Meta-Analysis of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Patients with Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria and Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quantity and Quality of Trials
3.2. Patient Characteristics
3.3. Surgical Approach and Resection Type
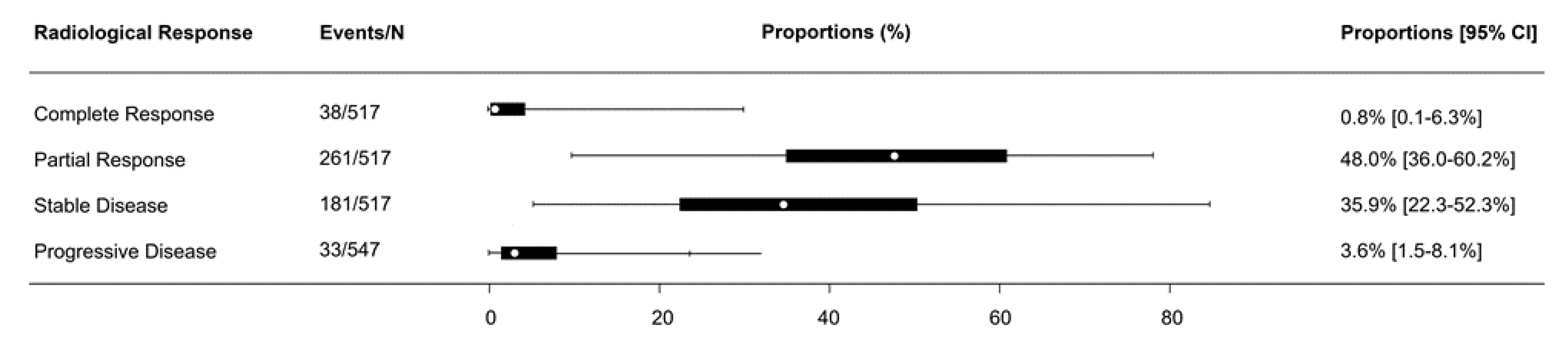
3.4. Radiological Response
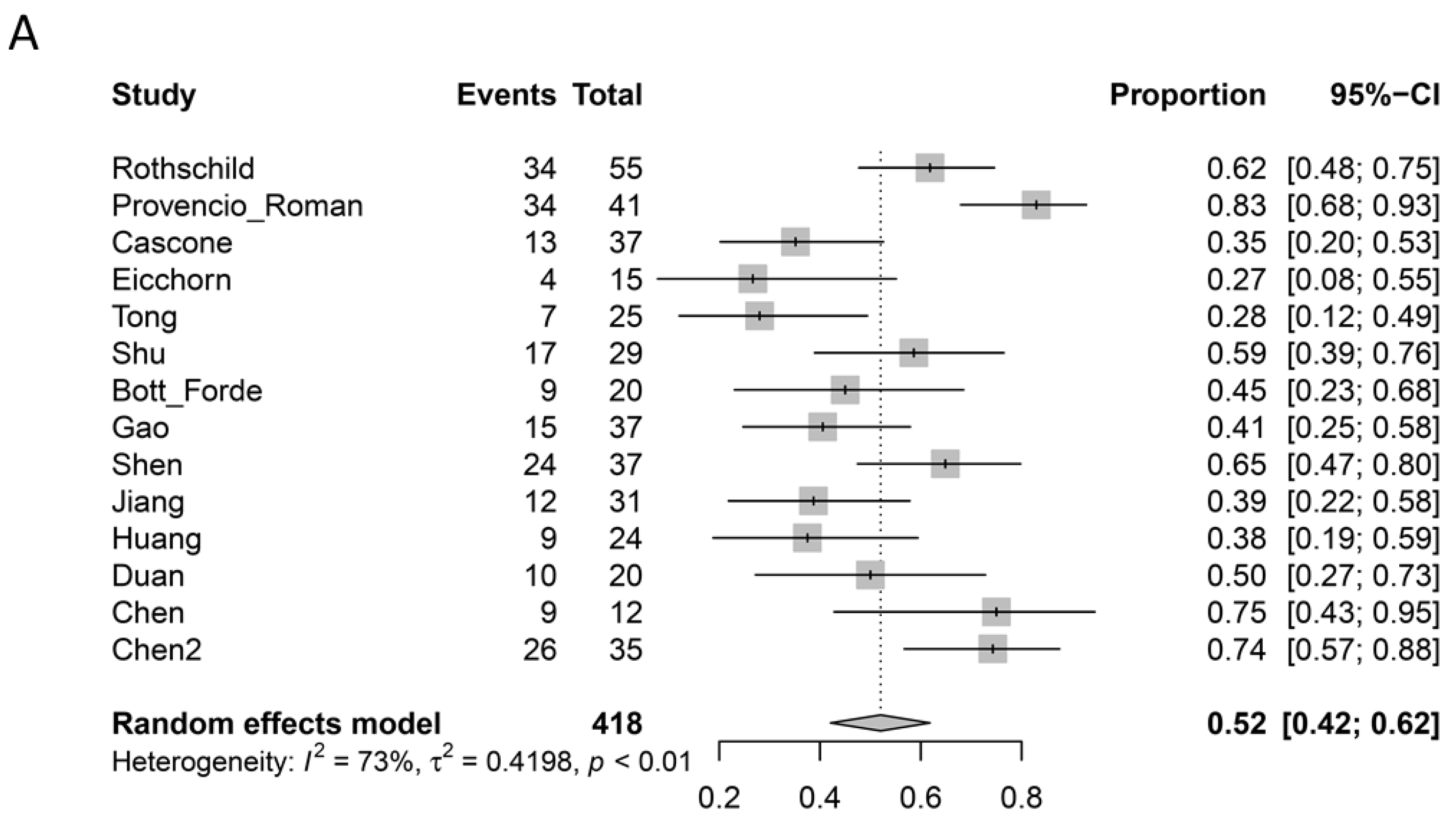
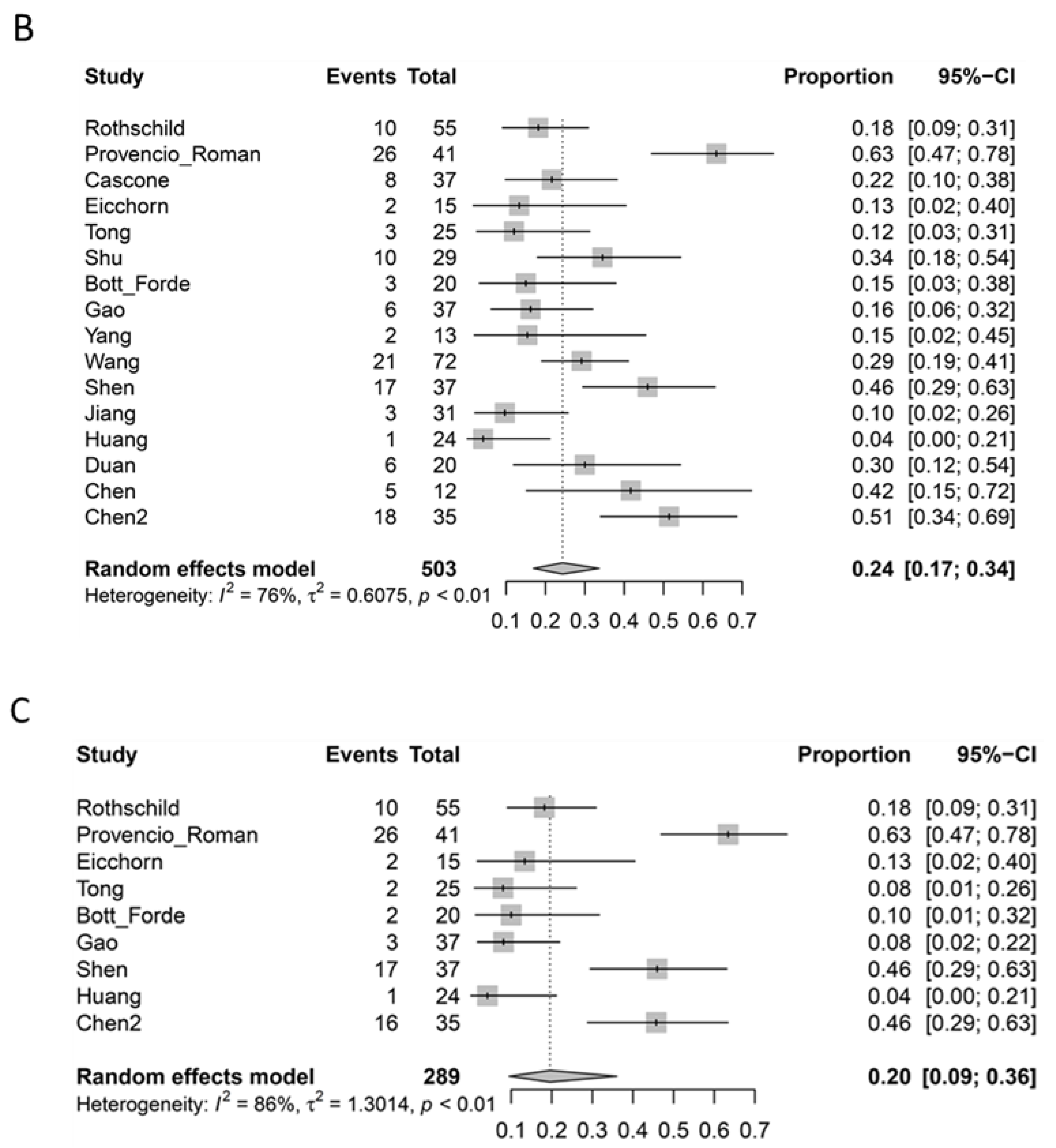
3.5. Pathological Response
3.6. Mortality and Morbidity
3.7. Overall Survival and Disease-Free Survival
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICI | immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| VATS | video assisted thoracoscopic surgery |
| RECIST | response evaluation criteria in solid tumors |
| MPR | major pathological response |
| pCR | complete pathological response |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
References
- Herbst, R.S.; Giaccone, G.; de Marinis, F.; Reinmuth, N.; Vergnenegre, A.; Barrio, C.H.; Morise, M.; Felip, E.; Andric, Z.; Geater, S.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of PD-L1-Selected Patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group NM-aC. Preoperative chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet 2014, 383, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Blake, S.J.; Yong, M.C.; Harjunpaa, H.; Ngiow, S.F.; Takeda, K.; Young, A.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Allen, S.; Smyth, M.J.; et al. Improved Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Compared to Adjuvant Immunotherapy to Eradicate Metastatic Disease. Cancer Dis. 2016, 6, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Meta-analysis of Proportions Using Generalized Linear Mixed Models. Epidemiology 2020, 31, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, S.I.; Zippelius, A.; Eboulet, E.I.; Prince, S.S.; Betticher, D.; Bettini, A.; Fruh, M.; Joerger, M.; Ladinois, D.; Gelpke, H.; et al. SAKK 16/14: Durvalumab in Addition to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Stage IIIA(N2) Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer-A Multicenter Single-Arm Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencio, M.; Nadal, E.; Insa, A.; Garcia-Campelo, M.R.; Casal-Rubio, J.; Domine, M.; Majem, M.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Carpeno, J.D.C.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and nivolumab in resectable non-small-cell lung cancer (NADIM): An open-label, multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Román, A.; Campo-Cañaveral de la Cruz, J.L.; Macía, I.; Campuzano, I.E.; Almanzar, S.F.; Roel, M.D.; Munoz, C.G.; Garcia Fontan, E.M.; Trueba, I.M.; Vielva, L.R.; et al. Outcomes of surgical resection after neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in locally advanced stage IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, T.; William, W.N.; Weissferdt, A., Jr.; Leung, C.