Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart and Lung Diseases
Abstract
Introduction
Pathophysiology
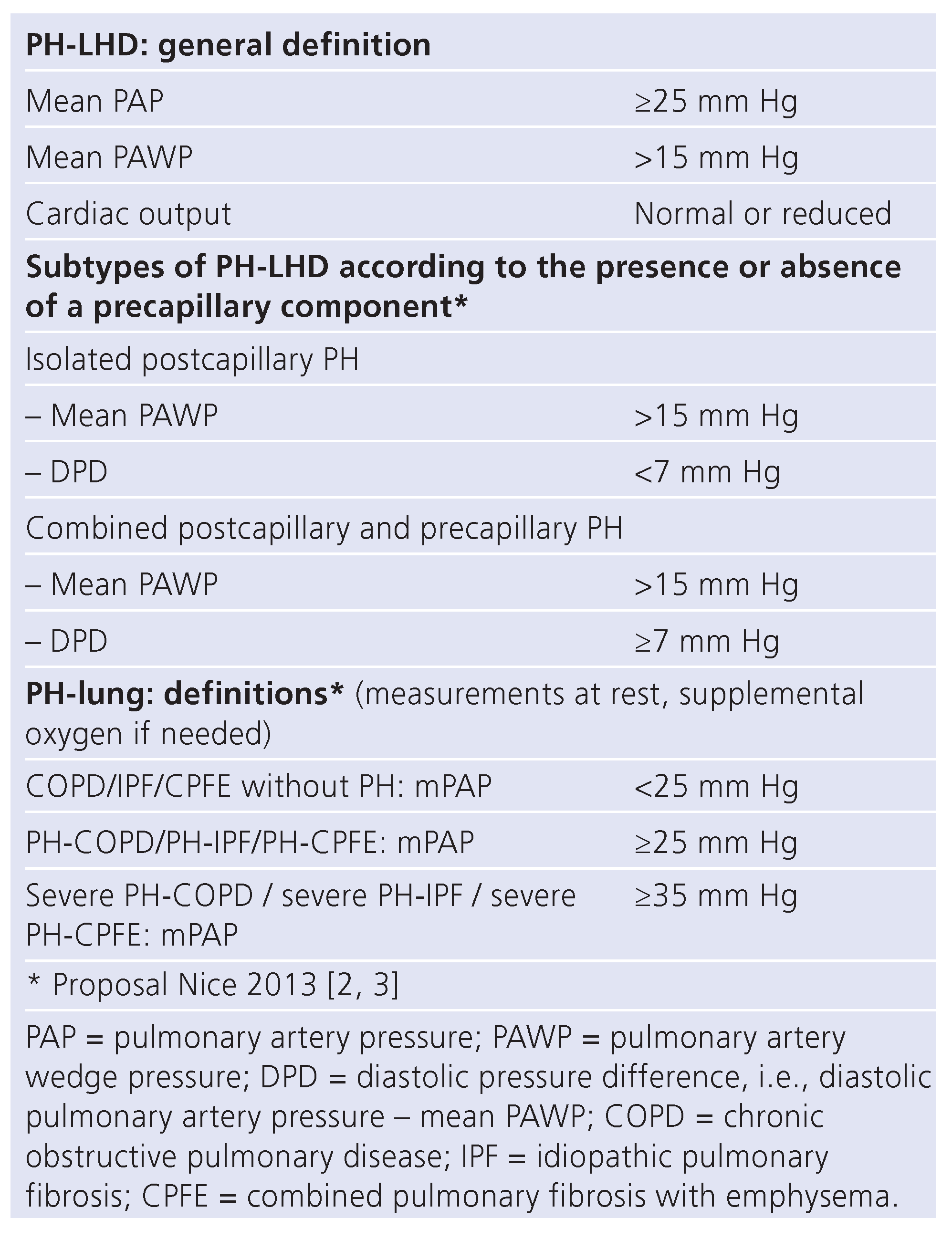
PH-LHD
PH-lung
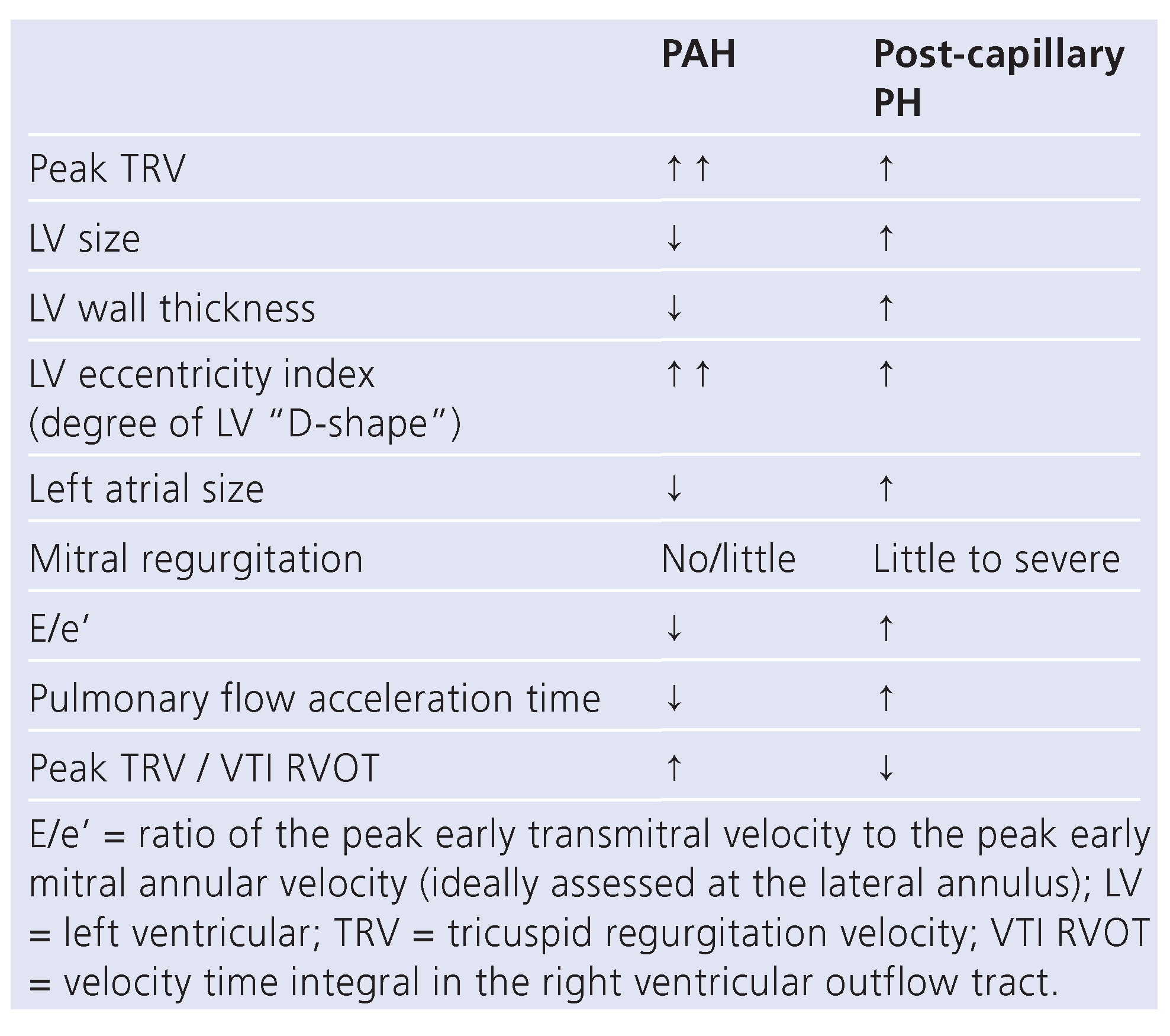
Assessment and definitions of PH-LHD
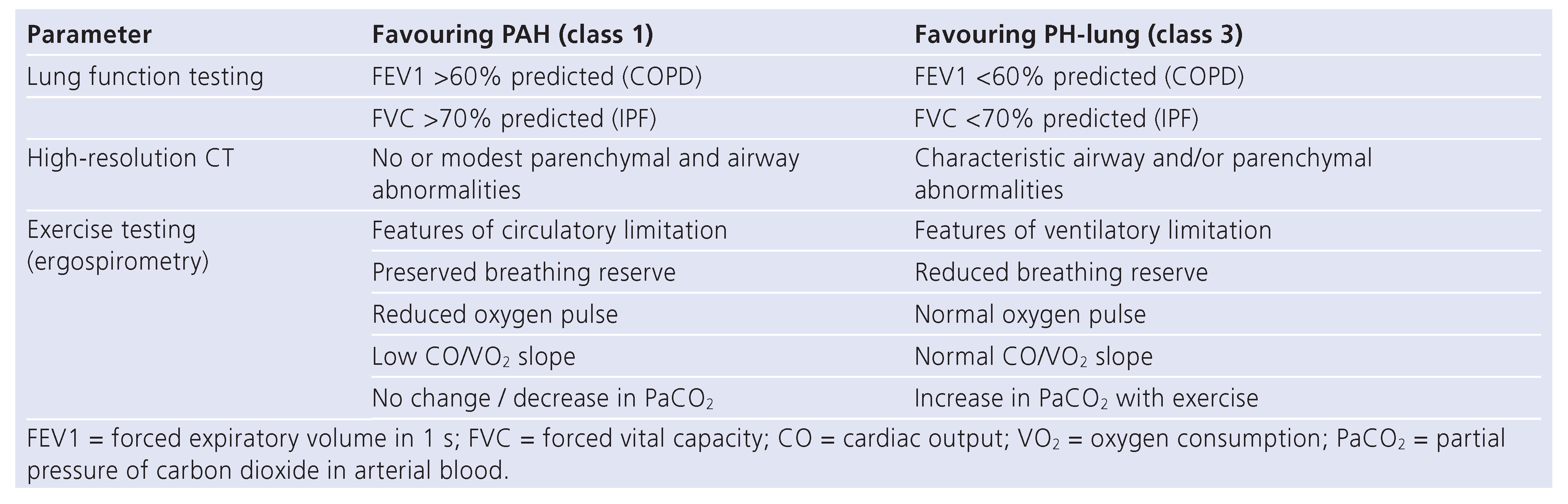
Assessment and definitions of PH-lung
Management of PH-LHD
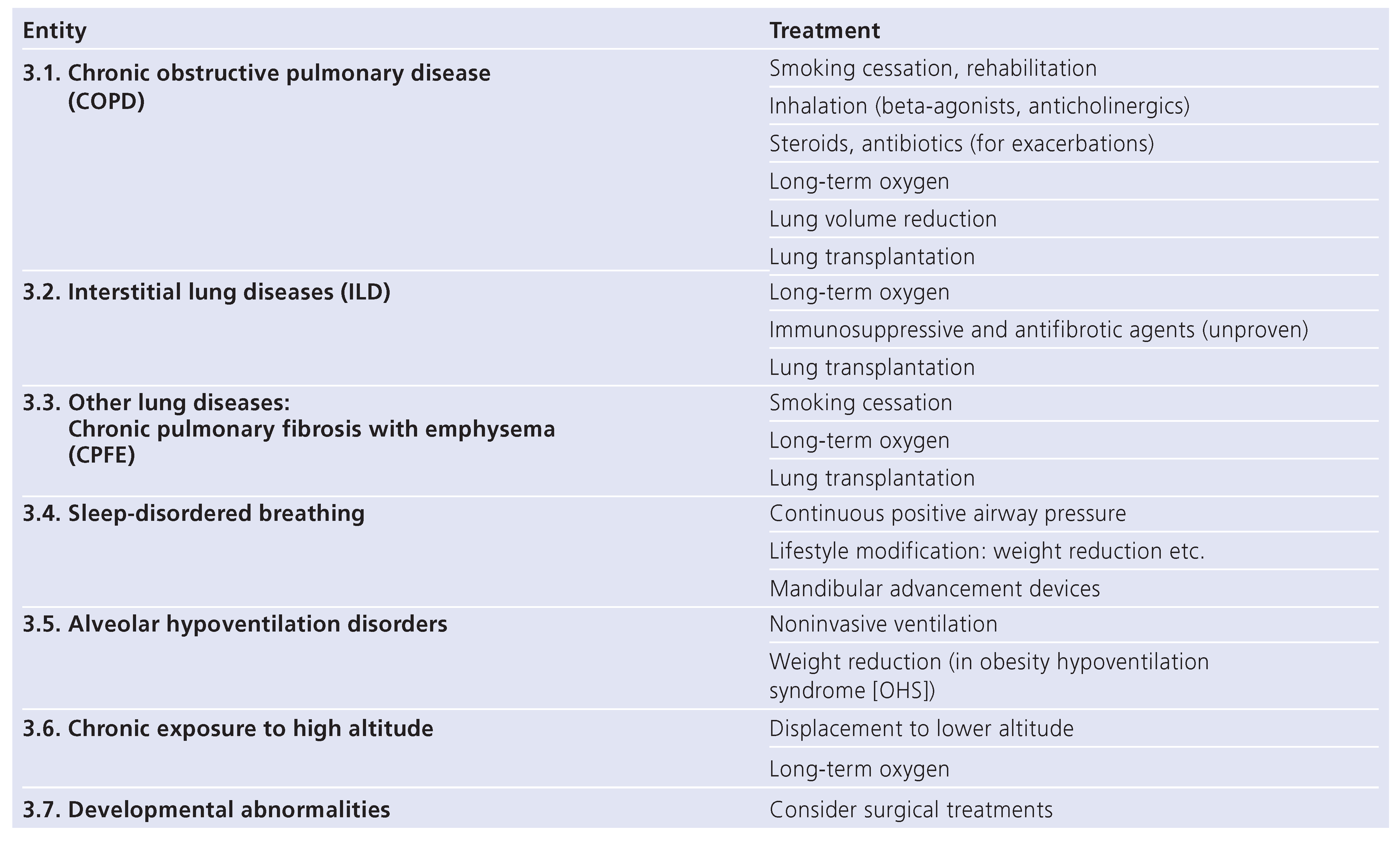
Management of PH-lung
Summary
Funding/potential competing interests:
List of Abbreviations
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CPFE | combined pulmonary fibrosis with emphysema |
| DPD | diastolic pressure difference |
| HFpEF | heart failure with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFrEF | heart failure with reduced ejection fraction |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| PAH | pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PAP | pulmonary artery pressure |
| PAWP | pulmonary artery wedge pressure |
| PDE-5 inhibitor | phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor |
| PH | pulmonary hypertension |
| PH-lung | pulmonary hypertension associated with lung disease |
| PH-LHD | pulmonary hypertension associated with left heart disease |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
| TPG | transpulmonary gradient |
| TRV | tricuspid regurgitation velocity |
References
- Simonneau, G.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Adatia, I.; Celermajer, D.; Denton, C.; Ghofrani, A.; et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am College Cardiol. 2013, 62, D34–D41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachiery, J.L.; Adir, Y.; Barbera, J.A.; Champion, H.; Coghlan, J.G.; Cottin, V.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart diseases. J Am College Cardiol. 2013, 62, D100–D108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, W.; Adir, Y.; Barbera, J.A.; Champion, H.; Coghlan, J.G.; Cottin, V.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung diseases. J Am College Cardiol. 2013, 62, D109–D116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald-Mammosser, M.; Weitzenblum, E.; Quoix, E.; Moser, G.; Chaouat, A.; Charpentier, C.; et al. Prognostic factors in COPD patients receiving long-term oxygen therapy. Importance of pulmonary artery pressure. Chest. 