Implication of RAS in Postnatal Cardiac Remodeling, Fibrosis and Dysfunction Induced by Fetal Undernutrition
Abstract
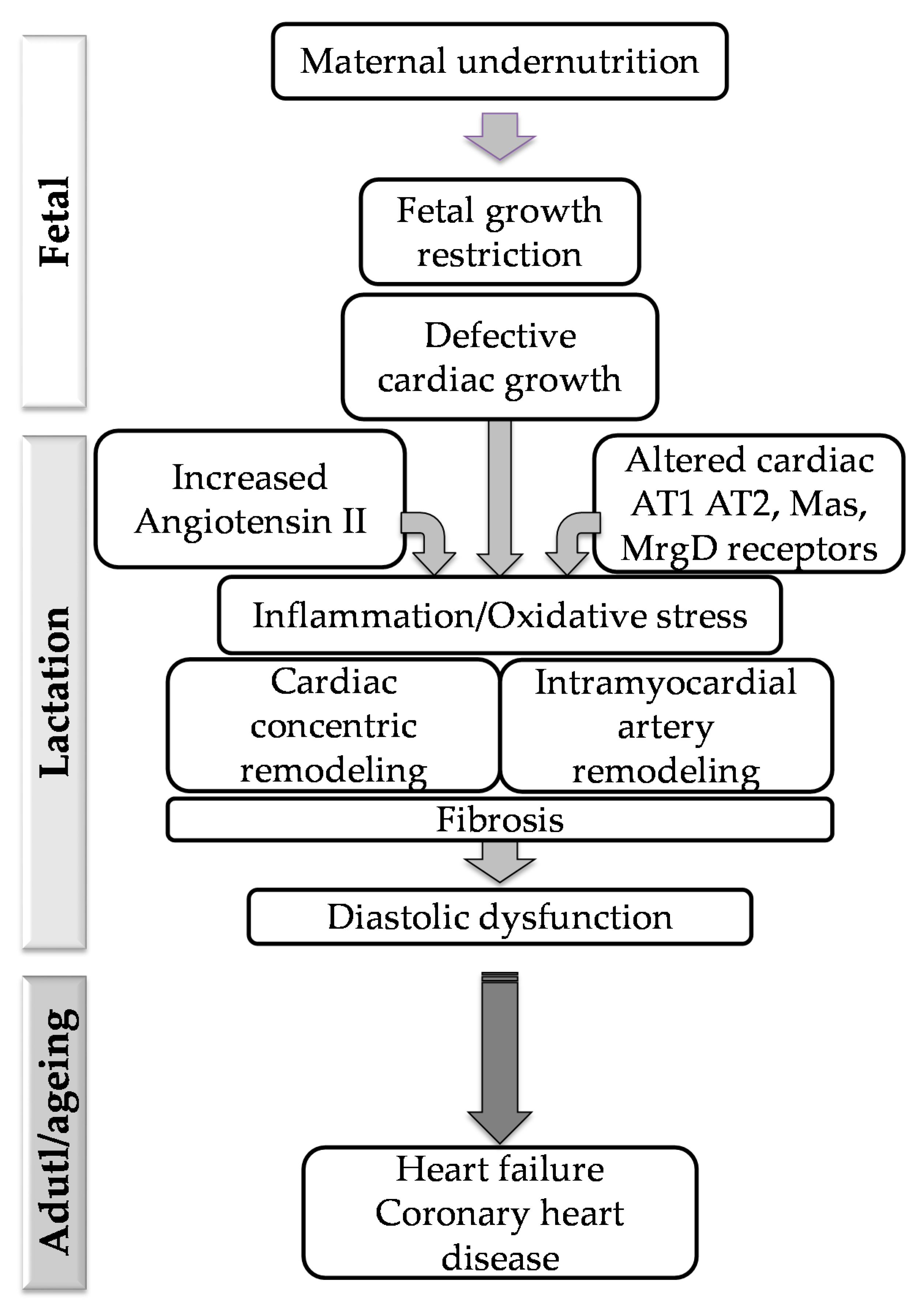
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maternal Undernutrition (MUN) Model
2.2. Experimental Protocols
2.3. Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
2.4. Hemodynamic Parameters
2.5. Histology
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Quantification of Plasma Ang II Levels
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Variables
3.2. Hemodynamic Parameters
3.3. Transthoracic Echocardiography
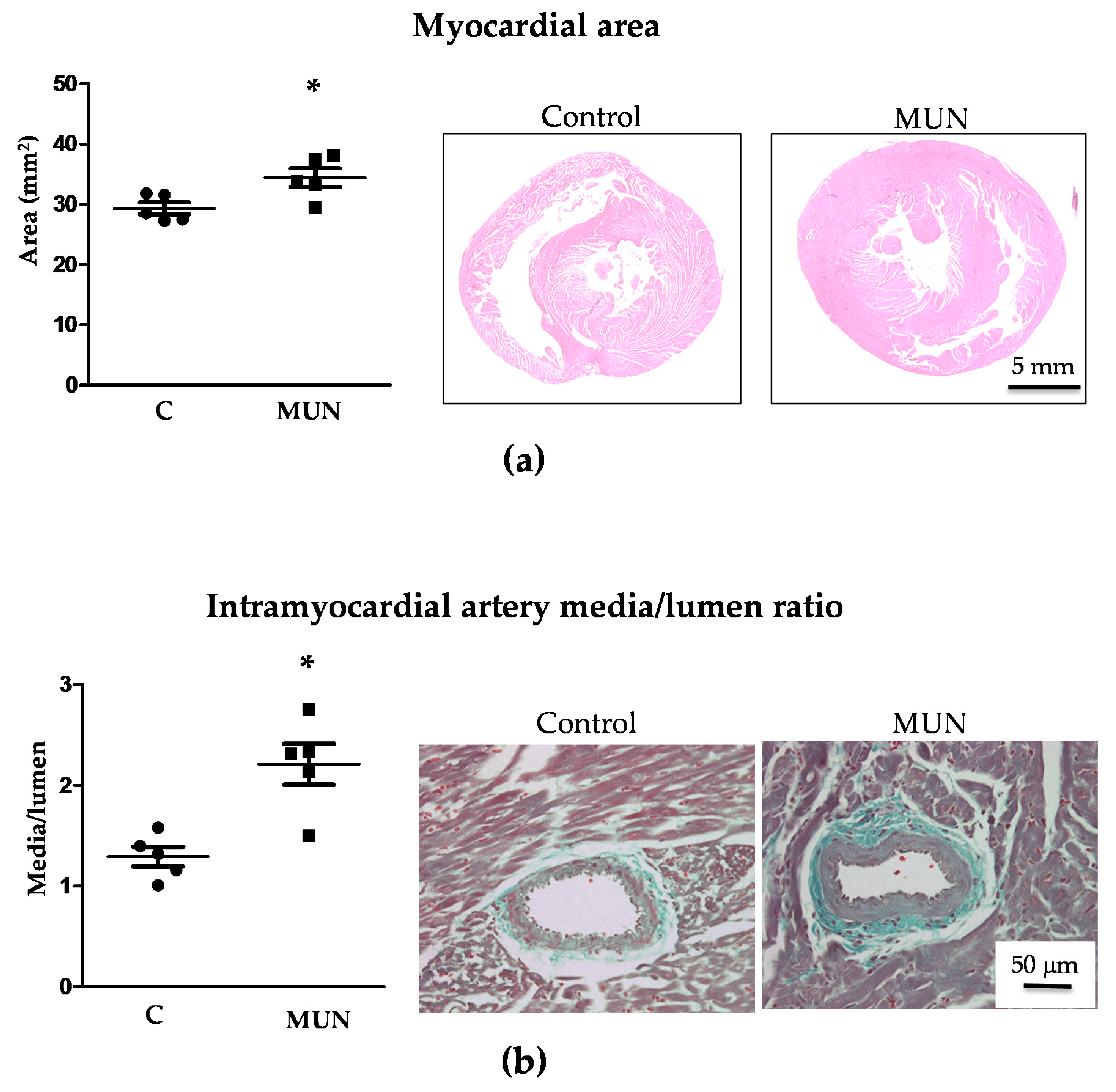
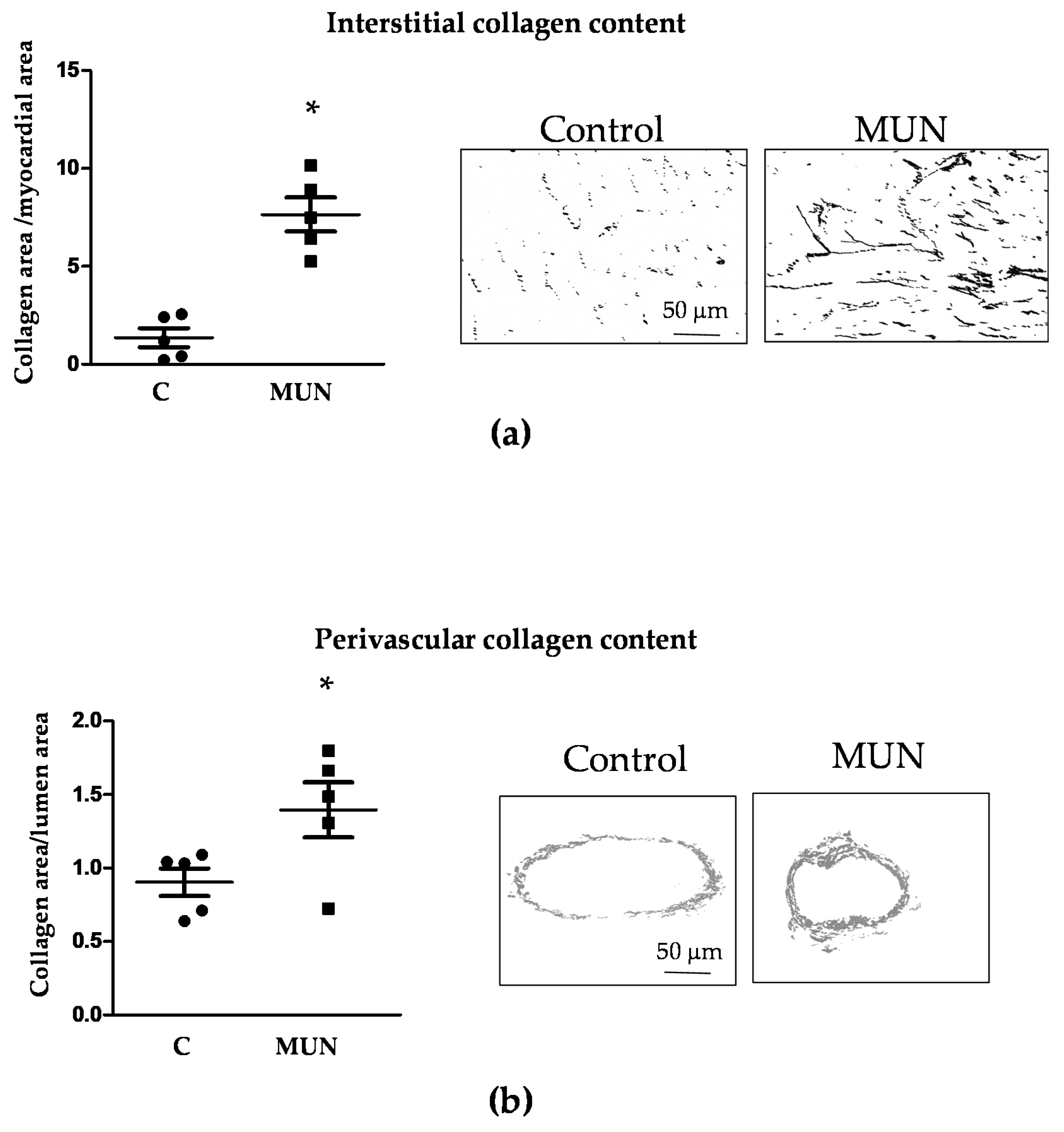
3.4. Heart and Intramyocardial Artery Morphology
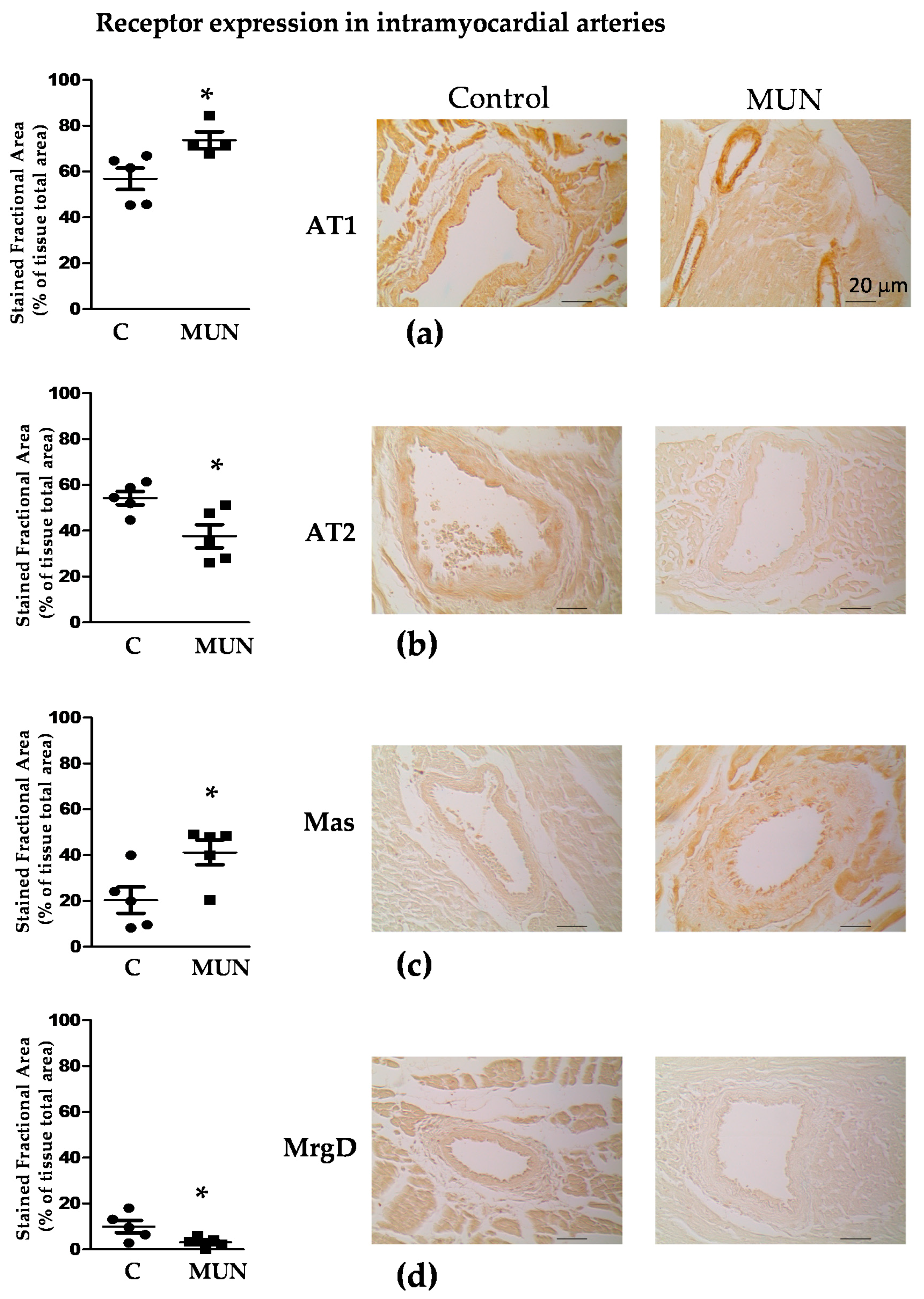
3.5. Expression Of RAS Receptors in Myocardium and Intramyocardial Arteries
3.6. Plasma Ang II Levels
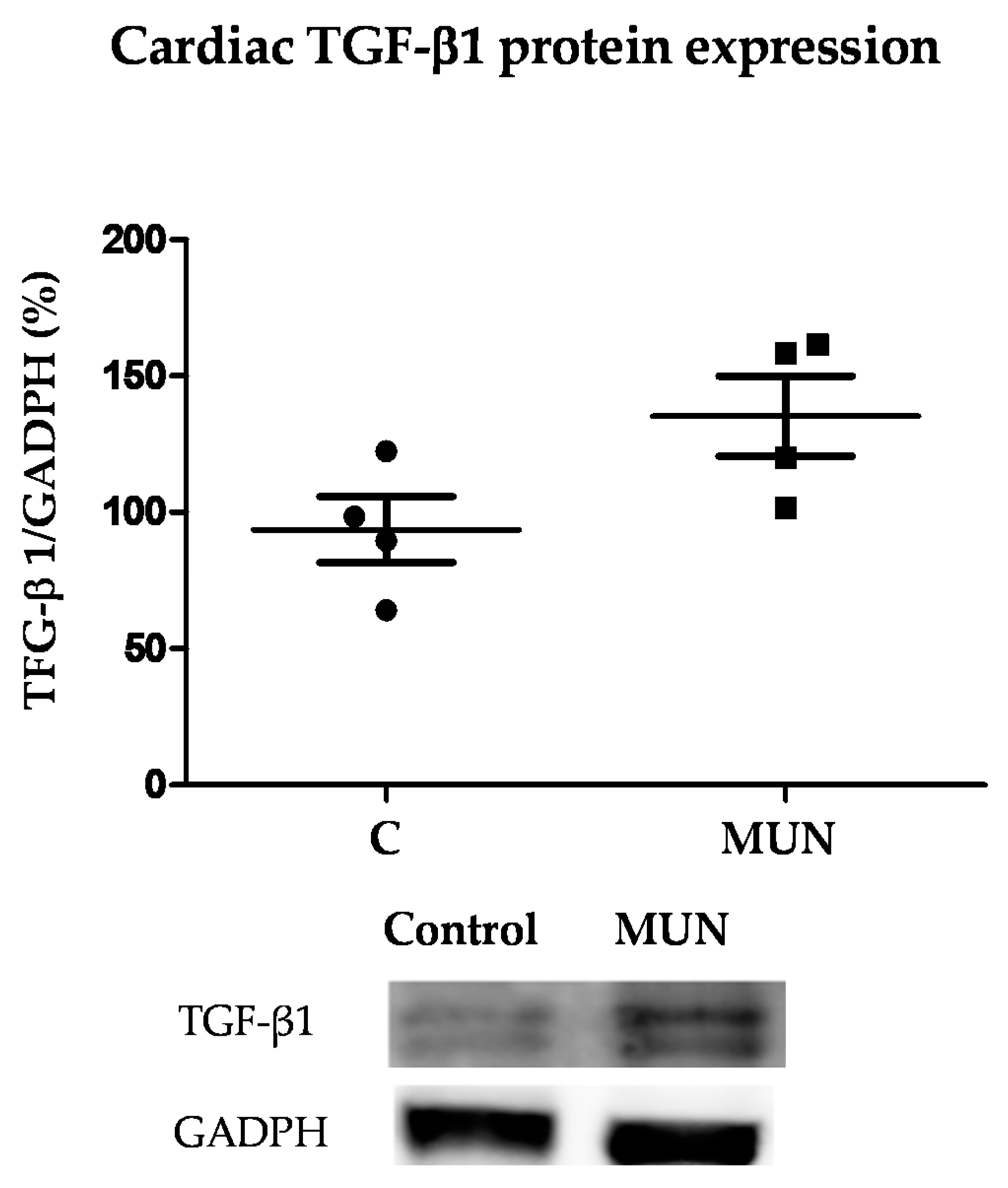
3.7. TGF-β1 Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roseboom, T.J.; Van Der Meulen, J.H.P.; Osmond, C.; Barker, D.J.P.; Ravelli, A.C.; Schroeder-Tanka, J.M.; Van Montfrans, G.A.; Michels, R.P.J.; Bleker, O.P. Coronary heart disease after prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine, 1944–45. Heart 2000, 84, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezmish, O.; Tare, M.; Parkington, H.C.; Morley, R.; Porrello, E.R.; Bubb, K.J.; Black, M.J. Maternal Vitamin D Deficiency Leads to Cardiac Hypertrophy in Rat Offspring. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 17, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.; Li, M.; Patel, R.; Reynolds, C.; Vickers, M. Let-7 miRNA Profiles Are Associated With the Reversal of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Hypertension in Adult Male Offspring From Mothers Undernourished During Pregnancy After Preweaning Growth Hormone Treatment. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Williams, S.J.; O’Brien, D.; Davidge, S.T. Hypoxia or nutrient restriction during pregnancy in rats leads to progressive cardiac remodeling and impairs postischemic recovery in adult male offspring. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embleton, N.D.; Korada, M.; Wood, C.L.; Pearce, M.S.; Swamy, R.; Cheetham, T.D. Catch-up growth and metabolic outcomes in adolescents born preterm. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.; Slopen, N.; Nelson, C.A.; Zeanah, C.H.; Georgieff, M.K.; Fox, N.A. Catch-up growth, metabolic, and cardiovascular risk in post-institutionalized Romanian adolescents. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.K. Catch-up growth in small for gestational age babies: Good or bad? Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2007, 14, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Valverde, D.; Rodríguez, P.R.; Gutierrez-Arzapalo, P.Y.; De Pablo, A.L.L.; González, M.C.; López-Giménez, R.; Somoza, B.; Arribas, S.M. Effect of Fetal Undernutrition and Postnatal Overfeeding on Rat Adipose Tissue and Organ Growth at Early Stages of Postnatal Development. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizarraga-Mollinedo, E.; Carreras-Badosa, G.; Xargay-Torrent, S.; Remesar, X.; Mas-Pares, B.; Prats-Puig, A.; de Zegher, F.; Ibáñez, L.; López-Bermejo, A.; Bassols, J. Catch-up growth in juvenile rats, fat expansion, and dysregulation of visceral adipose tissue. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Arzapalo, P.Y.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; López De Pablo, Á.L.; López-Giménez, M.R.; Condezo-Hoyos, L.; Greenwald, S.E.; González, M.D.C.; Arribas, S.M. Role of fetal nutrient restriction and postnatal catch-up growth on structural and mechanical alterations of rat aorta. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 5791–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.R.; de Pablo, A.L.L.; Condezo-Hoyos, L.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Aguilera, Y.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Gutierrez-Arzapalo, P.Y.