Radiation Oncologists’ Perspectives on Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Survey from Korean Oligometastasis Working Group
Abstract
1. Introduction
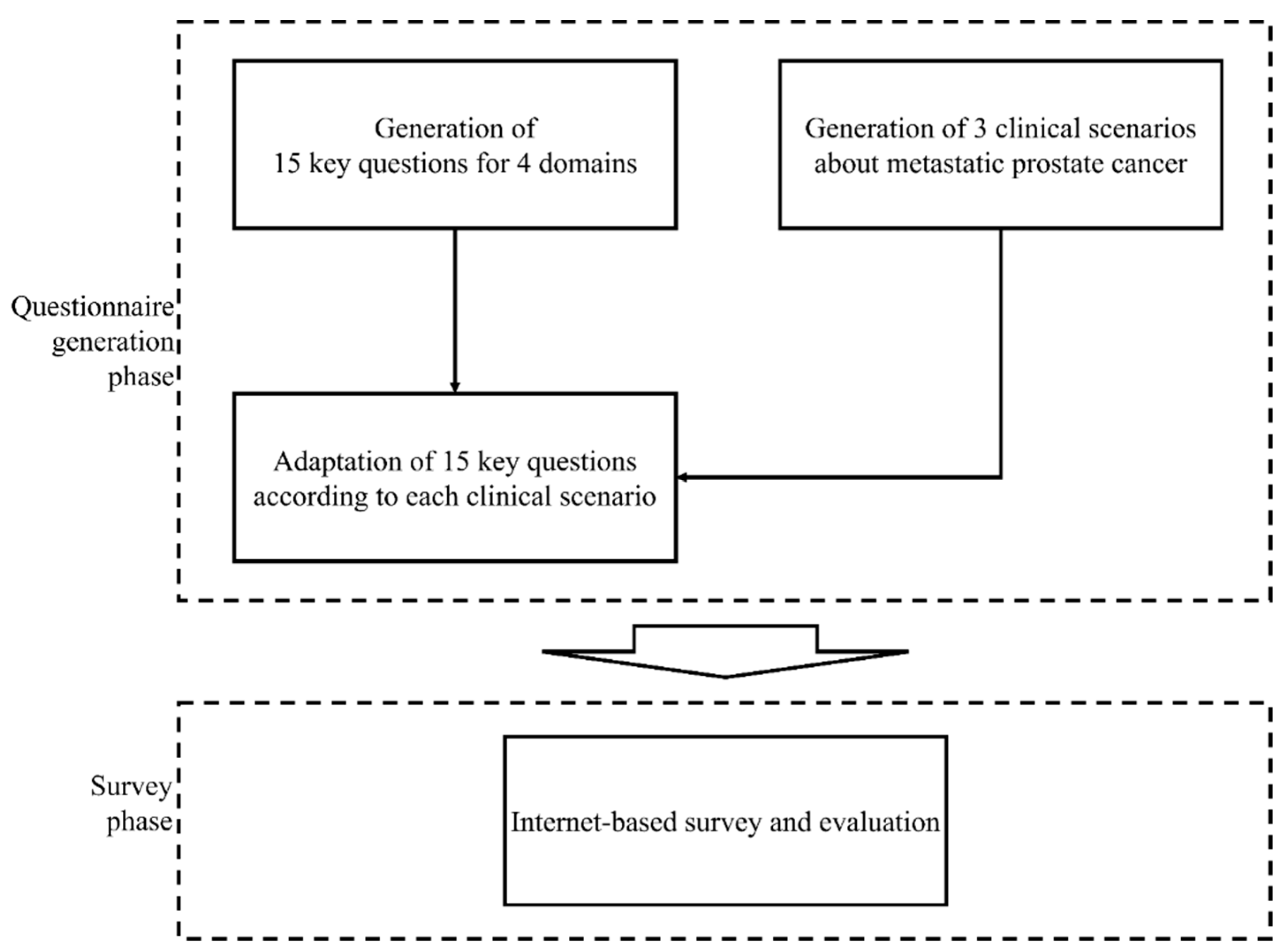
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Definitions
3.2. Diagnosis
3.3. Treatment
3.4. Endpoint
4. Discussion
4.1. Definitions
4.2. Diagnosis
4.3. Treatment
4.4. Endpoint
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ADT | Androgen deprivation therapy |
| BED | Biological effective dose |
| CRPC | Castration-resistant prostate cancer |
| ENRT | Elective nodal radiation therapy |
| ESTRO | European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology |
| KQ | Key questions |
| LN | Lymph node |
| MDLT | Metastasis-directed local therapies |
| mPC | Metastatic prostate cancer |
| MDRT | Metastasis-directed RT |
| OMD | Oligometastatic disease |
| OMPC | Oligometastatic prostate cancer |
| PC | Prostate cancer |
| PSA | Prostate-specific antigen |
| PSMA-PET | Prostate-specific membrane antigen positron-emission tomography |
| RT | Radiation therapy |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiation therapy |
References
- Hellman, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, C.H.; Cho, W.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Suh, Y.G.; Kim, K.H.; Chie, E.K.; Ahn, Y.C.; Oligometastasis Working Group, K.C.A. Role of Local Treatment for Oligometastasis: A Comparability-Based Meta-Analysis. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lievens, Y.; Guckenberger, M.; Gomez, D.; Hoyer, M.; Iyengar, P.; Kindts, I.; Mendez Romero, A.; Nevens, D.; Palma, D.; Park, C.; et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: An ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 148, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Vapiwala, N.; Schaeffer, E.M.; Ryan, C.J. Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Shrinking Subset or an Opportunity for Cure? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guckenberger, M.; Lievens, Y.; Bouma, A.B.; Collette, L.; Dekker, A.; deSouza, N.M.; Dingemans, A.C.; Fournier, B.; Hurkmans, C.; Lecouvet, F.E.; et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: A European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e18–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilli, T.; Achard, V.; Dal Pra, A.; Schmidt-Hegemann, N.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Lancia, A.; Ingrosso, G.; Alongi, F.; Aluwini, S.; Arcangeli, S.; et al. Recommendations for radiation therapy in oligometastatic prostate cancer: An ESTRO-ACROP Delphi consensus. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 176, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, M.J.; Smith, A.; Miah, S.; Shah, T.T.; Winkler, M.; Khoo, V.; Ahmed, H.U. Targeting Oligometastasis with Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy or Surgery in Metastatic Hormone-sensitive Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of Prospective Clinical Trials. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohaus, F.; Zophel, K.; Lock, S.; Wirth, M.; Kotzerke, J.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M.; Troost, E.G.C.; Holscher, T. Can Local Ablative Radiotherapy Revert Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer to an Earlier Stage of Disease? Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Takahara, T.; Arita, Y.; Ishii, C.; Uchida, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Toda, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Kijima, T.; Yokoyama, M.; et al. Progressive Site-Directed Therapy for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Localization of the Progressive Site as a Prognostic Factor. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluwini, S.S.; Mehra, N.; Lolkema, M.P.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Yakar, D.; Stoevelaar, H.; van der Poel, H.; Dutch Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Working, G.; Busstra, M.; de Jong, I.J.; et al. Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: Results of a Dutch Multidisciplinary Consensus Meeting. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevens, D.; Jongen, A.; Kindts, I.; Billiet, C.; Deseyne, P.; Joye, I.; Lievens, Y.; Guckenberger, M. Completeness of Reporting Oligometastatic Disease Characteristics in the Literature and Influence on Oligometastatic Disease Classification Using the ESTRO/EORTC Nomenclature. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbato, F.; Fendler, W.P.; Rauscher, I.; Herrmann, K.; Wetter, A.; Ferdinandus, J.; Seifert, R.; Nader, M.; Rahbar, K.; Hadaschik, B.; et al. PSMA-PET for the assessment of metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer volume of disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendler, W.P.; Weber, M.; Iravani, A.; Hofman, M.S.; Calais, J.; Czernin, J.; Ilhan, H.; Saad, F.; Small, E.J.; Smith, M.R.; et al. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Ligand Positron Emission Tomography in Men with Nonmetastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7448–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H. An Update of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Theranostics in Prostate Cancer. Korean J. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 20, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surcel, C.; Kretschmer, A.; Mirvald, C.; Sinescu, I.; Heidegger, I.; Tsaur, I. Molecular Mechanisms Related with Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer-Is It Just a Matter of Numbers? Cancers 2022, 14, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdett, S.; Boeve, L.M.; Ingleby, F.C.; Fisher, D.J.; Rydzewska, L.H.; Vale, C.L.; van Andel, G.; Clarke, N.W.; Hulshof, M.C.; James, N.D.; et al. Prostate Radiotherapy for Metastatic Hormone-sensitive Prostate Cancer: A STOPCAP Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive CAncer Network. Prostate Cancer (Version 1.2023). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/rectal.