Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effect of the Anti-Obesity Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in an In Vitro Model of Neuroinflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
2.4. Cell Counting Kit (CCK-8) Assay
2.5. Preparation of Cell Lysate
2.6. Supernatant Protein Precipitation
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
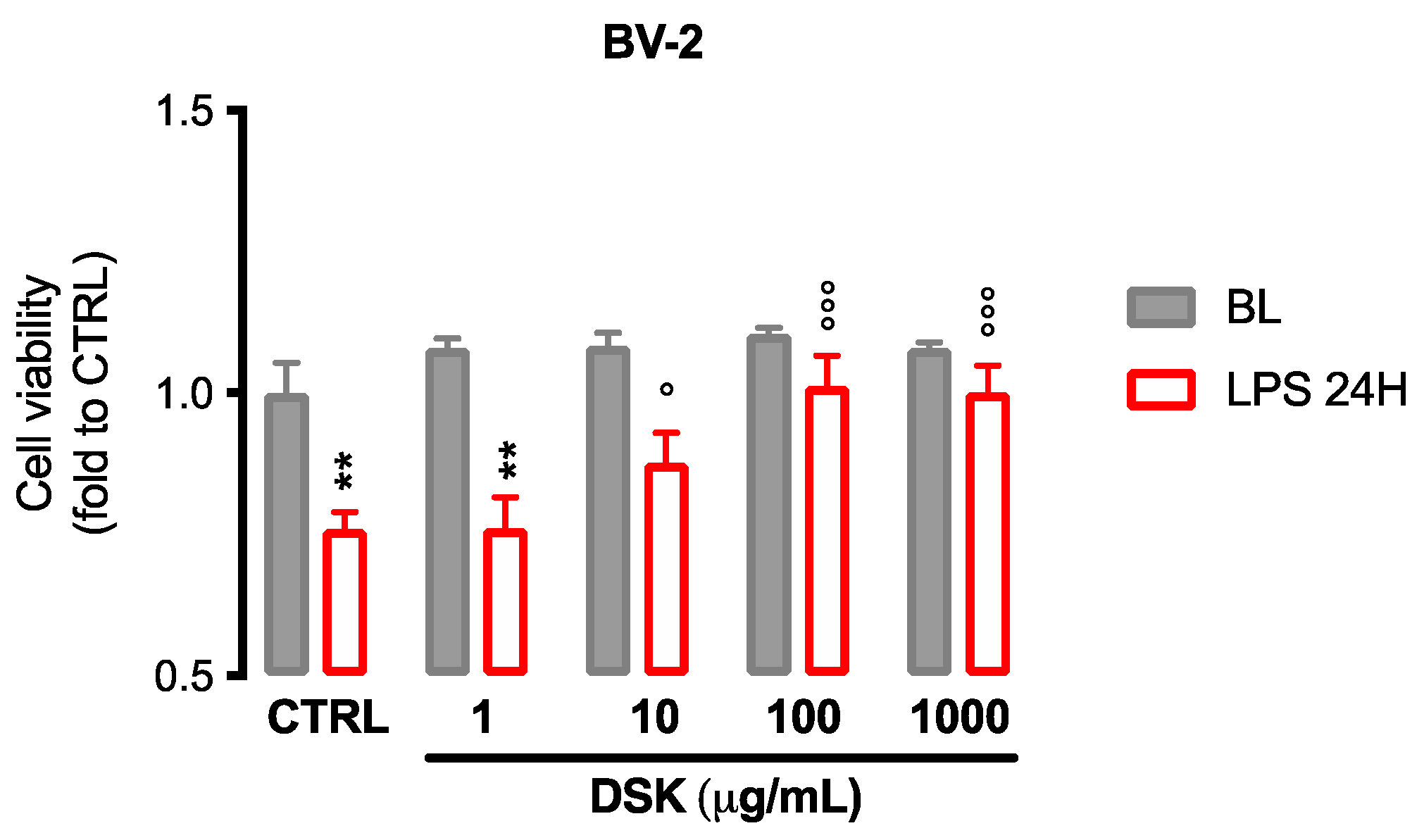
3.1. DSK Reduced Cytotoxicity Induced by LPS in Microglia Cells
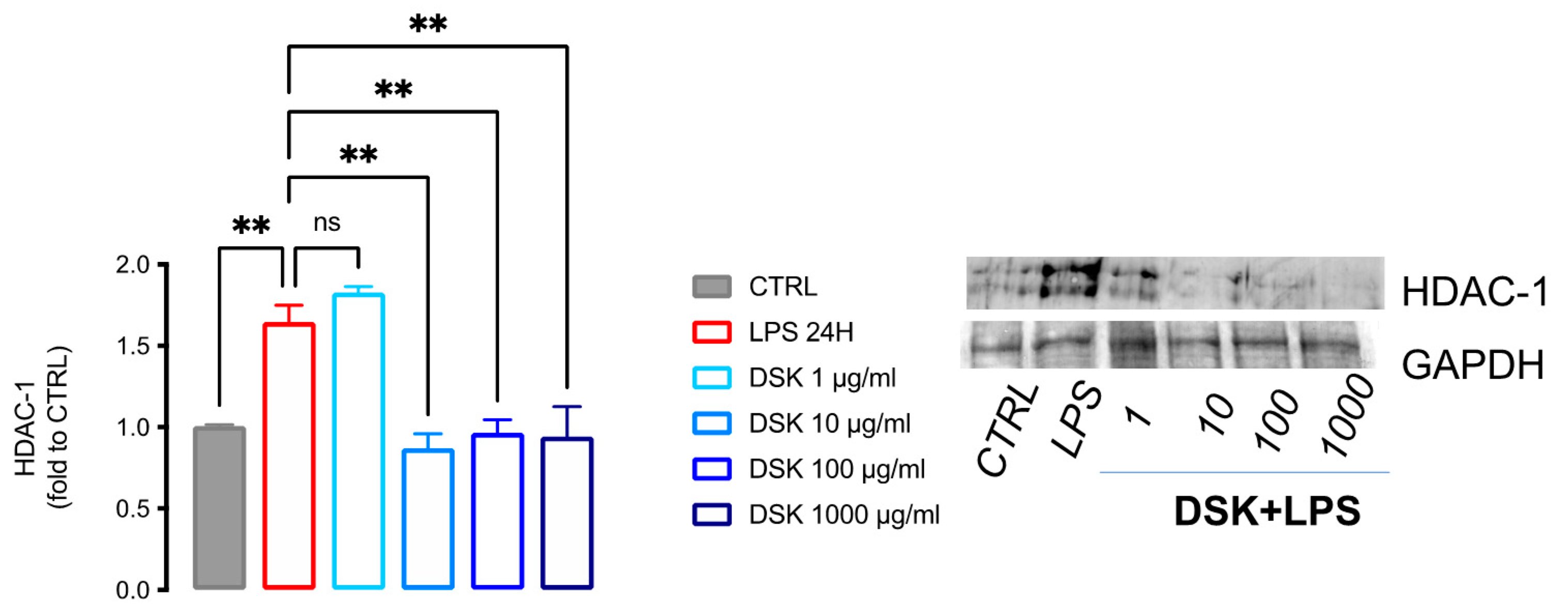
3.2. DSK Reduced HDAC-1 Protein Levels in LPS-Stimulated BV2
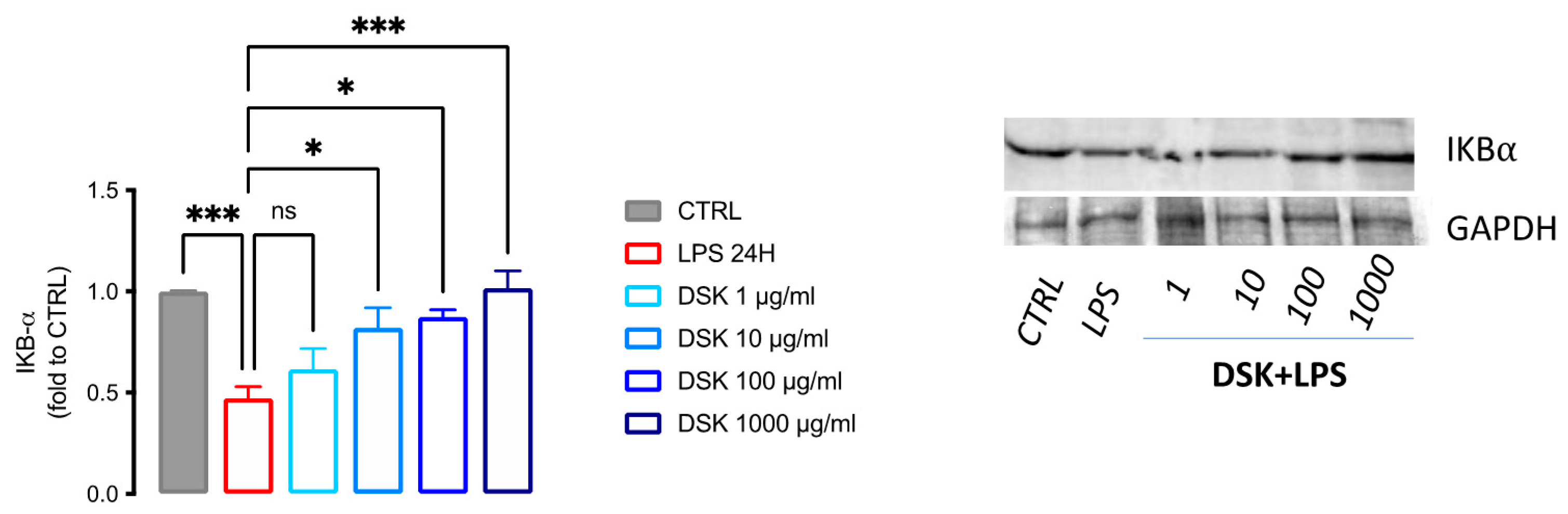
3.3. Activation of NF-κB Pathway Was Reduced by DSK Treatment in LPS-Stimulated BV2
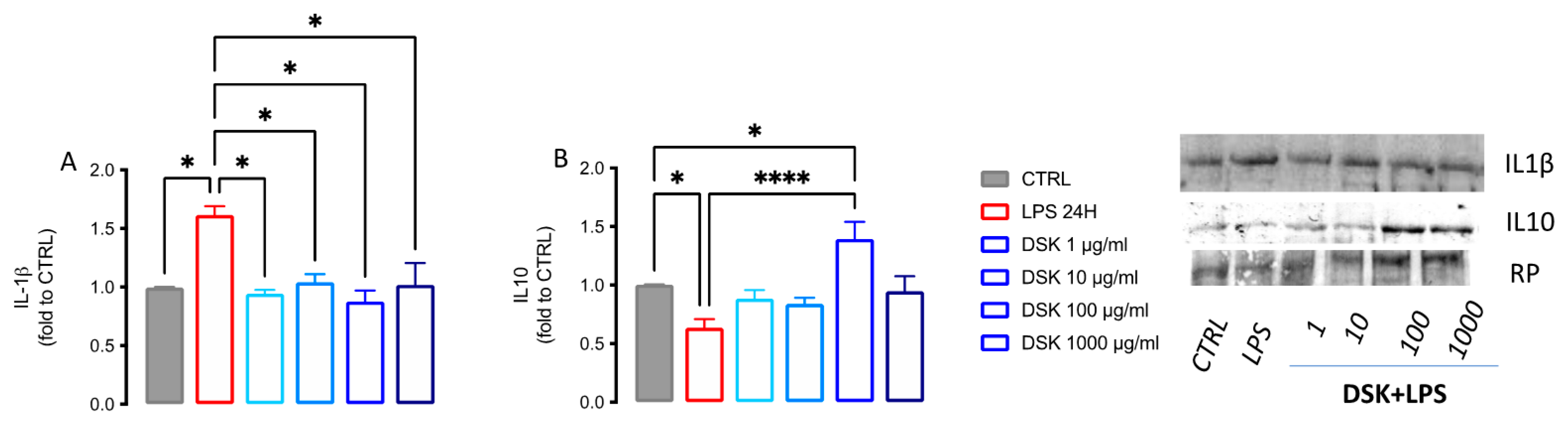
3.4. DSK Modulates Levels of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Released from LPS-Stimulated BV2 Cells
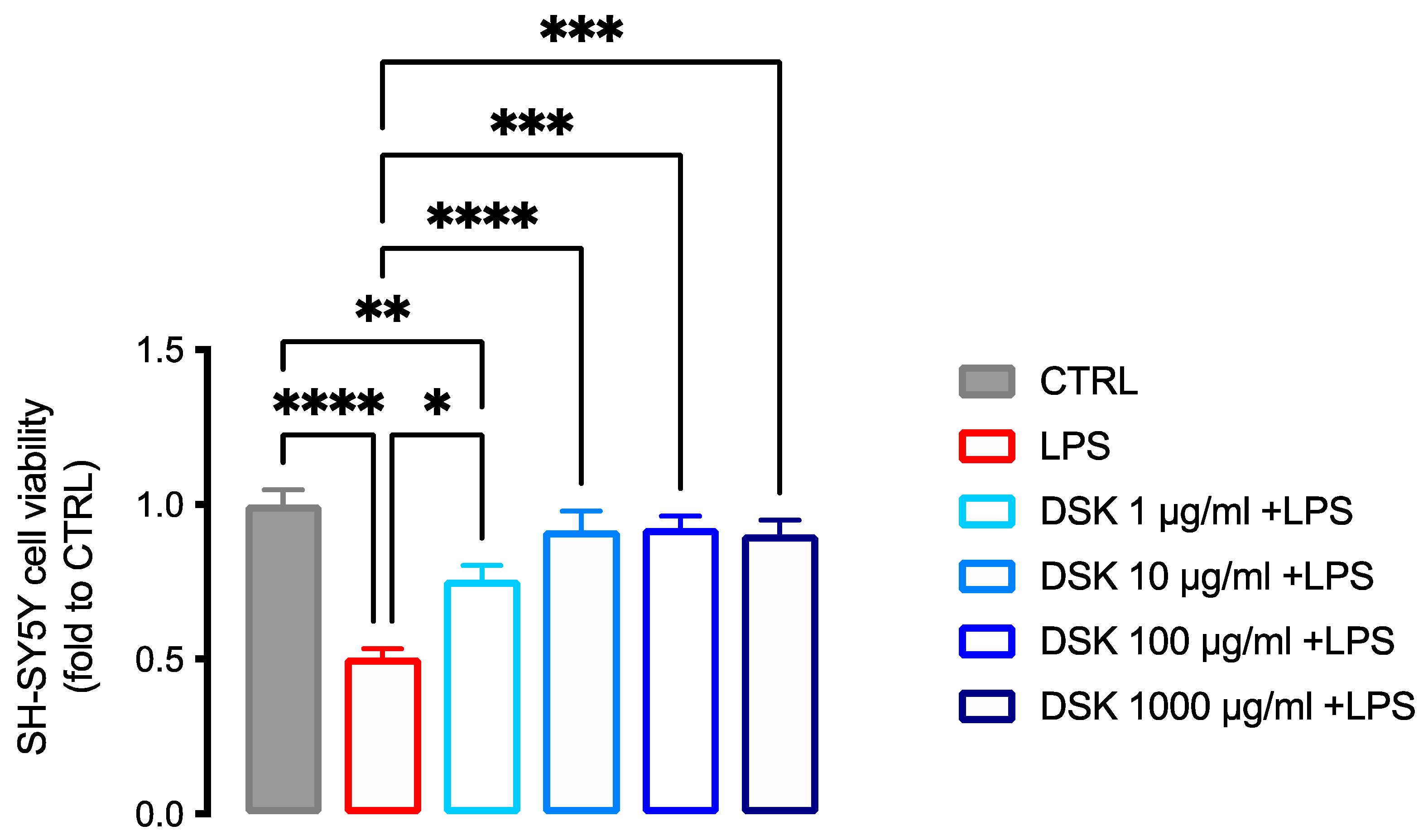
3.5. Neuroprotective Effect of DSK on Inflammation-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The Epidemiological Burden of Obesity in Childhood: A Worldwide Epidemic Requiring Urgent Action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Janssens, A.C.J.W. Predicting Polygenic Obesity Using Genetic Information. Cell Metabolism 2017, 25, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayeux, R.; Stern, Y. Epidemiology of Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marsland, A.L.; Walsh, C.; Lockwood, K.; John-Henderson, N.A. The Effects of Acute Psychological Stress on Circulating and Stimulated Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, L.; Knoefel, J.; Bhaskar, K. The Neuropathology and Cerebrovascular Mechanisms of Dementia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 36, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Keller, J.N.; Morrison, C.D. Obesity and Vulnerability of the CNS. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2009, 1792, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saijo, K.; Glass, C.K. Microglial Cell Origin and Phenotypes in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Bautista, R.J.