Abstract
Multilingualism has become an integral part of our present lifestyle. India has twenty two registered official languages with English and Hindi being most widely used for all official activities across the nation. As both these languages are introduced later in life, it was hypothesised that comprehensive reading will be better and faster if the native medium was used. Therefore present study aimed to evaluate the differences in performance while using one of the four Indian Dravidian vernaculars (Tamil, Telugu Kannada and Malayalam) and two nonvernacular (English and Hindi) languages for onscreen reading task. A multidimensional approach including physiological (Eye movement recording), subjective (Language Experience And Proficiency Questionnaire, LEAP-Q, Legibility rating) and Objective (Reading time and Word processing rate) measurements were used to quantify the effects. Forty-four Indian infantry soldiers from each of the Dravidian language groups participated in the study. Volunteers read aloud two simple story passages onscreen in their respective vernacular and non-vernacular languages using both time bound and self-paced reading mode. Reading time was lower and word processing rate was higher respectively in case of vernacular than non-vernacular. Consideration of fixation count in both the modes of reading indicated better performance with vernaculars. Legibility score was better in Dravidian languages than others. Results indicated that reading text was faster in vernacular media followed by English and Hindi. Use of vernaculars in onscreen text display of high density workstation may therefore be recommended for easier and faster comprehension.
Introduction
In today’s world of rapid globalization, exposure to multilingual reading is very common. However, the extent of accurate comprehension may be related to the period of language acquisition in the lifetime of the concerned reader (Hyltenstam & Abrahamsson, 2003). India has diversified languages across the country with descendants of Dravidian languages mostly living in southern part of India. Among them Tamil, Malayalam, Telugu, and Kannada are the registered official languages under the constitution of India. These languages have been used in administration and literature since their first attested beginning in their respective states. Each of these four languages possess a great wealth of written texts and are characterized by a dichotomy between the standardized, formal language and colloquial speech. They seem to be very adaptive and experienced little difficulty in accommodating social, political, and economic changes that swept India in the 20th century (Krishnamurti, 2003).
Dravidian languages show extensive lexical (vocabulary) borrowing, but only a few traits of structural (either phonological or grammatical) borrowing from Indo-Aryan languages, whereas Indo-Aryan (Hindi) shows more structural than lexical borrowings from the Dravidian languages (Encyclopaedia Britannica 2008). Many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda (c. 1500 BC), which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian vocabulary (Krishnamurti, 2003).
Language dominance is an issue of debate in different domains, including academic research, education, public policy, commerce and clinical settings. With its influences on cognition and emotion the language dominance may predict cross-linguistic intermingling of syntactic processing (Rah, 2010). It may also govern bilingual lexical memory representation (Heredia, 1997), affect language choice for self-directed and silent speech (Dewaele, 2004), determine the language of mental calculations (Tamamaki, 1993) etc. Administrators use the construct of language dominance to determine the language in which, tests of academic and linguistic abilities should be carried out as a classification tool for multilingual education planning (Brunner, 2010).
Although dominance and proficiency, conceptually overlap in some respects, dominance is often associated with language proficiency (e.g. Tokowicz et al., 2004). Proficiency does not alone define language dominance. Literature shows one can be dominant in a language without being highly proficient in that language. The present study attempted to examine proficiency as one component of dominance.
Marshall (1987) investigated the mechanism of language processing in reading and writing. In contrast to listening, reading is a more complex task that we routinely perform. Time required for reading is dependent on a wide range of factors, ranging from lexical (e.g. word frequency; Mitchell & Green, 1978) and syntactic (e.g. negation; Just & Carpenter, 1971) to text level (e.g. thematic importance of sentences; Cirilo & Foss, 1980). This language cognition is dependent upon language acquisition, the process by which an individual acquires the capacity to perceive, produce and use the words to comprehend. However learning first language is successfully done by every normal child even without formal lessons. Language is one of those activities that emerges within the context of other cognitive abilities like memory, attention, problem solving etc. Piaget’s cognitive theory states that a child language reflects the development of his logical thinking and receiving skills in stages, with each period separated by age references (Piaget & Inhedler, 1969).
Reading acquisition is a complex process that relies on orthographic, phonological and syntactic knowledge (Kaushanskaya, 2011). Acquisition of literacy in the second language is known to depend on native language knowledge (Sparks et al., 2008). Readers move their eyes through a text during reading in order to acquire information about its content. Eye movements seem to reflect sentence comprehension process in a more varied fashion and there are systematic relations between fixation duration and the characteristics of the fixated words (Just & Carpenter, 1980). Altarriba et al. (1996) showed that the recording of eye-movements provided a multifaceted record which allowed the authors to reach the conclusion that although no effect of lexical probability was found in monolingual sentences, it had strong effect on mixed language sentences.
A number of recent reported studies across the globe investigated the effects of eye movements on reading in various aspects. Some of them investigated lexical access and representation in bilinguals (Blumenfeld & Marian, 2011; Duyck et al., 2007; Felser et al., 2009 and Flecken, 2011), syntactic ambiguity resolution effects of using sentences with ambiguous phrases (Dussias & Sagarra, 2007; Roberts et.al., 2008), attention (Godfroid et al., 2013), and cognitive processes during specific tasks, such as evaluation in terms of second language testing (Bax & Weir, 2012) and video-based second language listening (Winke et al., 2013). Yu et al. (2010) investigated to find out the effect of reading orientation, on reading speed. However till date there was no reported study that attempted to identify the effects of time constraint on language processing in multilingual population.
Different eye movement-reading models made some serious attempts to explain eye-mind link or interaction between lexical processing and eye movement control. However no such model really explains the processing of different languages those are having syntactic as well as morphological difference. It is known that reading speed (as word processing rate) and reading time are very important measurement to identify language processing (Just & Carpenter, 1987; Ni et al., 1998; Deutsch & Bentin, 2001). Studies by previous authors (Marian et al., 2007; Lim et al., 2008; Gollan et al., 2012) showed that multilinguals are able to assess their language experience and language ability, which corresponds with behavioural measure of linguistic performance.
Indian soldiers with Dravidian vernacular need to speak and read Hindi and English during their exposure to a multilingual and multi-ethnic occupational environment. Though verbal communication in English and Hindi may be effective for Indian soldiers, reading the written communication poses problem and affects performance to a great extent. Hindi in India is the most commonly used official language. In the modern era, the military operations are digitized across broad variety of applications for optimised rapid and uninterrupted communication among different command posts and control units. Less frequent exposure and unfamiliarity with the written form of a language may increase the rate of error and reduce performance, which may subsequently affect the performance of the individual as well as the other operators working under the same network.
Thus, the question is raised that whether the use of various vernaculars along with English and Hindi can facilitate and enhance the occupational performance in various in-house and field operations in Indian Army? Do early age of acquisition and late immersion to a specific language can really create some effect on onscreen command control handling? Till date no such study has been reported on this multilingual aspect of information processing in civilian or army population in India. The present study hypothesised that using vernacular language will improve reading performance in terms of cognition during onscreen reading of text when compared with Hindi and English. A novel approach of simultaneously using eye movement recording as physiological measure, reading time and word processing rate as objective measure and Language Experience And Proficiency Questionnaire (LEAP-Q) as a subjective measure have been applied in this study.
Language Experience and Proficiency Questionnaire (LEAP-Q) provides independent data for each of a language used by a multilingual rather than a composite score relating strengths in one language with the other language. This questionnaire is intended for use with healthy adult bilinguals and multilinguals (both sequential and simultaneous) from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds who have attained at least high school levels of literacy (Marian et al., 2007).
