Abstract
Background: The use of chemotherapy near end of life (EOL) for various cancers is increasing and has been shown to be associated with delayed access to palliative care (PC) and increased aggressiveness in EOL care, without any benefit on survival. Methods: This retrospective study included 90 patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who received at least one line of palliative systemic anticancer therapy (SACT) and died between 1 November 2014, and 31 October 2016, at Institut universitaire de cardiologie et de pneumologie de Québec (IUCPQ). Our primary objective was to evaluate the proportion of patients with NSCLC receiving SACT within 30 days of death. Secondary outcomes were to determine the mean and median delays between the administration of the last treatment and death, and to evaluate if there were differences in characteristics and outcomes (including overall survival (OS)) between patients treated or not within 30 days of death. Results: In our cohort, 22% of patients received SACT within 30 days of death. For the entire cohort, the mean delay between the last treatment and death was 94 days, and the median was 57 days. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of baseline characteristics. Use of SACT near EOL was associated with decreased access to PC, higher rates of in hospital death, decreased use of medical aid in dying (MAiD), and a shorter median OS (4.0 vs. 9.0 months). Conclusions: In this retrospective cohort of patients with metastatic NSCLC, 22% of patients received SACT within 30 days of death, with a negative impact on access to PC, higher rates of in hospital death, decreased use of MAiD and palliative sedation, and a shorter median OS.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide [1], with a 5-year survival of 19% [2]. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the predominant form of the disease, accounting for approximately 85% of cases [3]. Among newly diagnosed patients with NSCLC, 40% present with metastatic disease [4]. The ultimate objective of treating advanced NSCLC with the sequential use of systemic anticancer therapies (SACTs) is to improve overall survival (OS) while maintaining or improving quality of life.
In the last decade, targeted therapies with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have become standard first-line therapy for patients with driver oncogenes, with median survival in phase 3 trials beyond 3 years for patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations [5,6], and beyond 4 years for those with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements [7,8]. Another significant advance was the use of immunotherapy to target immune checkpoint pathways to prevent or reduce tumor-mediated immune suppression. Nivolumab, pembrolizumab (for patients with programmed cell death ligand (PD-L1) ≥ 1%) and atezolizumab were all initially approved in 2015 and 2016 for second-line therapy of NSCLC after phase 3 trials showing their superiority over docetaxel [9,10,11,12]. Recently, immunotherapy became a standard of care for all patients in the first-line setting unless contraindicated, as a monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy, depending on PD-L1 expression [13].
Even if these treatments might prolong survival or reduce symptoms, not all patients will benefit, and many will experience adverse effects. Furthermore, SACT might prevent the patient from preparing for death, delay access to palliative care (PC) or preclude entry into hospice [14,15]. Multiple studies show that palliative chemotherapy is increasingly given near death for incurable cancer, with a non-negligible impact on healthcare costs [16]. In a US community practice in 2006, chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC was given within 1 month and 2 weeks of death to 43% and 20% of patients, respectively [17]. There is also literature showing that patients receiving targeted therapy for metastatic NSCLC within 30 days of death are more likely to undergo aggressive end-of-life (EOL) care, including multiple emergency visits, prolonged hospitalization, admission to intensive care units, and late hospice referrals [18,19]. Similar data exist for immune checkpoint inhibitors, but not specifically for patients with NSCLC. Their use in the last 30 days in 157 patients with multiple tumor sites was associated with poor Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), lower hospice enrollment, and dying in the hospital [20]. The rate of chemotherapy administration near the EOL has been proposed as an indicator for the assessment of quality of care in cancer patients [21], but these recommendations were made before the widespread use of TKIs and immunotherapy.
Given the lack of recent literature on the subject, we sought to explore the use and impacts of SACT including chemotherapy, TKIs and immunotherapy near EOL, specifically in patients with NSCLC. Our primary objective was to evaluate the proportion of patients with NSCLC receiving palliative SACT within 30 days of death at our center. Secondary outcomes were to determine the mean and median delays between the administration of the last treatment and death, and to evaluate if there were differences in characteristics and outcomes (including OS) between patients treated or not within 30 days of death.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This retrospective study included all patients with metastatic NSCLC who received at least one line of palliative SACT and who died between 1 November 2014, and 31 October 2016, at Institut universitaire de cardiologie et de pneumologie de Québec (IUCPQ). Patients were identified from the Oncology Database (SICTO), which is a regional database in Quebec City, and data collection was performed from chart review. The study was approved by our institutional Research Ethics Committee.
