Focus on Therapeutic Options for Surgically Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Based on Novel Biomarkers
Abstract
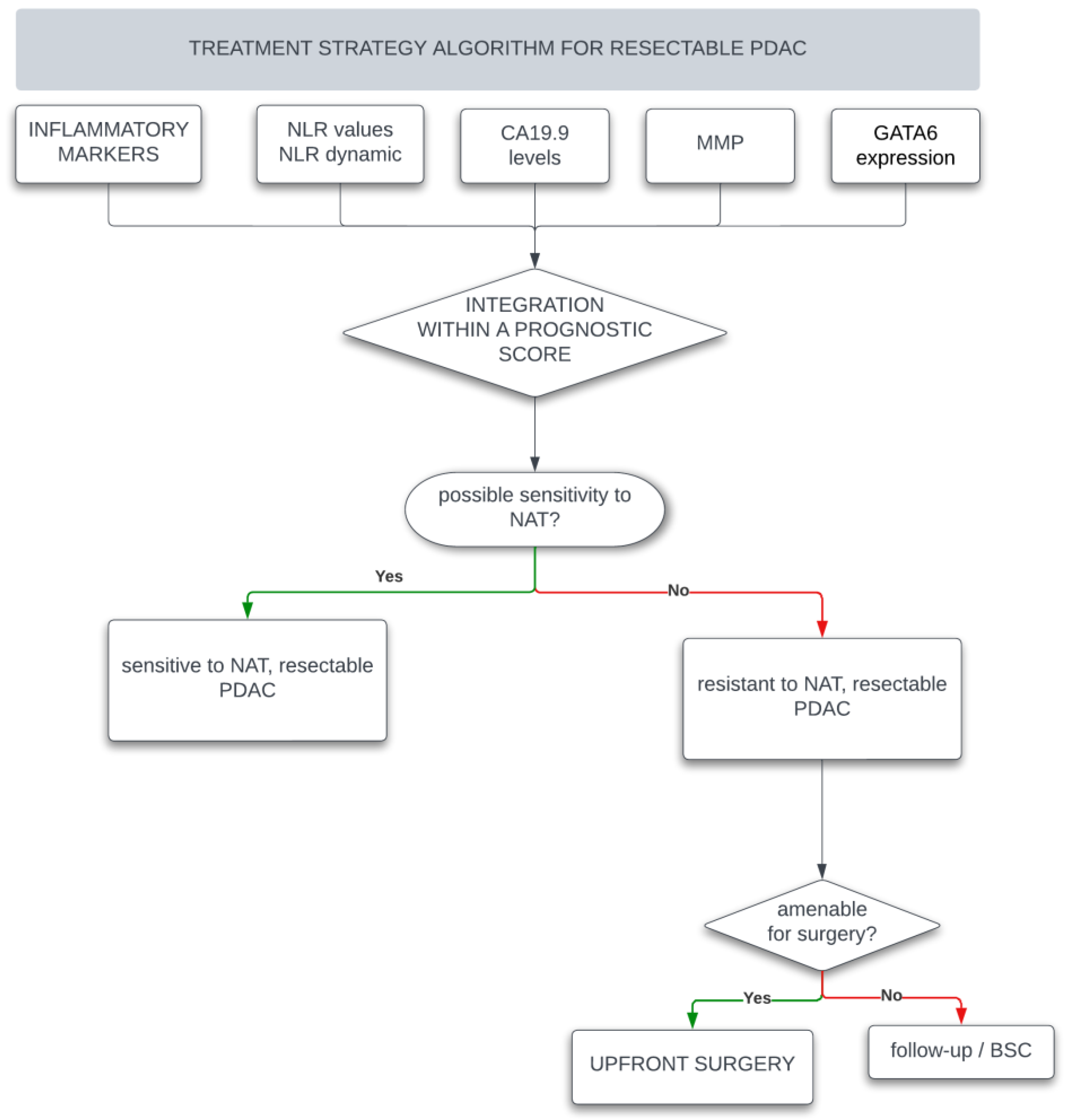
1. Introduction
2. Tumor Immune Microenvironment
3. Prognostically Significant Tumor Immune Biomarkers
4. Predictive and Prognostic Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio
5. Predictive and Prognostic Role of Inflammatory Markers
6. Predictive and Prognostic Role of Tumor Secreted Biomarkers
7. Combined Biomarkers Scores
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linee Guida CARCINOMA DEL PANCREAS ESOCRINO Edizione 2021. Available online: https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/8403839/LG_270_ca_pancreas_agg2021 (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Kommalapati, A.; Tella, S.H.; Goyal, G.; Ma, W.W.; Mahipal, A. Contemporary management of localized resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, D.; Fou, L.; Hasler, E.; Hawkins, J.; O’Connell, S.; Pelone, F.; Callaway, M.; Campbell, F.; Capel, M.; Charnley, R.; et al. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer in adults: A summary of guidelines from the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versteijne, E.; Vogel, J.A.; Besselink, M.G.; Busch, O.R.C.; Wilmink, J.W.; Daams, J.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Koerkamp, B.G.; Rasch, C.R.N.; van Tienhoven, G. Meta-analysis comparing upfront surgery with neoadjuvant treatment in patients with resectable or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsano, R.; Tommasi, C.; Garajova, I. State of the Art for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: Where Are We Now? Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dam, J.L.; Janssen, Q.P.; Besselink, M.G.; Homs, M.Y.; van Santvoort, H.C.; van Tienhoven, G.; de Wilde, R.F.; Wilmink, J.W.; van Eijck, C.H.; Koerkamp, B.G.; et al. Neoadjuvant therapy or upfront surgery for resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 160, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufferlein, T.; Uhl, W.; Kornmann, M.; Algül, H.; Friess, H.; König, A.; Ghadimi, M.; Gallmeier, E.; Bartsch, D.; Lutz, M.; et al. Perioperative or only adjuvant gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel for resectable pancreatic cancer (NEONAX)—A randomized phase II trial of the AIO pancreatic cancer group. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Lambert, A.; Ducreux, M. Adjuvant and neoadjuvant approaches in pancreatic cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2023, 35, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.E.; Wo, J.Y.; Ryan, D.P.; Jiang, W.; Yeap, B.Y.; Drapek, L.C.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; et al. Total Neoadjuvant Therapy with FOLFIRINOX Followed by Individualized Chemoradiotherapy for Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempero, M.A.; Malafa, M.P.; Al-Hawary, M.; Behrman, S.W.; Benson, A.B.; Cardin, D.B.; Chiorean, E.G.; Chung, V.; Czito, B.; Del Chiaro, M.; et al. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, S.; Pavlakis, N.; Itchins, M.; Arena, J.; Mittal, A.; Hudson, A.; Colvin, E.; Sahni, S.; Diakos, C.; Chan, D.; et al. The Prognostic and Predictive Role of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), and Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio (LMR) as Biomarkers in Resected Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, G.; Prakash, L.; Wang, H.; Bhosale, P.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Wolff, R.; Fogelman, D.; Overman, M.; Pant, S.; Javle, M.; et al. Radiographic and Serologic Predictors of Pathologic Major Response to Preoperative Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2019, 273, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, U.; Sun, H.; Hinz, U.; Klaiber, U.; Tanaka, M.; Liu, B.; Sachsenmaier, M.; Springfeld, C.; Michalski, C.W.; Büchler, M.W.; et al. Induction chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer: CA 19-9 may predict resectability and survival. HPB 2020, 22, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redegalli, M.; Lena, M.S.; Cangi, M.G.; Smart, C.E.; Mori, M.; Fiorino, C.