In military scenario, the time constraint is an important issue and may be responsible for many human errors. This criterion needs to be evaluated for improving the performance of operators and reducing accidents and errors. Such studies may help to improve the conceptual understanding of the task requirement within time constraint domain.
The present study was therefore designed to investigate the differences in performance of each of the Dravidian vernaculars (Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam) as compared to Hindi and English language during onscreen reading of text.
Methods
Participants
A total number of 200 infantry soldiers (50 participants from each of the Dravidian vernacular group viz. Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam) from Indian Armed Forces volunteered in this study. They had 10-12 years of formal education in respective vernacular medium. Volunteers spoke their vernacular as first language, English as second language and Hindi as a lately acquired third language. The volunteers were healthy, physically active males having normal or corrected-to-normal vision with a visual acuity of 6/6”. The present study protocol conformed to the ethical norms of the declaration of Helsinki (2008) and was cleared by the ethical committee of the authors’ institution. Before participation, the volunteers were thoroughly briefed about purpose of the experiment and they gave an informed consent for the study.
Experimental protocol
From the common moral stories of Aesop fables, two stories were selected as the onscreen reading material. Originally the stories were in English and were subsequently translated to respective vernaculars and Hindi by the language experts applying specific language Unicode in Microsoft Word. In this study two reading modes were applied, namely free reading or self-paced reading (without time restriction) and time bound reading (with one minute time constraint). Participant who were not able to read any of the languages or were relatively slow readers (volunteers having poor idea of alphabets of the specific language and having difficulty to comprehend) were rejected summarily. Finally reading time data of 44 subjects in each vernacular group was analysed after passing the normality criterion (α=0.05) by Shapiro-wilk test. This ensured that the data was not skewed.
Participants were seated comfortably in front of a 19 inch LCD monitor with 4:3 aspect ratio. Same text in different languages was displayed onscreen, one at a time. They were instructed to read the text loudly and comprehensively. Loud reading tasks were chosen as it could be easily and precisely monitored. The tasks (self-paced and time bound Hindi, English & vernacular reading) were randomized in different days for each subject. They read their vernacular in two reading modes on the different days followed by English and Hindi. During these two modes of reading, eye movement measures (Fixation count, fixation frequency, fixation duration and fixation dispersion) were recorded by portable eye movement recorder (I view X, SMI, Germany) based on dual purkinje image technique with a sampling rate of 200 Hz. Fixation dispersion gives the overall ideas of the eye positioning in the specific area of interest and the displacement of eye axis during the task (Blignaut & Beelders, 2009). In the instrument, SMI I-view X, 200 Hz (used in the present study), average fixation dispersion was given in pixel (px.). It gives the information about the stability of gaze pathway during reading process. A five point calibration (one point at the center and others in the four corners of the screen) was applied to calibrate the eye with the screen, before each experimental session.