2.2. Data Collection
Demographic data collected for this study included age, gender, and smoking status. The medical charts were also reviewed for histology, biomarker results (EGFR, ALK, PD-L1), stage at initial diagnosis, number of organs involved, presence of brain metastasis. Information on treatment and outcomes were collected: use of palliative radiation, type and number of lines of systemic therapy received, ECOG PS and level of care at last cycle before death, reason for treatment discontinuation, PC team involvement, as well as cause, place and date of death.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Patient demographics and clinical characteristics were summarized using descriptive methods. Data were expressed using mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median ± interquartile range (IQR) for continuous variables, or as percentage for categorical data. Throughout the analysis, we compared patients who received palliative SACT within 30 days of death to those who did not. Categorical and continuous variables were compared using Fisher’s exact test and one-way analysis of variance, respectively. We constructed survival curves using Kaplan-Meier estimates, and used the log-rank test for between-group comparisons. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was performed to model survival at follow-up, with adjustment for baseline characteristics and comorbidities. Variables with a probability value < 0.20 were candidates for multivariable regression modelling using a forward approach. We tested the assumption of proportional hazards using cumulative sums of Martingale residual plots. Statistical significance was present with a two-tailed p value < 0.05. Analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Patients
One hundred and 83 patients were identified from the Oncology Database. After excluding 34 patients who did not receive SACT and 40 patients with a histopathological diagnosis other than NSCLC, 109 patients were eligible. Of these, 19 patients were diagnosed at our center but were transferred to their referring institution for treatment and lost to follow-up. Hence, 90 patients were included in the analysis (Figure 1).
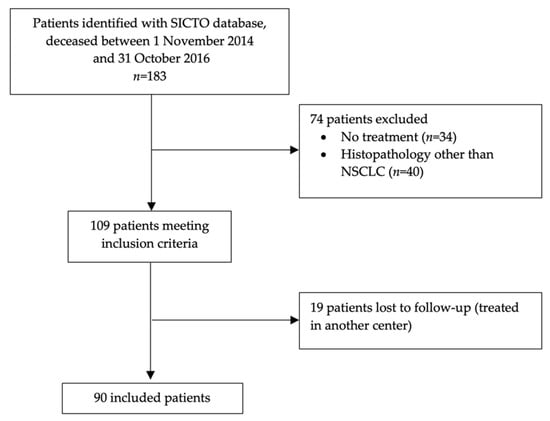
Figure 1.
Patient-flow diagram.
Baseline characteristics of all patients are summarized in Table 1. Most patients were male, former or current smokers, and had an adenocarcinoma without a driver alteration. Only 12% of patients carried an EGFR mutation and 3% an ALK rearrangement. PD-L1 status was unknown for 85% of patients, as at the time first-line immunotherapy was not available, and second-line nivolumab was approved for all comers. The population was divided in two groups, with 20 patients (22%) who received SACT within 30 days of death, and 70 (78%) who did not. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. There were a higher proportion of adenocarcinoma (85% vs. 71%) and ALK rearrangements (10% vs. 1%) in the group receiving treatment near EOL, but the differences were not significant (both p values = 0.05).

Table 1.
Baseline patient characteristics and outcomes.
3.2. Systemic Treatments
Lines and duration of systemic therapy are shown in Table 2. The most frequently use regimens were platinum-doublet chemotherapy in first line (81%) and immunotherapy in second line (58%). Median number of cycles received and duration of treatment decreased with increasing lines of treatment.

Table 2.
Lines and duration of systemic therapy.
