Surgical Management of Craniovertebral Junction Schwannomas: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Synthesis and Quality Assessment
3. Results
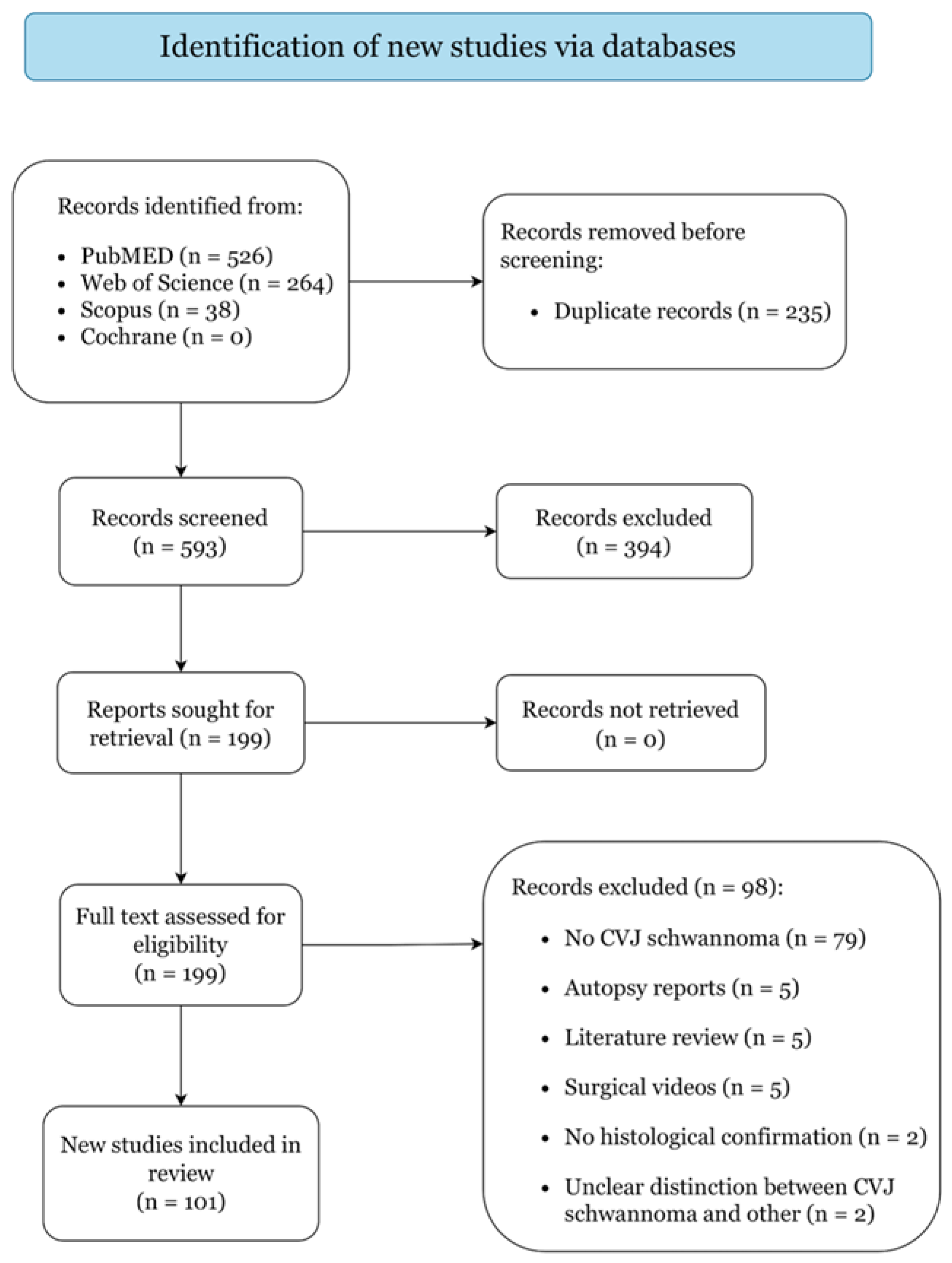
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Patient Characteristics and Clinical Presentation
3.3. Tumor Origin and Radiological Features
3.4. Management Strategies
3.5. Treatment Outcomes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesnel, A.M.; Santos, F. Evaluation and Management of Facial Nerve Schwannoma. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 51, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Link, M.J. Vestibular Schwannomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, M.P.; Mroz, T.E.; Benzel, E.C. Craniovertebral Junction. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, A7–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.D.; Bruner, H.J.; Maiman, D.J. Anatomic and Biomechanical Considerations of the Craniovertebral Junction. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, A2–A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlato, C.; Tessitore, E.; Schonauer, C.; Moraci, A. Management of benign craniovertebral junction tumors. Acta Neurochir. 2003, 145, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkarubo, A.N.; Andreev, D.N.; Konovalov, N.A.; Zelenkov, P.V.; Lubnin, A.J.; Chernov, I.V.; Koval, K.V. Surgical Treatment of Skull Base Tumors, Extending to Craniovertebral Junction. World Neurosurg. 2017, 99, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulding, H.D.; Bilsky, M.H. Metastases to the Craniovertebral Junction. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, A113–A118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, D.D.; Martirosyan, N.L.; Verma, K.; Safavi-Abbasi, S.; Porter, R.W.; Theodore, N.; Sonntag, V.K.H.; Dickman, C.A.; Spetzler, R.F. Surgical management and outcome of schwannomas in the craniocervical region. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; He, J.; Zhan, X.; He, M.; Zong, S.; Xiao, Z. Occipito-cervical fusion following gross total resection for the treatment of spinal extramedullary tumors in craniocervical junction: A retrospective case series. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goel, A.; Kaswa, A.; Shah, A.; Rai, S.; Gore, S.; Dharurkar, P. Extraspinal-Interdural Surgical Approach for C2 Neurinomas—Report of an Experience with 50 Cases. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, Y.R.; Menezes, A.H.; Traynelis, V.C. Posterolateral Approaches to the Craniovertebral Junction. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, A135–A140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Haider, A.S.; Cohen-Gadol, A. The Far-Lateral Suboccipital Approach to the Lesions of the Craniovertebral Junction. World Neurosurg. 2021, 155, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, B.E.; Foote, R.L.; Stafford, S.L. Stereotactic radiosurgery: The preferred management for patients with nonvestibular schwannomas? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2002, 52, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, S. Non-Vestibular Schwannoma Radiosurgery. Prog. Neurol. Surg. 2019, 34, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.A.; Clarke, M.; Rovers, M.; Riley, R.D.; Simmonds, M.; Stewart, G.; Tierney, J.F. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data. JAMA 2015, 313, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howick, J.; Chalmers, I.; Glasziou, P.; Greenhalgh, T.; Heneghan, C.; Liberati, A.; Moschetti, I.; Phillips, B.; Thornton, H. Explanation of the 2011 Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (OCEBM) Levels of Evidence (Background Document). Available online: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; 2020; Available online: https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-08 (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Takami, T.; Yamagata, T.; Chokyu, I.; Ikeda, H.; Tsuyuguchi, N.; Ohata, K. Surgery of spinal nerve sheath tumors originating from C1 or C2 of high cervical spine. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2010, 50, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suri, A.; Bansal, S.; Sharma, B.; Mahapatra, A.; Kale, S.; Chandra, P.; Singh, M.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M. Management of Hypoglossal Schwannomas: Single Institutional Experience of 14 Cases. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2014, 75, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebelt, B.D.; Haider, A.S.; Steele, W.J.; Krishna, C.; Blacklock, J.B. Spinal Schwannoma and Meningioma Mimicking a Single Mass at the Craniocervical Junction Subsequent to Remote Radiation Therapy for Acne Vulgaris. World Neurosurg. 2016, 93, e13–e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kim, J.H. False localizing sign caused by schwannoma in cervical spinal canal at C1-2 level. Medicine 2018, 97, e12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamizo, A.; Suzuki, S.O.; Shimogawa, T.; Amano, T.; Mizoguchi, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Sasaki, T. Concurrent spinal nerve root schwannoma and meningioma mimicking single-component schwannoma. Neuropathology 2012, 32, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oichi, T.; Chikuda, H.; Morikawa, T.; Mori, H.; Kitamura, D.; Higuchi, J.; Taniguchi, Y.; Matsubayashi, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Tanaka, S. Concurrent spinal schwannoma and meningioma mimicking a single cervical dumbbell-shaped tumor: Case report. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, S.; Kajihara, Y.; Abiko, M.; Mitsuhara, T.; Takeda, M.; Karlowee, V.; Yamaguchi, S.; Amatya, V.J.; Kurisu, K. Concurrent Schwannoma and Meningioma Arising in the Same Spinal Level: A Report of Two Cases. NMC Case Rep. J. 2018, 5, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, C.; Ahn, J.-G.; Huh, H.-Y.; Park, C.-K. Cervical Schwannoma Presenting with Acute Intracranial Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2010, 47, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, S.; Inaba, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Shimizu, K.; Murakami, H. Hypoglossal nerve schwannoma with intratumoral hemorrhage. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2012, 29, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, Y.; Grossi, P.M.; Bulsara, K.R.; Taniguchi, R.M.; Friedman, A.H.; Fukushima, T. Microsurgical Management of Hypoglossal Schwannomas Over 3 Decades. Oper. Neurosurg. 2011, 69, ons121–ons140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftahy, A.K.; Groll, M.; Barz, M.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; Meyer, B.; Negwer, C.; Gempt, J. Surgical Management of Jugular Foramen Schwannomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockard, H.A.; Sen, C.N. The transoral approach for the management of intradural lesions at the craniovertebral junction. Neurosurgery 1991, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, M. Endoscopic Transoral Approach for Extracranial Hypoglossal Schwannoma. ORL 2011, 73, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, F.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Liang, J.; Li, M.; Ling, F. Surgical treatment of dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannoma via a pure endoscopic transoral approach. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.G.; Backer, R.J.; Kletzker, G.R.; Mishler, E.T.; Loosmore, J.L.; Leonetti, J.P.; Bigelow, D.C. Surgical management of transcranial hypoglossal schwannomas. Am. J. Otol. 1995, 16, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Kadri, P.A.S.; Al-Mefty, O. Surgical treatment of dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas. Neurosurg. Focus 2004, 17, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.K.; Kwon, T.H.; Chung, H.S. C-1 Root Schwannoma with Aggressive Lateral Mass Invasion. Yonsei Med. J. 2005, 46, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heiroth, H.-J.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Steiger, H.-J.; Hänggi, D. A cylindrical extracranial cranial base neurinoma of the hypoglossal nerve: A rare tumor with a rare localization: Case report. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, E212–E213. discussion E213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Tang, J.; Meng, G.; Zhang, J. Using a modified far-lateral approach to remove hypoglossal neurilemmomas: Notes on technique. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Nonaka, Y.; Hirai, H.; Shima, A.; Suzuki, F.; Matsuda, M.; Fukushima, T. Single-stage total resection of giant dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannoma: A case report. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachniadin, A.; Widi Nugroho, S.; Ananda Aman, R.; Ichwan, S.; Tandian, D.; Susanto, E.; Watanabe, K.; Nonaka, Y. A Dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannoma managed by a combination of open surgery and endoscopic assistance. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2021, 25, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kusaka, G.; Takashima, K.; Kamochi, H.; Shinoda, S. Intraoperative monitoring during surgery for hypoglossal schwannoma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.; Kimmell, K.T.; Replogle, R. Resection of an Occipital-Cervical Junction Schwannoma through a modified minimally invasive approach: Technical Note. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Park, H.; Lee, K.-S.; Park, S.W.; Hong, C.-K. Single-Stage Operation for Giant Schwannoma at the Craniocervical Junction with Minimal Laminectomy: A Case Report and Literature Review. Korean J. Spine 2016, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Shimizu, S.; Oka, H.; Nakahara, K.; Utsuki, S.; Fujii, K. Usefulness of transcervical approach for surgical treatment of hypoglossal schwannoma with paraspinal extension: Case report. Surg. Neurol. 2006, 65, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, H.; Kito, A.; Maki, H.; Hattori, K.; Noda, T.; Wada, K. Schwannoma originating from lower cranial nerves: Report of 4 cases. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Ogawa, K.; Kawase, T. Hypoglossal neurinoma--two case reports. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2000, 40, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marinelli, J.P.; Lohse, C.M.; Carlson, M.L. Incidence of Vestibular Schwannoma over the Past Half-Century: A Population-Based Study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Liang, J.; Guo, H.; Song, G.; Bao, Y. Trigeminal schwannoma: A single-center experience with 43 cases and review of literature. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 35, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbing, D.-L.; Schulz, A.; Morrison, H. Pathomechanisms in schwannoma development and progression. Oncogene 2020, 39, 5421–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Büttner, R.; Hagel, C.; Baader, S.L.; Kluwe, L.; Salamon, J.; Mautner, V.-F.; Mindos, T.; Parkinson, D.B.; Gehlhausen, J.R.; et al. The importance of nerve microenvironment for schwannoma development. