Artemisia gmelinii Extract Alleviates Allergic Airway Inflammation via Balancing TH1/TH2 Homeostasis and Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AGE Inhibited the OVA-Induced Allergic Symptoms
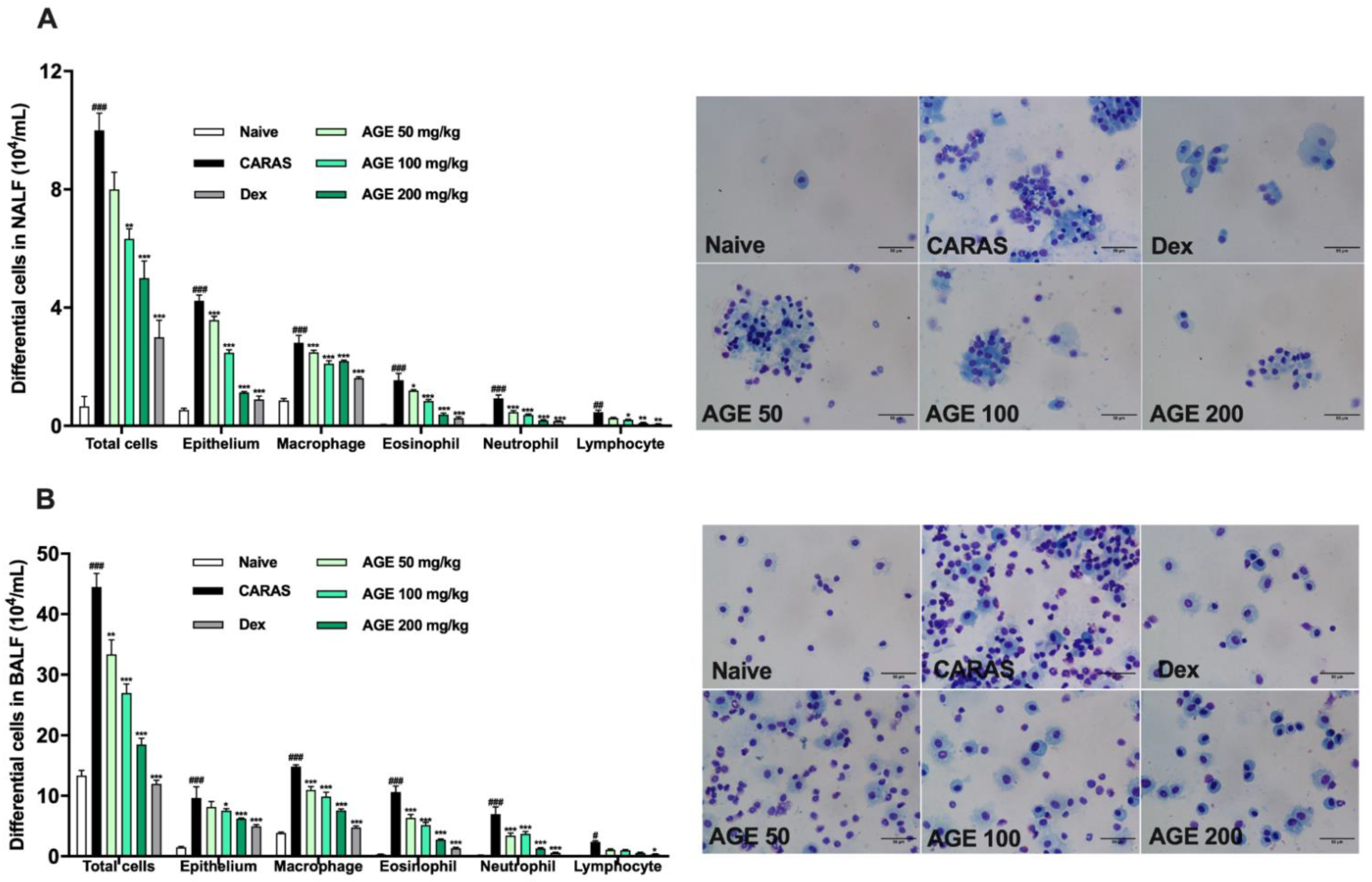
2.2. AGE Treatment Decreased the Infiltration of Inflammatory Cells in NALF and BALF
2.3. AGE Ameliorated Nasal Mucosa Swelling, Goblet Cell Hyperplasia, and Infiltration of Eosinophil in the Nasal Tissue
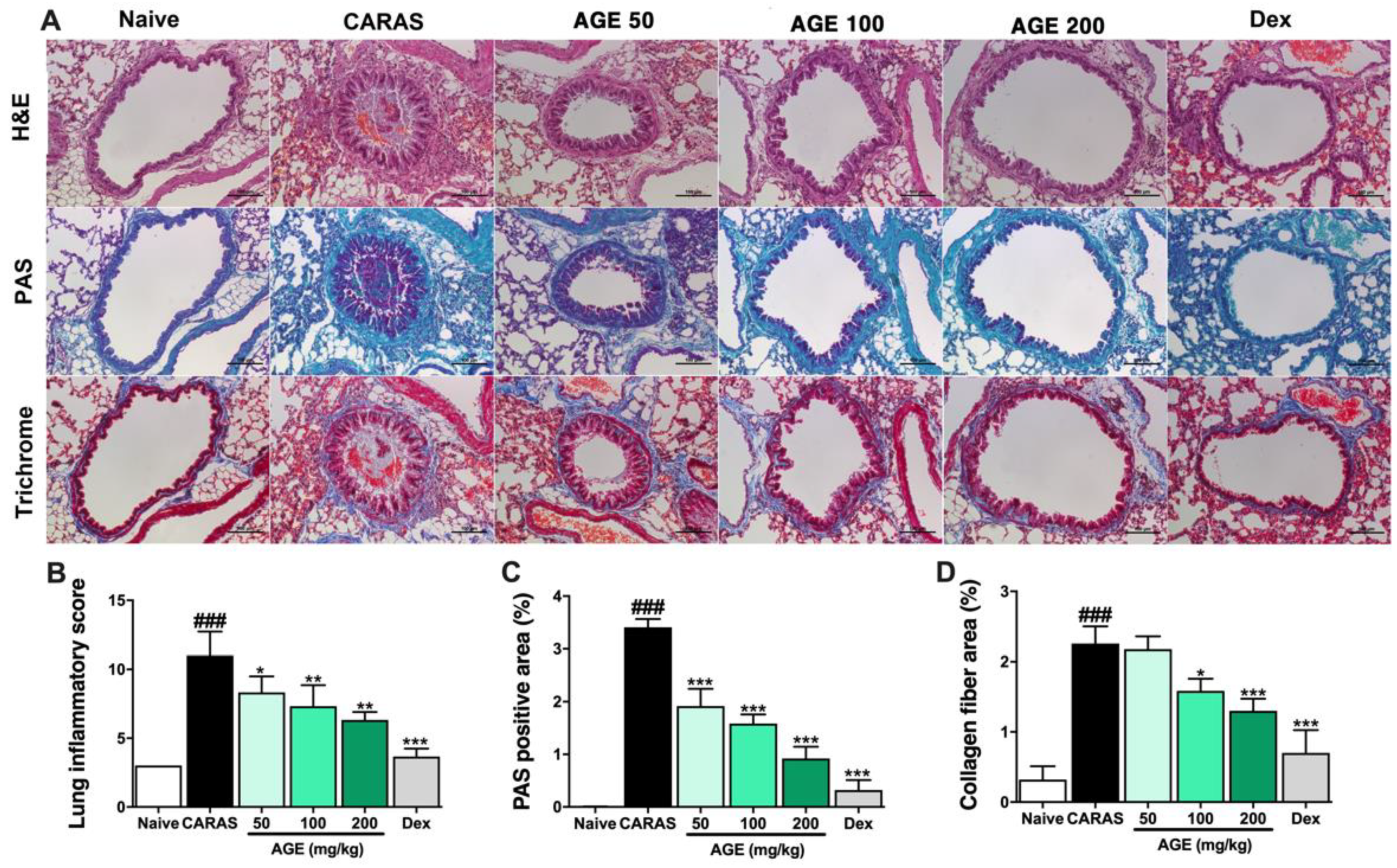
2.4. AGE Effectively Suppressed Inflammation, Mucus Secretion, and Collagen Deposition in the Lung Tissue
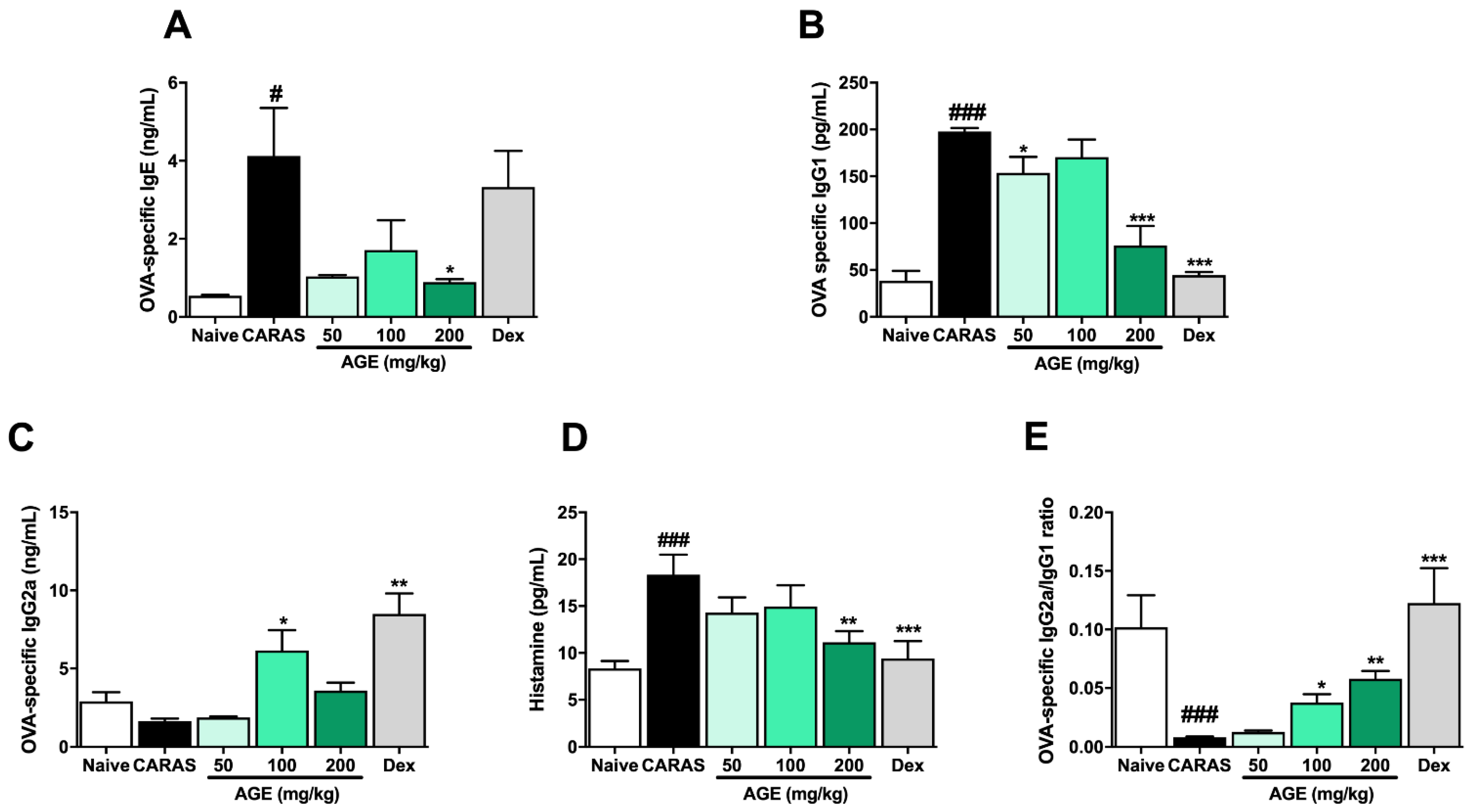
2.5. AGE Treatment Suppressed Allergic Responses by Regulating Serum Antigen-Specific-Immunoglobulins
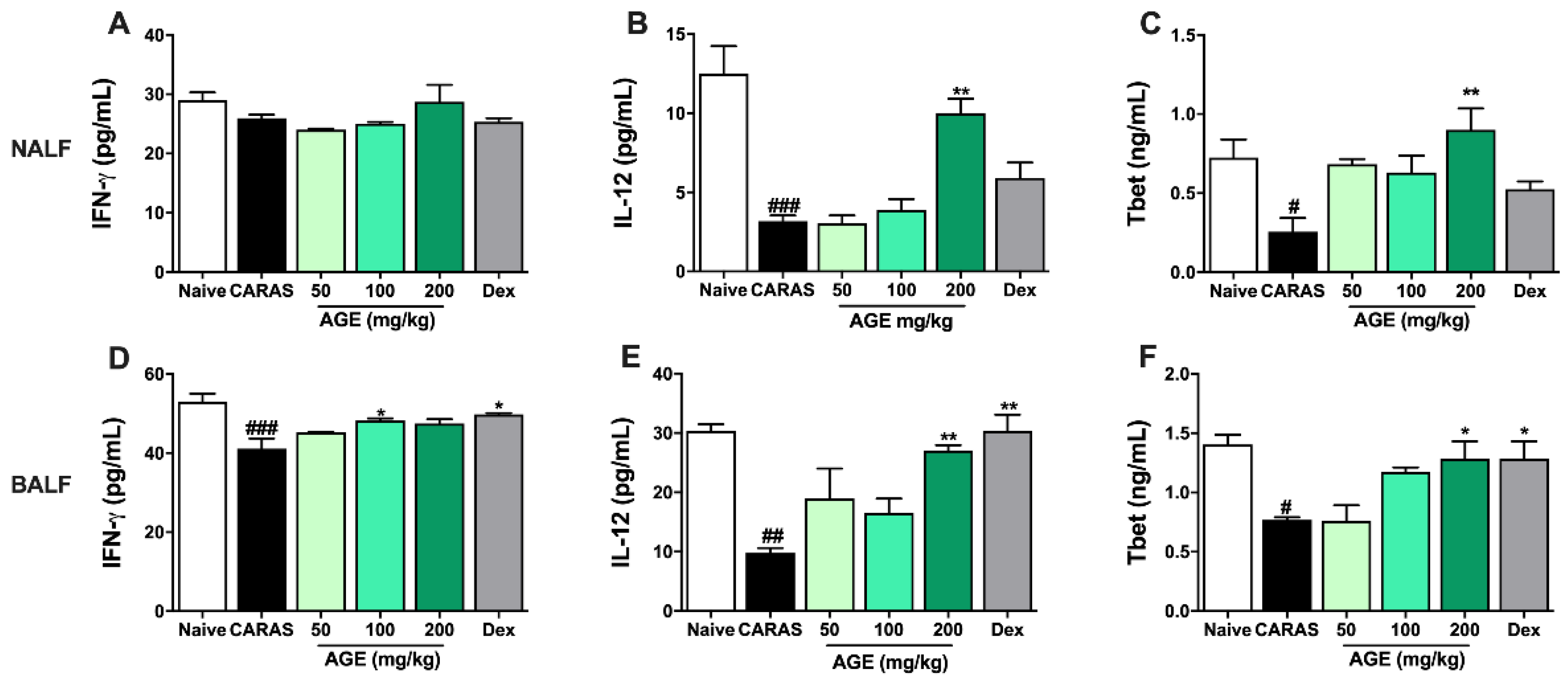
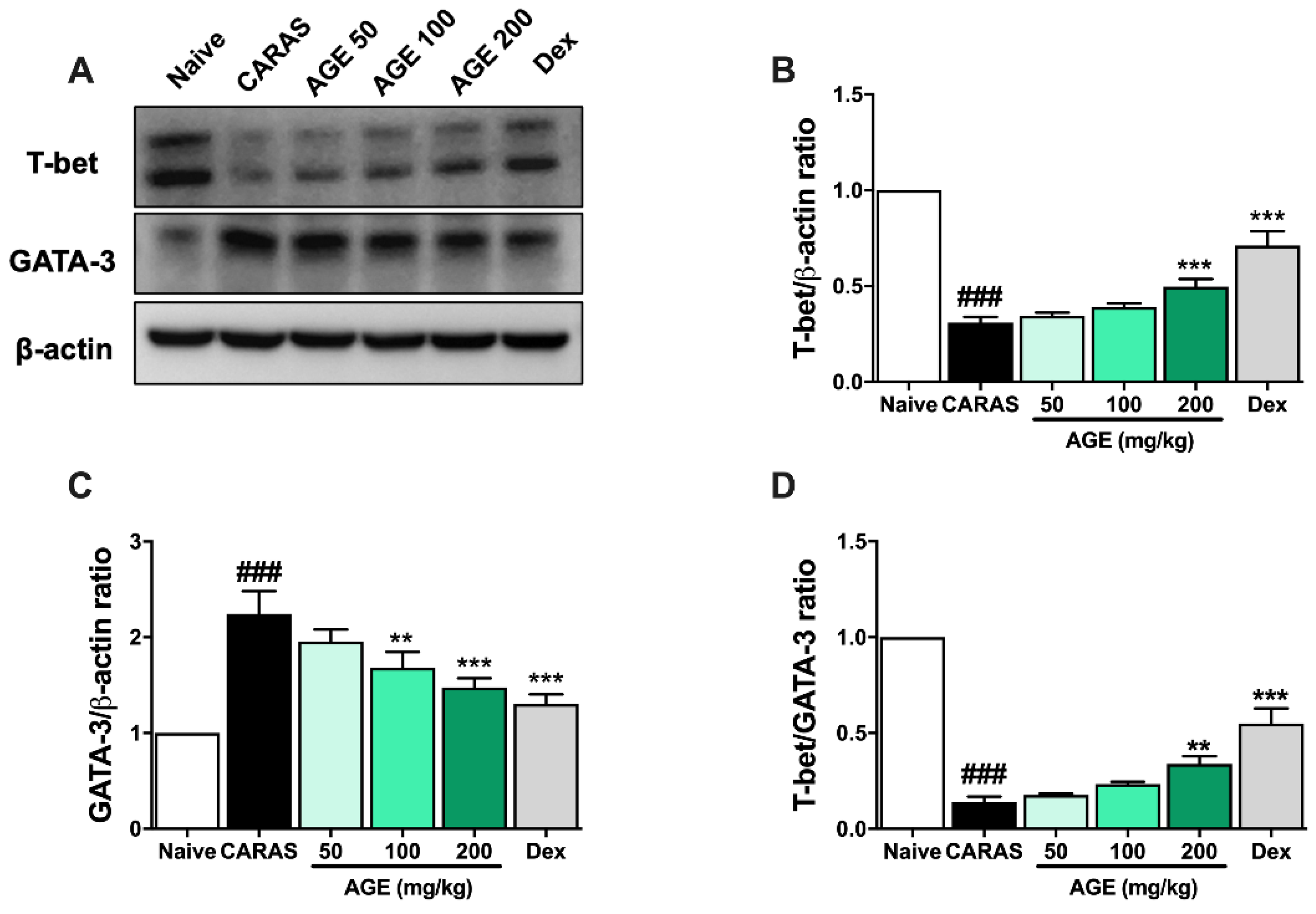
2.6. AGE Increased TH1 Cytokines and TH1 Transcription Factor in NALF and BALF
2.7. AGE Decrease TH2 Cytokines and TH2 Transcription Factor in NALF and BALF
2.8. AGE Decreased the Expression of Transcription Factors in Lung Tissues of CARAS Mice
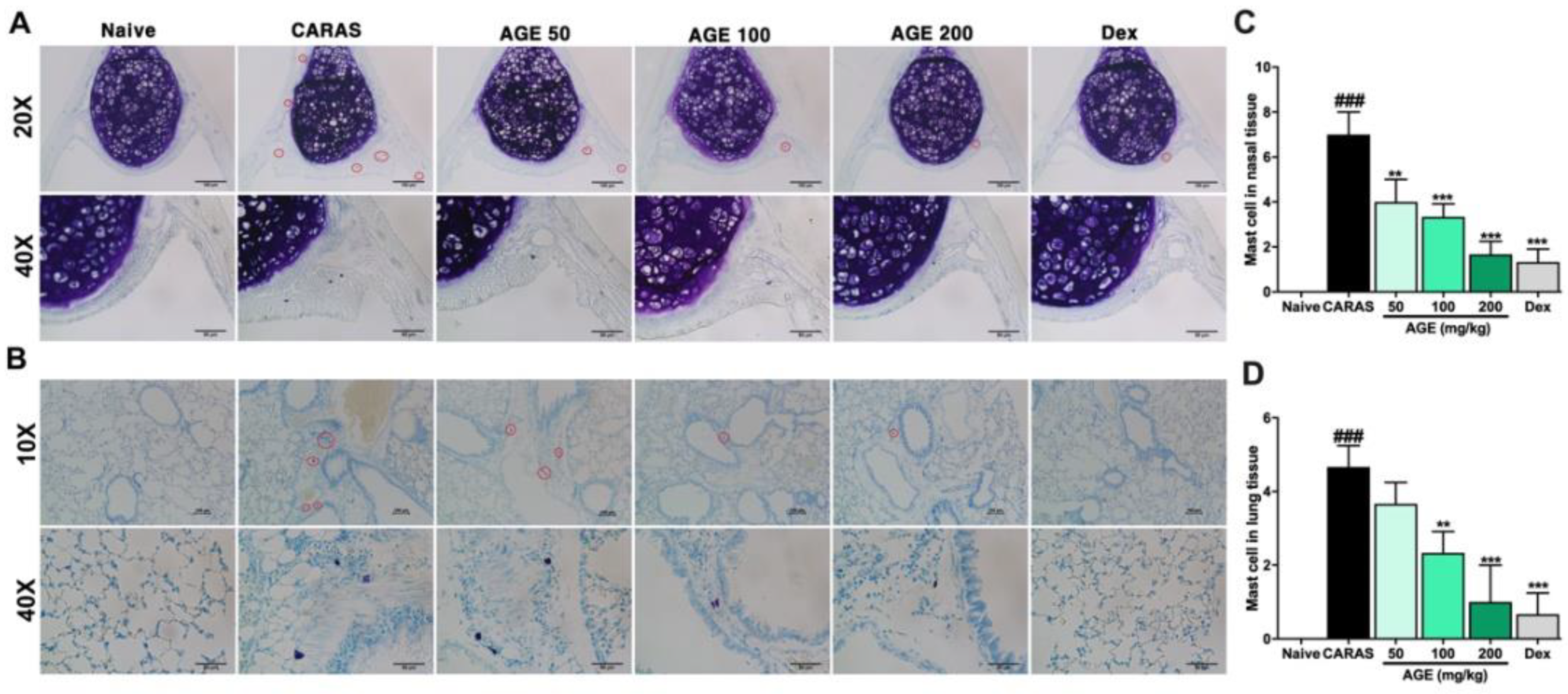
2.9. AGE Directly Inhibited Mast Cell Degranulation In Vitro and Mast Cell Infiltration in the Nasal and Lung Tissue In Vivo Experiment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Artemisia gmelinii Extract
4.2. CARAS Model Establishment and Treatment
4.3. Nasal Symptoms
