Assessment of Cognitive Biases in Augmented Reality: Beyond Eye Tracking
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Participants
Design
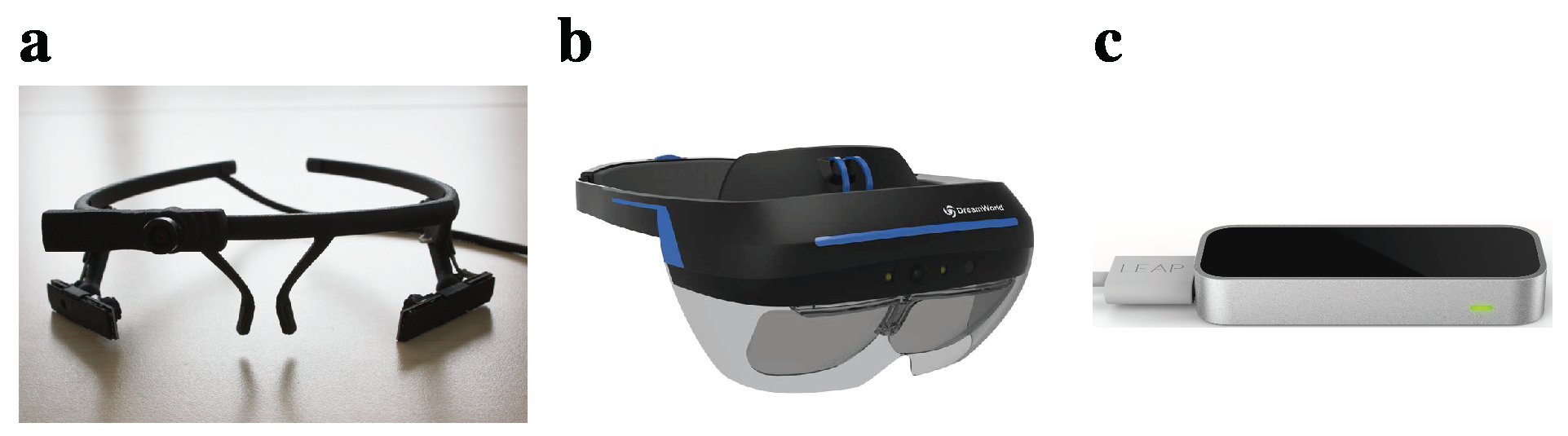
Materials
Procedure
Data collection and pre-processing
Biometric measures
Velocity distributions
 of the head, hand and gaze (just 2 dimensions so:
of the head, hand and gaze (just 2 dimensions so:  In comparison with point measures (e.g., means, medians, standard deviations) distributions preserves significantly more information about a sample and thus allows for more accurate analysis. To approximate the distributions, we used histograms with bin edges obtained when applying the Freedman-Diaconis rule (Freedman & Diaconis, 1981) to the combined velocity values from all the datasets of a given modality. The rule is particularly suitable for velocity data with heavy-tailed distributions (see examples in Figure 4).
In comparison with point measures (e.g., means, medians, standard deviations) distributions preserves significantly more information about a sample and thus allows for more accurate analysis. To approximate the distributions, we used histograms with bin edges obtained when applying the Freedman-Diaconis rule (Freedman & Diaconis, 1981) to the combined velocity values from all the datasets of a given modality. The rule is particularly suitable for velocity data with heavy-tailed distributions (see examples in Figure 4).Earth mover’s distance
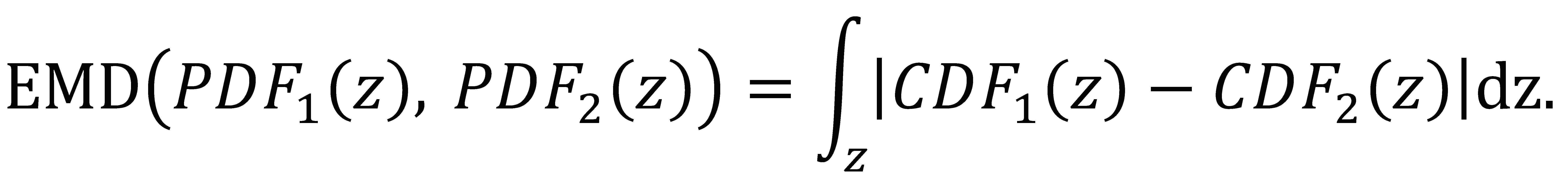
Correlation matrices
Riemannian distance
 where λn are the N eigenvalues of a matrix
where λn are the N eigenvalues of a matrix  (or equivalently
(or equivalently 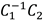 ) (Congedo et al., 2017; Słowiński et al., 2019).
