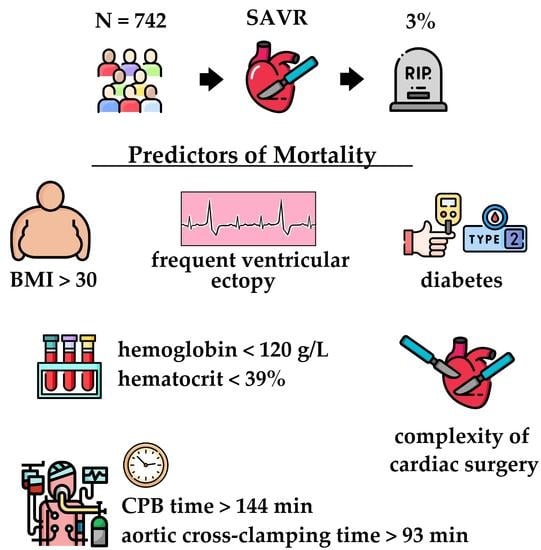
Predictors of Mortality Following Aortic Valve Replacement in Aortic Stenosis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Endpoint
2.5. Surgery
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Patients
3.2. ROC Curve Analysis
3.3. Uni- and Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blindman, B.R.; Dweck, M.R.; Lancellotti, P.; Généreux, P.; Piérard, L.A.; O’hara, P.T.; Bonow, R.O. Management of Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis: Evolving Concepts in Timing of Valve Replacement. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2020, 13, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Roger, V.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013, 127, e6–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iung, B.; Vahanian, A. Epidemiology of acquired valvular heart disease. Can. J. Cardiol. 2014, 30, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eveborn, G.W.; Schirmer, H.; Heggelund, G.; Lunde, P.; Rasmussen, K. The evolving epidemiology of valvular aortic stenosis. the Tromsø study. Heart 2013, 99, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaden, J.J.; Nkomo, V.T.; Enriquez-Sarano, M. The global burden of aortic stenosis. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Nishimura, R.A.; Bonow, R.O.; Carabello, B.A.; Erwin, J.P., 3rd; Gentile, F.; Jneid, H.; Krieger, E.V.; Mack, M.; McLeod, C.; et al. 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Valvular Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2021, 143, e72–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, A.R.; Wang, E.H.Z. Therapeutic Controversies in the Medical Management of Valvular Heart Disease. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. ESC/EACTS Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 727–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, P.; Pibarot, P.; Tribouilloy, C.; Lancellotti, P.; Maisano, F.; Iung, B.; Piérard, L. European Society of Cardiology Council on Valvular Heart Disease. Multiple and Mixed Valvular Heart Diseases. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimard, B.H.; Safford, R.E.; Burns, E.L. Aortic Stenosis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Phys. 2016, 93, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar, A.; Thaden, J.J.; Nkomo, V.T. Management of Patients with Aortic Valve Stenosis. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, J.; Postigo, A.; Baumgartner, H. The year in cardiovascular medicine 2020: Valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundt, T.M.; Jneid, H. Guideline Update on Indications for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Based on the 2020 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guidelines for Management of Valvular Heart Disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1088–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockeria, L.A.; Bockeria, O.L.; Sanakoev, M.K.; Le, T.G.; Satyukova, A.S.; Ispiryan, A.Y.; Klimchuk, I.Y.; Fatulaev, Z.F.; Petrosyan, A.D.; Shvartz, V.A. Simultaneous surgical correction of atrial fibrillation and aortic valve replacement: Immediate results after surgery. Russ. Open Med. J. 2016, 5, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antonini-Canterin, F.; Di Nora, C.; Cervesato, E.; Zito, C.; Carerj, S.; Ravasel, A.; Cosei, I.; Popescu, A.C.; Popescu, B.A. Value of ejection fraction/velocity ratio in the prognostic stratification of patients with asymptomatic aortic valve stenosis. Echocardiography 2018, 35, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovic, M.; Putnik, S.; Penicka, M.; Doros, G.; Deja, M.A.; Kockova, R.; Kotrc, M.; Glaveckaite, S.; Gasparovic, H.; Pavlovic, N.; et al. AVATAR-trial investigators. Aortic Valve ReplAcemenT versus Conservative Treatment in Asymptomatic SeveRe Aortic Stenosis: The AVATAR Trial. Circulation 2021, 145, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Garg, A.; Parashar, A.; Svensson, L.G.