Ammonia Cycling and Emerging Secondary Aerosols from Arable Agriculture: A European and Irish Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Precursor Species’ Dynamics and SIA Formation
2.1. Source Appointment and Emission
2.2. Atmospheric Chemistry of NH3 and SIA Formation
2.3. Atmospheric Chemistry of PM Formation
2.4. Controlling Factors of Emission and Transport
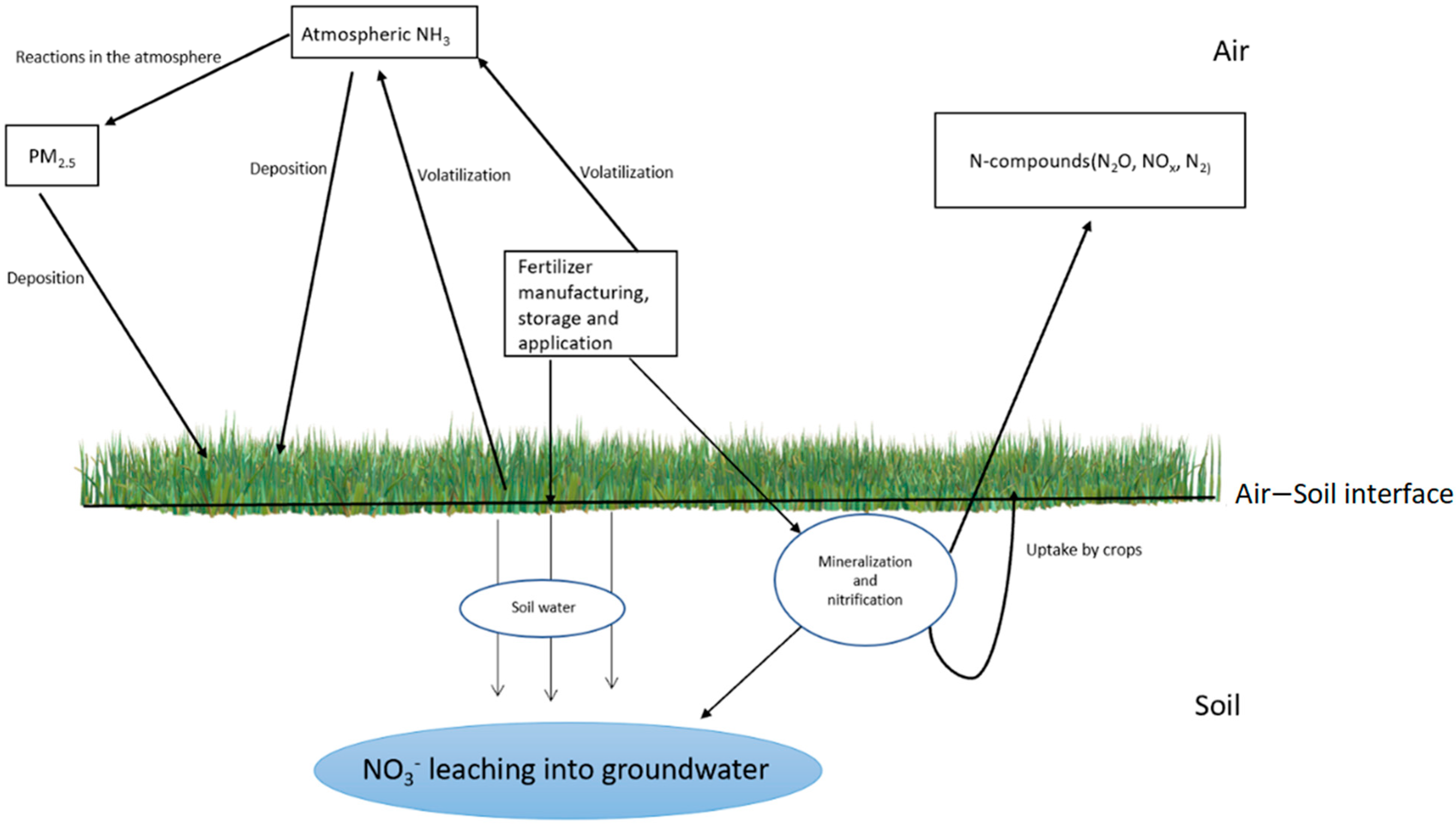
3. Linking the Soil–Water–Atmosphere Nexus
3.1. Direct Source Measurement: State-of-the-Art Techniques Currently in Use
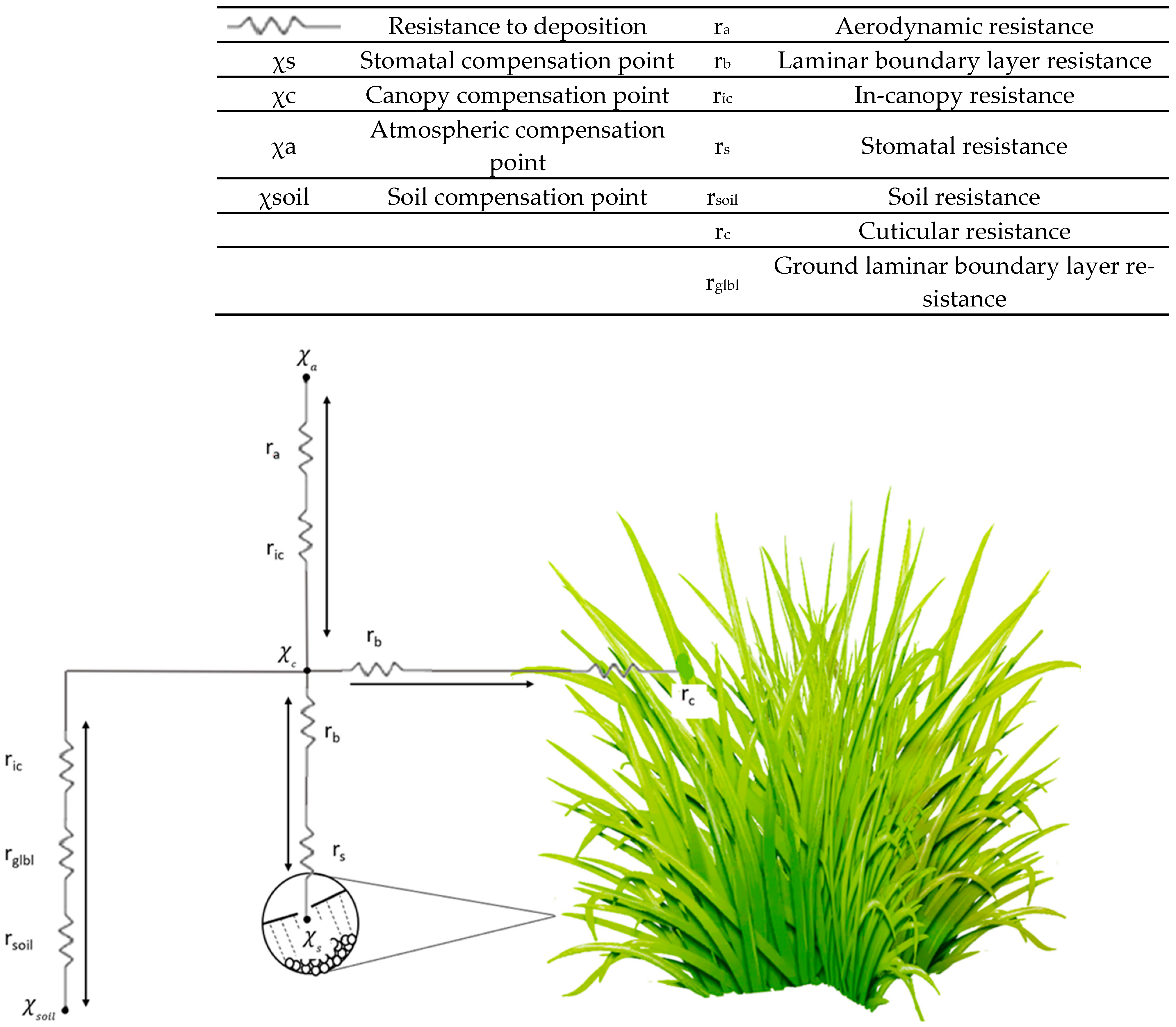
3.2. Modelling of NH3 and SIA
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morán, M.; Ferreira, J.; Martins, H.; Monteiro, A.; Borrego, C.; González, J.A. Ammonia Agriculture Emissions: From EMEP to a High Resolution Inventory. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Aneja, V.P.; Balasubramanian, R. Ammonia in the Atmosphere: A Review on Emission Sources, Atmospheric Chemistry and Deposition on Terrestrial Bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8092–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupa, S.V. Effects of Atmospheric Ammonia (NH3) on Terrestrial Vegetation: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 179–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.N.; Dentener, F.J.; Capone, D.G.; Boyer, E.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Asner, G.P.; Cleveland, C.C.; Green, P.A.; Holland, E.A.; et al. Nitrogen Cycles: Past, Present, and Future. Biogeochemistry 2004, 70, 153–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Cape, J.N.; Reis, S.; Sheppard, L.J.; Jenkins, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. The Global Nitrogen Cycle in the Twentyfirst Century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J. The Global Nitrogen Cycle: Past, Present and Future. Sci. China. Ser. C Life Sci./Chin. Acad. Sci. 2005, 48 (Suppl. 2), 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Lewicki, R.; Griffin, R.J.; Tittel, F.K.; Lonsdale, C.R.; Stevens, R.G.; Pierce, J.R.; Malloy, Q.G.J.; Travis, S.A.; Bobmanuel, L.M.; et al. Role of Atmospheric Ammonia in Particulate Matter Formation in Houston during Summertime. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petetin, H.; Sciare, J.; Bressi, M.; Gros, V.; Rosso, A.; Sanchez, O.