Increased Microsaccade Rate in Individuals with ADHD Traits
Abstract
:Introduction
Methods
Participants
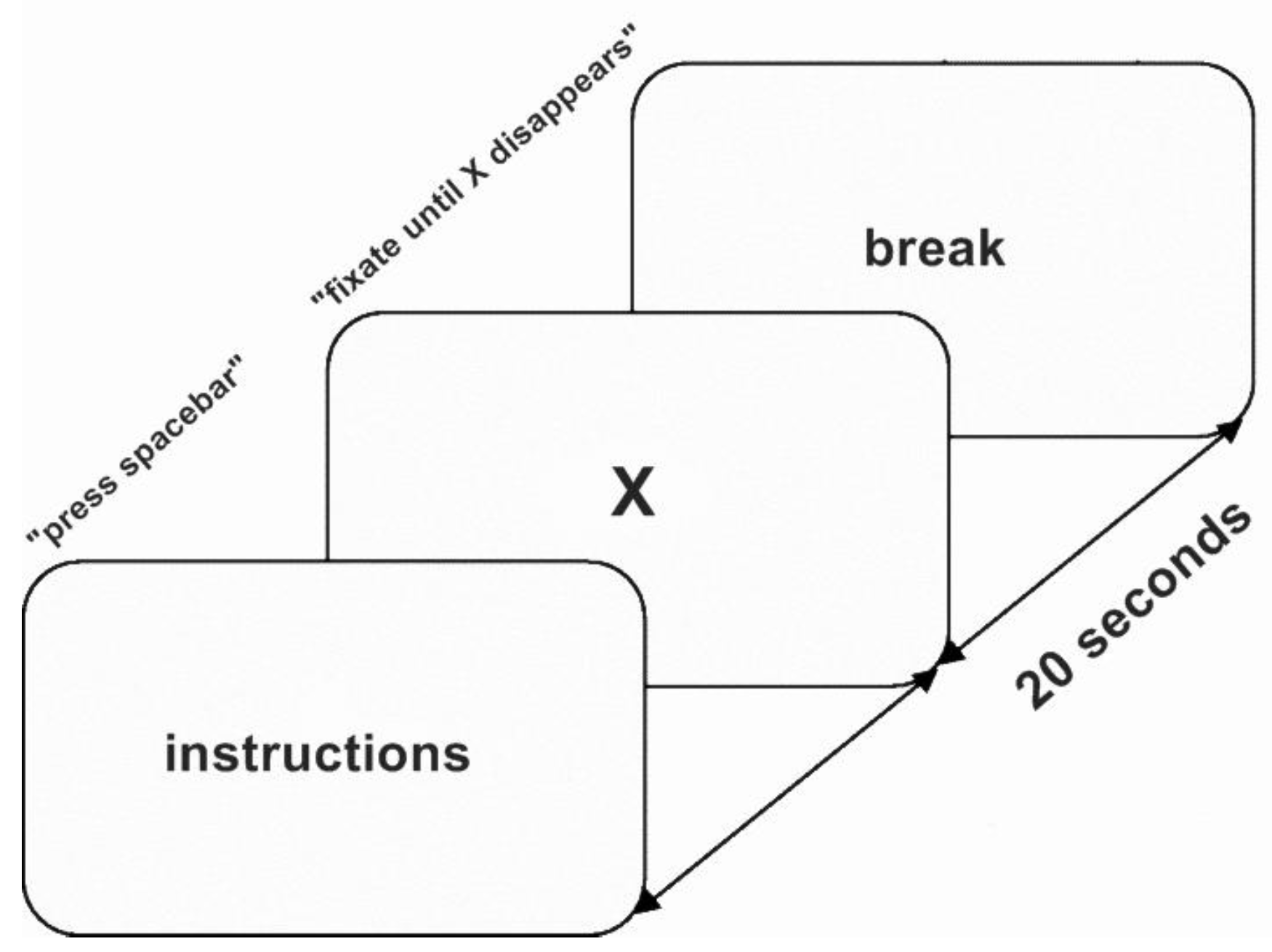
