Effect of Exercise on Vascular Function and Blood Lipids in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
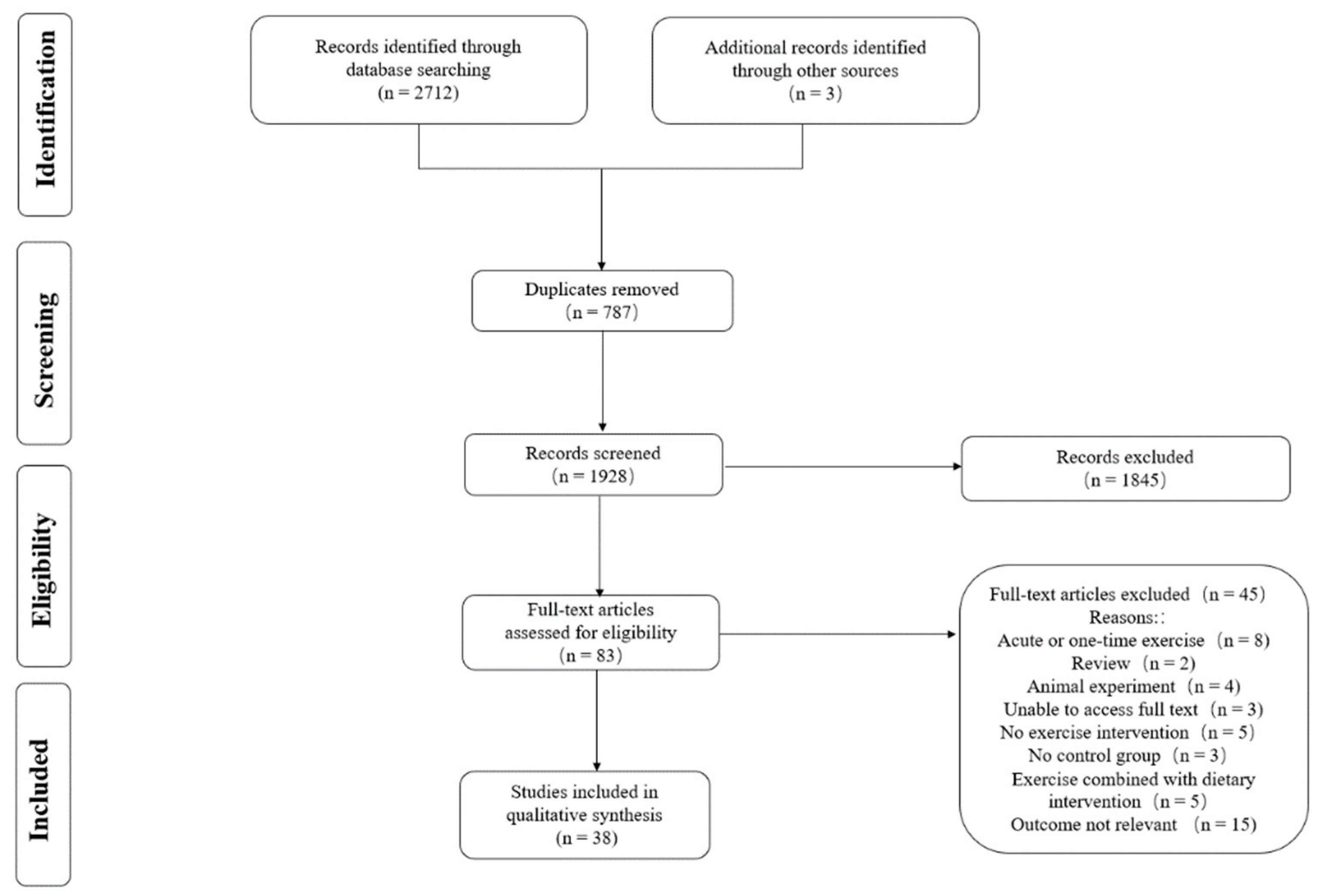
3.1. Literature Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. ROB
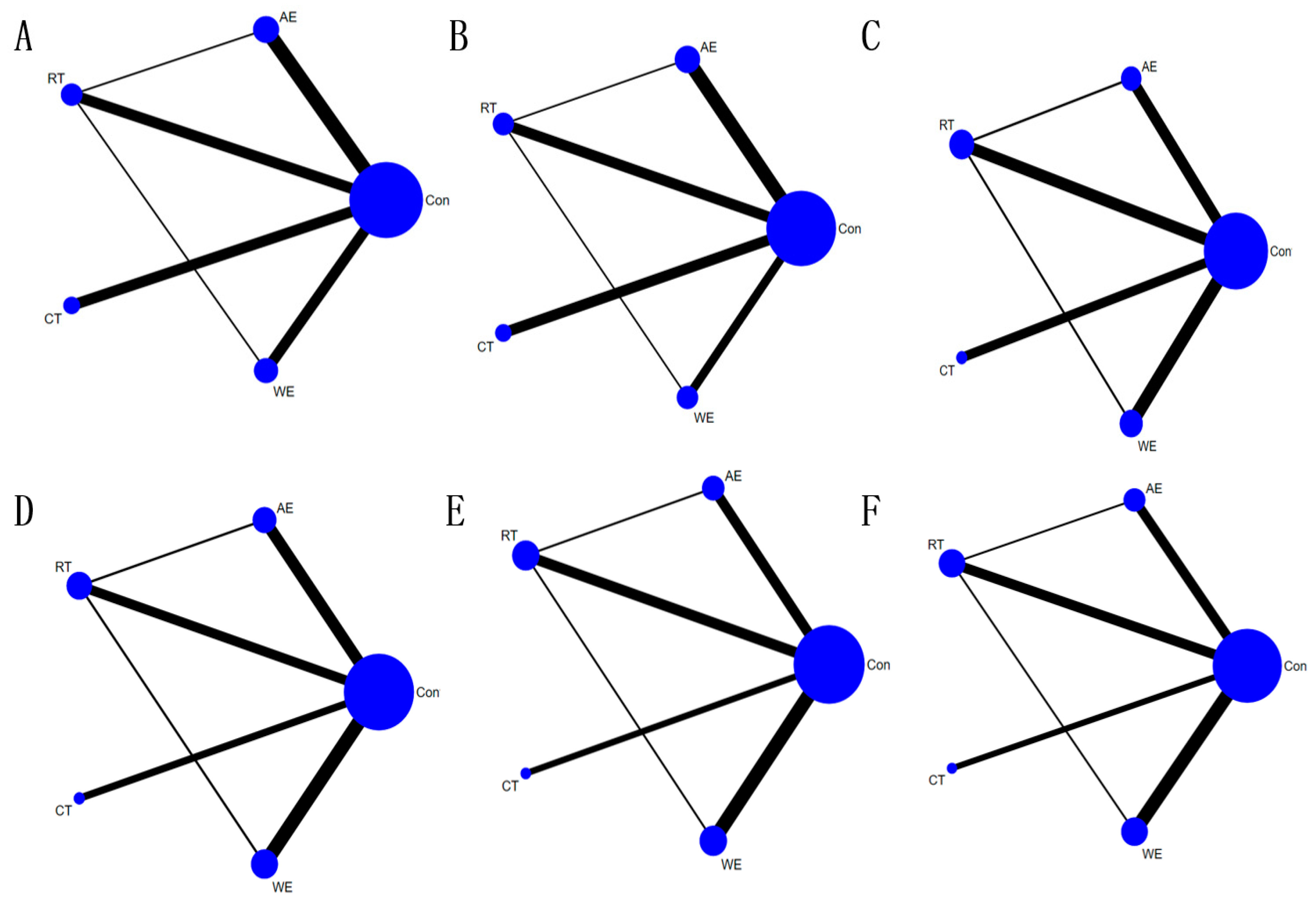
3.4. Pairwise Meta-Analysis and NMA
3.4.1. PWV
3.4.2. SBP
3.4.3. DBP
3.4.4. TC
3.4.5. TG
3.4.6. LDL-C
3.4.7. HDL-C
3.5. Publication Bias or Small Sample Effect Test
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Exercise on PWV, SBP, and DBP in Postmenopausal Women
4.2. Effect of Exercise on Blood Lipid Levels in Postmenopausal Women
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendis, S.; Puska, P.; Norrving, B.; World Health Organization; World Heart Federation; World Stroke Organization. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cardiovascular Diseases. World Health Organization Web Site. World Health Organization, 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Yusuf, S.; Joseph, P.; Rangarajan, S.; Islam, S.; Mente, A.; Hystad, P.; Brauer, M.; Kutty, V.R.; Gupta, R.; Wielgosz, A.; et al. Modifiable Risk Factors, Cardiovascular Disease, and Mortality in 155,722 Individuals from 21 High-income, Middle-income, and Low-income Countries (PURE): A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismar, H.; Diel, I.; Ziegler, R.; Pfeilschifter, J. Increased Cytokine Secretion by Human Bone Marrow Cells after Menopause or Discontinuation of Estrogen Replacement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, J.E.; Martin, K.A. Clinical practice. Postmenopausal Hormone-Replacement Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.E. Estrogen and Vascular Function. Vasc. Pharm. 2002, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, K.L.; Hildreth, K.L.; Meditz, A.L.; Deane, K.D.; Kohrt, W.M. Endothelial Function Is Impaired across the Stages of the Menopause Transition in Healthy Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 4692–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Despres, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2015 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, L.J.; Alagona, P., Jr.; Clark, B.A., III; Drozda, J.P., Jr.; Saldivar, F.; Wilson, S.R.; Poe, C.; Hart, M. The Worldwide Envronment of Cardiovascular Disease: Prevalence, Diagnosis, Therapy, and Policy Issues: A Report from the American College of Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2012, 60, S1–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandanpour, N.; Armon, M.P.; Jennings, B.; Clark, A.; Meyer, F.J. The Association between Ankle Brachial Pressure Index and Pulse Wave Velocity: Clinical Implication of Pulse Wave Velocity. Angiology 2009, 60, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beral, V.; Million Women Study, C. Breast Cancer and Hormone-Replacement Therapy in the Million Women Study. Lancet 2003, 362, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.J.; Hopman, M.T.; Padilla, J.; Laughlin, M.H.; Thijssen, D.H. Vascular Adaptation to Exercise in Humans: Role of Hemodynamic Stimuli. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 495–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.J.; Smith, K.J. Effects of Exercise on Vascular Function, Structure, and Health in Humans. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrup, C.M.; Egelund, J.; Nyberg, M.; Lundberg Slingsby, M.H.; Andersen, C.B.; Logstrup, S.; Bangsbo, J.; Suetta, C.; Stallknecht, B.; Hellsten, Y. Effects of High-Intensity Training on Cardiovascular RiskFactors in Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Women. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 384.e1–384.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Tomas, C.; Chulvi-Medrano, I.; Carrasco, J.J.; Alakhdar, Y. Effect of a 1-year Elastic Band Resistance Exercise Program on Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Postmenopausal Women. Menopause 2018, 25, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, X.; Yin, H.; Sun, Z.; Zugel, M.; Steinacker, J.M.; Schumann, U. Exercise Training and Endothelial Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Wong, A.; Son, W.M.; Pekas, E.J. Effects of Heated Water-Based Versus Land-Based Exercise Training on Vascular Function in Individuals with Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-Analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mersy, D.J. Health Benefits of Aerobic Exercise. Postgrad. Med. 1991, 90, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howley, E.T. Type of Activity: Resistance, Aerobic and Leisure Versus Occupational Physical Activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, S364–S369; discussion S419–S420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; He, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effectiveness of Aquatic Exercise for Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Z. Rheumatol. 2015, 74, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Yoon, B.H.; Shin, I.S.; Bae, J.M. Network Meta-analysis: Application and Practice Using Stata. Epidemiol. Health 2017, 39, e2017047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbuagbaw, L.; Rochwerg, B.; Jaeschke, R.; Heels-Andsell, D.; Alhazzani, W.; Thabane, L.; Guyatt, G.H. Approaches to interpreting and choosing the best treatments in network meta-analyses. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Song, T.J.; Song, D.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.S.; Nam, C.M.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Heo, J.H. Brachial-ankle Pulse Wave Velocity is a Strong Predictor for Mortality in Patients with Acute Stroke. Hypertension 2014, 64, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, K. Physical activity in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Phys. Ther. 1996, 76, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manojlovic, M.; Protic-Gava, B.; Maksimovic, N.; Scepanovic, T.; Pocek, S.; Roklicer, R.; Drid, P. Effects of Combined Resistance and Aerobic Training on Arterial Stiffness in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.D.; Malone, E.; Florida-James, G. Vascular Ageing and Exercise: Focus on Cellular Reparative Processes. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 3583956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, B.M.; Rossi, F.E.; Cholewa, J.M.; Lira, F.S. Regular Physical Activity and Vascular Aging. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 3715–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettehad, D.; Emdin, C.A.; Kiran, A.; Anderson, S.G.; Callender, T.; Emberson, J.; Chalmers, J.; Rodgers, A.; Rahimi, K. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Rawlings, A.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Coresh, J.; Selvin, E. Diastolic Blood Pressure, Subclinical Myocardial Damage, and Cardiac Events: Implications for Blood Pressure Control. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Petiot, E.; Ford, I.; Greenlaw, N.; Ferrari, R.; Fox, K.M.; Tardif, J.C.; Tendera, M.; Tavazzi, L.; Bhatt, D.L.; Steg, P.G.; et al. Cardiovascular event rates and mortality according to achieved systolic and diastolic blood pressure in patients with stable coronary artery disease: An international cohort study. Lancet 2016, 388, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminia, M.; Daneshkhah, A.; Jalali, R.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Salari, N.; Mohammadi, M. The Effect of Exercise on the Older Adult′s Blood Pressure Suffering Hypertension: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Clinical Trial Studies. Int. J. Hypertens 2020, 2020, 2786120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.S.; Yang, Y. The Effect of Aquatic Exercise on Cardiovascular Health in Postmenopausal Women: A Meta-Analysis. China Sport Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S.; Higgs, E.A. The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl. 1), S193–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, D.; Silva, V.; Prestes, J.; Rica, R.L.; Serra, A.J.; Bocalini, D.S.; Pontes, F.L., Jr. Hypotensive response after water-walking and land-walking exercise sessions in healthy trained and untrained women. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2011, 4, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, V.A.; Smart, N.A. Exercise training for blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e004473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, H.; Boardman, H.; Deiseroth, A.; Moholdt, T.; Simonenko, M.; Krankel, N.; Niebauer, J.; Tiberi, M.; Abreu, A.; Solberg, E.E.; et al. Personalized exercise prescription in the prevention and treatment of arterial hypertension: A Consensus Document from the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC) and the ESC Council on Hypertension. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadpour, N.; Tartibian, B.; Kosar, S.N. Effects of aerobic exercise training on ACE and ADRB2 gene expression, plasma angiotensin II level, and flow-mediated dilation: A study on obese postmenopausal women with prehypertension. Menopause 2017, 24, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, T.; Nesreen, E.; Ramadhan, O. Effects of exercise training on postmenopausal hypertension: Implications on nitric oxide levels. Med. J. Malays. 2013, 68, 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, D.L.; Earnest, C.P.; Blair, S.N.; Church, T.S. The effect of different doses of aerobic exercise training on endothelial function in postmenopausal women with elevated blood pressure: Results from the DREW study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.R.; Barcelos, L.C.; Oliveira, A.A.; Furlanetto Junior, R.; Martins, F.M.; Orsatti, C.L.; Resende, E.A.; Orsatti, F.L. Effect of resistance training on muscular strength and indicators of abdominal adiposity, metabolic risk, and inflammation in postmenopausal women: Controlled and randomized clinical trial of efficacy of training volume. Age 2016, 38, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumor, K.; Shoemaker-Moyle, M.; Nistala, R.; Whaley-Connell, A. Arterial Stiffness in Hypertension: An Update. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigent, C.; Keech, A.; Kearney, P.M.; Blackwell, L.; Buck, G.; Pollicino, C.; Kirby, A.; Sourjina, T.; Peto, R.; Collins, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: Prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 2005, 366, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.; Daviglus, M.L.; Garside, D.B.; Dyer, A.R.; Greenland, P.; Neaton, J.D. Relationship of baseline serum cholesterol levels in 3 large cohorts of younger men to long-term coronary, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality and to longevity. JAMA 2000, 284, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschuren, W.M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Bloemberg, B.P.; Kromhout, D.; Menotti, A.; Aravanis, C.; Blackburn, H.; Buzina, R.; Dontas, A.S.; Fidanza, F.; et al. Serum total cholesterol and long-term coronary heart disease mortality in different cultures. Twenty-five-year follow-up of the seven countries study. JAMA 1995, 274, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Joint Committee on the Revision of Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Adult Dyslipidemia. Guidelines for Prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults in China (2016 revised edition). Chin. Circ. J. 2016, 31, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, Y.; Nogami, Y. The effect of regular aquatic exercise on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Penumetcha, M.; Santanam, N.; Liu, Y.G.; Garelnabi, M.; Parthasarathy, S. Exercise Might Favor Reverse Cholesterol Transport and Lipoprotein Clearance: Potential mechanism for its anti-atherosclerotic effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1723, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, I.R.; Stout, R.W. Effects of Insulin and Glucose on the Cells of the Arterial Wall: Interaction of insulin with dibutyryl cyclic AMP and low density lipoprotein in arterial cells. Diabete Metab. 1987, 13, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cunha, P.M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Nunes, J.P.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Nascimento, M.A.; Moraes, G.K.; Sugihara, P.J.; Barbosa, D.S.; Venturini, D.; Cyrino, E.S. Resistance training performed with single-set is sufficient to reduce cardiovascular risk factors in untrained older women: The randomized clinical trial. Active Aging Longitudinal Study. Arch. Gerontol Geriatr. 2019, 81, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy Ali, K.; Wonnerth, A.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J. Cardiovascular disease risk reduction by raising HDL cholesterol--current therapies and future opportunities. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voight, B.F.; Peloso, G.M.; Orho-Melander, M.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Barbalic, M.; Jensen, M.K.; Hindy, G.; Holm, H.; Ding, E.L.; Johnson, T.; et al. Plasma HDL cholesterol and risk of myocardial infarction: A mendelian randomisation study. Lancet 2012, 380, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Beedie, C.; Jimenez, A. Differential effects of aerobic exercise, resistance training and combined exercise modalities on cholesterol and the lipid profile: Review, synthesis and recommendations. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Grundy, S.M.; Unger, R.H. Comparison of effects of high and low carbohydrate diets on plasma lipoproteins and insulin sensitivity in patients with mild NIDDM. Diabetes 1992, 41, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F, H.Z. Effects of 12-week walking exercise and diet control program on body composition and blood fat in postmenopausal women. Phys. Educ. 2001, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gorski, J. Muscle triglyceride metabolism during exercise. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1992, 70, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokanson, J.E.; Austin, M.A. Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: A meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. J. Cardiovasc. Risk 1996, 3, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, V.; Farabad, E.; Azadbakht, L. Epidemiologic evidence on serum adiponectin level and lipid profile. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Langfort, J.; Ploug, T.; Ihlemann, J.; Holm, C.; Galbo, H. Stimulation of hormone-sensitive lipase activity by contractions in rat skeletal muscle. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, C.; Slotboom, J.; Hoppeler, H.; Kreis, R. In vivo determination of intra-myocellular lipids in human muscle by means of localized 1H-MR-spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 37, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambalis, K.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Kavouras, S.A.; Sidossis, L.S. Responses of blood lipids to aerobic, resistance, and combined aerobic with resistance exercise training: A systematic review of current evidence. Angiology 2009, 60, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egli, L.; Lecoultre, V.; Theytaz, F.; Campos, V.; Hodson, L.; Schneiter, P.; Mittendorfer, B.; Patterson, B.W.; Fielding, B.A.; Gerber, P.A.; et al. Exercise prevents fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia in healthy young subjects. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenowatz, C.; Sui, X.; Fritz, S.; Lavie, C.J.; Beattie, P.F.; Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N. The Association between Resistance Exercise and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Women. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2015, 18, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alberga, A.S.; Prud′homme, D.; Kenny, G.P.; Goldfield, G.S.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Gougeon, R.; Phillips, P.; Malcolm, J.; Wells, G.; Doucette, S.; et al. Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Training on Abdominal Fat, Apolipoproteins and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein in Adolescents with Obesity: The HEARTY Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Obesity 2015, 39, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, G.A.; Kelley, K.S.; Pate, R.R. Exercise and Adiposity in Overweight and Obese Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Aerobic exercise (AE) | Exercise training designed to improve the efficiency and capacity of the cardiorespiratory system [20]. |
| Resistance training (RT) | Exercise training designed to improve the strength, power, endurance, and size of skeletal muscles [21]. |
| Combined training (CT) | A combination of AE and RT. |
| Water exercise (WE) | Refers to the use of physical and other characteristics of water for exercise in the water environment, including AE in water and RT in water [22]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xin, C.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, H. Effect of Exercise on Vascular Function and Blood Lipids in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912074
Xin C, Ye M, Zhang Q, He H. Effect of Exercise on Vascular Function and Blood Lipids in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912074
Chicago/Turabian StyleXin, Chenxi, Mingyi Ye, Qianqian Zhang, and Hui He. 2022. "Effect of Exercise on Vascular Function and Blood Lipids in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912074
APA StyleXin, C., Ye, M., Zhang, Q., & He, H. (2022). Effect of Exercise on Vascular Function and Blood Lipids in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912074