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Petit, J.E.; Beekmann, M. Assessing the Ammonium Nitrate Formation Regime in the Paris Megacity and Its Representation in the CHIMERE Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10419–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrara, R.M.; Loubet, B.; Di Tommasi, P.; Bertolini, T.; Magliulo, V.; Cellier, P.; Eugster, W.; Rana, G. Eddy Covariance Measurement of Ammonia Fluxes: Comparison of High Frequency Correction Methodologies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 158–159, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylor, R.; Myles, L.; Sibble, D.; Caldwell, J.; Xing, J. Recent Trends in Gas-Phase Ammonia and PM2.5 Ammonium in the Southeast United States. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Backes, A.M.; Aulinger, A.; Bieser, J.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M. Ammonia Emissions in Europe, Part II: How Ammonia Emission Abatement Strategies Affect Secondary Aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Backes, A.; Aulinger, A.; Bieser, J.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M. Ammonia Emissions in Europe, Part I: Development of a Dynamical Ammonia Emission Inventory. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, C.A.; Brook, R.D.; Burnett, R.T.; Dockery, D.W. How Is Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Risk Affected by Duration and Intensity of Fine Particulate Matter Exposure? An Integration of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2011, 4, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priewus, H.; Schutte-Postma, E. Notes on the Particulate Matter Standards in the European Union and the Netherlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 1155–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fine, P.M.; Sioutas, C.; Solomon, P.A. Secondary Particulate Matter in the United States: Insights from the Particulate Matter Supersites Program and Related Studies. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 234–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, G. Ammonia Volatilization. Dev. Plant Soil Sci. 1997, 77, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, A.; Misstear, B.; Broderick, B. Air Quality Modelling for Ireland; EPA: Wexford, Ireland, 2019.