Materials and Procedure
Data Analysis
Results
ASRS Scores
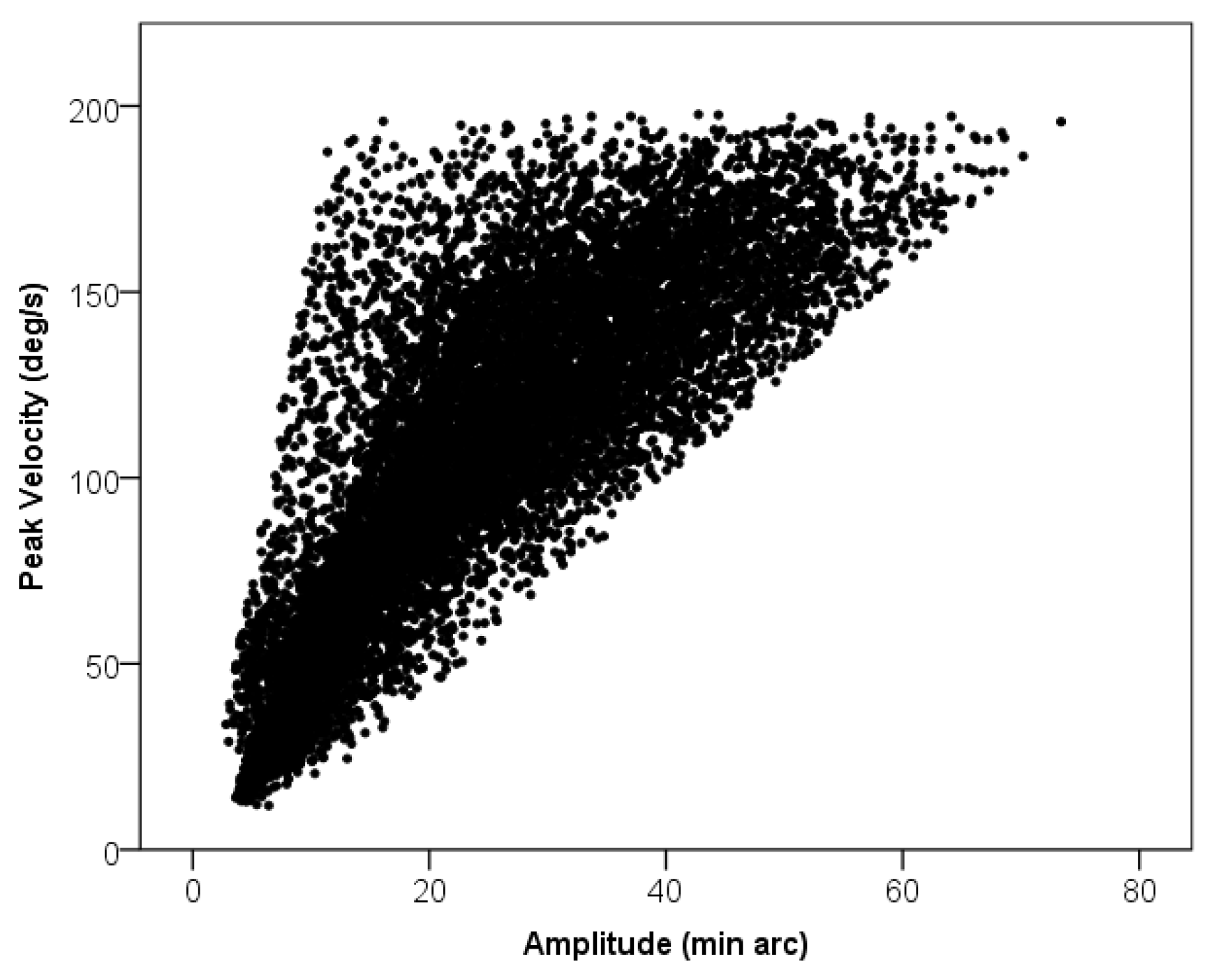
Microsaccade Features
