Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia and Its Impact on Survival in Patients with Brain Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
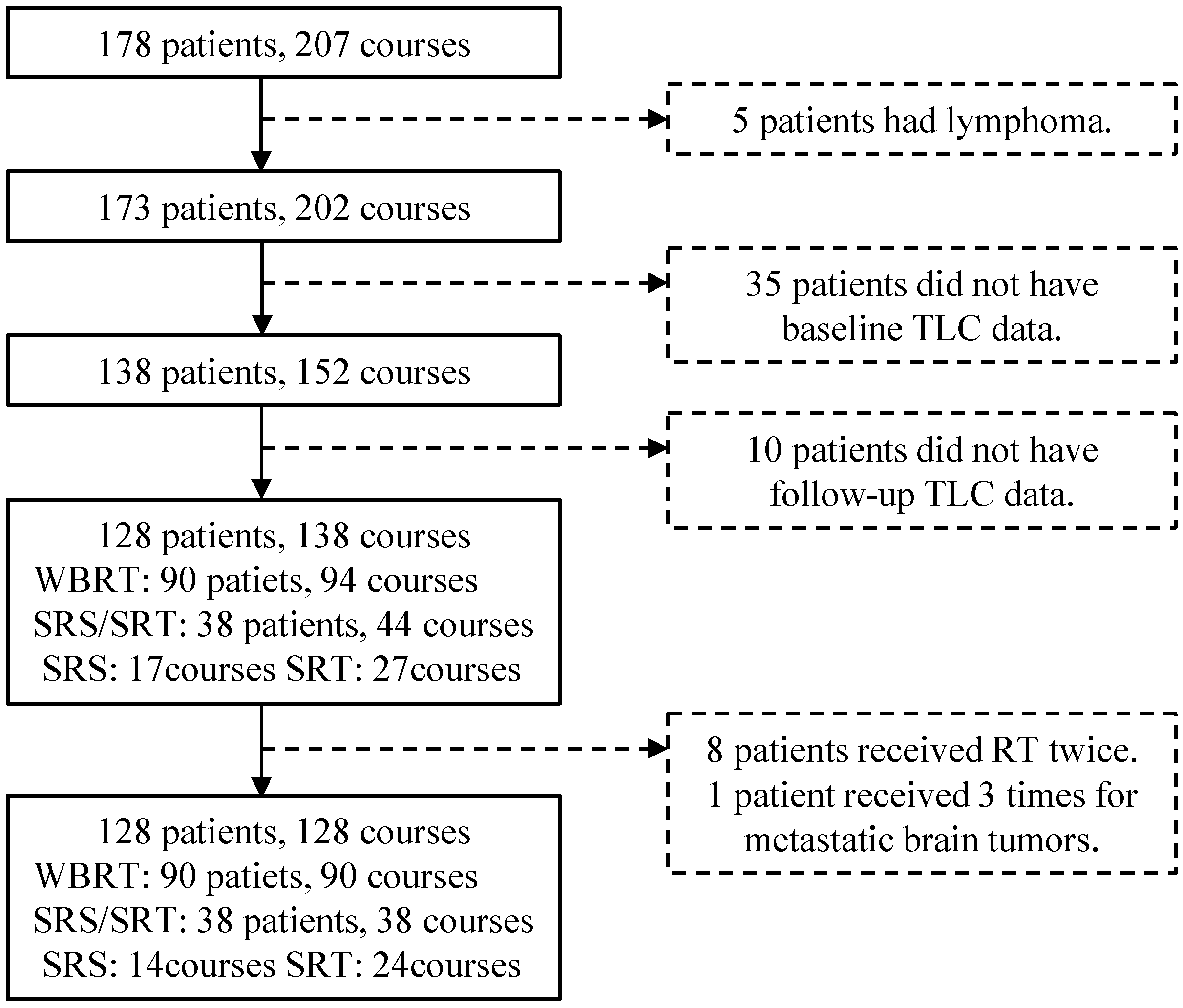
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Treatment Information
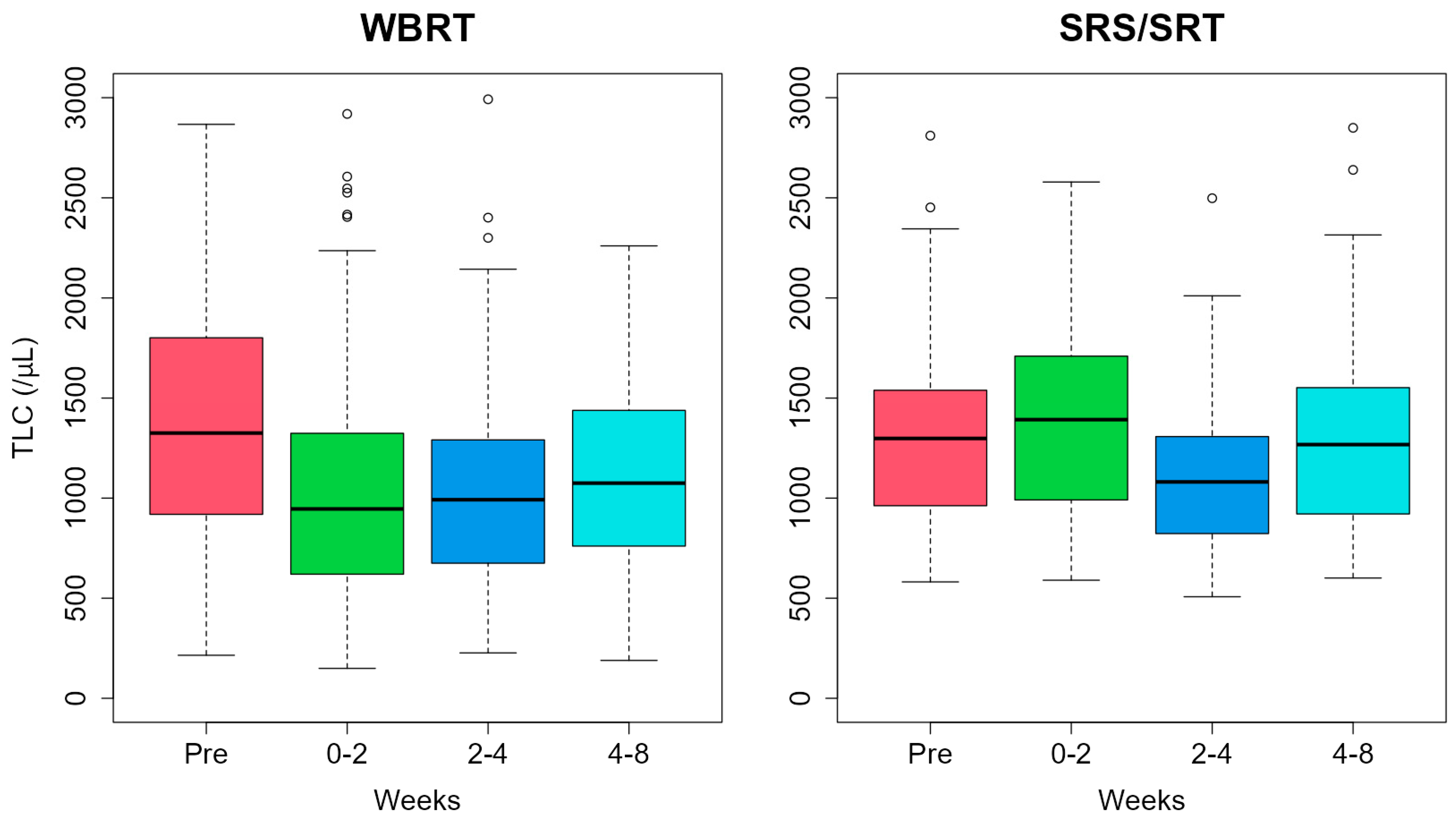
3.2. Changes in TLC and Lymphopenia-Related Factors
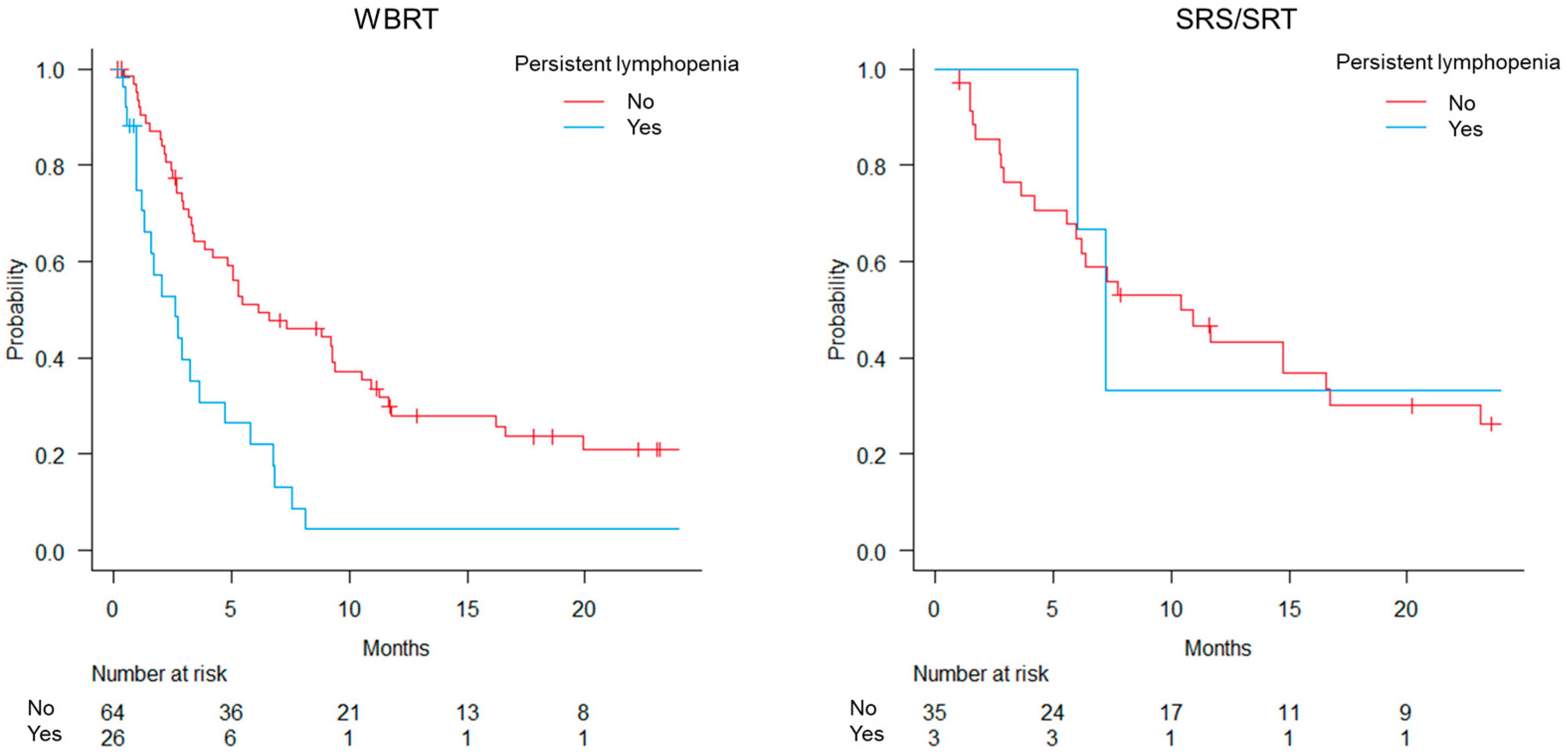
3.3. Overall Survival
3.4. PCI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, M.N.; Lloyd, N.; Wong, R.K.; Chow, E.; Rakovitch, E.; Laperriere, N.; Xu, W.; Sahgal, A. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD003869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Central Nervous System Cancers. Version 1. 2023. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cns.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afghahi, A.; Purington, N.; Han, S.S.; Desai, M.; Pierson, E.; Mathur, M.B.; Seto, T.; Thompson, C.A.; Rigdon, J.; Telli, M.L.; et al. Higher absolute lymphocyte counts predict lower mortality from early-stage triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Fujiwara, H.; Konishi, H.; Kiuchi, J.; Ohashi, T.; Shimizu, H.; Arita, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Morimura, R.; et al. Absolute lymphocyte count and C-reactive protein-albumin ratio can predict prognosis and adverse events in patients with recurrent esophageal cancer treated with nivolumab therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xu, W.; Hu, X.; Martínez, D.A.S.; Romero, J.L.A.; Yan, M.; Dai, Y.; Wang, H. Circulating blood biomarkers correlated with the prognosis of advanced triple negative breast cancer. BMC Womens Health 2024, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizaki, J.; Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Yonesaka, K.; Kudo, K.; Kaneda, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Peripheral blood biomarkers associated with clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damen, P.J.; Kroese, T.E.; van