Before the experiment subjective Language Experience And Proficiency-Questionnaire (LEAP-Q, Marian et al., 2007) was used to identify the exposure and proficiency in different languages. On completion of the experiment, each participant also ranked the legibility of the text on a 5-point rating scale ranging from very easy (1) to very hard (5).
Statistical treatment of the data
Each vernacular group of subjects were exposed to three languages (vernacular, Hindi and English), in two different reading modes (self-paced and time bound), during which we measure dependent variables. The study had a repeated measures design. The independent variables were the combinations of language and reading mode. The dependent variables were physiological variables i.e. eye movement variables (e.g. fixation count, fixation frequency, fixation duration, fixation dispersion), reading time and word processing rate. Language and reading mode trials were analysed by 3 (languages: vernacular, English and Hindi) x 2 (reading modes: self-paced, time bound), repeated measures ANOVA to find out the effect of different language and time constraint on physiological variables. Repeated measures ANOVA was applied separately on each of the reading modes (self-paced and time bound) in respect to the languages used (Dravidian, English and Hindi). Following this, a Bonferroni post hoc test was applied for pairwise comparison of the dependent variables in different languages. The level of significance was considered at p<0.05.
In case of Legibility score, non-parametric Friedman test was performed followed by post hoc Dunn’s test for multiple comparison.
Results
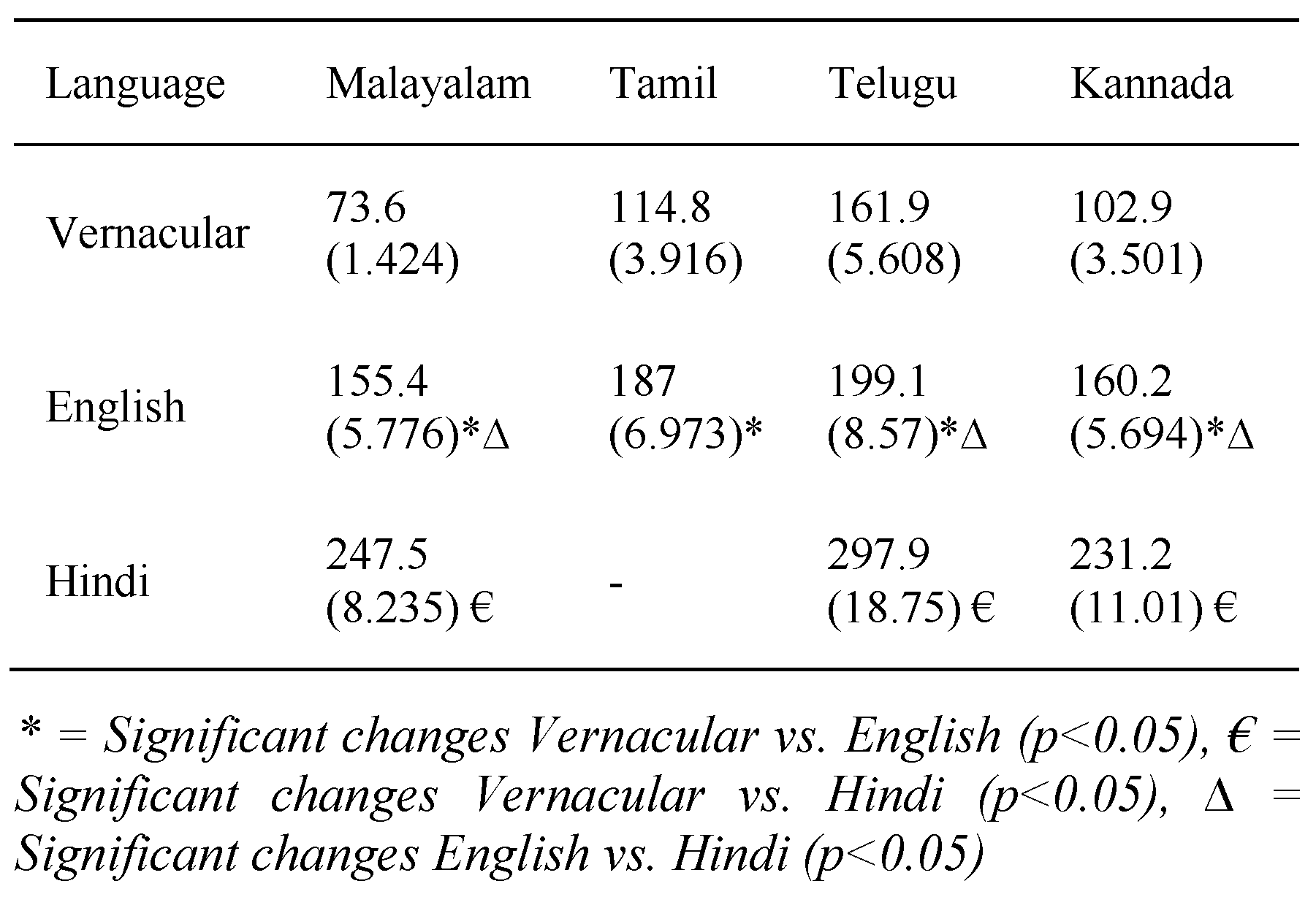
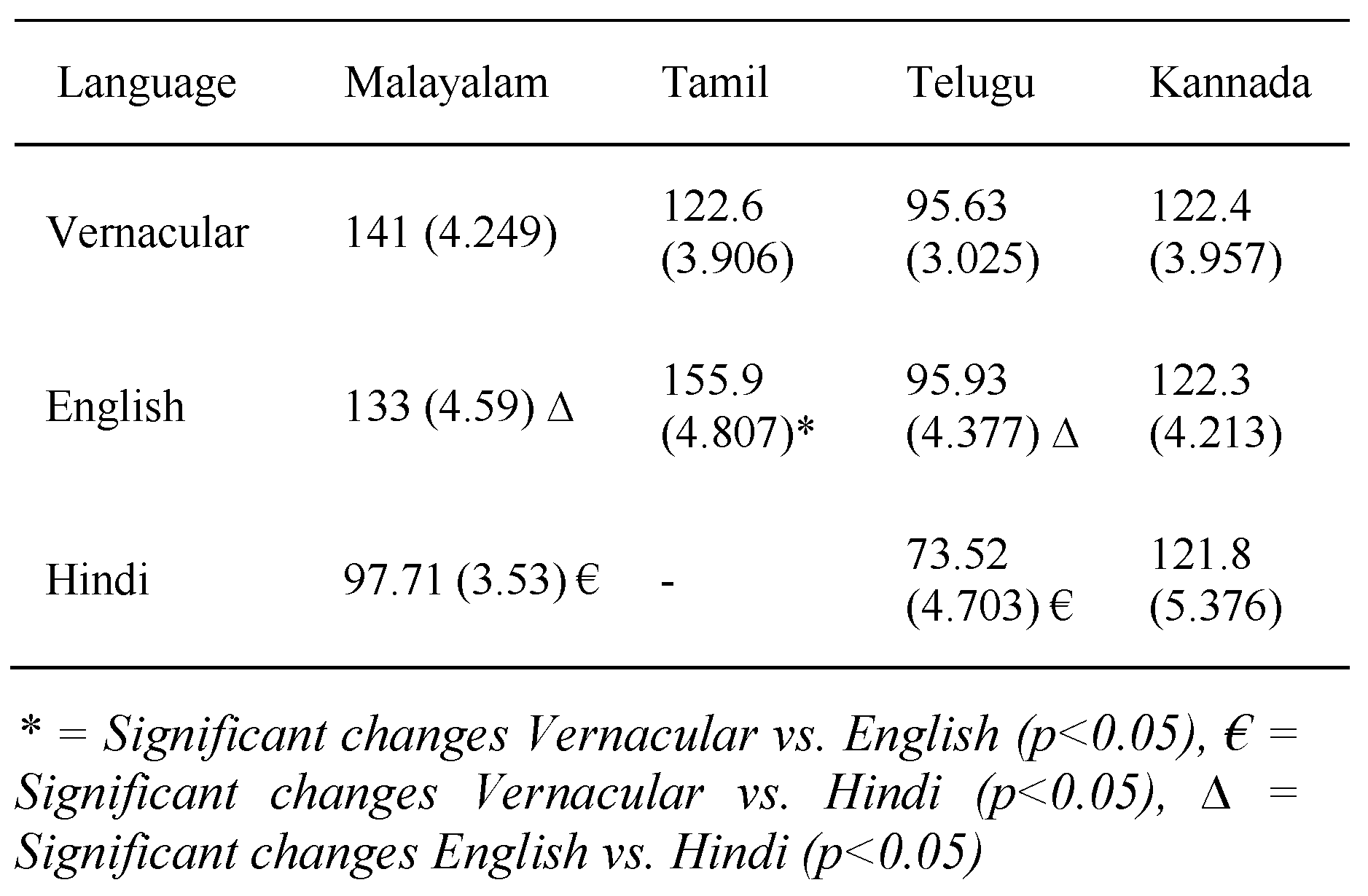
Table-1 represents the total time taken for reading the onscreen texts presented in their respective vernacular as well as English and Hindi by four Dravidian population groups. In self-paced/free reading mode, time taken for each of the Dravidian vernacular languages was significantly lower than non-vernacular and among Hindi and English they took significantly higher time to read Hindi (Table-1). In this mode, Malayalam population took minimum (73.6 (1.424) sec.) and Telugu population took maximum (161.9 (5.608) sec) time. Similar trend was observed for English and Hindi reading time for Malayalam and Telugu population.

Table-1.
Total time taken (SEM) in self-paced reading mode. All the values are presented in seconds.
Word processing rate measures number of words processed per minute (wpm). Table-2 shows that the word processing rate was minimum (95.63 (3.025) wpm) for Telugu, and maximum (141 (4.249) wpm) for Malayalam population. English word processing rate was lowest (95.93 (4.377) wpm) in Telugu group and highest (155.9 (4.807) wpm) for Tamil group. Among Tamil population studied, only three volunteers were able to read Hindi. Hence their reading time and word processing rate were not incorporated in this study. Word processing rate for Hindi was highest in Kannada group (121.8 ± 5.376) and minimum for Telugu group (73.52±4.703). Word processing rate for Malayalam and Telugu language groups were significantly higher in vernacular than Hindi. In these two language groups English word processing rate were significantly higher than Hindi. In case of Tamil group, English word processing rate was significantly higher than vernacular and among Kannada vernacular group, word processing rate were almost same in case of each language they have read.

Table-2.
Word processing rate (SEM) in different languages presented in No. of words/min.