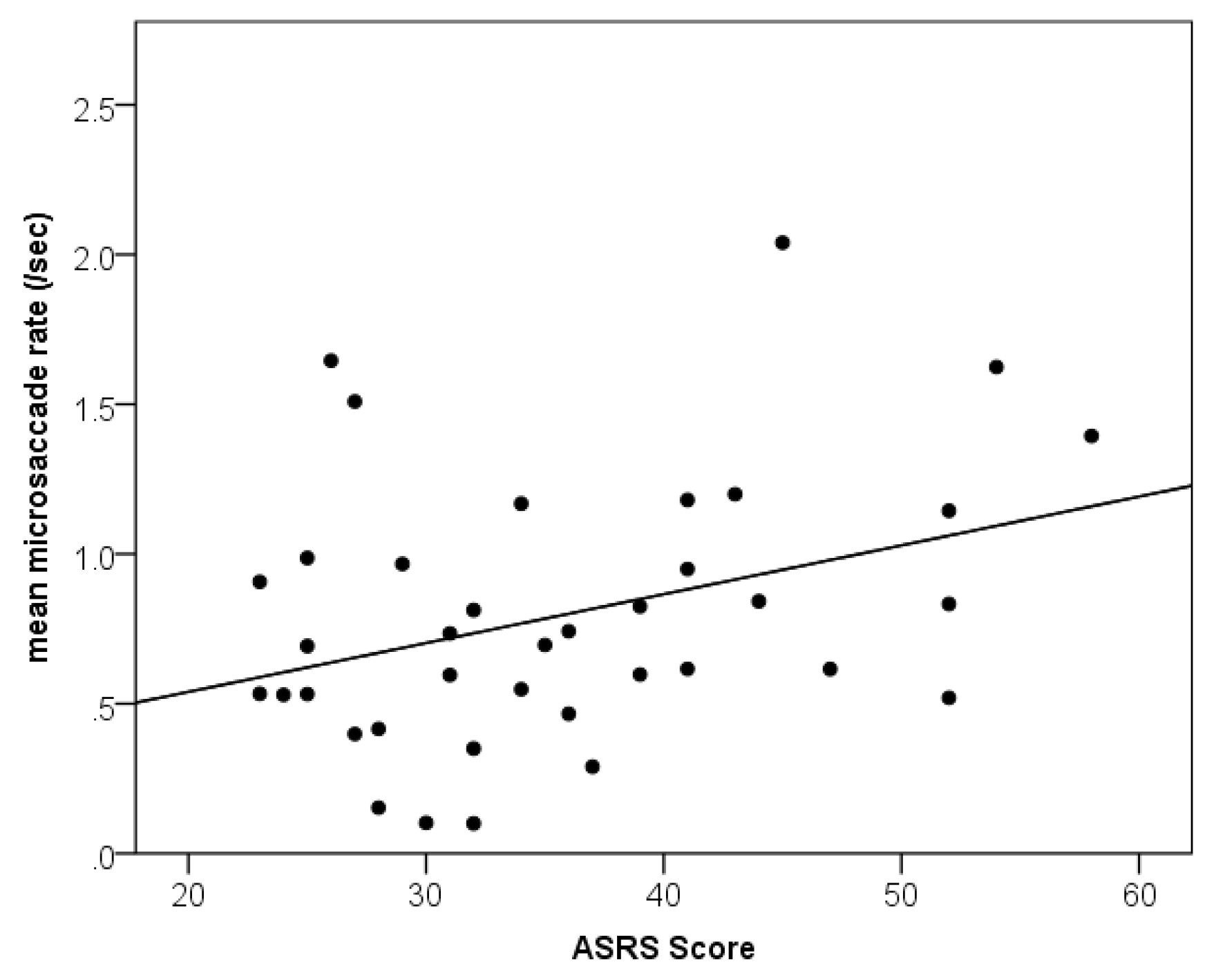
Relationship between ADHD Traits and Microsaccades
ADHD Traits and Tracking Noise
Discussion
A biomarker for ADHD?