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Navia, J.L.; Mick, S.; Kapadia, S.R. In-hospital mortality and stroke after surgical aortic valve replacement: A nationwide perspective. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 150, 571–578.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlacu, A.; Covic, A.; Cinteza, M.; Lupu, P.M.; Deac, R.; Tinica, G. Exploring Current Evidence on the Past, the Present, and the Future of the Heart Team: A Narrative Review. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 2020, 9241081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.S.L.; Ashokkumar, S.; Newcomb, A.; MacIsaac, A.I.; Whitbourn, R.J.; Palmer, S. Contemporary review of severe aortic stenosis. Intern. Med. J. 2019, 49, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambler, G.; Omar, R.Z.; Royston, P.; Kinsman, R.; Keogh, B.E.; Taylor, K.M. Generic, simple risk stratification model for heart valve surgery. Circulation 2005, 112, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, F.H.; Peterson, E.D.; Coombs, L.P.; DeLong, E.R.; Jamieson, W.R.; Shroyer, A.L.W.; Grover, F.L. Prediction of operative mortality after valve replacement surgery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacinto, O.; Satriano, U.; Nenna, A.; Spadaccio, C.; Lusini, M.; Mastroianni, C.; Nappi, F.; Chello, M. Inflammatory Response and Endothelial Dysfunction Following Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Pathophysiology and Pharmacological Targets. Recent. Pat. Inflamm. Allergy. Drug. Discov. 2019, 13, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson Jr, R.J.; Cascio, W.E.; Schreiner, P.J.; Crow, R.S.; Rautaharju, P.M.; Heiss, G. Prevalence of premature ventricular contractions in a population of African American and white men and women: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Am. Heart J. 2002, 143, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, G.M. Evaluation and Management of Premature Ventricular Complexes. Circulation 2020, 141, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markman, T.M.; Nazarian, S. Treatment of ventricular arrhythmias: What’s New? Trends. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 29, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataklte, F.; Erqou, S.; Laukkanen, J.; Kaptoge, S. Meta-analysis of ventricular premature complexes and their relation to cardiac mortality in general populations. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Liu, K.; Fan, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Mao, H.; Xu, X.; et al. The Association Between Obesity and Risk of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 534294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Straten, A.H.; Külcü, K.; Özdemir, H.I.; Elenbaas, T.W.; Soliman Hamad, M.A. Preoperative hemoglobin level as a predictor of mortality after aortic valve replacement. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 27, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cladellas, M.; Bruguera, J.; Comín, J.; Vila, J.; de Jaime, E.; Martí, J.; Gomez, M. Is pre-operative anaemia a risk marker for in-hospital mortality and morbidity after valve replacement? Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antonini-Canterin, F.; Di Nora, C.; Poli, S.; Sparacino, L.; Cosei, I.; Ravasel, A.; Popescu, A.C.; Popescu, B.A. Obesity, Cardiac Remodeling, and Metabolic Profile: Validation of a New Simple Index beyond Body Mass Index. J. Cardiovasc. Echogr. 2018, 28, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.C. Preventive Strategies for Minimizing Hemodilution in the Cardiac Surgery Patient During Cardiopulmonary Bypass. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariscalco, G.; Biancari, F.; Zanobini, M.; Cottini, M.; Piffaretti, G.; Saccocci, M.; Banach, M.; Beghi, C.; Angelini, G.D. Bedside tool for predicting the risk of postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery: The POAF score. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2014, 3, e000752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Mitesh, S.; Gkogkou, A.; Geladari, E. Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Is there Any Relationship? Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinica, G.; Brinza, C.; Covic, A.; Popa, I.V.; Tarus, A.; Bacusca, A.E.; Burlacu, A. Determinants of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: A systematic review. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, D.Y.; Cook, D.L.; Rivera, I.M. Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection and Evaluation. Am. Fam. Phys. 2017, 96, 776–783. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nora, C.; Cervesato, E.; Cosei, I.; Ravasel, A.; Popescu, B.A.; Zito, C.; Carerj, S.; Antonini-Canterin, F.; Popescu, A.C. New classification of geometric ventricular patterns in severe aortic stenosis: Could it be clinically useful? Echocardiography 2018, 35, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | All | Mortality | No Mortality | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 742 | 22 | 720 | |
| Age, years | 63(57; 69) | 66 (62; 70) | 63 (56; 69) | 0.131 |
| Male gender, % | 58 | 45 | 58 | 0.225 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28(25; 32) | 31 (28; 34) | 28.4 (25; 32) | 0.025 |
| Weight, kg | 80 (70; 89) | 78 (72; 92) | 80 (70; 89) | 0.620 |
| BSA, m2 | 1.9 (1.85; 2.01) | 1.9 (1.83; 2.04) | 1.9 (1.86; 2.01) | 0.125 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 93 | 93 | 93 | 0.987 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0.427 |
| IHD, n (%) | 51 | 79 | 50 | 0.035 |
| Prior AMI, n (%) | 7 | 21 | 6 | 0.022 |
| Stroke, n (%) | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0.409 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 14 | 38 | 13 | 0.006 |
| COPD, n (%) | 6 | 7 | 6 | 0.803 |
| CKD, n (%) | 11.7 | 22.7 | 11 | 0.104 |
| CHF NYHA class III-IV, % | 71.5 | 69 | 71.6 | 0.849 |
| ASD, n (%) | <1 | 7 | <1 | 0.004 |
| VSD, n (%) | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0.871 |
| MV disease, % | 10 | 32 | 9.5 | <0.001 |
| TV disease, % | 9.2 | 22.7 | 8.8 | 0.025 |
| Arrhythmia | 23 | 41 | 23 | 0.049 |
| AF, % | 13 | 18 | 12 | 0.419 |
| Atrial flutter, % | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0.588 |
| FVE, % | 2 | 14 | 2 | <0.001 |
| VT, % | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0.844 |
| Sick sinus syndrome, % | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0.746 |
| AV block, % | 3 | 14 | 3 | 0.014 |
| Sinus rhythm, % | 87 | 93 | 87 | 0.692 |
| Cerebrovascular disease, % | 28 | 50 | 28 | 0.074 |
| Peripheral vascular disease, % | 22 | 36 | 22 | 0.223 |
| Concomitant oncological disease, % | 9 | 7 | 9 | 0.799 |