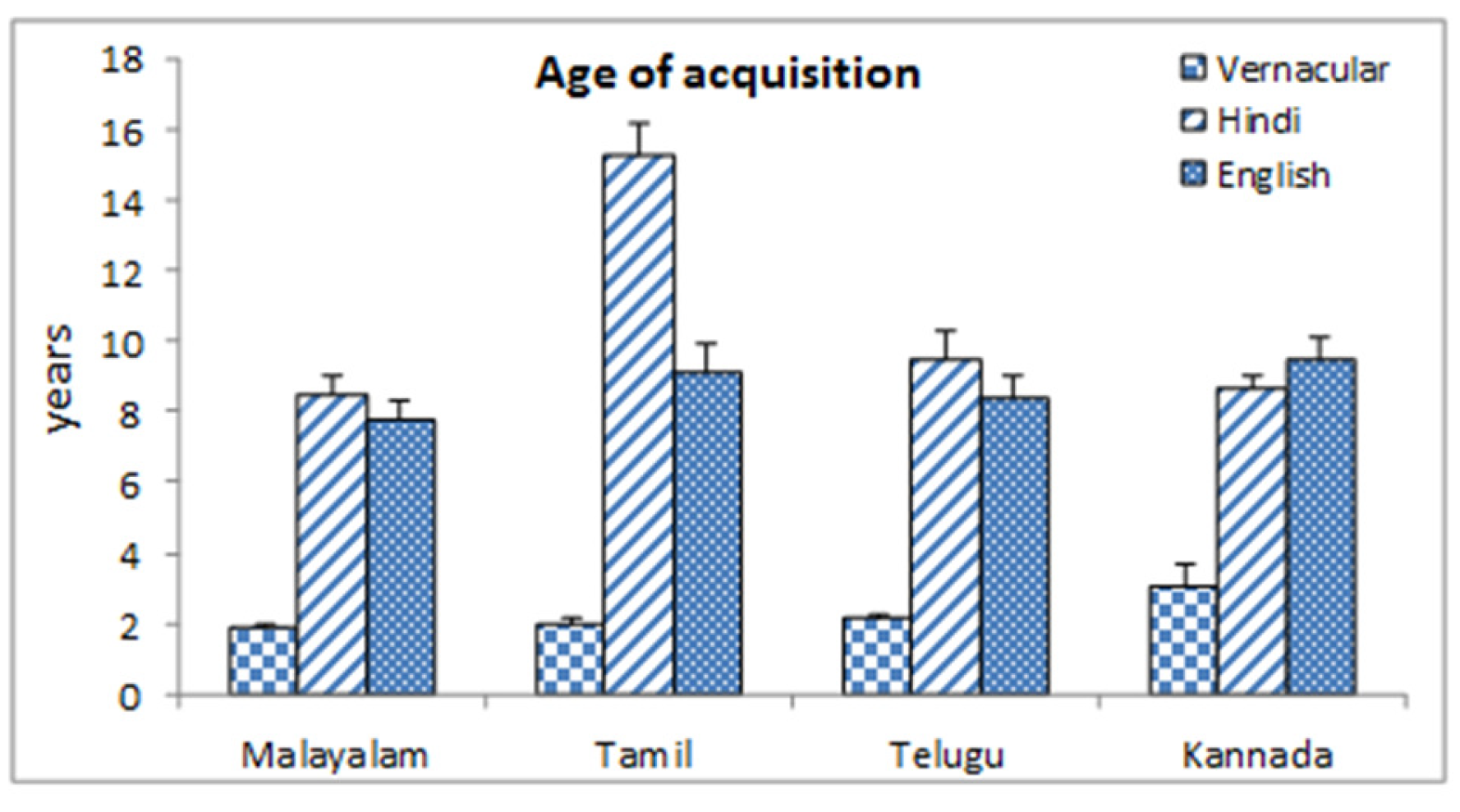
Figure-1 shows that for all the four language groups, the age of acquisition (in years) of vernacular language was minimum (1.84 (0.17) yrs.) for Malayalam group and maximum in Kannada (2.42 (0.33) yrs.) group. The acquisition of English started earliest at 7.79 (0.84) yrs. in Malayalam group and latest at 9.49 (0.64) yrs. for Kannada group. Results indicated that Malayalam population starts learning Hindi earliest among the groups at 8.45 (0.98) yrs. whereas Tamil group reported a very late acquisition of Hindi language at 15.26 (0.62) yrs.
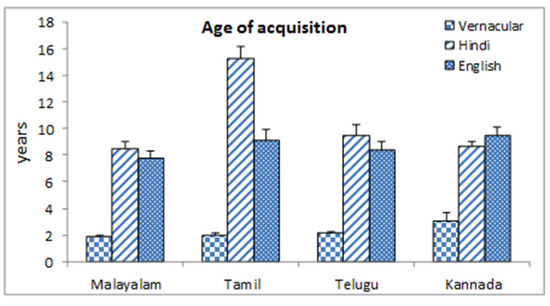
Figure-1.
Starting years of language acquisition
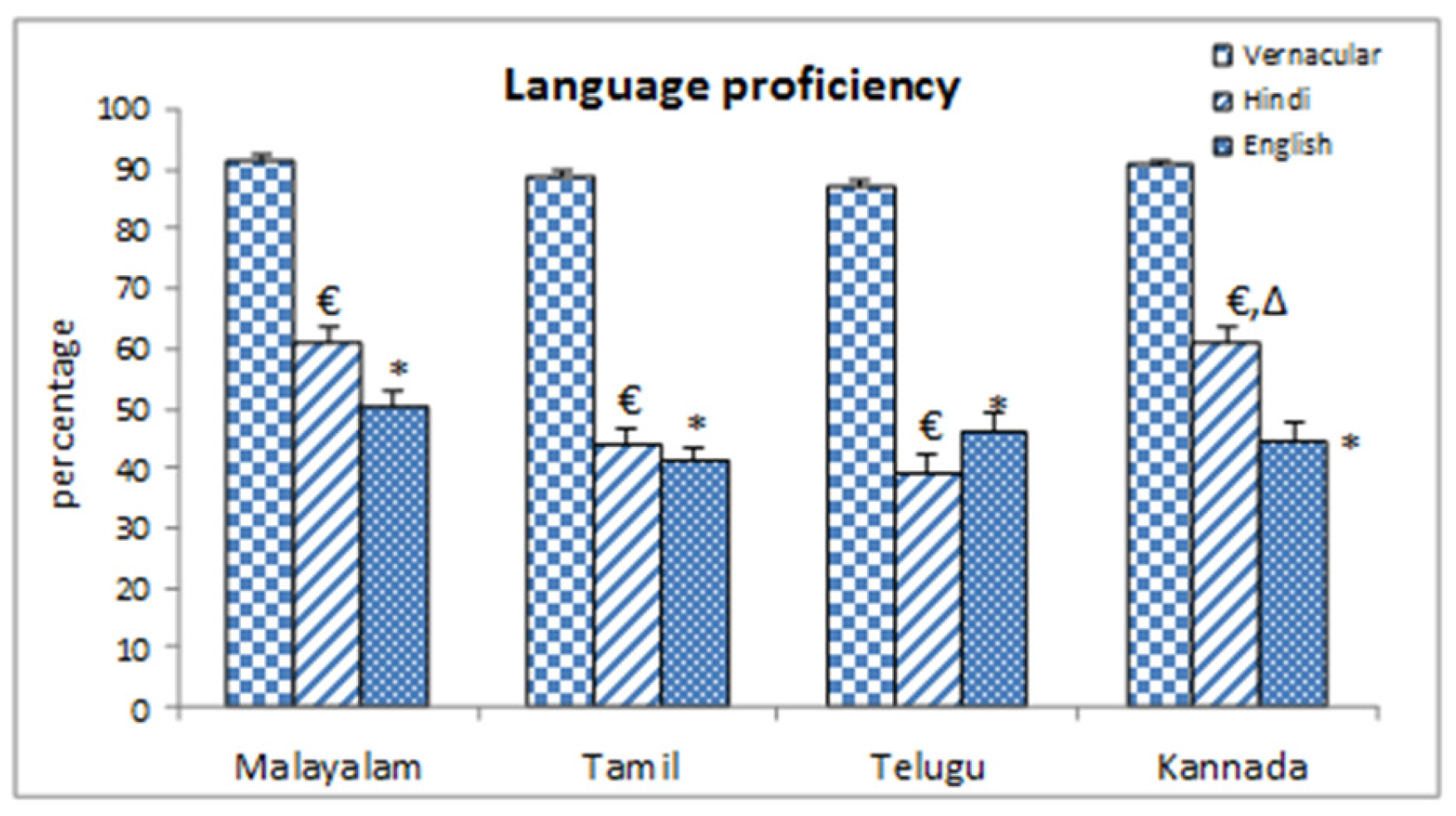
Self-reported language as proficiency was reported higher in case of vernaculars for all Dravidian population (Figure-2) as compared to other non-vernacular languages.
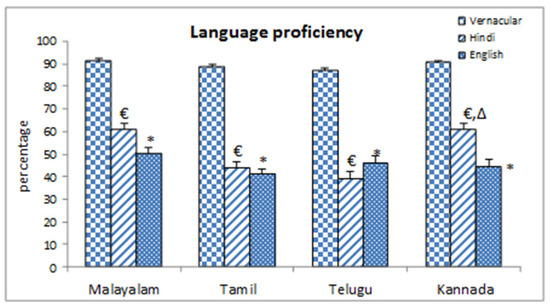
Figure-2.
