Abstract
Introduction: Lung cancer constitutes the most common cause of cancer death. Phase angle (PhA) has been related to lung cancer prognosis, which implies that the identification of dietary or other factors that could predict or modify PhA may have beneficial effects. Νutritional interventions have been linked with positive changes in PhA in certain types of cancer. Aim: The present study aimed to investigate the relationships between dietary habits/nutrition and PhA in NSCLC patients. Methods: The sample consisted of 82 male patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC; stage IV) from the ‘Theageneio’ Cancer Hospital (Thessaloniki, Greece). Several parameters were assessed, such as body mass index (BMI), lean mass, PhA, Mediterranean diet score (MedDietScore), dietary patterns, smoking, resting metabolic rate, resting oxygen consumption (VO2), ventilation rate, and physical activity. Results: According to our results, a dietary pattern rich in potatoes and animal proteins (meat and poultry) was a significant determinant of PhA (B ± SE, p: 0.165 ± 0.08, p = 0.05) in multiple linear regression models after adjusting for age, smoking, lean tissue, and MedDietScore. Conclusion: In conclusion, dietary patterns may affect PhA, suggesting the crucial role of protein in cancer management and the prevention of sarcopenia.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer constitutes the most common cause of cancer death [1]. Patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represent the majority of lung cancer cases (~85%), while patients with the more aggressive small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) type represent ~10–15% of lung cancer cases [2]. The type of treatment seems to affect the undesirable effects of the treatment, with new therapeutic approaches, such as immunotherapy, being very promising [3]. One previous study in such patients revealed that a combined treatment of immunotherapy and chemotherapy acts effectively as it seems to prolong the survival rate [4].
Both NSCLC and SCLC lung cancer are associated with malnutrition and sarcopenia, which affect survival and the effectiveness of treatments [5]. Body composition analysis, and especially bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), can provide data on classic parameters, such as fat mass, lean body mass, etc., and also on patients’ phase angle (PhA). PhA is a direct measurement of the human body’s cell integrity, has a prognostic value in lung cancer, as has recently been suggested [6], and may change during cancer therapy [7]. More particularly, low values of PhA and sarcopenia are connected to lung cancer [6] and other types of cancer [8] prognosis through various mechanisms, including inflammation and oxidative stress [6]. Indeed, inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a) have been negatively related to PhA measurements [9,10,11], while the antioxidant capacity of the plasma has been positively correlated with PhA [11].
In parallel, an altered redox status has been reported in lung cancer patients [12,13]. This oxidative environment may derive from common behaviors, such as smoking and bad nutritional habits, as well as from disease-related factors, such as chronic inflammation, anorexia, and the depletion of antioxidant enzymes [14]. Moreover, a balanced diet containing antioxidants and anti-inflammatory substances may reduce the advancement of lung cancer and enhance tissue regeneration [15]. There are few data sources connecting diet, sarcopenia, and PhA in cancer patients. Indeed, several dietary interventions have been conducted to combat sarcopenia in patients with lung cancer, with mixed results (protein, oral nutritional supplements with omega-3 fatty acids, multimodal interventions, etc.) [6]. Moreover, dietary factors, such as omega-3 fatty acids, have recently been related to PhA measurements [16,17] and nutritional interventions have been found to increase PhA in colorectal cancer patients [18]. However, there are no data on the relationship between diet and PhA measurements as a surrogate of sarcopenia in patients with lung cancer. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the relationships between dietary habits and PhA in NSCLC patients.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
In the present study, 82 NSCLC (stage IV) male patients from the ‘Theageneio’ Cancer Hospital (Thessaloniki, Greece) were included. Our study was approved by our investigational review board (‘Theageneio’ Cancer Hospital, Thessaloniki, Greece). Written informed consent was given by all patients. All patients were diagnosed and had first-line treatment. The study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975 (revised in 1983).
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
Weight and height were measured to the nearest 0.1 kg and 0.1 cm, correspondingly, with a digital scale (SECA 769) and a stadiometer (SECA 220). Measurements were taken in light clothing and without shoes. BMI was then calculated as the ratio of weight (kg) divided by height squared (m2). Waist circumference (cm) was measured after a moderate expiration between the superior iliac crest and the lower rib margin in the midaxillary line. Hip circumference (cm) was measured at the level of the buttocks as the maximal horizontal circumference. Waist to hip ratio was then determined.