4.4. Nasal Lavage Fluid (NALF), Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) Collection, and Analysis
4.5. Determination of OVA-Specific Immunoglobulins and Histamine in Serum
4.6. Histological Examination
4.7. Quantification of Cytokines
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Rat Peritoneal Mast Cell Degranulation
4.10. Mast Cell Viability Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiksten, J.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Makela, M. Primary Prevention of Airway Allergy. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2018, 5, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoner, D.P. Allergic rhinitis: Definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, detection, and diagnosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Asthma, E.; Prevention, P. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, S94–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compalati, E.; Ridolo, E.; Passalacqua, G.; Braido, F.; Villa, E.; Canonica, G.W. The link between allergic rhinitis and asthma: The united airways disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R.; Bunnag, C.; Khaltaev, N.; Bousquet, J. Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma in Asia Pacific and the ARIA Update 2008. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, S212–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva Ferreira, L.K.D.; Paiva Ferreira, L.A.M.; Montiro, T.M.; Bezerra, G.C.; Bernardo, L.R.; Piuvezam, M.R. Combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS). Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.K.; Shao, Z. Pathogenesis of allergic airway inflammation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajoui, O.; Janani, R.; Tulic, M.; Joubert, P.; Ronis, T.; Hamid, Q.; Zheng, H.; Mazer, B.D. Synthesis of IL-13 by human B lymphocytes: Regulation and role in IgE production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.M.; Abraham, S.N. New roles for mast cells in modulating allergic reactions and immunity against pathogens. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M.; Piliponsky, A.M. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Kim, H.G.; Choi, M.K.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Wang, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Son, S.W.; Hwang, S.Y.; Son, C.G. Artemisia capillaris extract protects against bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, J.C. Extraction optimization for obtaining Artemisia capillaris extract with high anti-inflammatory activity in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 872718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Lee, I.S. Effects of Artemisia capillaris ethyl acetate fraction on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 179, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Lee, H.; Seo, C.S.; Lim, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Shin, H. Artemisia capillaris inhibits atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in Dermatophagoides farinae-sensitized Nc/Nga mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naclerio, R.M. Allergic rhinitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun Baris, S.; Vural, C.; Yaprak, B.; Onyilmaz, T.; Tuncel, D.; Vatansever, S.; Isken, T.; Basyigit, I.; Boyaci, H.; Yildiz, F. The effects of sildenafil on smoke induced lung inflammation in rats. Malays. J. Pathol. 2016, 38, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, J.; Uceda, M.; Ziegler, O.; Lindo, F.; Herrera-Perez, E.; Huicho, L. Association between allergic rhinitis and asthma control in Peruvian school children: A cross-sectional study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 861213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Jacot, W.; Vignola, A.M.; Bachert, C.; Va. an Cauwenberge, P. Allergic rhinitis: A disease remodeling the upper airways? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountford, A.P.; Fisher, A.; Wilson, R.A. The profile of IgG1 and IgG2a antibody responses in mice exposed to Schistosoma mansoni. Parasite Immunol. 1994, 16, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, J.R.; Bartram, R.E.; Knight, P.A.; Miller, H.R.; Garrod, D.R.; Grencis, R.K. Mast cells disrupt epithelial barrier function during enteric nematode infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7761–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrien, C.N.; Menzies-Gow, A. The Biology of Eosinophils and Their Role in Asthma. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, D.; Wong, C.K.; Tsang, M.S.; Chu, I.M.; Liu, D.; Zhu, J.; Chu, M.; Lam, C.W. Activation of Eosinophils Interacting with Bronchial Epithelial Cells by Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37: Implications in Allergic Asthma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite-de-Moraes, M.; Hammad, H.; Dy, M. Crosstalk between Innate and Adaptive Cells on Allergic Process. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 720568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Greenfeder, S.; Umland, S.P.; Cuss, F.M.; Chapman, R.W.; Egan, R.W. Th2 cytokines and asthma. The role of interleukin-5 in allergic eosinophilic disease. Respir. Res. 2001, 2, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.T.; Stelts, D.M.; Zurcher, J.A.; Adams, G.K., 3rd; Egan, R.W.; Kreutner, W.; Watnick, A.S.; Jones, H.; Chapman, R.W. Involvement of IL-5 in a murine model of allergic pulmonary inflammation: Prophylactic and therapeutic effect of an anti-IL-5 antibody. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1995, 13, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonte, M.G.; Schopf, L.R.; Neben, T.Y.; Cheever, A.W.; Donaldson, D.D.; Wynn, T.A. IL-13 is a key regulatory cytokine for Th2 cell-mediated pulmonary granuloma formation and IgE responses induced by Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 920–930. [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Yasuo, M.; Tsushima, K.; Yoshida, K.; Ise, H.; Yamaya, M. Modulation of mucus production by interleukin-13 receptor alpha2 in the human airway epithelium. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzina, I.G.; Keegan, A.D.; Heller, N.M.; Rook, G.A.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Atamas, S.P. Regulation of inflammation by interleukin-4: A review of “alternatives”. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Ouyang, W. The function role of GATA-3 in Th1 and Th2 differentiation. Immunol. Res. 2003, 28, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.L.; Song, J.; Xiong, P.; Cao, P.P.; Liao, B.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zeng, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Disease-specific T-helper cell polarizing function of lesional dendritic cells in different types of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Ranganath, S.H.; Weindel, K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Murphy, T.L.; Sha, W.C.; Murphy, K.M. Inhibition of Th1 development mediated by GATA-3 through an IL-4-independent mechanism. Immunity 1998, 9, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ren, F.; Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D. Expression of Th1 and Th2 cytokine-associated transcription factors, T-bet and GATA-3, in the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, N.; Peel, T.J.; Schroder, A.; Aniscenko, J.; Walton, R.P.; Finotto, S.; Johnston, S.L. Tbet Deficiency Causes T Helper Cell Dependent Airways Eosinophilia and Mucus Hypersecretion in Response to Rhinovirus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halova, I.; Draberova, L.; Draber, P. Mast cell chemotaxis—Chemoattractants and signaling pathways. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.T.; Fan, Y.; Piao, C.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Shin, D.U.; Jung, S.Y.; Hyeon, E.; Song, C.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, H.S.; et al. Piper Nigrum extract improves OVA-induced nasal epithelial barrier dysfunction via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Cell Immunol. 2020, 351, 104035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Yan, G.H.; Chai, O.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Lim, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.S.; Han, E.H.; Kim, H.T.; et al. Inhibitory effects of Agaricus blazei on mast cell-mediated anaphylaxis-like reactions. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.V.; Piao, C.H.; Fan, Y.J.; Yu, Z.N.; Lee, S.-Y.; Song, C.H.; Shin, H.S.; Chai, O.H. Artemisia gmelinii Extract Alleviates Allergic Airway Inflammation via Balancing TH1/TH2 Homeostasis and Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315377
Nguyen TV, Piao CH, Fan YJ, Yu ZN, Lee S-Y, Song CH, Shin HS, Chai OH. Artemisia gmelinii Extract Alleviates Allergic Airway Inflammation via Balancing TH1/TH2 Homeostasis and Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):15377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315377
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi Van, Chun Hua Piao, Yan Jing Fan, Zhen Nan Yu, So-Young Lee, Chang Ho Song, Hee Soon Shin, and Ok Hee Chai. 2022. "Artemisia gmelinii Extract Alleviates Allergic Airway Inflammation via Balancing TH1/TH2 Homeostasis and Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 15377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315377
APA StyleNguyen, T. V., Piao, C. H., Fan, Y. J., Yu, Z. N., Lee, S.-Y., Song, C. H., Shin, H. S., & Chai, O. H. (2022). Artemisia gmelinii Extract Alleviates Allergic Airway Inflammation via Balancing TH1/TH2 Homeostasis and Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 15377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315377





