Binocular Coordination During Smooth Pursuit in Dyslexia: A Multiple Case Study
Abstract
:Introduction
Methods
Participants
Oculomotor task
Eye movement recording
Data analysis
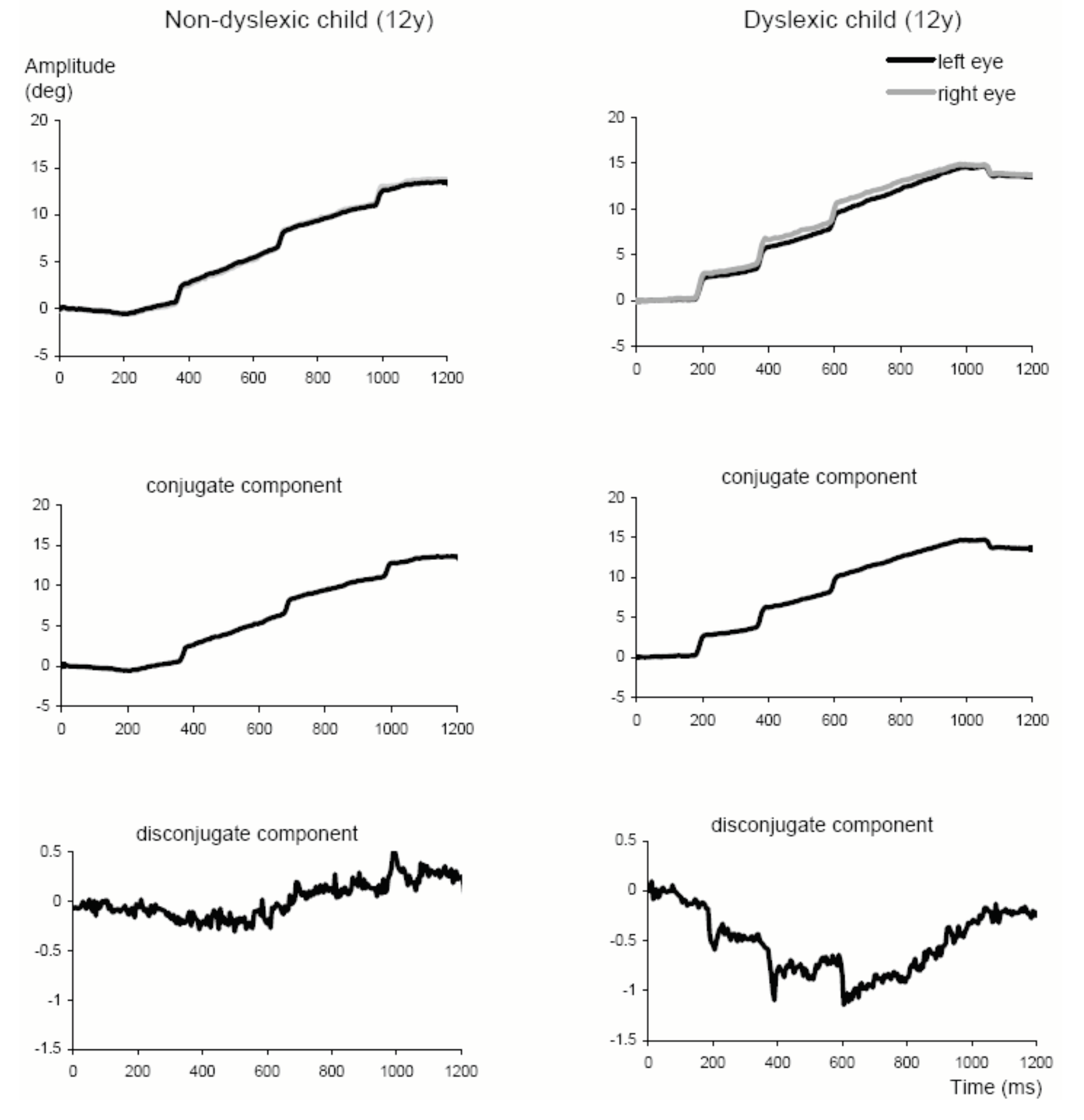
Results
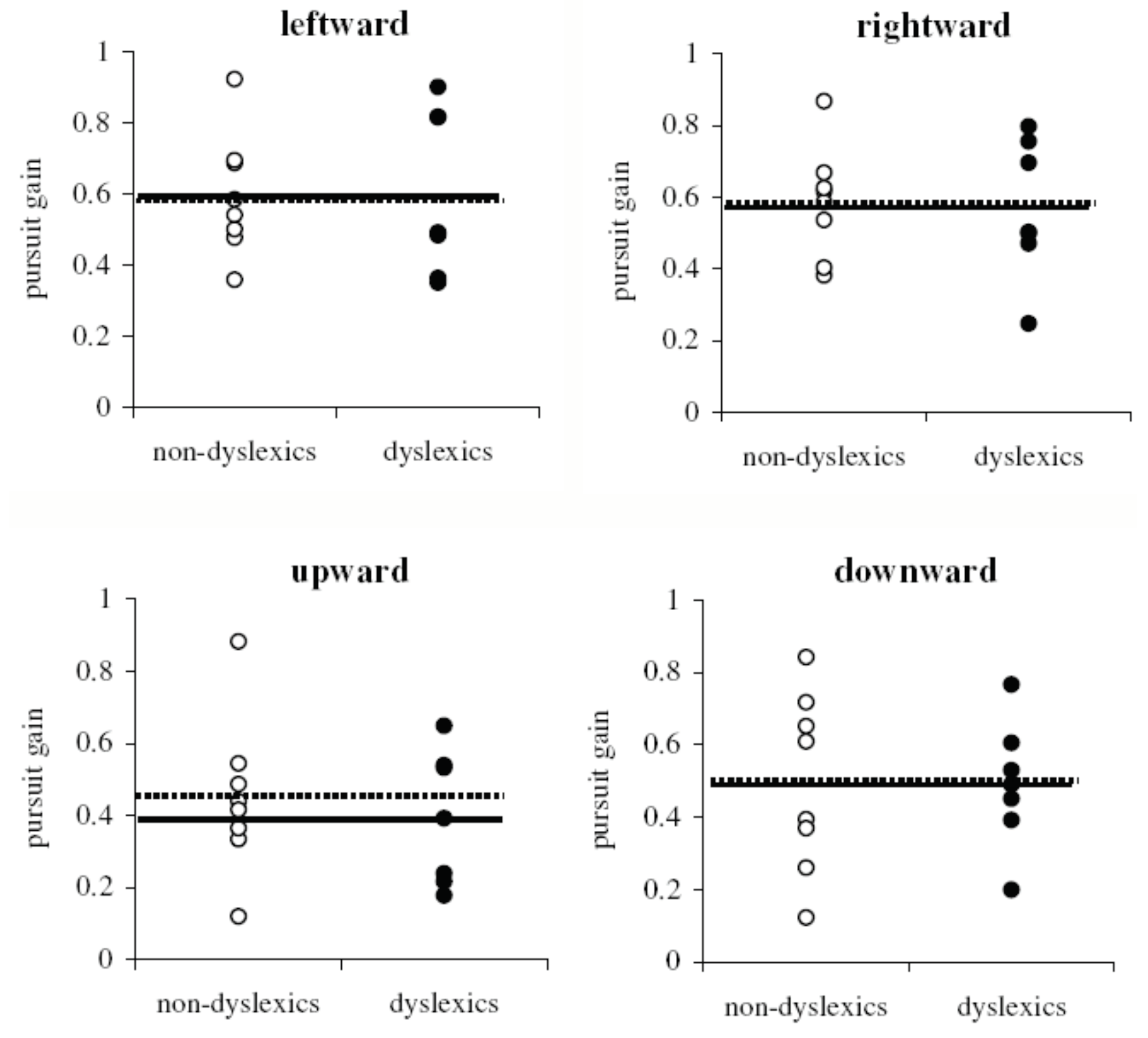
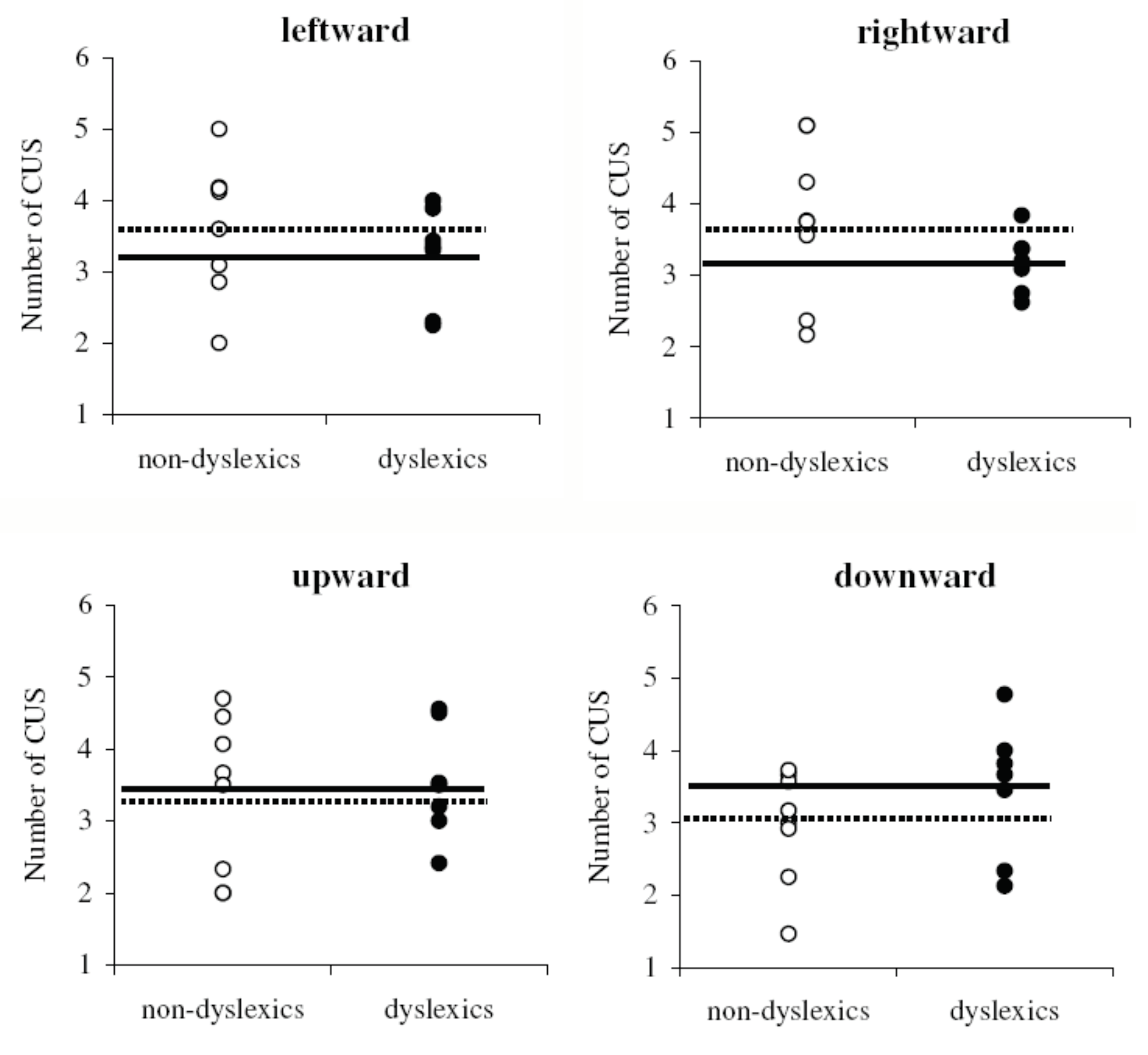
Pursuit parameters
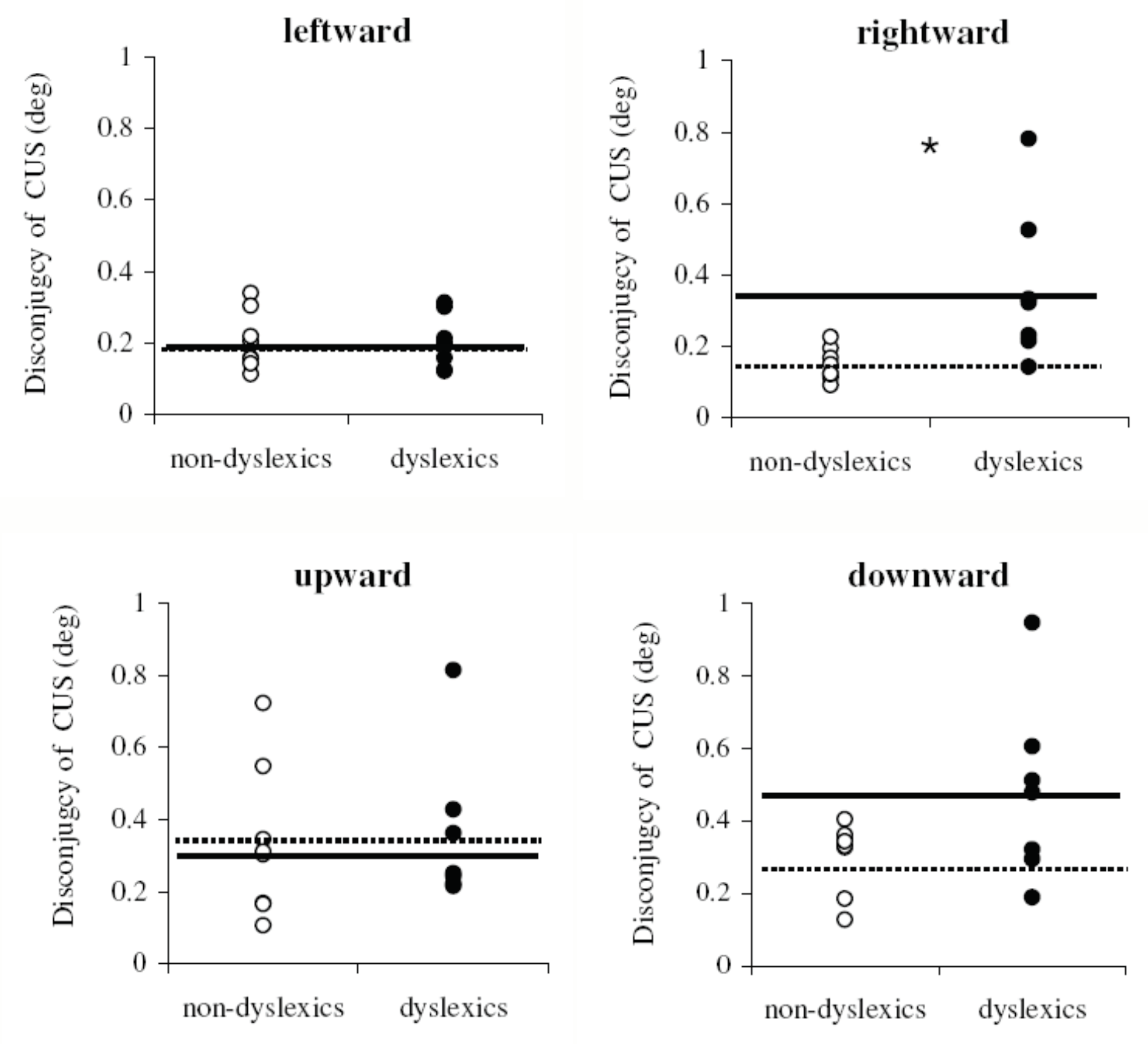
Disconjugacy values
Discussion
Similar characteristics of SP in normal and dyslexic children
Direction specific pursuit disconjugacy in dyslexics
References
- Barkovich, A.J. 2000. Concepts of myelin and myelination in neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21, 6: 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biscaldi, M., B. Fischer, and F. Aiple. 1994. Saccadic eye movements of dyslexic and normal reading children. Perception 23, 1: 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biscaldi, M., S. Gezeck, and V. Stuhr. 1998. Poor saccadic control correlates with dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 36, 11: 1189–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Black, J.L., D.W. Collins, J.N. De Roach, and S.R. Zubrick. 1984. Smooth pursuit eye movements in normal and dyslexic children. Percept Mot Skills 59, 1: 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bucci, M.P., D. Bremond-Gignac, and Z. Kapoula. 2008a. Latency of saccades and vergence eye movements in dyslexic children. Exp Brain Res 188, 1: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P., D. Bremond-Gignac, and Z. Kapoula. 2008b. Poor binocular coordination of saccades in dyslexic children. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246, 3: 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callu, D., I. Giannopulu, S. Escolano, F. Cusin, M. Jac-quier-Roux, and G. Dellatolas. 