2.3. Body Composition Measurements
Body composition was assessed with the BIA method by using the Bodystat Quadscan 4000, which is a tetrapolar and multiple-frequency device measuring impedance at 5, 50, 100, and 200 kHz. The measurement was performed according to the instructions of the manufacturer by attaching two sensing electrodes to the wrist and ankle and two current electrodes to the dorsum of the hand and foot (right side of the patient). Measurements were performed in bare feet. Total body fat percentage, total lean mass, total body, and extracellular and intracellular water were estimated by sex-specific equations from the equipment. Phase angle (at 50 Khz) was calculated as follows [18]:
Phase angle = (resistance/reactance) × (180/π).
2.4. Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) Measurement and Related Parameters
RMR measurement was done with the portable indirect calorimeter Fitmate GS (Cosmed, Rome, Italy). Subjects were asked to lie in a supine position and rest for 20 min in a silent room. Calibration was performed before each measurement. VO2 and ventilation rate were also measured in mL/min and Lt/min, respectively [19].
2.5. Dietary Habits
A short 11-item food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) was administered to assess the usual intake of major food groups. The Mediterranean diet score (MedDietScore) was used to assess Mediterranean diet adherence, with appropriate transformations in food portions if needed [20]. The score ranges from 0 to 55, with a greater score indicating higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
2.6. Physical Activity Habits
Patients filled in the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) questionnaire (short form) [21].
2.7. Smoking Habits
The number of cigarettes and the years of smoking were recorded. Then, pack years were assessed as a measure of tobacco exposure for each subject by multiplying a pack of cigarettes per day by smoking years.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Normality was tested with the Kolmogorov–Smirnoff criterion. Normally distributed continuous variables are presented as mean values ± standard deviation, while skewed variables served as the median and interquartile ranges. Categorical variables are presented as relative frequencies (%). Spearman correlation coefficients were evaluated to test correlations, in order to account for non-linear associations and/or the associations between skewed variables.
Principal component analysis (PCA) was applied to identify the a posteriori dietary patterns and meal patterns. To decide the number of components to be retained from the factor analysis, the eigenvalues that were derived from the correlation matrix of the standardized variables were examined. Components with an eigenvalue greater than 1 were retained for the data analyses. Moreover, the scree plot was used to confirm the previous decision. Based on the principle that the component scores are interpreted similarly to correlation coefficients (i.e., higher absolute scores indicate that the food group contributes most to the construction of the component), the food patterns (4 patterns in total) were defined in relation to those scores of variables that correlated most closely with the component (absolute loading value > 0.45). The orthogonal rotation, using the varimax option, was employed to derive optimal, non-correlated dietary patterns. The information was rotated to increase the representation of each food as a component.
Linear regression models were applied to identify the variables that predict PhA. Briefly, PhA was considered the dependent variable, and various basic, anthropometric and dietary characteristics were considered the independent variables i.e., age, lean mass, MedDietScore, smoking (pack years), and dietary patterns identified by the PCA analysis. In order to distinguish the effects of dietary patterns from adherence to the Mediterranean diet, these variables were entered into the same model.
All reported p-values were two-sided (significance level 5%). SPSS v22 software was used for statistical analysis (IBM Corp. Released 2013, Armonk, NY, USA: IBM Corp.). The level of statistical significance was set at 5%. The statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS 18.0 for Windows, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for all the analyses.
3. Results
The basic characteristics of patients participating in this study are presented in Table 1. It is noted that only two subjects reported moderate physical activity and the rest of them reported low physical activity. Moreover, the BMI of patients was 26.9 ± 5 kg/m2, denoting the presence of underweight and overweight patients. The total lean mass was 57.4 ± 10.6 kg and the PhA was 5.1 ± 0.8°.

Table 1.
Basic characteristics of participants.
In Table 2, the basic dietary characteristics of the subjects are presented. The median consumption of legumes and fish was once per week, while the median consumption of meat and poultry was twice per week. The median consumption of olive oil, vegetables, and dairy corresponded to one or more portions per day, while fruit consumption was lower. The median and interquartile range of the MedDietScore of the participants was 31 and 29.0–33.0, respectively. The patients reported low alcohol intake (median intake: one portion/week).

Table 2.
Dietary characteristics of patients with lung cancer.
Figure 1 and Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials show the factor loadings for the identification of dietary patterns from PCA analysis. Briefly, four dietary patterns were identified that explained 57.4% of the total variance: Pattern 1 was characterized by the high consumption of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, pattern 2 by a high intake of potatoes, meat, and poultry, and pattern 3 by high olive oil and low alcohol consumption, while pattern 4 was characterized by high legume and fish consumption.