- Doyle, B.; Cummins, T.; Augustenborg, C.; Aherne, J. Ambient Atmospheric Ammonia in Ireland, 2013–2014; EPA: Wexford, Ireland, 2017.
- Directive 2008/50/EC. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008L0050&from=en (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- De Kluizenaar, Y.; Farrell, E.P. Ammonia Monitoring in Ireland—A Full Year of Monitoring; EPA: Wexford, Ireland, 2000.
- Schiferl, L.D.; Heald, C.L.; Nowak, J.B.; Holloway, J.S.; Neuman, J.A.; Bahreini, R.; Pollack, I.B.; Ryerson, T.B.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Murphy, J.G. An Investigation of Ammonia and Inorganic Particulate Matter in California during the CalNex Campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1883–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J.G.J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Van der Hoek, K.W.; Berdowski, J.J.M. Global Air Emission Inventories for Anthropogenic Sources of NOx, NH3 and N2O in 1990. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, V.P.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Erisman, J.W.; Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Battye, W. Reactive Nitrogen Emissions from Crop and Livestock Farming in India. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswall, T. The Biogeochemical Nitrogen Cycle. In Some Perspectives of the Major Biogeochemical Cycles; Linkens, G.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK; New York, NY, USA; Brisbane, Australia; Toronto, ON, Canada, 1981; pp. 25–50. ISBN 0471279897. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, M.; Simon, J. Chapter Nineteen—Production of Recombinant Multiheme Cytochromes c in Wolinella Succinogenes. In Research on Nitrification and Related Processes, Part A; Klotz, M.G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 486, pp. 429–446. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Widdison, P.E.; Burt, T.P. Nitrogen Cycle. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Jørgensen, S.E., Fath, B.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 2526–2533. ISBN 978-0-08-045405-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, P.; Roldán, M.D.; Castillo, F.; Moreno-Vivián, C. Nitrogen Cycle. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology; Schaechter, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 299–321. ISBN 978-0-12-373944-5. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, L.D.; do Nascimento, C.A.C.; Vitti, G.C.; Luz, P.H.D.; Guedes, E.M.S. Loss of Ammonia from Nitrogen Fertilizers Applied to Maize and Soybean Straw. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2013, 37, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leip, A.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Grizzetti, B.; Lassaletta, L.; Reis, S.; Simpson, D.; Sutton, M.A.; De Vries, W.; Weiss, F.; et al. Impacts of European Livestock Production: Nitrogen, Sulphur, Phosphorus and Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Land-Use, Water Eutrophication and Biodiversity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basosi, R.; Spinelli, D.; Fierro, A.; Jez, S. Mineral Nitrogen Fertilizers: Environmental Impact of Production and Use. In Fertilizers: Components, Uses in Agriculture and Environmental Impacts; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3–43. ISBN 9781633210585. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Batjes, N.H. Estimation of Global NH3 Volatilization Loss from Synthetic Fertilizers and Animal Manure Applied to Arable Lands and Grasslands. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 8-1–8-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klein, C.; Novoa, R.S.; Ogle, S.; Smith, K.; Rochette, P.; Wirth, T.; McConkey, B.; Mosier, A.; Rypdal, K.; Walsh, M. N2O Emissions from Managed Soils, and CO2 Emissions from Lime and Urea Application. In IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; IPCC: Hayama, Japan, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, V.P.; Roelle, P.A.; Murray, G.C.; Southerland, J.; Erisman, J.W.; Fowler, D.; Asman, W.A.H.; Patni, N. Atmospheric Nitrogen Compounds. II: Emissions, Transport, Transformation, Deposition and Assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W.; Bleeker, A.; Galloway, J.; Sutton, M.S. Reduced Nitrogen in Ecology and the Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelleghan, D.B.; Hayes, E.T.; Everard, M.; Curran, T.P. Mapping Ammonia Risk on Sensitive Habitats in Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Clark, C.M.; Grimm, N.B.; Jackson, R.B.; Law, B.E.; Thornton, P.E.; Townsend, A.R.; Martin, R. Biogeochemical Cycles; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia Volatilization from Synthetic Fertilizers and Its Mitigation Strategies: A Global Synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Bouwman, L.; Cassman, K.G.; van Es, H.M.; McCrackin, M.L.; Beusen, A.H.W. Losses of Ammonia and Nitrate from Agriculture and Their Effect on Nitrogen Recovery in the European Union and the United States between 1900 and 2050. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skjøth, C.A.; Geels, C. The Effect of Climate and Climate Change on Ammonia Emissions in Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Lee, D.S.; Asman, W.A.H.; Dentener, F.J.; Van Der Hoek, K.W.; Olivier, J.G.J. A Global High-Resolution Emission Inventory for Ammonia. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 11, 561–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangmeier, A.; Hadwiger-Fangmeier, A.; Van der Eerden, L.; Jäger, H.-J. Effects of Atmospheric Ammonia on Vegetation—A Review. Environ. Pollut. 1994, 86, 43–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, M.A.; Pitcairn, C.E.R.; Fowler, D. The Exchange of Ammonia Between the Atmosphere and Plant Communities. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1993, 24, 301–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Lindberg, S.E. Dry Deposition of Reactive Nitrogen Compounds: A Review of Leaf, Canopy and Non-Foliar Measurements. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 1615–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, G.M. Atmospheric Deposition of Nutrients and Pollutants in North America. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, R.P. Chemistry of Atmospheres, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-19-850375-X. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.B.; Arya, S.P.; Aneja, V.P. Ammonia Flux and Dry Deposition Velocity from Near-Surface Concentration Gradient Measurements over a Grass Surface in North Carolina. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3469–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delon, C.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Serça, D.; Loubet, B.; Camara, N.; Gardrat, E.; Saneh, I.; Fensholt, R.; Tagesson, T.; Le Dantec, V.; et al. Soil and Vegetation-Atmosphere Exchange of NO, NH3, and N2O from Field Measurements in a Semi Arid Grazed Ecosystem in Senegal. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 156, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, J.; Stewart, G.R. The Deposition of Atmospheric Ammonia and Its Effects on Plants. New Phytol. 1993, 125, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, R.L.; Mathur, R.; Pleim, J.E.; Walker, J.T. Fate of Ammonia Emissions at the Local to Regional Scale as Simulated by the Community Multiscale Air Quality Model. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2010, 1, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loubet, B.; Sutton, M.A.; Milford, C.; Cellier, P. Investigation of the Interaction between Sources and Sinks of Atmospheric Ammonia in an Upland Landscape Using a Simplified Dispersion-Exchange Model. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleim, J.E.; Bash, J.O.; Walker, J.T.; Cooter, E.J. Development and Evaluation of an Ammonia Bidirectional Flux Parameterization for Air Quality Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 3794–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleim, J.E.; Ran, L.; Appel, W.; Shephard, M.W.; Cady-Pereira, K. New Bidirectional Ammonia Flux Model in an Air Quality Model Coupled With an Agricultural Model. J. Adv. Modeling Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 2934–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sutton, M.A.; Schjorring, J.K.; Wyers, G.P. Plant-Atmosphere Exchange of Ammonia. Philos. Trans.-R. Soc. Lond. A 1995, 351, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Moncrieff, J.B.; Fowler, D. Deposition of Atmospheric Ammonia to Moorlands. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 75, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Fowler, D.; Moncrieft, J.B.; Storeton-West, R.L. The Exchange of Atmospheric Ammonia with Vegetated Surfaces. II: Fertilized Vegetation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 1047–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warneck, P. Chemistry of the Natural Atmosphere; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, M.M.; Rendell, A.R.; Jickells, T.D. Atmospheric Scavenging Processes over the North Sea. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, J.M. Atmospheric Deposition. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 275–285. ISBN 9780080914565. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, B.C. Sulfate Washout Ratios in Winter Storms. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A.; LaRoche, J.; Altieri, K.; Arrigo, K.R.; Baker, A.R.; Capone, D.G.; Cornell, S.; Dentener, F.; Galloway, J.; Ganeshram, R.S.; et al. Impacts of Atmospheric Anthropogenic Nitrogen on the Open Ocean. Science 2008, 320, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, P.K.; Chan, W.H.; Chung, D.; Tang, A.J.S. Scavenging Ratios of Acidic Pollutants and Their Use in Long-Range Transport Models. Atmos. Environ. 1985, 19, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granat, L. On the Relation between PH and the Chemical Composition in Atmospheric Precipitation. Tellus 1972, 24, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hontoria, C.; Saa, A.; Almorox, J.; Cuadra, L.; Sánchez, A.; Gascó, J.M. The Chemical Composition of Precipitation in Madrid. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 146, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.L.; Galloway, J.N. Quantifying the Relationship between Atmospheric Transport and the Chemical Composition of Precipitation on Bermuda. Tellus B 1988, 40, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuzzi, S.; Baltensperger, U.; Carslaw, K.; Decesari, S.; Van Der Gon, H.D.; Facchini, M.C.; Fowler, D.; Nazionale, C. Particulate Matter, Air Quality and Climate: Lessons Learned and Furture Needs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8217–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wu, W.S.; Wang, T. Summertime PM2.5 Ionic Species in Four Major Cities of China: Nitrate Formation in an Ammonia-Deficient Atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, W.G. Overview of PM2.5 Sources and Control Strategies. Fuel Process. Technol. 2000, 65, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, G.; Weagle, C.L.; Murdymootoo, K.K.; Ring, A.; Ritchie, Y.; Stone, E.; Walsh, A.; Akoshile, C.; Anh, N.X.; Balasubramanian, R.; et al. Variation in Global Chemical Composition of PM2.5: Emerging Results from SPARTAN. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9629–9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vayenas, D.V.; Takahama, S.; Davidson, C.I.; Pandis, S.N. Simulation of the Thermodynamics and Removal Processes in the Sulfate-Ammonia-Nitric Acid System during Winter: Implications for PM2.5 Control Strategies. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, H.; Monteiro, A.; Ferreira, J.; Gama, C.; Ribeiro, I.; Borrego, C.; Miranda, A.I. The Role of Ammonia on Particulate Matter Pollution over Portugal. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 57, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Van Dingenen, R.; Alastuey, A.; Bauer, H.; Birmili, W.; Cyrys, J.; Flentje, H.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hansson, H.C.; et al. A European Aerosol Phenomenology—3: Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Particulate Matter from 60 Rural, Urban, and Kerbside Sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.; Strader, R.; Davidson, C. Airborne Reduced Nitrogen: Ammonia Emissions from Agriculture and Other Sources. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, M.; Kuwahara, T. Chapter 2—Emission Regulations. In Design for Additive Manufacturing; Okubo, M., Kuwahara, T., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 25–51. ISBN 978-0-12-812307-2. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, B.; Miller, B. Sulfur Oxides Formation and Control. In Fossil Fuel Emissions Control Technologies; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 197–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.A.; Murphy, J.G. 10—The Science of Smog: A Chemical Understanding of Ground Level Ozone and Fine Particulate Matter. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Zeman, F.B.T.-M.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 205–230. ISBN 978-0-85709-046-1. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, B. Chapter 10—Cleaning of Product Gas of Gasification. In Basu Pyrolysis and Torrefaction, 3rd ed.; Basu, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 373–391. ISBN 978-0-12-812992-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; Cong, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Comparison of Dry and Wet Deposition of Particulate Matter in Near-Surface Waters during Summer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loosmore, G.A.; Cederwall, R.T. Precipitation Scavenging of Atmospheric Aerosols for Emergency Response Applications: Testing an Updated Model with New Real-Time Data. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, U. Assessment of Atmospheric Emissions and Depositions of Major Nr Species in Indian Region. In The Indian Nitrogen Assessment: Sources of Reactive Nitrogen, Environmental and Climate Effects, Management Options, and Policies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 427–444. ISBN 9780128119044. [Google Scholar]