1995, 107, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorr, A.F.; Wainright, J.L.; Cors, C.S.; Lettieri, C.J.; Nathan, S.D. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with pulmonary fibrosis awaiting lung transplant. Eur Respir J. 2007, 30, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Cordier, J.F. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: An experimental and clinically relevant phenotype. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005, 172, 1605–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S.; Michelakis, E. The mechanism(s) of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction: Potassium channels, redox O(2) sensors, and controversies. News Physiol Sci. 2002, 17, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Galie, N.; Hoeper, M.M.; Humbert, M.; Torbicki, A.; Vachiery, J.L.; Barbera, J.A.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2009, 30, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- McGoon, M.; Gutterman, D.; Steen, V.; Barst, R.; McCrory, D.C.; Fortin, T.A.; et al. Screening, early detection, and diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2004, 126, 14S–34S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.A.; Rajagopalan, N.; Mathier, M.A.; Shroff, S.G.; Pinsky, M.R.; Lopez-Candales, A. Tissue Doppler imaging of right ventricular decompensation in pulmonary hypertension. Congest Heart Fail. 2009, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenappan, T.; Shah, S.J.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Collander, B.; Vallakati, A.; Shroff, P.; et al. Clinical characteristics of pulmonary hypertension in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opotowsky, A.R.; Ojeda, J.; Rogers, F.; Prasanna, V.; Clair, M.; Moko, L.; et al. A simple echocardiographic prediction rule for hemodynamics in pulmonary hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012, 5, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.E.; Fortuin, F.D.; Schiller, N.B.; Appleton, C.P.; Moreno, C.A.; Lester, S.J. A simple method for noninvasive estimation