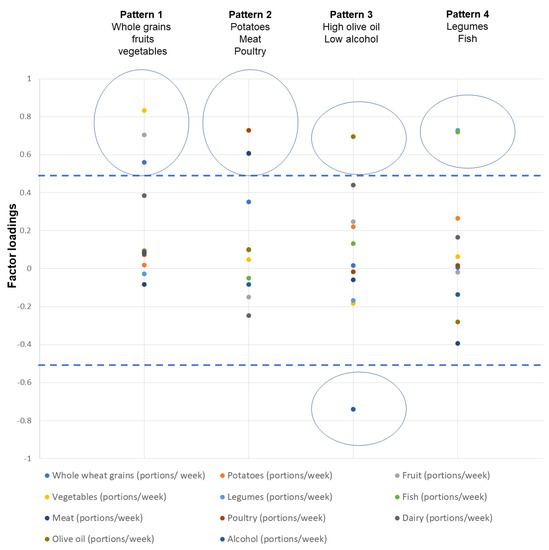
Figure 1.
Component loadings and identified dietary patterns through principal component analysis.
Higher absolute values of the loadings indicate that the food is correlated with the respective component. Food groups with absolute loadings greater than 0.5 (see dashed lines) correspond to a specific component. Circles denote the clustering of foods in one component. In total, four components were identified.
Table 3 shows the Spearman correlations between PhA and basic characteristics, anthropometric variables, and the dietary habits of participants. The only significant correlations that were found were between lean mass (kg) (rho = 0.247, p = 0.02), food pattern 2 (potato, meat, and poultry; rho = 0.254, p = 0.02), and PhA.

Table 3.
Spearman correlation coefficients between PhA and several parameters.
In Table 4, the linear regression models are shown, with PhA as a dependent variable. As can clearly be seen, NSCLC patients’ PhA could be better explained/determined by the combination of age, lean mass, and a dietary pattern rich in potatoes, meat, and poultry. The investigated dietary pattern explained PhA independently of age, lean mass, and Mediterranean diet adherence, as expressed by MedDietScore. The total variance explained in the whole model was ~24%.

Table 4.
Linear regression, with PhA as a dependent variable.
4. Discussion
The main finding of the present study was that a dietary pattern rich in potatoes, meat and poultry seems to determine NSCLC patients’ PhA, independently of their age, lean tissue, and MedDietScore.
Low values of PhA have been linked with lung cancer prognosis [6], which implies that the identification of dietary or other factors that could predict or modify PhA may have beneficial prognostic effects. Indeed, several studies report strong correlations between nutrition/nutritional habits and PhA [16,17] Nutritional interventions have been found to increase PhA in colorectal cancer patients [18], while no data exist regarding lung cancer patients.
In the present study, a dietary pattern rich in potatoes and animal proteins (meat and poultry) was positively related to PhA. Interestingly, PhA has recently been reported to be positively associated with meat consumption [22], while it seems to increase after a ketogenic diet independent of weight loss [23]. Of course, in our study, it was mostly a high-protein dietary scheme, rather than a ketogenic pattern that was a significant determinant of PhA. This can be concluded easily since, in the same pattern, high-protein choices (meat, poultry), as well as carbohydrate choices (potatoes), were present. In this context, our results possibly reflect the role of protein sources in cancer management and the prevention of lean mass reduction and sarcopenia [19,24], which, in turn, could influence body composition parameters, such as PhA [6,25].
It is noted that in the present study, no correlation was documented between PhA and other food groups, such as fish, fruits, legumes, and vegetables. This is in contrast with other studies reporting the protective effect of a Mediterranean diet and omega-3 regarding PhA [6,16,17,26]. This discrepancy may be due to the specific features of the present sample. In other words, in disease states, such as cancer, it is possible that the diet-PhA associations are differentiated. As evidenced by our results, food groups recommended for sarcopenia in cancer patients, such as animal protein sources [27], may be more important in determining PhA than a diet rich in antioxidants, which modifies PhA in healthy subjects [26].
The relationship of PhA with age and lean mass has been widely described in the literature. More particularly, PhA decreases with age in both apparently healthy individuals [28,29,30] and cancer patients [31], reflecting a deterioration in cellular integrity and/or body composition alterations [32], which is in line with our findings. In the present study, PhA was positively related to lean mass, as was expected according to the existing literature [28,30,33]. In the same context, PhA has been positively associated with functional fitness and better physical function in older adults [34], which depends on muscle mass [35].