3.3. Treatments and Outcomes According to the Timing of Last Systemic Therapy
For the entire cohort, the mean delay between the last treatment and death was 94 days, and the median was 57 days. When compared with patients not treated near EOL, patients receiving SACT within 30 days of death received similar numbers of lines of therapy, and a similar proportion of immunotherapy (Table 3). There was a tendency for an increased use of TKIs in the group treated near EOL, which was not statistically significant. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of ECOG PS and level of care. Patients not treated in the last 30 days of life were more likely to be seen by the PC team, and to receive medical aid in dying (MAiD) or palliative sedation. They also were more likely to die in a hospice or at home, as opposed to at the hospital. Only one patient died from treatment toxicity, in the group treated near EOL.

Table 3.
Treatments and outcomes according to timing of last systemic therapy.
After adjusting for other factors influencing OS in our multivariable model, patients not treated in the last 30 days of life had a longer median OS (time from diagnosis of metastatic disease to death) than patients receiving SACT within 30 days of death (9.0 vs. 4.0 months) (Figure 2).
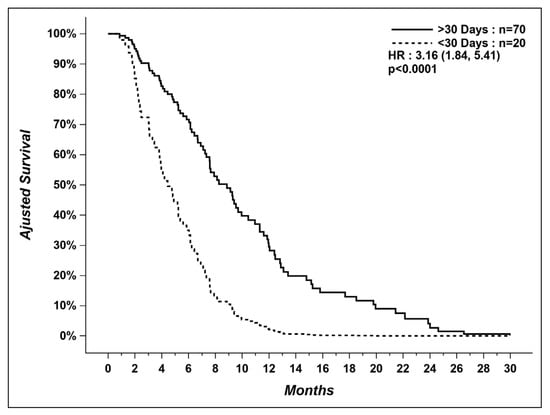
Figure 2.
Overall survival of patients who received systemic therapy within last 30 days versus patients who did not.
In the group of patients treated in the last 30 days, we could not find the cause of death for two patients, and two other patients died from unexpected causes (1 arrived at the emergency room with cardiopulmonary arrest and 1 died from pulmonary hemorrhage caused by anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation). Even after excluding these four patients, patients not treated in the last 30 days still had a longer median OS (9.0 vs. 4.4 months) (Figure 3).
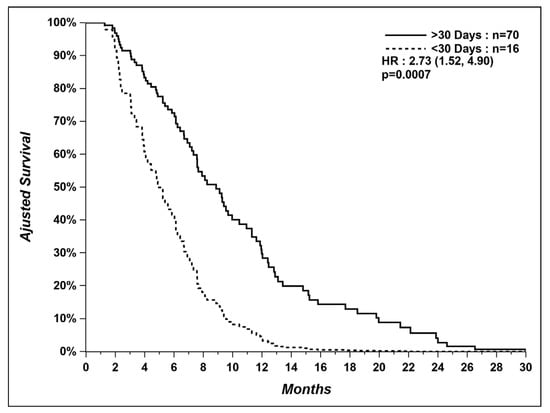
Figure 3.
Overall survival of patients who received systemic therapy within last 30 days versus patients who did not, after excluding patients with unexpected and unknown causes of death.
4. Discussion
In this retrospective study of patients receiving SACT for metastatic NSCLC, 22% of patients were treated within 30 days of death. This study being retrospective, it was not easy to understand why these patients were treated near EOL, as there were no statistically significant differences in terms of baseline characteristics between these patients and those not treated within 30 days of death. However, there was a tendency for a higher proportion of patients with EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements and for an increased use of TKIs in the group treated near EOL. It is not uncommon to continue TKI therapy beyond progression in the clinical setting, and this approach has shown survival benefits compared with switching to chemotherapy [22,23]. Patients can still experience quick clinical deterioration when using this strategy, and this might be an explanation for some of the rapid deaths in the group treated near EOL. There was also a tendency for a higher proportion of patients on first-line therapy and a lower proportion on third line or beyond in the group treated within 30 days of death. This could be explained by a higher proportion of patients with more aggressive disease leading to rapid and/or unexpected deterioration. There is consistent evidence that a significant proportion of patients with non-oncogene-addicted advanced NSCLC derive no or only limited benefit from first-line chemotherapy [24].