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, L. A. Clinical presentations of adult patients with ADHD. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2004, 65 Suppl 3, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, I. T.; Munoz, D. P. Attentional blink in adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Experimental Brain Research 2003, 152(2), 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A. F. Stimulants: therapeutic actions in ADHD. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31(11), 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, S.; Pedrotti, M.; Bridgeman, B. Microsaccades and exploratory saccades in a naturalistic environment. Journal of Eye Movement Research 2011, 4(2). [Google Scholar]
- Buttross, S. Attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder and its deceivers. Current Problems in Pediatrics 2000, 30(2), 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K. M.; Devonshire, I. M.; Reynolds, J. N. J.; Overton, P. G. Enhanced visual responses in the superior colliculus in an animal model of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and their suppression by d-amphetamine. Neuroscience 2014, 274, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Dimigen, O.; Valsecchi, M.; Sommer, W.; Kliegl, R. Human microsaccade-related visual brain responses. The Journal of Neuroscience 2009, 29(39), 12321–12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditchburn, R.; Ginsborg, B. Vision with a stabilized retinal image. Dodge, R. (1907). An experimental study of visual fixation. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied 1952, 8(4), i–95. [Google Scholar]
- Dursun, S. M; Wright, N.; Reveley, M. A. Effects of amphetamine on saccadic eye movements in man: possible relevance to schizophrenia? Journal of Psychopharmacology 1999, 13(3), 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R. Microsaccades: A microcosm for research on oculomotor control, attention, and visual perception. Progress in Brain Research 2006, 154, 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Engbert, R.; Kliegl, R. Microsaccades uncover the orientation of covert attention. Vision Research 2003a, 43(9), 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Engbert, R.; Kliegl, R. Hyönä, J., Radach, R., Deubel, H., Eds.; Binocular coordination in microsaccades. In The mind’s eyes: Cognitive and applied aspects of eye movements; North Holland, 2003b; pp. 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, M.; Tsitsiashvili, E.; Bonneh, Y. S.; Sterkin, A.; Wygnanski-Jaffe, T.; Epstein, T.; Polat, U. Adhd subjects fail to suppress eye blinks and microsaccades while anticipating visual stimuli but recover with medication. Vision Research 2014, 101, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yan, H.; Sun, H. J. Modulation of microsaccade rate by task difficulty revealed through between-and within-trial comparisons. Journal of Vision 2015, 15(3), 3-3. [Google Scholar]
- Goffart, L.; Hafed, Z. M.; Krauzlis, R. J. Visual fixation as equilibrium: evidence from superior colliculus inactivation. The Journal of Neuroscience 2012, 32(31), 10627–10636. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, T. D.; Bastain, T. M.; Israel, M. E.; Hommer, D. W.; Castellanos, F. X. Altered performance on an ocular fixation task in attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry 2001, 50(8), 633–635. [Google Scholar]
- Gowan, JD; Coizet, V; Devonshire, IM; Overton, PG. Damphetamine depresses visual responses in the rat superior colliculus: A possible mechanism for amphetamineinduced decreases in distractibility. Journal of Neural Transmission 115(3), 377–387.