) (Congedo et al., 2017; Słowiński et al., 2019).Data analysis
Multi-dimensional scaling
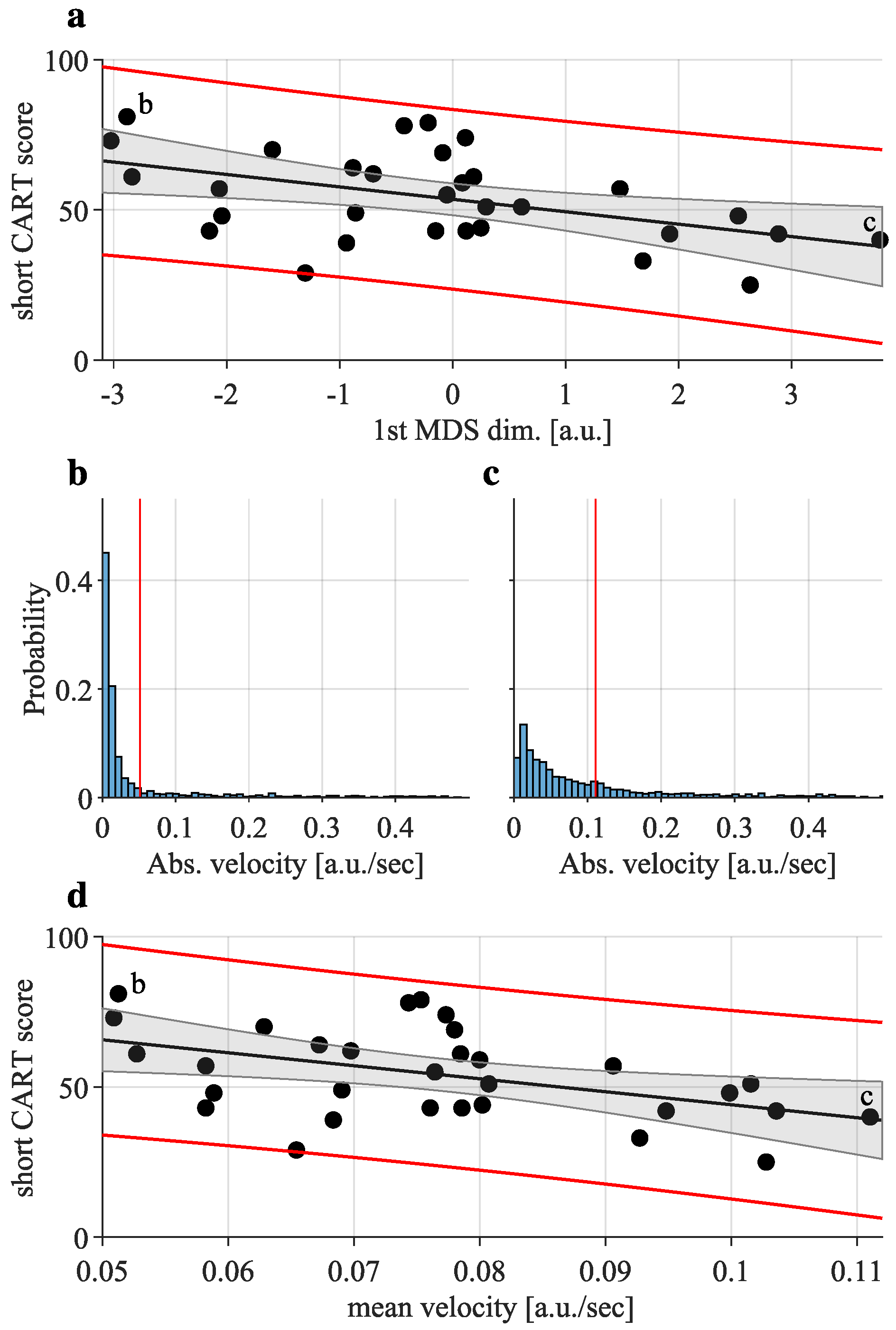
Regression analysis
Results
Task Performance
Movement Modalities (Velocity distributions)
Coordination Patterns
Discussion
Synthesis of findings
Limitations
Future Research/Exploitation
Ethics and Conflict of Interest
Acknowledgements
References
- Anastasopoulos, D., J. Naushahi, S. Sklavos, and A. M. Bronstein. 2015. Fast gaze reorientations by combined movements of the eye, head, trunk and lower extremities. Experimental Brain Research 233, 5: 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Araújo, D., K. Davids, and R. Hristovski. 2006. The ecological dynamics of decision making in sport. Psychology of Sport and Exercise 7, 6: 653–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, M. C., and K. Lee. 2009. The HEXACO–60: A short measure of the major dimensions of personality. Journal of Personality Assessment 91, 4: 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J., M. S. García-Vázquez, J. Benois-Pineau, L. M. Gutierrez-Robledo, and J.-F. Dartigues. 2018. Computational techniques for eye movements analysis towards supporting early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2018: Article 2676409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, V. 2021. The measurement of individual differences in cognitive biases: A review and improvement. Frontiers in Psychology 12: Article 630177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal-Barby, J. S., and H. Krieger. 2015. Cognitive biases and heuristics in medical decision making: A critical review using a systematic search strategy. Medical Decision Making: An International Journal of the Society for Medical Decision Making 35, 4: 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S., and L. Guibas. 