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Balzano, G.; Falconi, M.; Reni, M.; et al. Proposal for a New Pathologic Prognostic Index after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PINC). Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3492–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Fujimori, N.; Ohno, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Teramatsu, K.; Takamatsu, Y.; Takeno, A.; Oono, T.; Abe, T.; Ideno, N.; et al. Predictive factors of operability after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: A single-center retrospective study. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.d.C.; Bianchi, A.; Deshpande, N.U.; Sharma, P.; Mehra, S.; Garrido, V.T.; Saigh, S.J.; England, J.; Hosein, P.J.; Kwon, D.; et al. Neutrophil-mediated fibroblast-tumor cell il-6/stat-3 signaling underlies the association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio dynamics and chemotherapy response in localized pancreatic cancer: A hybrid clinical-preclinical study. Elife 2022, 11, e78921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y.; Hodges, J.C.; Barclay, D.; Brand, R.; Simmons, R.L.; Lee, K.K.; Paniccia, A.; Murthy, P.; et al. Baseline plasma inflammatory profile is associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Immunother. 2021, 44, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Huang, Z.; Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y. Quantitative definitions of pain, CA19-9, and tumor size as high-risk features of resectable pancreatic cancer: A single-center retrospective cohort study. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.H.; Hwang, H.K.; Lee, W.J.; Kang, C.M. Systemic inflammation response index correlates with survival and predicts oncological outcome of resected pancreatic cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Pancreatology 2022, 22, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, P.; Zenati, M.S.; Al Abbas, A.I.; Rieser, C.J.; Bahary, N.; Lotze, M.T.; ZehIII, H.J.; Zureikat, A.; Boone, B.A. Prognostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) After Neoadjuvant Therapy for Patients with Resected Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, S.B.; Pinese, M.; Jamieson, N.B.; Scarlett, C.J.; Colvin, E.K.; Pajic, M.; Johns, A.L.; Humphris, J.L.; Wu, J.; Cowley, M.J.; et al. Precision Oncology in Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Han, H.-S.; Kim, S.T.; Hwang, I.; Chun, Y.-O. The impact of acute inflammation on progression and metastasis in pancreatic cancer animal model. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoucair, S.; Chen, J.; Martinson, J.R.; Habib, J.R.; Kinny-Köster, B.; Pu, N.; van Oosten, A.F.; Javed, A.A.; Shin, E.J.; Ali, S.Z.; et al. Association of Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 Expression with Pathologic Response after Neoadjuvant Treatment in Patients with Resected Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Surg. 2022, 157, e221362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swidnicka-Siergiejko, A.K.; Gomez-Chou, S.B.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Deng, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Ji, B.; Azizian, N.; Daniluk, J.; Lu, W.; et al. Chronic inflammation initiates multiple forms of K-Ras-independent mouse pancreatic cancer in the absence of TP53. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3149–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Luo, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Gu, J.; Qi, X.; Wu, T. The prognostic value of CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) in cancers: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15068–15076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Kim, H.; Shi, J. Neutrophil in the Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.F.B.; Mortensen, M.B.; Detlefsen, S. Key players in pancreatic cancer-stroma interaction: Cancer-associated fibroblasts, endothelial and inflammatory cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2678–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Masamune, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Inflammation and pancreatic cancer: Disease promoter and new therapeutic target. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, P.; Hanahan, D. Breaching the Cancer Fortress. Science 2009, 324, 1400–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, Ç.U.; Karabulut, M.; Karabulut, S.; Alis, H.; Gonenc, M.; Dagoglu, N.; Serilmez, M.; Tas, F. Circulating interleukin-18 (IL-18) is a predictor of response to gemcitabine based chemotherapy in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, W.; Lytle, N.K.; Huang, P.; Yuan, X.; Dann, A.M.; Ridinger-Saison, M.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Antal, C.E.; Liang, G.; et al. Targeting LIF-mediated paracrine interaction for pancreatic cancer therapy and monitoring. Nature 2019, 569, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Byrne, K.T.; Yan, F.; Yamazoe, T.; Chen, Z.; Baslan, T.; Richman, L.P.; Lin, J.H.; Sun, Y.H.; Rech, A.J.; et al. Tumor Cell-Intrinsic Factors Underlie Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Infiltration and Response to Immunotherapy. Immunity 2018, 49, 178–193.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saung, M.T.; Zheng, L. Adding combination immunotherapy consisting of cancer vaccine, anti-PD-1 and anti-CSF1R antibodies to gemcitabine improves anti-tumor efficacy in murine model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann. Pancreat. Cancer 2019, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Tang, T.; Liang, T. Identification of tumor antigens and immune subtypes of pancreatic adenocarcinoma for mRNA vaccine development. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Mugaanyi, J.; Cai, X.; Lu, C.; Lu, C. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma associated immune-gene signature as a novo risk factor for clinical prognosis prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, K.; Castillo, C.F.-D.; Liss, A.S. Epigenetic regulation of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in the era of cancer immunotherapy. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, M. Construction of a cancer-associated fibroblasts-related long non-coding RNA signature to predict prognosis and immune landscape in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 989719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Qu, Z.; Chi, D.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, C. Characterization of anoikis-based molecular heterogeneity in pancreatic cancer and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and its association with tumor immune microenvironment and metabolic remodeling. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1153909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Dong, D. An Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis of ADAMTS12 and Its Potential Implications in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 849717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; He, C.; Yao, H.; Liang, W.; Ye, X.; Ruan, J.; Lin, L.; Zou, J.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. GLUT1 Regulates the Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Promotes Tumor Metastasis in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma via ncRNA-mediated Network. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 2540–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Ke, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Z.-P.; Hu, P.; Wu, X. SQLE, A Key Enzyme in Cholesterol Metabolism, Correlates with Tumor Immune Infiltration and Immunotherapy Outcome of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 864244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.; Huang, X. Identification of SHCBP1 as a potential biomarker involving diagnosis, prognosis, and tumor immune microenvironment across multiple cancers. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 3106–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Guo, Y.; Mo, Z. TLR3 serves as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and is closely correlated with immune microenvironment in three types of cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 905988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Zuo, R.; Sa, Y.; Ma, Z.; OuYang, H. Interferon alpha-inducible protein 27 (IFI27) is a prognostic marker for pancreatic cancer based on comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 8515–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shen, J.; Li, T.; Xu, Y. Quantification of m6A RNA methylation modulators pattern was a potential biomarker for prognosis and associated with tumor immune microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Analysis of N6-Methyladenosine Modification Patterns and Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 752025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yin, L.; Xu, Q.; Xiang, J.; Xu, R. N6-methyladenosine methylation modification patterns reveal immune profiling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Ling, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Zheng, R. Construction and Validation of an Immune-Based Prognostic Model for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Based on Public Databases. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 702102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, L.; Ji, J.; Xie, R.; Wu, C.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Peng, C.; et al. Identification of KRAS G12V associated clonal neoantigens and immune microenvironment in long-term survival of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosein, A.N.; Dangol, G.; Okumura, T.; Roszik, J.; Rajapakshe, K.; Siemann, M.; Zaid, M.; Ghosh, B.; Monberg, M.; Guerrero, P.A.; et al. Loss of Rnf43 Accelerates Kras-Mediated Neoplasia and Remodels the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1303–1318.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hong, D.S. Targeting KRAS: Crossroads of Signaling and Immune Inhibition. J. Immunother. Precis. Oncol. 2022, 5, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridlender, Z.G.; Sun, J.; Kim, S.; Kapoor, V.; Cheng, G.; Ling, L.; Worthen, G.S.; Albelda, S.M. Polarization of Tumor-Associated Neutrophil Phenotype by TGF-β: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoustidis, A.; Neofytou, K.; Neves, M.C.; Giakoustidis, D.; Louri, E.; Cunningham, D.; Mudan, S. Identifying the role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelets-to-lymphocyte ratio as prognostic markers in patients undergoing resection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2018, 22, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.-P.; Xu, X.-Y.; Ji, Y.; Huang, P.-W. The Prognostic Value of Preoperative Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Resected Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Nakata, K.; Kibe, S.; Mori, Y.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ohuchida, K.; Ohtsuka, T.; Oda, Y.; Nakamura, M. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Nutritional and Immunological Factors in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 3996–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Pyo, J.-S.; Son, B.K. Prognostic roles of inflammatory markers in pancreatic cancer: Comparison between the neutro-phil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 9745601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Huang, T.L.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Hardacre, J.M.; Siegel, C.; Ammori, J.B. Pretherapy neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio do not predict survival in resectable pancreatic cancer. HPB 2018, 20, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, J.S.; Vos, E.L.; Mcintyre, C.A.; Chou, J.F.; Gonen, M.; Tang, L.H.; Soares, K.C.; Balachandran, V.P.; Kingham, T.P.; D’Angelica, M.I.; et al. Change in Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio During Neoadjuvant Treatment Does Not Predict Pathological Response and Survival in Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Am. Surg. 2022, 88, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, E.A.