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Pataer, A.; Godoy, M.C.B.; Carter, B.W.; Federico, L.; Reuben, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in operable non-small cell lung cancer: The phase 2 randomized NEOSTAR trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, F.; Klotz, L.V.; Kriegsmann, M.; Bischoff, H.; Schneider, M.A.; Muley, T.; Kriegsmann, K.; Haberkorn, U.; Heussel, C.P.; Savai, R.; et al. Neoadjuvant anti-programmed death-1 immunotherapy by pembrolizumab in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: First clinical experience. Lung Cancer 2021, 153, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.C.; Gu, L.; Wang, X.; Wigle, D.A.; Phillips, J.D.; Harpole, D.H.; Klapper, J.A.; Sporn, T.; Ready, N.E.; D’Amico, T.A. Perioperative outcomes of pulmonary resection after neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.A.; Gainor, J.F.; Awad, M.M.; Chiuzan, C.; Grigg, C.M.; Pabani, A.; Garofano, R.F.; Stoopler, M.B.; Cheng, S.K.; White, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant atezolizumab and chemotherapy in patients with resectable non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, M.J.; Yang, S.C.; Park, B.J.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Rusch, V.W.; Isbell, J.M.; Downey, R.J.; Brahmer, J.R.; Battafarano, R.; Bush, E.; et al. Initial results of pulmonary resection after neoadjuvant nivolumab in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 158, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, P.M.; Chaft, J.E.; Smith, K.N.; Anagnostou, V.; Cottrell, T.R.; Hellman, M.D.; Zahurak, M.; Yang, S.C.; Jones, D.R.; Broderick, S.; et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 Blockade in Resectable Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Li, N.; Gao, S.; Xue, Q.; Ying, J.; Wang, S.; Tao, X.; Zhao, J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor (Sintilimab) in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.J.; McSherry, F.; Mayne, N.R.; Wang, X.; Berry, M.F.; Tong, B.; Harpole, D.H.; D’Amico, T.A.; Christensen, J.D.; Ready, N.E.; et al. Surgical Outcomes After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Ipilimumab for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Cai, L.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y. The safety and efficacy of neoadjuvant programmed death 1 inhibitor therapy with surgical resection in stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Y. Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab with chemotherapy for the treatment of stage IIB-IIIB resectable lung squamous cell carcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Rong, W.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Ning, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. The surgical perspective in neoadjuvant immunotherapy for resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Qiu, T.; Liu, A.; Dong, T.; Su, W.; Du, W.; et al. Perioperative safety and feasibility outcomes of stage IIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer following neoadjuvant immunotherapy or neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A retrospective study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, T.; Luo, Z.; Tong, L.