of pulmonary vascular resistance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003, 41, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeder, M.T.; Karapanagiotidis, S.; Dewar, E.M.; Gamboni, S.E.; Htun, N.; Kaye, D.M. Accuracy of Doppler echocardiography to estimate key hemodynamic variables in subjects with normal left ventricular ejection fraction. J Card Fail. 2011, 17, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunig, E.; Weissmann, S.; Ehlken, N.; Fijalkowska, A.; Fischer, C.; Fourme, T.; et al. Stress Doppler echocardiography in relatives of patients with idiopathic and familial pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results of a multicenter European analysis of pulmonary artery pressure response to exercise and hypoxia. Circulation 2009, 119, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Bogaard, H.J.; Condliffe, R.; Frantz, R.; Khanna, D.; Kurzyna, M.; et al. Definitions and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013, 62, D42–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, M.T.; Thompson, B.R.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Kaye, D.M. Hemodynamic basis of exercise limitation in patients with heart failure and normal ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010, 56, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, I.M.; Hemnes, A.R.; Pugh, M.E.; Brittain, E.L.; Zhao, D.X.; Piana, R.N.; et al. High prevalence of occult pulmonary venous hypertension revealed by fluid challenge in pulmonary hypertension. Circ Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcasoy, S.M.; Christie, J.D.; Ferrari, V.A.; Sutton, M.S.; Zisman, D.A.; Blumenthal, N.P.; et al. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2003, 167, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.R.; Criner, G.J.; Fishman, A.P.; Hassoun, P.M.; Minai, O.A.; Scharf, S.M.; et al. Estimating pulmonary artery pressures by echocardiography in patients with emphysema. Eur Respir J. 2007, 30, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahanian, A.; Alfieri, O.; Andreotti, F.; Antunes, M.J.; Baron-Esquivias, G.; Baumgartner, H.; et al. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease (version 2012). Eur Heart J. 2012, 33, 2451–2496. [Google Scholar]
