Implications for Self-Management among African Caribbean Adults with Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health Disorders: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
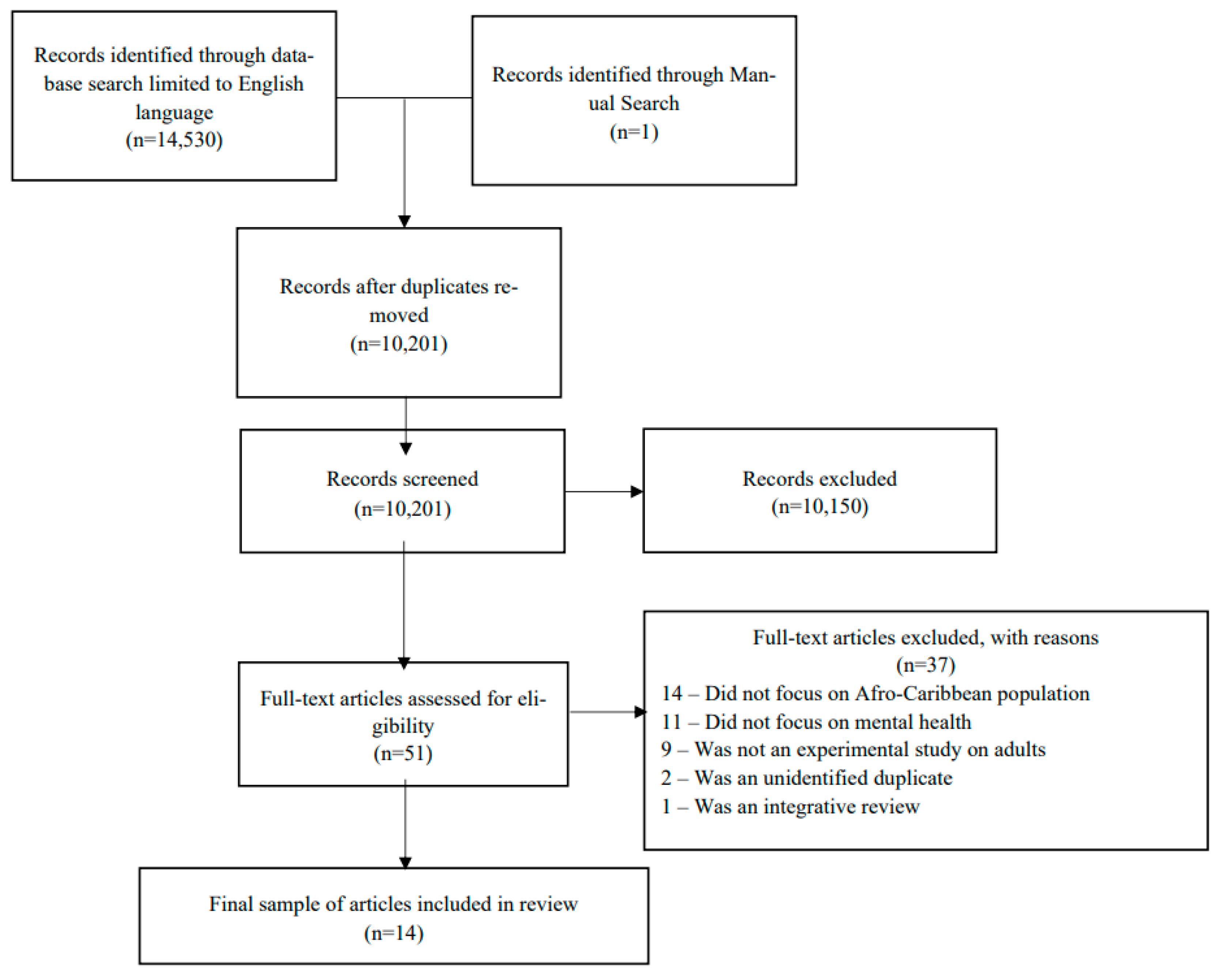
2. Materials and Methods
- Population: African Caribbean adults with one or more NCDs, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular conditions.
- Intervention: Treatment for type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, including exercise, healthy eating, blood glucose testing, and medication.