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Afzal, M.Z.; Correale, P.; Liu, H.; Jiang, T.; et al. Neoadjuvant programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: An open-label, multicenter, single-arm study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ning, J.; Campisi, A.; Dell’Amore, A.; Ciarrocchi, A.P.; Li, Z.; Song, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Stella, F.; et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitors and chemotherapy for locally advanced NSCLC: A retrospective study. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, B.; Xu, F.; Hui, Z.; Zhao, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Provencio, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in resectable stage IIIA/IIIB non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstraw, P.; Crowley, J.; Chansky, K.; Giroux, D.J.; Groome, P.A.; Rami-Porta, R.; Postmus, P.E.; Rusch, V.; Sobin, L. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuch, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar]
- Chaft, J.E.; Rusch, V.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Paik, P.K.; Finley, D.J.; Kris, M.G.; Price, K.A.R.; Azzoli, C.G.; Fury, M.G.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Phase II trial of neoadjuvant bevacizumab plus chemotherapy and adjuvant bevacizumab in patients with resectable nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Chaft, J.E.; William, W.N., Jr.; Rusch, V.; Pisters, K.M.W.; Kalhor, N.; Pataer, A.; Travis, W.D.; Swisher, S.G.; Kris, M.G.; et al. Pathological response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable non-small-cell lung cancers: Proposal for the use of major pathological response as a surrogate endpoint. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e42–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Mostofian, F.; Ivanovic, J.; Gilbert, S.; Maziak, D.E.; Shamji, F.M.; Sundaresan, S.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Seely, A.J.E. All grades of severity of postoperative adverse events are associated with prolonged length of stay after lung cancer resection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dy, G.K.; Bogner, P.N.; Tan, W.; Demmy, T.L.; Farooq, A.; Chen, H.; Yendamuri, S.S.; Nwogu, C.E.; Bushunow, P.W.; Gannon, J.; et al. Phase II Study of Perioperative Chemotherapy with Cisplatin and Pemetrexed in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajaram, R.; Mohanty, S.; Bentrem, D.J.; Pavey, E.S.; Odell, D.D.; Bharat, A.; Bilimoria, K.Y.; DeCamp, M.M. Nationwide Assessment of Robotic Lobectomy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, B.J.; Yang, H.X.