Abstract
Saponins are steroidal or triterpenoid glycoside that is distinguished by the soap-forming nature. Different saponins have been characterized and purified and are gaining attention in cancer chemotherapy. Saponins possess high structural diversity, which is linked to the anticancer activities. Several studies have reported the role of saponins in cancer and the mechanism of actions, including cell-cycle arrest, antioxidant activity, cellular invasion inhibition, induction of apoptosis and autophagy. Despite the extensive research and significant anticancer effects of saponins, there are currently no known FDA-approved saponin-based anticancer drugs. This can be attributed to a number of limitations, including toxicities and drug-likeness properties. Recent studies have explored options such as combination therapy and drug delivery systems to ensure increased efficacy and decreased toxicity in saponin. This review discusses the current knowledge on different saponins, their anticancer activity and mechanisms of action, as well as promising research within the last two decades and recommendations for future studies.
1. Introduction
Cancer is a group of diseases that is characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation. This unconstrained cell growth has the potential to invade nearby and distant tissues causing life-threatening complications []. Cancer is a global health challenge and is one of the leading causes of death in both developing and developed countries []. An epidemiological study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) noted that cancer accounted for the deaths of 7.6 million individuals in 2018, and this figure was expected to double by 2030 []. Several treatment options have been sought to treat cancer, the most common of which is chemotherapy. This treatment involves using drugs/chemical agents to destroy rapidly dividing cells and ultimately prevent the spread to other normal cells in the body. Despite the success rate of chemotherapy, patients continue to suffer from several side effects, such as general weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite and infections. In addition, the lack of selectivity and toxicity of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved anticancer drugs has resulted in a significant drawback in the treatment of cancer []. Therefore, the search for alternative therapeutic agents in the treatment of cancer is imperative.
Traditional plants contain phytochemical compounds, which are mainly secondary metabolites used by plants to ensure survival and fecundity. Phytochemical compounds of medicinal importance include glucosinolates, alkaloids, triterpenoid, flavonoids, saponins, pigments and tannins. Various studies investigated the use of secondary plant metabolites in traditional medicine. These secondary metabolites displayed different biological activities, such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, antiviral and anticancer properties. Approximately 60% of anticancer drugs in clinical use and preclinical trials (vinca alkaloids (vinblastine and vincristine), etoposide, paclitaxel, camptothecin, topotecan, irinotecan, curcumin, resveratrol, genistein, allicin, lycopene, diosgenin, beta-carotene, dactinomycin, bleomycin and doxorubicin, paclitaxel and camptothecin) are derived from plants [,,]. These plant-derived anticancer drugs are widely accepted and generally perceived as relatively safe in terms of toxicity. The significant success achieved so far in using natural compounds as chemotherapeutic alternatives has spurred research interest in other secondary metabolites, such as saponins.
Saponins are a class of structurally diverse phytochemicals that are naturally found in higher plants, marine organisms and microorganisms. This group has displayed various pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antiviral, cardioprotective, immunoregulatory effects and anticancer activity [,]. The profound impact of saponins on cancer cells has gained significant research interest in the pharmaceutical sector. These compounds have demonstrated outstanding potential in inhibiting different cancer cells under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Despite the substantial progress made in recent years, the use of saponins as an anticancer agent has faced certain drawbacks, mainly due to their toxicity and poor pharmacokinetic properties. Therefore, this review comprehensively explores the potential of saponins as an anticancer agent by using various mechanisms; this includes the poorly studied pathways, such as those involved in ferroptosis and necroptosis. Furthermore, the current knowledge on the use of saponins as a chemotherapeutic agent and the window of opportunities it presents for future research were also explored.
2. Classification of Saponins
2.1. Sources of Saponins
Saponins can be obtained from two primary sources, namely natural and synthetic. Saponins acquired from natural organisms are termed “natural”, while those derived from the artificial route via laboratory synthesis are known as “synthetic”.
2.1.1. Synthetic Saponins
Saponins are synthesized artificially by derivatization of saponins obtained from natural sources or via de novo synthesis. Various natural saponins, such as oleanane, ursane, lupane, dammarane, cholestane, spirostane, furostane and cardenolide can be synthesized chemically, using numerous techniques []. However, there are some drawbacks to these methods, such as low yield, toxicity and stringent reaction conditions. In recent years, the use of Schmidt trichloroacetimidate in activating sugars has shown great potential []. Although the mechanisms involving the chemical synthesis of saponins are beyond the scope of this review, it should be noted that the synthetic approach associated with saponin purification from a natural source forestalls the challenge of low yield and purity []. Additionally, this methodology allows for a structure-based optimization that will enable the design of saponins equipped with desirable structural features.
2.1.2. Natural Sources of Saponins
Historically, saponins were primarily derived from vegetables and herbs. Saponins from herbs include soapwort, ginseng, ginsenosides, gypenosides, soapberry rhizomes from the Liliaceae, Dioscoreaceae, Agavaceae, Primulaceae, Sapotaceae and Caryophyllaceae families [,]. Furthermore, different types of saponins can be isolated within the same plant species. Saponins were initially thought to be endemic to plants but were later discovered in non-plant sources. In the last three decades, marine organisms have been identified as significant sources of saponins. More specifically, organisms belonging to the phylum Echinodermata are rich sources of saponins. Tian et al. identified three groups of saponins (asterosaponins, cyclic glycosides and polyhydroxysteroidal glycosides) in starfish and sea cucumbers [].
2.2. Classification Based on the Structure
A typical saponin molecule is made up of distinct structural components consisting of an isoprenoid unit and a sugar residue. The former is referred to as the aglycone component, while the latter is called glycone. Acid hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond between glycone and aglycone of saponins can be used to separate these structural units. The biological activities of saponins are due to their unique structure and amphiphilic nature. It consists of a hydrophilic sugar moiety and a hydrophobic genin (called sapogenin). Additionally, aglycones may possess steroids or triterpenes structure, which is used to classify saponins.
Triterpenoid saponins (basic) consist of four or five rings, with a 30-carbon backbone structure derived from 2,3-oxidosqualene []. The pentacyclic triterpenoids are the most abundant in plants, and they include oleananes, lupanes, ursanes and derivatives (such as saikosaponins) (Figure 1).
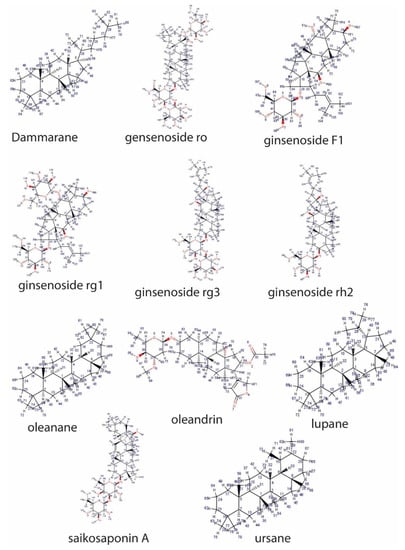
Figure 1.
Representative sapogenin structure of triterpenoid saponins.
The less common tetracyclic triterpenoid saponins are dammaranes and their derivatives (including ginsenosides), while the steroidal sapogenins are 27-carbon sugar conjugates of steroids consisting of a five- or six-ring skeleton known as spirostane and furostane, respectively. These include dioscin, diosgenin, polyphyllin D, timosaponin AII, cardenolide and cholestane (Figure 2).
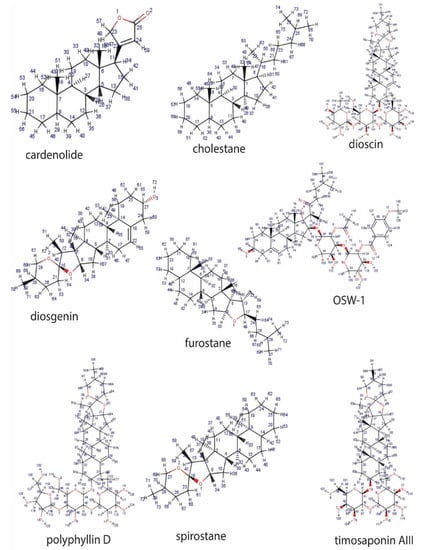
Figure 2.
Representative sapogenin structure of steroid saponins.
Saponins also differ in structural composition, linkage and the number of sugar chains. Usually, the sugar chain may consist of one or more monosaccharide residues attached at C-3 []. Based on the number of sugar residues, saponins are classified as monodesmodic, bidesmodic and polydesmodic, if they contain one, two and more than two sugar residues, respectively. Saponins are also named based on the nature of the sugar residue present on their chain. Glucose containing saponins are regarded as glucosides, while galactose containing saponins are galactosides.