1997. The earth mover’s distance: Lower bounds and invariance under translation [Technical Report]. Defense Technical Information Center. http://i.stanford.edu/pub/cstr/reports/cs/tr/97/1597/CS-TR-97-1597.pdf.
- Congedo, M., A. Barachant, and R. Bhatia. 2017. Riemannian geometry for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces: A primer and a review. Brain-Computer Interfaces 4, 3: 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreamworld AR. n.d.Dream Glass AR Headset. Dreamworld AR. Retrieved November 1, 2022, from https://www.dreamworldvision.com/.
- Ehrlinger, J., W. O. Readinger, and B. Kim. 2016. Edited by H. S. Friedman. Decision-making and cognitive biases. In Encyclopedia of Mental Health. Elsevier. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R., and R. Kliegl. 2003. Microsaccades uncover the orientation of covert attention. Vision Research 43, 9: 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D., and P. Diaconis. 1981. On the histogram as a density estimator: L2 theory. Zeitschrift Für Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie Und Verwandte Gebiete 57, 4: 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigerenzer, G., and W. Gaissmaier. 2011. Heuristic decision making. Annual Review of Psychology 62, 1: 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigerenzer, G., and P. M. Todd. 2001. Simple heuristics that make us smart. Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- HEXACO. n.d.The HEXACO Personality Inventory—Revised. Retrieved November 1, 2022, from http://hexaco.org/hexaco-inventory.
