Levels of Physical Activity, Obesity and Related Factors in Young Adults Aged 18–30 During 2009–2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Design
2.2. Outcome Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
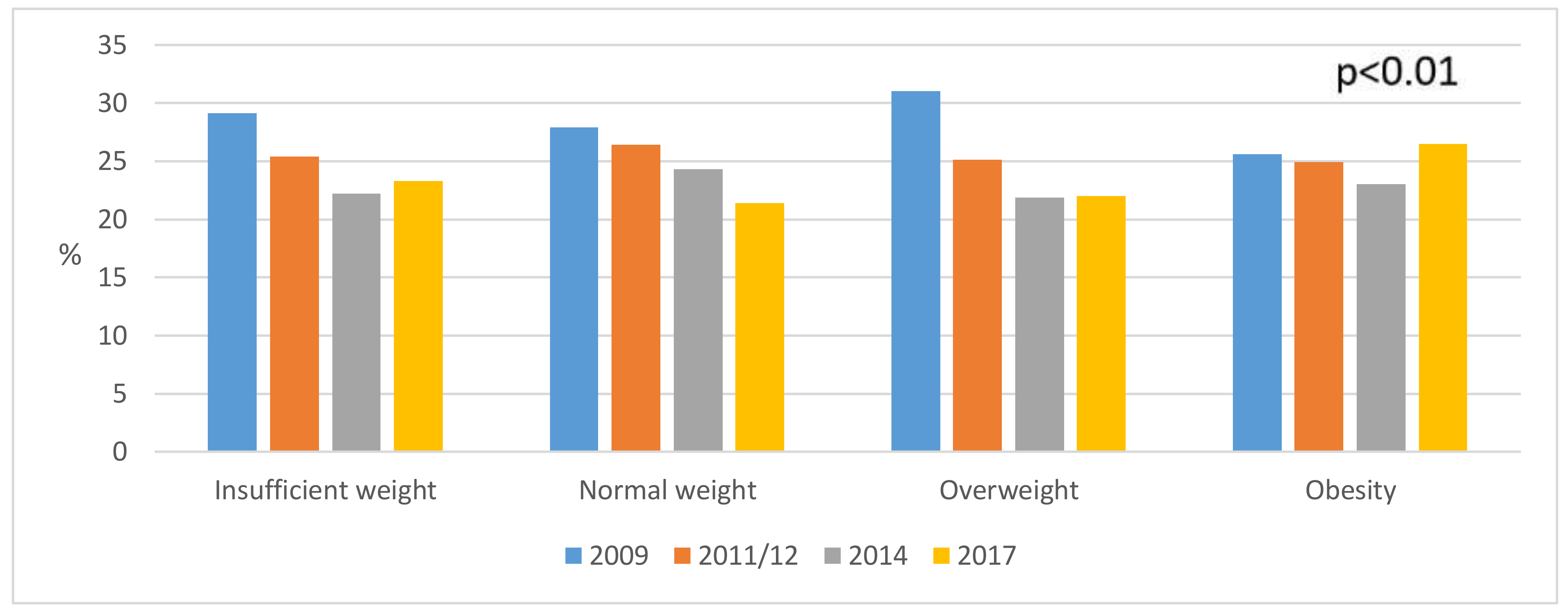
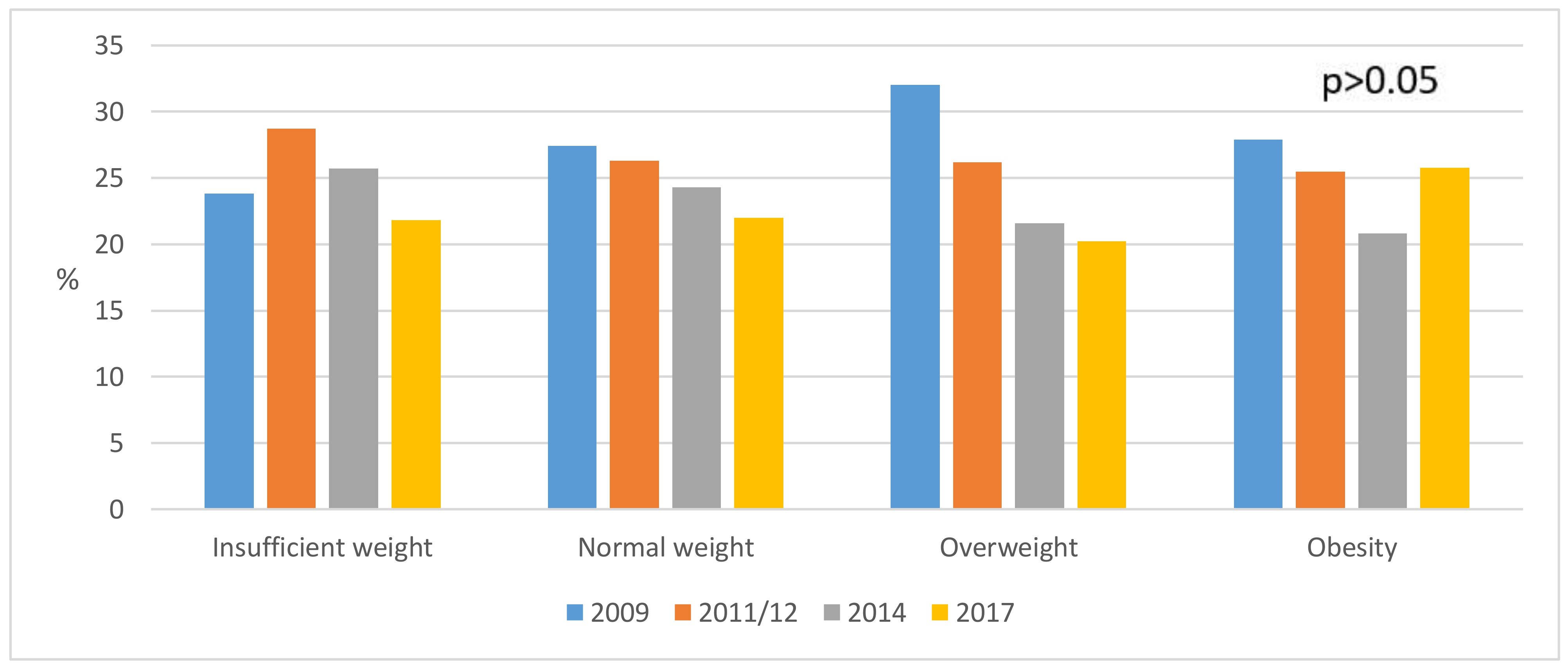
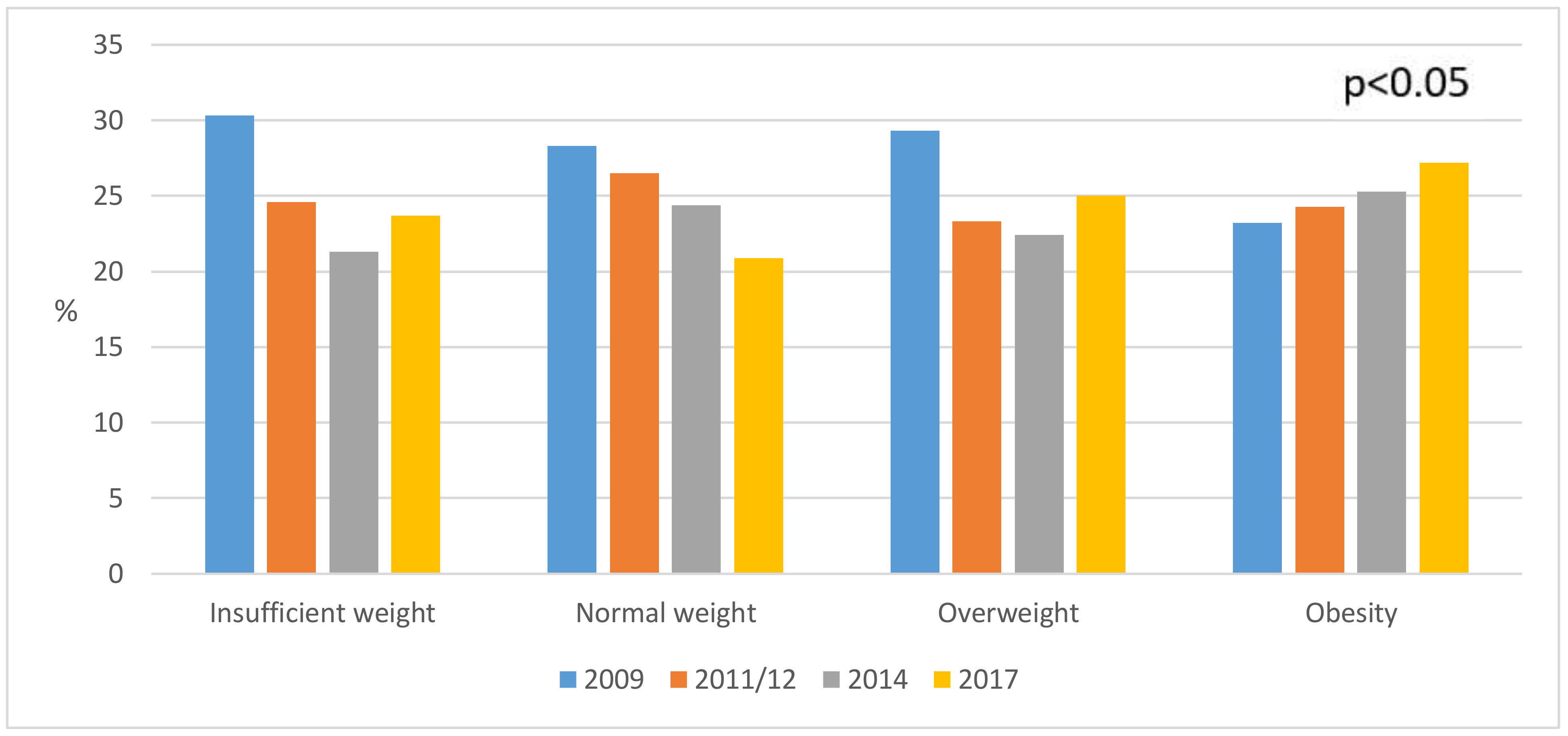
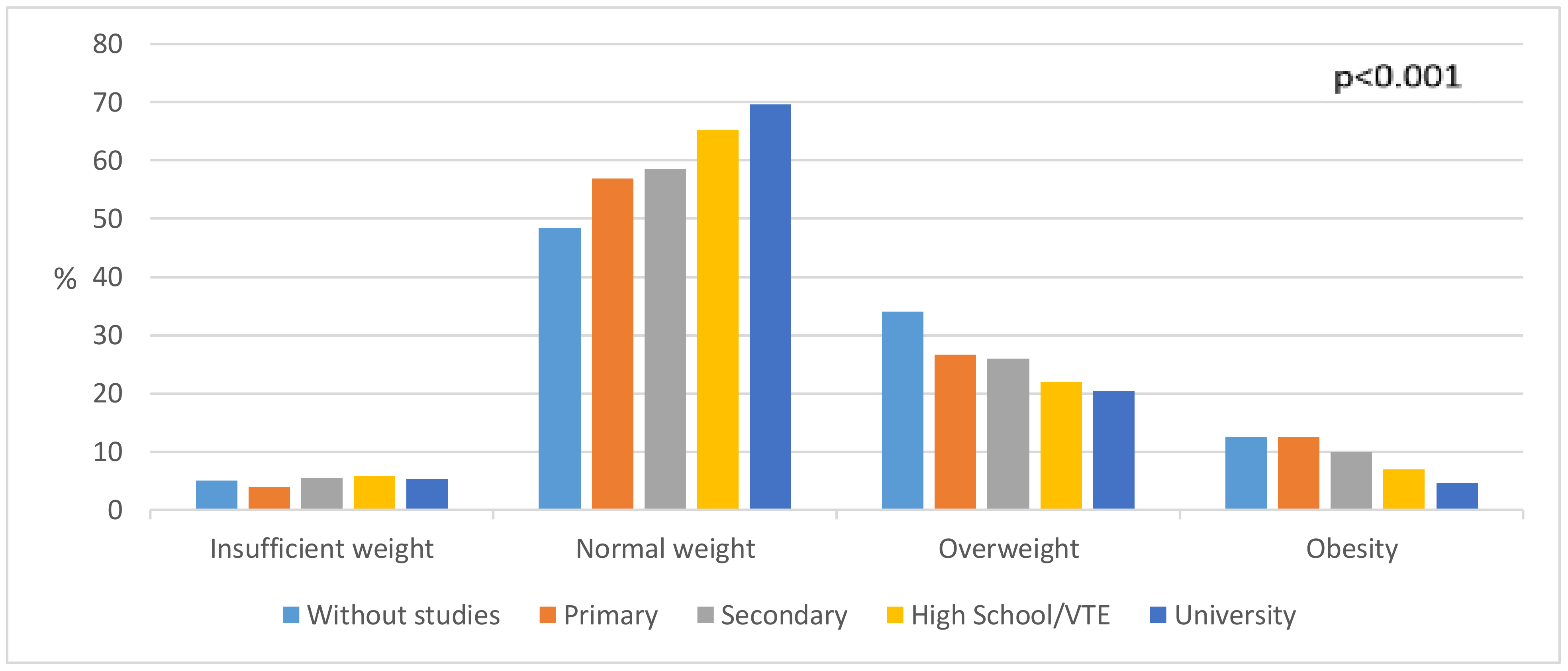
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carson, V.; Hunter, S.; Kuzik, N.; Wiebe, S.A.; Spence, J.C.; Friedman, A.; Tremblay, M.S.; Slater, L.; Hinkley, T. Systematic review of physical activity and cognitive development in early childhood. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiano, A.E.; Marker, A.M.; Martin, C.K.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Physical activity, mental health, and weight gain in a longitudinal observational cohort of nonobese young adults. Obesity 2016, 24, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INE. Población Residente Por Fecha, SExo Y Edad. 2018. Available online: http://www.ine.es (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Drenowatz, C.; Gribben, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hand, G.A.; Shook, R.P.; Burgess, S.; Blair, S.N. The Association of Physical Activity during Weekdays and Weekend with Body Composition in Young Adults. J. Obes. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, E.; Lavie, C.J.; McDonald, S.M.; Thomas, D.M.; Hébert, J.R.; Ross, S.E.; McIver, K.L.; Malina, R.M.; Blair, S.N. Maternal Inactivity: 45-Year Trends in Mothers’ Use of Time. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, G.R.; Virk, J.S. Driving towards obesity: A systematized literature review on the association between motor vehicle travel time and distance and weight status in adults. Prev. Med. Baltim. 2014, 66, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, R.P.; Hand, G.A.; Drenowatz, C.; Hebert, J.R.; Paluch, A.E.; Blundell, J.E.; Hill, J.O.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N. Low levels of physical activity are associated with dysregulation of energy intake and fat mass gain over 1 year. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskinen, T.; Kujala, U.M. Health-Related Findings among Twin Pairs Discordant for Leisure-Time Physical Activity for 32 Years: The TWINACTIVE Study Synopsis. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2015, 18, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arem, H.; Moore, S.C.; Patel, A.; Hartge, P.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Visvanathan, K.; Campbell, P.T.; Freedman, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Adami, H.-O.; et al. Leisure Time Physical Activity and Mortality. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Thompson, P.D. Exercise Is Medicine: At any dose? JAMA 2015, 314, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnohr, P.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Marott, J.L.; Lange, P.; Jensen, G.B. Dose of jogging and long-term mortality: The Copenhagen City Heart Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laddu, D.R.; Rana, J.S.; Murillo, R.; Sorel, M.E.