3. Anticancer Mechanisms of Saponin
The anticancer activities of saponins include anti-proliferation, anti-metastasis, anti-angiogenesis and reversal of multidrug resistance (MDR). These effects are brought about by induction of apoptosis, promotion of cell differentiation, immune-modulatory effects, bile acid–binding and amelioration of carcinogen-induced cell proliferation []. Different molecular mechanisms are involved in the anticancer activity of saponins (Table 1). It should be noted that the mechanism of anticancer action of saponins is strongly related to the nature of the structural moieties, including the aglycone moiety, the length and linkage of the glycosidic chain, the presence of a functional carboxylic group on the aglycone chain, the number of sugar molecules and hydroxyl group, position of the hydroxyl group, stereo-selectivity and the type of sugar molecule on the glycine chain [,,]. This section considers the critical processes in cancer-cell development and how different saponins help to inhibit cancer at various stages.

Table 1.
Anticancer activities of saponins and sapogenins.
3.1. Chemoprevention and Saponin
Chemoprevention is the use of a chemotherapeutic agent to halt or restrict tumor development before the onset of cellular invasion. The chemopreventive action of saponins involves anti-inflammation, redox potential modulation and cell proliferation inhibition through different pathways (Figure 3).
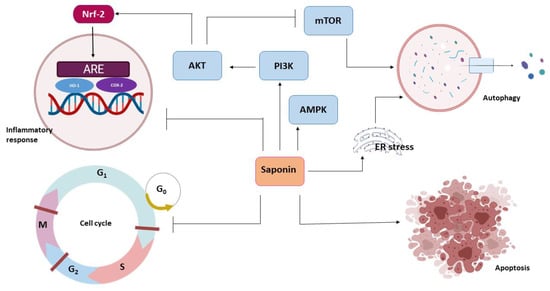
Figure 3.
Anticancer effects of saponins.
3.1.1. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
The immune system triggers an inflammatory response to foreign invaders as part of the body’s defense mechanism. Nonetheless, excessive or chronic inflammation is associated with different pathological conditions, one of which is cancer []. Due to the link between cancer and inflammation, several anti-inflammatory drugs help to decrease the incidence of cancer. Most inflammatory drugs have been designed to selectively target proteins, such as nuclear factor Kappa B (NF-κB), IL-6/STAT3, IL-23/Th-17 and cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2), which are responsible for inflammatory response. Similar to other anti-inflammatory drugs, some saponins can regulate the expression of a number of these proteins.
The inducible transcription factor, NF-κB, stimulates the expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-survival genes. These can be activated via a canonical pathway involving TNF-α, T-cell and B-cell receptors. Triggering this protein in cancer cells leads to activation of cell-cycle proteins, metalloproteinase and apoptotic proteins. Reports have identified saponins that inhibit NF-κB and inhibitory kappa B kinase (IKK). For instance, Paris saponin II, a steroidal saponin, inhibits IKK-b, a protein involved in the canonical pathway of NF-κB activation, leading to cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis activation []. Moreover, Raddeanin A, a triterpenoid, inactivates NF-κB by preventing the phosphorylation of Ikkb-α. A study by Xia et al. likewise reported the downregulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway by saponins of Patrinia villosa, which led to a significant inhibition in colorectal cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis [].
In addition, saponin fractions from marine spiny brittle starfish extract were found to inhibit TNF-α and Cox-2 []. Triterpenoid saponin from Conyza blinii showed heightened anticancer activity via p65-dependent NF-κB inhibition []. Dammarane triterpenoid isolated from Cyclocarya paliurus mediates anti-inflammatory activity by lowering TNF-α, PGE2 and IL-6 expression []. Structure-dependent activity studies of different triterpenoid isoforms revealed cyclocarioside X as a potent chemopreventive agent, which shows significant inhibition of COX-2, iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) and NF-κB/p65 in raw 264.7 cells. The role of saponins in regulating proteins involved in inflammatory pathways undermines its critical chemopreventive potentials.
3.1.2. Modulation of Redox Potential
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) encompass free radical oxygen intermediates involved in tumor cell proliferation, genomic instability, resistance to apoptosis and tumor invasion []. An imbalance between free-radical production and the antioxidant defense system leads to oxidative stress implicated in cancer initiation. By acting as free radical scavengers, modulating the redox signaling pathway and increasing the expression of antioxidant enzymes, saponins can help to correct the redox imbalance []. Purified bacosides, a triterpenoid saponin from Bacopa monnieri, has shown significant 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity. Moreover, Choudhry et al. reported that saponin based nano-emulsification improves the antioxidant properties of Vitamins A and E in AML-12 cells []. Furthermore, saponins derived from Panax notoginseng increase the expression of the antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase-1 by increasing the phosphorylation of AKT protein and the activity of Nrf2 [].
Saponins have also shown pro-oxidant activity in cancer cells in addition to their antioxidative activity. Dysregulation of redox signaling is a feature in most cancer cells. Cancer cells survive oxidative burst by upregulating the antioxidant defense system via antioxidant response element (ARE). Blocking cancer-cell antioxidant defense systems would increase ROS-induced oxidative damage, resulting in cancer-cell death []. Triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia gigantifolia cause cell death in triple-negative breast cancer cells by increasing the generation of reactive oxygen species, activating ERK and AKT and inducing apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway []. Kim et al. also observed that hederagenin obtained from Hedera helix mediates cell damage in head and neck cancer cells by reducing glutathione reductase activity, increasing ROS and inhibiting the Nrf2-ARE pathway [].
3.1.3. Cell-Cycle Arrest
Cell progression through the cell cycle is mediated by crucial proteins such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) and regulated by checkpoint kinases such as Polo-like kinase, aurora kinase and CDK inhibitors []. Cancer cells often show mutations in protein kinases (CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, chk1, Wee1 and PLK1) involved in cell proliferation. Targeting these proteins have become an attractive chemopreventive strategy to mitigate abnormal cell proliferation in cancer cells []. Recently, saponins have shown attractive anticancer potentials by modulating cell-cycle proteins, including cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and checkpoint proteins, to terminate cancer-cell progression.
Prior to proliferative stimulus, cells in the resting stage (G0) progresses through the G1, S, G2 and M phase of the cell cycle. Different saponins regulate cell progression at each phase of the cell cycle. Furostan-type steroidal genin from edible spears of triguero HT asparagus decreased the expression of cyclin A, D and E by mediating G0/G1 arrest in human colon cancer cells []. A similar cell-cycle suppression at the G0/G1 phase has also been observed in Paris saponin VII treated human leukemia cells (K562/ADR) []. Saponins also decrease cyclin B1/D1 and CDK2/4/6 protein expression. Chikusetsu saponin IV, a methyl ester of a ginsenoside purified from Panacis japonica, has similarly shown the capacity to decrease cell-cycle progression through the S-phase []. Moreover, the compound was shown to inhibit the expression of cyclin D1, CDK2 and CDK6. Yaoming et al. reported cell-cycle arrest in the S-phase by triterpenoid saponin from Camellia sinensis in the human ovarian cancer cell []. The cellular inhibition was achieved by downregulating Cdc25A, Cdk2 and CyclinD1 expression. More so, Paris saponin I have shown G2/M1 arrest in gastric cancer cells by upregulating the activity of p21, a checkpoint protein []. Recently, a steroidal saponin purified from the rhizome of Paris polyphylla var. latifolia was shown to induce the expression of p21 and downregulated the expression of cdc25C, Cyclin B1 and cdc2, thereby inducing G2/M phase arrest in human colorectal cancer [].
In a normal cell, damage to cellular components (such as DNA damage) will prevent the progress of the cell through the cell cycle. However, cancer cells are unresponsive to proteins associated with the regulation of the cell cycle. Targeting checkpoint proteins such as ChK (checkpoint protein), p21 and Wee1 have become an interesting therapeutic target by many anticancer drugs []. Treatment of HepG2 cells with hellebrigenin causes DNA damage activating ATM, Chk1, Chk2 and CDK1/Cyclin B1 kinase resulting in G2/M-phase cell-cycle arrest []. Diosgenin has similarly shown activation of Cdc25C phosphatase, which triggers the Cdc2-cyclin B pathway mediating G2/M cell-cycle arrest in breast cancer [].
3.2. Cytotoxicity Effects of Saponins
In addition to side their chemopreventive actions, saponins show cytotoxic effects in cancer cells. Saponin treatment in cancer cells can stimulate autophagic cell death, decrease nitric oxide production and cause cytoskeleton integrity disassembly. Their cytotoxic effects can be initiated either by apoptosis or non-apoptotic stimulation of cell death. Extensive literature search has revealed the significant ability of saponins to induce cancer-cell death through apoptosis, ferroptosis, oncotic necrosis, necroptosis and autophagy.