- Hoppe, S., T. Loetscher, S. A. Morey, and A. Bulling. 2018. Eye movements during everyday behavior predict personality traits. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 12: 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacowitz, D. M. 2005. The gaze of the optimist. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 31, 3: 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovancevic-Misic, J., and M. Hayhoe. 2009. Adaptive Gaze Control in Natural Environments. Journal of Neuroscience 29, 19: 6234–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahneman, D. 2013. Thinking, fast and slow. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. [Google Scholar]
- Kassner, M., W. Patera, and A. Bulling. 2014. Pupil: An open source platform for pervasive eye tracking and mobile gaze-based interaction. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct Publication. pp. 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. J., N. Adluru, B. B. Bendlin, S. C. Johnson, B. C. Vemuri, and V. Singh. 2014. Edited by D. Fleet, T. Pajdla, B. Schiele and T. Tuytelaars. Canonical correlation analysis on Riemannian manifolds and its applications. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014. Springer International Publishing: pp. 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G. 2015. A naturalistic decision making perspective on studying intuitive decision making. Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition 4, 3: 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M. F. 2009. Vision, eye movements, and natural behavior. Visual Neuroscience 26, 1: 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levina, E., and P. Bickel. 2001. The earth mover’s distance is the Mallows distance: Some insights from statistics. Proceedings Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. ICCV 2001 2: 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebers, J., P. Horn, C. Burschik, U. Gruenefeld, and S. Schneegass. 2021. Using gaze behavior and head orientation for implicit identification in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology. p. Article 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, S., M. Gahalawat, T. Guha, and R. Subramanian. 2021. Head matters: explainable human-centered trait prediction from head motion dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Multimodal Interaction. pp. 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, D. P., M. O. Craig, E. A. Stewart, and P. Y. Warren. 2017. Thinking fast, not slow: How cognitive biases may contribute to racial disparities in the use of force in police-citizen encounters. Journal of Criminal Justice 53: 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, F. J. M., R. Baddeley, and N. Canagarajah. 2012. Eye Movements to Natural Images as a Function of Sex and Personality. PLoS ONE 7, 11: Article e47870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskulus, M., and S. Verduyn-Lunel. 2011. Wasserstein distances in the analysis of time series and dynamical systems. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena 240, 1: 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaeizadeh, S., I. E. Dror, and R. M. Morgan. 2014. Cognitive bias in forensic anthropology: Visual assessment of skeletal remains is susceptible to confirmation bias. Science & Justice 54, 3: 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niechwiej-Szwedo, E., D. Gonzalez, M. Nouredanesh, and J. Tung. 2018. Evaluation of the Leap Motion Controller during the performance of visually-guided upper limb movements. PLoS ONE 13, 3: Article e0193639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orquin, J. L., and S. Mueller Loose. 2013. Attention and choice: A review on eye movements in decision making. Acta Psychologica 144, 1: 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, E., and S. Schofield. 2018. Cognitive bias in clinical medicine. Journal of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh 48, 3: 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oullier, O., and F. Basso. 2010. Embodied economics: How bodily information shapes the social coordination dynamics of decision-making. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 365, 1538: 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeuffer, K., M. J. Geiger, S. Prange, L. Mecke, D. Buschek, and F. Alt. 2019. Behavioural biometrics in VR: Identifying people from body motion and relations in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. p. Article 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupil Labs Calibration. 2020. Hmd-eyes [C#]. Pupil Labs. March 19. https://github.com/pupil-labs/hmdeyes/blob/a0ad8ce5bb1e115a886d986a9c48af316364ce9e/docs/Developer.md#calibration.
- Raab, M., and G. Gigerenzer. 2015. The power of simplicity: A fast-and-frugal heuristics approach to performance science. Frontiers in Psychology 6: Article 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauthmann, J. F., C. T. Seubert, P. Sachse, and M. R. Furtner. 2012. Eyes as windows to the soul: Gazing behavior is related to personality. Journal of Research in Personality 46, 2: 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riby, D. M., and P. J. B. Hancock. 2008. Viewing it differently: Social scene perception in Williams syndrome and Autism. Neuropsychologia 46, 11: 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risko, E. F., N. C. Anderson, S. Lanthier, and A. Kingstone. 2012. Curious eyes: Individual differences in personality predict eye movement behavior in sceneviewing. Cognition 122, 1: 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, P. E. 2011. Building and solving odd-one-out classification problems: A systematic approach. Intelligence 39, 5: 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattuck, L. G., N. L. Miller, and K. E. Kemmerer. 2009. Tactical decision making under conditions of uncertainty: An empirical study. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting 53, 4: 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H. A. 1979. Rational decision making in business organizations. The American Economic Review 69, 4: 493–513. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1808698.