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S. Minimally invasive (robotic assisted thoracic surgery and video-assisted thoracic surgery) lobectomy for the treatment of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, S406–S413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakanishi, R.; Fujino, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Shinohara, S.; Oyama, T. Thoracoscopic anatomic pulmonary resection for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Dacic, S.; Wistuba, I.; Sholl, L.; Adusumilli, P.; Bubendorf, L.; Bunn, P.; Cascone, T.; Chaft, J.; Chen, G.; et al. IASLC Multidisciplinary Recommendations for Pathologic Assessment of Lung Cancer Resection Specimens After Neoadjuvant Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 709–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wislez, M.; Mazières, J.; Lavolé, A.; Zalcman, G.; Carre, O.; Egenod, T.; Caliandro, R.; Gervais, R.; Jeannin, G.; Molinier, O.; et al. 1214O Neoadjuvant durvalumab in resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Preliminary results from a multicenter study (IFCT-1601 IONESCO). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Adam, J.; Cozic, N.; Chaput-Gras, N.; Planchard, D.; Mezquita, L.; Remon Masip, J.; Lavaud, P.; Naltet, C.; Gazzah, A.; et al. 1215O-SC Neoadjuvant atezolizumab (A) for resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Results from the phase II PRINCEPS trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S794–S795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Institution | Recruitment Period | F/U (Months) | Immunotherapy | Chemotherapy | Adjuvant Immunotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rothschild, 2021 [5] | 14 institutions in Sweden | 6/2016–1/2019 | 29 | Durvalumab (750 mg) 2 cycles | Cisplatin + docetaxel | Durvalumab 26 cycles |
| NADIM Provencio, 2021 [6] Roman, 2021 [7] | 18 institutions in Spain | 4/2017–8/2018 | 24 | Nivolumab (360 mg) 3 cycles | Paclitaxel + carboplatin 3 cycles | Nivolumab (240 mg q2w for 4 months then 480 mg q4w for 8 months) |
| NEOSTAR Cascone, 2021 [8] | MD Anderson Cancer Center, USA | 6/2017–11/2018 | 22 | Nivolumab (3 mg/kg on D1, 15, 29) 3 cycles or Nivolumab 3 cycles + Ipilimumab (1 mg/kg on D1 only) | NS | NS |
| NEOMUN Eichhorn, 2021 [9] | Heidelberg University Hospital, Germany | 5/2018–3/2020 | NS | Pembrolizumab (200 mg) 2 cycles | NS | NS |
| Tong, 2021 [10] | Mayo Clinic; Dartmouth- Hitchcock; Duke University, USA | 4/2017–2/2019 | 11 | Pembrolizumab (200 mg) 2 cycles | NS | Pembrolizumab 4 cycles |
| Shu, 2020 [11] | Columbia University; MGH; BWH; Vanderbilt University Medical Center, USA | 5/2016–3/019 | 13 | Atezolizumab (1200 mg) 4 cycles | Paclitaxel + carboplatin 4 cycles | NS |
| Bott, 2019 [12] Forde, 2018 [13] | Johns Hopkins; MSKCC, USA | 8/2015–10/2016 | 20 | Nivolumab (3 mg/kg) 2 cycles | NS | NS |
| Gao, 2020 [14] | PUMC | 3/2018–3/2019 | 3 | Sintilimab (200 mg) 2 cycles | NS | Sintilimab |
| Yang, 2018 [15] | Duke University Medical Centre, USA | 3/2013–12/2015 | 24 | Ipilimumab (10 mg/kg) 2 cycles | Paclitaxel + cisplatin or carboplatin 3 cycles | NS |