Hillegersberg, R.; Schuit, E.; Peters, M.; Verhoeff, J.J.; Lin, S.H.; van Rossum, P.S. The influence of severe radiation-induced lymphopenia on overall survival in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y. Lymphocytopenia and survival after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, H.K.; Kim, N.; Yoon, H.I.; Kang, S.-G.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.; Baek, J.G.; Chang, J.H.; Suh, C.-O. Clinical predictors of radiation-induced lymphopenia in patients receiving chemoradiation for glioblastoma: Clinical usefulness of intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the immuno-oncology era. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yovino, S.; Kleinberg, L.; Grossman, S.A.; Narayanan, M.; Ford, E. The etiology of treatment-related lymphopenia in patients with malignant gliomas: Modeling radiation dose to circulating lymphocytes explains clinical observations and suggests methods of modifying the impact of radiation on immune cells. Cancer Investig. 2013, 31, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, L.; Perol, D.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Petit, T.; Blay, J.-Y.; Carrie, C.; Bachelot, T. Lymphopenia: A new independent prognostic factor for survival in patients treated with whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases from breast carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2005, 76, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayman, J.A.; Callahan, J.W.; Herschtal, A.; Everitt, S.; Binns, D.S.; Hicks, R.J.; Mac Manus, M. Distribution of proliferating bone marrow in adult cancer patients determined using FLT-PET imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.R.; Leggett, R.W. Reference values for resting blood flow to organs of man. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 1989, 10, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesulu, B.P.; Mallick, S.; Lin, S.H.; Krishnan, S. A systematic review of the influence of radiation-induced lymphopenia on survival outcomes in solid tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 123, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Nakamatsu, K.; Anami, S.; Fukuda, K.; Inada, M.; Tatebe, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Kanamori, S.; Monzen, H.; Nishimura, Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival after whole-brain radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. In Vivo 2019, 33, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, R.; Liu, A.Y.; Brown, P.D.; Mahajan, A.; Dinh, J.; Chung, C.; McAvoy, S.; McAleer, M.F.; Lin, S.H.; Li, J.; et al. Proton therapy reduces the likelihood of high-grade radiation-induced lymphopenia in glioblastoma patients: Phase II randomized study of protons vs photons. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Ahn, S.; Park, J.-S.; Song, J.H.; Hong, Y.-K.; Jeun, S.-S. Effect of cumulative dexamethasone dose during concomitant chemoradiation on lymphopenia in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2020, 8, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudra, S.; Hui, C.; Rao, Y.J.; Samson, P.; Lin, A.J.; Chang, X.; Tsien, C.; Fergus, S.; Mullen, D.; Yang, D.; et al. Effect of radiation treatment volume reduction on lymphopenia in patients receiving chemoradiotherapy for glioblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; DeWees, T.A.; Badiyan, S.N.; Speirs, C.K.; Mullen, D.F.; Fergus, S.; Tran, D.D.; Linette, G.; Campian, J.L.; Chicoine, M.R.; et al. Clinical and dosimetric predictors of acute severe lymphopenia during radiation therapy and concurrent temozolomide for high-grade glioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, M.W.; Amoozgar, Z.; Repiton, P.; Morris, R.; Maksoud, S.; Hla, M.; Zaniewski, E.; Noske, D.P.; Haas, W.; Breyne, K.; et al. Glioblastoma extracellular vesicles modulate immune PD-L1 expression in accessory macrophages upon radiotherapy. iScience 2024, 27, 108807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, L.R.; Bang, A.; Mahal, B.A.; Taylor, A.; Krishnan, M.; Spektor, A.; Cagney, D.N.; Aizer, A.A.; Alexander, B.M.; Rahma, O.; et