3.2.1. Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a programmed form of cell death characterized by cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation and membrane blebbing. It may be initiated either at the plasma membrane (extrinsic pathway) or inside the cell and is critical in regulating tissue development and homeostasis []. Apoptosis is the most studied form of cell death, and unlike other forms of cell death, it is well regulated and not accompanied by an inflammatory response. The induction of apoptosis of tumor cells is an effective way of treating tumours. Compelling evidence has shown that most cytotoxic agents used in cancer therapy can induce apoptosis [].
Saponins can induce apoptosis through a series of reactions involving the activation of a protease family of enzymes known as caspase. Other caspases independent apoptosis pathways have also been described in the mechanism of cell death by saponins. In this section, we consider the cellular mechanism of cell death by saponins and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism of the induction (Figure 4).
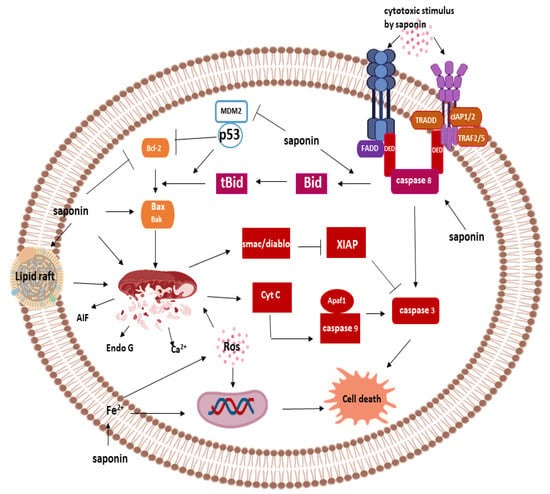
Figure 4.
Cell-death mechanisms of saponins.
Saponins and Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis
Caspases are cysteine dependent aspartate specific proteases that mediate the initiation and execution phase of apoptosis. These enzymes are synthesized in their inactive form known as pro-enzyme or zymogens and can be activated via a receptor-mediated pathway or the mitochondria-dependent pathway. While the former is known as the extrinsic pathway, the latter also called the intrinsic pathway. Saponins can initiate a caspase-dependent pathway of apoptosis via both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathway.
Extrinsic Pathway and Saponins
The extrinsic pathway is initiated by the binding of ligand to members of the TNF superfamily of protein, including Fas receptor, TNF-α and TRAIL. Saponins can activate the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis by activating the Fas receptor leading to the recruitment of adaptor molecule called Fas-associated death domain (FADD) []. The recruitment of FADD triggers the conscription of Pro-caspase 8 in saponin treated cancer cells to form death induced signaling complex (DISC) [,]. Upon recruitment, procaspase-8 is released from DISC as the active caspase-8 via a proximity-induced activation mechanism. Activation of caspase-8 leads to downstream activation of the executioner caspase-3 and cleavage of poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) mediating the proteolysis of cellular components []. Caspase-8 activation is the defining factor in the extrinsic apoptosis pathway, and activation of this protein can be induced by different saponins [].
Cellular activation of caspase-8 by saponins via the intrinsic pathway might not be sufficient to induce apoptosis []; as a result, some saponins rely on cell death machinery via the BCl-2 family of protein (Bid) which mediates crosstalk with the intrinsic apoptosis pathway []. Caspase-8 activates tBid by protein cleavage to form an active Bid, which subsequently activates downstream pro-apoptotic proteins, Bax and Bak, causing mitochondria membrane permeabilization and activation of effector caspases []. Furthermore, since p53 mutation in cancer cells can inhibit apoptosis in the intrinsic pathway, this pathway of cell death offers an alternative route of eliminating cancer in p53 mutant cells [].
Intrinsic Pathway and Saponins
The intrinsic pathway is a mitochondria-dependent pathway of apoptosis, and it is the most reported mechanism of apoptosis induction by chemotherapeutic agents. Saponins can stimulate the release of pro-apoptotic factors, cytochrome C, Ca2+ and Smac/DIABLO, from the mitochondria via cytotoxic action or ROS production [,]. These ROS/cytotoxic stimuli disrupt the mitochondria to initiate the apoptosis process. Pro-apoptotic cytochrome C binds Apaf-1 to form the apoptosome complex required for the activation of pro-caspase-9. Upon activation, caspase-9 cleaves executioner caspase-3, activating the protein and the downstream apoptosis process. Activation of apoptosis by saponins via the intrinsic route involves the inhibition of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and activation of pro-apoptotic proteins caspase-9 and caspase-3 [].
Saponins also mediate the intrinsic pathway via mechanisms involving the activation of p53 proteins []. Activation of p53 can be achieved by the inhibition of MDM2 via direct interaction or by binding to the alternative reading frame (ARF) []. Activation of p53 causes the inhibition of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and activation of pro-apoptotic Bax, Noxa and Bad, leading to depolarization of mitochondria and the release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria []. This protein then mediates executioner caspase -3 and -9 activation []. Furthermore, saponins can stimulate Smac/Diablo to subsequently inhibits the activity of XIAP (inhibitor of executioner caspase-3), thereby stimulating apoptosis [].
Saponin and Caspase Independent Apoptosis
Saponins are capable of inducing cell death via pathways independent of caspases but show morphological features typical of apoptotic cell death. In this form of cell death, caspases are not activated, and their stimulation may not play any active roles in mediating cell death []. Before the permeabilization of the mitochondria, different pro-apoptotic factors are released into the inter-membrane space, some of which are cytochrome C, Ca2+, Smac/DIABLO, HtrA2/Omi, AIF (Apoptosis-inducing factor) and Endonuclease G. While some of the proteins mediate apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway as earlier discussed, AIF, HtrA2/Omi and Endo G translocate into the nucleus where they bind to DNA resulting in chromatin condensation.
Preceding the release of pro-apoptotic proteins (such as AIF) is the permeabilization of the membrane—this process plays a critical role in the overall apoptosis process and is termed as the committed steps. One of the alternative pathways of cell death induction by saponins involve pore formation on the membrane []. Saponins are capable of binding to the cholesterol-rich segment of the membrane or the membrane lipid raft. The cytotoxicity of some saponins can be greatly influenced by the cholesterol content []. The binding of saponins to the lipid raft may be the initial upstream process of mediating cytotoxic activity in multidrug-resistant cancer cells before the release of pro-apoptotic Endo-G and AIF [].
AIF and Endo G have become attractive targets due to their role in caspase-independent apoptosis. Saponins, including dioscin, can induce caspase-independent apoptosis by activating AIF []. Although the activation of AIF by saponins is linked to increased ROS generation, a ROS-independent mechanism activation has also been described [,,,]. Also, saponins can stimulate the release of Endo G, resulting in their migration to the nucleus, where these bind to chromatin and break the phosphodiester linkage in the nucleotide chain to generate nucleosomal fragments [,]. In addition to the pivotal role played by Endo G and AIF, HtrA2/Omi also mediates caspase-independent apoptosis. This pathway of death mechanism may prove an invaluable tool to destroy cancer cells resistant to caspase activation.
3.2.2. Ferroptosis, Oncotic Necrosis and Necroptosis
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent programmed cell death characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides []. Different saponins such as ardisiacrispin B, spirostanol saponin, diosgenin saponin, oleanane triterpenoid saponin derivatives and ruscogenin have demonstrated iron-dependent programmed cell death following treatment on cancer cells [,,]. Cancer cell depends on iron for DNA synthesis—an essential step in the cell cycle. Iron overload, however, can cause oxidative damage in cancer cells via the Fenton reaction []. This mechanism holds great promise to prevent both drug-sensitive and resistant cancer cells from proliferating [].
Furthermore, Gao et al. discovered a novel form of cell death in tumor cells in which exposure to trisaccharide saponin derivatives induced cell swelling followed by cell membrane perturbation and destruction of the cytoskeletal network in the form of cell death known as oncotic necrosis []. Polyphyllin D and progenin III can induce programmed necrosis/necroptosis in cancer cells [,,]. The molecular mechanism by which saponins exert necroptosis is not fully known, but similar to apoptotic cell death, it involves the activation of Caspase 8 as observed in the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis [].