In the present study, no correlations were observed between PhA and RMR. There are no data on the relationship between PhA and RMR in lung cancer patients. Interestingly, PhA has been found to be a significant predictor of resting energy expenditure in athletes [36], healthy subjects [37,38], and patients with Crohn’s disease [39], possibly reflecting the association of PhA with lean mass and muscle quality [40]. This discrepancy may be due to the inherent differences in the studied populations since we included only male subjects with advanced-stage NSCLC. It has also been noted that the proposed prediction equations of RMR, including PhA, constitute more complex functions with additional variables [37,38], so no direct comparison can be made with our results.
The present study included only men. Sex disparities have been documented in lung cancer incidence [41] and sex may also influence treatment outcomes (such as in the case of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and anti-programmed cell-death protein 1 (PD1) inhibitors) [42] or treatment complications [3]. Moreover, there are sex-related body composition [43] and PhA differences [28], and, possibly, sex differences in diet-related behaviors [44]. In this context, the sole inclusion of men can better reflect the net associations of diet with the PhA.
Along with the interpretation of our results, several limitations should be considered. Firstly, etiologic and/or mechanistic conclusions are difficult to draw from the present study since no dietary intervention was performed. Several caveats in the estimation of dietary intake may have taken place since self-reported data were used. Patients did not provide information about the type and source of meat nor on the way of cooking it. It should also be noted that no biochemical indices were available to assess the inflammatory or nutrient status. Last but not least, we have no data on segmental PhA measurements. However, it has been shown that whole-body PhA is a better predictor of malnutrition in cancer patients when several measurements are compared [31].
In conclusion, the results of the present study suggest that a diet rich in meat, poultry, and potatoes is a determinant of phase angle in male lung cancer patients. A potential change of PhA through diet is of particular importance for the clinical management of lung cancer patients and may have implications for their prognosis. Nevertheless, further well-designed intervention studies are needed to confirm or refute our findings.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/curroncol29110637/s1, Table S1: Component loadings derived using Principal Component Analysis for the identification of dietary patterns
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.V., D.M., D.G., M.R., T.T., M.M., P.P., K.K., F.S.K., P.Z. and S.K.P.; methodology, T.T., M.M., P.P., K.K., F.S.K., D.M., M.R., R.O., D.G., P.Z. and S.K.P.; formal analysis, S.M. and S.K.P.; investigation, T.T., M.P., F.P., M.M., P.P., K.K., S.M., F.S.K. and D.G.; resources, T.T., M.M., P.P., K.K., D.M., M.R., R.O., D.G., F.S.K. and S.K.P.; data curation, P.D., M.P., F.P. and M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, P.D.; writing—review and editing, S.M., P.Z. and S.K.P.; supervision, P.Z. and S.K.P.; project administration, D.M., M.R., R.O., D.G., T.T., M.P., F.P., M.M., P.P. and K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the investigational review board of (‘Theageneio’ Cancer Hospital, Thessaloniki, Greece, Protocol No: 16/07/2018 issue number: 14385) and was performed according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was acquired from the patients.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was acquired from the patients.
Data Availability Statement
The date are available if requested from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
BIA: bioelectrical impedance analysis; BMI: body mass index; MedDietSCore: Mediterranean diet score; NSCLC: non-small-cell lung cancer; PhA: phase angle; R: resistance; SCLC: small-cell lung cancer; SD: standard deviation; Xc: capacitive reactance.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Früh, M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Besse, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Hendriks, L.E.; Lantuejoul, S.; Peters, S.; Reguart, N.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiouda, T.; Sardeli, C.; Porpodis, K.; Pilikidou, M.; Apostolidis, G.; Kyrka, K.; Miziou, A.; Kyrka, K.; Tsingerlioti, Z.; Papadopoulou, S.; et al. Sex Differences and Adverse Effects between Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilikidou, M.; Palyvou, F.; Papadopoulou, S.; Tsiouda, T.; Tsekitsidi, E.; Arvaniti, K.; Miziou, A.; Tsingerlioti, Z.; Apostolidis, G.; Ntiloudis, R.; et al. Lung Cancer, Treatment and Nutritional Status. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarik, M.; Hronek, M.; Zadak, Z. Clinically Relevant Determinants of Body Composition, Function and Nutritional Status as Mortality Predictors in Lung Cancer Patients. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Voulgaridou, G.; Papadopoulou, S. Cancer, Phase Angle and Sarcopenia: The Role of Diet in Connection with Lung Cancer Prognosis. Lung 2022, 200, 347–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Tsiouda, T.; Pilikidou, M.; Palyvou, F.; Tsekitsidi, E.; Voulgaridou, G.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Papadopoulou, S.K. Changes in Body Weight, Body Composition, Phase Angle, and Resting Metabolic Rate in Male Patients with Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Therapy. submitted for publication.
