Incorporation of Prior Knowledge and Habits While Solving Anagrams
Abstract
:Introduction
Methods
Participants
Apparatus
Procedure
Results
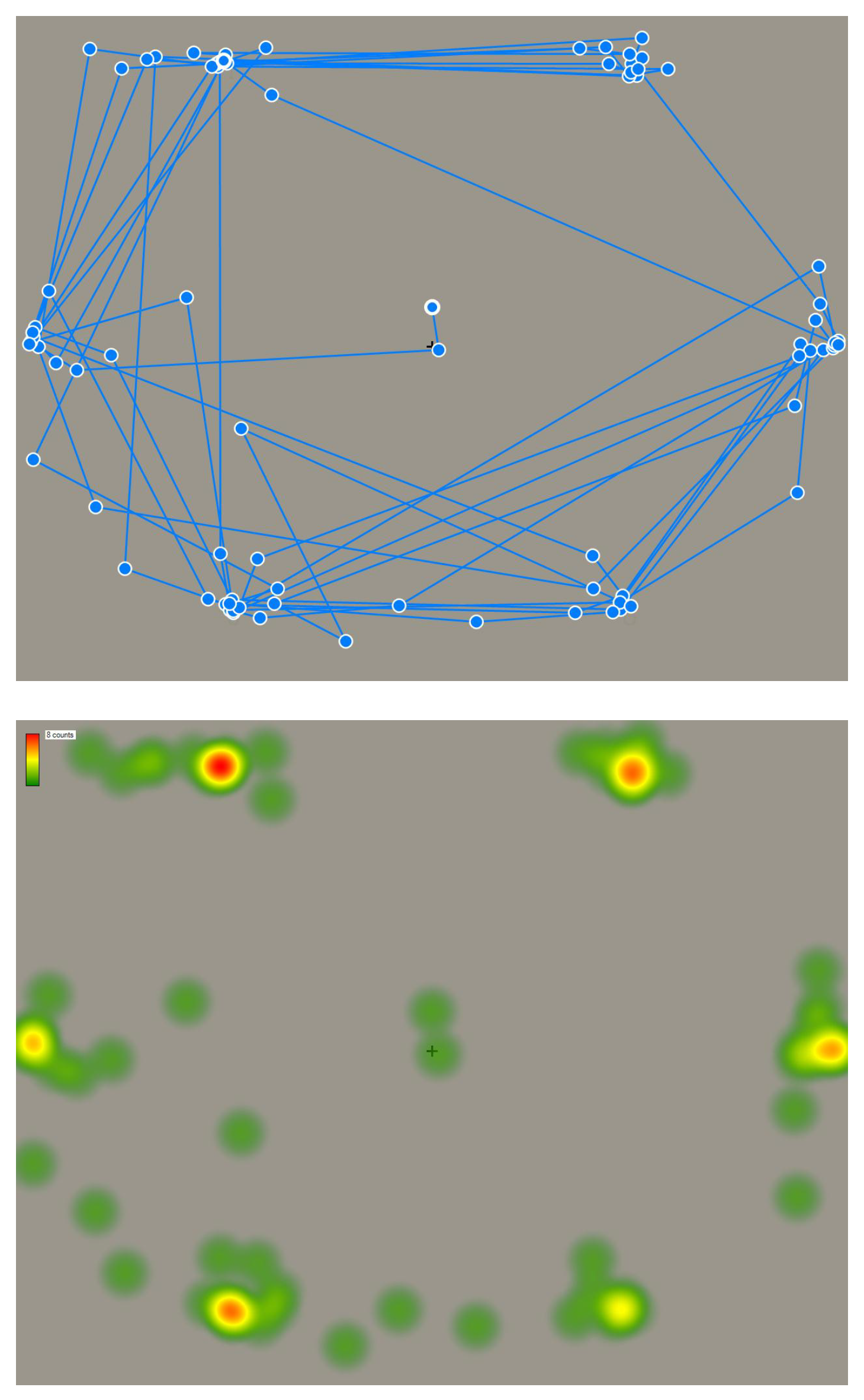
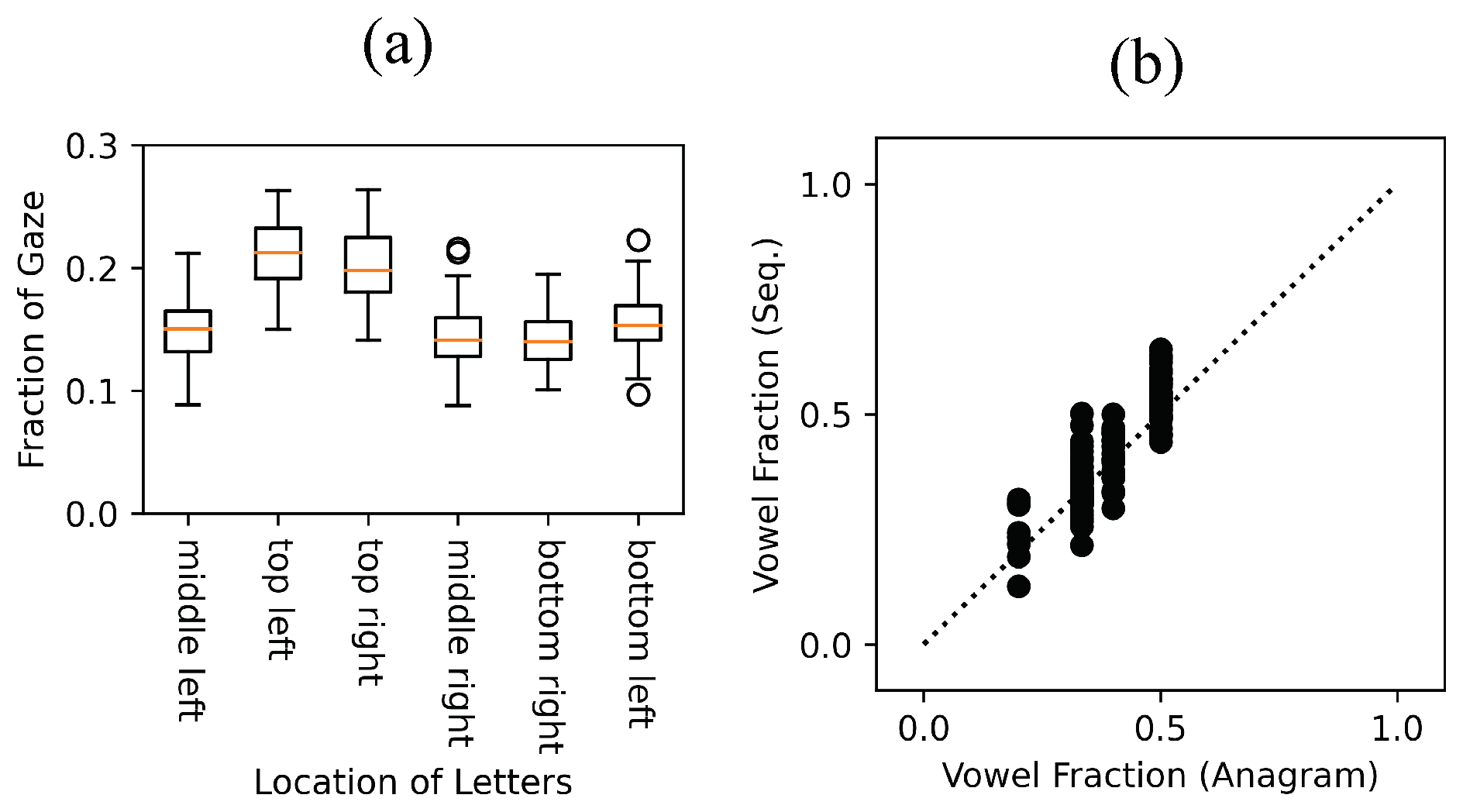
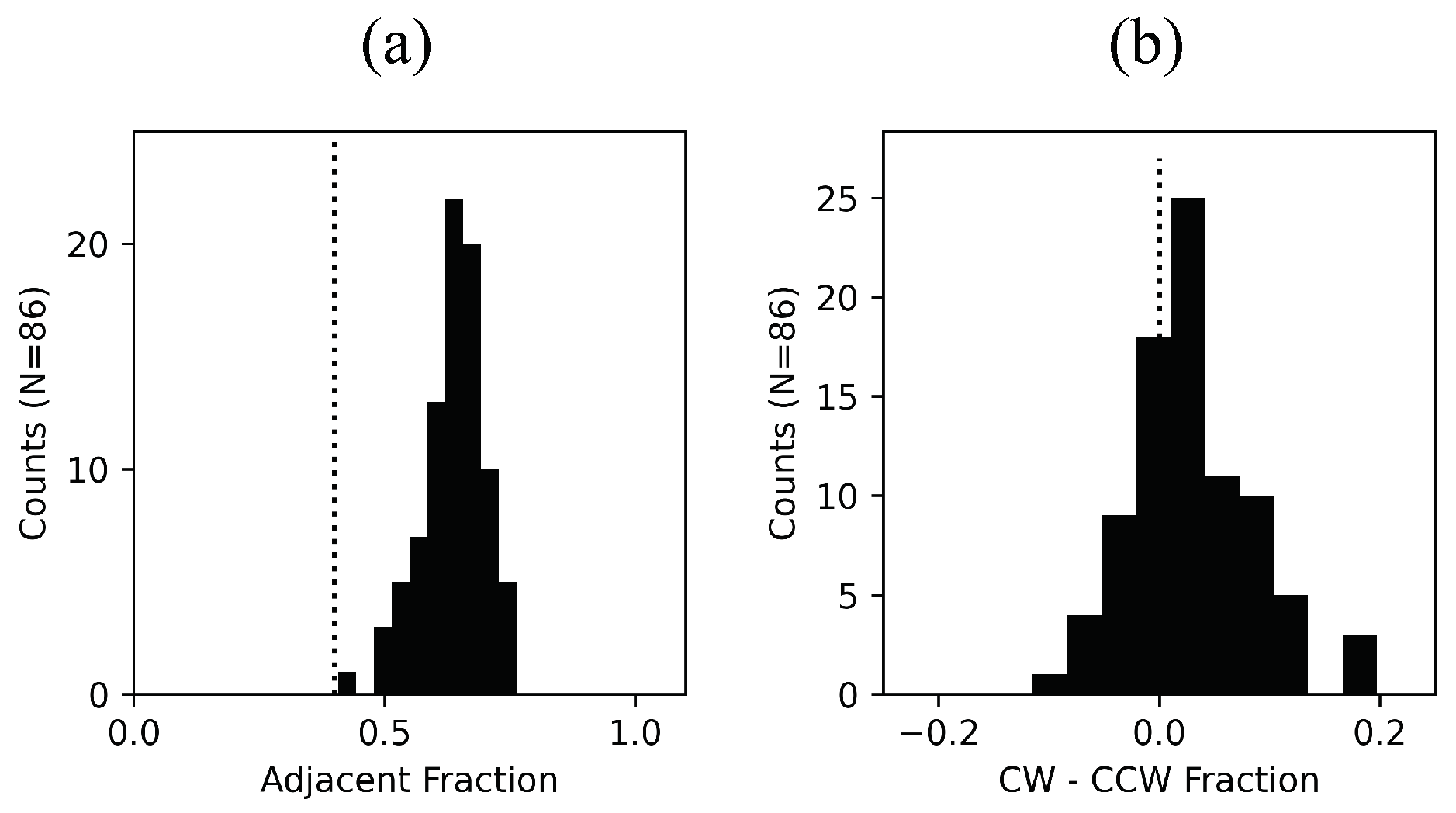
Result #1: Habitual Scanning Patterns Strongly Influence the Gaze Sequence
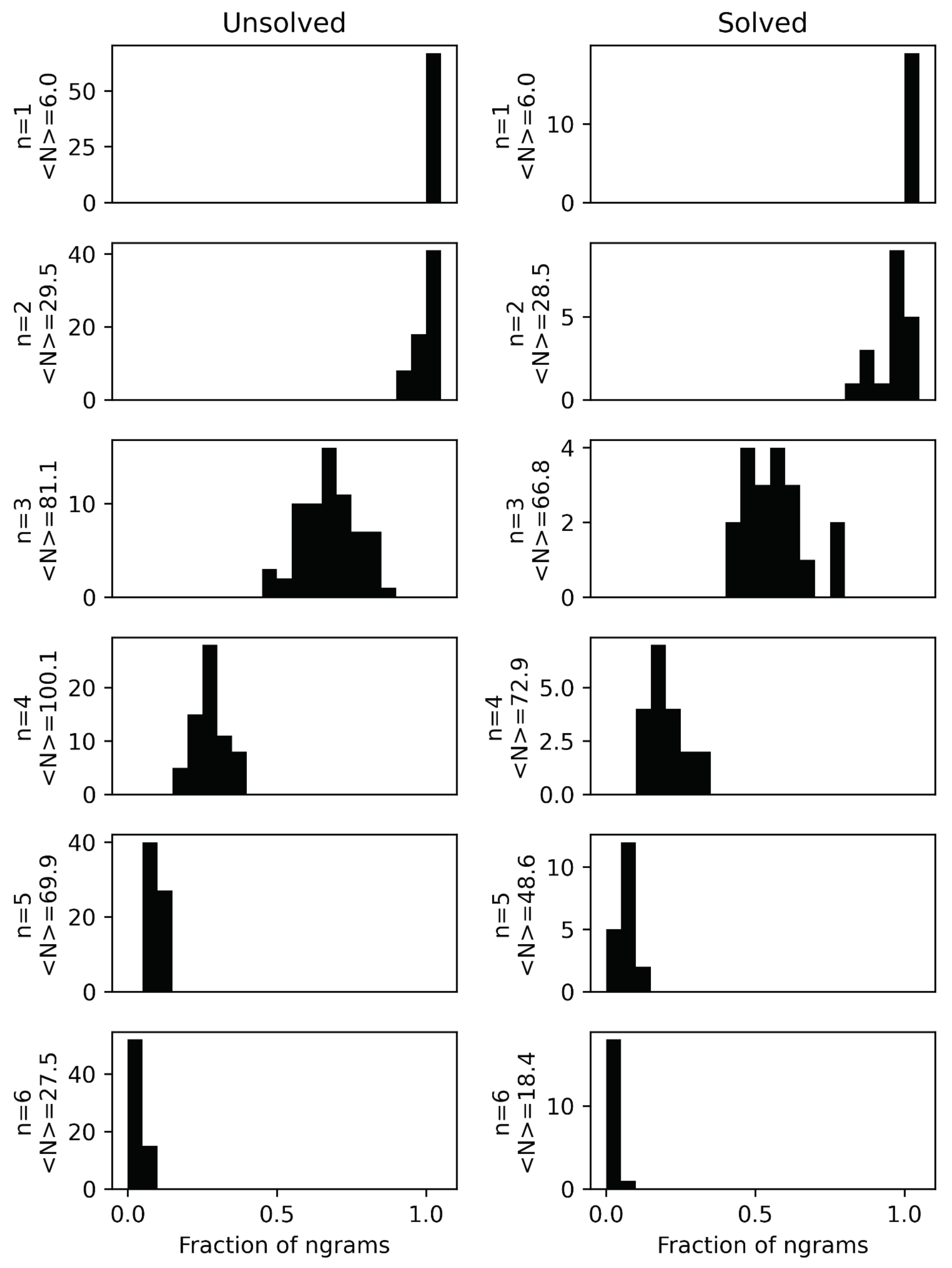
Result #2: The Knowledge of Language Statistics Influences Problem-Solving Behavior
Result #3: The Gaze Patterns on a Suggestive Solution Bigram Do Not Differ Whether the Participant Was Able to Solve the Anagram Puzzle or Not
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, G. S., B. A. Converse, A. H. Hales, and L. E. Klotz. 2021. People systematically overlook subtractive changes. Nature 592: 258–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benedek, M., R. Stoise, S. Walcher, and C. Körner. 2017. Eye behavior associated with internally versus externally directed cognition. Frontiers in Psychology 8: 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, C., and D. Ford. 1961. A study of the statistics of letters in English words. Information and Control 4: 48–67. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, B., and T. Griffiths. 2016. Algorithms to live by: The computer science of human decisions. New York: Henry Holt and Co., Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, S. E., and R. M. Shiffrin. 2013. Edited by C. Chubb, B. A. Dosher, Z.-L. Lu. and R. M. Shiffrin. Short-term visual priming across eye movements. In Human information processing: Vision, memory, and attention. American Psychological Association: pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezalova, J., and S. Popelka. 