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.; Manson, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. Interrelationships among Circulating Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, and Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Women. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, P.B.; Wolfe, R.R.; Shenkin, A. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, M.J.; Morrison, D.S.; Talwar, D.; Balmer, S.M.; O’Reilly, D.S.J.; Foulis, A.K.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. An inflammation-based prognostic score (mGPS) predicts cancer survival independent of tumour site: A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, P.; Carrillo-de Santa Pau, E.; Cox, T.; Sainz, B.; Dusetti, N.; Greenhalf, W.; Rinaldi, L.; Costello, E.; Ghaneh, P.; Malats, N.; et al. GATA6 regulates EMT and tumour dissemination, and is a marker of response to adjuvant chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Jang, G.-H.; Grant, R.C.; Wilson, J.M.; Notta, F.; O’kane, G.M.; Knox, J.J.; Gallinger, S.; Fischer, S. The value of GATA6 immunohistochemistry and computer-assisted diagnosis to predict clinical outcome in advanced pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, P.L.S.U.; Carvalho, L.; Fernandes, M.L.C.; Botrus, G.; Martins, R.D.S.; da Silva, E.F.; dos Santos, S.S.M.B.; Taniwaki, L.; Taranto, P.; Dutra, A.C.P.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or upfront surgery in localized pancreatic cancer: A contemporary analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zenati, M.S.; Rieser, C.J.; Al-Abbas, A.; Lee, K.K.; Singhi, A.D.; Bahary, N.; Hogg, M.E.; Zeh, H.J.; Zureikat, A.H. CA19-9 Change During Neoadjuvant Therapy May Guide the Need for Additional Adjuvant Therapy Following Resected Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 3950–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.-W.; Shen, J.; Gao, J.-H.; Shi, X.-H.; Gao, S.-Z.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Yuan, W.-L.; Lin, L.; Jin, G. A preoperative risk model for early recurrence after radical resection may facilitate initial treatment decisions concerning the use of neoadjuvant therapy for patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Surgery 2020, 168, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy endows CD9 with prognostic value that differs between tumor and stromal areas in patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Okano, K.; Sato, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Shimomura, A.; Nagao, M.; Matsukawa, H.; Ando, Y.; Suto, H.; Oshima, M.; et al. Tumor metabolic alterations after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy predict postoperative recurrence in patients with pancreatic cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 52, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.E.; Humphreys, M.J.; Campbell, F.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Boyd, M.T. Comprehensive Analysis of Matrix Metalloproteinase and Tissue Inhibitor Expression in Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2832–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Egami, H.; Abe, M.; Nozawa, F.; Hirota, M.; Ogawa, M. Involvement of MMP-7 in invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through activation of the EGFR mediated MEK–ERK signal transduction pathway. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slapak, E.J.; Duitman, J.; Tekin, C.; Bijlsma, M.F.; Spek, C.A. Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression? Biology 2020, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, K.F.; van Till, J.O.; Boermeester, M.A.; de Reuver, P.R.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Kate, F.J.T.; Busch, O.R.; van Gulik, T.M.; Gouma, D.J.; et al. Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 in Plasma and Pancreatic Juice as a Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hank, T.; Sandini, M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Ryan, D.P.