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Phillips, R.; Shi, W.Y.; Deek, M.; Radwan, N.; Lim, S.J.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Rowe, S.P.; Ross, A.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Deville, C.; et al. Outcomes of Observation vs Stereotactic Ablative Radiation for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: The ORIOLE Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, R.; Mathews, L.; Liu, M.; Schellenberg, D.; Mou, B.; Berrang, T.; Harrow, S.; Correa, R.J.M.; Bhat, V.; Pai, H.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 1-3 Oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-3): Study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bleser, E.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Pasquier, D.; Zilli, T.; Van As, N.; Siva, S.; Fodor, A.; Dirix, P.; Gomez-Iturriaga, A.; Trippa, F.; et al. Metastasis-directed Therapy in Treating Nodal Oligorecurrent Prostate Cancer: A Multi-institutional Analysis Comparing the Outcome and Toxicity of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy and Elective Nodal Radiotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ost, P.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Van As, N.; Zilli, T.; Tree, A.; Henderson, D.; Orecchia, R.; Casamassima, F.; Surgo, A.; Miralbell, R.; et al. Pattern of Progression after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Nodal Recurrences. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 28, e115–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruycker, A.; Spiessens, A.; Dirix, P.; Koutsouvelis, N.; Semac, I.; Liefhooghe, N.; Gomez-Iturriaga, A.; Everaerts, W.; Otte, F.; Papachristofilou, A.; et al. PEACE V—Salvage Treatment of OligoRecurrent nodal prostate cancer Metastases (STORM): A study protocol for a randomized controlled phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Urm, S.; Cho, H. Analysis of biologically equivalent dose of stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary and metastatic lung tumors. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Iglesias, A.L.; Morillo-Macias, V.; Santafe-Jimenez, A.; Ferrer-Albiach, C. Bone-only oligometastatic prostate cancer: Can SABR improve outcomes? A single-center experience. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2022, 40, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ost, P.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; As, N.V.; Zilli, T.; Muacevic, A.; Olivier, K.; Henderson, D.; Casamassima, F.; Orecchia, R.; Surgo, A.; et al. Progression-free Survival Following Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer Treatment-naive Recurrence: A Multi-institutional Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelius, I.R.; Bentzen, S.M. Meta-analysis of the alpha/beta ratio for prostate cancer in the presence of an overall time factor: Bad news, good news, or no news? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Gao, X.S.; Li, X.; Ma, M.; Qi, X.; Shibamoto, Y. Variability of alpha/beta ratios for prostate cancer with the fractionation schedule: Caution against using the linear-quadratic model for hypofractionated radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Park, H.J.; Jang, W.I.; Jeong, B.K.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, A.R. Long-term results and PSA kinetics after robotic SBRT for prostate cancer: Multicenter retrospective study in Korea (Korean radiation oncology group study 15-01). Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, P.; Laudicella, R.; Lanzafame, H.; Farolfi, A.; Mapelli, P.; Picchio, M.; Burger, I.A.; Iagaru, A.; Minutoli, F.; Evangelista, L. PSMA and Choline PET for the Assessment of Response to Therapy and Survival Outcomes in Prostate Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review from the Literature. Cancers 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Questions | Response | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Questions for demographics of respondents | n (%) | |
| Q1. How many years have you practiced as a radiation oncologist? | <10 | 15 (33.3) |
| 10–20 | 12 (26.7) | |
| 20–30 | 15 (33.3) | |
| >30 | 3 (6.7) | |
| Q2. What is the average number of new patient(s) treated by responder per month? | <10 | 4 (8.9) |
| 10–20 | 10 (22.2) | |
| 20–30 | 11 (24.4) | |
| >30 | 20 (44.4) | |
| Q3. Do you participate in the treatment of OMD? | Yes | 44 (97.8) |
| No | 1 (2.2) | |
| Q4. What is the average number of OMD patient(s) treated by responder per year? | <10 | 24 (53.3) |
| 10–20 | 6 (13.3) | |
| 20–30 | 5 (11.1) | |
| >30 | 10 (22.2) | |
| Q5. Which site do you apply SBRT to in your clinical practice? (multiple choices) | None | 9 (20.0) |
| Bone | 30 (66.7) | |
| Lung | 29 (64.4) | |
| Liver | 20 (44.4) | |
| LN | 17 (37.8) | |
| Brain | 21 (46.7) | |
| Key questions for clinical issues | Adapted questions and choices | n/total n (%) |
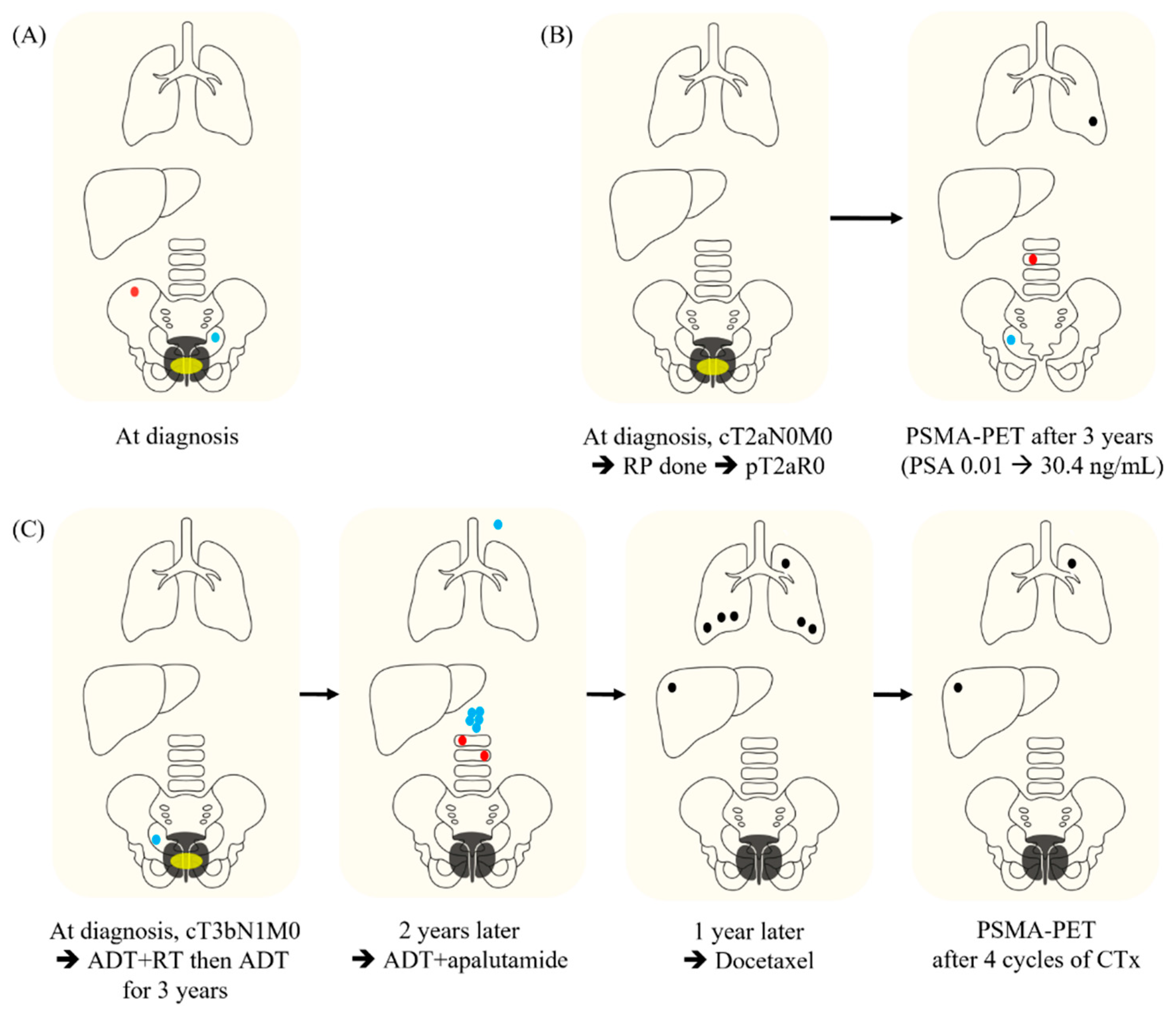
| Definition KQ1. Does the definition of OMPC depend on the sites of metastasis? KQ2. Are there criteria in the number of metastases or metastatic organs for the definition of OMPC? KQ3. Is the definition of OMPC limited to the concept of low-volume metastasis? KQ4. Are there criteria for the maximum size of metastases for the definition of OMPC? KQ5. Does the OMPC include the induced oligometastatic disease from polymetastatic disease after systemic therapy? KQ6. Is the concept of OMPC valid for CRPC? | Which case can be included in OMPC? (multiple choices) | |
| Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 | 40/43 (93.0) 30/43 (69.8) 18/39 (46.2) | |
| If Case 3 is not included in the category of OMPC, what can be the reason? (multiple choices) | ||
| History of polymetastasis Progression to CRPC Insufficiency in test for confirmation of OMPC This case is included in the category of OMPC. | 21/39 (53.8) 6/39 (15.4) 1/39 (2.6) 18/39 (46.2) | |
| Diagnosis | ||
| KQ7. Is there a PSMA-PET requirement to define OMPC? | Is PSMA-PET required to confirm OMPC in Case 1? | |
| Yes No | 26/43 (60.5) 17/43 (39.5) | |