- Giardina, M.; Buffa, P. A New Approach for Modeling Dry Deposition Velocity of Particles. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 180, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Easter, R.C.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L.; Fast, J.D.; Ghan, S.J.; Wang, H.; Berg, L.K.; Barth, M.C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Aerosol Transport and Wet Scavenging in Deep Convective Clouds: A Case Study and Model Evaluation Using a Multiple Passive Tracer Analysis Approach. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Ghosh, A.; Das, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Raha, S. Below-Cloud Scavenging of Size-Segregated Aerosols and Its Effect on Rainwater Acidity and Nutrient Deposition: A Long-Term (2009–2018) and Real-Time Observation over Eastern Himalaya. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santachiara, G.; Prodi, F.; Belosi, F. Atmospheric Aerosol Scavenging Processes and the Role of Thermo- and Diffusio-Phoretic Forces. Atmos. Res. 2013, 128, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, C.; Neubauer, S.C. Chapter 16-Salt Marsh Biogeochemistry—An Overview. In Coastal Wetlands; Perillo, G.M.E., Wolanski, E., Cahoon, D.R., Hopkinson, C.S.B.T.-C.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 539–596. ISBN 978-0-444-63893-9. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, P.; Darrah, T.H.; Erel, Y. Medical Geochemistry: Geological Materials and Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–194. ISBN ISBN 978-94-007-4372-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J. A Cluster Analysis of Long Range Air Transport Pathways and Associated Pollutant Concentrations within the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Chapter 2-Air; EPA: Wexford, Ireland, 2016.
- Rosenfeld, D. Cloud-Aerosol-Precipitation Interactions Based of Satellite Retrieved Vertical Profiles of Cloud Microstructure. In Remote Sensing of Aerosols, Clouds and Precipitation; Islam, T., Hu, Y., Kokhanovsky, A., Wang, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 129–152. ISBN 978-0-12-810437-8. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, D.A.; Albrecht, B.; Cox, S.; Johnson, D.; Minnis, P.; Rossow, W.; Starr, D.O. On Fire at Ten. In Advances in Geophysics; Dmowska, R., Saltzman, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 38, pp. 37–177. ISBN 0065-2687. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.K. Scavenging and Transportation of Aerosol Particles by Ice Crystals in Clouds. In Ice Microdynamics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 152–196. ISBN 978-0-12-734603-8. [Google Scholar]
- Herckes, P.; Collett, J.L. TROPOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY & COMPOSITION | Cloud Chemistry. In Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences, 2nd ed.; North, G.R., Pyle, J., Zhang, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 218–225. ISBN 978-0-12-382225-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, R.E. Interaction Between Future Climate and Terrestrial Carbon and Nitrogen. In The Future of the World’s Climate, 2nd ed.; Henderson-Sellers, A., McGuffie, K.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 289–308. ISBN 978-0-12-386917-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, U. AEROSOLS | Aerosol–Cloud Interactions and Their Radiative Forcing. In Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences, 2nd ed.; North, G.R., Pyle, J., Zhang, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 17–22. ISBN 978-0-12-382225-3. [Google Scholar]
- Deshler, T. CHEMISTRY OF THE ATMOSPHERE | Observations for Chemistry (In Situ): Particles. In Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Science; North, G.R., Pyle, J., Zhang, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 379–386. ISBN 978-0-12-382225-3. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, W.-K.; Matsui, T. NUMERICAL MODELS | Cloud-System Resolving Modeling and Aerosols. In Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences, 2nd ed.; DitionNorth, G.R., Pyle, J., Zhang, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 222–231. ISBN 978-0-12-382225-3. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, A.L.; Underwood, G.M.; Grassian, V.H. A Laboratory Study of the Heterogeneous Reaction of Nitric Acid on Calcium Carbonate Particles. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2000, 105, 29053–29064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squizzato, S.; Masiol, M.; Brunelli, A.; Pistollato, S.; Tarabotti, E.; Rampazzo, G.; Pavoni, B. Factors Determining the Formation of Secondary Inorganic Aerosol: A Case Study in the Po Valley (Italy). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvern, R.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Kim, P.S.; Marais, E.A.; Turner, J.R.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L. Inconsistency of Ammonium-Sulfate Aerosol Ratios with Thermodynamic Models in the Eastern US: A Possible Role of Organic Aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5107–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xue, L.; Wang, W. Formation of Aqueous-Phase Secondary Organic Aerosols from Glycolaldehyde and Ammonium Sulfate/Amines: A Kinetic and Mechanistic Study. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämeri, K.; Väkevä, M.; Hansson, H.C.; Laaksonen, A. Hygroscopic Growth of Ultrafine Ammonium Sulphate Aerosol Measured Using an Ultrafine Tandem Differential Mobility Analyzer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 22231–22242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.J.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Koch, D.M. Global Concentrations of Tropospheric Sulfate, Nitrate, and Ammonium Aerosol Simulated in a General Circulation Model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 13791–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, F.; Rong, M.; Lin, L.; Yao, Q.; Huang, Y. Introduction. In Novel Nanomaterials for Biomedical, Environmental and Energy Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–36. ISBN 9780128144978. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, P.B.C.; Garland, R.M. Outdoor Air Pollution. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 73, pp. 73–96. ISBN 9780444636058. [Google Scholar]