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; Fernandez-Alfonso, M.S.; González, M.D.C.; et al. Fetal undernutrition is associated with perinatal sex-dependent alterations in oxidative status. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; López De Pablo, Á.L.; García-Prieto, C.F.; Somoza, B.; Quintana-Villamandos, B.; De Diego, J.J.G.; Gutierrez-Arzapalo, P.Y.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Arribas, S.M. Long term effects of fetal undernutrition on rat heart. Role of hypertension and oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povlsen, A.L.; Grimm, D.; Wehland, M.; Infanger, M.; Krüger, M. The Vasoactive Mas Receptor in Essential Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Torres, E.; Oyarzun, A.P.; Mondaca-Ruff, D.; Azocar, A.; Castro, P.F.; Jalil, J.E.; Chiong, M.; Lavandero, S.; Ocaranza, M.P. ACE2 and vasoactive peptides: Novel players in cardiovascular/renal remodeling and hypertension. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 9, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizada, M.K.; Ferreira, A.J. ACE2: A New Target for Cardiovascular Disease Therapeutics. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 50, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittana, N. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-Angiotensin 1-7/1-9 system: Novel promising targets for heart failure treatment. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, B.T.; Dasinger, J.H.; Intapad, S. Fetal Programming and Cardiovascular Pathology. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 997–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.S.; Cooke, C.-L.; Davidge, S.T. In Utero Origins of Hypertension: Mechanisms and Targets for Therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 549–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A.M.; Shaltout, H.A.; Washburn, L.K.; Hendricks, A.S.; Diz, D.I.; Chappell, M.C. Fetal programming and the angiotensin-(1-7) axis: A review of the experimental and clinical data. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, H.; Moss, T.J.; Gatford, K.L.; Moritz, K.M.; Akison, L.; Fullston, T.; Hryciw, D.H.; Maloney, C.; Morris, M.; Wooldridge, A.L.; et al. A review of fundamental principles for animal models of DOHaD research: An Australian perspective. J. Dev. Orig. Heal. Dis. 2016, 7, 449–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, R.G.W. Recovering The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique. Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 2018, 43, 622–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Villamandos, B.; De Diego, J.J.G.; Delgado-Martos, M.J.; Muñoz-Valverde, D.; Soto-Montenegro, M.L.; Desco, M.; Delgado-Baeza, E. Dronedarone produces early regression of myocardial remodelling in structural heart disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahn, D.J.; DeMaria, A.; Kisslo, J.; Weyman, A. Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: Results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation 1978, 58, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devereux, R.B. Detection of left ventricular hypertrophy by M-mode echocardiography. Anatomic validation, standardization, and comparison to other methods. Hypertension 1987, 9, II19–II26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, L.C.U.; Bignolas, G.; Brentani, R.R. Picrosirius staining plus polarization microscopy, a specific method for collagen detection in tissue sections. J. Mol. Histol. 1979, 11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, C.; Leal, S.; Logan, K.; Rocha-Pereira, C.; Soares, A.S.; Rocha, E.; Goncalves, J.; Fresco, P. Immunohistochemical localization of angiotensin II receptor types 1 and 2 in the mesenteric artery from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2007, 70, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, M.E.; Fernley, R.T.; Nakamura, Y.; Moeller, I.; Aldred, G.P.; Ferraro, T.; Penschow, J.D.; McKinley, M.J.; Oldfield, B.J. Characterization of a specific antibody to the rat angiotensin II AT1 receptor. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1999, 47, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Cheda, B.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Valenzuela, R.; Perez-Costas, E.; Melendez-Ferro, M.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. The intracellular angiotensin system buffers deleterious effects of the extracellular paracrine system. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Muralidharan, A.; Smith, M.T. Attenuation of the Infiltration of Angiotensin II Expressing CD3+ T-Cells and the Modulation of Nerve Growth Factor in Lumbar Dorsal Root Ganglia—A Possible Mechanism Underpinning Analgesia Produced by EMA300, An Angiotensin II Type 2 (AT2) Receptor Antagonist. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.T.; Wyse, B.D.; Edwards, S.R. Small Molecule Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor (AT2R) Antagonists as Novel Analgesics for Neuropathic Pain: Comparative Pharmacokinetics, Radioligand Binding, and Efficacy in Rats. Pain Med. 2013, 14, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Suxiao Jiuxin Pill protects cardiomyocytes against mitochondrial injury and alters gene expression during ischemic injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 3523–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, M.R.; Cornel, L.M. Multiple complex somatosensory systems in mature rat molars defined by immunohistochemistry. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 85, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirado, R.; Carceller, H.; Castillo-Gómez, E.; Castrén, E.; Nacher, J. Automated analysis of images for molecular quantification in immunohistochemistry. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforest, S.; Pelletier, M.; Michaud, A.; Daris, M.; Descamps, J.; Soulet, D.; Jensen, M.D.; Tchernof, A. Histomorphometric analyses of human adipose tissues using intact, flash-frozen samples. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yin, H.; Yuan, H.; Gu, J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Shi, L.; Chen, D.; Xie, B. Immunohistochemical quantification of expression of a tight junction protein, claudin-7, in human lung cancer samples using digital image analysis method. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 155, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.; Diniz, C.; Sá, C.; Goncalves, J.; Soares, A.S.; Rocha-Pereira, C.; Fresco, P. Semiautomated computer-assisted image analysis to quantify 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride-immunostained small tissues. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 357, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarry-Adkins, J.L.; Martin-Gronert, M.S.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.S.; Hargreaves, I.; Alfaradhi, M.Z.; Land, J.M.; Aiken, C.E.; Ozanne, S. Poor maternal nutrition followed by accelerated postnatal growth leads to alterations in DNA damage and repair, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and oxidative defense capacity in rat heart. FASEB J. 2012, 27, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomat, A.L.; Juriol, L.V.; Gobetto, M.N.; Veiras, L.C.; Abregú, F.M.G.; Zilberman, J.; Fasoli, H.; Elesgaray, R.; Costa, M. Ángeles; Arranz, C.T. Morphological and functional effects on cardiac tissue induced by moderate zinc deficiency during prenatal and postnatal life in male and female rats. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H1574–H1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, A.D.S.; Mandarim-De-Lacerda, C.A. Effects of ACE inhibition during fetal development on cardiac microvasculature in adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 101, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berecek, K.H.; Reaves, P.; Raizada, M. Effects of early perturbation of the renin–angiotensin system on cardiovascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 42, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, M.; Itoh, H.; Yura, S.; Mogami, H.; Suga, S.