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Qadan, M.; Wo, J.Y.; Klaiber, U.; Weekes, C.D.; Weniger, M.; et al. A Combination of Biochemical and Pathological Parameters Improves Prediction of Postresection Survival after Preoperative Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulat, C.; Canivet, C.; Touraine, C.; Gourgou, S.; Napoleon, B.; Palazzo, L.; Flori, N.; Piessen, G.; Guibert, P.; Truant, S.; et al. A new score to predict the resectability of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: The BACAP score. Cancers 2020, 12, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarker | % Tumor Regression (p Value) | DFS in Months (p Value) | Median OS in Months (p Value) | Value Cutoff | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLR | p = 0.03 | NA | NA | 150 | Maloney et al., 2023 [11] |
| Post-treatment CA19.9 | Higher likelihood of pMR for lower CA19.9 values (p < 0.01) | NA | NA | 37 U/mL | Perri et al., 2021 [12] |
| post-NACT CA19.9 | NA | NA | 35.2 (above cutoff) vs. 19.4 (below cutoff) (p = 0.038) | 91.8 U/mL | Heger et al., 2020 [13] |
| Perineural invasion (present) | NA | p = 0.016 | p = 0.006 | NA | Redegalli et al., 2022 [14] |
| Lymph node ratio | NA | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | NA | Redegalli et al., 2022 [14] |
| Stroma-to-neoplasia ratio | NA | p = 0.021 | p = 0.002 | NA | Redegalli et al., 2022 [14] |
| PINC | NA | p < 0.0002 | p < 0.0001 | ≥0.599 | Redegalli et al., 2022 [14] |
| NLR | p = 0.012 | NA | NA | NA | Murakami et al., 2022 [15] |
| NLR pre-chemo + ∆NLR | NA | p = 0.006 | p = 0.002 | NA | Silva et al., 2022 [16] |
| IL2Ra | p = 0.045 | NA | NA | NA | Chopra et al., 2021 [17] |
| Biomarker | Median RFS in Months (p Value) | Median OS in Months (p Value) | Median DFS in Months (p Value) | Value Cutoff | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | NA | 13.0 above cutoff, 32.4 below cutoff (p = 0.001) | NA | 5 | Maloney et al., 2023 [11] |
| NLR | NA | 18.8 below cutoff vs. 10.6 above cutoff (p < 0.001) | NA | 3.69 | Xu et al., 2021 [18] |
| PLR | NA | 20.20 below cutoff vs. 16.50 above cutoff (p = 0.031) | NA | 141.7 | Xu et al., 2021 [18] |
| CA19.9 | NA | 14.2 above cutoff, 19.4 below cutoff (p = 0.004) | NA | 1000 U/mL | Xu et al., 2021 [18] |
| mGPS | NA | p = 0.028 | NA | NA | Maloney et al., 2023 [11] |
| SIRIpost-neoadjuvant | NA | NA | p = 0.030 | 0.8710 | Kim et al., 2022 [19] |
| SIRIquotient | NA | p = 0.037 | NA | 0.9516 | Kim et al., 2022 [19] |
| SII | NA | p = 0.05 | NA | 900 | Murthy et al., 2020 [20] |
| S100A2 | NA | p < 0.001 | NA | NA | Dreyer et al., 2020 [21] |
| S100A4 | NA | p < 0.001 | NA | NA | Dreyer et al., 2020 [21] |
| T-CD9 | p = 0.007 | NA | NA | NA | Ahn X et al., 2022 [22] |
| S-CD9 | NA | p = 0.005 | NA | NA | Ahn X et al., 2022 [22] |
| MMP-7 | 37.3 (negative value) vs. 13.8 (positive value), p = 0.03 | 38.2 (negative value) vs. 27.6 (positive value), p = 0.049 | NA | IHC positivity | Shoucair et al., 2022 [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivari, A.; Agnetti, V.; Garajová, I. Focus on Therapeutic Options for Surgically Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Based on Novel Biomarkers. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 6462-6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070475
Olivari A, Agnetti V, Garajová I. Focus on Therapeutic Options for Surgically Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Based on Novel Biomarkers. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(7):6462-6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070475
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivari, Alessandro, Virginia Agnetti, and Ingrid Garajová. 2023. "Focus on Therapeutic Options for Surgically Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Based on Novel Biomarkers" Current Oncology 30, no. 7: 6462-6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070475
APA StyleOlivari, A., Agnetti, V., & Garajová, I. (2023). Focus on Therapeutic Options for Surgically Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Based on Novel Biomarkers. Current Oncology, 30(7), 6462-6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070475