3.2.3. Autophagy and Saponin
Autophagy is a mechanism adopted by cells to remove dysfunctional or redundant cellular components, which are later recycled to meet the metabolic needs of starving cells. It plays a dichotomous role in cancer-cell death and pro-survival mechanisms []. Autophagy can cause apoptotic cell death, but it may also help cancer cells survive oxidative stress and metabolic stress by recycling defective cell components. Despite the significant progress made to understand the mechanism of autophagy, the question of whether to stimulate or inhibit autophagy in cancer therapeutics remains debatable []. Several studies on cancer have shown that autophagy promotes cell survival in cancer cells; however, excessive autophagy exceeding cellular repair capacity stimulates cell death []. While most anticancer agents seem to inhibit autophagy, some have also shown an ability to stimulate autophagy. Purified Pulsatilla saponin D (SB365) from Pulsatilla chinensis showed a dual role by inducing the early event of autophagy (autophagosome formation) and inhibiting the latter stage of autophagy (autophagic flux) []. Zhang et al. noted that SB365 increased microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) and p62 expressions in HeLa cells []. The LC3 protein is involved in the formation of autophagosome, while p62 can degrade LC3 protein to inhibit autophagic flux. The authors, however, concluded that the inhibition of autophagic flux by increasing p62 expression might play a significant role in the anticancer activity of SB365 against HeLa cells.
Different molecular pathways, including mTOR, MAPK, AMPK and JNK, are implicated in the regulation of autophagy []. However, the PI3/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, which mediates crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis, appears to be the most studied [,]. Xie et al. reported the induction of autophagy by Paris saponins from Paris polyphyllae through the downregulation of Akt/mTOR in breast cancer cells []. Triterpenoid glycosides are also reported to induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway []. Promoting autophagy through mTOR inhibition might be an effective way of cancer chemoprevention by preventing the accumulation of metabolic stress [,].
The cytotoxic stress response is another mechanism through which autophagy can be activated. This process involves the P13/AKT pathway and can be stimulated by saponin []. The saponins extracted from Camellia sinensis flowers induced ROS dependent autophagy in ovarian cancer cells, resulting in the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway []. Recent evidence has suggested that a specific protein known as AMPK can act downstream of MAPK to induce autophagy []. The AMPK protein is an energy stress response protein that facilitates metabolic activity in cells to generate more ATP, which in turn causes oxidative stress through the generation of ROS. In NSCLC cells, treatment with Paris saponin VII was shown to increase the expression of AMPK and its downstream effector, ulk1, which are critical in inducing autophagy []. In vitro and in vivo studies have also demonstrated the induction of autophagy by saponins via the JNK pathway [,].
Due to autophagic flux often associated with the growth of tumours, recent studies have primarily focused on identifying autophagy inhibitors [,,]. Moreover, inhibiting autophagy help in preventing tumor immune invasion []. A study by Liu et al. identified triterpenoid saponins from Conyza blini capable of eliciting cytotoxic activity in HeLa cells through the inhibition of autophagy []. Paradoxically, activation of autophagy has been shown to trigger T-cell cytotoxicity reducing cancer-cell growth []. Therefore, further studies are needed to understand how saponins modulate autophagy to prevent cancer progression.
3.3. Metastasis and Saponins
In chronic cases, tumor cells migrate from their primary site through the lymphatic or blood system and subsequently colonize distant tissues and organs []. This process is known as tumor metastasis, and it accounts for 90% of cancer-associated mortality []. Metastatic cancer cells have acquired multiple genetic alterations that enable them to survive at a distant site. The processes involved in metastasis are quite complex because these entail different alterations that result in stimulation of angiogenesis, local invasion attachment, basement membrane disruption, matrix proteolysis and stimulation of growth factors among others [].
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels to deliver nutrients and oxygen to a distant site, and it is critical for the colonisation of secondary tumours. Saponins have been identified with the potential to inhibit the formation of new blood vessels in tumor cells []. For example, ginsenoside-Rb2, a dammarane saponin, slows down tumor metastasis of B16-BL6 by inhibiting tumor-induced angiogenesis []. Chan et al. highlighted that polyphyllin D suppresses the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells in vitro and inhibits intersegmental vessel (ISV) formation in zebrafish []. Similarly, Panax notoginseng has also been shown to restore defective ISV in zebrafish larva [].
Yang et al. also reported that Paris saponin II (PSII) inhibited angiogenesis at low concentration in cancer cells and showed no toxicity to normal endothelial cells []. The anti-angiogenic activity was linked to the potential of PSII to modulate the expression of NF-κB. By downregulating NF-κB expression, PSII reduced the activity of the downstream proteins such as VEGF, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. The VEGF protein has been implicated in angiogenesis and lymphogenesis, and its activity is mediated by binding VEGF receptor (a tyrosine kinase receptor). Raddeanin A (RA) is an active triterpenoid saponin from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Anemone raddeana which inhibits the phosphorylation of VEGFR2 by VEGF []. The authors noted that RA binds to the ATP binding pocket of VEGFR2 and hinders its phosphorylation by VEGF, thereby preventing the activation of downstream effector proteins such as PLCγ1, JAK2, FAK, Src and Akt []. Additionally, sulfated saponin purified from sea cucumber can inhibit the phosphorylated form of VEGFR2 and the consequent downstream signaling pathway required for the mitogenic activity of VEGF in the endothelial cell [].
Another mechanism through which saponin interferes with metastasis is by inhibiting cell adhesion molecules. Attachment of tumor cell to extracellular matrix (EM) and other similar cells is important for metastasis. Different proteins such as integrins, CD44, ICAM and VLA-4 are responsible for the cellular attachment of cancer cells []. Paris polyphylla can decrease the expression of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in cancer cells []. Furthermore, Wang et al. have also reported significant inhibition of inflammation-induced endothelial adhesion molecule by saponin from Panax notogingseng []. Likewise, a saponin monomer from dwarf lilyturf tuber inhibits hypoxia-induced integrin expression in the human breast cancer cell [].
Cancer cells undergoing metastasis show a lack of adhesion by inhibiting molecules such as E-cadherin required for homotypic cell–cell interaction. Reduced expression of the adhesion molecule E-cadherin in cancer cells increases cell mobility, as such molecules that increase E-cadherin expression impede tumor metastasis. The activity of E-cadherin is regulated by protein such as Cdc42 and Rac1 []. These proteins are Rho GTPases, and their expressions are upregulated by saponins. For example, saponin fractions from Asparagus officinalis activate Cdc42 and Rac1 []. Furthermore, Ardipusilloside I also stimulate the activity of Rac1. By stimulating these upstream proteins, saponins can inhibit cell migration [].
Perhaps one of the most studied deregulations in metastasis is tissue remodeling. It involves a family of proteins known as the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP). During metastasis, the tumor cell traverses the extracellular matrix (EM) barrier. This process is critical for cancer-cell invasion, and it includes the proteolytic degradation of the EM by enzymes such as MMP2 and MMP9. Upregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 are particularly noted in cancer cells. By targeting multiple proteins participating in tissue remodeling pathways, saponins can significantly reduce cancer metastasis under in vitro and in vivo conditions [,]. Several saponins have been identified with significant potential to specifically inhibit matrix degeneration protein such as MMP-2, vimentin and MMP-9 [,]. In particular, ginsenoside Rd inhibits the expression of MMP-2, MMP-1 and MMP-7 [].
Furthermore, NF-κB and certain protein kinase (such as MAPK, ERK, JNK, p38 and P13/AKT) regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) proteins (MMP and MMP2). []. The inhibitory potential of specific saponins is linked to their ability to suppress the phosphorylation of some of these protein kinases and inhibit TNF-α induced NF-κB activation [,]. For example, kalopanaxasaponin A, a triterpenoid saponin, inhibits the expression of MMP-9 in breast cancer cell by modulating P13/AKT and PKC pathways []. Ginseng saponin also inhibits MMP-9 in human astroglioma cell expression by suppressing activator protein-1 and MAPK []. In addition, trillium saponins downregulate MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in HuH-7 cells [].
The activity of matrix metalloproteinase can be further regulated by endogenous inhibitors, including tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP) and extracellular inducers of matrix metalloproteinase (EMMPRIN) [,]. While the former works by reducing the activity of MMP, the latter stimulates the activity of MMP. Diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, inhibits EMMPRIN and stimulates TIMP-2 expression in PC-3 cells []. Moreover, soybean saponins can stimulate TIMP-2 expression in colon cancer cells []. Similarly, Shuli et al. reported the upregulation of tumour cell TIMP-2 expression following Rhizoma paridis saponin treatment []. However, further studies are needed to understand MMP role in cancer and their regulation by saponins since it has been observed that increased TIMP-2 expression in glioblastoma patients is accompanied by severe adverse effects [].