- Greenberg, L. M.; Waldmant, I. D. Developmental normative data on the test of variables of attention (tovaTM). Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 1993, 34(6), 1019–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Hafed, Z. M. Alteration of visual perception prior to microsaccades. Neuron 2013, 77(4), 775–786. [Google Scholar]
- Hafed, Z. M.; Lovejoy, L. P.; Krauzlis, R. J. Modulation of microsaccades in monkey during a covert visual attention task. The Journal of Neuroscience 2011, 31(43), 15219–15230. [Google Scholar]
- Hafed, Z. M.; Krauzlis, R. J. Microsaccadic suppression of visual bursts in the primate superior colliculus. The Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 30(28), 9542–9547. [Google Scholar]
- Hafed, Z. M.; Clark, J. J. Microsaccades as an overt measure of covert attention shifts. Vision Research 2002, 42(22), 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hafed, Z. M.; Goffart, L.; Krauzlis, R. J. A neural mechanism for microsaccade generation in the primate superior colliculus. Science 2009, 323(5916), 940–943. [Google Scholar]
- Hafed, Z. M.; Lovejoy, L. P.; Krauzlis, R. J. Superior colliculus inactivation alters the relationship between covert visual attention and microsaccades. European Journal of Neuroscience 2013, 37(7), 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermens, F. Dummy eye measurements of microsaccades: Testing the influence of system noise and head movements on microsaccade detection in a popular video-based eye tracker. Journal of Eye Movement Research 2015, 8(1), 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hermens, F.; Walker, R. What determines the direction of microsaccades? Journal of Eye Movement Research 2010, 3(4), 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak, J. J.; Achenbach, T. M.; Althoff, R. R.; Pine, D. S. A dimensional approach to developmental psychopathology. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 2007, 16(S1), S16–S23. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, R. C.; Adler, L.; Ames, M.; Demler, O.; Faraone, S.; Hiripi, E.; Walters, E. E. The World Health Organization adult ADHD self-report scale (ASRS): a short screening scale for use in the general population. Psychological Medicine 2005, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Laubrock, J.; Engbert, R.; Kliegl, R. Microsaccade dynamics during covert attention. Vision Research 2005, 45(6), 721–730. [Google Scholar]
- Lindhiem, O.; Yu, L.; Grasso, D. J.; Kolko, D. J.; Youngstrom, E. A. Adapting the posterior probability of diagnosis index to enhance evidence based screening an application to ADHD in primary care. Assessment 2014, 1073191114540748. [Google Scholar]
- Loe, I. M.; Feldman, H. M.; Yasui, E.; Luna, B. Oculomotor performance identifies underlying cognitive deficits in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 2009, 48(4), 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.; Hamshere, M. L.; Stergiakouli, E.; O'Donovan, M. C.; Thapar, A. Genetic risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder contributes to neurodevelopmental traits in the general population. Biological Psychiatry 2014, 76, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Conde, S.; Macknik, S. L.; Hubel, D. H. The role of fixational eye movements in visual perception. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2004, 5(3), 229–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathôt, S.; Schreij, D.; Theeuwes, J. OpenSesame: an open-source, graphical experiment builder for the social sciences. Behavior Research Methods 2012, 44(2), 314–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCamy, M. B.; Otero-Millan, J.; Macknik, S. L.; Yang, Y.; Troncoso, X. G.; Baer, S. M.; MartinezConde, S. Microsaccadic efficacy and contribution to foveal and peripheral vision. The Journal of Neuroscience 2012, 32(27), 9194–9204. [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt, T. E.; Arseneault, L.; Jaffee, S. R.; Kim-Cohen, J.; Koenen, K. C.; Odgers, C. L.; Viding, E. Research review: Dsm-V conduct disorder: research needs for an evidence base. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 2008, 49(1), 3–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munoz, D. P.; Armstrong, I. T.; Hampton, K. A.; Moore, K. D. Altered control of visual fixation and saccadic eye movements in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Neurophysiology 2003, 90(1), 503–514. [Google Scholar]
- Otero-Millan, J.; Macknik, S. L.; Martinez-Conde, S. Fixational eye movements and binocular vision. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience 2014, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Otero-Millan, J.; Macknik, S. L.; Martinez-Conde, S. Microsaccades and blinks trigger illusory rotation in the “rotating snakes” illusion. The Journal of Neuroscience 2012, 32(17), 6043–6051. [Google Scholar]