Self reported language proficiency level. * = Significant changes Vernacular vs. English (p˂0.05), € = Significant changes Vernacular vs. Hindi (p˂0.05), ∆ = Significant changes English vs. Hindi (p˂0.05).
Hindi proficiency was maximum in Kannada (61.20 (2.57) %) and Malayalam (61.14 (2.28) %), lowest in Telugu population (39.16 (3.06) %). Proficiency level in English was maximum in Malayalam (50.03 (2.72) %) and minimum for Tamil (40.96 (2.53) %) population. For all the four language groups, non-vernacular (English and Hindi) proficiency were reported significantly lower than vernacular. In case of Kannada language group, language proficiency was also reported significantly higher in Hindi than English.
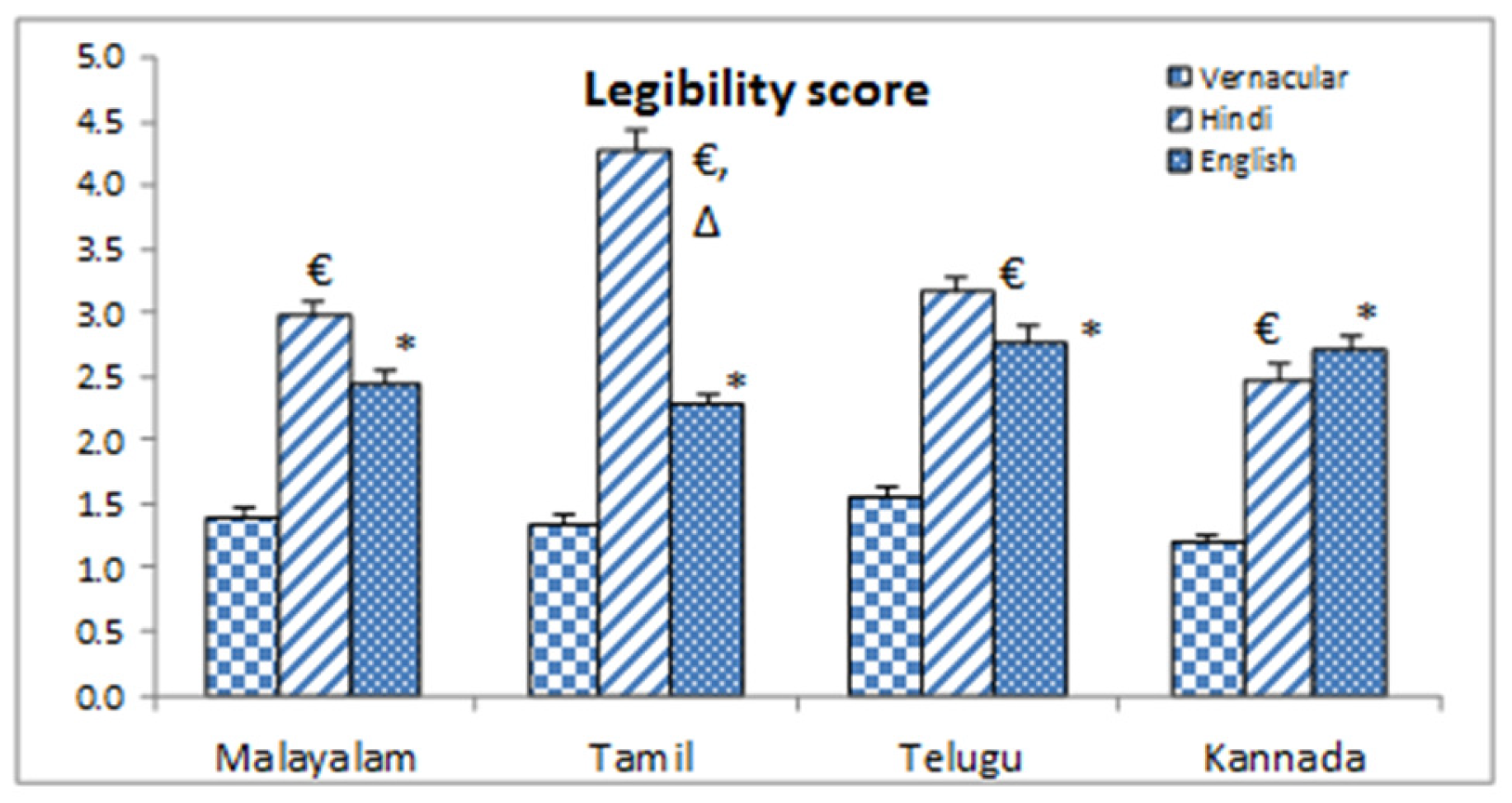
Volunteers from each of the four vernacular groups rated their vernacular as ‘very easy’ in self-reported legibility scale (Figure-3). For English it was between ‘Easy’ and ‘Moderate’ and for Hindi it was ‘Moderate’ to ‘Hard’ for Malayalam, Telugu and Kannada Language group (Figure-3). Tamil population rated Hindi in between ‘Hard’ and ‘Very hard’, but for all those language groups legibility score was significantly higher in Hindi than their own vernacular.
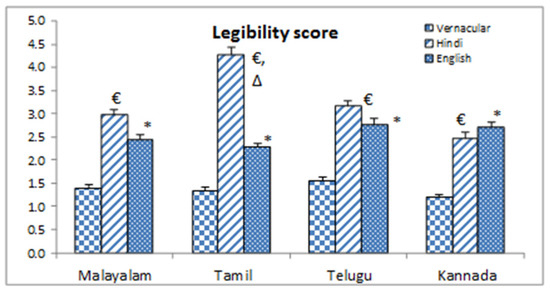
Figure-3.
self reported legibility score. * = Significant changes Vernacular vs. English (p˂0.05), € = Significant changes Vernacular vs. Hindi (p˂0.05), ∆ = Significant changes English vs. Hindi (p˂0.05).