al. The impact of radiation therapy on lymphocyte count and survival in metastatic cancer patients receiving PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, C.; Koenig, J.; Sborov, K.; Gibbs, I.; Gensheimer, M.; Soltys, S.; Pollom, E. Impact of lymphopenia on survival following stereotactic radiosurgery and immune-checkpoint inhibitors among patients with brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Patients n = 128 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years (range) | 70 (34–87) | |
| Sex | Male | 88 |
| Female | 40 | |
| KPS | 0–60 | 35 |
| 70–80 | 37 | |
| 90–100 | 56 | |
| Primary tumor site | Lung (NSCLC or NOS) | 55 |
| Lung (small cell) | 33 | |
| Breast | 9 | |
| Stomach | 6 | |
| Colon and rectum | 4 | |
| Others | 21 | |
| Prior history of RT | None | 83 |
| Cranial | 8 | |
| Extra-cranial | 37 | |
| Prior RT courses | 1 course | 35 |
| 2 courses | 7 | |
| 3+ courses | 3 | |
| Methods of RT | WBRT | 90 |
| SRS/SRT | 38 | |
| Systemic therapy before RT | No | 53 |
| Yes | 75 | |
| Concurrent extra-cranial RT | No | 125 |
| Yes | 3 | |
| Concurrent systemic therapy | No | 114 |
| Yes | 14 | |
| Steroid use during RT | No | 57 |
| Yes | 71 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Yes | No | OR [95% CI] | p-Value | OR [95% CI] | p-Value | |
| Age | <70 years | 14 | 48 | Reference | 0.98 | ||
| ≥70 years | 15 | 51 | 1.01 [0.44–2.31] | ||||
| Sex | Male | 14 | 74 | Reference | 0.008 * | Reference | 0.022 * |
| Female | 15 | 25 | 3.17 [1.34–7.48] | 3.72 [1.21–11.40] | |||
| KPS score | 90–100 | 6 | 50 | Reference | <0.001 * | Reference | 0.23 |
| 70–80 | 10 | 27 | 3.09 [1.01–9.41] | 2.20 [0.56–8.56] | |||
| 0–60 | 13 | 22 | 4.92 [1.66–14.60] | 3.16 [0.83–12.00] | |||
| History of RT | No | 12 | 71 | Reference | 0.004 * | Reference | 0.018 * |
| Yes | 17 | 28 | 3.59 [1.52–8.48] | 3.91 [1.27–12.10] | |||
| Number of brain metastasis | 1 | 6 | 25 | Reference | 0.74 | ||
| 2–3 | 6 | 24 | 1.04 [0.29–3.68] | ||||
| ≥4 | 17 | 50 | 1.42 [0.50–4.04] | ||||