2005. Smooth pursuit eye movements are associated with phonological awareness in preschool children. Brain Cogn 58, 2: 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Chevrie-Muller, C., A.M. Simon, and S. Fournier. 1997. Batterie language oral écrit, mémoire, attention (L2MA). Editions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, A.H., J. Ditterich, K. Druen, U. Schonfeld, and C. Steineke. 2002. Using high frame rate CMOS sensors for three-dimensional eye tracking. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 34, 4: 549–560. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen, P., L. Bradley, S. Fowler, and J. Stein. 1991. What children see affects how they read. Dev Med Child Neurol 33, 9: 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen, P.L., P.C. Hansen, J.L. Hutton, V. Evangelinou, and J.F. Stein. 1998. Magnocellular visual function and children’s single word reading. Vision Res 38, 3: 471–482. [Google Scholar]
- de Brouwer, S., D. Yuksel, G. Blohm, M. Missal, and P. Lefevre. 2002. What triggers catch-up saccades during visual tracking? J Neurophysiol 87, 3: 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, G.F., J.F. Stein, H.M. Wood, and F.B. Wood. 1994. Differences in eye movements and reading problems in dyslexic and normal children. Vision Res 34, 10: 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L., J.A. Jesberger, L.A. Abel, and H.Y. Meltzer. 1992. Catch-up saccade amplitude is related to square wave jerk rate. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33, 1: 228–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, J., S. Tanaka, J.D. Williams, and K. Fukushima. 2005. Voluntary control of saccadic and smooth-pursuit eye movements in children with learning disorders. Brain Dev 27, 8: 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M., C.M. Harris, F. Shawkat, and D. Taylor. 1997. Smooth pursuit development in infants. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol 25, 3: 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.K., W.L. Hong, D.W. Hommer, S.D. Ham-burger, F.X. Castellanos, J.A. Frazier, J.N. Giedd, C.T. Gordon, B.I. Karp, K. McKenna, and J.L. Rapoport. 1996. Smooth pursuit eye movements in childhood-onset schizophrenia: comparison with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and normal controls. Biol Psychiatry 40, 11: 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, J., M. Caravolas, and P.C. Knox. 2006. Smooth pursuit eye movements and phonological processing in adults with dyslexia. Cognitive neuropsychology 23, 8: 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoula, Z., M.P. Bucci, F. Jurion, J. Ayoun, F. Afkhami, and D. Bremond-Gignac. 2007. Evidence for frequent divergence impairment in French dyslexic children: Deficit of convergence relaxation or of divergence per se? Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245, 7: 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoula, Z., R. Ganem, S. Poncet, D. Gintautas, T. Eggert, D. Bremond-Gignac, and M.P. Bucci. 2008. Free exploration of painting uncovers particularly loose yoking of saccades in dyslexics. Dyslexia. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanis, J., W.G. Iacono, and M. Harris. 1998. Development of oculomotor functioning in preadolescence, adolescence, and adulthood. Psychophysiology 35, 1: 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauzlis, R.J., M.A. Basso, and R.H. Wurtz. 2000. Discharge properties of neurons in the rostral superior colliculus of the monkey during smooth-pursuit eye movements. J Neurophysiol 84, 2: 876–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumra, S., A. Sporn, D.W. Hommer, R. Nicolson, G. Thaker, E. Israel, M. Lenane, J. Bedwell, L.K. Jacobsen, P. Gochman, and J.L. Rapoport. 