| KQ8. Is there any biochemical marker representing occult polymetastasis? | Can a steep PSA increase be a marker for the exclusion of OMPC in Case 2? | |
| Yes No | 13/43 (30.2) 30/43 (69.8) | |
| Treatment | ||
| KQ9. Should primary prostate cancer be controlled? | Which local treatment do you recommend for primary tumor in Case 1? (multiple choice) | |
| Definitive treatment is not recommended. RP + PLND RP + PLND + adjuvant RT Definitive RT | 3/43 (7.0) 0/43 (0.0) 6/43 (14.0) 40/43 (93.0) | |
| KQ10. Are additional metastasis-directed local therapies including surgery, radiofrequency ablation, and/or RT for OMPC beneficial over the systemic therapy only? KQ11. Should metastasis-directed RT for OMPC encompass the whole metastatic disease burden? | Is MDL(R)T required? | |
| For Case 1 | ||
| Yes (MDRT for all metastatic lesions is required.) | 42/43 (97.7) | |
| For Case 2 (multiple choices) | ||
| MDRT for all metastatic lesion Resection of lung metastasis and RT for other lesions | 25/43 (58.1) 19/43 (44.2) | |
| For Case 3 | ||
| RT for whole metastatic lesions | 28/39 (71.8) | |
| KQ12. Is cessation of systemic therapy possible if metastasis-directed RT alone shows the local control of oligometastases? | Is STx required even if LC is achieved after MDRT? | |
| For Case 1 (multiple choices) | ||
| Yes | 34/43 (79.1) | |
| ADT but if local treatment is applied and PSA levels are undetectable, discontinuation of ADT | 12/43 (27.9) | |
| Systemic therapy is not recommended. | 1/43 (2.3) | |
| For Case 2: NA | ||
| For Case 3 | ||
| Yes No | 34/39 (87.2) 5/39 (12.8) | |
| KQ13. Is there a recommended optimal timing for the metastasis-directed RT for OMPC? | What is the optimal timing for MDRT? (multiple choices) For Case 1 | |
| Same timing as local treatment for primary tumor | 40/43 (93.0) | |
| For Case 2 | ||
| Concurrently with STx Prior to STx 2–3 months after initiation of STx When lesion-related symptoms develop while maintaining STx When PSA rises during the maintenance of systemic therapy | 17/43 (39.5) 1/43 (2.3) 22/43 (51.2) 11/43 (25.6) 11/43 (25.6) | |
| For Case 3: NA | ||
| KQ14. Are there recommended dose-fractionation regimens for the metastasis-directed RT for OMPC? | What are the recommended dose-fractionation regimens for MDRT? (multiple choices) | |
| For Case 1 | ||
| For pelvic bone metastasis | ||
| Palliative RT dose (eg., 30 Gy/10–12 fx, 20 Gy/4–5 fx, 8 Gy/1 fx, etc., or similar dose-fx scheme) | 7/43 (16.3) | |
| SBRT (≤5 fractions) (eg., 18–24 Gy/1 fx, 20–24 Gy/2 fx, 21–30 Gy/3 fx, etc., or similar dose-fx scheme) | 25/43 (58.1) | |
| Moderate dose RT (eg., 30–36 Gy/6 fx, 40–48 Gy/8 fx, 40–50 Gy/10 fx, 39–45 Gy/13–15 fx, etc., or similar dose-fx scheme) | 18/43 (41.9) | |
| Definitive dose with conventional fx (eg., 50–60 Gy in 20–30 fx, etc., with 1.8–2.0 Gy per fx) | 15/43 (34.9) | |
| For Case 2 | ||
| For spine metastasis | ||
| Palliative RT dose SBRT (≤5 fractions) Moderate dose RT Definitive dose with conventional fx | 10/43 (23.3) 30/43 (69.8) 13/43 (30.2) 2/43 (4.7) | |