Similar to what has been reported in other studies [14,15,18,19,20], the use of SACT near EOL had a negative impact on PC access, which is unfortunate with the growing evidence for the benefits of PC in patients with advanced cancer. Temel and colleagues [25] published a landmark randomized clinical trial showing that patients with NSCLC who received PC referral at time of diagnosis had improved quality of life, mood, and increased survival, with less use of aggressive medical treatments at the end of life. The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) recommend that all patients with advanced cancer receive integrated PC services early in their disease course [26]. Unfortunately, a Canadian study showed that PC is not accessed early or systematically in Canada [27], as confirmed in our small cohort.
In our study, there was also a tendency for a higher proportion of patients dying in the hospital when receiving SACT within last 30 days of life, which has also been proposed as an indicator for the assessment of quality of care in cancer patients [21]. There is a paucity of recent data regarding the place of death in patients with lung cancer and other tumor types, but the proportion of patients dying in an acute hospital ranges from 28% to 60% [28,29,30]. Our numbers seem higher than what has been reported, which might be explained by many factors. MAiD and palliative sedation are only performed in hospital in our city. Furthermore, our hospital has a palliative care ward which is similar to a hospice and most patients admitted on this ward are terminally ill. There were significant differences between our two groups of patients in the cause of death, with patients receiving MAiD or palliative sedation only in the group not having received SACT near EOL. MAiD and palliative sedation are part of EOL care that should be accessible for all patients.
Our study also showed that patients receiving SACT within 30 days of death had a significant shorter survival compared to patients who had their last treatment > 30 days before death (4.0 vs. 9.0 months). Other studies have found no benefit of SACT near EOL on survival [15,31], but to our knowledge, this is the first report suggesting a detrimental effect. It is hard to determine if the shorter survival observed is explained by SACT, or by decreased access to PC, or by other factors, such as quick clinical deterioration when continuing TKIs beyond progression or different tumor biology/aggressiveness, as discussed earlier.
Limitations
Our results are limited by the retrospective and unicentric nature of the study. Furthermore, our sample was small, probably explaining lack of power to demonstrate significant differences between our two groups of patients. The proportion of patients with driver alterations was low, so we could not make any conclusions specifically on the use of targeted therapy near EOL. We had no information on patient-reported outcomes and quality of life. Additionally, the study was performed on patients treated between 2014 and 2016, before the widespread use of immunotherapy as a first-line treatment, as a monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy.
5. Conclusions
In this retrospective cohort of patients with metastatic NSCLC who received at least one line of palliative SACT and died between 2014 and 2016, 22% were treated within 30 days of death. Receiving treatment near EOL was associated with decreased access to PC, higher rates of in hospital death, decreased use of MAiD and palliative sedation, and a shorter median OS.
With rapidly evolving treatment options and new algorithms for the treatment of metastatic NSCLC, more studies are needed to assess the use of various SACT near EOL and its impact on outcomes. Still, our results show that a significant proportion of patients with advanced NSCLC continue to receive SACT near death, and likely reflect recent patterns of EOL care for patient with lung cancer in Canada. There is a need for increased and early integration of palliative care for patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-É.B., C.L. and Y.L.; methodology, M.-É.B. and C.L.; software, M.-É.B. and C.L.; validation, M.-É.B. and C.L.; formal analysis, M.-É.B. and C.L.; investigation, M.-É.B. and C.L.; resources, M.-É.B. and C.L.; data curation, M.-É.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-É.B. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, M.-É.B., C.L. and Y.L.; visualization, M.-É.B. and C.L.; supervision, C.L.; project administration, M.-É.B. and C.L.; funding acquisition, not applicable. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Institut Universitaire de Cardiologie et de Pneumologie de Québec (protocol code 2018-2941, 21542, on 8 September 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the fact that it was a retrospective chart review with no impact on patients.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Serge Simard, MSc stats, from the Centre de recherche de l’Institut universitaire de cardiologie et de pneumologie de Québec, Université Laval, Québec, for statistical analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Society, A.C. Cancer Facts & Figures 2020; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgensztern, D.; Ng, S.H.; Gao, F.; Govindan, R. Trends in stage distribution for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A National Cancer Database survey. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.-W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.-J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.H.; Schneider, B.J.; Temin, S., Jr.; Baker, S.; Brahmer, J.; Ellis, P.M.; Gaspar, L.E.; Haddad, R.Y.; Hesketh, P.J.; Jain, D.; et al. Therapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer without driver alterations: ASCO and OH (CCO) joint guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1608–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, S.E.; Smith, T.J. The role of chemotherapy at the end of life. JAMA 2008, 299, 2667–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, A.M.; Landrum, M.B.; Neville, B.A.; Ayanian, J.Z.; Earle, C.C. The effect on survival of continuing chemotherapy to near death. BMC Palliat. Care 2011, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bylicki, O.; Didier, M.; Riviere, F.; Margery, J.; Grassin, F.; Chouaid, C. Lung cancer and end-of-life care: A systematic review and thematic synthesis of aggressive inpatient care. BMJ Supportive Palliat. Care 2019, 9, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murillo, J.R.; Koeller, J. Chemotherapy given near the end of life by community oncologists for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 2006, 11, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Chuong, K.P.; Kuo, R.N. Impact of targeted therapy on the quality of end-of-life care for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A population-based study in Taiwan. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2018, 55, 798–807.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauman, J.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Muzikansky, A.; Gallagher, E.; Scribner, E.; Temel, B.; Sequist, L.V.; Heist, R.S.; Temel, J.S. End-of-life care in patients with metastatic lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J. Palliat. Med. 2016, 19, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisch, C.; Hagiwara, Y.; Gilbertson-White, S.; Gao, Y.; Lyckholm, L. Immune checkpoint inhibitor use near the end of life is associated with poor performance status, lower hospice enrollement, and dying in the hospital. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2020, 37, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, C.C.; Park, E.R.; Lai, B.; Weeks, J.C.; Ayanian, J.Z.; Block, S. Identifying potential indicators of the quality of end-of-life cancer care from administrative data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishie, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tamiya, A.; Mimori, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Omachi, N.; Asami, K.; Okishio, K.; Atagi, S.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors beyond progressive disease: A retrospective analysis for Japanese patients with activating EGFR mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Jänne, P.A.; Bartlett, C.H.; Tang, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Otterson, G.A.; Crinò, L.; Selaru, P.; Cohen, D.P.; Clark, J.W.; et al. Clinical benefit of continuing ALK inhibition with crizotinib beyond initial disease progression in patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Kerr, K.M.; Grohé, C.; Manegold, C.; Pavlakis, N.; Paz-Ares, L.; Huber, R.M.; Popat, S.; Thatcher, N.; Park, K.; et al. Defining aggressive or early progressing nononcogene-addicted non-small-cell lung cancer: A separate disease entity? Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 1363–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Temel, J.S.; Greer, J.A.; Muzikansky, A.; Gallagher, E.R.; Admane, S.; Jackson, V.A.; Dahlin, C.M.; Blinderman, C.D.; Jacobsen, J.; Pirl, W.F.; et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrell, B.R.; Temel, J.S.; Temin, S.; Alesi, E.R.; Balboni, T.A.; Basch, E.M.; Firn, J.I.; Paice, J.A.; Peppercorn, J.M.; Phillips, T.; et al. Integration of palliative care into standard oncology care: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Access to Palliative Care in Canada. Ottawa: Canadian Institute for Health Information. 2018. Available online: www.cihi.ca/sites/default/files/document/access-palliative-care-2018-en-web.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- O’Dowd, E.L.; McKeever, T.M.; Baldwin, D.R.; Hubbard, R.B. Place of Death in Patients with Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study from 2004-2013. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161399. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, J.L.; Barbera, L.; Bremner, K.E.; Yabroff, K.R.; Hoch, J.; Barrett, M.J.; Luo, J.; Krahn, M. End-of-Life Care for Lung Cancer Patients in the United States and Ontario. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeb, K.; Morris, K.; Kasman, N. CIHI Survery: Dying of Cancer in Canada’s Acute Care Facilities. Healthc. Q. 2005, 8, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.A.; Zhang, B.; Keating, N.L.; Weeks, J.C.; Prigerson, H.G. Associations between palliative chemotherapy and adult cancer patients’ end of life care and place of death: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2014, 348, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).