Inhibition of miR-33a-5p in Macrophage-like Cells In Vitro Promotes apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Maintenance
2.2. Lentiviral Transduction
2.3. Cholesterol-Loading MOVAS Cells to Induce MLC Trans-Differentiation
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Cholesterol Efflux Assays
2.6. RT-qPCR
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
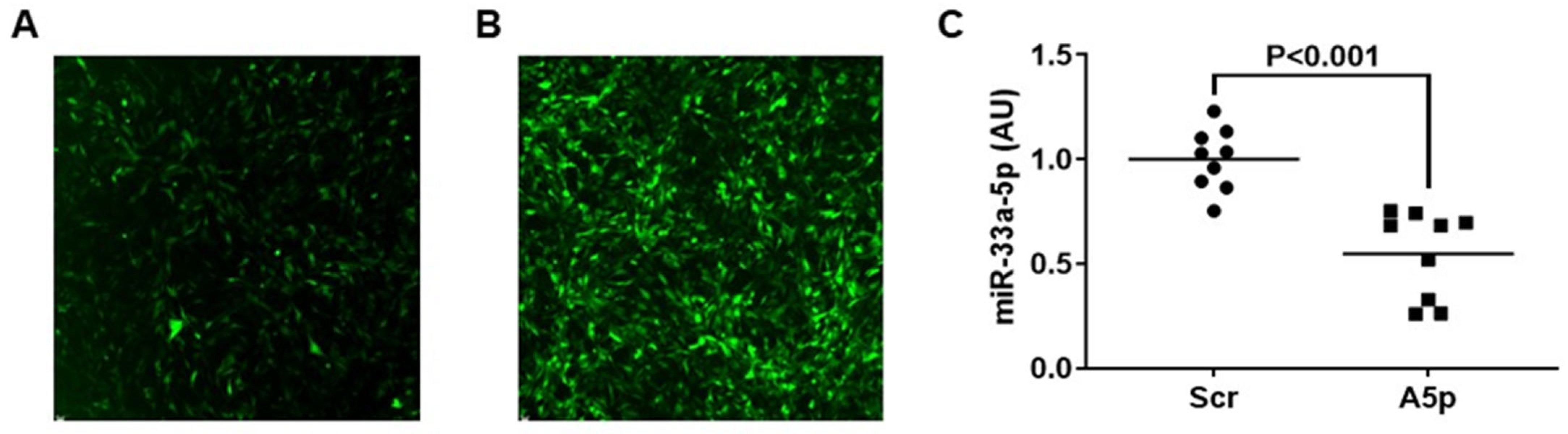
3.1. Transducing MOVAS Cells with LV-AntimiR33a5p Decreases miR-33a-5p Expression
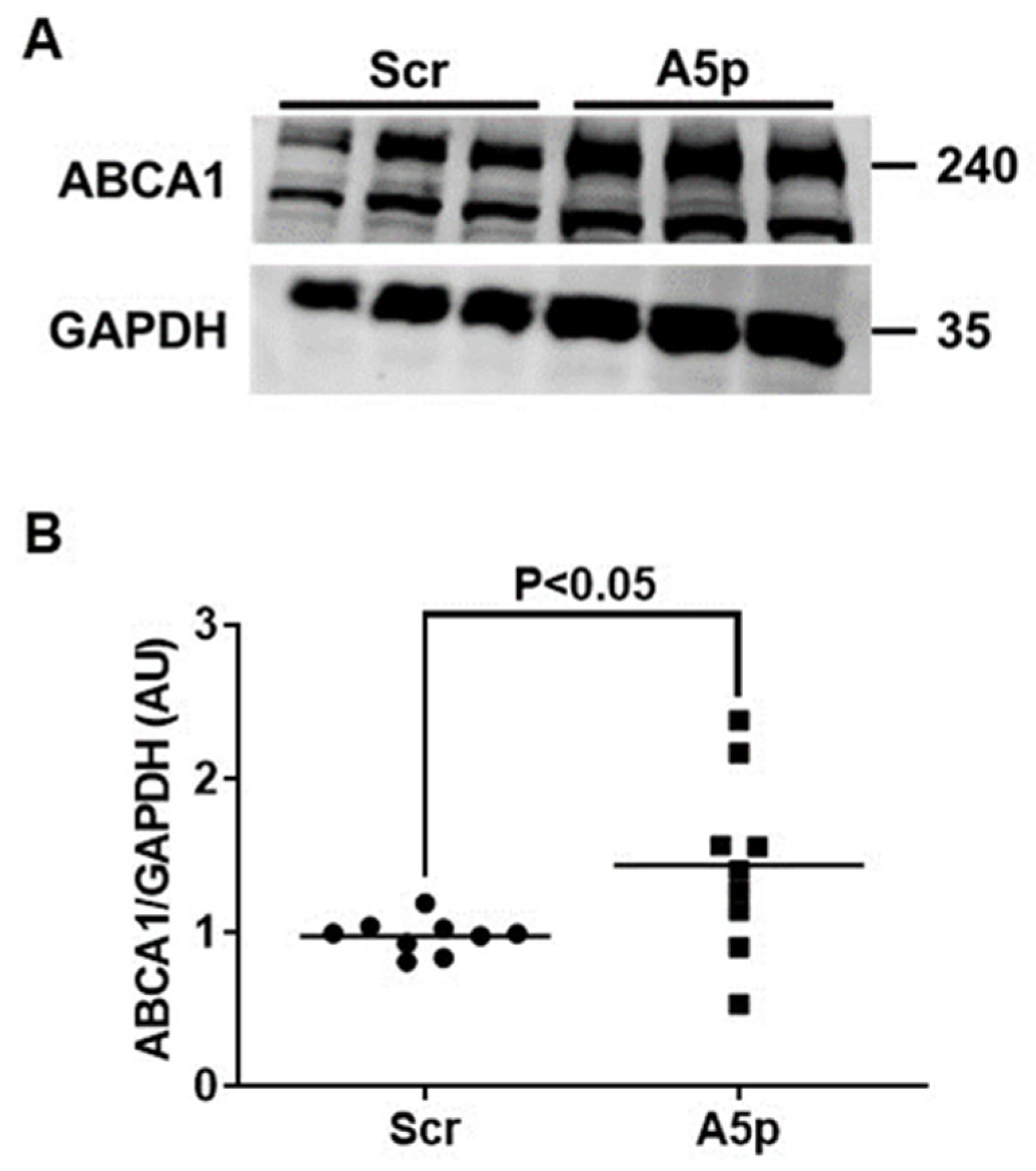
3.2. Reduction of miR-33a-5p Expression in MOVAS MLC Results in Upregulation of ABCA1 Protein Expression
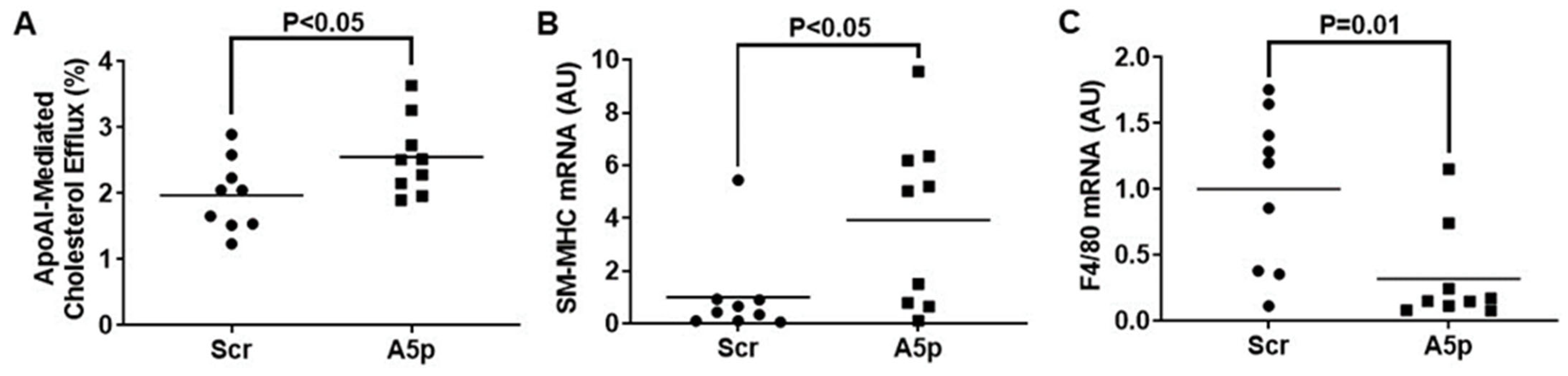
3.3. Inhibiting miR-33a-5p in MOVAS MLC Enhances apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux Which Promotes Restoration of VSMC Phenotype
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pahwa, R.; Jialal, I. Atherosclerosis; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pentikainen, M.O.; Oorni, K.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Kovanen, P.T. Modified LDL—Trigger of atherosclerosis and inflammation in the arterial intima. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 247, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahverdian, S.; Pannu, P.S.; Francis, G.A. Contribution of monocyte-derived macrophages and smooth muscle cells to arterial foam cell formation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Nikiforov, N.G.; Starodubova, A.V.; Popkova, T.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Macrophages and Foam Cells: Brief Overview of Their Role, Linkage, and Targeting Potential in Atherosclerosis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahverdian, S.; Chehroudi, A.C.; McManus, B.M.; Abraham, T.; Francis, G.A. Contribution of intimal smooth muscle cells to cholesterol accumulation and macrophage-like cells in human atherosclerosis. Circulation 2014, 129, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feil, S.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Lukowski, R.; Essmann, F.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schaller, M.; Feil, R. Transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells to macrophage-like cells during atherogenesis. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dubland, J.A.; Allahverdian, S.; Asonye, E.; Sahin, B.; Jaw, J.E.; Sin, D.D.; Seidman, M.A.; Leeper, N.J.; Francis, G.A. Smooth Muscle Cells Contribute the Majority of Foam Cells in ApoE (Apolipoprotein E)-Deficient Mouse Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, M.R.; Sinha, S.; Owens, G.K. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.A. The Greatly Under-Represented Role of Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Ather. Rep. 2023, 25, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.X.; Shapiro, M.; Trogan, E.; Fisher, E.A. Transdifferentiation of mouse aortic smooth muscle cells to a macrophage-like state after cholesterol loading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13531–13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esobi, I.C.; Barksdale, C.; Heard-Tate, C.; Reigers Powell, R.; Bruce, T.F.; Stamatikos, A. MOVAS Cells: A Versatile Cell Line for Studying Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Cholesterol Metabolism. Lipids 2021, 56, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vengrenyuk, Y.; Nishi, H.; Long, X.; Ouimet, M.; Savji, N.; Martinez, F.O.; Cassella, C.P.; Moore, K.J.; Ramsey, S.A.; Miano, J.M.; et al. Cholesterol loading reprograms the microRNA-143/145-myocardin axis to convert aortic smooth muscle cells to a dysfunctional macrophage-like phenotype. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oram, J.F.; Lawn, R.M. ABCA1: The gatekeeper for eliminating excess tissue cholesterol. J. Lipid. Res. 2001, 42, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.; Liu, B.; Persaud, S.J. Effects of miR-33 Deficiency on Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases: Implications for Therapeutic Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, L.; Azzam, K.M.; Lin, W.C.; Rai, P.; Lowe, J.M.; Gabor, K.A.; Madenspacher, J.H.; Aloor, J.J.; Parks, J.S.; Naar, A.M.; et al. MicroRNA-33 Regulates the Innate Immune Response via ATP Binding Cassette Transporter-mediated Remodeling of Membrane Microdomains. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 19651–19660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, K.J.; Suarez, Y.; Davalos, A.; Parathath, S.; Fitzgerald, M.L.; Tamehiro, N.; Fisher, E.A.; Moore, K.J.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Science 2010, 328, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi-Shoushtari, S.H.; Kristo, F.; Li, Y.; Shioda, T.; Cohen, D.E.; Gerszten, R.E.; Naar, A.M. MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis. Science 2010, 328, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.L.; Goedeke, L.; Suarez, Y.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. miR-33 in cardiometabolic diseases: Lessons learned from novel animal models and approaches. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.J.; Sheedy, F.J.; Esau, C.C.; Hussain, F.N.; Temel, R.E.; Parathath, S.; van Gils, J.M.; Rayner, A.J.; Chang, A.N.; Suarez, Y.; et al. Antagonism of miR-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol transport and regression of atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfran-Duque, A.; Lin, C.S.; Goedeke, L.; Suarez, Y.