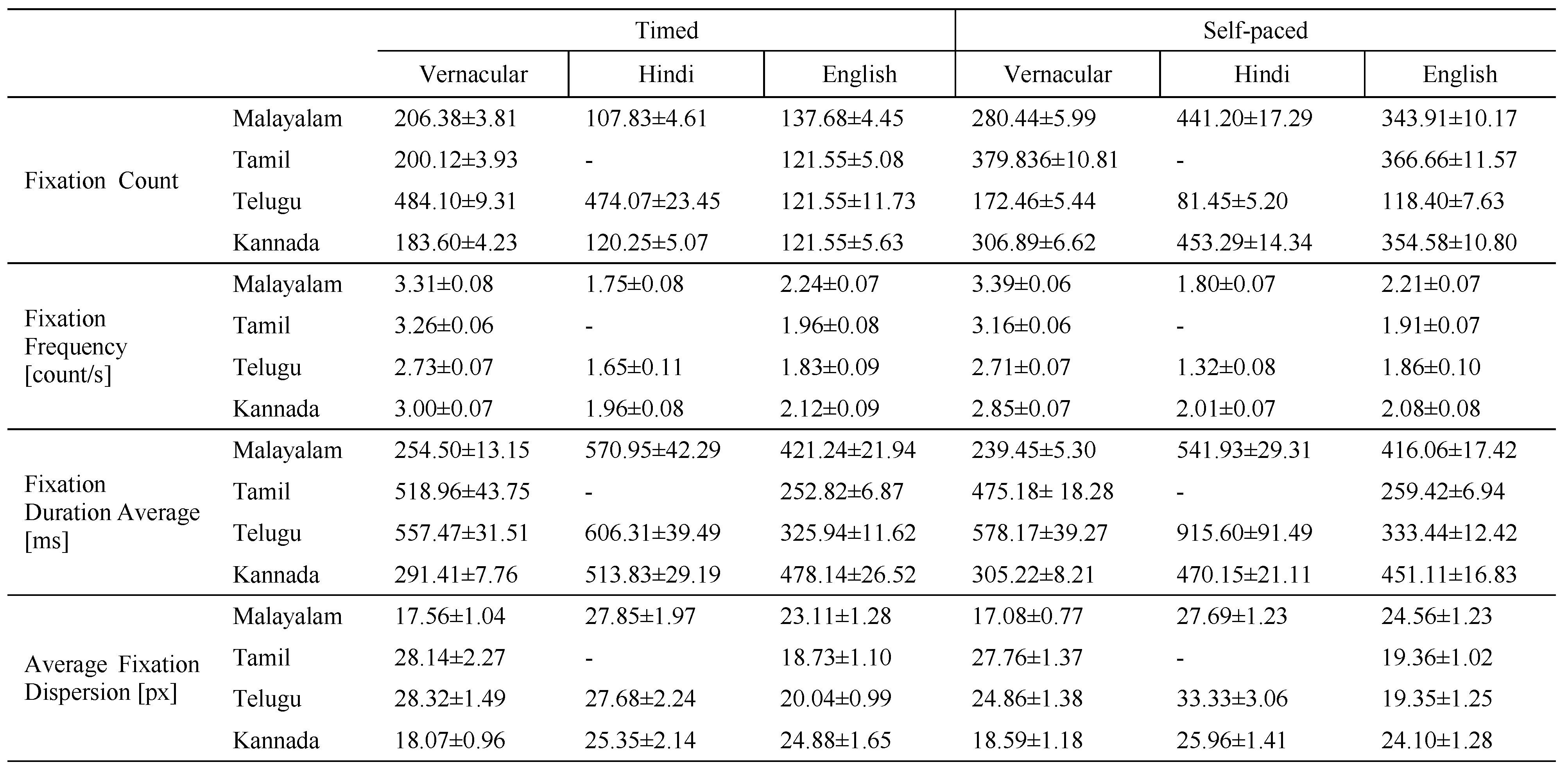
Among eye movement variables the different fixation parameters in three languages and two different modes of reading were analysed. The values of fixation count, fixation frequency, average fixation duration and fixation dispersion have been presented in Table-3. Statistical analysis (ANOVA) of these parameters are given in Table-4.

Table 3.
Fixation variables for different Dravidian language groups (n = 44) while reading vernacular and non-vernacular in time bound and self-paced manner. Data presented as mean± SEM. SEM= Standard error of mean.

Table 4.
ANOVA shows the effect of languages and mode on fixation parameters among dravidian language group
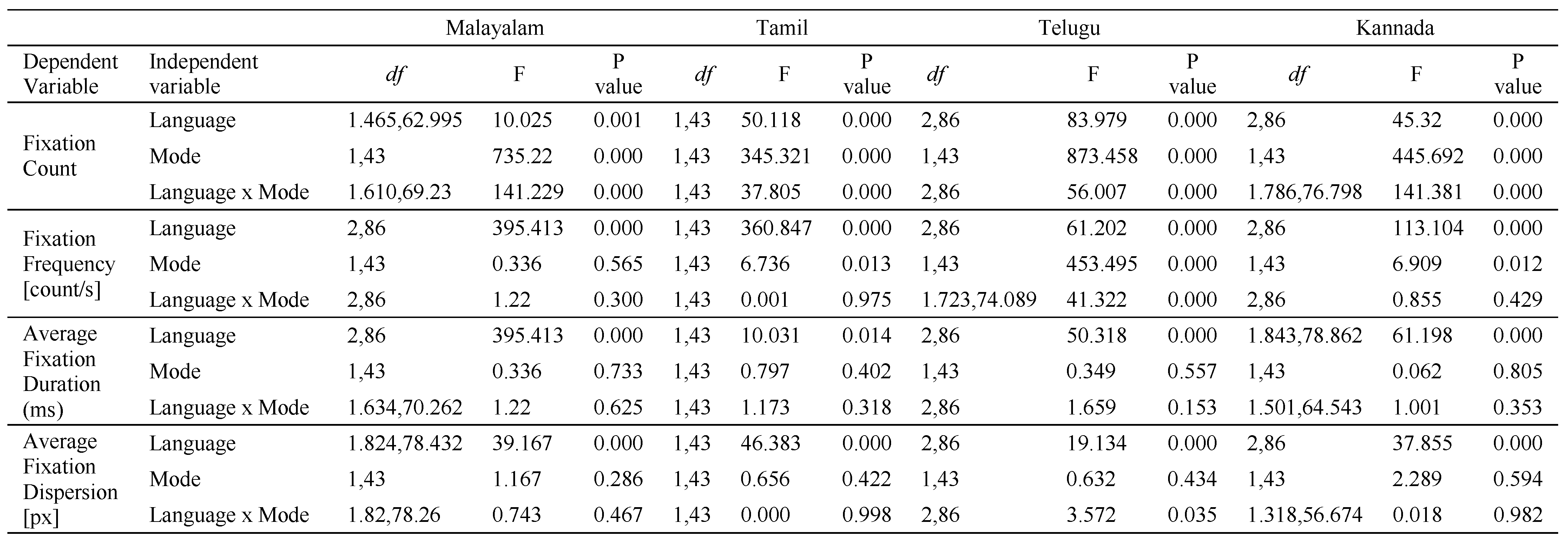
Fixation count: Analysis revealed that there was a significant interaction between language and mode of reading for all four Dravidian languages. For the Dravidian languages, the interaction between language and mode separately was found to be significant. The combined effect of language and mode was also significant for all Dravidian languages (Table-3). The main effect of language was significant in all Dravidian languages, i.e. Malayalam (F (1.465, 62.995) = 10.025, P=0.001), Tamil (F (1, 43) = 50.118, P<0.001), Telugu (F (2, 86) = 83.979, P<0.001) and Kannada (F (2, 86) = 45.32, P<0.001). Main effect of mode was significant for all the language groups, i.e. Malayalam (F (1, 43) = 735.22, P<0.001), Tamil (F (1, 43) = 345.321, P<0.001), Telugu (F (1, 43) = 873.458, P<0.001) and Kannada (F (1, 43) =445.692, P<0.001). The interaction of language and reading mode was also significant in all the language groups i.e. Malayalam (F (1.610, 69.23) = 141.229, P<0.001), Tamil (F (1, 43) = 37.805, P<0.001), Telugu (F (2, 86) = 56.007, P<0.001), and Kannada (F (1.786, 76.798) = 141.381, P<0.001).
Fixation frequency: The main effect of language was significant in all Dravidian languages, i.e. Malayalam (F (2, 86) = 395.413, P<0.001), Tamil (F (1, 43) = 360.847, P<0.001), Telugu (F (2, 86) = 61.202, P<0.001) and Kannada (F (2, 86) = 113.104, P<0.001). Main effect of mode was significant for Tamil (F (1, 43) = 6.736, P<0.05), Telugu (F (1, 43) = 453.495, P<0.001) and Kannada (F (1, 43) = 6.909, P<0.05), but not significant for Malayalam vernacular group. The interaction of language and reading mode was not significant in Malayalam, Tamil and Kannada but was significant in Telugu (F (1.723, 74.089) = 41.322, P<0.05).