- Andreae, M.O. Correlation between Cloud Condensation Nuclei Concentration and Aerosol Optical Thickness in Remote and Polluted Regions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lohmann, U.; Luond, F.; Mahrt, F.; Lohmann, U.; Luond, F.; Mahrt, F. Cloud Droplet Formation and Köhler Theory. In An Introduction to Clouds; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 155–185. ISBN 9781139087513. [Google Scholar]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Gundersen, P.; Ambus, P.; Augustin, J.; Beier, C.; Boeckx, P.; Dannenmann, M.; Sanchez Gimeno, B.; Ibrom, A.; Kiese, R.; et al. Nitrogen Processes in Terrestrial Ecosystems. In The European Nitrogen Assessment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 99–125. ISBN 9780511976988. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A.; De Carvalho, C.J.R.; Figueira, A.M.; Ishida, F.Y.; Ometto, J.P.H.B.; Nardoto, G.B.; Sabá, R.T.; Hayashi, S.N.; Leal, E.C.; Vieira, I.C.G.; et al. Recuperation of Nitrogen Cycling in Amazonian Forests Following Agricultural Abandonment. Nature 2007, 447, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.E.; Koch, D.; Unger, N.; Metzger, S.M.; Shindell, D.T.; Streets, D.G. Nitrate Aerosols Today and in 2030: A Global Simulation Including Aerosols and Tropospheric Ozone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5043–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seigneur, C. Air Pollution: Concept, Theory and Application; Belin/Humensis, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781108481632. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, G.; Berry, T.-A.; Wallis, S.; Poyner, D. Temperature and Humidity Effects on Particulate Matter Concentrations in a Sub-Tropical Climate During Winter. Int. Proc. Chem. Biol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 102, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, P.H.; Wilson, J.C. Droplet Phase (Heterogeneous) and Gas Phase (Homogeneous) Contributions to Secondary Ambient Aerosol Formation as Functions of Relative Humidity. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 5101–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y. Roles of Relative Humidity in Aerosol Pollution Aggravation over Central China during Wintertime. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Gong, Y. Foreshowing of the Western Pacific Tropical Cyclone Track to PM10 Air Pollution Episode in the Beijing Area. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Kanaroglou, P. The Effect of Temperature Inversions on Ground-Level Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) and Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Using Temperature Profiles from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5085–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.T.; Trinh, T.T.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, T.D.H.; Tu, B.M. Temperature Inversion and Air Pollution Relationship, and Its Effects on Human Health in Hanoi City, Vietnam. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, T.W.; Holland, L.A. Synoptic and Local Weather Conditions Associated With PM2.5 Concentration in Carlisle, Pennsylvania. Middle States Geogr. 2010, 43, 72–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Ma, H.; Lau, A.K.H.; Chan, P.W.; Yu, J.Z.; Xue, J. Enhancement in Secondary Particulate Matter Production Due to Mountain Trapping. Atmos. Res. 2014, 147–148, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, S.; Palazoglu, A.; Singh, A.; Soong, S.-T.; Tanrikulu, S. Identification of Weather Patterns Impacting 24-h Average Fine Particulate Matter Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flechard, C.; Massad, R.S.; Loubet, B.; Personne, E. Advances in Undertsanding Models and Parameterisations of Biosphere-Atmosphere Ammonia Exchange. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2013, 10, 5385–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, J.J.; Li, Y.; Bae, M.S.; Demerjian, K.L.; Hou, J.; Zhou, X.; Jensen, B.; Pryor, S.C. A Laboratory Intercomparison of Real-Time Gaseous Ammonia Measurement Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8412–8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Tang, Y.S.; Miners, B.; Fowler, D. A New Diffusion Denuder System for Long-Term, Regional Monitoring of Atmospheric Ammonia and Ammonium. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2001, 1, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.; Spirig, C.; Wolff, V.; Trebs, I.; Flechard, C.; Wisthaler, A.; Schnitzhofer, R.; Hansel, A.; Neftel, A. Intercomparison of Ammonia Measurement Techniques at an Intensively Managed Grassland Site (Oensingen, Switzerland). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, T.; Marino, R.; Schwede, D.; Howarth, R.; Sparks, J.; Sparks, K. Atmospheric Ammonia Measurements at Low Concentration Sites in the Northeastern USA: Implications for Total Nitrogen Deposition and Comparison with CMAQ Estimates. Biogeochemistry 2015, 122, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bobrutzki, K.; Braban, C.F.; Famulari, D.; Jones, S.K.; Blackall, T.; Smith, T.E.L.; Blom, M.; Coe, H.; Gallagher, M.; Ghalaieny, M.; et al. Field Inter-Comparison of Eleven Atmospheric Ammonia Measurement Techniques. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dammers, E.; Schaap, M.; Haaima, M.; Palm, M.; Wichink Kruit, R.J.; Volten, H.; Hensen, A.; Swart, D.; Erisman, J.W. Measuring Atmospheric Ammonia with Remote Sensing Campaign: Part 1—Characterisation of Vertical Ammonia Concentration Profile in the Centre of The Netherlands. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Satsangi, G.S.; Khare, P.; Lakhani, A.; Maharaj Kumari, K.; Srivastava, S.S. Multiphase Measurement of Atmospheric Ammonia. Chemosphere Glob. Chang. Sci. 2001, 3, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, V.P.; Bunton, B.; Walker, J.T.; Malik, B.P. Measurement and Analysis of Atmospheric Ammonia Emissions from Anaerobic Lagoons. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, G.H.; Rumburg, B.; Havig, J.; Lamb, B.; Westberg, H.; Yonge, D.; Johnson, K.; Kincaid, R. Measurement of Atmospheric Ammonia at a Dairy Using Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy in the Mid-Ultraviolet. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milford, C.; Theobald, M.; Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A. Dynamics of Ammonia Exchange in Response to Cutting and Fertilising in an Intensively-Managed Grassland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 5, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A.; Gut, A.; San, R.; Husted, S.; Schjoerring, J.K. Sources and Sinks of Ammonia within an Oilseed Rape Canopy. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine. Local Roots a Vision for Growth for the Irish Agricultural Economy for the Next 10 Years. Terms of Reference for the 2025 Agri-Food Strategy Committee; Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine: Dublin, Ireland, 2015.