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Allen, N.B.; Gabriel, K.P.; Carnethon, M.R.; Liu, K.; Reis, J.P.; et al. 25-Year Physical Activity Trajectories and Development of Subclinical Coronary Artery Disease as Measured by Coronary Artery Calcium: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, W.L.; Lee, I.M.; Pate, R.R.; Powell, K.E.; Blair, S.N.; Franklin, B.A.; Macera, C.A.; Heath, G.W.; Thompson, P.D.; Bauman, A. Physical Activity and Public Health: Updated Recommendation for Adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007, 116, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, C.; Lyass, A.; Larson, M.G.; Spartano, N.L.; Vita, J.A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Murabito, J.M.; Esliger, D.W.; Blease, S.J.; Hamburg, N.M.; et al. Physical Activity Measured by Accelerometry and its Associations with Cardiac Structure and Vascular Function in Young and Middle-Aged Adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Lee, I.-M. Sedentary behaviour and life expectancy in the USA: A cause-deleted life table analysis. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e000828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.V.; Murthy, V.L.; Colangelo, L.A.; Reis, J.; Venkatesh, B.A.; Sharma, R.; Abbasi, S.A.; Goff, D.C.; Carr, J.J.; Rana, J.S.; et al. Association of Fitness in Young Adulthood with Survival and Cardiovascular Risk. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo-Aguilera, J.A.; Carmona-Torres, J.M.; García-Pinillos, F.; Latorre-Román, P.Á. Effects of a 10-week functional training programme on pain, mood state, depression, and sleep in healthy older adults. Psychogeriatrics 2018, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 84, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Informe de la Comisión Para Acabar Con la Obesidad Infantil. World Health Organization. 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/end-childhood-obesity/publications/echo-report/es/ (accessed on 22 December 2018).
- Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A.; Levy, D.; Carter, R.; Mabry, P.L.; Finegood, D.T.; Huang, T.; Marsh, T.; Moodie, M.L. Changing the future of obesity: Science, policy, and action. Lancet 2011, 378, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinami, L.; O’Loughlin, E.K.; Brunet, J.; Dugas, E.N.; Constantin, E.; Sabiston, C.M.; O’Loughlin, J. Associations between physical activity and sedentary behavior with sleep quality and quantity in young adults. Sleep Health 2017, 3, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Deng, X.; Lu, C. Associations between Sleep Duration and Overweight/Obesity: Results from 66,817 Chinese Adolescents. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Costigan, S.A.; Williams, R.L.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Kennedy, S.G.; Robards, S.L.; Allen, J.; Collins, C.E.; Callister, R.; Germov, J. Effectiveness of interventions targeting physical activity, nutrition and healthy weight for university and college students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, A.; Cooper, R.S. Physical activity does not influence obesity risk: Time to clarify the public health message. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugas, L.R.; Harders, R.; Merrill, S.; Ebersole, K.; Shoham, D.A.; Rush, E.C.; Assah, F.K.; Forrester, T.