Average fixation duration: In all four Dravidian language groups, i.e., Malayalam (F (2, 86) = 395.413, P<0.001), Tamil (F (1, 43) = 10.031, P<0.05), Telugu (F (2, 86) = 50.318, P<0.001), Kannada (F (1.843, 78.862) = 61.198, P<0.001) only independent effect of language was found significant. The independent effect of mode and interaction effect of mode x language were not significant.
Average fixation dispersion: Analysis of the data shows that only independent effect of language was significant for all four Dravidian vernacular groups i.e. Malayalam (F (1.824, 78.432) = 39.167, P<0.001), Tamil (F (1, 43) = 46.383, P<0.001), Telugu (F (2, 86) = 19.134, P<0.001) and Kannada (F (2, 86) = 37.855, P<0.001), but the independent effect of reading mode was not evident (Table-3). Interaction effect of language and mode was not significant among Malayalam, Tamil and Kannada vernacular groups but found to be significant in Telugu (F (2.86) = 3.572, P<0.05) population only.
Discussion
The present study was designed to evaluate the effect of using four Indian Dravidian vernacular language during onscreen reading process as compared to non-vernacular Hindi and English languages. It is known that ‘Language’ may act as a critical onscreen stressor (Dussias & Sagarra 2007; Felser et al., 2009). Therefore choosing proper working language may optimize the performance for a cognitive task and may greatly affect the productivity of the individual worker or communications among the operators working under the same network through information sharing. Psycholinguists have used a variety of behavioural measures to study how non-vernacular speakers engage during online exchange and comprehension of linguistic knowledge (Gennari et al., 2002). Fixational eye movements seem to enhance the visibility of the ‘word’ as the input of information takes place during fixation only and timely comprehension is an essential factor for military operations.
The word processing rate was lowest in Hindi, indicating that time constraint put higher cognitive load on the volunteers for reading this language (Poole et al., 2004; Rayner, 1998). Hindi was rated by the participants as ‘moderately’ (Figure-3) legible, but reading Hindi shows significant decrease in fixation count across the languages. In self-paced reading the marginal means of fixation count were overall higher for Hindi (Table-3), along with more time taken in Hindi while reading self-paced manner. This indicated that Hindi reading process may be more difficult than English and vernaculars and the result corroborated with the results of Ehrlich and Rayner (1981), Rayner and Well, (1996). When subjects underwent self-paced reading, they could read more words causing higher fixation counts which might have caused significant result in modal effect (Poole et al., 2004).
An interaction analysis reveals the significant difference between the marginal means of fixation frequency for the exposure to different languages across time bound reading. For time bound reading and self-paced reading the marginal means of fixation frequency in Malayalam, Tamil, Telugu and Kannada were different (Table-3). In self-paced reading the marginal means of fixation frequency were lowest in Hindi and highest in vernaculars. Researchers found that higher fixation frequency indicated quick acquisition of information during easier lexical processing (Rayner, 1998; Reichle et al., 2003). For early acquired language the fixation frequency was higher and for late acquired language, fixation frequency was lower in case of reading (Juhasz & Rayner, 2006), indicating easier lexical processing in case of early acquired language and difficulties in late acquired language (Rayner, 1998; Reichle et al., 2003). The results of our study suggests that participants acquired the vernacular language much early, hence they could process vernacular languages much easily and with a smoother lexical processing than non-vernacular.
For time bound reading and self-paced reading the marginal means of fixation duration for Malayalam and Kannada vernacular language were lower followed by English and Hindi. In case of Telugu and Tamil language group mean fixation duration in both the modes of reading was found to be lower for English. As established by the previous studies, fixation duration is a good indicator of language comprehension and controlled by several important factors, like lexical ambiguity (Rayner & Duffy, 1986), age of acquisition (Juhasz & Rayner, 2003), word familiarity (Juhasz & Rayner, 2003,2006), contextual constraint (Ehrlich & Rayner, 1981) and morphology (Hyönä & Pollatsek, 1998; Pollatsek et.al., 2000). It was observed that as the acquisition of vernacular was at very early age hence the fixation duration was found to be lower during reading (except Tamil population). In case of Hindi, due to late acquisition of language, (may be with less word familiarity and high lexical ambiguity) there was higher fixation duration. For Tamil participants, the fixation duration in vernacular was found to be much higher than English. Similar results were observed by previous studies (Hyönä & Pollatsek, 1998; Pollatsek et.al., 2000) and they suggested that morphological complexity could cause higher fixation duration in reading. Similarly in our study, the anomaly observed in Tamil participants may be due to the morphological effects of the languages. Tamil language has typographically more roundish words than English and almost every word has ascendants and descendants that cause complexity of word typeface. Another interesting observation in case of Tamil reading was the reading time, which was less in vernacular reading than English. Therefore higher fixation duration with low reading time indicated that the observation of present study were not because of lexical ambiguity but due to morphology of the typeface.
Authors have not come across any reported studies available that indicated specific effects of fixation dispersion on language processing. However it was hypothesized by previous studies that the numbers, positions, sizes and durations of fixation were function of the matrices used for dispersion in a dispersion based fixation detecting algorithm (Krassanakis et al., 2014; Nyström & Holmqvist, 2010; Urruty et al., 2007). In self-paced reading the marginal means of fixation dispersion was not significant. For time bound reading the marginal means of average fixation dispersion in all four Dravidian languages were significantly lower than Hindi. We have observed a significant main effect of language on this parameter for all language group studied. This indicated that the deviation of eye fixation through horizontal (‘x’) and vertical (‘y’) axis, may be due to the changes of workload imposed by combined effects of time constraint along with variation in languages.
Conclusion:
Reading time, proficiency score, word processing rate studied under present experimental protocol are a few of the indicators of efficiency of language processing in a given task. The subjective and experimental data of present study suggest that an early acquired language brought about better language proficiency, lower reading time and higher word processing rate. Our study elucidated the prominent effect of language on fixational eye movements. Fixation count was the main parameter that showed both language and time constraint effects. This could be due to the fact that fixation count is a summation based and any accumulative change is always more in case of self-paced reading. Results of this study may help in formulating recommendation regarding choice of language as a media for high density onscreen information processing operation requiring quick and accurate decision taking as in military and industrial operation.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the volunteers for their kind participation and professors of Modern Indian Literature of Delhi University for helping in the translation of different languages. Experiments were performed in 28 Madras Regiment at Delhi Cant, Delhi, India.
References
- Altarriba, J., J.F. Kroll, A. Scholl, and K. Rayner. 1996. The influence of lexical and conceptual constraints onreading mixed-language sentences:Evidence fromeye-fixations and reading times. Memory & Cognition 24: 477–492. [Google Scholar]
- Bax, S., and C. Weir. 2012. Investigating learners’ cognitive reading processes during a computer-based CAE reading test. University of Cambridge ESOL Examinations Research Notes 47: 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Blignaut, P., and T. Beelders. 2009. The effect of fixational eye movements on fixation identification with a dispersion-based fixation detection algorithm. Journal of Eye Movement Research 2, 5: 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld, H. K., and V. Marian. 2011. Bilingualism influences inhibitory control in auditory comprehension. Cognition 118: 245–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brunner, J. 2010. Bilingual Education and English as a Second Language Programs Summary Report, Z009-Z010. Austin Independent School District, Department of Program Evaluation. See http://archive.austinisd.org/inside/docs/ope_09_67__Bilingual_Education_and_English_as_a_Second_Language.pdf (accessed 29 May 2012).