| Wang, 2021 [16] | Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, China | 9/2019–7/2020 | NS | Nivolumab (200 mg), pembrolizumab (100 mg), camrelizumab (200 mg) 2 cycles | Paclitaxel + carboplatin q3w | NS |
| Shen, 2021 [17] | Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, China | 6/2019–7/2020 | 7 | Pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg) 2 cycles | Paclitaxel + carboplatin 2 cycles | NS |
| Jiang, 2021 [18] | Shanghai Chest Hospital, China | 9/2018–4/2020 | NS | Pembrolizumab or nivolumab 3 cycles | NS | Variable |
| Huang, 2021 [19] | Qingdao University Hospital, China | 6/2019–12/2020 | NS | Nivolumab (3 mg/kg) 2 cycles | NS | NS |
| Duan, 2021 [20] | Tangdu Hospital; Chongqing Medical University, China | 6/2018–6/2020 | NS | Sintilimab or nivolumab or pembrolizumab, 3–4 cycles | Pemetrexed + cisplatin or Paclitaxel + nedaplatin or Gemcitabine + nedaplatin or Paclitaxel + Carboplatin 3–4 cycles | NS |
| Chen, 2021 [21] | Shanghai Chest Hospital, China | 1/2019–3/2020 | 18 | Pembrolizumab 4 cycles or nivolumab 2 cycles | Carboplatin and paclitaxel | Variable |
| Chen, 2021 [22] | Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital | 1/2019–5/2020 | 13 | Pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg) 2 cycles q3w | Cisplatin + paclitaxel liposome or pemetrexed q3w | NS |
| Histopathology | Clinical Stage | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy | Operation (%) | Male (%) | Age | Smoking History (%) | SCC | ADC | Other | IA | IB | IIA | IIB | IIIA | IIIB | |||
| Rothschild [5] | 62 ^ | 55 | 88.7% | 35 | 52.2% | 61 | 64 | 92.3% | 22 | 37 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 0 |
| Provencio [6] * Roman [7] * | 46 | 41 | 89.1% | 34 | 73.9% | 63 | 46 | 100% | 16 | 26 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 45 | 0 |
| Cascone [8] * | 44 | 39 | 88.6% | 28 | 63.6% | 65.6 | 36 | 81.8% | 17 | 26 | 1 | 8 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 0 |
| Eicchorn [9] * | 15 | 15 | 100% | 7 | 46.7% | 59.8 | - | - | 2 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 9 | 0 |
| Tong [10] | 30 | 25 | 83.3% | 16 | 53.3% | 72 | 26 | 86.7% | 17 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 0 |
| Shu [11] | 30 | 29 | 96.7% | 15 | 50.0% | 67 | 30 | 100% | 12 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 23 | 0 |
| Bott [12] Forde [13] | 22 | 20 | 90.9% | 10 | 45.5% | 67 | 18 | 81.8% | 5 | 14 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 0 |
| Gao [14] * | 40 | 39 | 97.5% | 33 | 82.5% | 62 | 32 | 80.0% | 33 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 13 | 10 | 8 |
| Yang [15] | 24 | 13 | 54.2% | 12 | 50.0% | 65 | 23 | 95.8% | 9 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 19 | 0 |
| Wang [16] | 72 | 72 | 100% | 66 | 91.7% | 62.2 | 60 | 83.3% | 66 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 72 | 0 |
| Shen [17] | 37 | 37 | 100% | 35 | 94.6% | 62.8 | 31 | 83.8% | 37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 28 | 6 |