- Allegrini, I.; De Santis, F.; Di Palo, V.; Febo, A.; Perrino, C.; Possanzini, M.; Liberti, A. Annular Denuder Method for Sampling Reactive Gases and Aerosols in the Atmosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 1987, 67, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim Tang, Y.; Braban, C.F.; Dragosits, U.; Simmons, I.; Leaver, D.; Van Dijk, N.; Poskitt, J.; Thacker, S.; Patel, M.; Carter, H.; et al. Acid Gases and Aerosol Measurements in the UK (1999–2015): Regional Distributions and Trends. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16293–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.S.; Braban, C.F.; Dragosits, U.; Dore, A.J.; Simmons, I.; Van Dijk, N.; Poskitt, J.; Dos Santos Pereira, G.; Keenan, P.O.; Conolly, C.; et al. Drivers for Spatial, Temporal and Long-Term Trends in Atmospheric Ammonia and Ammonium in the UK. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 705–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, J.P.; Schilt, S.; Rochat, E.; Thévenaz, L. Ammonia Trace Measurements at Ppb Level Based on Near-IR Photoacoustic Spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2006, 85, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmohl, A.; Miklos, A.; Hess, P. Detection of Ammonia by Photoacoustic Spectroscopy with Semiconductor Lasers. Opt. Soc. Am. 2020, 41, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszár, H.; Pogány, A.; Bozóki, Z.; Mohácsi, Á.; Horváth, L.; Szabó, G. Ammonia Monitoring at Ppb Level Using Photoacoustic Spectroscopy for Environmental Application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, F.; Zeng, H. Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy Measurements of High-Pressure Ammonium Dinitramide Combustion. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Miners, B.; Tang, Y.S.; Milford, C.; Wyers, G.P.; Duyzer, J.H.; Fowler, D. Comparison of Low Cost Measurement Techniques for Long-Term Monitoring of Atmospheric Ammonia. J. Environ. Monit. 2001, 3, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinert, S.; McGovern, F.; Jennings, G. New Transboundary Air Pollution Monitoring Capacity for Ireland; Johnstown Castle: Wexford, Ireland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss, R.; Duyzer, J.; Wyers, P. The Influence of Gas-to-Particle Conversion on Measurements of Ammonia Exchange over Forest. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichink Kruit, R.J.; Aben, J.; de Vries, W.; Sauter, F.; van der Swaluw, E.; van Zanten, M.C.; van Pul, W.A.J. Modelling Trends in Ammonia in the Netherlands over the Period 1990–2014. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 154, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöll, U.; Brümmer, C.; Schrader, F.; Ammann, C.; Ibrom, A.; Flechard, C.R.; Nelson, D.D.; Zahniser, M.; Kutsch, W.L. Surface-Atmosphere Exchange of Ammonia over Peatland Using QCL-Based Eddy-Covariance Measurements and Inferential Modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11283–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrader, F.; Brümmer, C.; Flechard, C.R.; Kruit, R.J.W.; Van Zanten, M.C.; Zöll, U.; Hensen, A.; Erisman, J.W. Non-Stomatal Exchange in Ammonia Dry Deposition Models: Comparison of Two State-of-the-Art Approaches. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13417–13430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruit, R.J.W.; van Pul, W.A.J.; Sauter, F.J.; van den Broek, M.; Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A.; Krol, M.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Modeling the Surface-Atmosphere Exchange of Ammonia. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiba, U.; Drewer, J.; Tang, Y.S.; van Dijk, N.; Helfter, C.; Nemitz, E.; Famulari, D.; Cape, J.N.; Jones, S.K.; Twigg, M.; et al. Biosphere-Atmosphere Exchange of Reactive Nitrogen and Greenhouse Gases at the NitroEurope Core Flux Measurement Sites: Measurement Strategy and First Data Sets. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, K.S.; Arya, S.P.; Aneja, V.P. Modeling Studies of Ammonia Dispersion and Dry Deposition at Some Hog Farms in North Carolina. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geels, C.; Andersen, H.V.; Ambelas Skjøth, C.; Christensen, J.H.; Ellermann, T.; Løfstrøm, P.; Gyldenkærne, S.; Brandt, J.; Hansen, K.M.; Frohn, L.M.; et al. Improved Modelling of Atmospheric Ammonia over Denmark Using the Coupled Modelling System DAMOS. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 2625–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wright, L.P.; Asman, W.A.H. Bi-Directional Air-Surface Exchange of Atmospheric Ammonia: A Review of Measurements and a Development of a Big-Leaf Model for Applications in Regional-Scale Air-Quality Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D20310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Nemitz, E.; Erisman, J.W.; Beier, C.; Bahl, K.B.; Cellier, P.; de Vries, W.; Cotrufo, F.; Skiba, U.; Di Marco, C.; et al. Challenges in Quantifying Biosphere–Atmosphere Exchange of Nitrogen Species. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asman, W.A.H.; Sutton, M.A.; Schjørring, J.K. Ammonia: Emission, Atmospheric Transport and Deposition. New Phytol. 