2001. Smooth pursuit eye-tracking impairment in childhood-onset psychotic disorders. Am J Psychiatry 158, 8: 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langaas, T., M. Mon-Williams, J.P. Wann, E. Pascal, and C. Thompson. 1998. Eye movements, prematurity and developmental co-ordination disorder. Vision Res 38, 12: 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, R.J., and D.S. Zee. 2006. The neurology of eye movements (fourth edition). Oxford University Press: pp. 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Moschner, C., T.J. Crawford, W. Heide, P. Trillenberg, D. Kompf, and C. Kennard. 1999. Deficits of smooth pursuit initiation in patients with degenerative cerebellar lesions. Brain 122, Pt 11: 2147–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson, R.I., A.J. Fawcett, and P. Dean. 2001. Devel-opmental dyslexia: The cerebellar deficit hypothesis. Trends Neurosci 24, 9: 508–511. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlidis, G.T. 1981. Do eye movements hold the key to dyslexia? Neuropsychologia 19, 1: 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, C., J. Andersson, E. Paulesu, and J.F. Demonet. 2009. When all hypotheses are right: A multifocal account of dyslexia. Hum Brain Mapp. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, C., A. Karmiloff-Smith, M.A. Lee, R.M. Dixon, J. Grant, A.M. Blamire, C.H. Thompson, P. Styles, and G.K. Radda. 1998. Brain biochemistry in Wil-liams syndrome: Evidence for a role of the cerebellum in cognition? Neurology 51, 1: 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramus, F., S. Rosen, S.C. Dakin, B.L. Day, J.M. Castellote, S. White, and U. Frith. 2003. Theories of de-velopmental dyslexia: insights from a multiple case study of dyslexic adults. Brain 126, Pt 4: 841–865. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, M., and J. Barroso. 2002. Delayed pursuit of health care among HIV-positive gay men enrolled in a longitudinal research study. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care 13, 4: 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rashbass, C. 1961. The relationship between saccadic and smooth tracking eye movements. J Physiol 159, 326–338. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R.G., A.D. Radant, and D.W. Hommer. 1993. A developmental study of smooth pursuit eye movements in normal children from 7 to 15 years of age. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 32, 4: 783–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snashall, S.E. 1983. Vestibular function tests in chil-dren. J R Soc Med 76, 7: 555–559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sparks, D.L., and M.F. Jay. 1986. The functional organization of the primate superior colliculus: A motor perspective. Prog Brain Res 64, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J. 2001. The magnocellular theory of developmental dyslexia. Dyslexia 7, 1: 12–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.F., A.J. Richardson, and M.S. Fowler. 2000. Monocular occlusion can improve binocular control and reading in dyslexics. Brain 123, Pt 1: 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.F., P.M. Riddell, and S. Fowler. 1988. Disordered vergence control in dyslexic children. Br J Oph-thalmol 72, 3: 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, M., D.S. Zee, and R.J. Tamargo. 2000. Effects of lesions of the oculomotor cerebellar vermis on eye movements in primate: Smooth pursuit. J Neuro-physiol 83, 4: 2047–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Takarae, Y., N.J. Minshew, B. Luna, C.M. Krisky, and J.A. Sweeney. 