Vanillin and Its Derivatives: A Critical Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Infective, Wound-Healing, Neuroprotective, and Anti-Cancer Health-Promoting Benefits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Quality Assessment
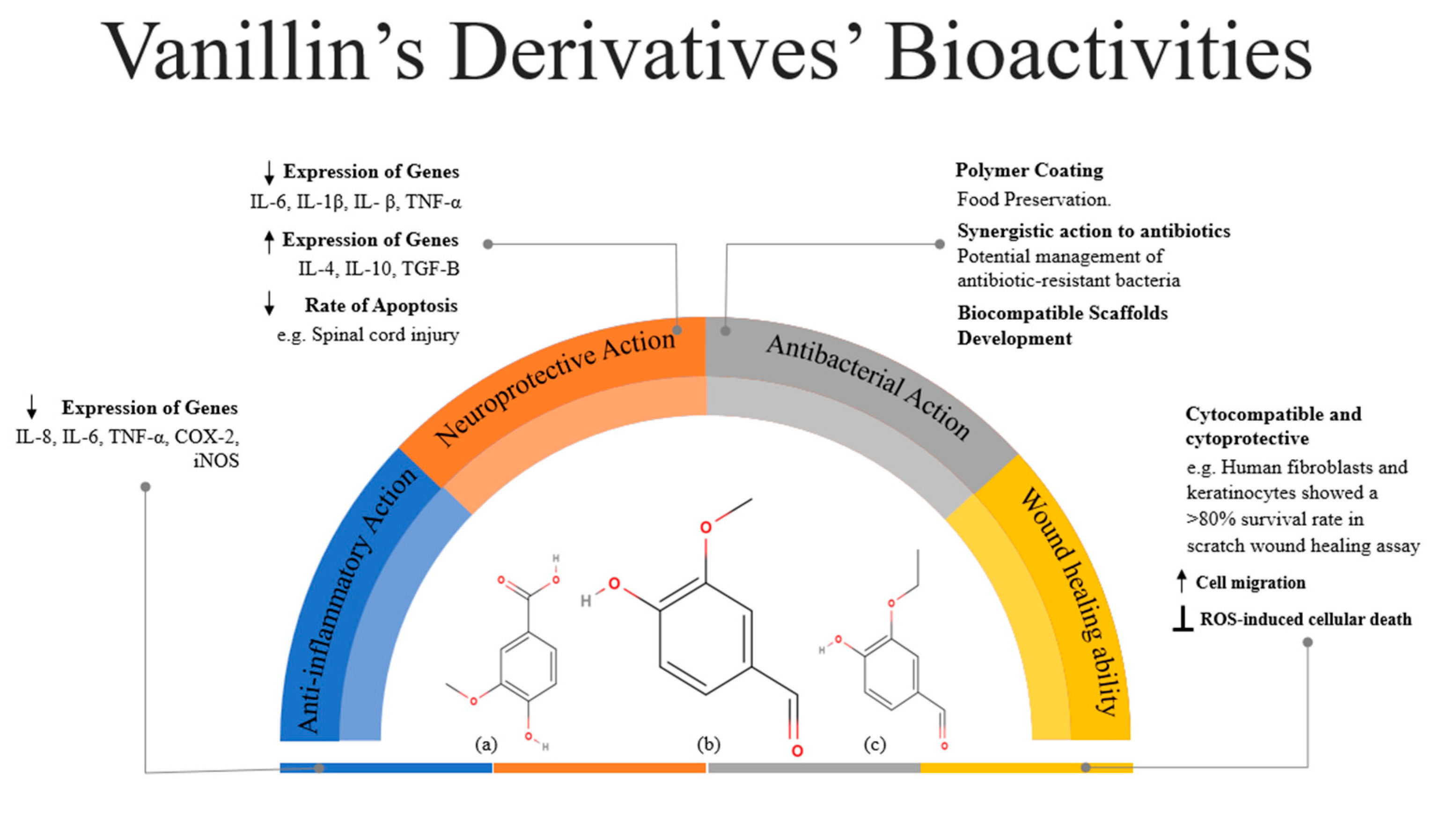
3. Bioactive Actions of Vanillin
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Action
3.2. Neuroprotective Action
3.3. Antibacterial Action
3.4. Wound-Healing Ability
4. Anti-Cancer Action
4.1. Melanoma
4.2. Colorectal Cancer
4.3. Breast Cancer
5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, A.U. An Overview of Inflammation: Mechanism and Consequences. Front. Biol. 2011, 6, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma-den Boer, M.M.; Van Wetten, M.-L.; Pruimboom, L. Chronic Inflammatory Diseases Are Stimulated by Current Lifestyle: How Diet, Stress Levels and Medication Prevent Our Body from Recovering. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, E.; Sinjari, B.; Falasca, K.; Reale, M.; Caputi, S.; Jagarlapodii, S.; Murmura, G. Assessment of the Vanillin Anti-Inflammatory and Regenerative Potentials in Inflamed Primary Human Gingival Fibroblast. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 5562340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.E.; Na, J.Y.; Park, Y.-D.; Lee, J.S. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of Vanillin Through the Regulation of Inflammatory Factors and NF-κB Signaling in LPS-Stimulated Microglia. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation, Not Cholesterol, Is a Cause of Chronic Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Savill, J. Resolution of Inflammation: The Beginning Programs the End. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, S.; Kaufmann, S.H.E. Infection, Inflammation, and Chronic Diseases: Consequences of a Modern Lifestyle. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, K.; Patrignani, P. New Insights into the Use of Currently Available Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignogna, C.; Costanzo, S.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Ruggiero, E.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Esposito, S.; De Curtis, A.; Persichillo, M.; Cerletti, C.; et al. The Inflammatory Potential of the Diet as a Link between Food Processing and Low-Grade Inflammation: An Analysis on 21,315 Participants to the Moli-Sani Study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, I.S.; Choue, R. Obesity, Inflammation and Diet. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Pérez, D.L.; Leyva-López, N.; Gutierrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Heredia, J.B. Phenolic Compounds: Natural Alternative in Inflammation Treatment. A Review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1131412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontaxi, N.-I.; Panoutsopoulou, E.; Ofrydopolou, A.; Tsoupras, A. Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Grape Pomace and Tomato Bioactives as Ingredients in Sun Oils against UV Radiation for Skin Protection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M. Elucidation of The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Vanillin In Lps-Activated THP-1 Cells. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakoczy, K.; Szlasa, W.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Therapeutic Role of Vanillin Receptors in Cancer. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, D. Vanillin: A Promising Biosourced Building Block for the Preparation of Various Heterocycles. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 949355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Ni, V.L.J.; O’Mahony, É.; Karali, M. Winemaking: “With One Stone, Two Birds”? A Holistic Review of the Bio-Functional Compounds, Applications and Health Benefits of Wine and Wineries’ By-Products. Fermentation 2023, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwar, P.; Ghufran Saeed, S.M.; Tsoupras, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Boateng, I.D. Effect of Electrolyzed Watermelon Rind Flour on Unleavened Flatbread Quality, Techno-Functional Properties, Minerals, Bioactivities, and Consumer Preferences. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.S.; Rookes, J.E.; Cahill, D.M.; Lenka, S.K. Vanillin: A Review on the Therapeutic Prospects of a Popular Flavouring Molecule. Adv. Tradit. Med. (ADTM) 2021, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Hua, S.; Sun, C.; Huang, L. Antibacterial Mechanism of Vanillin against Escherichia coli O157: H7. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, D.J.; Stratford, M.; Gasson, M.J.; Ueckert, J.; Bos, A.; Narbad, A. Mode of Antimicrobial Action of Vanillin against Escherichia coli, Lactobacillus Plantarum and Listeria Innocua. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunde, A.; Mohammed, A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Tajuddeen, N.; Shuaibu, M.N. Vanillin: A Food Additive with Multiple Biological Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2022, 5, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-M.; Chen, F.-Y.; Li, C.-C.; Lo, H.-Y.; Liao, Y.-F.; Ho, T.-Y.; Hsiang, C.-Y. Oral Administration of Vanillin Improves Imiquimod-Induced Psoriatic Skin Inflammation in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10233–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makni, M.; Chtourou, Y.; Fetoui, H.; Garoui, E.M.; Boudawara, T.; Zeghal, N. Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Properties of Vanillin in Carbon Tetrachloride-Treated Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, D.-F.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Liu, D.; Xu, S.-Y.; Chen, G.-X.; Huang, B.-X.; Ren, W.-Z.; Wang, W.; Fu, S.-P.; et al. Vanillin Protects Dopaminergic Neurons against Inflammation-Mediated Cell Death by Inhibiting ERK1/2, P38 and the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-L.; Chen, J.-C.; Li, C.-C.; Lo, H.-Y.; Ho, T.-Y.; Hsiang, C.-Y. Vanillin Improves and Prevents Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-Induced Colitis in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Su, Z.; Wang, Q.; Hou, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Vanillin Protects Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting ERK1/2, P38 and NF-κB Pathway. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2081–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salau, V.F.; Erukainure, O.L.; Olofinsan, K.O.; Msomi, N.Z.; Ijomone, O.M.; Islam, M.S. Vanillin Improves Glucose Homeostasis and Modulates Metabolic Activities Linked to Type 2 Diabetes in Fructose–Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 130, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Hu, G.; Kan, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, Q.; Xu, D.; Ma, H.; Cao, Y.; Huang, B.; et al. Vanillin Protects the Blood–Milk Barrier and Inhibits the Inflammatory Response in LPS-Induced Mastitis in Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 365, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, S.; Peferoen, L.A.N.; Vogel, D.Y.S.; Breur, M.; Van Der Valk, P.; Baker, D.; Van Noort, J.M. Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases—An Update. Immunology 2014, 142, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A. Inflammation, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Environmental Exposures. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1035, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.-B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.-M.; Ma, L.; Zhang, W.-J.; Zheng, P.; Sun, T.; Niu, J.-G.; Liu, N.; Yu, J.-Q. Neuroprotective Effect of Vanillin on Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage in Neonatal Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lou, X.; Xu, S.; Du, J.; Wu, J. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1α) reduced inflammation in spinal cord injury via miR-380-3p/NLRP3 by Circ 0001723. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, C.; Manivasagam, T.; Nataraj, J.; Justin Thenmozhi, A.; Essa, M.M. Neurosupportive Role of Vanillin, a Natural Phenolic Compound, on Rotenone Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 626028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Sarkaki, A.; Rashno, M.; Farbood, Y. Memory Deficits and Hippocampal Inflammation in Cerebral Hypoperfusion and Reperfusion in Male Rats: Neuroprotective Role of Vanillic Acid. Life Sci. 2018, 211, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, C.; Liccardo, M.; Sirangelo, I. Overview of the Role of Vanillin in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Neuropathophysiological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, L.; Mondal, A.C. Vanillin Mitigates the MPTP-Induced α-Synucleinopathy in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Insights into the Involvement of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrouji, M.; Yasmin, S.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Sharaf, S.E.; Shahwan, M.; Furkan, M.; Khan, R.H.; Shamsi, A. Comprehensive Spectroscopic and Computational Insight into the Binding of Vanillin with Human Transferrin: Targeting Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1397332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Khurana, N.; Kaur, S.; Ali, N.; AlAsmari, A.F.; Waseem, M.; Iqbal, M.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Sharma, N. The Multifactorial Role of Vanillin in Amelioration of Aluminium Chloride and D-Galactose Induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 954, 175832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Saad, H.; Kharrat, N.; Driss, D.; Gargouri, M.; Marrakchi, R.; Jammoussi, K.; Magné, C.; Boudawara, T.; Ellouz Chaabouni, S.; Zeghal, K.M.; et al. Effects of Vanillin on Potassium Bromate-Induced Neurotoxicity in Adult Mice: Impact on Behavior, Oxidative Stress, Genes Expression, Inflammation and Fatty Acid Composition. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 123, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buslovich, A.; Horev, B.; Rodov, V.; Gedanken, A.; Poverenov, E. One-Step Surface Grafting of Organic Nanoparticles: In Situ Deposition of Antimicrobial Agents Vanillin and Chitosan on Polyethylene Packaging Films. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, C.F.; Camilo, C.J.; Do Nascimento Silva, M.K.; De Freitas, T.S.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Coutinho, H.D.M. Vanillin Selectively Modulates the Action of Antibiotics against Resistant Bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, N.; Chan, S.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Chua, S.L. Vanillin Inhibits PqsR-Mediated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6496–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.S.; Sharma, M.M.; Das, R.K.; Rookes, J.; Cahill, D.; Lenka, S.K. Vanillin Mediated Green Synthesis and Application of Gold Nanoparticles for Reversal of Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Qadri, T.; Hussain, Z.; Saeed, A.; Channar, P.A.; Shehzadi, S.A.; Hassan, M.; Larik, F.A.; Mahmood, T.; Malik, A. Synthesis, Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Docking Study of Vanillin Derived 1,4-Disubstituted 1,2,3-Triazoles as Inhibitors of Bacterial DNA Synthesis. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasagoudr, S.S.; Hegde, V.G.; Vanjeri, V.N.; Chougale, R.B.; Masti, S.P. Ethyl Vanillin Incorporated Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Active Films for Food Packaging Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, L.; Díaz De Greñu, B.; Della Bella, E.; Pagani, S.; Torricelli, P.; Vivancos, J.L.; Ruiz-Rico, M.; Barat, J.M.; Aznar, E.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Commercial Calcium Phosphate Based Materials Functionalized with Vanillin. Acta Biomater. 2018, 81, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Ozkok, F.; Ozel, A.E.; Cakir, E.; Akyuz, S. Synthesis, FT-IR and NMR Characterization, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities, and DNA Docking Analysis of a New Vanillin-Derived Imine Compound. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1236, 130288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, N.; Awad, S.; Elfiky, M. Vanillin-Crosslinked Chitosan/ZnO Nanocomposites as a Drug Delivery System for 5-Fluorouracil: Study on the Release Behavior via Mesoporous ZrO2–Co3O4 Nanoparticles Modified Sensor and Antitumor Activity. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 21422–21439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Rhee, M.S. Highly Enhanced Bactericidal Effects of Medium Chain Fatty Acids (Caprylic, Capric, and Lauric Acid) Combined with Edible Plant Essential Oils (Carvacrol, Eugenol, β-Resorcylic Acid, Trans-Cinnamaldehyde, Thymol, and Vanillin) against Escherichia coli O157:H7. Food Control 2016, 60, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cai, H.; Yuan, T.; Li, S.; Gan, X.; Song, B. Novel Vanillin Derivatives Containing a 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Moiety as Potential Antibacterial Agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafezi Moghaddam, R.; Dadfarnia, S.; Haji Shabani, A.M.; Shirmardi, S.P.; Hafezi Moghaddam, Z. Fabrication of Two Hydrogels Composites through the Coupling of Gelatin with Ethyl Vanillin/Polyvinyl Alcohol Using Electron Beam Irradiation for Ciprofloxacin Delivery. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 8407–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Tang, X.; Mo, F.; Fu, L.; Lin, B. Self-Healing Chitosan/Vanillin Hydrogels Based on Schiff-Base Bond/Hydrogen Bond Hybrid Linkages. Polym. Test. 2018, 66, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Li, R.; Ye, S.; Ni, P.; Shan, J.; Yuan, T.; Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. Vanillin Enhances the Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol-Chitosan Hydrogel Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneetha, M.; Hemalatha, D.; Kim, H.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Han, S.S. Vanillin/Fungal-Derived Carboxy Methyl Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogels Prepared by Freeze-Thawing for Wound Dressing Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 130910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftime, M.-M.; Rosca, I.; Sandu, A.-I.; Marin, L. Chitosan Crosslinking with a Vanillin Isomer toward Self-Healing Hydrogels with Antifungal Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsuebpol, C.; Burapapadh, K.; Chowjaroen, V.; Changsan, N. The Radical Scavenging Activity of Vanillin and Its Impact on the Healing Properties of Wounds. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2023, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aragão Tavares, E.; De Medeiros, W.M.T.Q.; De Assis Pontes, T.P.; Barbosa, M.M.; De Araújo, A.A.; De Araújo, R.F.; Figueiredo, J.G.; Leitão, R.C.; Da Silva Martins, C.; Da Silva, F.O.N.; et al. Chitosan Membrane Modified With a New Zinc(II)-Vanillin Complex Improves Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; A, R.; Ge, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Su, H.; Yan, M.; Xi, Y.; Fan, Y. Research on a Novel Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Lysine/Vanillin Wound Dressing: Biocompatibility, Bioactivity and Antimicrobial Activity. Burns 2014, 40, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-J.; Lee, Y.-M.; Oh, T.-I.; Kim, B.; Lim, B.-O.; Lim, J.-H. Vanillin Suppresses Cell Motility by Inhibiting STAT3-Mediated HIF-1α mRNA Expression in Malignant Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Kang, J.; Park, W.Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.; Kang, M.-W.; Kwak, H.J.; Um, J.-Y. Vanillic Acid Improves Comorbidity of Cancer and Obesity through STAT3 Regulation in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese and B16BL6 Melanoma-Injected Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marton, A.; Kúsz, E.; Kolozsi, C.; Tubak, V.; Zagotto, G.; Buzás, K.; Quintieri, L.; Vizler, C. Vanillin Analogues O-Vanillin and 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzaldehyde Inhibit NFĸB Activation and Suppress Growth of A375 Human Melanoma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5743–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NFκB P65 and Strategies for Therapeutic Manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourhadi, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Abediny, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Vaseghi, G. The Inhibitory Effects of Vanillin on the Growth of Melanoma by Reducing Nuclear Factor-κB Activation. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2022, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Jiang, R.; Sun, L.; Zhao, D. Vanillic Acid in Panax Ginseng Root Extract Inhibits Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells via Inhibition of the NO/PKG Signaling Pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, W.M.T.Q.; De Medeiros, M.J.C.; Carvalho, E.M.; De Lima, J.A.; Da S. Oliveira, V.; De B. Pontes, A.C.F.; Da Silva, F.O.N.; Ellena, J.A.; De O. Rocha, H.A.; De Sousa, E.H.S.; et al. A Vanillin-Based Copper(ii) Metal Complex with a DNA-Mediated Apoptotic Activity. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16873–16886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Pafli, S.; Stylianoudakis, C.; Ladomenou, K.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Philippopoulos, A. Anti-Inflammatory and Antithrombotic Potential of Metal-Based Complexes and Porphyrins. Compounds 2024, 4, 376–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; El-Khatib, R.M.; Abdel-Fatah, S.M.; Moustafa, H.; Alsalme, A.M.; Nafady, A. Novel Cr (III), Fe (III) and Ru (III) Vanillin Based Metallo-Pharmaceuticals for Cancer and Inflammation Treatment: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Appl. Organom. Chemis 2019, 33, e5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Ding, H.; Hung, W.J.; Liang, C. Antioxidative Characteristics and Inhibition of A-melanocyte-stimulating Hormone-stimulated Melanogenesis of Vanillin and Vanillic Acid from Origanum vulgare. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.; Yazan, L.S.; Ismail, N.; Ismail, M. Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Line HT-29 Induced by Vanillin. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.A.; Shaughnessy, D.T.; Mure, K.; Leszczynska, J.; Ward, W.O.; Umbach, D.M.; Xu, Z.; Ducharme, D.; Taylor, J.A.; DeMarini, D.M.; et al. Antimutagenicity of Cinnamaldehyde and Vanillin in Human Cells: Global Gene Expression and Possible Role of DNA Damage and Repair. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2007, 616, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-M.; Lee, Y.-C.; Li, C.-C.; Lo, H.-Y.; Chen, F.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hsiang, C.-Y.; Ho, T.-Y. Vanillin-Ameliorated Development of Azoxymethane/Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Murine Colorectal Cancer: The Involvement of Proteasome/Nuclear Factor-κB/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5563–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Sakurai, H.; Kawasaki, N.; Choo, M.-K.; Saitoh, Y.; Aozuka, Y.; Singhirunnusorn, P.; Ruchirawat, S.; Svasti, J.; Saiki, I. Vanillin Suppresses in Vitro Invasion and in Vivo Metastasis of Mouse Breast Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 25, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.-A.; Wu, S.-L.; Lo, H.-Y.; Hsiang, C.-Y.; Ho, T.-Y. Vanillin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression through Down-Regulation of Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, D.P.; Sivalingam, N. Vanillin Extracted from Proso and Barnyard Millets Induce Apoptotic Cell Death in HT-29 Human Colon Cancer Cell Line. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 72, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kong, B.; Tong, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zeng, J.; Yu, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J. Vanillin Downregulates NNMT and Attenuates NNMT-related Resistance to 5-fluorouracil via ROS-induced Cell Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, C.; Kang, Y.; Nadarajah, V.D.; Hamzah, A.S.; Pichika, M.R. Drug-like Dietary Vanilloids Induce Anticancer Activity through Proliferation Inhibition and Regulation of Bcl-related Apoptotic Proteins. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S. Vanillic Acid Suppresses HIF-1α Expression via Inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 and Raf/MEK/ERK Pathways in Human Colon Cancer HCT116 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahron, H.; Khaidir, S.S.; Tajuddin, A.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Yamin, B.