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Luke, A. Energy expenditure in adults living in developing compared with industrialized countries: A meta-analysis of doubly labeled water studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevijvere, S.; Chow, C.C.; Hall, K.D.; Umali, E.; Swinburn, B.A. Increased food energy supply as a major driver of the obesity epidemic: A global analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 93, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.N.; Archer, E.; Hand, G.A. Commentary: Luke and Cooper are wrong: Physical activity has a crucial role in weight management and determinants of obesity. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1836–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P. The role of physical activity and exercise in obesity and weight management: Time for critical appraisal. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piirtola, M.; Kaprio, J.; Waller, K.; Heikkilä, K.; Koskenvuo, M.; Svedberg, P.; Silventoinen, K.; Kujala, U.M.; Ropponen, A. Leisure-time physical inactivity and association with body mass index: A Finnish Twin Study with a 35-year follow-up. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, F.J.; Livingstone, K.M.; Worsley, A.; McNaughton, S.A. Examining the correlates of meal skipping in Australian young adults. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munt, A.E.; Partridge, S.R.; Allman-Farinelli, M. The barriers and enablers of healthy eating among young adults: A missing piece of the obesity puzzle: A scoping review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad; Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Europea de Salud en España EESE 2009; Madrid, Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. 2010. Available online: www.ine.es (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad; Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Europea de Salud en España EESE 2014; Madrid, Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. 2015. Available online: www.ine.es (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad; Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Nacional de Salud España ENSE 2011/12; Madrid, Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. 2013. Available online: www.ine.es (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad; Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Nacional de Salud España ENSE 2017; Madrid, Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. 2018. Available online: www.ine.es (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Domingo-Salvany, A.; Bacigalupe, A.; Carrasco, J.M.; Espelt, A.; Ferrando, J.; Borrell, C. Propuestas de clase social neoweberiana y neomarxista a partir de la Clasificación Nacional de Ocupaciones 2011. Gac. Sanit. 2013, 27, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, C.; Ueck, P.; Mergl, R.; Gordon, G.; Hegerl, U.; Himmerich, H. Physical activity in depressed and non-depressed patients with obesity. Eat Weight Disord—Stud Anorexia. Bulim Obes. 2018, 23, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Depresion. World Health Organization. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Ball, K.; Burton, N.W.; Brown, W.J. A Prospective Study of Overweight, Physical Activity, and Depressive Symptoms in Young Women. Obesity 2009, 17, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkeset, O.; Romundstad, P.; Evans, J.; Gunnell, D. Association of Adult Body Mass Index and Height with Anxiety, Depression, and Suicide in the General Population: The HUNT Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 167, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhew, I.C.; Richardson, L.P.; Lymp, J.; McTiernan, A.; McCauley, E.; Vander Stoep, A. Measurement matters in the association between early adolescent depressive symptoms and body mass index. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2008, 30, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blough, J.; Loprinzi, P.D. Experimentally investigating the joint effects of physical activity and sedentary behavior on depression and anxiety: A randomized controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 239, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.P.; Hetrick, S.E.; Rosenbaum, S.; Purcell, R.; Parker, A.G. Treating depression with physical activity in adolescents and young adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankel, S.J.; Loenneke, J.P.; Loprinzi, P.D. Mild Depressive Symptoms among Americans in Relation to Physical Activity, Current Overweight/Obesity, and Self-Reported History of Overweight/Obesity. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2016, 23, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.C.; Sharp, S.J.; Ekelund, U.; Thompson, S.G.; Mander, A.P.; Turner, R.M.; Jebb, S.A.; Lindroos, A.K. Objectively Measured Physical Activity and Fat Mass in Children: A Bias-Adjusted Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, S.; Van Der Walt, M.; Al-Kuwari, M.G. One-Year assessment of physical activity level in adult Qatari females: A pedometer-based longitudinal study. Int. J. Womens Health 2016, 8, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Joseph, R.P.; Royse, K.E.; Benitez, T.J.; Pekmezi, D.W. Physical activity and quality of life among university students: Exploring self-efficacy, self-esteem, and affect as potential mediators. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.H.; Carlin, A.; Woods, C.; Nevill, A.; MacDonncha, C.; Ferguson, K.; Murphy, N. Active Students Are Healthier and Happier Than Their Inactive Peers: The Results of a Large Representative Cross-Sectional Study of University Students in Ireland. J. Phys. Act. Health 2018, 15, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laredo-Aguilera, J.A.; Carmona-Torres, J.M.; Cobo-Cuenca, A.I.; García-Pinillos, F.; Latorre-Román, P.A. Handgrip Strength is Associated with Psychological Functioning, Mood and Sleep in Women over 65 Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelusi, C.; Altieri, P.; Gambineri, A.; Repaci, A.; Cavazza, C.; Fanelli, F.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Pagotto, U.; Pasquali, R. Behavioral, socio-environmental, educational and demographic correlates of excess body weight in Italian adolescents and young adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.; Backholer, K.; Wong, E.; Palermo, C.; Keating, C.; Peeters, A. Trends in child and adolescent obesity prevalence in economically advanced countries according to socioeconomic position: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balhareth, A.; Meertens, R.; Kremers, S.; Sleddens, E. Overweight and obesity among adults in the Gulf States: A systematic literature review of correlates of weight, weight-related behaviours, and interventions. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 763–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, N.E.; Sirard, J.R.; Kulbok, P.A.; DeBoer, M.D.; Erickson, J.M. Sedentary behavior and physical activity of young adult university students. Res. Nurs. Health 2018, 41, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.Z.; Varela, A.R.; de Lira, B.A.; Contiero, L.C.; Carneiro, M.D.; de Souza, P.; de Toledo Nóbrega, J.O.; Júnior, F.B. Weight status, physical activity and eating habits of young adults in Midwest Brazil. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, T.; Clarke, P.; Dwan, R. The Relationship between Physical Activity and Alcohol Use among Adults in the United States. Am. J. Health Promot. 2017, 31, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, B.C.; Wolfenden, L.; Gillham, K.; Kingsland, M.; Richardson, B.; Wiggers, J. Is alcohol and community sport a good mix? Alcohol management, consumption and social capital in community sports clubs. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2015, 39, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, J.; Bonilla, Z. Factors Affecting Nutrition and Physical Activity Behaviors of Hispanic Families with Young Children: Implications for Obesity Policies and Programs. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2018, 50, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores Mateo, G.; Granado-Font, E.; Ferré-Grau, C.; Montaña-Carreras, X. Mobile Phone Apps to Promote Weight Loss and Increase Physical Activity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2015, 17, e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, M.; Pope, Z.; Gao, Z. Examining Young Children’s Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviors in an Exergaming Program Using Accelerometry. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Pope, Z.; Lee, J.; Gao, Z. Virtual Reality Exercise for Anxiety and Depression: A Preliminary Review of Current Research in an Emerging Field. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | 2009 n = 2879 (%) | 2011/2012 n = 2637 (%) | 2014 n = 2350 (%) | 2017 n = 2195 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 24.81 (SD 3.8) | 24.62(SD 3.76) | 24.68 (SD 3.76) | 24.37 (SD 3.82) | 0.15 |
| Sex | |||||
| Men | 1414 (49.1) | 1290 (48.9) | 1126 (47.9) | 1056 (48.6) | 0.787 |
| Women | 1465 (50.9) | 1347 (51.1) | 1224 (52.1) | 1139 (51.4) | |
| Smoke | |||||
| Yes | 1127 (40.3) | 978 (37.1) | 803 (34.2) | 667 (30.4) | <0.001 |
| No | 1671 (59.7) | 1657 (62.9) | 1545 (65.8) | 1527 (69.6) | |
| Nationality | |||||
| Spanish | 2478 (86.1) | 2298 (87.1) | 2056 (87.5) | 1931 (88) | 0.211 |
| Foreigner | 401 (13.9) | 229 (12.9) | 294 (12.5) | 264 (12) | |
| Marital status | |||||
| Single | 2298 (79.7) | 2203 (83.6) | 1896 (80.7) | 1811 (82.6) | 0.014 |
| Married | 546 (19) | 405 (15.4) | 426 (18.1) | 361 (16.4) | |
| Widowed | 2 (0.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.1) | 1 (0) | |
| Separated | 11 (0.4) | 6 (0.2) | 14 (0.6) | 11 (0.5) | |
| Divorced | 22 (0.8) | 21 (0,8) | 11 (0.5) | 11 (0.5) | |
| Level of education | <0.001 | ||||
| Without studies | 89 (3.1) | Not Registered | 58 (2.5) | 34 (1.5) | |
| Primary | 348 (12.1) | 200 (8.5) | 131 (6) | ||
| Secondary | 683 (23.7) | 618 (26.3) | 603 (27.5) | ||
| High School/VTE | 1220 (43.4) | 1015 (43.2) | 992 (45.2) | ||
| University | 539 (18.7) | 459 (19.5) | 435 (19.8) | ||
| Social Class | |||||