2004. Pursuit eye movement deficits in autism. Brain 127, Pt 12: 2584–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.R., and J.C. Lynch. 1996. Functionally defined smooth and saccadic eye movement subregions in the frontal eye field of Cebus monkeys. J Neurophysiol 76, 4: 2740–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Vernet, M., Q. Yang, G. Daunys, C. Orssaud, T. Eggert, and Z. Kapoula. 2008. How the brain obeys Her-ing’s law: a TMS study of the posterior parietal cortex. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49, 1: 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Versino, M., O. Hurko, and D.S. Zee. 1996. Disorders of binocular control of eye movements in patients with cerebellar dysfunction. Brain 119, Pt 6: 1933–1950. [Google Scholar]


Copyright © 2010. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Vernet, M.; Bucci, M.-P.; Kapoula, Z. Binocular Coordination During Smooth Pursuit in Dyslexia: A Multiple Case Study. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2009, 3, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.3.3.2
Yang Q, Vernet M, Bucci M-P, Kapoula Z. Binocular Coordination During Smooth Pursuit in Dyslexia: A Multiple Case Study. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2009; 3(3):1-8. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.3.3.2
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qing, Marine Vernet, Maria-Pia Bucci, and Zoi Kapoula. 2009. "Binocular Coordination During Smooth Pursuit in Dyslexia: A Multiple Case Study" Journal of Eye Movement Research 3, no. 3: 1-8. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.3.3.2
APA StyleYang, Q., Vernet, M., Bucci, M.-P., & Kapoula, Z. (2009). Binocular Coordination During Smooth Pursuit in Dyslexia: A Multiple Case Study. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 3(3), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.3.3.2