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Mono- and Dinuclear Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes of a Schiff Base Derived from o-Vanillin. Polyhedron 2019, 161, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, X.; Song, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, R.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. A Vanillin Derivative Suppresses the Growth of HT29 Cells through the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 849, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, R.; Du, K.; Syed, A.; et al. IPM712, a Vanillin Derivative as Potential Antitumor Agents, Displays Better Antitumor Activity in Colorectal Cancers Cell Lines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbiny, N.M.; Younis, N.N.; Shaheen, M.A.; Elseweidy, M.M. The Synergistic Effect between Vanillin and Doxorubicin in Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Solid Tumor and MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cell Line. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, C.R.; Paidesetty, S.K.; Sarathbabu, S.; Dehury, B.; Senthil Kumar, N.; Padhy, R.N. Molecular Dynamics Simulation, Synthesis and Topoisomerase Inhibitory Actions of Vanillin Derivatives: A Systematic Computational Structural Integument. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 11653–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dang, C.; Tai, X.; Xue, L.; Meng, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J. VALD-3, a Schiff Base Ligand Synthesized from o-Vanillin Derivatives, Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, D.P.; Soares, A.K.N.; De Sousa, D.P. Overview of the Role of Vanillin on Redox Status and Cancer Development. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9734816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.R.; Balsa, L.M.; Del Plá, J.; García-Tojal, J.; Pis-Diez, R.; Parajón-Costa, B.S.; León, I.E.; González-Baró, A.C. Synthesis, Characterization, DFT Calculations and Anticancer Activity of a New Oxidovanadium(iv) Complex with a Ligand Derived from o-Vanillin and Thiophene. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 11784–11794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, O.; Celik, I.; Dogan, R.; Atalay, A.; Shoman, M.E.; Ali, T.F.S.; Beshr, E.A.M.; Mohamed, M.; Alaaeldin, E.; Shawky, A.M.; et al. Vanillin-Based Indolin-2-One Derivative Bearing a Pyridyl Moiety as a Promising Anti-Breast Cancer Agent via Anti-Estrogenic Activity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6968–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, T.; Khan, F.I.; Lobb, K.A.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I. Identification and Evaluation of Bioactive Natural Products as Potential Inhibitors of Human Microtubule Affinity-Regulating Kinase 4 (MARK4). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 1813–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, M.; Shamsi, A.; Queen, A.; Shahbaaz, M.; Khan, P.; Hussain, A.; Alajmi, M.F.; Rizwanul Haque, Q.M.; Imtaiyaz Hassan, M. Targeting Cyclin-dependent Kinase 6 by Vanillin Inhibits Proliferation of Breast and Lung Cancer Cells: Combined Computational and Biochemical Studies. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghih, Z.; Neshat, A.; Wojtczak, A.; Faghih, Z.; Mohammadi, Z.; Varestan, S. Palladium (II) Complexes Based on Schiff Base Ligands Derived from Ortho-Vanillin; Synthesis, Characterization and Cytotoxic Studies. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2018, 471, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abla, M.; Waked, A.; Trombotto, S.; Maalouf, M. Synthesis and Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Hyaluronic Acid/Vanillin Conjugates. Macro Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2200190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, L.S.; Fávero, G.M.; De Camargo, L.E.A.; Mainardes, R.M.; Khalil, N.M. Effect of the O-Methyl Catechols Apocynin, Curcumin and Vanillin on the Cytotoxicity Activity of Tamoxifen. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2013, 28, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaraj, S.; Palanisamy, U.M.; Kadhar Mohamed, M.S.B.; Gangasalam, A.; Maria, G.A.; Kandasamy, R. Curcumin Drug Delivery by Vanillin-Chitosan Coated with Calcium Ferrite Hybrid Nanoparticles as Carrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 116, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baqami, N.; Hamza, R. Synergistic Antioxidant Capacities of Vanillin and Chitosan Nanoparticles against Reactive Oxygen Species, Hepatotoxicity, and Genotoxicity Induced by Aging in Male Wistar Rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil Kumar, R.; Naveena, S.; Praveen, S.; Yogadharshini, N. Therapeutic Aspects of Biologically Potent Vanillin Derivatives: A Critical Review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2023, 13, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fache, M.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Vanillin, a Key-Intermediate of Biobased Polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 68, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specifc Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2021 | [3] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [14] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [29] |
|
|
|
| 2017 | [23] |
| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specific Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2019 | [4] |
|
|
|
| 2017 | [25] |
|
|
|
| 2015 | [34] |
|
|
|
| 2017 | [40] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [33] |
| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specific Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2017 | [42] |
|
|
|
| 2021 | [48] |
|
|
|
| 2022 | [49] |
|
|
|
| 2020 | [46] |
|
|
|
| 2016 | [50] |
|
|
|
| 2020 | [51] |
| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specific Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2019 | [58] |
|
|
|
| 2022 | [52] |
|
|
|
| 2023 | [57] |
|
|
|
| 2014 | [59] |
| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specific Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2016 | [62] |
|
|
|
| 2017 | [60] |
|
|
|
| 2020 | [61] |
|
|
|
| 2018 | [66] |
|
|
|
| 2010 | [69] |
|
|
|
| 2022 | [64] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [65] |
| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specific Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2009 | [70] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [80] |
|
|
|
| 2020 | [81] |
|
|
|
| 2018 | [72] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [68] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [75] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [79] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [78] |
|
|
|
| 2018 | [77] |
| Hypothesis | Study Design | Main Findings | Specific Benefits | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 2016 | [82] |
|
|
|
| 2021 | [89] |
|
|
|
| 2021 | [84] |
|
|
|
| 2019 | [86] |
|
|
|
| 2018 | [90] |
|
|
|
| 2021 | [83] |
|
|
|
| 2018 | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kafali, M.; Finos, M.A.; Tsoupras, A. Vanillin and Its Derivatives: A Critical Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Infective, Wound-Healing, Neuroprotective, and Anti-Cancer Health-Promoting Benefits. Nutraceuticals 2024, 4, 522-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4040030
Kafali M, Finos MA, Tsoupras A. Vanillin and Its Derivatives: A Critical Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Infective, Wound-Healing, Neuroprotective, and Anti-Cancer Health-Promoting Benefits. Nutraceuticals. 2024; 4(4):522-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKafali, Magdalini, Marios Argyrios Finos, and Alexandros Tsoupras. 2024. "Vanillin and Its Derivatives: A Critical Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Infective, Wound-Healing, Neuroprotective, and Anti-Cancer Health-Promoting Benefits" Nutraceuticals 4, no. 4: 522-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4040030
APA StyleKafali, M., Finos, M. A., & Tsoupras, A. (2024). Vanillin and Its Derivatives: A Critical Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Infective, Wound-Healing, Neuroprotective, and Anti-Cancer Health-Promoting Benefits. Nutraceuticals, 4(4), 522-561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals4040030