| Classes I and II | Not Registered | 434 (17.1) | 381 (17) | 367 (17.5) | 0.086 |
| Classes III and IV | 836 (33) | 677 (30.1) | 621 (29.5) | ||
| Classes V and VI | 1266 (49.9) | 1187 (52.9) | 1116 (53) | ||
| Body Mass Index | |||||
| Insufficient weight | 152 (5.5) | 133 (5.3) | 116 (5.1) | 122 (5.7) | 0.008 |
| Normal weight | 1722 (62.3) | 1630 (64.8) | 1501 (65.7) | 1320 (61.8) | |
| Overweight | 695 (25.2) | 563 (22.4) | 492 (21.6) | 493 (23.1) | |
| Obesity | 193 (7) | 188 (7.5) | 174 (7.6) | 200 (9.4) | |
| Self-perceived health status | |||||
| Very good | 973 (33.8) | 967 (36.7) | 895 (38) | 873 (39.8) | 0.004 |
| Good | 1595 (55.4) | 1389 (52.6) | 1174 (50) | 1071 (48.8) | |
| Regulate/bad/very bad | 311 (10.8) | 281 (10.7) | 281 (12) | 251 (11.4) |
| Characteristics | Sedentary n = 2464(34.4%) | Occasionally PA n = 1933(26.9%) | PA Several Times/Month n = 1458(20.3%) | PA Several Times/Week n = 1320(18.4%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Men | 883 (35.8) | 760 (39.3) | 969 (66.5) | 857 (64.9) | <0.001 |
| Women | 1581 (64.2) | 1173 (60.7) | 489 (33.5) | 463 (35.1) | |
| Nationality | |||||
| Spanish | 2066 (83.8) | 1677 (86.8) | 1325 (90.9) | 1212 (91.8) | <0.001 |
| Foreigner | 398 (16.2) | 256 (13.2) | 133 (9.1) | 108 (8.2) | |
| Self-perceived health status | |||||
| Very good | 745 (30.2) | 730 (37.8) | 630 (43.2) | 627 (47.5) | <0.001 |
| Good | 1347 (54.7) | 979 (50.6) | 713 (48.9) | 594 (45) | |
| Regulate/bad/very bad | 372 (15.1) | 224 (11.6) | 115 (7.9) | 99 (7.5) | |
| Depression | |||||
| Yes | 110 (4.5) | 69 (3.6) | 25 (1.7) | 22 (1.7) | <0.001 |
| No | 2354 (95.5) | 1863 (96.4) | 1432 (98.3) | 1298 (98.3) | |
| Year Survey | |||||
| 2011/2012 | 1038 (42.1) | 652 (33.7) | 569 (39) | 376 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| 2014 | 698 (28.3) | 687 (35.5) | 477 (32.7) | 489 (36.6) | |
| 2017 | 728 (29.5) | 594 (30.7) | 412 (28.3) | 461 (34.9) | |
| Consumption of alcohol | |||||
| Daily | 57 (2.3) | 60 (3.1) | 36 (2.5) | 28 (2.1) | <0.001 |
| 3–6 times/week | 88 (3.6) | 86 (4.5) | 80 (5.5) | 53 (4) | |
| 1–2 times/week | 559 (22.7) | 421 (21.8) | 444 (30.5) | 406 (30.8) | |
| 1–3 times/month | 948 (38.5) | 831 (43) | 634 (43.5) | 598 (45.3) | |
| Teetotaler | 812 (33) | 534 (27.6) | 263 (18.1) | 235 (17.8) | |
| Smoke | |||||
| Yes | 984 (39.9) | 656 (34) | 463 (31.8) | 344 (26.1) | <0.001 |
| No | 1480 (60.1) | 1274 (66) | 994 (68.2) | 976 (73.9) | |
| Ability to concentrate | |||||
| Better than usual | 52 (3) | 44 (3.5) | 41 (4.2) | 46 (5.5) | 0.003 |
| As usual | 1503 (85.4) | 1076 (86.6) | 844 (86.1) | 725 (86.8) | |
| Worse than usual | 205 (11.6) | 122 (9.8) | 95 (9.7) | 64 (7.7) | |
| Loss of sleep due to worries | |||||
| No, absolutely | 721 (41) | 502 (40.4) | 428 (43.7) | 445 (53.4) | <0.001 |
| No more than normal | 679 (38.6) | 483 (38.9) | 396 (40.4) | 247 (29.6) | |
| More than normal | 360 (20.5) | 257 (20.7) | 156 (15.9) | 142 (17) | |
| Ability to decide | |||||
| More than usual | 126 (7.2) | 109 (8.8) | 84 (8.6) | 89 (10.7) | <0.001 |
| As usual | 1541 (87.6) | 1095 (88.2) | 859 (87.7) | 727 (87.1) | |
| Less than usual | 93 (5.3) | 38 (3.1) | 36 (3.7) | 19 (2.3) | |
| Ability to face problems | |||||
| More than usual | 96 (5.5) | 77 (6.2) | 46 (4.7) | 67 (8) | <0.001 |
| As usual | 1560 (88.7) | 1106 (89) | 896 (91.5) | 754 (90.4) | |