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Königsberg, M.; López Díaz Guerrero, N.E. Obesity: Pathophysiology, Monosodium Glutamate-Induced Model and Anti-Obesity Medicinal Plants. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauzour, D. Dietary Polyphenols as Modulators of Brain Functions: Biological Actions and Molecular Mechanisms Underpinning Their Beneficial Effects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 914273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borgonetti, V.; Governa, P.; Biagi, M.; Dalia, P.; Corsi, L.; Rhodiola Rosea, L. Modulates Inflammatory Processes in a CRH-Activated BV2 Cell Model. Phytomedicine 2020, 68, 153143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.-H.; Liao, W.-C.; Chang, H.-M. Comparison of Antitumor Activity of Vitamins K1, K2 and K3 on Human Tumor Cells by Two (MTT and SRB) Cell Viability Assays. Life Sci. 1993, 52, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonetti, V.; Governa, P.; Biagi, M.; Pellati, F.; Galeotti, N. Zingiber Officinale Roscoe Rhizome Extract Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting Neuroinflammation in Mice. Phytomedicine 2020, 78, 153307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isacchi, B.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Iacopi, R.; Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N.; Bilia, A.R. Liposomal Formulation to Increase Stability and Prolong Antineuropathic Activity of Verbascoside. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanelli, M.N.; Borgonetti, V.; Galeotti, N. Dual BET/HDAC Inhibition to Relieve Neuropathic Pain: Recent Advances, Perspectives, and Future Opportunities. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 173, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, N.; Liu, P.; Liu, L.; Tang, M.; Cheng, G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Three-Dimensional Graphene Foams Cultured with Microglial Cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6930–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; Vargas, J.; Hoffmann, A. Signaling via the NFkB system. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanjabi, S.; Zenewicz, L.A.; Kamanaka, M.; Flavell, R.A. Anti-Inflammatory and pro-Inflammatory Roles of TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-22 in Immunity and Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.-S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global Burden of Obesity in 2005 and Projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Obesity-Induced Inflammatory Changes in Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.A.; Spencer, S.J. Obesity and Neuroinflammation: A Pathway to Cognitive Impairment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 42, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, J.P.; Yi, C.-X.; Schur, E.A.; Guyenet, S.J.; Hwang, B.H.; Dietrich, M.O.; Zhao, X.; Sarruf, D.A.; Izgur, V.; Maravilla, K.R.; et al. Obesity Is Associated with Hypothalamic Injury in Rodents and Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vainchtein, I.D.; Molofsky, A.V. Astrocytes and Microglia: In Sickness and in Health. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazon, J.N.; de Mello, A.H.; Ferreira, G.K.; Rezin, G.T. The Impact of Obesity on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Life Sci. 2017, 182, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmani, M.; Eftekhari, Z.; Saki, K.; Fazeli-Moghadam, E.; Jelodari, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Obesity Phytotherapy: Review of Native Herbs Used in Traditional Medicine for Obesity. J. Evid. -Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2015, 21, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.; Shastri, A.; Su, R.; Bapat, P.; Kwun, I.; Shen, C.-L. Novel Insights of Dietary Polyphenols and Obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacs, E.M.R.; Lejeune, M.P.G.M.; Nijs, I.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Effects of Green Tea on Weight Maintenance after Body-Weight Loss. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 91, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maki, K.C.; Reeves, M.S.; Farmer, M.; Yasunaga, K.; Matsuo, N.; Katsuragi, Y.; Komikado, M.; Tokimitsu, I.; Wilder, D.; Jones, F.; et al. Green Tea Catechin Consumption Enhances Exercise-Induced Abdominal Fat Loss in Overweight and Obese Adults. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, T.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I. A Green Tea Extract High in Catechins Reduces Body Fat and Cardiovascular Risks in Humans. Obesity 2007, 15, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliburska, J.; Bogdanski, P.; Szulinska, M.; Stepien, M.; Pupek-Musialik, D.; Jablecka, A. Effects of Green Tea Supplementation on Elements, Total Antioxidants, Lipids, and Glucose Values in the Serum of Obese Patients. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 149, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimifard, M.; Maqbool, F.; Moeini-Nodeh, S.; Niaz, K.; Abdollahi, M.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M.; Nabavi, S.F. Targeting the TLR4 Signaling Pathway by Polyphenols: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Neuroinflammation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhaya, A.; Tsurumi, A.; Rahme, L.G. NF-ΚBp50 and HDAC1 Interaction Is Implicated in the Host Tolerance to Infection Mediated by the Bacterial Quorum Sensing Signal 2-Aminoacetophenone. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgonetti, V.; Galeotti, N. Combined Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases and BET Family Proteins as Epigenetic Therapy for Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.D.; Guandalini, L.; Romanelli, M.N.; Galeotti, N. The New HDAC1 Inhibitor LG325 Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain in a Mouse Model. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 160, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ye, J.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Wu, W.; Lin, W.; Lin, W.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, S. Valproic Acid Attenuates Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Inflammation via STAT1 and NF-ΚB Pathway Dependent of HDAC3. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denk, F.; Huang, W.; Sidders, B.; Bithell, A.; Crow, M.; Grist, J.; Sharma, S.; Ziemek, D.; Rice, A.S.C.; Buckley, N.J.; et al. HDAC Inhibitors Attenuate the Development of Hypersensitivity in Models of Neuropathic Pain. PAIN 2013, 154, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shih, R.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. NF-KappaB Signaling Pathways in Neurological Inflammation: A Mini Review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Quan, N. Microglia and CNS Interleukin-1: Beyond Immunological Concepts. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, D.Y.; Simonyi, A.; Cui, J.; Lubahn, D.B.; Gu, Z.; Sun, G.Y. Botanical Polyphenols Mitigate Microglial Activation and Microglia-Induced Neurotoxicity: Role of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2. NeuroMolecular Med. 2016, 18, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Yun, S.W.; Han, M.J.; Jang, S.E.; Kim, D.H. IL-10 Expression-Inducing Gut Bacteria Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Hyperlipidemia in Mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Xiao, Y. IL-10/STAT3 Is Reduced in Childhood Obesity with Hypertriglyceridemia and Is Related to Triglyceride Level in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lainez, N.M.; Coss, D. Obesity, Neuroinflammation, and Reproductive Function. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2719–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.D.; Quattrone, A.; Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N. PKC-Mediated HuD-GAP43 Pathway Activation in a Mouse Model of Antiretroviral Painful Neuropathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 81, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, Y.S.; Hulsebosch, C.E.; Leem, J.W. Neuronal-Glial Interactions Maintain Chronic Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 2480689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béchade, C.; Colasse, S.; Diana, M.A.; Rouault, M.; Bessis, A. NOS2 Expression Is Restricted to Neurons in the Healthy Brain but Is Triggered in Microglia upon Inflammation. Glia 2014, 62, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Components | g/L |