| Parameters | All | Mortality | No Mortality | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 742 | 22 | 720 | |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||
| LVEF, % | 64 (58; 67) | 63 (58; 67) | 64 (58; 67) | 0.974 |
| LVEDD/BSA, cm/m2 | 2.6 (2.3; 2.9) | 2.99 (2.72; 3.77) | 2.6 (2.3; 2.9) | 0.001 |
| LVESD/BSA, cm/m2 | 1.68(1.49; 1.93) | 1.98 (1.75; 2.12) | 1.67(1.49; 1.91) | 0.008 |
| LVEDV/BSA, mL/m2 | 61.5 (49; 78) | 67 (59; 116) | 61.4 (50; 78) | 0.103 |
| LVESV/BSA, mL/m2 | 22 (17; 30) | 26 (22; 31) | 22 (17; 30) | 0.152 |
| Peak gradient, mm Hg | 96 (80; 112) | 95 (86; 105) | 96 (80; 112) | 0.912 |
| Peak velocity, m/s | 3.5 (2.8; 4.2) | 3.7 (2.9; 4.2) | 3.5 (2.8; 4.2) | 0.451 |
| Mean gradient, mm Hg | 55 (44; 66) | 58 (45; 62) | 54 (44; 67) | 0.944 |
| Fibrous ring of the aortic valve, mm | 23 (22; 25) | 22 (21; 25) | 23 (22; 25) | 0.174 |
| Bicuspid aortic valve, % | 14.8 | 9 | 15 | 0.201 |
| Moderate AR, % | 21 | 36 | 21 | 0.401 |
| Severe AR, % | 5.9 | 9 | 5.8 | 0.733 |
| EOA, cm2 | 0.7 (0.55; 0.8) | 0.65 (0.6; 0.8) | 0.7 (0.55; 0.8) | 0.233 |
| LA volume, mL3 | 109 (90; 140) | 132 (102; 145) | 109 (90; 140) | 0.542 |
| Laboratory parameters | ||||
| Hemoglobin level, g/L | 136 (126; 146) | 118 (111; 134) | 137 (127; 146) | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit, % | 41 (38; 44) | 36.5 (35; 39) | 41 (38; 44) | <0.001 |
| WBC, 109/L | 7.2 (6; 8.6) | 7.1 (6.6; 8.8) | 7.2 (6; 8.6) | 0.539 |
| Neutrophils, 109/L | 4.6 (3.6; 5.6) | 4.8 (3.7; 5.5) | 4.6 (3.6; 5.6) | 0.549 |
| Neutrophils, % | 60 (53; 65) | 67 (58; 71) | 59 (53; 65) | 0.032 |
| glucose, mmoL/L | 5.3 (4.9; 5.9) | 5.7 (5; 7,4) | 5.3 (4.9; 5.9) | 0.059 |
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 4.1 (3.7; 4.7) | 4.7 (4.3; 4.9) | 4.05 (3.6; 4.6) | 0.064 |
| Creatinine, mkmoL/L | 82 (72; 96) | 87 (69; 108) | 82 (72; 96) | 0.481 |
| eGFR, mL/min | 87 (69; 103) | 75 (62; 100) | 87 (69; 103) | 0.129 |
| eGFR, mL/min per 1,73 m2 (MDRD) | 78(66; 90) | 71(51; 90) | 78(66; 89) | 0.154 |
| Drug therapy | ||||
| Beta-blockers, % | 49 | 64 | 49 | 0.403 |
| ACE inhibitors, % | 31 | 18 | 32 | 0.448 |
| ARA, % | 17 | 27 | 16 | 0.536 |
| Calcium antagonists, % | 12 | 27 | 11 | 0.363 |
| Statins, % | 32 | 36 | 32 | 0.802 |
| Nitrates, % | 8 | 9 | 8 | 0.964 |
| Thiazide diuretics, % | 9 | 0 | 10 | 0.576 |
| Loop diuretics, % | 12 | 27 | 11 | 0.369 |
| Potassium-sparing diuretics, % | 21 | 36 | 21 | 0.386 |
| Antiarrhythmic drugs, % | 5 | 9 | 5 | 0.813 |
| Parameters | All | Mortality | No Mortality | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 742 | 22 | 720 | |
| CPB time, min | 137 (120; 163) | 185 (149; 215) | 137 (120; 161) | <0.001 |
| ACC time, min | 69 (61; 85) | 78 (65; 125) | 69 (61; 84) | 0.029 |
| AVR + CABG, % | 13.4 | 22.7 | 13 | 0.440 |
| AVR + MVR, % | 7 | 22.7 | 6.5 | <0.001 |
| AVR + MV plasty,% | 3.2 | 9 | 3 | 0.629 |
| AVR + MV repair (in total),% | 10 | 31.8 | 9.5 | <0.001 |
| AVR + TVR,% | <1 | 0 | <1 | 0.982 |
| AVR + TV plasty,% | 9 | 22.7 | 8.6 | <0.001 |
| AVR + TV repair (in total),% | 9.2 | 22.7 | 8.8 | 0.025 |
| AVR + CryoMaze procedure,% | 2.9 | 9 | 2.8 | 0.614 |
| 3 and more procedures,% | 8.3 | 27.3 | 7.8 | 0.001 |
| ICU time, days | 1 (1; 1) | 6 (2; 12) | 1 (1; 1) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay, days | 7 (6; 9) | 19 (12; 21) | 7 (6; 9) | 0.005 |
| Parameters | Cut-Off Point | AUC (CI) | Se | Sp | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | >62 | 0.594 (0.558–0.630) | 77.3 | 45.6 | 0.594 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | >30 | 0.640 (0.605–0.675) | 72.7 | 56.8 | 0.027 |