| Less than usual | 103 (5.9) | 59 (4.8) | 37 (3.8) | 13 (1.6) | |
| Loss of self-confidence | |||||
| No, absolutely | 1225 (69.6) | 908 (73.1) | 707 (72.1) | 658 (78.8) | <0.001 |
| Equal o more than normal | 536 (30.4) | 334 (26.9) | 273 (27.9) | 177 (21.2) | |
| Feeling happy | |||||
| More than usual | 153 (8.7) | 123 (9.9) | 79 (8.1) | 112 (13.4) | <0.001 |
| As usual | 1494 (84.8) | 1062 (85.5) | 871 (89.1) | 691 (82.8) | |
| Less than usual | 114 (6.5) | 57 (4.6) | 28 (2.9) | 32 (3.8) |
| Characteristics | Insufficient Weight n = 523(5.4%) | Normal Weight n = 6173(63.7%) | Overweight n = 2243(23.1%) | Obesity n = 755(7.8%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Men | 101 (19.3) | 2831 (45.9) | 1414 (63) | 384 (50.9) | <0.001 |
| Women | 422 (80.7) | 3342 (54.1) | 829 (37) | 371 (49.1) | |
| Nationality | |||||
| Spanish | 469 (89.7) | 5425 (87.9) | 1910 (85.2) | 658 (87.2) | 0.003 |
| Foreigner | 54 (10.3) | 748 (12.1) | 333 (14.8) | 97 (12.8) | |
| Age | |||||
| 18–22 | 263 (50.3) | 2174 (35.2) | 527 (23.5) | 165 (21.9) | <0.001 |
| 23–26 | 145 (27.7) | 1864 (30.2) | 629 (28) | 201 (27.8) | |
| 27–30 | 115 (22) | 2135 (34.6) | 1087 (48.5) | 380 (50.3) | |
| Marital status | |||||
| Single | 470 (89.9 | 5204 (84.3) | 1704 (76) | 539 (71.4) | <0.001 |
| Married | 49 (9.4) | 894 (14.5) | 513 (22.9) | 212 (28.1) | |
| Wid/Sepa/Divor | 4 (0.8) | 73 (1.2) | 26 (1.2) | 4 (0.5) | |
| Social Class | |||||
| Class I and II | 78 (22.4) | 811 (19) | 218 (14.5) | 48 (9) | <0.001 |
| Class III and IV | 118 (33.9) | 1360 (32) | 435 (29) | 165 (30.8) | |
| Class V and VI | 152 (43.7) | 2090 (49) | 847 (56.5) | 323 (51.3) | |
| Self-perceived health status | |||||
| Very good | 178 (34) | 2418 (39.3) | 773 (34.5) | 197 (26.1) | <0.001 |
| Good | 274 (52.4) | 3135 (50.8) | 1208 (53.9) | 428 (56.7) | |
| Regulate/bad/very bad | 71 (13.6) | 610 (9.9) | 262 (11.6) | 130 (17.2) | |
| Depression | |||||
| Yes | 17 (3.3) | 155 (2.5) | 73 (3.3) | 44 (5.8) | <0.001 |
| No | 506 (96.7) | 6017 (97.5) | 2170 (96.7) | 711 (94.2) | |
| PA frequency | |||||
| Sedentary | 156 (42) | 1377 (31) | 538 (34.9) | 269 (47.9) | <0.001 |
| Occasionally PA | 92 (24.8) | 1211 (27.2) | 387 (25) | 170 (30.2) | |
| PA several times/month | 70 (18.9) | 952 (21.4) | 339 (21.9) | 66 (11.7) | |
| PA several times/week | 53 (14.3) | 907 (20.4) | 282 (18.2) | 57 (10.1) | |
| Consumption of alcohol | |||||
| Daily | 11 (2.1) | 139 (2.3) | 75 (3.4) | 13 (1.7) | <0.001 |
| 3–6 times/week | 17 (3.3) | 266 (4.3) | 109 (4.9) | 15 (2) | |
| 1–2 times/week | 91 (17.6) | 1364 (22.3) | 521 (23.5) | 121 (16.2) | |
| 1–3 times/month | 262 (50.8) | 2893 (47.2) | 947 (42.7) | 330 (44.2) | |
| Teetotaler | 135 (26.2) | 1468 (2I) | 566 (25.5) | 268 (35.9) | |
| Anxiety | |||||
| Yes | 29 (5.5) | 249 (4) | 100 (4.5) | 55 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| No | 494 (94.5) | 5921 (96) | 2142 (95.5) | 700 (92.7) | |
| Weight | |||||
| <50 kg | 332 (63.5) | 430 (7) | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| 51–70 kg | 191 (36.5) | 4363 (70.7) | 468 (20.9) | 4 (0.5) | |
| 71–90 kg | 0 (0) | 1367 (22.1) | 1530 (68.2) | 315 (41.7) | |
| 91–110 kg | 0 (0) | 13 (0.2) | 242 (10.8) | 322 (42.6) | |
| >110 kg | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.1) | 114 (15.1) | |
| Feel that you are worth nothing | |||||
| No, absolutely | 200 (78.7) | 2418 (82.2) | 834 (79.2) | 300 (77.3) | 0.001 |
