Safety and Feasibility of Steerable Radiofrequency Ablation in Combination with Cementoplasty for the Treatment of Large Extraspinal Bone Metastases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Study Design
2.2. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) and Cementoplasty Procedure
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
- radiation is no longer an option because the maximum tolerable dose has been reached;
- pain prevents lying in the prone position for radiation therapy planning and course of treatment;
- tumor histology is a radiation-resistant tumor and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is not available.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coleman, R.E. Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12 Pt 2, 6243s–6249s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- So, A.; Chin, J.; Fleshner, N.; Saad, F. Management of skeletal-related events in patients with advanced prostate cancer and bone metastases: Incorporating new agents into clinical practice. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2012, 6, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Moos, R.; Costa, L.; Gonzalez-Suarez, E.; Terpos, E.; Niepel, D.; Body, J.J. Management of bone health in solid tumours: From bisphosphonates to a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 76, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2021. Metastatic Spine Tumors. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cns.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Moynagh, M.R.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.R. Thermal Ablation of Bone Metastases. Semin Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.; Byrne, C.; Pusceddu, C.; Buy, X.; Tsoumakidou, G.; Filippiadis, D. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Thermal Ablation of Bone Tumours. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2022, 45, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Eber, M.R.; Widner, D.B.; Shiozawa, Y. Role of the Bone Microenvironment in the Development of Painful Complications of Skeletal Metastases. Cancers 2018, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anchala, P.R.; Irving, W.D.; Hillen, T.J.; Friedman, M.V.; Georgy, B.A.; Coldwell, D.M.; Tran, N.D.; Vrionis, F.D.; Brook, A.; Jennings, J.W. Treatment of metastatic spinal lesions with a navigational bipolar radiofrequency ablation device: A multicenter retrospective study. Pain Physician 2014, 17, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Hillen, T.J.; Anchala, P.; Friedman, M.V.; Jennings, J.W. Treatment of metastatic posterior vertebral body osseous tumors by using a targeted bipolar radiofrequency ablation device: Technical note. Radiology 2014, 273, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagla, S.; Sayed, D.; Smirniotopoulos, J.; Brower, J.; Neal Rutledge, J.; Dick, B.; Carlisle, J.; Lekht, I.; Georgy, B. Multicenter Prospective Clinical Series Evaluating Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Painful Spine Metastases. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Staso, M.; Zugaro, L.; Gravina, G.L.; Bonfili, P.; Marampon, F.; di Nicola, L.; Conchiglia, A.; Ventura, L.; Franzese, P.; Gallucci, M.; et al. A feasibility study of percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation followed by Radiotherapy in the management of painful osteolytic bone metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, C.; Lutz, S.T. External beam radiotherapy and bone metastases. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2014, 3, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, R.; Hadji, P.; Body, J.J.; Santini, D.; Chow, E.; Terpos, E.; Oudard, S.; Bruland, Ø.; Flamen, P.; Kurth, A.; et al. Bone health in cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, L.D.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Wittig, J.C. Chondroblastoma: Radiofrequency ablation—Alternative to surgical resection in selected cases. Radiology 2009, 251, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Goetz, M.P.; Rubin, J.; Atwell, T.D.; Farrell, M.A.; Welch, T.J.; Maus, T.P. Image-guided ablation of painful metastatic bone tumors: A new and effective approach to a difficult problem. Skelet. Radiol. 2006, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusceddu, C.; De Francesco, D.; Melis, L.; Ballicu, N.; Fancellu, A. The Role of a Navigational Radiofrequency Ablation Device and Concurrent Vertebral Augmentation for Treatment of Difficult-to-Reach Spinal Metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4004–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.N.; Huang, A.J.; Vaswani, D.; Chang, R.O.; Jennings, J.W. Combination acetabular radiofrequency ablation and cementoplasty using a navigational radiofrequency ablation device and ultrahigh viscosity cement: Technical note. Skelet. Radiol. 2016, 45, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.N.; Tomasian, A.; Chang, R.O.; Jennings, J.W. Treatment of Osteoid Osteomas Using a Navigational Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation System. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 768–772, Erratum in Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 41, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasian, A.; Wallace, A.N.; Hillen, T.J.; Jennings, J.W. Percutaneous Ablation in Painful Bone Tumors. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2016, 20, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, A.; Shaaban, M.H.; Reyad, R.M.; Ragab, A.S.; Sami, M.A. Combined percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and cementoplasty for the treatment of extraspinal painful bone metastases: A prospective study. J. Egypt Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 30, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Yamakado, K.; Maeda, M.; Yasuda, M.; Akeboshi, M.; Takaki, H.; Hamada, A.; Takeda, K. Radiofrequency ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of bone malignancies. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004, 15, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, P.L.; Rashid, F.; Heran, M.K.; Papirny, M.; Liu, D.M.; Malfair, D.; Badii, M.; Clarkson, P.W. Combined cementoplasty and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of painful neoplastic lesions of bone. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.H.; Wu, C.G.; Gu, Y.F.; He, C.J.; Li, M.H.; Cheng, Y.D. Combination radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous osteoplasty for palliative treatment of painful extraspinal bone metastases: A single-center experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

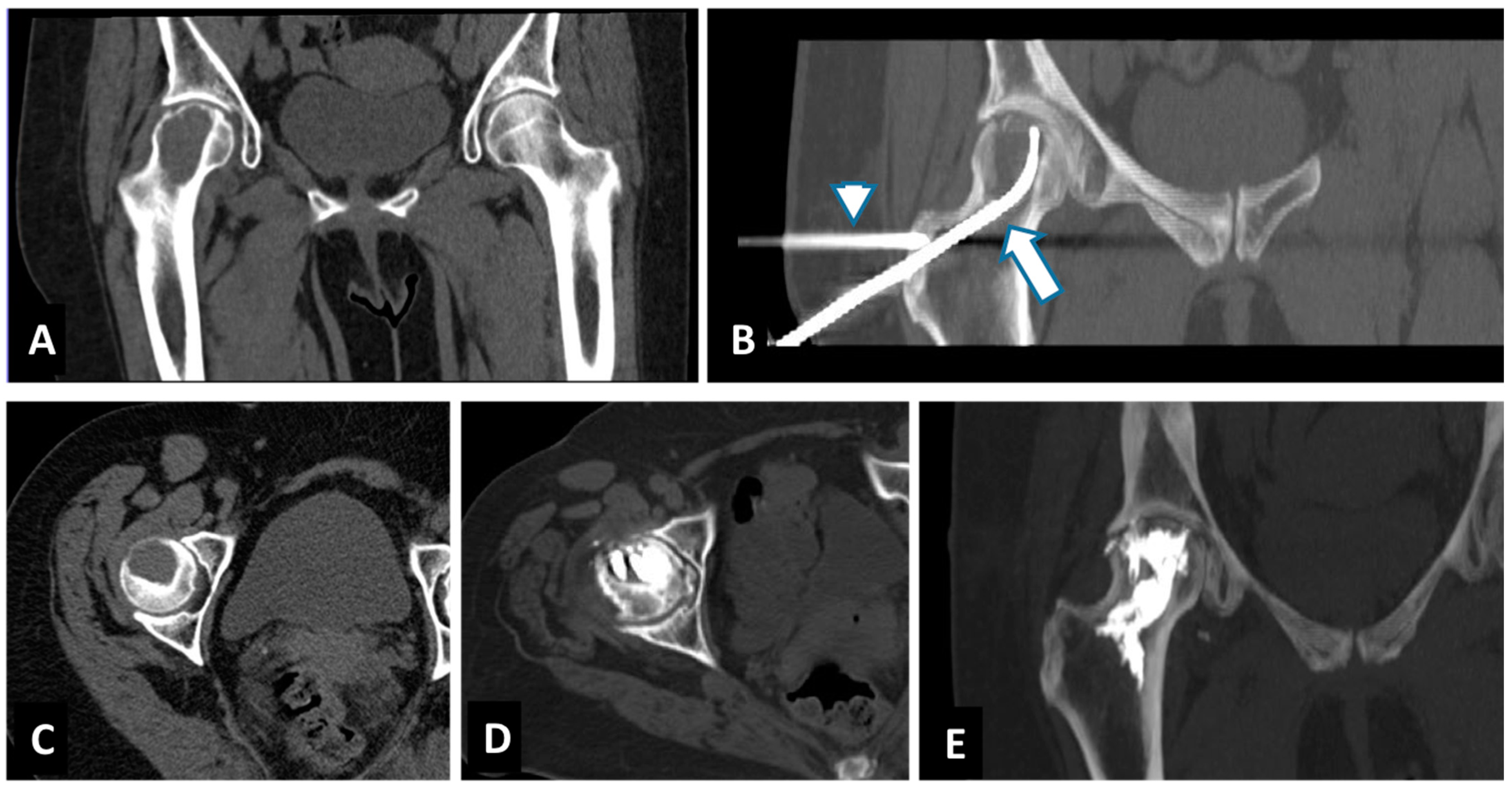
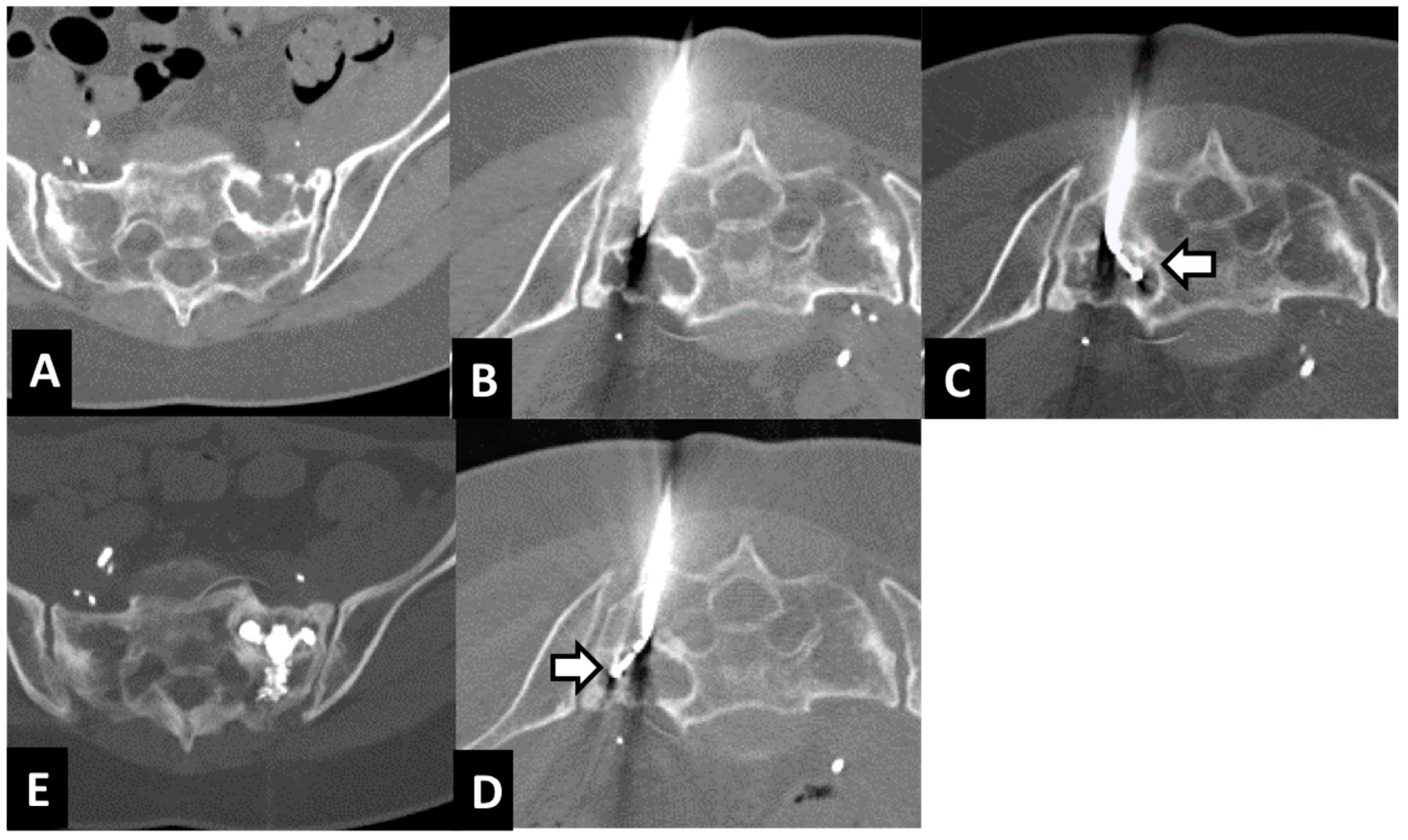

| Age—Gender | Primary Tumor | Site of Lesion | Size of Lesion mm | Mobility Recovery | VAS before RFA | VAS after: 1 w, 1 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m | Cementoplasty | Complication | Imaging after 1 y Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70—W | Breast | left acetabulum | 35 × 30 × 25 mm | 2 1 | 7 | 3 0 0 0 0 | 7 cc | leakage cement | CT |
| 62—W | Breast | left ilium | 12 × 8 × 19 mm | 2 1 | 6 | 3 0 0 0 0 | 4 cc | none | MRI |
| 79—M | Renal cell carcinoma | left ilium | 32 × 35 × 30 mm | 3 1 | 8 | 2 0 0 2 1 | 4 cc | none | CT |
| 61—W | Breast | left femur | 25 × 25 × 30 mm | 3 1 | 7 | 1 0 0 1 N/A | 4 cc | none | CT |
| 67—W | Breast | right ilium | 30 × 22 × 37 mm | 3 1 | 6 | 0 0 0 0 0 | 8 cc | none | CT |
| 59—W | Breast | left acetabulum + quadrilateral lamina | 34 × 34 × 18 mm | 3 2 | 8 | 4 4 2 0 0 | 5 cc | none | CT |
| 81—W | Breast | right acetabulum | 10 × 15 × 20 mm | 3 1 | 7 | 1 0 1 2 N/A | 5 cc | none | CT-MRI |
| 57—M | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | right ilium | 15 × 14 × 18 mm | 1 1 | 6 | 0 1 1 0 0 | 4 cc | none | CT |
| 69—M | Breast cancer | right humerum | 25 × 25 × 30 mm | 3 1 | 8 | 2 2 0 0 0 | 6 cc | none | CT |
| 69—M | Renal cell carcinoma | sacrum | 30 × 32 × 28 mm | 2 1 | 7 | 3 1 0 0 0 | 4 cc | none | CT |