- Cirilo, R. K., and D. J. Foss. 1980. Text structure and reading time for sentences. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behaviour 19: 96–109. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, A., and S. Bentin. 2001. Syntactic and semantic factors in processing gender agreement in Hebrew: Evidence from ERPs and eye movements. Journal of Memory and Language 45, 2: 200–224. [Google Scholar]
- Dewaele, J.-M. 2004. Edited by M.S. Schmid, B. Kopke, M. Kejser and L. Weilemar. Perceived language dominance and language preference for emotional speech: The implications for attrition research. In First Language Attrition: Interdisciplinary perspectives on methodological issues. Amsterdam/Philadelphia, PA: Benjamins, pp. 81–104. [Google Scholar]
- Encyclopaedia Britannica. 2008. Dravidian languages. Encyclopaedia Britannica Online. Jun. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Declaration of Helsinki. World Medical Association. Available from: http://www.wma.net/e/ethicsunit/helsinki.htm (accessed on 24 June 2008).
- Dussias, P. E., and N. Sagarra. 2007. The effect of exposure on syntactic parsing in Spanish English bilinguals. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 10: 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Duyck, W., E. Van Assche, D. Drieghe, and R. J. Hartsuiker. 2007. Visual word recognition by bilinguals in a sentence context: Evidence for non-selective lexical access. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 33: 663–679. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, S. F., and K. Rayner. 1981. Contextual effects on word perception and eye movements during reading. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 20: 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felser, C., M. Sato, and N. Bertenshaw. 2009. The on-line application of binding Principle A in English as a second language. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 12: 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecken, M. 2011. Event conceptualization by early Dutch-German bilinguals: Insights from linguistic and eye-tracking data. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 14: 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gennari, S., S. Sloman, B. Malt, and T. Fitch. 2002. Motion events in language and cognition. Cognition 83: 49–79. [Google Scholar]
- Godfroid, A., F. Boers, and A. Housen. 2013. Gauging the role of attention in L2 vocabulary acquisition by means of eye-tracking. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 35, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gollan, T.H., G.H. Weissberger, E. Runnqvist, R.I. Montoya, and C.M. Cera. 2012. Self-ratings of spoken language dominance: A Multilingual Naming Test (MINT) and preliminary norms for young and aging Spanish-English bilinguals. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 15: 594–615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heredia, R. 1997. Bilingual memory and hierarchical models: A case for language dominance. Current Directions in Psychological Science 6: 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hyltenstam, K., and N. Abrahamsson. 2003. Edited by K. Fraurud and K. Hyltenstam. Age of onset and ultimate attainment in near-native speakers of Swedish. In Multilingualism in global and local perspectives. Selected papers from the 8th Nordic conference on bilingualism, November 1–3, 2001, Stockholm Rinkeby. Stockholm: Centre for Research on Bilingualism, Stockholm University, and Rinkeby Institute of Multilingual Research, pp. 319–340. [Google Scholar]
- Hyönä, J., and A. Pollatsek. 1998. Reading Finnish compound words: Eye fixations are affected by component morphemes. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 24: 1612–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Juhasz, B.J., and K. Rayner. 2003. Investigating the effects of a set of intercorrelated variables on eye fixation durations in reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 29: 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juhasz, B.J., and K. Rayner. 2006. The role of age-of-acquisition and word frequency in reading: Evidence from eye fixation durations. Visual Cognition 13: 846–863. [Google Scholar]
- Just, M. A., and P. A. Carpenter. 1980. A theory of reading: From eye fixations to comprehension. Psychological Review 87, 4: 329–354. [Google Scholar]
- Just, M. A., and P. A. Carpenter. 1987. The psychology of reading and language comprehension. Boston: Allyn and Bacon. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushanskaya, M., H.K. Blumenfeld, and V. Marian. 2011. The relationship between vocabulary and short-term memory measures in monolingual and bilingual speakers. The International Journal of Bilingualism 15, 4: 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krassanakis, V., V. Filippakopoulou, and B. Nakos. 2014. Eyemmv toolbox:An eye movement post-analysis tool based on a two-step spatial dispersion threshold for fixation identification. Journal of Eye Movement Research 7, 1: 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurti, Bhadriraju. 2003. The Dravidian Languages. Cambridge University Press: ISBN 0-521-77111-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, V.P.C., S.J. Rickard Liow, M. Lincoln, Y.K. Chan, and M. Onslow. 2008. Determining language dominance in English-Mandarin bilinguals: Development of a self-report classification tool for clinical use. Applied Psycholinguistics 29: 389–412. [Google Scholar]
- Marian, V., H.K. Blumenfeld, and M. Kaushanskaya. 2007. The Language Experience and Proficiency Questionnaire (LEAP-Q): Assessing language profiles in bilinguals and multilinguals. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 50: 940–967. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J. C. 1987. Language Learning, Language Acquisition, or Language Growth? In Modgil and Modgil, eds., 41-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, D.C., and D.W. Green. 1978. The effects of context and content on immediate processing in reading. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 30: 609–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, W., J. D. Fodor, S. Crain, and D. Shankweiler. 1998. Anomaly detection: Eye movement patterns. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 27, 5: 515–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nyström, M., and K. Holmqvist. 2010. An adaptive algorithm for fixation, saccade, and glissade detection in eyetracking data. Behav Res Methods 42, 1: 188–204. [Google Scholar]
- Piaget, Jean, and Bärbel Inhedler. 1969. The psychology of the child. Basic Books: ISBN 0465095003. ISBN-13 9780465095001. [Google Scholar]
- Pollatsek, A., J. Hyönä, and R. Bertram. 2000. The role of morphological constituents in reading Finnish compound words. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 26: 820–833. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, A., L. J. Ball, and P. Phillips. 2004. In search of salience: A response time and eye movement analysis of bookmark recognition. In peopleand computers XVIII-Design for Life: Proceedings of HCI 2004. Edited by S. Fincher, P. Markopolous, D. Moore and R. Ruddle. London: Springer-Verlag Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Rah, A. 2010. Transfer in L3 sentence processing: Evidence from relative clause attach-ment ambiguities. International Journal of Multilingualism 7: 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, K. 1998. Eye movements in reading and information processing: 20 years of research. Psychological Bulletin 124, 3: 372–422. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, K., and S. Duffy. 1986. Lexical complexity and fixation times in reading: Effects of word frequency, verb complexity, and lexical ambiguity. Memory & Cognition 14: 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, K., and A. D. Well. 1996. Effects of contextual constraint on eye movements in reading: A further examination. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 3: 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Reichle, E. D., K. Rayner, and A. Pollatsek. 2003. The E-Z Reader model of eye movement control in reading: Comparisons to other models. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 26: 445–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L., M. Gullberg, and P. Indefrey. 2008. Online pronoun resolution in L2 discourse: L1 influence and general learner effects. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 30: 333–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R., J. Patton, L. Ganschow, N. Humbach, and J. Javorsky. 2008. Early L1 reading and spelling skills predict later L2 reading and spelling skills. Journal of Educational Psychology 100: 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamamaki, K. 1993. Language dominance in bilinguals' arithmetic operations according to their language use. Language Learning 43: 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokowicz, N., E.B. Michael, and J.F. Kroll. 2004. The roles of study-abroad experience and working memory capacity in the types of errors made during translation. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 7: 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urruty, T., S. Lew, N. Ihadeddene, and D. A. Simovici. 2007. Detecting eye fixations by projection clustering. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winke, P., S. Gass, and T. Sydorenko. 2013. Factors influencing the use of captions by foreign language learners: An eye-tracking study. The Modern Language Journal 97, 1: 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D., H. Park, D. Gerold, and G. E. Legge. 2010. Comparing reading speed for horizontal and vertical English text. Journal of Vision 10, 2: 21, 1–17. http://journalofvision.org/10/2/21/. [CrossRef]
Copyright © 2015. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.