- Comparator: Usual care.
- Outcomes: Successful NCD self-management, successful mental health outcomes.
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Appraisal/Risk of Bias
2.4. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Data Synthesis
3.1.1. Comorbid Mental Health Problems and Chronic NCDs
3.1.2. Factors That Mitigate or Mediate the Association between Mental Health Problems and Chronic NCDs
Factors Influencing Self-Management
Association between Mental Health and NCD Outcomes
- Risk Factors
3.1.3. Varied Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samuels, T.A.; Guell, C.; Legetic, B.; Unwin, N. Policy initiatives, culture and the prevention and control of chronic noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) in the Caribbean. Ethn. Health 2012, 17, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyne, M.S. Diabetes in the Caribbean: Trouble in paradise. Insulin 2009, 4, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas Ninth Edition. In IDF Diabetes Atlas. International Diabetes Federation. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Jones, S.; Tillin, T.; Park, C.; Williams, S.; Rapala, A.; Al Saikhan, L.; Eastwood, S.V.; Richards, M.; Hughes, A.D.; Chaturvedi, N. Cohort Profile Update: Southall and Brent Revisited (SABRE) study: A UK population-based comparison of cardiovascular disease and diabetes in people of European, South Asian and African Caribbean heritage. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1441–1442e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidulescu, A.; Francis, D.K.; Ferguson, T.S.; Bennett, N.R.; Hennis, A.J.; Wilks, R.; Harris, E.N.; MacLeish, M.; Sullivan, L.W.; on behalf of the U.S. Caribbean Alliance for Health Disparities Research Group (USCAHDR). Disparities in hypertension among black Caribbean populations: A scoping review by the U.S. Caribbean Alliance for Health Disparities Research Group (USCAHDR). Int. J. Equity Health 2015, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo, J.L.; Jones, D.W.; Materson, B.J.; Oparil, S.; Wright, J.T.; et al. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, & National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: The JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003, 289, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, P.A.; Gough, L. Self-management: A comprehensive approach to management of chronic conditions. Am. J. Public. Health 2014, 104, e25–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, M.; Schulman-Green, D.; Knafl, K.; Reynolds, N.R. A revised self- and family management framework. Nurs. Outlook 2015, 63, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospedales, C.; Samuels, T.; Cummings, R.; Gollop, G.; Greene, E. Raising the priority of chronic noncommunicable diseases in the Caribbean. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2011, 30, 393–400. Available online: https://www.scielosp.org/article/rpsp/2011.v30n4/393-400/ (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Brown, C.R.; Hambleton, I.R.; Sobers-Grannum, N.; Hercules, S.M.; Unwin, N.; Nigel Harris, E.; Wilks, R.; MacLeish, M.; Sullivan, L.; Murphy, M.M. Social determinants of depression and suicidal behavior in the Caribbean: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, N.; Conway, C.A. Medical and Mental Health Comorbidities Among Minority Racial/Ethnic Groups in the United States. J. Soc. Behav. Health Sci. 2020, 14, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R.; González, H.M.; Neighbors, H.; Nesse, R.; Abelson, J.M.; Sweetman, J.; Jackson, J.S. Prevalence and Distribution of Major Depressive Disorder in African Americans, Caribbean Blacks, and Non-Hispanic Whites. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himle, J.A.; Baser, R.E.; Taylor, R.J.; Campbell, R.D.; Jackson, J.S. Anxiety disorders among African Americans, blacks of Caribbean descent, and non-Hispanic whites in the United States. J. Anxiety Disord. 2009, 23, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, J.S.; Tanenbaum, M.L.; Commissariat, P.V. Psychosocial factors in medication adherence and diabetes self-management: Implications for research and practice. Am. Psychol. 2016, 71, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Hey, S.; Hu, F. Global etiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axon, R.N.; Gebregziabher, M.; Hunt, K.J.; Lynch, C.P.; Payne, E.; Walker, R.J.; Egede, L.E. Comorbid depression is differentially associated with longitudinal medication nonadherence by race/ethnicity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine 2016, 95, e3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormel, J.; Von Korff, M.; Burger, H.; Scott, K.; Demyttenaere, K.; Huang, Y.Q.; Posada-Villa, J.; Lepine, J.P.; Angermeyer, M.; Levinson, D.; et al. Mental disorders among persons with heart disease—results from World Mental Health surveys. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2007, 29, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kretchy, I.A.; Owusu-Daaku, F.T.; Danquah, S.A. Mental health in hypertension: Assessing symptoms of anxiety, depression and stress on anti-hypertensive medication adherence. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 2014, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawfik, G.M.; Dila, K.A.S.; Mohamed, M.Y.F.; Tam, D.N.H.; Kien, N.D.; Ahmed, A.M.; Huy, N.T. A step by step guide for conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis with simulation data. Trop. Med. Health 2019, 47, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.; Prince, M.; Richards, M.; Brayne, C.; Mann, A. Stroke, vascular risk factors and depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2001, 178, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watkins, D.C.; Assari, S.; Johnson-Lawrence, V. Race and Ethnic Group Differences in Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder, Generalized Anxiety Disorder, and Chronic Medical Conditions. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2015, 2, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seecheran, N.; Jagdeo, C.-L.; Seecheran, R.; Seecheran, V.; Persad, S.; Peram, L.; Evans, M.; Edwards, J.; Thackoorcharan, S.; Davis, S.; et al. Screening for depressive symptoms in cardiovascular patients at a tertiary centre in Trinidad and Tobago: Investigation of correlates in the SAD CAT study. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederick, F.; Maharajh, H. Prevalence of depression in type 2 diabetic patients in Trinidad and Tobago. West Indian Med. J. 2013, 62, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huffman, F.G.; Vallasciani, M.; Vaccaro, J.A.; Exebio, J.C.; Zarini, G.G.; Nayer, A.; Ajabshir, S. The association of depression and perceived stress with beta cell function between African and Haitian Americans with and without type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2013, 3, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Caluwé, L.; van Buitenen, N.; Gelan, P.J.; Crunelle, C.L.; Thomas, R.; Casseres, S.; Matthys, F.; van Harten, P.; Cahn, W. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its associated risk factors in an African–Caribbean population with severe mental illness. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 281, 112558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, M.; Glover, L.M.; Norwood, A.F.; Jordan, C.; Min, Y.I.; Brewer, L.C.; Kubzansky, L.D. Optimism and cardiovascular health among African Americans in the Jackson Heart Study. Prev. Med. 2019, 129, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, M.; Glover, L.S.M.; Gebreab, S.Y.; Spruill, T.M. Cumulative psychosocial factors are associated with cardiovascular disease risk factors and management among African Americans in the Jackson Heart Study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assari, S.; Lankarani, M.M. Association between obesity and depression among American Black: Role of ethnicity and gender. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2014, 1, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins-McNeil, J. Psychosocial characteristics and cardiovascular risk in African Americans with diabetes. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2006, 20, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magny-Normilus, C.; Whittemore, R.; Wexler, D.J.; Schnipper, J.L.; Nunez-Smith, M.; Fu, M.R. Barriers to type 2 diabetes management among older adult Haitian immigrants. Sci. Diabetes Self-Manag. Care 2021, 47, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, F.; Peirano, F.; Vargas, J.I.; Zamora, F.X.; López-Lastra, M.; Núñez, R.; Soza, J.; González, K.; Estay, D.; Barchiesi, B.; et al. Infectious and non-infectious diseases burden among Haitian immigrants in Chile: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, D.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Teresi, J.A.; Eimicke, J.P.; Findley, S.E.; Carrasquillo, O.; Palmas, W. High rates of depressive symptoms in low-income urban Hispanics of Caribbean origin with poorly controlled diabetes: Correlates and risk factors. J. Health Care Poor Underserved 2014, 25, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.F.; Cheng, J.; McCarter, G. Associations between diabetes-related distress and cardiovascular complication risks in patients with type 2 diabetes and lower socioeconomic status: A pilot study. Diabetes Spectr. 2019, 32, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health. Study Quality Assessment Tools | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Schmidt, C.B.; Potter van Loon, B.J.; Torensma, B.; Snoek, F.J.; Honig, A. Ethnic minorities with diabetes differ in depressive and anxiety symptoms and diabetes-distress. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1204237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.T.; Kim, K.B.; Ko, J.; Jang, Y.; Levine, D.; Lee, H.B. Role of depression in diabetes management in an ethnic minority population: A case of Korean Americans with type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, e000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lankarani, M.M.; Assari, S. Association between number of comorbid medical conditions and depression among individuals with diabetes; race and ethnic variations. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2015, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanayakkara, N.; Pease, A.; Ranasinha, S.; Wischer, N.; Andrikopoulos, S.; Speight, J.; de Courten, B.; Zoungas, S. Depression and diabetes distress in adults with type 2 diabetes: Results from the Australian National Diabetes Audit (ANDA) 2016. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, R.J.; Gebregziabher, M.; Martin-Harris, B.; Egede, L.E. Quantifying Direct Effects of Social Determinants of Health on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenhow, L. Perceptions of Health, Weight, and Body Image among Afro-Caribbean Women in the U.S. Virgin Islands. Master Thesis, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2012. Available online: https://cdr.lib.unc.edu/concern/masters_papers/dr26z0098 (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Magny-Normilus, C.; Whittemore, R. Haitian Immigrants and Type 2 Diabetes: An Integrative Review. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2019, 22, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Purpose | Design | Location/ Country | Sample | Age Range | Ethnicity | Measures | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | To examine the association between stroke, vascular risk factors, and depression | Cross-sectional | South London | 287 | 55–75 | African Caribbean | Stroke, HTN, T2D, angina, height, weight, waist to hip, smoking, and physical activity |
|
| [21] | To test whether differences between race and ethnic groups exist for major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) with one or more chronic medical conditions | Cross-sectional | US | 5889 | 18+ | African American, African Caribbean, and European American | Socio-economic status, MDD, GAD, and chronic medical conditions |
|
| [22] | To determine any associations among patient demographics, comorbidities, and cardiovascular/depressive symptoms | Cross-sectional | Trinidad and Tobago | 1203 | 18+ | South Asian, African Caribbean, Multiracial/Other | HTN, cerebro-vascular events, kidney disease, pulmonary disease, and depression |
|
| [23] | To describe the statistical prevalence of depression in type 2 diabetes (T2D) | Cross-sectional | Trinidad and Tobago | 128 | 21+ | Indo-Trinidadian | Socioeconomic status, glucose control, medical complications, and depression |
|
| [24] | To assess associations between depressive symptoms and perceived stress with beta-cell function | Cross-sectional | Miami, Dade, and Broward CountiesFlorida/US | 462,696 | 18+ | African and Haitian Americans | Fasting plasma glucose, weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, lipid panel, serum insulin concentration, Beck depression inventory, depression, and stress |
|
| [25] | To determine the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with severe mental illness | Cross-sectional | Island of Curacao | 350 | 18–84 | African Caribbean | Cardiovascular disease, HTN, hyper-glycemia, T2D, obesity, total cholesterol, metabolic syndrome, psychiatric diagnoses, and substance disorder and use |
|
| [26] | To examine the associations between positive optimistic orientation and LS7 among African Americans | Cross-sectional | Jackson, MS/US | 4734 | 35–85 | African American | Optimism, LS7 components, demographics, socioeconomic status, depression HTN, HLD, and blood glucose |
|
| [27] | To demonstrate the cumulative effects of individual psychosocial factors and CVD risk factors by sex | Cross-sectional | Jackson, MS/US | 4806 | 35–84 | African American | Cynicism, anger, depression, global and weekly stress, major life events, cardiovascular disease, and risk factors |
|
| [28] | To compare differing racial/ethnic populations for associations between NCDs and medical comorbidities | Cross-sectional | US | 6082 | 18+ | African American, African Caribbean, European American | Demographics, NCDs, medical comorbidities, GAD, and MDD |
|
| [29] | To examine the ability for depression, anxiety, and social support to predict cardiovascular disease risk in those with no previous cardiovascular events | Cross-sectional | Southern US | 57 | 35–74 | African American | Social support, cardiovascular disease risk, depression, and anxiety |
|
| [30] | To describe the experiences of older adult Haitian Immigrants in managing T2D | Qualitative, Observational | Northern US | 20 | 65+ | Haitian Immigrants | HbA1c, HTN, emotions, culture, and education |
|