At the secondary site, tumor cells rapidly proliferate as a result of increased levels of growth factors. Different autocrine and paracrine growth factors such as bFGF, IGF-I and EGF are released by metastatic cells []. These growth factors have become therapeutic targets for certain anticancer drugs since their stimulation is essential for the rapid growth of cancer cell at distant sites []. Saponin DT13 can potentially block metastasis through the inhibition of tissue factor (TF) []. Timosaponin AIII suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced tumor invasion []. Zhuang et al. also reported that dihydrodiosgenin inhibited metastasis by suppressing endothelial cell-derived factor VIII and altering platelet function []. Beyond the direct role of the saponins on multiple pathways involved in metastasis, saponins can also be broken down in the body to yield secondary metabolites with potential anti-metastasis activity. For example, saponin metabolites from gut metabolism have shown significant metastasis inhibitory activity [].
3.4. Saponin in Multidrug Resistant Cancer
The difficulty associated with drug resistance remains a hurdle in the chemotherapeutic treatment of cancers. Several reports have documented the anticancer activity of saponins against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant cancer-cell lines. Drug resistance in cancer is linked to several determinants, including increased tumor burden and metastasis, multiple chromosomal aberrations, physical barriers to chemotherapeutic agents, tumor micro-environment, adaptive cancer immune response and untargeted oncogenic drivers []. Saponins have been described as being able to modulate some of the target effectors, such as pgp (p-glycoprotein) and Ras, to elicit cytotoxic activity against resistant cancer cells. Saponins have shown potent p-glycoprotein (an efflux pump highly expressed in many cancer resistant cells) inhibiting activity [,]. Similarly, in resistant cell lines, the Ras protein (an oncogenic driver) can be inhibited by Paris saponin VII to stop colorectal cancer from spreading []. Some saponins have also demonstrated the ability to reverse multidrug resistance in cancer cells and target angiogenesis in resistant cell lines [,]. As a result of their potency to treat multidrug resistance, saponins are explored in combination therapy with other standard drugs to increase the therapeutic effect of current anticancer regimens against drug-resistant cancer cells [].
Another challenge in cancer therapy is the elimination of cancer stem cells. These cells are capable of growing after effective treatment with chemotherapeutic agents []. Interestingly, saponins have shown inhibitory activity against cancer stem cell via a cell death mechanism involving the Wnt/β- catenin signaling pathway [].
4. Limitations and Prospects
The number of purified saponins with anticancer activity has increased significantly over the last two decades. Despite the widespread research and reports on the anticancer property of saponins and their derivatives, there are no FDA approved saponin-based anticancer drug []. Most of the studies describing the anticancer effect of saponins are from in vitro experiments, and there are only limited in vivo and clinical trial data currently available. This limitation is a result of many factors ranging from drug-likeness property to toxicity index. There have also been concerns about the purity of natural saponins and their availability. This section considers the factors limiting the success of saponins as anticancer drugs and the future directions for better outcomes.
Saponins possess a significantly high molecular weight (around 741 to 1808 Da) and a consequent high number of rotatable hydrogen bonds, total polar surface area and hydrogen bond donors and acceptors []. Generally, drugs with low molecular weight, high lipophilicity and fewer hydrogen bond donors and acceptor are usually more bioavailable []. Saponin glycone has a notably lower oral bioavailability compared to aglycone saponin []. For several low orally bioavailable drugs, high dose oral administration or alternative route such as intravenous and intramuscular routes are usually explored. However, intravenous administration of saponins is not a likely option to be explored since studies have shown that saponins possess high hemolytic activity, which may lead to anemia []. The hemolytic activities of saponins are mediated by erythrocyte membrane permeabilization via interaction with the cholesterol of the plasma membrane [,]. This activity is linked to critical carboxylic and hydroxyl functional groups of triterpenoid saponins [].
The activity of saponins is dose-dependent, and a significant increase in oral dosage would mean a significant increase in bioavailability and action, which can significantly increase saponin toxicity []. Sub-acute, acute and chronic dose of saponins is associated with nephrotoxicity, hepatoxicity and cardiotoxicity [,]. There are, however, reports of non-toxic saponins even at higher concentration following oral administration in animal models [,]. While several saponins are hemolytic, a few recently identified saponins, including soya sapogenol, Astragalus membranaceus saponins and Bupleurum chinense saponins, have been shown to be non-hemolytic [,].
Structural optimization of saponin may prove to be very important in improving the drug-like property of saponins. Several anticancer drugs obtained from plants, such as paclitaxel, are structural derivatives of plant compounds. A detailed understanding of the structure-activity relationship of saponins would prove as an invaluable tool to guide the development of bioavailable saponins as a potential anticancer drug candidate. Studies on QSAR of saponins to identify the functional groups responsible for the hemolytic and cytotoxic activity have shown promising outcomes, in addition to structural modification to ensure selective action of the saponins. For example, QSAR and QSPR studies of saponins isolated from Pulsatilla chinensis showed that cytotoxic activity of the saponin was independent of its hemolytic activity. This technique would help to identify potent cancer-specific drug candidates [].
Targeted drug delivery is an alternative approach that could be explored further to increase the efficacy of saponins. Nanoparticles, due to their size, can evade clearance by plasma binding protein and reticuloendothelial system. Nano-encapsulation not only extends the drug circulation time, but it also reduces the toxicity to normal cells. For instance, loading saponins into human serum albumin nanocomposites resulted in improved anticancer drug efficacy and no toxicity to healthy cells []. In addition, drug-delivery vehicles involving micelles, self-assembled nano drugs and liposomes can be functionalized by targeting moiety, such as cell-penetrating peptides, to improve selectivity and reduce toxicity [,].
One of the most promising areas in saponin anticancer research is combination therapy. There is different evidence that has shown that saponins can be combined with other chemotherapeutic and radiotherapy treatments to improve efficacy and reduce toxicity [,]. In combination with radiation treatment, saponins induce apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in cancer cells, thereby sensitizing resistant cancer cells to radiation treatment [,]. Similarly, Saponins are also utilized as adjuvants to boost the body’s immunological response against cancer [,]. In addition, saponins have also been shown to have synergistic therapeutic effects when combined with conventional anticancer drugs [,]. Targeted saponin delivery and combination therapy appear to hold the best promise for developing saponin derived anticancer agents in the near future.
5. Concluding Remarks
The overwhelming evidence from several studies has shown the different anticancer effects of saponins. Previous research has largely linked the anticancer action to membrane permeabilization (which leads to apoptosis); however, more recently discovered saponins have demonstrated enhanced chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic action, utilizing different cytotoxic pathways. Some of these saponins have been demonstrated to have antioxidant properties as well as the ability to control the expression of proteins involved in cell cycle, cancer progression and metastasis. Despite the progress made so far in the use of saponin for cancer treatment, toxicity and low bioavailability remain significant obstacles. Moreover, another difficulty is the fact that the role of diverse saponin scaffolds in anticancer action is unknown, making drug optimization challenging. Combination therapy and more efficient drug delivery technologies, both of which have been used in saponins research have shown the best promise so far. The evidence from these studies, on the other hand, is primarily from in vitro investigations and is quite limited. Further structure-dependent activity and preclinical and clinical studies are therefore essential to ensure the translation of saponin based anticancer drugs from bench to bedside.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.O.E. and O.I.; methodology, O.O.E., F.O. and E.O.A.; writing—original draft preparation, E.O.A., O.I. and F.O.; writing—review and editing, O.O.E., O.I. and F.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO. Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment; World Global Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.E.S.; Shoela, S.; Marzouk, M.M.; Sleem, A.A. A sulphated flavone glycoside from Livistona australis and its antioxidant and cytotoxic activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Kaur, P.; Shukla, S.; Abbas, A.; Fu, P.; Gupta, S. Plant flavone apigenin inhibits HDAC and remodels chromatin to induce growth arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo study. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameh, S.J.; Tarfa, F.D.; Ebeshi, B.U. Traditional herbal management of sickle cell anemia: Lessons from Nigeria. Anemia 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Gao, F.; Sun, X.; Bi, H.; Zhu, Y. Paris saponin VII suppresses osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by inhibiting MMP-2/9 production via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3199–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Shen, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Si, H.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; Gao, E.; Liu, S. Structure-activity relationships of 3-O-β-chacotriosyl oleanane-type triterpenoids as potential H5N1 entry inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 119, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.-P.; Liang, P.-H. Biological and pharmacological effects of synthetic saponins. Molecules 2020, 25, 4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, C.; Legault, J.; Pichette, A. Recent progress in the synthesis of naturally occurring triterpenoid saponins. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2009, 6, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Laval, S.; Yu, B. Chemical synthesis of saponins. In Horton DBT-A in CC and B; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 137–226. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chou, G.-X.; Wu, T.; Guo, Y.-L.; Wang, S.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Wang, Z.-T. Steroidal sapogenins and glycosides from the rhizomes of dioscorea bulbifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbourn, A.E. Saponins in cereals. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Li, X.-B.; Zhang, S.-S.; He, Q.-X.; Hou, H.-R.; Dang, L.; Guo, J.-L.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yu, T.; Peng, D.-J.; et al. LC-MS/MS identification of novel saponins from the viscera of sea cucumber apostichopus japonicus. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2018, 54, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Sobolewska, D. Saponins as cytotoxic agents: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 425–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-H.; Li, T.; Fong, C.M.V.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.-J.; Wang, Y.-T.; Huang, M.-Q.; Lu, J.-J. Saponins from Chinese medicines as anticancer agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevrenova, R.; Weng, A.; Voutguenne-Nazabadioko, L.; Thakur, M.; Doytchinova, I. Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on saponins as cytotoxicity enhancers. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2015, 12, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Shu, Z.; Xu, Q.-M.; Liu, Y.-L.; Li, X.-R.; Wang, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-L. Cytotoxic activity of Pulsatilla chinensis saponins and their structure–activity relationship. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.A.; Qin, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: In vitro and in vivo activities, structure-activity relationships, and molecular mechanisms of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-J.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Y.; Wong, R.N.-S.; Wu, Q.-Y. Diosgenin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human leukemia K562 cells with the disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 55, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvanalakshmi, G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Dharmarajan, A.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P.; Warrier, S. Breast cancer stem-like cells are inhibited by diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, by the attenuation of the Wnt β-catenin signaling via the Wnt antagonist secreted frizzled related protein-4. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, L.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Han, X.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Peng, J. Dioscin suppresses human laryngeal cancer cells growth via induction of cell-cycle arrest and MAPK-mediated mitochondrial-derived apoptosis and inhibition of tumor invasion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 774, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tao, X.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Peng, J. Dioscin induces apoptosis in human cervical carcinoma hela and siha cells through ROS-mediated DNA damage and the mitochondrial signaling pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-A.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Sung, E.-G.; Song, I.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Sohn, H.-Y.; Lee, T.-J. Dioscin induces caspase-independent apoptosis through activation of apoptosis-inducing factor in breast cancer cells. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Hara, F.; Yasui, T.; Uga, N.; Naoe, A. Polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin in Paris polyphylla, induces apoptosis and necroptosis cell death of neuroblastoma cells. Pediatric Surg. Int. 2017, 33, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cai, H.; Meng, X. Polyphyllin D induces apoptosis and differentiation in K562 human leukemia cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Cheung, K.L.; Lau, I.P.; Yu, W.S.; Fung, K.P.; Yu, B.; Loo, J.F.; Kong, S.K. Polyphyllin D induces apoptosis in human erythrocytes through Ca 2+ rise and membrane permeabilisation. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Chan, J.Y.-W.; Kong, S.-K.; Yu, B.; Eng-Choon, V.O.; Nai-Ching, H.W.; Chung-Wai, T.M.; Fung, K.-P.; Yuet-Wa, J.C. Effects of polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin inParis Polyphylla, in growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells and in xenograft. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, N.; Rasul, A.; Hussain, G.; Anwar, H.; Shah, M.A.; Sarfraz, I.; Riaz, A.; Batool, R.; Shahbaz, M.; Hussain, A.; et al. Oleandrin: A bioactive phytochemical and potential cancer killer via multiple cellular signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. A systematic review of the active saikosaponins and extracts isolated from Radix Bupleuri and their applications. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 620–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-F.; Wang, X.; Kang, H.-F.; Bai, M.-H.; Guan, H.-T.; Wang, Z.-W.; Zan, Y.; Song, L.-Q.; Min, W.-L.; Lin, S. Saikosaponin-D enhances radiosensitivity of hepatoma cells under hypoxic conditions by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014, 33, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, F.-M.; Ma, D.-L.; Cheung, Y.-W.; Lok, C.-N.; Yan, K.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Xu, S.; Ko, B.C.-B.; He, Q.-Y.; et al. Proteomic and transcriptomic study on the action of a cytotoxic saponin (Polyphyllin D): Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathways. Proteomics 2008, 8, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-J.; Nie, X.-Q.; Liu, D.; Bian, K. Effects of four kinds of Chinese medicine monomer on growth of PANC-1 xenograft tumor and studying of molecular mechanism. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Nho, K.J.; Chun, J.M.; Kim, H.K. Induction of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by timosaponin A-III. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 45, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Yang, C.-W.; Wang, J.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Tseng, L.-M.; King, K.-L.; Chen, W.-S.; Chiu, J.-H.; Shyr, Y.-M. Timosaponin AIII suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced invasive activity through sustained ERK activation in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, F.; Fan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H.; Yu, P.; Ma, J. Effective cytotoxic activity of OSW-1 on colon cancer by inducing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabed, R.; Hanashima, S.; Murata, M.; Sakurai, K. Interactions of OSW-1 with lipid bilayers in comparison with digitonin and soyasaponin. Langmuir 2020, 36, 3600–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Sasaki, K.; Fukutani, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Ohsawa, I.; Yohda, M.; Sakurai, K. Anticancer saponin OSW-1 is a novel class of selective Golgi stress inducer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhuang, J.; Tang, S.; Yu, J.; Tian, J.; Feng, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Meta-analysis of the association between the dietary inflammatory index (DII) and breast cancer risk. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 73, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ye, K.; Zhang, B.; Xin, Q.; Li, P.; Kong, A.-N.; Wen, X.; Yang, J. Paris Saponin II inhibits colorectal carcinogenesis by regulating mitochondrial fission and NF-κB pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, B.; Yan, Q.; Ruan, S. Effects of saponins of patrinia villosa against invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer cell through NF-κB signaling pathway and EMT. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharara, J.; Amini, E.; Salek-Abdollahi, F. Anti-inflammatory properties of saponin fraction from Ophiocoma erinaceus. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 638–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Liu, H.; Qin, P.; Hu, C.; Man, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Diao, A. Saponin fraction isolated from Conyza blinii H. Lév. demonstrates strong anticancer activity that is due to its NF-κB inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Deng, S.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Hao, L.; Zhang, G.; Su, S.; Xu, X.; Yang, R. 3, 4-Seco-dammarane triterpenoid saponins with anti-inflammatory activity isolated from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morry, J.; Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Yantasee, W. Oxidative stress in cancer and fibrosis: Opportunity for therapeutic intervention with antioxidant compounds, enzymes, and nanoparticles. Redox. Biol. 2017, 11, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwash, B.M.J. Triterpenoid saponins investigation and pharmacological (cytotoxic and antioxidant) properties of Bacopa monnieri L. cultivated in Iraq. Baghdad Sci. J. 2018, 15, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhry, Q.N.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, T.G.; Pan, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J. Saponin-based nanoemulsification improves the antioxidant properties of vitamin A and E in AML-12 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Hu, H.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Du, S. Panax notoginseng saponins protect cerebral microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced barrier dysfunction via activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznarkowska, A.; Kostecka, A.; Meller, K.; Bielawski, K.P. Inhibition of cancer antioxidant defense by natural compounds. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.-H.; Wang, L.-H.; Yu, T.-F.; Wang, Y.-N.; Yan, H.; Liu, P.; Yan, C. Triterpenoid Saponin AG8 from Ardisia gigantifolia stapf. induces triple negative breast cancer cells apoptosis through oxidative stress pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 7963212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Baek, S.; Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Roh, J.-L. Hederagenin induces apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cells by inhibiting the Nrf2-ARE antioxidant pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5498908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Cell cycle regulation and anticancer drug discovery. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, S.; Muriana, F.J.; Guillen, R.; Jimenez-Araujo, A.; Arcos, R.R.; Lopez, S. Saponins from edible spears of wild asparagus inhibit AKT, p70S6K, and ERK signalling, and induce apoptosis through G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer HCT-116 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Hu, G.; Wang, A.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Jia, J. Paris saponin VII induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by regulating Akt/MAPK pathway and inhibition of P-glycoprotein in K562/ADR cells. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Q.-S.; Meng, F.-C.; Tang, Z.-H.; Chen, X.; Lin, L.-G.; Chen, P.; Qiang, W.-A.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zhang, Q.-W. Chikusetsusaponin IVa methyl ester induces G1 cell cycle arrest, triggers apoptosis and inhibits migration and invasion in ovarian cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, N.; Rankin, G.O.; Li, B.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Tu, Y.; Chen, Y.C. Anti-proliferative effect and cell cycle arrest induced by saponins extracted from tea (Camellia sinensis) flower in human ovarian cancer cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Du, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J. Paris saponin I sensitises gastric cancer cell lines to cisplatin via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 3798. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Li, R.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Liu, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. PP9, a steroidal saponin, induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 331, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.-J.; Hu, L.-P.; Peng, Q.-L.; Yang, X.-L.; Bai, L.-L.; Yiu, A.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.-Y.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhang, D.-M. Hellebrigenin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through inhibition of Akt. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-L.; Lin, J.-Y.; Shieh, J.-C.; Yeh, H.-F.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Shen, C.