| Jiang [18] * | 31 | 31 | 100% | 29 | 93.5% | 61 | 7 | 22.6% | 22 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 16 | 10 |
| Huang [19] * | 25 | 24 | 96.0% | 16 | 64.0% | 62.9 | 15 | 60.0% | 8 | 13 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 |
| Duan [20] | 23 | 20 | 87.0% | 22 | 95.7% | 61.8 | 22 | 95.7% | 19 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 9 |
| Chen [21] * | 12 | 12 | 100% | 9 | 75.0% | 61 | 9 | 75.0% | 4 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 5 |
| Chen [22] * | 35 | 35 | 100% | 29 | 82.9% | 62.2 | 27 | 77.1% | 26 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 4 |
| Total | 548 | 507 | 95.9% | 396 | 73.7% | IQR (61.5–65.5) | 446 | 81.7% | 56.6% | 36.9% | 4.2% | 0.1% | 0.2% | 2.3% | 6.2% | 78.0% | 1.0% |
| Resection Margin | Type of Surgery | Surgical Approach | Final Immunotherapy to Surgery | Blood Loss | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | R0 | R1 | R2 | Pneumonectomy | Bilobectomy | Lobectomy | Sleeve Lobectomy | Wedge | Other | Exploratory | Thoracotomy | MIS | Conversion to Open | Median Days | Delay (n) | Time (min) | Blood Loss (mL) | Transfusion |
| Rothschild [5] | 51 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 43 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Provencio [6], Roman [7] | 41 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 32 | 3 | 0 | - | 0 | 24/41 | 17/41 | 4/41 | - | 0 | 195 | - | 1 |
| Cascone [8] | 39 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 31 | 8 | - | - | - |
| Eicchorn [9] | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - |
| Tong [10] | 22 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 18 | 2 | - | 1 | - | 7/25 | 18/25 | 5/25 | 26 | 1 | 305 | - | 2 |
| Shu [11] | 26 | - | - | 3 | 4 | 19 | 0 | 0 | - | 3 | 14/29 | 12/29 | - | 27 | 0 | - | - | 2 |
| Bott [12] Forde [13] | 20 | - | - | 2 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 14/20 | 6/20 | 7/20 | 18 | 0 | 228 | 100 | - |
| Gao [14] | 36 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 5 | 18 | 1 | 0 | - | 2 | 29/39 | 10/39 | - | - | 2 | - | - | - |
| Yang [15] | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 1 | - | - | 4/13 | 9/13 | 3/13 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 |
| Wang [16] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | - | - | - |
| Shen [17] | 37 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 22 | 6 | - | - | - | 12/37 | 25/37 | - | - | - | 184 | - | - |
| Jiang [18] | 24 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 18 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23/31 | 8/31 | 1 | 34 | - | 158 | 200 | 2 |
| Huang [19] | 23 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 19 | - | - | 1 | - | 0/24 | 24/24 | - | 29 | 0 | 196 | 92 | - |
| Duan [20] | 19 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 5 | 0 | - | 0 | 6/20 | 14/20 | 2/20 | - | - | 250 | 212.5 | 2 |
| Chen [21] | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 0 | - | 0 | 9/12 | 3/12 | - | 28 | 1 | 140 | 200 | - |