| Extracranial cancer | No | 9 | 33 | Reference | 0.82 | ||
| Yes | 20 | 66 | 1.11 [0.46–2.71] | ||||
| Systemic therapy before RT | No | 10 | 43 | Reference | |||
| Yes | 19 | 56 | 1.49 [0.63–3.52] | ||||
| TLC before RT | ≥800/µL | 15 | 94 | Reference | <0.001 * | Reference | <0.001 * |
| <800/µL | 14 | 5 | 17.50 [5.51–55.80] | 14.40 [3.57–58.20] | |||
| Methods of RT | SRS/SRT | 3 | 35 | Reference | 0.016 * | Reference | 0.027 * |
| WBRT | 26 | 64 | 4.74 [1.34–16.80] | 6.25 [1.23–31.70] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishida, N.; Matsuo, Y.; Fukuda, J.; Ri, A.; Tatsuno, S.; Uehara, T.; Inada, M.; Matsuura, T.; Doi, H.; Nakamatsu, K.; et al. Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia and Its Impact on Survival in Patients with Brain Metastasis. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 4559-4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080340
Ishida N, Matsuo Y, Fukuda J, Ri A, Tatsuno S, Uehara T, Inada M, Matsuura T, Doi H, Nakamatsu K, et al. Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia and Its Impact on Survival in Patients with Brain Metastasis. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(8):4559-4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080340
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshida, Naoko, Yukinori Matsuo, Junki Fukuda, Aritoshi Ri, Saori Tatsuno, Takuya Uehara, Masahiro Inada, Tomohiro Matsuura, Hiroshi Doi, Kiyoshi Nakamatsu, and et al. 2024. "Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia and Its Impact on Survival in Patients with Brain Metastasis" Current Oncology 31, no. 8: 4559-4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080340
APA StyleIshida, N., Matsuo, Y., Fukuda, J., Ri, A., Tatsuno, S., Uehara, T., Inada, M., Matsuura, T., Doi, H., Nakamatsu, K., & Hosono, M. (2024). Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia and Its Impact on Survival in Patients with Brain Metastasis. Current Oncology, 31(8), 4559-4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31080340