| 55—M | Renal cell carcinoma | left acetabulum | 18 × 15 × 25 mm | 2 1 | 6 | 1 1 0 0 0 | 4 cc | none | CT |
| 61—W | Breast | right femur | 35 × 25 × 52 mm | 3 1 | 9 | 3 0 0 0 0 | 10 cc | leakage cement | CT-MRI |
| 48—W | Breast | left ilium | 30 × 31 × 34 mm | 2 1 | 6 | 2 1 1 0 1 | 7 cc | none | CT |
| 66—M | Sarcoma | sacrum | 28 × 20 × 33 mm | 1 1 | 5 | 0 0 0 0 N/A | 6 cc | leakage cement | CT |
| 63—W | Breast | sacrum | 30 × 25 × 35 mm | 1 1 | 7 | 1 0 0 0 0 | 6 cc | none | CT |
| 62—W | Breast | right acetabulum | 20 × 20 × 32 mm | 2 1 | 5 | 2 1 1 0 0 | 7 cc | none | CT |
| 62—W | Breast | sacrum | 25 × 22 × 37 mm | 2 1 | 7 | 2 2 0 0 0 | 7 cc | none | CT |
| 1 Month after RFA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Ambulation | Limited Painful Ambulation | Use of Wheelchair | Bedridden | ||
| Before RFA | Normal ambulation | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Limited painful ambulation | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Use of wheelchair | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bedridden | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pusceddu, C.; De Francesco, D.; Ballicu, N.; Santucci, D.; Marsico, S.; Venturini, M.; Fior, D.; Moramarco, L.P.; Faiella, E. Safety and Feasibility of Steerable Radiofrequency Ablation in Combination with Cementoplasty for the Treatment of Large Extraspinal Bone Metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5891-5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080465
Pusceddu C, De Francesco D, Ballicu N, Santucci D, Marsico S, Venturini M, Fior D, Moramarco LP, Faiella E. Safety and Feasibility of Steerable Radiofrequency Ablation in Combination with Cementoplasty for the Treatment of Large Extraspinal Bone Metastases. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(8):5891-5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080465
Chicago/Turabian StylePusceddu, Claudio, Davide De Francesco, Nicola Ballicu, Domiziana Santucci, Salvatore Marsico, Massimo Venturini, Davide Fior, Lorenzo Paolo Moramarco, and Eliodoro Faiella. 2022. "Safety and Feasibility of Steerable Radiofrequency Ablation in Combination with Cementoplasty for the Treatment of Large Extraspinal Bone Metastases" Current Oncology 29, no. 8: 5891-5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080465
APA StylePusceddu, C., De Francesco, D., Ballicu, N., Santucci, D., Marsico, S., Venturini, M., Fior, D., Moramarco, L. P., & Faiella, E. (2022). Safety and Feasibility of Steerable Radiofrequency Ablation in Combination with Cementoplasty for the Treatment of Large Extraspinal Bone Metastases. Current Oncology, 29(8), 5891-5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080465