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. Micro-RNAs and High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfran-Duque, A.; Ramirez, C.M.; Goedeke, L.; Lin, C.S.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. microRNAs and HDL life cycle. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, M.; Lei, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Zuo, Z.; He, Q.; Huang, W.; et al. Effects of miR-33a-5P on ABCA1/G1-mediated cholesterol efflux under inflammatory stress in THP-1 macrophages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echesabal-Chen, J.; Huang, K.; Vojtech, L.; Oladosu, O.; Esobi, I.; Sachdeva, R.; Vyavahare, N.; Jo, H.; Stamatikos, A. Constructing Lipoparticles Capable of Endothelial Cell-Derived Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Anti-miR-33a-5p to Cultured Macrophages. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 5631–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esobi, I.C.; Oladosu, O.; Echesabal-Chen, J.; Powell, R.R.; Bruce, T.; Stamatikos, A. miR-33a Expression Attenuates ABCA1-Dependent Cholesterol Efflux and Promotes Macrophage-Like Cell Transdifferentiation in Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Lipids 2023, 2023, 8241899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedeke, L.; Vales-Lara, F.M.; Fenstermaker, M.; Cirera-Salinas, D.; Chamorro-Jorganes, A.; Ramirez, C.M.; Mattison, J.A.; de Cabo, R.; Suarez, Y.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. A regulatory role for microRNA 33* in controlling lipid metabolism gene expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Wacker, B.K.; Stamatikos, A.; Sethuraman, M.; Komandur, K.; Dichek, D.A. Jugular Vein Injection of High-Titer Lentiviral Vectors Does Not Transduce the Aorta-Brief Report. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladosu, O.; Esobi, I.C.; Powell, R.R.; Bruce, T.; Stamatikos, A. Dissecting the Impact of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell ABCA1 versus ABCG1 Expression on Cholesterol Efflux and Macrophage-like Cell Transdifferentiation: The Role of SR-BI. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfbauer, G.; Glick, J.M.; Minor, L.K.; Rothblat, G.H. Development of the smooth muscle foam cell: Uptake of macrophage lipid inclusions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 7760–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Pitman, M.; Oladosu, O.; Echesabal-Chen, J.; Vojtech, L.; Esobi, I.; Larsen, J.; Jo, H.; Stamatikos, A. The Impact of MiR-33a-5p Inhibition in Pro-Inflammatory Endothelial Cells. Diseases 2023, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvan-Charvet, L.; Wang, N.; Tall, A.R. Role of HDL, ABCA1, and ABCG1 transporters in cholesterol efflux and immune responses. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Xuan, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Jin, H.; Dong, H. How vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switching contributes to vascular disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, L.; Wang, L.; Lui, K.O.; He, B.; Zhou, B. Smooth muscle-derived macrophage-like cells contribute to multiple cell lineages in the atherosclerotic plaque. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miano, J.M.; Cserjesi, P.; Ligon, K.L.; Periasamy, M.; Olson, E.N. Smooth muscle myosin heavy chain exclusively marks the smooth muscle lineage during mouse embryogenesis. Circ. Res. 1994, 75, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Faunce, D.E.; Stacey, M.; Terajewicz, A.; Nakamura, T.; Zhang-Hoover, J.; Kerley, M.; Mucenski, M.L.; Gordon, S.; Stein-Streilein, J. The macrophage F4/80 receptor is required for the induction of antigen-specific efferent regulatory T cells in peripheral tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos Cassado, A. F4/80 as a Major Macrophage Marker: The Case of the Peritoneum and Spleen. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2017, 62, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.; Owens, G.K. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, L.S.; Gomez, D.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Salmon, M.; Alencar, G.F.; Haskins, R.M.; Swiatlowska, P.; Newman, A.A.; Greene, E.S.; Straub, A.C.; et al. KLF4-dependent phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells has a key role in atherosclerotic plaque pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naar, A.M. miR-33: A Metabolic Conundrum. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naar, A.M. Anti-atherosclerosis or No Anti-atherosclerosis: That is the miR-33 question. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marquart, T.J.; Wu, J.; Lusis, A.J.; Baldan, A. Anti-miR-33 therapy does not alter the progression of atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedeke, L.; Salerno, A.; Ramirez, C.M.; Guo, L.; Allen, R.M.; Yin, X.; Langley, S.R.; Esau, C.; Wanschel, A.; Fisher, E.A.; et al. Long-term therapeutic silencing of miR-33 increases circulating triglyceride levels and hepatic lipid accumulation in mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oller, J.; Mendez-Barbero, N.; Ruiz, E.J.; Villahoz, S.; Renard, M.; Canelas, L.I.; Briones, A.M.; Alberca, R.; Lozano-Vidal, N.; Hurle, M.A.; et