- Słowiński, P., F. Alderisio, C. Zhai, Y. Shen, P. Tino, C. Bortolon, D. Capdevielle, L. Cohen, M. Khoramshahi, A. Billard, R. Salesse, M. Gueugnon, L. Marin, B. G. Bardy, M. di Bernardo, S. Raffard, and K. Tsaneva-Atanasova. 2017. Unravelling socio-motor biomarkers in schizophrenia. npj Schizophrenia 3: Article 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Słowiński, P., H. Baldemir, G. Wood, O. Alizadehkhaiyat, G. Coyles, S. Vine, G. Williams, K. Tsaneva-Atanasova, and M. Wilson. 2019. Gaze training supports self-organization of movement coordination in children with developmental coordination disorder. Scientific Reports 9, 1: Article 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słowiński, P., C. Zhai, F. Alderisio, R. Salesse, M. Gueugnon, L. Marin, B. G. Bardy, M. di Bernardo, and K. Tsaneva-Atanasova. 2016. Dynamic similarity promotes interpersonal coordination in joint action. Journal of The Royal Society Interface 13, 116: Article 20151093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G. 2018. Step away from stepwise. Journal of Big Data 5, 1: Article 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanovich, K. E. 2016. The comprehensive assessment of rational thinking. Educational Psychologist 51, 1: 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanovich, K. E., R. F. West, and M. E. Toplak. 2018. The rationality quotient: Toward a test of rational thinking. The MIT Press: https://mitpress.mit.edu/9780262535274/the-rationality-quotient/.
- Street, J. O., R. J. Carroll, and D. Ruppert. 1988. A note on computing robust regression estimates via iteratively reweighted least squares. The American Statistician 42, 2: 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S. S. 2008. Edited by M. J. Metzger and A. J. Flanagin. The MAIN Model: A Heuristic Approach to Understanding Technology Effects on Credibility. In Digital media, youth, and credibility. The MIT Press: pp. 73–100. https://mitpress.mit.edu/9780262562324/digital-media-youthand-credibility/.
- Sundar, S. S., M. D. Molina, and E. Cho. 2021. Seeing is believing: Is video modality more powerful in spreading fake news via online messaging apps? Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 26, 6: 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, G. J., and M. L. Rizzo. 2013. The distance correlation t-test of independence in high dimension. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 117: 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.-H., I. G. M. Cameron, G. Pari, J. N. Reynolds, D. P. Munoz, and L. Itti. 2013. High-throughput classification of clinical populations from natural viewing eye movements. Journal of Neurology 260, 1: 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultraleap. 2022. Leap Motion Controller [Data Sheet]. Ultraleap. https://www.ultraleap.com/datasheets/Leap_Motion_Controller_Datasheet.pdf.