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallini, R.; Tancredi, A.; Casalbore, P.; Mercanti, D.; Larocca, L.M.; Consales, A.; Lauretti, L.; Fernandez, E. Neurofibromatosis type 2: Growth stimulation of mixed acoustic schwannoma by concurrent adjacent meningioma: Possible role of growth factors. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Paek, S.H.; Chi, J.G.; Chun, Y.K.; Han, D.H. Mixed tumour of schwannoma and meningioma components in a patient with NF-2. Acta Neurochir. 1997, 139, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Li, Z.-J.; Li, X.-J.; Qian, H.-P.; Meng, X.-L.; Xu, Z.-G. Triple dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, D.; Camenzuli, C.; Psaila, J.; Božanić, S.; Calleja-Agius, J. A locally destructive, completely asymptomatic, C1-root schwannoma with base of skull invasion: A case report. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umana, G.; Scalia, G.; Chaurasia, B.; Fricia, M.; Passanisi, M.; Graziano, F.; Nicoletti, G.; Cicero, S. Perimedullary arteriovenous fistulas of the craniovertebral junction: A systematic review. J. Craniovertebr. Junction Spine 2020, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzo, G.; Umana, G.E.; Giuffrida, M.; Furnari, M.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Scalia, G. Intramedullary craniovertebral junction metastasis leading to the diagnosis of underlying renal cell carcinoma. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2020, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visocchi, M.; Germano’, A.; Umana, G.; Richiello, A.; Raudino, G.; Eldella, A.M.; Iacopino, G.; Barbagallo, G. Direct and Oblique Approaches to the Craniovertebral Junction: Nuances of Microsurgical and Endoscope-Assisted Techniques Along with a Review of the Literature. In Trends in Reconstructive Neurosurgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, J.; Bruneau, M.; Berhouma, M.; Cornelius, J.F.; Cavallo, L.M.; Daniel, R.T.; Froelich, S.; Jouanneau, E.; Meling, T.R.; Messerer, M.; et al. Management of non-vestibular schwannomas in adult patients: A systematic review and consensus statement on behalf of the EANS skull base section Part III: Lower cranial nerve schwannomas, jugular foramen (CN IX, X, XI) and hypoglossal schwannoma (XII). Acta Neurochir. 2021, 164, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisciano, P.; Ferini, G.; Ogasawara, C.; Wahood, W.; Bin Alamer, O.; Gupta, A.D.; Scalia, G.; Larsen, A.M.G.; Yu, K.; Umana, G.E.; et al. Orbital Metastases: A Systematic Review of Clinical Characteristics, Management Strategies, and Treatment Outcomes. Cancers 2021, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisciano, P.; Haider, A.S.; Sabahi, M.; Nwagwu, C.D.; Bin Alamer, O.; Scalia, G.; Umana, G.E.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Yu, K.; et al. Primary Skull Base Chondrosarcomas: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbaro, S.; Mirone, G.; Makiese, O.; Bresson, D.; George, B. Dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas: Surgical management, outcome and complications on a series of 16 patients. Neurosurg. Rev. 2009, 32, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, F.; Meneghelli, P. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring for Craniovertebral Junction Surgery. In Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Visocchi, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 125, pp. 369–380. ISBN 978-3-319-62514-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ou, S.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wu, A.-H.; Wu, P.-F.; Wang, Y.-B. Microsurgical management of dumbbell C1 and C2 schwannomas via the far lateral approach. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Fukumura, M.; Toda, M. Cystic Dumbbell-Shaped C1 Schwannoma with Intracranial Extension and Hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.E.; Salehi-Allameh, B.; Habermehl, D.; Kessel, K.A.; Welzel, T.; Debus, J. Clinical response and tumor control based on long-term follow-up and patient-reported outcomes in patients with chemodectomas of the skull base and head and neck region treated with highly conformal radiation therapy. Head Neck 2014, 36, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiesen, T.; Svensson, M.; Lundgren, J.; Kihlström, L.; Parisotto, R.; Bagger-Sjöbäck, D. Hypoglossal schwannoma—successful reinnervation and functional recovery of the tongue following tumour removal and nerve grafting. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Kato, T.; Kida, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Iwai, Y.; Kondoh, T.; Tsugawa, T.; Sato, M.; Sato, M.; Nagano, O.; et al. Gamma Knife surgery for patients with jugular foramen schwannomas: A multiinstitutional retrospective study in Japan. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kano, H.; Meola, A.; Yang, H.; Guo, W.-Y.; Martínez-Alvarez, R.; Martínez-Moreno, N.; Urgosik, D.; Liscak, R.; Cohen-Inbar, O.; Sheehan, J.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for jugular foramen schwannomas: An international multicenter study. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Cohort size (no.) | 353 |
| Demographics | |
| Age (years), median (range) | 46 (4–79) |
| Gender (male) | 177 (50.1%) |
| Syndromes | No. (%) |
| Neurofibromatosis type 1 | 1 (0.3%) |
| Neurofibromatosis type 2 | 10 (2.8%) |
| Presenting Symptoms | No. (%) |
| Duration (months), median (range) | 6 (0–180) |
| Neck pain | 107 (30.3%) |
| Headache | 93 (26.3%) |
| Sensory deficit | 92 (26.1%) |
| Dysphagia/Swallowing difficulty | 64 (18.1%) |
| Ataxia/Gait disturbance | 62 (17.6%) |
| Hoarseness | 52 (15.7%) |
| Motor weakness | 38 (10.8%) |
| Speech disorder | 38 (10.8%) |
| Tongue atrophy | 35 (9.9%) |
| Hearing disturbance | 35 (9.9%) |
| Vertigo | 32 (9.1%) |
| Tetraparesis | 28 (7.9%) |
| Diplopia | 21 (5.9%) |
| Hemiparesis | 20 (5.7%) |
| Paraparesis | 17 (4.8%) |
| Neck mass | 16 (4.5%) |
| No symptoms | 2 (0.6%) |
| Cranial Nerve Neuropathies | No. (%) |
| V | 7 (2%) |
| VII | 24 (6.8%) |
| VIII | 27 (7.6%) |
| IX | 82 (23.2%) |
| X | 86 (24.4%) |
| XI | 30 (8.5%) |
| XII | 110 (31.2%) |
| Multiple | 96 (27.2%) |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Tumor Laterality (n = 296) | No. (%) |
| Left | 172 (58.1%) |
| Right | 117 (39.5%) |
| Bilateral | 6 (2%) |
| Midline | 1 (0.3%) |
| Nerve of Origin | No. (%) |
| Cranial nerve IX | 15 (4.2%) |
| Cranial nerve X | 7 (2%) |
| Cranial nerve XI | 15 (4.2%) |
| Cranial nerve IX–X–XI | 44 (12.5%) |
| Cranial nerve XII | 104 (29.4%) |
| Spinal nerve C1 | 46 (13%) |
| Spinal nerve C2 | 109 (30.9%) |
| Spinal nerve C1–C2 | 15 (4.2%) |
| Intracranial/Extracranial (n = 319) | No. (%) |
| Intracranial | 87 (27.3%) |
| Extracranial | 144 (45.1%) |
| Intracranial and Extracranial | 88 (27.6%) |
| Intradural/Extradural (n = 319) | No. (%) |
| Intradural | 129 (40.4%) |
| Extradural | 49 (15.4%) |
| Intradural and Extradural | 141 (44.2%) |
| Location | No. (%) |
| Jugular foramen | 71 (86.5%) |
| Hypoglossal canal | 100 (28.3%) |
| Jugular foramen and Hypoglossal canal | 6 (1.7%) |
| Foramen magnum | 5 (1.4%) |
| Foramen magnum and Hypoglossal canal | 3 (0.8%) |
| Foramen magnum and C1 | 27 (7.6%) |
| Foramen magnum and C1–C2 | 7 (2%) |
| C1–C2 vertebra/foramen | 131 (37.1%) |
| Radiological Findings | No. (%) |
| Erosion occipital condyle/cervical facet joint | 66 (18.7%) |
| Displaced vertebral artery | 31 (8.8%) |
| Compression brainstem | 23 (6.5%) |
| Occlusion internal jugular vein/jugular bulb | 20 (5.7%) |
| Invasion cerebellopontine angle/internal meatus | 13 (3.7%) |
| Obstruction 4th ventricle | 9 (2.5%) |