| Chen [22] | 35 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 9 | - | - | 14 # | - | 34/35 | 1/35 | - | 33 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Overall | 97.3% | 1.7% | 0.6% | 8.6% | 12.1% | 67.5% | 7.8% | 0.9% | 5.0% | 1.4% | 51.7% | 47.4% | 12.4% | IQR (27– 32) | 2.0% | IQR (171–239) | 96–207 | 6.9% |
| Radiological Response * | Pathological Response | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | CR | PR | SD | PD | Major Pathological Response | Complete Pathological Response Primary Lesion | Complete Pathological Response Primary Lesion + Nodes |
| Rothschild [5] | 4/62 | 32/62 | 16/62 | 7/62 | 34/55 | 10/55 | 10/55 |
| Provencio [6] Roman [7] | 2/46 | 33/46 | 11/46 | 0 | 34/41 | 26/41 | 26/41 |
| Cascone [8] | 1/44 | 8/44 | 28/44 | 6/44 | 13/37 | 8/37 | - |
| Eicchorn [9] | 0 | 4/15 | 10/15 | 0 | 4/15 ^ | 2/15 | 2/15 |
| Tong [10] | - | - | - | 1/30 | 7/25 | 3/25 | 2/25 |
| Shu [11] | 0 | 19/30 | 9/30 | 2/30 | 17/29 | 10/29 | - |
| Bott [12] Forde [13] | 0 | 2/21 | 18/21 | 1/21 | 9/20 | 3/20 | 2/20 |
| Gao [14] | 0 | 8/40 | 28/40 | 4/40 | 15/37 | 6/37 | 3/37 |
| Yang [15] | 0 | 14/24 | 2/24 | 8/24 | - | 2/13 | - |
| Wang [16] | 21/72 | 47/72 | 3/72 | 1/72 | - | 21/72 | - |
| Shen [17] | 10/37 | 22/37 | 5/37 | 0 | 24/37 | 17/37 | 17/37 |
| Jiang [18] | 0 | 24/31 | 5/31 | 2/31 | 12/31 | 3/31 | - |
| Huang [19] | 0 | 8/25 | 16/25 | 1/25 | 9/24 | 1/24 | 1/24 |
| Duan [20] | 0 | 17/23 | 6/23 | 0 | 10/20 | 6/20 | - |
| Chen [21] | 0 | 6/12 | 6/12 | 0 | 9/12 ^ | 5/12 | - |
| Chen [22] | 0 | 17/35 | 18/35 | 0 | 26/35 | 18/35 | 16/35 |
| Total | 0.8% | 48.0% | 35.9% | 3.6% | 52.0% | 24.3% | 19.6% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, C.; Le, A.; Bott, M.; Yang, C.-F.J.; Gossot, D.; Melfi, F.; Tian, D.H.; Guo, A. Meta-Analysis of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Patients with Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4686-4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060395
Cao C, Le A, Bott M, Yang C-FJ, Gossot D, Melfi F, Tian DH, Guo A. Meta-Analysis of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Patients with Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(6):4686-4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060395
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Christopher, Anthony Le, Matthew Bott, Chi-Fu Jeffrey Yang, Dominique Gossot, Franca Melfi, David H. Tian, and Allen Guo. 2021. "Meta-Analysis of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Patients with Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Current Oncology 28, no. 6: 4686-4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060395
APA StyleCao, C., Le, A., Bott, M., Yang, C.-F. J., Gossot, D., Melfi, F., Tian, D. H., & Guo, A. (2021). Meta-Analysis of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Patients with Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Current Oncology, 28(6), 4686-4701. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060395