- Williams, B. S. 2010. Heuristics and Biases in Military Decision Making. Military Review 90, 5: 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, C., Z. Luo, D. Watling, and S. Durant. 2022. Twenty seconds of visual behaviour on social media gives insight into personality. Scientific Reports 12: Article 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








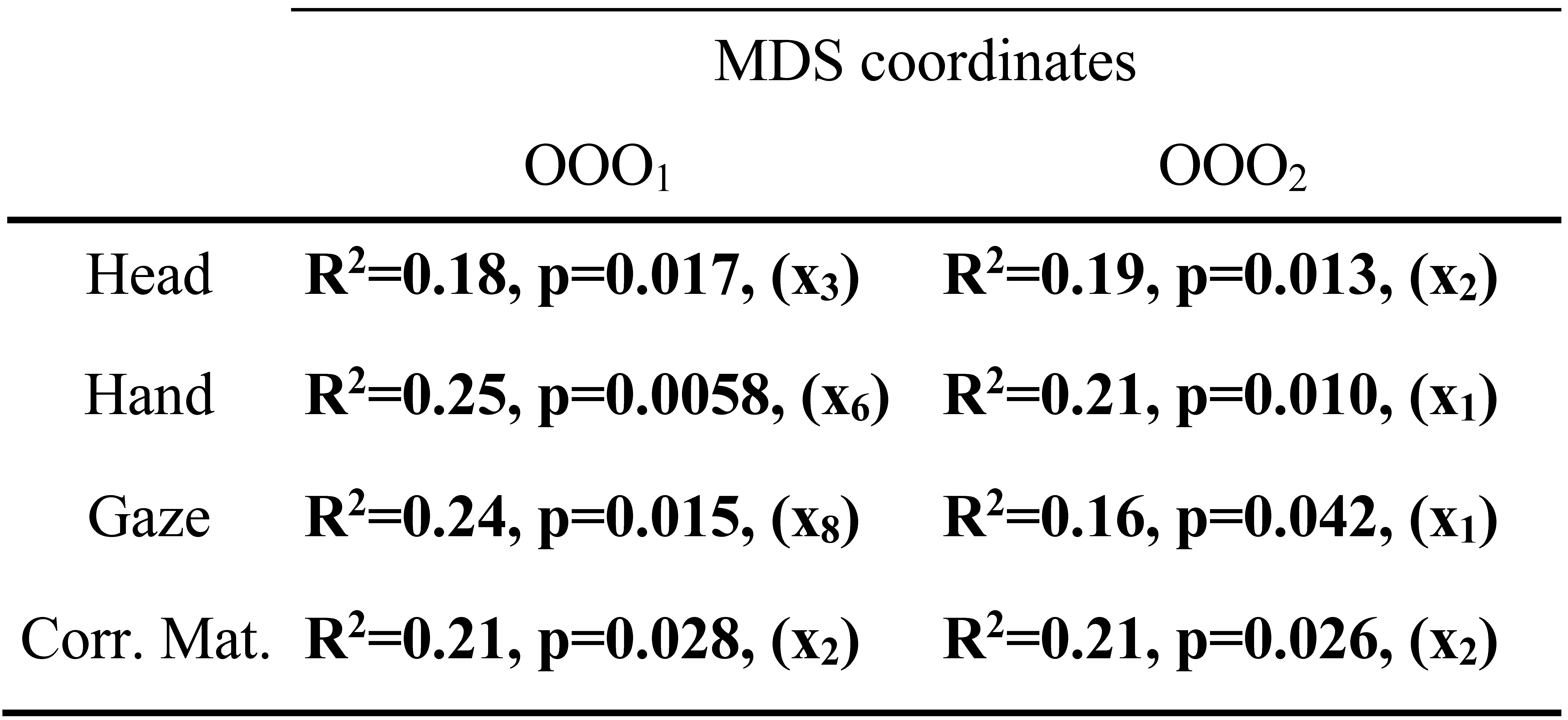
| CART | Head | Hand | Gaze | Corr. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OOO1 | 32 | 31 | 29 | 24 | 24 |
| OOO2 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 26 | 25 |

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Słowiński, P.; Grindley, B.; Muncie, H.; Harris, D.J.; Vine, S.J.; Wilson, M.R. Assessment of Cognitive Biases in Augmented Reality: Beyond Eye Tracking. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2022, 15, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.3.4
Słowiński P, Grindley B, Muncie H, Harris DJ, Vine SJ, Wilson MR. Assessment of Cognitive Biases in Augmented Reality: Beyond Eye Tracking. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2022; 15(3):1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.3.4
Chicago/Turabian StyleSłowiński, Piotr, Ben Grindley, Helen Muncie, David J Harris, Samuel J Vine, and Mark R Wilson. 2022. "Assessment of Cognitive Biases in Augmented Reality: Beyond Eye Tracking" Journal of Eye Movement Research 15, no. 3: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.3.4
APA StyleSłowiński, P., Grindley, B., Muncie, H., Harris, D. J., Vine, S. J., & Wilson, M. R. (2022). Assessment of Cognitive Biases in Augmented Reality: Beyond Eye Tracking. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 15(3), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.15.3.4