| For LN metastasis | ||
| Palliative dose RT to LN only Hypofractionated high-dose RT to LN only High-dose conventional RT to LN only: 14.0 High-dose conventional RT to whole pelvis | 3/43 (7.0) 29/43 (67.4) 6/43 (14.0) 10/43 (23.3) | |
| For lung metastasis | ||
| Palliative dose RT SBRT with BED10 ≥ 100 Gy SBRT with BED3 ≥ 100 Gy Moderate-dose RT Definitive dose with conventional fx | 4/43 (9.3) 27/43 (62.8) 14/43 (32.6) 15/43 (43.9) 3/43 (7.0) | |
| For Case 3 | ||
| For lung and liver metastasis | ||
| Palliative dose RT SBRT with BED10 ≥ 100 Gy SBRT with BED3 ≥ 100 Gy Moderate-dose RT Definitive dose with conventional fx | 7/39 (17.9) 24/39 (61.5) 9/39 (23.1) 14/39 (35.9) 1/39 (2.6) | |
| Endpoint | ||
| KQ15. What endpoints are important for OMPC? | Which parameter represents the outcome of MDRT? (multiple choices) | |
| For Case 1 | ||
| Radiological response of RT target New lesion PSA response | 33/43 (76.7) 32/43 (74.4) 37/43 (86.1) | |
| For Case 2 | ||
| Radiological response of RT target New lesion PSA response | 35/43 (81.4) 31/43 (72.1) 31/43 (72.1) | |
| For Case 3: NA Do you think PSMA-PET is necessary to evaluate remission after RT in Case 3? | ||
| Yes No | 24/39 (61.5) 15/39 (38.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, G.S.; Park, S.; Rim, C.H.; Cho, W.K.; Chang, A.R.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, Y.C.; Chie, E.K., on behalf of the Oligometastasis Working Group, Korean Cancer Association. Radiation Oncologists’ Perspectives on Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Survey from Korean Oligometastasis Working Group. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 3239-3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31060245
Yoo GS, Park S, Rim CH, Cho WK, Chang AR, Kim YS, Ahn YC, Chie EK on behalf of the Oligometastasis Working Group, Korean Cancer Association. Radiation Oncologists’ Perspectives on Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Survey from Korean Oligometastasis Working Group. Current Oncology. 2024; 31(6):3239-3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31060245
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Gyu Sang, Sunmin Park, Chai Hong Rim, Won Kyung Cho, Ah Ram Chang, Young Seok Kim, Yong Chan Ahn, and Eui Kyu Chie on behalf of the Oligometastasis Working Group, Korean Cancer Association. 2024. "Radiation Oncologists’ Perspectives on Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Survey from Korean Oligometastasis Working Group" Current Oncology 31, no. 6: 3239-3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31060245
APA StyleYoo, G. S., Park, S., Rim, C. H., Cho, W. K., Chang, A. R., Kim, Y. S., Ahn, Y. C., & Chie, E. K., on behalf of the Oligometastasis Working Group, Korean Cancer Association. (2024). Radiation Oncologists’ Perspectives on Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer: A Survey from Korean Oligometastasis Working Group. Current Oncology, 31(6), 3239-3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol31060245






