 | 0.5443 |
| Index of Buses | VaR | CVaR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | 1.0080 | 1.0563 | 0.0047 |
| 35 | 1.0058 | 1.0500 | 0.0052 |
| 38 | 1.0099 | 1.0415 | 0.0165 |
| 31 | 1.0004 | 1.0112 | 0.0298 |
| 32 | 1.0020 | 1.0125 | 0.0342 |
| 33 | 1.0022 | 1.0184 | 0.0456 |
| 34 | 1.0041 | 1.0220 | 0.0509 |
| 37 | 1.0094 | 1.0310 | 0.0531 |
| 22 | 0.9771 | 0.9785 | 0.0839 |
| 23 | 0.9783 | 0.9717 | 0.0958 |
| Index of Buses | VaR | CVaR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 0.96009 | 0.97545 | 0.00010 |
| 8 | 0.94381 | 0.97604 | 0.00013 |
| 61 | 0.98000 | 0.98078 | 0.00014 |
| 48 | 0.97000 | 0.98978 | 0.00016 |
| 25 | 0.96036 | 0.99256 | 0.00028 |
| 62 | 0.98011 | 0.98429 | 0.00042 |
| 59 | 0.98000 | 0.98215 | 0.00049 |
| 26 | 0.96115 | 0.96660 | 0.00055 |
| 23 | 0.96002 | 0.96533 | 0.00063 |
| 67 | 0.98441 | 0.98525 | 0.00079 |
| 60 | 0.98000 | 0.98079 | 0.00080 |
| 4 | 0.93872 | 0.93944 | 0.00081 |
| 5 | 0.94218 | 0.94575 | 0.00091 |
| 9 | 0.94436 | 0.96281 | 0.00091 |
| 66 | 0.98400 | 0.99140 | 0.00092 |
| 50 | 0.97100 | 0.97690 | 0.00096 |
| 46 | 0.96930 | 0.98513 | 0.00096 |
| 73 | 0.98500 | 0.98588 | 0.00096 |
| 47 | 0.96944 | 0.98228 | 0.00096 |
| 49 | 0.97000 | 0.99735 | 0.00097 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, W.; Zhang, B.; Ding, H.; Li, H. Risk-Based Probabilistic Voltage Stability Assessment in Uncertain Power System. Energies 2017, 10, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020180
Deng W, Zhang B, Ding H, Li H. Risk-Based Probabilistic Voltage Stability Assessment in Uncertain Power System. Energies. 2017; 10(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Weisi, Buhan Zhang, Hongfa Ding, and Hang Li. 2017. "Risk-Based Probabilistic Voltage Stability Assessment in Uncertain Power System" Energies 10, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020180
APA StyleDeng, W., Zhang, B., Ding, H., & Li, H. (2017). Risk-Based Probabilistic Voltage Stability Assessment in Uncertain Power System. Energies, 10(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10020180