|---|---|
| Cinnamon: Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume | 90 |
| Orthosiphon: Orthosiphon stamineus Benth | 90 |
| Green Tea: Camellia sinensis L. Kuntze | 90 |
| Mate: Ilex paraguariensis A.St.Hill | 70 |
| Gymnema: Gymnema sylvestre R. Br | 70 |
| Bean: Phaseolus vulgaris L. | 60 |
| Pineapple: Ananas comosus L. Merr. | 40 |
| Migliarino: Lithospermum officinale L. | 40 |
| Horsetail: Equisetum arvense L. | 40 |
| Romice: Rumex crispus L. | 30 |
| Asparagus: Asparagus officinalis L | 30 |
| Fennel: Foeniculum vulgare Miller | 30 |
| Birch: Betuta pendolo Roth. | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borgonetti, V.; Cenci, L.; Galeotti, N. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effect of the Anti-Obesity Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in an In Vitro Model of Neuroinflammation. Nutraceuticals 2022, 2, 22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals2010002
Borgonetti V, Cenci L, Galeotti N. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effect of the Anti-Obesity Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in an In Vitro Model of Neuroinflammation. Nutraceuticals. 2022; 2(1):22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorgonetti, Vittoria, Lorenzo Cenci, and Nicoletta Galeotti. 2022. "Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effect of the Anti-Obesity Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in an In Vitro Model of Neuroinflammation" Nutraceuticals 2, no. 1: 22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals2010002
APA StyleBorgonetti, V., Cenci, L., & Galeotti, N. (2022). Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effect of the Anti-Obesity Dietary Supplement Dekosilhue® in an In Vitro Model of Neuroinflammation. Nutraceuticals, 2(1), 22-31. https://doi.org/10.3390/nutraceuticals2010002