- McMurray, J.J.; Adamopoulos, S.; Anker, S.D.; Auricchio, A.; Bohm, M.; Dickstein, K.; et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2012, 33, 1787–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Mullens, W.; Borowski, A.G.; Curtin, R.J.; Thomas, J.D.; Tang, W.H. Tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of intracardiac filling pressure in decompensated patients with advanced systolic heart failure. Circulation 2009, 119, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Shah, R.; Shahzad, K.; Camuso, J.M.; Pappagianopoulos, P.P.; Hung, J.; et al. Sildenafil improves exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with systolic heart failure and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2007, 116, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonderman, D.; Ghio, S.; Felix, S.B.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Michelakis, E.; Mitrovic, V.; et al. Riociguat for patients with pulmonary hypertension caused by systolic left ventricular dysfunction: A phase IIb double-blind, ran domized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging hemodynamic study. Circulation 2013, 128, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, M.T.; Rickli, H. [Heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction]. Praxis 2013, 102, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrom, A.; Andersson, B.; Edner, M.; Nylander, E.; Persson, H.; Dahlstrom, U. Effect of carvedilol on diastolic function in patients with diastolic heart failure and preserved systolic function. Results of the Swedish Doppler-echocardiographic study (SWEDIC). Eur J Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmala, W.; Holland, D.J.; Rojek, A.; Wright, L.; Przewlocka-Kosmala, M.; Marwick, T.H. Effect of If-channel inhibition on hemodynamic status and exercise tolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A randomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.S.; Layug, B.