| [31] | To acquire the basic health information of the Haitian adult population living in Chile | Cross-sectional | Chile | 499 | 18+ | Haitian born immigrants in Chile | BMI, blood pressure, lipids, nutritional status, diabetes, substance use, quality of life, physical activity, mood, and depression, and renal function |
|
| [32] | To assess the prevalence and correlation of depression and T2D self-management and control | Cross-sectional | Northern Manhattan/US | 360 | 35–70 | Hispanics of Caribbean Origin | Depression, antidepressant use, stressful life events, education, HbA1c, and medication adherence. |
|
| [33] | To assess associations between diabetes- related stress and predicted cardiovascular risks and complications. | Cross-Sectional | East Oakland, US | 48 | 40–80 | European American, African Caribbean, Asian-Indian | PAID scores, HbA1c, HDL, LDL, Afib, BP, and smoking status |
|
| Study | [20] | [32] | [24] | [31] | [25] | [29] | [27] | [28] | [23] | [21] | [23] | [22] | [26] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Was the research question or objective in this paper clearly stated? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Was the study population clearly specified and defined? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Was the participation rate of eligible persons at least 50%? | Y | Y | NR | Y | NR | NR | NR | Y | Y | NR | Y | Y | NR |
| Were all the subjects selected or recruited from the same or similar populations (including the same time period)? Were inclusion and exclusion criteria for being in the study prespecified and applied uniformly to all participants? | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Was a sample size justification, power description, or variance and effect estimates provided? | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | NA | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| For the analyses in this paper, were the exposure(s) of interest measured prior to the outcome(s) being measured? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | NA | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | NA |
| Was the timeframe sufficient so that one could reasonably expect to see an association between exposure and outcome if it existed? | Y | NA | NA | Y | NA | NA | NA | Y | Y | Y | NA | Y | NA |
| For exposures that can vary in amount or level, did the study examine different levels of the exposure as related to the outcome (e.g., categories of exposure, or exposure measured as continuous variable)? | NA | Y | Y | NA | Y | N | Y | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Were the exposure measures (independent variables) clearly defined, valid, reliable, and implemented consistently across all study participants? | NA | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Y |
| Was the exposure(s) assessed more than once over time? | N | N | N | NA | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Were the outcome measures (dependent variables) clearly defined, valid, reliable, and implemented consistently across all study participants? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Were the outcome assessors blinded to the exposure status of participants? | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Was loss to follow-up after baseline 20% or less? | Y | Y | NR | Y | Y | NR | NA | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | NA |
| Were key potential confounding variables measured and adjusted statistically for their impact on the relationship between exposure(s) and outcome(s)? | NA | Y | Y | NA | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Quality Score (Good, Fair, or Poor) | Good | Good | Fair | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| No. | Item | Guide Questions | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain 1: Research team and reflexivity | |||
| Personal characteristics | |||
| 1 | Interviewer/facilitator | Which author/s conducted the interview or focus group? | CMN |
| 2 | Credentials | What were the researcher’s credentials?, e.g., PhD, MD | PhD |
| 3 | Occupation | What was their occupation at the time of the study? | Research Scholar |
| 4 | Gender | Was the researcher male or female? | F |
| 5 | Experience and training | What experience or training did the researcher have? | Previous experience in qualitative research |
| Relationship with participants | |||
| 6 | Relationship established | Was a relationship established prior to study commencement? | No |
| 7 | Participant knowledge of the interviewer | What did the participants know about the researcher?, e.g., personal goals, reasons for doing the research | Unknown |
| 8 | Interviewer characteristics | What characteristics were reported about the interviewer/facilitator?, e.g., Bias, assumptions, reasons and interests in the research topic. | None |
| Domain 2: Study Design | |||
| Theoretical framework | |||
| 9 | Methodological orientation and theory | What methodological orientation was stated to underpin the study?, e.g., grounded theory, discourse analysis, ethnography, phenomenology, content analysis | Descriptive data analysis |