-I.; Makino, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Sagawa, N.; Fujii, S. Undernutrition in Utero Augments Systolic Blood Pressure and Cardiac Remodeling in Adult Mouse Offspring: Possible Involvement of Local Cardiac Angiotensin System in Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular Disease. Endocrinol. 2007, 148, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Sadoshima, J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Tang, Q.; Luo, B.; Zhang, L.; Lin, L.; Han, L.; Hao, M.; Li, M.; Yu, L.; Li, M. Klotho inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and dysfunction in mice through suppression of transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 859, 172549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C. A Novel Paradigm for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuiessa, S.A.; Wedn, A.M.; El-Gowilly, S.M.; Helmy, M.M.; El-Mas, M.M. Pre-eclamptic Fetal Programming Alters Neuroinflammatory and Cardiovascular Consequences of Endotoxemia in Sex-Specific Manners. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 373, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Tabet, F.; Schiffrin, E.L. Redox-dependent signalling by angiotensin II and vascular remodelling in hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2003, 30, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, W.C. Local Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Systems and Cardiovascular Diseases. Med Clin. N. Am. 2017, 101, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, P.; Jagadeesh, G. A century old renin–angiotensin system still grows with endless possibilities: AT1 receptor signaling cascades in cardiovascular physiopathology. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, A.A.; Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V.; Ventura, H.O.; Gilliland, Y.E.; Shah, S.; Cash, M.E. Current Perspectives on Left Ventricular Geometry in Systemic Hypertension. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 59, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, A.H.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Huber, H.F.; Nathanielsz, P.; Clarke, G.D. Cardiac remodelling in a baboon model of intrauterine growth restriction mimics accelerated ageing. J. Physiol. 2016, 595, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Vieira-Rocha, M.S.; Quintana-Villamandos, B.; Monedero-Cobeta, I.; Prachaney, P.; López de Pablo, A.L.; González, M.d.C.; Morato, M.; Diniz, C.; Arribas, S.M. Implication of RAS in Postnatal Cardiac Remodeling, Fibrosis and Dysfunction Induced by Fetal Undernutrition. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 273-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28020018
Rodríguez-Rodríguez P, Vieira-Rocha MS, Quintana-Villamandos B, Monedero-Cobeta I, Prachaney P, López de Pablo AL, González MdC, Morato M, Diniz C, Arribas SM. Implication of RAS in Postnatal Cardiac Remodeling, Fibrosis and Dysfunction Induced by Fetal Undernutrition. Pathophysiology. 2021; 28(2):273-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Rodríguez, Pilar, Maria Sofía Vieira-Rocha, Begoña Quintana-Villamandos, Ignacio Monedero-Cobeta, Parichat Prachaney, Angel Luis López de Pablo, Maria del Carmen González, Manuela Morato, Carmen Diniz, and Silvia M. Arribas. 2021. "Implication of RAS in Postnatal Cardiac Remodeling, Fibrosis and Dysfunction Induced by Fetal Undernutrition" Pathophysiology 28, no. 2: 273-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28020018
APA StyleRodríguez-Rodríguez, P., Vieira-Rocha, M. S., Quintana-Villamandos, B., Monedero-Cobeta, I., Prachaney, P., López de Pablo, A. L., González, M. d. C., Morato, M., Diniz, C., & Arribas, S. M. (2021). Implication of RAS in Postnatal Cardiac Remodeling, Fibrosis and Dysfunction Induced by Fetal Undernutrition. Pathophysiology, 28(2), 273-290. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28020018