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Belardinelli, L.; Lee, S.; Sander, J.; et al. RAnoLazIne for the treatment of diastolic heart failure in patients with preserved ejection fraction: The RALI-DHF proof-of-concept study. JACC Heart failure 2013, 1, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, F.; Gelbrich, G.; Dungen, H.D.; Frohling, S.; Wachter, R.; Stahrenberg, R.; et al. Exercise training improves exercise capacity and diastolic function in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Results of the Ex-DHF (Exercise training in Diastolic Heart Failure) pilot study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1780–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, M.M.; Chen, H.H.; Borlaug, B.A.; Semigran, M.J.; Lee, K.L.; Lewis, G.; et al. Effect of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition on exercise capacity and clinical status in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 126–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzi, M.; Vicenzi, M.; Arena, R.; Guazzi, M.D. Pulmonary hypertension in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A target of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition in a 1–year study. Circulation 2011, 124, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, I.; Santos, S.; Gea, J.; Guell, R.; Torres, F.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; et al. Sildenafil to improve respiratory rehabilitation outcomes in COPD: A controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 2013, 42, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Gimeno, E.; Munoz, P.A.; Pizarro, S.; Gistau, C.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; et al. Hemodynamic and gas exchange effects of sildenafil in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010, 181, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, D.; Rasch, H.; Linka, A.; Di Valentino, M.; Meyer, A.; Brutsche, M.; et al. A randomised, controlled trial of bosentan in severe COPD. Eur Respir J. 2008, 32, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badesch, D.B.; Feldman, J.; Keogh, A.; Mathier, M.A.; Oudiz, R.J.; Shapiro, S.; et al. ARIES-3: Ambrisentan therapy in a diverse population of patients with pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovascular therapeutics 2012, 30, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.E., Jr. , Brown, K.K.; Raghu, G.; du Bois, R.M.; Lynch, D.A.; Martinez, F.; et al. BUILD-3: A randomized, controlled trial of bosentan in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011, 184, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Anstrom, K.J.; Schwarz, M.I.; Zisman, D.A. Sildenafil improves walk distance in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2007, 131, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.K.; Bach, D.S.; Hagan, P.G.; Yow, E.; Flaherty, K.R.; Toews, G.B.; et al. Sildenafil preserves exercise capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and right-sided ventricular dysfunction. Chest 2013, 143, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.A.; Garcia-Rio, F.; Alonso-Fernandez, A.; Martinez, I.; Villamor, J. Pulmonary hypertension in obstructive sleep apnoea: Effects of continuous positive airway pressure: A randomized, controlled cross-over study. Eur Heart J. 2006, 27, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
© 2014 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Maeder, M.T.; Kleiner, R.; Weilenmann, D.; Schoch, O.D. Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart and Lung Diseases. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 17, 320. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2014.00278
Maeder MT, Kleiner R, Weilenmann D, Schoch OD. Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart and Lung Diseases. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2014; 17(11):320. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2014.00278
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaeder, Micha T., Rebekka Kleiner, Daniel Weilenmann, and Otto D. Schoch. 2014. "Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart and Lung Diseases" Cardiovascular Medicine 17, no. 11: 320. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2014.00278
APA StyleMaeder, M. T., Kleiner, R., Weilenmann, D., & Schoch, O. D. (2014). Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart and Lung Diseases. Cardiovascular Medicine, 17(11), 320. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2014.00278