- Mantzorou, M.; Tolia, M.; Poultsidi, A.; Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Papandreou, D.; Giaginis, C. Can Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and BMI Be a Prognostic Tool in Head and Neck Cancer Patients? A Review of the Evidence. Cancers 2020, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pugliese, G.; Laudisio, D.; de Alteriis, G.; Graziadio, C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Phase Angle as an Easy Diagnostic Tool of Meta-Inflammation for the Nutritionist. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreto, F.; de França, N.A.G.; Gondo, F.F.; Callegari, A.; Corrente, J.E.; Burini, R.C.; de Oliveira, E.P. High C-Reactive Protein Instead of Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with Lower Bioimpedance Phase Angle in Individuals Clinically Screened for a Lifestyle Modification Program. Nutrire 2017, 42, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeleri, C.M.; Cavaglieri, C.R.; de Souza, M.F.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Antunes, M.; Nabbuco, H.C.G.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Silva, A.M.; Cyrino, E.S. Phase Angle Is Related with Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Older Women. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 102, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabłocka-Słowińska, K.; Płaczkowska, S.; Prescha, A.; Pawełczyk, K.; Porębska, I.; Kosacka, M.; Pawlik-Sobecka, L.; Grajeta, H. Serum and Whole Blood Zn, Cu and Mn Profiles and Their Relation to Redox Status in Lung Cancer Patients. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 45, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabłocka-Słowińska, K.; Płaczkowska, S.; Prescha, A.; Pawełczyk, K.; Kosacka, M.; Porębska, I.; Grajeta, H. Systemic Redox Status in Lung Cancer Patients Is Related to Altered Glucose Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabłocka-Słowińska, K.; Porębska, I.; Gołecki, M.; Kosacka, M.; Pawełczyk, K.; Pawlik-Sobecka, L.; Zarębska, K.; Grajeta, H. Total Antioxidant Status in Lung Cancer Is Associated with Levels of Endogenous Antioxidants and Disease Stage Rather than Lifestyle Factors—Preliminary Study. Contemp. Oncol. Współczesna Onkol. 2016, 4, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, A.; Bilmin, K.; Chmielewska–Ignatowicz, T.; Pawlikowski, J.; Religioni, U.; Merks, P. The Role of Nutritional Support in Malnourished Patients With Lung Cancer. In Vivo 2021, 35, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderJagt, D.J.; Trujillo, M.R.; Bode-Thomas, F.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chuang, L.-T.; Glew, R.H. Phase Angle Correlates with N-3 Fatty Acids and Cholesterol in Red Cells of Nigerian Children with Sickle Cell Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2003, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderJagt, D.J. Phase Angle and N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Sickle Cell Disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2002, 87, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical Phase Angle and Impedance Vector Analysis—Clinical Relevance and Applicability of Impedance Parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidantsis, K.; Methenitis, S.; Ketselidi, K.; Vagianou, K.; Skepastianos, P.; Hatzitolios, A.; Mourouglakis, A.; Kaprara, A.; Hassapidou, M.; Nomikos, T.; et al. Comparison of Short-Term Hypocaloric High-Protein Diets with a Hypocaloric Mediterranean Diet: Effect on Body Composition and Health-Related Blood Markers in Overweight and Sedentary Young Participants. Nutrition 2021, 91–92, 111365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary Patterns: A Mediterranean Diet Score and Its Relation to Clinical and Biological Markers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagströmer, M.; Oja, P.; Sjöström, M. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ): A Study of Concurrent and Construct Validity. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaremków, A.; Markiewicz-Górka, I.; Hajdusianek, W.; Gać, P. Relationships between Body Composition Parameters and Phase Angle as Related to Lifestyle among Young People. JCM 2021, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Aprano, S.; Vetrani, C.; de Alteriis, G.; Varcamonti, L.; Verde, L.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Phase Angle as an Easy Diagnostic Tool for the Nutritionist in the Evaluation of Inflammatory Changes during the Active Stage of a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN Practical Guideline: Clinical Nutrition in Cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington-Rauth, M.; Baptista, F.; Sardinha, L.B. BIA-Assessed Cellular Hydration and Muscle Performance in Youth, Adults, and Older Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Macchia, P.; Di Somma, C.; Falco, A.; Savanelli, M.