2016. ScanGraph: A Novel Scanpath Comparison Method Using Visualisation of Graph Cliques. Journal of Eye Movement Research 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgin, F. H., E. Doyle, and L. Egan. 2008. Upper-left gaze bias reveals competing search strategies in a reverse Stroop task. Acta Psychologica 127, 2: 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J., M. Glaholt, and E. Reingold. 2011. Eye movements reveal solution knowledge prior to insight. Consciousness and Cognition 20: 768–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J., and E. Reingold. 2014. The Einstellung effect in anagram problem solving: Evidence from eye movements. Frontiers in Psychology 5: 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, D., E. Brown, J. Chu-Carroll, J. Fan, D. Gondek, A. A. Kalyanpur, A. Lally, J. W. Murdock, E. Nyberg, J. Prager, N. Schlaefer, and C. Welty. 2010. Building Watson: An Overview of the DeepQA Project. AI Magazine 31, 3: 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C., and D. Bavelier. 2003. Action video game modifies visual selective attention. Nature 423: 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, T. L. 2011. Rethinking language: How probabilities shape the words we use. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108, 10: 3825–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, F. E., and G. Beck. 1972. Extension of sample sizes and percentage points for significance tests of outlying observations. Technometrics 14, 4: 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K., K. Meints, C. Hall, S. Hall, and D. Mills. 2009. Left gaze bias in humans, rhesus monkeys and domestic dogs. Animal Cognition 12: 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S., T. Häikiö, K. Olli, and J. Kaakinen. 