- Otero-Millan, J.; Troncoso, X. G.; Macknik, S. L.; Serrano-Pedraza, I.; Martinez-Conde, S. Saccades and microsaccades during visual fixation, exploration, and search: foundations for a common saccadic generator. Journal of Vision 2008, 8(14), 21. [Google Scholar]
- Overton, P. G. Collicular dysfunction in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Medical Hypotheses 2008, 70(6), 1121–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Pastukhov, A.; Braun, J. Rare but precious: microsaccades are highly informative about attentional allocation. Vision Research 2010, 50(12), 1173–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, T. R.; Hafed, Z. M.; Dash, S.; Lomber, S. G.; Corneil, B. D. A Causal Role for the Cortical Frontal Eye Fields in Microsaccade Deployment. PLoS Biol 2016, 14(8), e1002531. [Google Scholar]
- Peirce, J. W. Psychopy—psychophysics software in python. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2007, 162(1), 8–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polner, B.; Aichert, D.; Macare, C.; Costa, A.; Ettinger, U. Gently restless: Association of ADHD-like traits with response inhibition and interference control. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2014, 265(8), 689–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poynter, W.; Barber, M.; Inman, J.; Wiggins, C. Individuals exhibit idiosyncratic eyemovement behavior profiles across tasks. Vision Research 2013, 89, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, M.; Kirsch, P.; Hennig, J. Inferring candidate genes for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) assessed by the World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS). Journal of Neural Transmission 2006, 113(7), 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfs, M. Microsaccades: small steps on a long way. Vision Research 2009, 49(20), 2415–2441. [Google Scholar]
- Rolfs, M.; Laubrock, J.; Kliegl, R. Shortening and prolongation of saccade latencies following microsaccades. Experimental Brain Research 2006, 169(3), 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Siegenthaler, E.; Costela, F. M.; McCamy, M. B.; Di Stasi, L. L.; Otero-Millan, J.; Sonderegger, A.; Groner, R.; Macknik, S.; Martinez-Conde, S. Task difficulty in mental arithmetic affects microsaccadic rates and magnitudes. European Journal of Neuroscience 2014, 39(2), 287–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shalev, L.; Ben-Simon, A.; Mevorach, C.; Cohen, Y.; Tsal, Y. Conjunctive Continuous Performance Task (CCPT)—A pure measure sustained attention. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49(9), 2584–2591. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, E. Clinical foundations of hyperactivity research. Behavioral Brain Research 1998, 94(1), 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Thaler, L.; Schütz, A.; Goodale, M.; Gegenfurtner, K. What is the best fixation target? the effect of target shape on stability of fixational eye movements. Vision Research 2013, 76, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, M.; Turatto, M. Microsaccadic responses in a bimodal oddball task. Psychological Research 2009, 73(1), 23–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willard, A.; Lueck, C. J. Ocular motor disorders. Current Opinion in Neurology 2014, 27(1), 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Kita, S. Attentional shifts by gaze direction in voluntary orienting: evidence from a microsaccade study. Experimental Brain Research 2012, 223(2), 291–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zelnik, N.; Bennett-Back, O.; Miari, W.; Goez, H. R.; Fattal-Valevski, A. Is the test of variables of attention reliable for the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (adhd)? Journal of Child Neurology 2012, 27(6), 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, B.; Crider, A.; Stark, L. Saccadic suppression associated with microsaccades. Quarterly Progress Report 1964, 74, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
Copyright © 2024. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share and Cite
Panagiotidi, M.; Overton, P.; Stafford, T. Increased Microsaccade Rate in Individuals with ADHD Traits. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2017, 10, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.10.1.6
Panagiotidi M, Overton P, Stafford T. Increased Microsaccade Rate in Individuals with ADHD Traits. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2017; 10(1):1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.10.1.6
Chicago/Turabian StylePanagiotidi, Maria, Paul Overton, and Tom Stafford. 2017. "Increased Microsaccade Rate in Individuals with ADHD Traits" Journal of Eye Movement Research 10, no. 1: 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.10.1.6
APA StylePanagiotidi, M., Overton, P., & Stafford, T. (2017). Increased Microsaccade Rate in Individuals with ADHD Traits. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 10(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.10.1.6