al. Nitric oxide mediates aortic disease in mice deficient in the metalloprotease Adamts1 and in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, R.; Buckler, J.M.; Tang, C.; Kim, F.; Dichek, D.A. Helper-dependent adenoviral vectors are superior in vitro to first-generation vectors for endothelial cell-targeted gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.L.; White, K.M.; Lavery, C.A.; Custers, J.; Waddington, S.N.; Baker, A.H. Pseudotyping the adenovirus serotype 5 capsid with both the fibre and penton of serotype 35 enhances vascular smooth muscle cell transduction. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, P.; Blanchard, V.; Francis, G.A. Smooth Muscle Cell-Macrophage Interactions Leading to Foam Cell Formation in Atherosclerosis: Location, Location, Location. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 921597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatikos, A.; Knight, E.; Vojtech, L.; Bi, L.; Wacker, B.K.; Tang, C.; Dichek, D.A. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of Anti-miR-33a-5p from Transduced Endothelial Cells Enhances Macrophage and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Cholesterol Efflux. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Dufour, J.M. Cell lines: Valuable tools or useless artifacts. Spermatogenesis 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oladosu, O.; Chin, E.; Barksdale, C.; Powell, R.R.; Bruce, T.; Stamatikos, A. Inhibition of miR-33a-5p in Macrophage-like Cells In Vitro Promotes apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux. Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 117-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31010009
Oladosu O, Chin E, Barksdale C, Powell RR, Bruce T, Stamatikos A. Inhibition of miR-33a-5p in Macrophage-like Cells In Vitro Promotes apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux. Pathophysiology. 2024; 31(1):117-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleOladosu, Olanrewaju, Emma Chin, Christian Barksdale, Rhonda R. Powell, Terri Bruce, and Alexis Stamatikos. 2024. "Inhibition of miR-33a-5p in Macrophage-like Cells In Vitro Promotes apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux" Pathophysiology 31, no. 1: 117-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31010009
APA StyleOladosu, O., Chin, E., Barksdale, C., Powell, R. R., Bruce, T., & Stamatikos, A. (2024). Inhibition of miR-33a-5p in Macrophage-like Cells In Vitro Promotes apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux. Pathophysiology, 31(1), 117-126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31010009