| Concurrent craniovertebral junction meningioma | 5 (1.4%) |
| Occlusion sigmoid/transverse sinuses | 4 (1.1%) |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 2 (0.6%) |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Extent of Surgical Resection | No. (%) |
| Gross Total Resection (100%) | 217 (61.5%) |
| Partial Resection (<100%) | 136 (38.5%) |
| Surgical Approach (n = 334) | No. (%) |
| Retrosigmoid approach | 129 (36.5%) |
| with suboccipital craniotomy | 82 (23.2%) |
| with transcondylar craniotomy | 26 (7.4%) |
| with suprajugular craniotomy | 8 (2.3%) |
| with suboccipital and transcondylar craniotomy and cervical laminectomy | 5 (1.4%) |
| with suboccipital and transcondylar craniotomy | 4 (1.1%) |
| with cervical laminectomy | 2 (0.6%) |
| with suboccipital craniotomy and cervical laminectomy | 1 (7.6%) |
| with transcondylar and suprajugular craniotomy | 1 (0.3%) |
| Far-lateral approach | 105 (29.7%) |
| with suboccipital craniotomy and cervical laminectomy | 53 (15%) |
| with suboccipital craniotomy | 52 (14.7%) |
| Posterior approach with cervical laminectomy | 95 (26.9%) |
| ELITE approach (Extreme lateral infrajugular transcondylar–transtubercular exposure) | 16 (4.5%) |
| Transoral endoscopic approach | 8 (2.3%) |
| Adjuvant Stereotactic Radiosurgery | 21 (5.9%) |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Post-Surgical Complications | 83 (23.5%) |
| Dysphagia | 26 (7.4%) |
| Cerebrospinal fluid leak | 21 (5.9%) |
| Aspiration pneumonia | 9 (2.5%) |
| Hemiparesis/hemiplegia | 9 (2.5%) |
| Hoarseness | 8 (2.3%) |
| Hydrocephalus | 4 (1.1%) |
| C2 anesthesia | 3 (0.8%) |
| Wound infection | 3 (0.8%) |
| Hearing loss | 2 (0.6%) |
| Meningitis | 2 (0.6%) |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 2 (0.6%) |
| Venous thrombosis | 1 (0.3%) |
| Post-surgery New Cranial Nerve Neuropathies | No. (%) |
| Total | 22 (6.2%) |
| VII | 1 (0.3%) |
| IX | 7 (2%) |
| X | 14 (4%) |
| XI | 6 (1.7%) |
| XII | 7 (2%) |
| Symptom Improvement | 311 (88.1%) |
| Improvement in pre-operative cranial nerve neuropathies | 36 (10.2%) |
| Complete resolution | 7 (2%) |
| Recurrence | 16 (4.5%) |
| Status | No. (%) |
| Alive | 346 (98%) |
| Dead | 7 (2%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palmisciano, P.; Ferini, G.; Watanabe, G.; Conching, A.; Ogasawara, C.; Scalia, G.; Bin-Alamer, O.; Haider, A.S.; Passanisi, M.; Maugeri, R.; et al. Surgical Management of Craniovertebral Junction Schwannomas: A Systematic Review. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4842-4855. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070384
Palmisciano P, Ferini G, Watanabe G, Conching A, Ogasawara C, Scalia G, Bin-Alamer O, Haider AS, Passanisi M, Maugeri R, et al. Surgical Management of Craniovertebral Junction Schwannomas: A Systematic Review. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(7):4842-4855. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070384
Chicago/Turabian StylePalmisciano, Paolo, Gianluca Ferini, Gina Watanabe, Andie Conching, Christian Ogasawara, Gianluca Scalia, Othman Bin-Alamer, Ali S. Haider, Maurizio Passanisi, Rosario Maugeri, and et al. 2022. "Surgical Management of Craniovertebral Junction Schwannomas: A Systematic Review" Current Oncology 29, no. 7: 4842-4855. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070384
APA StylePalmisciano, P., Ferini, G., Watanabe, G., Conching, A., Ogasawara, C., Scalia, G., Bin-Alamer, O., Haider, A. S., Passanisi, M., Maugeri, R., Hoz, S. S., Baldoncini, M., Campero, A., Salvati, M., Cohen-Gadol, A. A., & Umana, G. E. (2022). Surgical Management of Craniovertebral Junction Schwannomas: A Systematic Review. Current Oncology, 29(7), 4842-4855. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070384