1998, 139, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Sørensen, L.L.; Hertel, O.; Geels, C.; Skjøth, C.A.; Jensen, B.; Boegh, E. Ammonia Emissions from Deciduous Forest after Leaf Fall. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4577–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asaadi, A.; Arora, V.K.; Melton, J.R.; Bartlett, P. An Improved Parameterization of Leaf Area Index (LAI) Seasonality in the Canadian Land Surface Scheme (CLASS) and Canadian Terrestrial Ecosystem Model (CTEM) Modelling Framework. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 6885–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Walker, J.; Schwede, D.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Dennis, R.; Robarge, W. A New Model of Bi-Directional Ammonia Exchange between the Atmosphere and Biosphere: Ammonia Stomatal Compensation Point. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Spence, P.; Kimbrough, S.; Robarge, W. Inferential Model Estimates of Ammonia Dry Deposition in the Vicinity of a Swine Production Facility. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3407–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Reis, S.; Riddick, S.N.; Dragosits, U.; Nemitz, E.; Theobald, M.R.; Tang, Y.S.; Braban, C.F.; Vieno, M.; Dore, A.J.; et al. Towards a Climate-Dependent Paradigm of Ammonia Emission and Deposition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massad, R.S.; Loubet, B.; Tuzet, A.; Cellier, P. Relationship between Ammonia Stomatal Compensation Point and Nitrogen Metabolism in Arable Crops: Current Status of Knowledge and Potential Modelling Approaches. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 154, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolov, N.; Zeller, K. Efficient Retrieval of Vegetation Leaf Area Index and Canopy Clumping Factor from Satellite Data to Support Pollutant Deposition Assessments. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janhäll, S. Review on Urban Vegetation and Particle Air Pollution—Deposition and Dispersion. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, M.; Buffa, P.; Cervone, A.; Lombardo, C. Dry Deposition of Particle on Urban Areas. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1224, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariraj Mohan, S. An Overview of Particulate Dry Deposition: Measuring Methods, Deposition Velocity and Controlling Factors. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouznetsov, R.; Sofiev, M. A Methodology for Evaluation of Vertical Dispersion and Dry Deposition of Atmospheric Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Roux, G.; Hansson, S.V.; Claustres, A. Chapter 3—Inorganic Chemistry in the Mountain Critical Zone: Are the Mountain Water Towers of Contemporary Society Under Threat by Trace Contaminants? In Mountain Ice and Water; Greenwood, G.B., Shroder, J.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 21, pp. 131–154. ISBN 0928-2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.; Thimonier, A.; Clarke, N.; Staelens, J.; Žlindra, D.; Waldner, P.; Marchetto, A. Chapter 18—Atmospheric Deposition to Forest Ecosystems. In Forest Monitoring; Ferretti, M., Fischer, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 12, pp. 337–374. ISBN 1474-8177. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, B.H.; Aneja, V.P.; Tong, Q. Chemical Coupling between Ammonia, Acid Gases, and Fine Particles. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad, R.-S.; Loubet, B. (Eds.) Review and Integration of Biosphere-Atmosphere Modelling of Reactive Trace Gases and Volatile Aerosols; Springer: Versailles, France, 2013; ISBN 978-94-017-7284-6. [Google Scholar]
- Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B. Atmospheric Composition Forecasting in Europe. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pohl, V.; Gilmer, A.; Hellebust, S.; McGovern, E.; Cassidy, J.; Byers, V.; McGillicuddy, E.J.; Neeson, F.; O’Connor, D.J. Ammonia Cycling and Emerging Secondary Aerosols from Arable Agriculture: A European and Irish Perspective. Air 2023, 1, 37-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1010003
Pohl V, Gilmer A, Hellebust S, McGovern E, Cassidy J, Byers V, McGillicuddy EJ, Neeson F, O’Connor DJ. Ammonia Cycling and Emerging Secondary Aerosols from Arable Agriculture: A European and Irish Perspective. Air. 2023; 1(1):37-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1010003
Chicago/Turabian StylePohl, Vivien, Alan Gilmer, Stig Hellebust, Eugene McGovern, John Cassidy, Vivienne Byers, Eoin J. McGillicuddy, Finnian Neeson, and David J. O’Connor. 2023. "Ammonia Cycling and Emerging Secondary Aerosols from Arable Agriculture: A European and Irish Perspective" Air 1, no. 1: 37-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1010003
APA StylePohl, V., Gilmer, A., Hellebust, S., McGovern, E., Cassidy, J., Byers, V., McGillicuddy, E. J., Neeson, F., & O’Connor, D. J. (2023). Ammonia Cycling and Emerging Secondary Aerosols from Arable Agriculture: A European and Irish Perspective. Air, 1(1), 37-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/air1010003