2021. Eye Movements during dynamic scene viewing are affected by visual attention skills and events of the scene: Evidence from first-person shooter gameplay videos. Journal of Eye Movement Research 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B., and L. Ding. 2021. Sequential and simultaneous synthesis problem solving: A comparison of students’ gaze transitions. Physical Review Physics Education Research 17: 010126. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, I. T., and W. N. Schoenfeld. 1966. Oculomotor patterns during the solution of visually displayed anagrams. Journal of Experimental Psychology 72, 3: 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Knoblich, G., S. Ohlsson, and G. Raney. 2001. An eye movement study of insight problem solving. Memory and Cognition 29, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kowler, E. 2011. Eye movements: The past 25 years. Vision Research 51, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, C., M. Falker, J. Miklaus, L. Persello, S. Klöppel, T. Nef, and P. Urwyler. 2021. Application of eye tracking in puzzle games for adjunct cognitive markers: Pilot observational study in older adults. JMIR Serious Games 9, 1: e24151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapteva, E. M. 2016. Eye movements as indicator of solution knowledge in anagram solving. Experimental Psychology (Russia) 9, 3: 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., R. Donaldson, A. Subramaniam, H. Palmer, C. D. Champion, M. L. Cox, and L. G. Appelbaum. 2021. Developing expert gaze pattern in laparoscopic surgery requires more than behavioral training. Journal of Eye Movement Research 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V., K. Kavukcuoglu, D. Silver, A. A. Rusu, J. Veness, M. G. Bellemare, A. Graves, M. Riedmiller, A. K. Fidjeland, G. Ostrovski, and S. Petersen. 