-Y.; Cheng, C.-W. Induction of G2/M phase arrest by diosgenin via activation of chk1 kinase and cdc25c regulatory pathways to promote apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Bartoszewski, R.; Bartoszewska, S.; Kochan, K.; Adamska, A.; Kosiński, I.; Ochocka, J.R. Pennogenyl Saponins from Paris quadrifolia L. Induce Extrinsic and Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis in Human Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R. Platycodin D, a triterpenoid saponin from Platycodon grandiflorum, induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells by modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumor. Biol. 2014, 35, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.K.-S.; Auyeung, K.K.-W.; Mok, N.-L.; Wong, C.-M.; Cho, C.-H. Astragalus saponins modulate mTOR and ERK signaling to promote apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-H.; Chung, K.-S.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, N.-H.; Lee, K.-T. Compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, induces apoptosis via caspase-8-dependent pathway in HL-60 human leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, T.J. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.K.; Kang, K.A.; Lim, C.M.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, B.J.; Chang, W.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Hyun, J.W. Compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, induces mitochondria-dependent and caspase-dependent apoptosis via the generation of reactive oxygen species in human colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4916–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Bai, P.; Nguyen, T.M.B.; Xiao, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, G.; Hu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. The antitumoral effect of Paris Saponin I associated with the induction of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Zheng, L.; Dong, D.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Xu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Peng, J. Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, induces apoptosis and DNA damage through reactive oxygen species: A potential new drug for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Sun, J.; Hou, Z.; Luan, W.; Wang, S.; Cui, S.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y. Novel antitumor compound optimised from natural saponin Albiziabioside A induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and ferroptosis as a p53 activator through the mitochondrial pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawen, A. Apoptosis—An introduction. Bioessays 2003, 25, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Martin, S. Caspase-independent cell death. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Léonard, C.; Abouzi, M.; Akabi, F.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. α-Hederin induces apoptosis, membrane permeabilisation and morphologic changes in two cancer cell lines through a cholesterol-dependent mechanism. Planta. Med. 2016, 82, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Verstraeten, S.L.; Albert, M.; Paquot, A.; Muccioli, G.G.; Tyteca, D.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. Membrane cholesterol delays cellular apoptosis induced by ginsenoside Rh2, a steroid saponin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 352, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, U.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Koo, K.H.; Ye, S.-K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, Y.-N. Lipid raft modulation by Rp1 reverses multidrug re-sistance via inactivating MDR-1 and Src inhibition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holze, C.; Michaudel, C.; Mackowiak, C.; Haas, D.A.; Benda, C.; Hubel, P.; Pennemann, F.L.; Schnepf, D.; Wettmarshausen, J.; Braun, M.; et al. Oxeiptosis, a ROS-induced caspase-independent apoptosis-like cell-death pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.J.; Hwang, Y.-I. SB365, Pulsatilla saponin d induces caspase-independent cell death and augments the anticancer effect of temozolomide in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelens, X.; Festjens, N.; Walle LVande Van Gurp, M.; Van Loo, G.; Vandenabeele, P. Toxic proteins released from mito-chondria in cell death. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2861–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Lu, K.-W.; Yu, C.-S.; Chou, S.-T.; Lin, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lin, M.-L.; Chueh, F.-S.; Chen, S.-S.; et al. An experimental study on the antileukemia effects of gypenosides in vitro and in vivo. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 10, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, X. Endonuclease G is an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 412, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Dai, R.; Ismail, N.; Su, W.; Li, B. Ferroptosis and its potential role in human diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Ndontsa, B.L.; Kuete, V.; Nguekeu, Y.M.; Çelik, I.; Mbouangouere, R.; Tane, P.; Efferth, T. A naturally occuring triterpene saponin ardisiacrispin B displayed cytotoxic effects in multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells via ferroptotic and apoptotic cell death. Phytomedicine 2018, 43, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-L.; Lin, P.-L. Natural Saponin Formosanin C-induced Ferroptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In-volved Ferritinophagy. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Xiang, X.; Li, J.; Deng, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, J. Ruscogenin induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 43, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.; Gu, G.; Sun, B.; Cui, M.; Ji, M.; Lou, H.-X. Efficient synthesis of trisaccharide saponins and their tumor cell killing effects through oncotic necrosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Chi, G.F.; Nguenang, G.S.; Abdelfatah, S.; Sop, R.V.T.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Kuete, V.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of a naturally occuring spirostanol saponin, progenin III, towards a broad range of cancer cell lines by induction of apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Chem. Interact. 2020, 326, 109141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkermann, A.; Green, D.R. Necroptosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E. The role for autophagy in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.M.M.; Towers, C.G.; Thorburn, A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bao, J.; Wang, K.; Jia, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Chen, M.; Wan, J.-B.; Su, H.; Wang, Y. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits au-tophagic flux and synergistically enhances the anticancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents against HeLa cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Klionsky, D.J. An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 335, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy: From phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.-Z.; Li, M.-M.; Deng, P.-F.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, X.-P.; Hu, L.-B.; Chen, Z.; Jie, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F. Paris saponin-induced au-tophagy promotes breast cancer cell apoptosis via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 264, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Miao, T.; Liu, G.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Shen, L.; et al. Anemoside B4 exerts anti-cancer effect by inducing apoptosis and autophagy through inhibiton of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar]
- Steeves, M.A.; Dorsey, F.C.; Cleveland, J.L. Targeting the autophagy pathway for cancer chemoprevention. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinojima, N.; Yokoyama, T.; Kondo, Y.; Kondo, S. Roles of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in curcumin-induced autophagy. Autophagy 2007, 3, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.C.; Tu, Y. Saponins extracted from tea (Camellia Sinensis) flowers induces autophagy in ovarian cancer cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Dong, X.; Yap, J.; Hu, J. The MAPK and AMPK signalings: Interplay and implication in targeted cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Tong, S.; Wu, J.; Tian, L.; Qi, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y. Paris saponin VII extracted from Trillium tschonoskii induces autophagy and apoptosis in NSCLC cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Bao, J.; Li, P.; Chen, M.; Wan, J.-B.; Su, H.; Mei, Z.; He, C. Polyphyllin VII induces an autophagic cell death by activation of the JNK pathway and inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in HepG2 cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Deng, J.; Fan, D.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Fu, R.; Wang, S. Ginsenoside Rh4 induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death through activation of the ROS/JNK/p53 pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaravadi, R.; Kimmelman, A.C.; White, E. Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1913–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hu, C.; Sun, N.; Li, Y.; Man, S.; Liu, Z.; Diao, A.; Ma, L. A triterpenoidal saponin fraction of Conyza blinii H.Lév. is a dual-targeting autophagy inhibitor for HeLa cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24291–24297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza ASC de Gonçalves, L.B.; Lepique, A.P.; Araujo-Souza, D.; Savio, P. The role of autophagy in tumor immunolo-gy-complex mechanisms that may be explored therapeutically. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 2691. [Google Scholar]
- Koczurkiewicz, P.; Czyż, J.; Podolak, I.; Wójcik, K.; Galanty, A.; Janeczko, Z.; Michalik, M. Multidirectional effects of triterpene saponins on cancer cells—Mini-review of in vitro studies. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, E.C.; Chuaqui, R.F.; Liotta, L.A. General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1997, 80, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; YOO, Y.; Matsuzawa, K.; Sato, K.; Saiki, I.; Tonooka, S.; Samukawa, K.; Azuma, I. Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3, of red ginseng. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Mochizuki, M.; Saiki, I.; YOO, Y.; Samukawa, K.; Azuma, I. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by a saponin of panax ginseng, ginsenoside-Rb. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 17, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.-W.; Koon, J.C.-M.; Liu, X.; Detmar, M.; Yu, B.; Kong, S.-K.; Fung, K.P. Polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin from Paris polyphylla, inhibits endothelial cell functions in vitro and angiogenesis in zebrafish embryos in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-R.; Cheung, K.K.; Zhou, X.; Xie, R.-F.; Cheng, P.-P.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Hoi, P.M.; Wang, Y.-H.; et al. Amelioration of acute myocardial infarction by saponins from flower buds of Panax notoginseng via pro-angiogenesis and anti-apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 181, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zou, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Bai, P.; Xiao, X. Paris saponin II inhibits human ovarian cancer cell-induced an-giogenesis by modulating NF-κB signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.-J.; Luan, X.; Xu, J.-R.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.-R.; Gao, Y.-G.; Zhao, M.; Chen, H.-Z.; Fang, C. Raddeanin A, a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Anemone raddeana, suppresses the angiogenesis and growth of human colorectal tumor by inhibiting VEGFR2 signaling. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, X.; Tong, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liping, L.; Sun, P.; Lin, L.; Ding, J. PE, a new sulfated saponin from sea cucumber, Exhibits anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, J.-F.; Zou, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.-H.; Jiang, J.; Qin, D.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Liu, B.-X.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-T.; et al. The anti-lung cancer activities of steroidal saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara through enhanced immunostimulation in experimental lewis tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice and induction of apoptosis in the A549 cell line. Molecules 2013, 18, 12916–12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wan, J.-B.; Chan, S.-W.; Deng, Y.-H.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lee, S.-M. Comparative study on saponin fractions from Panax notoginseng inhibiting inflammation-induced endothelial adhesion molecule expression and monocyte adhesion. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lin, S.; Zhao, R.; Yu, B.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, L. The saponin monomer of dwarf lilyturf tuber, dt-13, reduces human breast cancer cell adhesion and migration during hypoxia via regulation of tissue factor. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lou, L.; Ye, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Jin, L.; He, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Deng, A.; et al. Ardipusilloside inhibits survival, invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuli, M.; Wenyuan, G.; Yanjun, Z.; Chaoyi, M.; Liu, Y.; Yiwen, L. Paridis saponins inhibiting carcinoma growth and metastasis In vitro and in vivo. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cui, J.; Du, X.; Yang, Q.; Jia, C.; Xiong, M.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) inhibits breast cancer metastasis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Cha, S.-W.; Lee, S.-G. Anti-metastatic effects of ginsenoside Rd via inactivation of MAPK signaling and induction of focal adhesion formation. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauvois, B. New facets of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers: Outside-in signaling and relationship to tumor progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2012, 1825, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, L. Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of Rhizoma Paridis saponins. Steroids 2009, 74, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Hwang, Y.S.; Park, K.-K.; Park, H.-J.; Seo, J.Y.; Chung, W.-Y. Kalopanaxsaponin A inhibits PMA-induced invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-9 via PI3K/Akt-and PKCδ-mediated signaling in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Car-cinogenesis 2009, 30, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.-H.; Woo, M.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, W.-K.; Hyun, J.-W.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Ginseng saponin metabolite suppresses phorbol ester-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through inhibition of activator protein-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in human astroglioma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Luan, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, W. Inhibitory effect of Trillium saponins on invasion and migration of HuH-7 cells by promoting human β defensin-2 expression. Chin. J. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 35, 526–532. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.-H.; Han, I.-H.; Sung, M.-K.; Yoo, H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, J.-S.; Kawada, T.; Yu, R. Soybean saponin inhibits tumor cell metastasis by modulating expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9 and TIMP-2. Cancer Lett. 2008, 261, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-S.; Shih, Y.-W.; Huang, H.-C.; Cheng, H.-W. Diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, inhibits migration and invasion of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells by reducing matrix metalloproteinases expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.V.; Jong, K.A.; Rajasekaran, A.K.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Mischel, P.S. Upregulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP)-2 promotes matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 activation and ce ll invasion in a human glioblastoma cell line. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-T.; Wu, J.-R.; Cheng, C.-C.; Wu, W.-S. The therapeutic targeting of HGF/c-met signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: Alternative approaches. Cancers 2017, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Xin, G.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Xing, Z.; Ji, C.; Du, J.; Niu, H.; Huang, W. Dihydrodiosgenin inhibits endothelial cell-derived factor VIII and platelet-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4871–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Guo, S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, T. Intestinal Metabolite Compound K of Ginseng Saponin Potently Attenuates Metastatic Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Augmenting Apoptosis via a Bid-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12753–12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Cheng, X.; Wink, M. Natural lignans from Arctium lappa modulate P-glycoprotein efflux function in multidrug resistant cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhai, Z.; Li, N.; Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Yuan, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yun, J.; et al. Steroidal saponin of Trillium tschonoskii. Reverses multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, F.; Meng, J.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, R.; Yue, Z.; et al. Paris saponin VII inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells through Ras signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, W.; Wu, M.; Pan, G.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Man, S.; Teng, Y.; Yu, P.; et al. Chemosensitizing effect of Paris Saponin I on Camptothecin and 10-hydroxycamptothecin in lung cancer cells via p38 MAPK, ERK, and Akt signaling pathways. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-X.; Yang, S.-W.; Li, P.-A.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.-Y.; Hao, Y.-X.; Yu, P.-W. The promotion of the transformation of quiescent gastric cancer stem cells by IL-17 and the underlying mechanisms. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Chaudhuri, P.K. Structural characteristics, bioavailability and cardioprotective potential of saponins. Integr. Med. Res. 2018, 7, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Basu, S.; Yang, Z.; Deb, A.; Hu, M. Bioavailability challenges associated with development of saponins as therapeutic and chemopreventive agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, T.; Teng, Y.; Wu, B.; You, M.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, M. Enhancement of oral bioavailability of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 through improved understanding of its absorption and efflux mechanisms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Han, L.; Duan, H.; Cui, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S. The derivatives of Pulsatilla saponin A, a bioactive compound from Pulsatilla chinensis: Their synthesis, cytotoxicity, haemolytic toxicity and mechanism of action. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwalek, M.; Lalun, N.; Bobichon, H.; Plé, K.; Voutquenne-Nazabadioko, L. Structure–activity relationships of some hed-eragenin diglycosides: Haemolysis, cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. (BBA) General Subj. 2006, 1760, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.N.Q.; Fukushima, E.O.; Muranaka, T. Structure and hemolytic activity relationships of triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witthawaskul, P.; Panthong, A.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Taesothikul, T.; Lertprasertsuke, N. Acute and subacute toxicities of the saponin mixture isolated from Schefflera leucantha Viguier. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Jin, W.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Shan, X.; Li, C.; Shan, L.; Efferth, T. In vivo cardiotoxicity induced by sodium aescinate in Zebrafish larvae. Molecules 2016, 21, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszek, W.; Junkuszew, M.; Stochmal, A. Determination and toxicity of saponins from Amaranthus cruentus seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3685–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Gong, G.; Li, D.; He, Y.; Zhao, Y. Acute toxicity and sub-chronic toxicity of steroidal saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis CH Wright in rodents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Haq, A.; Byrd, J.; Berhow, M.; Cartwright, A.; Bailey, C. Haemolytic and antimicrobial activities of saponin-rich extracts from guar meal. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-G.; Sun, H.-X.; Fang, W.-H. Haemolytic activities and adjuvant effect of Astragalus membranaceus saponins (AMS) on the immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vaccine 2005, 23, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbal, O.; Vural, T.; Malekghasemi, S.; Bozdoğan, B.; Denkbaş, E.B. Saponin loaded montmorillonite-human serum albumin nanocomposites as drug delivery system in colorectal cancer therapy. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. Mechanism of enhanced oral absorption of akebia saponin D by a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system loaded with phospholipid complex. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 45, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.-W.; Wang, F.-J.; Liew, O.-W.; Lu, Y.-Z.; Zhao, J. Analysis of triterpenoid saponins reveals insights into structural features associated with potent protein drug enhancement effects. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Davila, R.; Devisetty, K.; Szabo, A.; Sparapani, R.; Arce-Lara, C.; Gore, E.M.; Moran, A.; Williams, C.D.; Kelley, M.; Whittle, J. Cisplatin and etoposide versus carboplatin and paclitaxel with concurrent radiotherapy for stage III non–small-cell lung cancer: An analysis of veterans health administration data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Song, S.; Du, L.; Zhou, G.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, H. Paris Saponins enhance radiosensitivity in a ge-fitinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cell line by inducing apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle phase arrest. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.; Kang, K.A.; Chang, W.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, N.H.; Hyun, J.W. Effect of compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, combined with γ-Ray radiation in human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5777–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczurkiewicz, P.; Klaś, K.; Grabowska, K.; Piska, K.; Rogowska, K.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Michalik, M.; Pękala, E.; et al. Saponins as chemosensitizing substances that improve effectiveness and selectivity of anticancer drug—Minireview of in vitro studies. Phyther. Res. 2019, 33, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharara, J.; Amini, E.; Nikdel, N.; Salek-Abdollahi, F. The cytotoxicity of dacarbazine potentiated by sea cucumber saponin in resistant B16F10 melanoma cells through apoptosis induction. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2016, 8, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).