| LVESD/BSA, cm/m2 | >1.68 | 0.657(0.617–0.695) | 85.0 | 50.80 | 0.009 |
| LVEDD/BSA, cm/m2 | >2.39 | 0.647 (0.607–0.686) | 952 | 33.2 | 0.014 |
| ACC time, min | >93 | 0.676 (0.640–0.710) | 50.0 | 82.7 | 0.010 |
| CPB time, min | >144 | 0.809 (0.778–0.837) | 95.5 | 58.2 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin level, g/L | ≤120 | 0.762 (0.728–0.793) | 59.1 | 85.7 | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit, % | ≤39 | 0.755 (0.721–0.786) | 77.3 | 62.5 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils, % | >68 | 0.657 (0.615–0.697) | 50.0 | 87.3 | 0.067 |
| Preop creatinine level, mkmoL/L | >98 | 0.544(0.506–0.582) | 36.4 | 77.7 | 0.536 |
| eGFR, mL/min | ≤64 | 0.595(0.557–0.632) | 40.9 | 83.9 | 0.163 |
| eGFR, mL/min per 1,73 m2 (MDRD) | ≤67 | 0.584(0.551–0.626) | 50 | 73.5 | 0.212 |
| Risk of in-hospital death, (%) | >1.4 | 0.722(0.687–0.754) | 76.2 | 57.8 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Univariate Logistic Regression Analysis OR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 2.84 (1.15–7.01) | 0.019 |
| LVESD/BSA cm/m2 > 1.68 | 4.81 (1.03–22.5) | 0.023 |
| LVEDD/BSA cm/m2 > 2.39 | 5.01 (1.07–23.4) | 0.003 |
| IHD | 3.65 (1.01–13.2) | 0.029 |
| Prior AMI | 4.16 (1.11–15.7) | 0.064 |
| Diabetes | 3.88 (1.38–10.9) | 0.018 |
| Arrhythmia | 2.33 (0.98–5.57) | 0.063 |
| FVE | 9.78 (1.91–50.2) | 0.026 |
| AV block | 5.83 (1.19–28.2) | 0.067 |
| MV repair | 4.47 (1.76–11.3) | 0.004 |
| TV repair | 3.06 (1.09–8.58) | 0.053 |
| 3 and more procedures | 4.44 (1.67–11.8) | 0.007 |
| ACC time, min > 93 | 4.28 (1.7–10.77) | 0.003 |
| CPB time, min > 144 | 25.1 (3.3–189.1) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin level ≤ 120 g/L | 8.67 (3.6–20.83) | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit ≤ 39% | 5.64 (2.1–15.49) | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Coefficient | Standard Error | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| FVE | 2.358 | 0.953 | 0.013 |
| CPB time, min > 144 | 2.417 | 1.102 | 0.028 |
| BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 1.335 | 0.720 | 0.063 |
| IHD | 1.181 | 0.813 | 0.146 |
| Hemoglobin level ≤ 120 g/L | 1.107 | 0.811 | 0.172 |
| Hematocrit ≤ 39% | 0.765 | 0.820 | 0.351 |
| TV repair | 0.703 | 0.806 | 0.383 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shvartz, V.; Sokolskaya, M.; Petrosyan, A.; Ispiryan, A.; Donakanyan, S.; Bockeria, L.; Bockeria, O. Predictors of Mortality Following Aortic Valve Replacement in Aortic Stenosis Patients. Pathophysiology 2022, 29, 106-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010010
Shvartz V, Sokolskaya M, Petrosyan A, Ispiryan A, Donakanyan S, Bockeria L, Bockeria O. Predictors of Mortality Following Aortic Valve Replacement in Aortic Stenosis Patients. Pathophysiology. 2022; 29(1):106-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleShvartz, Vladimir, Maria Sokolskaya, Andrey Petrosyan, Artak Ispiryan, Sergey Donakanyan, Leo Bockeria, and Olga Bockeria. 2022. "Predictors of Mortality Following Aortic Valve Replacement in Aortic Stenosis Patients" Pathophysiology 29, no. 1: 106-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010010
APA StyleShvartz, V., Sokolskaya, M., Petrosyan, A., Ispiryan, A., Donakanyan, S., Bockeria, L., & Bockeria, O. (2022). Predictors of Mortality Following Aortic Valve Replacement in Aortic Stenosis Patients. Pathophysiology, 29(1), 106-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology29010010