2015. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518, 7540: 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M., N. Krucien, and F. Hermens. 2018. The eyes have it: Using eye tracking to inform information processing strategies in multi-attribute choices. Health Economics 27, 4: 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, A. C., D. I. Braun, and K. R. Gegenfurtner. 2011. Eye movements and perception: A selective review. Journal of Vision 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D., A. Huang, C. J. Maddison, A. Guez, L. Sifre, G. Van Den Driessche, J. Schrittwieser, I. Antonoglou, V. Panneershelvam, M. Lanctot, and S. Dieleman. 2016. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529: 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinitsyn, D. O., I. S. Bakulin, A. G. Poydasheva, A. L. Liudmila, E. I. Kremneva, D. Y. Lagoda, A. Y. Chernyavskiy, A. A. Medyntsev, N. A. Suponeva, and M. A. Piradov. 2020. Brain activations and functional connectivity patterns associated with insight-based and analytical anagram solving. Behavioral Sciences 10: 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H., E. Day, L. Kendhammer, J. N. Moore, S. A. Brown, and N. J. Pienta. 2016. Eye movement patterns in solving science ordering problems. Journal of Eye Movement Research 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, D. 2022. Wordle is a love story. The New York Times, January 3. [Google Scholar]
- Vaid, J., and M. Singh. 1989. Asymmetries in the perception of facial affect: Is there an influence of reading habits? Neuropsychologia 27, 10: 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulving, E., D. L. Schacter, and H. A. Stark. 1982. Priming effects in word-fragment completion are independent of recognition memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 8, 4: 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C., and C. C. Liu. 2021. Eye-movement study of high- and low-prior-knowledge students’ scientific argumentations with multiple representations. Physical Review Physics Education Research 17: 010125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarbus, A. L. 1967. Eye movements and vision. New York. [Google Scholar]





© 2022 by the authors. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Murray, J.; Sutter, A.; Lobifaro, A.; Cousens, G.; Kouh, M. Incorporation of Prior Knowledge and Habits While Solving Anagrams. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2022, 15, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.5.5
Murray J, Sutter A, Lobifaro A, Cousens G, Kouh M. Incorporation of Prior Knowledge and Habits While Solving Anagrams. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2022; 15(5):1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.5.5
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurray, Jesse, Andrew Sutter, Angelia Lobifaro, Graham Cousens, and Minjoon Kouh. 2022. "Incorporation of Prior Knowledge and Habits While Solving Anagrams" Journal of Eye Movement Research 15, no. 5: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.5.5
APA StyleMurray, J., Sutter, A., Lobifaro, A., Cousens, G., & Kouh, M. (2022). Incorporation of Prior Knowledge and Habits While Solving Anagrams. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 15(5), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.5.5