| Participant selection | |||
| 10 | Sampling | How were participants selected?, e.g., purposive, convenience, consecutive, snowball | Recruitment through flyers and meeting inclusion criteria. |
| 11 | Method of approach | How were participants approached?, e.g., face-to-face, telephone, mail, email | Flyers at local churches. |
| 12 | Sample size | How many participants were in the study? | 20 |
| 13 | Non-participation | How many people refused to participate or dropped out? Reasons? | unknown |
| Setting | |||
| 14 | Setting of data collection | Where was the data collected?, e.g., home, clinic, workplace | Face to face |
| 15 | Presence of nonparticipants | Was anyone else present besides the participants and researchers? | Unknown |
| 16 | Description of sample | What are the important characteristics of the sample?, e.g., demographic data, date | Haitian adults aged 65 or older, type 2 diabetes for at least one year, living in the US. |
| Data collection | |||
| 17 | Interview guide | Were questions, prompts, guides provided by the authors? Was it pilot tested? | Yes |
| 18 | Repeat interviews | Were repeat interviews carried out? If yes, how many? | No |
| 19 | Audio/visual recording | Did the research use audio or visual recording to collect the data? | Yes, audio recordings |
| 20 | Field notes | Were field notes made during and/or after the interview or focus group? | Yes |
| 21 | Duration | What was the duration of the inter views or focus group? | 40–90 min |
| 22 | Data saturation | Was data saturation discussed? | Yes |
| 23 | Transcripts returned | Were transcripts returned to participants for comment and/or correction? | No |
| Domain 3: Analysis and findings | |||
| Data analysis | |||
| 24 | Number of data coders | How many data coders coded the data? | 2 |
| 25 | Description of the coding tree | Did authors provide a description of the coding tree? | Yes |
| 26 | Derivation of themes | Were themes identified in advance or derived from the data? | Themes were derived from the data |
| 27 | Software | What software, if applicable, was used to manage the data? | NVivo 12 software IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows |
| 28 | Participant checking | Did participants provide feedback on the findings? | No |
| Reporting | |||
| 29 | Quotations presented | Were participant quotations presented to illustrate the themes/findings? Was each quotation identified?, e.g., participant number | Yes, quotations were presented and identified |
| 30 | Data and findings consistent | Was there consistency between the data presented and the findings? | Yes |
| 31 | Clarity of major themes | Were major themes clearly presented in the findings? | Yes |
| 32 | Clarity of minor themes | Is there a description of diverse cases or discussion of minor themes? | Yes |
| Themes | Supporting Studies |
|---|---|
| 1. Prevalence of comorbidity mental health problems and chronic noncommunicable diseases | [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] |
| 2. Factors that mitigate or mediate the association between mental health problems and chronic noncommunicable diseases | [23,24,25,26,27,28,30,31,32,33,34] |
| 2a. Factors influencing self-management | [26,27,29,30] |
| 2b. Association between mental health and noncommunicable disease outcomes | [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,32,33] |
| 2b1. Risk Factors | [23,24,25,26,27,28,31,32,33] |
| 2b2. Protective Factors | [24,31,33] |
| 3. Varied results | [27,28,29] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magny-Normilus, C.; Hassan, S.; Sanders, J.; Longhurst, C.; Lee, C.S.; Jurgens, C.Y. Implications for Self-Management among African Caribbean Adults with Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health Disorders: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112735
Magny-Normilus C, Hassan S, Sanders J, Longhurst C, Lee CS, Jurgens CY. Implications for Self-Management among African Caribbean Adults with Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health Disorders: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(11):2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112735
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagny-Normilus, Cherlie, Saria Hassan, Julie Sanders, Catrina Longhurst, Christopher S. Lee, and Corrine Y. Jurgens. 2022. "Implications for Self-Management among African Caribbean Adults with Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health Disorders: A Systematic Review" Biomedicines 10, no. 11: 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112735
APA StyleMagny-Normilus, C., Hassan, S., Sanders, J., Longhurst, C., Lee, C. S., & Jurgens, C. Y. (2022). Implications for Self-Management among African Caribbean Adults with Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health Disorders: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines, 10(11), 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112735






