Nondetectable Prostate Carcinoma (pT0) after Radical Prostatectomy: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
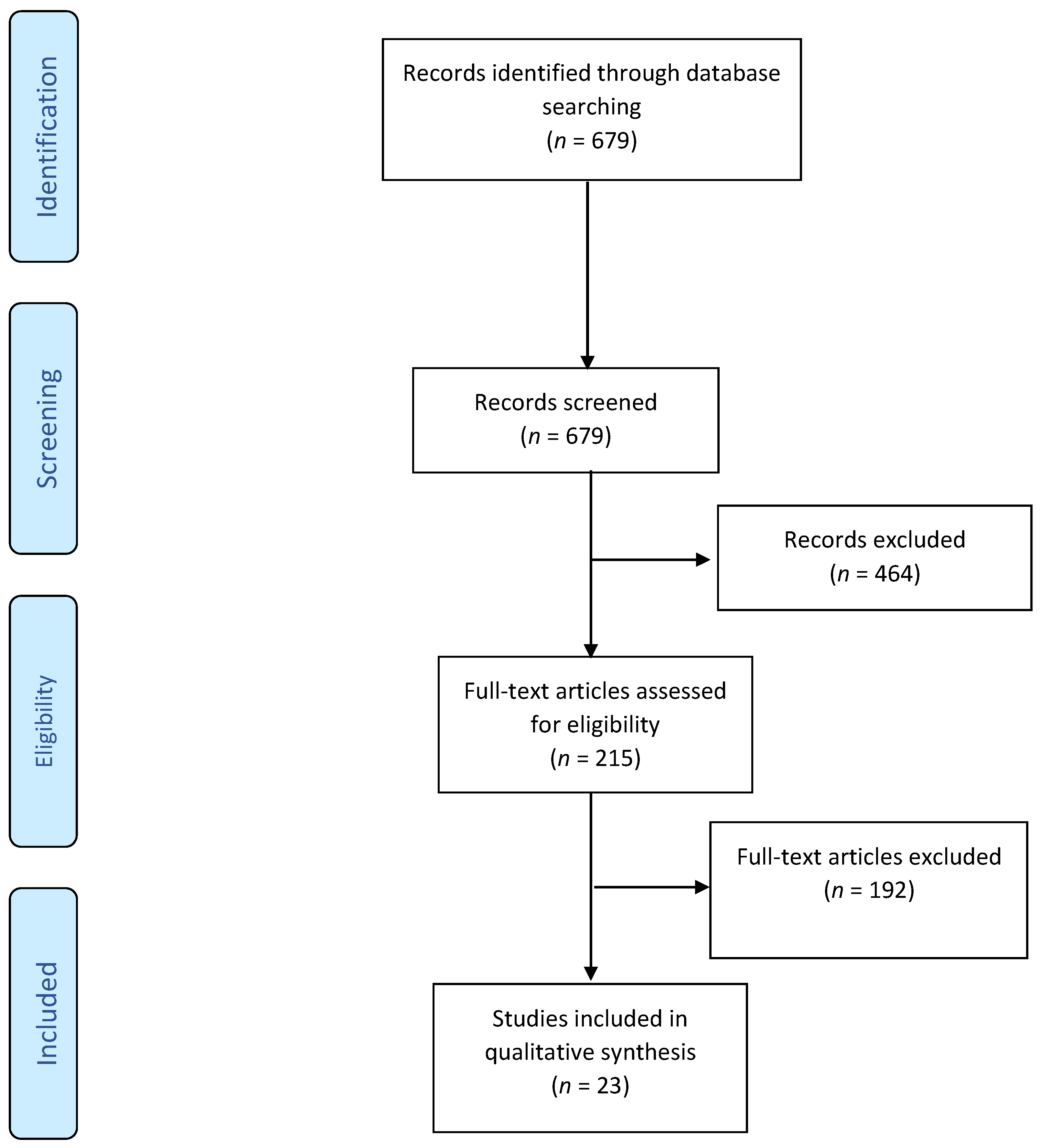
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Frequency and Possible Causes of Cancer Absence in Prostatectomy Specimen
3.2. Possible Pre-Operative Predictors of pT0 Stage
3.3. pT0 Stage following Hormonal Therapy
3.4. pT0 Diagnosis: Follow-Up and Oncological Outcomes
| Study | pT0 Cases (n) | Follow-Up Duration | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gurski et al. [23] | 23 | Reported as adequate | 26% developed biochemical recurrence |
| Knipper et al. [8] | 358 | 9 years | 3 cancer specific deaths (99.5% cancer-specific survival) |
| Chung et al. [17] | 28 | 68.37 months (median) | No clinical or biochemical recurrence |
| Moreira et al. [16] | 62 | 10.9 years (median) | 11% with disease recurrence 1.6% with systemic progression |
| Bream et al. [14] | 4 | 3 months–10 years | No clinical or biochemical recurrence |
| Bessède et al. [11] | 30 | 82 months (median) | No biochemical recurrence |
| Trpkov et al. [1] | 9 | 23.8 months (mean) | No clinical or biochemical recurrence |
| Descazeaud et al. [9] | 9 | 30 months (mean) | No clinical or biochemical recurrence |
| Köllermann et al. [13] | 36 | 47 months for the pT0 group (median) | 19.4% with biochemical recurrence |
| Bostwick et al. [3] | 38 | 9.6 years (mean) | No clinical recurrence No biochemical recurrence (PSA available only for 32 of 38 patients) |
| Herkommer et al. [10] | 13 | 62 months(median) | No clinical or biochemical recurrence |
| Köllermann et al. [22] | 38 | 47 months (median) | 18.4% with biochemical recurrence 7.9% with clinical recurrence |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trpkov, K.; Gao, Y.; Hay, R.; Yimaz, A. No residual cancer on radical prostatectomy after positive 10-core biopsy: Incidence, biopsy findings, and DNA specimen identity analysis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2006, 130, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, N.S.; Bégin, L.R.; Grody, W.W.; Novak, J.M.; Qian, J.; Bostwick, D.G. Minimal or No Cancer in Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1995, 19, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, D.G.; Bostwick, K.C. ’Vanishing’ prostate cancer in radical prostatectomy specimens: Incidence and long-term follow-up in 38 cases. Br. J. Urol. 2004, 94, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Hafez, M.; Berg, K.; Murphy, K.; Epstein, J.I. Little or no residual prostate cancer at radical prostatectomy: Vanishing cancer or switched specimen? A microsatellite analysis of specimen identity. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiuseppe, J.A.; Sauvageot, J.; Epstein, J.I. Increasing Incidence of Minimal Residual Cancer In Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskinovsky, A.M.; Sanderson, H.; Epstein, J.I. Characterization of minute adenocarcinomas of prostate at radical prostatectomy. Urol. 2004, 64, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bs, J.L.G.; Masterson, T.A.; Cheng, L.; Johnstone, P.A. pT0 prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 102, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, S.; Tilki, D.; Mazzone, E.; Mistretta, F.A.; Palumbo, C.; Pecoraro, A.; Tian, Z.; Briganti, A.; Saad, F.; Graefen, M.; et al. Contemporary clinicopathological characteristics of pT0 prostate cancer at radical prostatectomy: A population-based study. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2019, 37, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descazeaud, A.; Zerbib, M.; Flam, T.; Vieillefond, A.; Debré, B.; Peyromaure, M. Can pT0 Stage of Prostate Cancer be Predicted before Radical Prostatectomy? Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkommer, K.; Kuefer, R.; E Gschwend, J.; E Hautmann, R.; Volkmer, B.G. Pathological T0 prostate cancer without neoadjuvant therapy: Clinical presentation and follow-up. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessède, T.; Soulié, M.; Mottet, N.; Rebillard, X.; Peyromaure, M.; Ravery, V.; Salomon, L. Cancerology Committee of the French Urological Association Stage pT0 After Radical Prostatectomy With Previous Positive Biopsy Sets: A Multicenter Study. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Jeong, I.G.; Bang, J.K.; Cho, Y.M.; Ro, J.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Ahn, H.; Kim, C.-S. Preoperative Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of pT0 Prostate Cancer in Radical Prostatectomy. Korean J. Urol. 2010, 51, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köllermann, J.; Hopfenmüller, W.; Caprano, J.; Budde, A.; Weidenfeld, H.; Weidenfeld, M.; Helpap, B. Prognosis of stage pT0 after prolonged neoadjuvant endocrine therapy of prostate cancer: A matched-pair analysis. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bream, M.J.; Dahmoush, L.; Brown, J.A. pT0 Prostate Cancer: Predictive Clinicopathologic Features in an American Population. Curr. Urol. 2013, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Capitanio, U.; Briganti, A.; Suardi, N.; Gallina, A.; Salonia, A.; Freschi, M.; Rigatti, P.; Montorsi, F. When should we expect no residual tumor (pT0) once we submit incidental T1a-b prostate cancers to radical prostatectomy? Int. J. Urol. 2010, 18, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Gershman, B.; Rangel, L.J.; Boorjian, S.A.; Thompson, R.H.; Frank, I.; Tollefson, M.K.; Gettman, M.T.; Karnes, R.J. Evaluation of pT0 prostate cancer in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Br. J. Urol. 2016, 118, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chung, D.Y.; Goh, H.J.; Koh, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, W.S.; Choi, Y.D. Clinical significance of multiparametric MRI and PSA density as predictors of residual tumor (pT0) following radical prostatectomy for T1a-T1b (incidental) prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0210037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kwast, T.H.; Têtu, B.; Candas, B.; Gomez, J.L.; Cusan, L.; Labrie, F. Prolonged neoadjuvant combined androgen blockade leads to a further reduction of prostatic tumor volume: Three versus six months of endocrine therapy. Urology 1999, 53, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, M.; Häggman, M.; Brändstedt, S.; De La Torre, M.; Pedersen, K.; Jarlsfeldt, I.; Wijkström, H.; Busch, C. Histopathological changes in androgen-deprived localized prostatic cancer. A study in total prostatectomy specimens. Eur. Urol. 1993, 24, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Murphy, W.M. Histologic changes in prostate carcinomas treated with leuprolide (luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone effect). Distinction from poor tumor differentiation. Cancer 1994, 73, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köllermann, J.; Feek, U.; Müller, H.; Kaulfuss, U.; Oehler, U.; Helpap, B.; Köllermann, M. Nondetected tumor (pT0) after prolonged, neoadjuvant treatment of localized prostatic carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2000, 38, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köllermann, J.; Caprano, J.; Budde, A.; Weidenfeld, H.; Weidenfeld, M.; Hopfenmüller, W.; Helpap, B. Follow-up of nondetectable prostate carcinoma (pT0) after prolonged PSA-monitored neoadjuvant hormonal therapy followed by radical prostatectomy. Urology 2003, 62, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurski, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Peterson, A.C.; Brand, T.C. pT0 is not benign disease: There is risk of progression in patients with no cancer in radical prostatectomy specimens. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalampokis, N.; Grivas, N.; Karavitakis, M.; Leotsakos, I.; Katafigiotis, I.; Moschovas, M.C.; van der Poel, H.; European Association of Urology (EAU) Young Academic Urologists (YAU) Robotic Urology Working Group. Nondetectable Prostate Carcinoma (pT0) after Radical Prostatectomy: A Narrative Review. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1309-1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030111
Kalampokis N, Grivas N, Karavitakis M, Leotsakos I, Katafigiotis I, Moschovas MC, van der Poel H, European Association of Urology (EAU) Young Academic Urologists (YAU) Robotic Urology Working Group. Nondetectable Prostate Carcinoma (pT0) after Radical Prostatectomy: A Narrative Review. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(3):1309-1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalampokis, Nikolaos, Nikolaos Grivas, Markos Karavitakis, Ioannis Leotsakos, Ioannis Katafigiotis, Marcio Covas Moschovas, Henk van der Poel, and European Association of Urology (EAU) Young Academic Urologists (YAU) Robotic Urology Working Group. 2022. "Nondetectable Prostate Carcinoma (pT0) after Radical Prostatectomy: A Narrative Review" Current Oncology 29, no. 3: 1309-1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030111
APA StyleKalampokis, N., Grivas, N., Karavitakis, M., Leotsakos, I., Katafigiotis, I., Moschovas, M. C., van der Poel, H., & European Association of Urology (EAU) Young Academic Urologists (YAU) Robotic Urology Working Group. (2022). Nondetectable Prostate Carcinoma (pT0) after Radical Prostatectomy: A Narrative Review. Current Oncology, 29(3), 1309-1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29030111