| No more than normal | 46 (18.1) | 457 (15.5) | 185 (17.6) | 64 (16.5) | |
| More than normal | 8 (3.1) | 68 (2.3) | 34 (3.2) | 24 (6.8) | |
| Feeling unhappy | |||||
| No, absolutely | 132 (52) | 1829 (62.1) | 638 (60.6) | 210 (54.1) | 0.001 |
| Equal o more than normal | 122 (48) | 1116 (37.9) | 415 (39.4) | 178 (45.9) |
| OR (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Body Mass Index | ||
| Insufficient weight | 1.24 (0.71–2.17) | 0.458 |
| Normal weight | 1.66 (1.25–2.20) | 0.001 |
| Overweight/Obesity | Reference | |
| Consumption of alcohol | ||
| Daily | 1.21 (0.62–2.35) | 0.577 |
| 3–6 times/week | 0.966 (0.59–1.58) | 0.890 |
| 1–2 times/week | 1.97 (1.47–2.63) | <0.001 |
| 1–3 times/month | 1.56 (1.22–2) | <0.001 |
| Teetotaler | Reference | |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 2.63 (2.09–3.32) | <0.001 |
| Female | Reference | |
| Marital status | ||
| Single | 2.11 (1.58–2.8) | <0.001 |
| Married/Widowed/Separated/Divorced | Reference | |
| Level of education | ||
| Without education | Reference | |
| Primary | 1.04 (0.36–3.00 | 0.944 |
| Secondary | 1.59 (0.60–4.23) | 0.351 |
| High School/VTE | 1.98 (0.75–5.23) | 0.169 |
| University | 2.66 (0.99–7.18) | 0.054 |
| Feeling happy | ||
| More than usual | 1.97 (1.09–3.58) | 0.026 |
| As usual | 1.55 (0.91–2.66) | 0.110 |
| Less than usual | Reference | |
| Social class | ||
| Classes I and II | 1.34 (1.02–1.78) | 0.042 |
| Classes III and IV | 1.35 (1.08–1.70) | 0.008 |
| Classes V and VI | Reference | |
| Smoke | ||
| Yes | Reference | |
| No | 1.66 (1.33–2.08) | <0.001 |
| Weight | ||
| <50 kg | 1.11 (0.41–2.99) | 0.844 |
| 51–70 kg | 1.18 (0.48–2.91) | 0.717 |
| 71–90 kg | 1.98 (0.83–4.70) | 0.122 |
| 91–110 kg | 1.60 (0.65–3.99) | 0.310 |
| >110 kg | Reference |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laredo-Aguilera, J.A.; Cobo-Cuenca, A.I.; Santacruz-Salas, E.; Martins, M.M.; Rodríguez-Borrego, M.A.; López-Soto, P.J.; Carmona-Torres, J.M. Levels of Physical Activity, Obesity and Related Factors in Young Adults Aged 18–30 During 2009–2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204033
Laredo-Aguilera JA, Cobo-Cuenca AI, Santacruz-Salas E, Martins MM, Rodríguez-Borrego MA, López-Soto PJ, Carmona-Torres JM. Levels of Physical Activity, Obesity and Related Factors in Young Adults Aged 18–30 During 2009–2017. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):4033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204033
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaredo-Aguilera, José Alberto, Ana Isabel Cobo-Cuenca, Esmeralda Santacruz-Salas, María Manuela Martins, María Aurora Rodríguez-Borrego, Pablo Jesús López-Soto, and Juan Manuel Carmona-Torres. 2019. "Levels of Physical Activity, Obesity and Related Factors in Young Adults Aged 18–30 During 2009–2017" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 4033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204033
APA StyleLaredo-Aguilera, J. A., Cobo-Cuenca, A. I., Santacruz-Salas, E., Martins, M. M., Rodríguez-Borrego, M. A., López-Soto, P. J., & Carmona-Torres, J. M. (2019). Levels of Physical Activity, Obesity and Related Factors in Young Adults Aged 18–30 During 2009–2017. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 4033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16204033