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Mediterranean Diet and Phase Angle in a Sample of Adult Population: Results of a Pilot Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, K.L.; Arends, J.; Atherton, P.J.; Engelen, M.P.K.J.; Gonçalves, T.J.M.; Laviano, A.; Lobo, D.N.; Phillips, S.M.; Ravasco, P.; Deutz, N.E.P.; et al. The Importance of Protein Sources to Support Muscle Anabolism in Cancer: An Expert Group Opinion. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Silva, M.C.G.; Barros, A.J.D.; Wang, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Pierson, R.N. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Population Reference Values for Phase Angle by Age and Sex. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, R.; Floris, G.; Marini, E. Migration of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Healthy Elderly Subjects. Nutrition 2003, 19, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Bielemann, R.M.; Gallagher, D.; Heymsfield, S.B. Phase Angle and Its Determinants in Healthy Subjects: Influence of Body Composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhao, J. The Clinical Application Value of Phase Angle of Six Parts in Nutritional Evaluation of Tumor Patients. Support Care Cancer 2022, 30, 7983–7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K. Sarcopenia: A Contemporary Health Problem among Older Adult Populations. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecka-Massalska, T.; Powrózek, T.; Prendecka, M.; Mlak, R.; Sobieszek, G.; Brzozowski, W.; Brzozowska, A. Phase Angle as an Objective and Predictive Factor of Radiotherapy-Induced Changes in Body Composition of Male Patients With Head and Neck Cancer. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.N.; Nunes, C.L.; Francisco, S.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Cyrino, E.S.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Phase Angle Predicts Physical Function in Older Adults. Arch. Gerontol. Ger. 2020, 90, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, M.-Y.; Chang, K.-V.; Wu, W.-T.; Huang, K.-C.; Han, D.-S. Grip Strength and Demographic Variables Estimate Appendicular Muscle Mass Better Than Bioelectrical Impedance in Taiwanese Older Persons. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Di Vincenzo, O.; Cioffi, I.; Sammarco, R.; Morlino, D.; Scalfi, L. Resting Energy Expenditure in Elite Athletes: Development of New Predictive Equations Based on Anthropometric Variables and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Derived Phase Angle. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Sammarco, R.; Cioffi, I.; Morlino, D.; Di Vincenzo, O.; Speranza, E.; Pasanisi, F. New Predictive Equations for Estimating Resting Energy Expenditure in Subjects with Normal Weight and Overweight. Nutrition 2021, 84, 111105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Pasanisi, F.; Scalfi, L.; Colicchio, P.; Chelucci, M.; Contaldo, F. The Prediction of Basal Metabolic Rate in Young Adult, Severely Obese Patients Using Single-Frequency Bioimpedance Analysis. Acta Diabetol. 2003, 40, s139–s141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Cioffi, I.; Morlino, D.; Vincenzo, O.D.; Pagano, M.C.; Imperatore, N.; Alfonsi, L.; Santarpia, L.; Castiglione, F.; Scalfi, L.; et al. New Predictive Equations for Estimating Resting Energy Expenditure in Adults With Crohn’s Disease. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks, M.; Kon, S.S.C.; Jones, S.E.; Canavan, J.L.; Nolan, C.M.; Higginson, I.J.; Gao, W.; Polkey, M.I.; Man, W.D.-C. Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle Relates to Function, Disease Severity and Prognosis in Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Miller, K.D.; Ma, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Islami, F.; Devesa, S.S.; Thun, M.J. Higher Lung Cancer Incidence in Young Women Than Young Men in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.A.; Vallejos, C.S.; Raez, L.E.; Mas, L.A.; Ruiz, R.; Torres-Roman, J.S.; Morante, Z.; Araujo, J.M.; Gómez, H.L.; Aguilar, A.; et al. Gender and Outcomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Old Prognostic Variable Comes Back for Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy? ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Nomikos, T.; Fragopoulou, E.; Panagiotakos, D.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C.; Antonopoulou, S. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) Activity, Platelet-Activating Factor Acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) in Leukocytes and Body Composition in Healthy Adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2009, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Dedes, V.; Syka, D.; Tzirogiannis, K.; Panoutsopoulos, G.I. Mediterranean Diet, a Posteriori Dietary Patterns, Time-Related Meal Patterns and Adiposity: Results from a Cross-Sectional Study in University Students. Diseases 2022, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).