An Exploratory Model of Psychosocial Factors and Healthy Habits in University Students of Physical Education Depending on Gender
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Design
2.2. Measures
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mega, C.; Ronconi, L.; De Beni, R. What makes a good student? How emotions, self-regulated learning, and motivation contribute to academic achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 106, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Muros-Molina, J.J.; Espejo-Garcés, T.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Linares-Manrique, M. Adherence to Mediterranean diet in university students and its relationship with digital leisure habits. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, D.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Deliens, T.; Deforche, B. Can changes in psychosocial factors and residency explain the decrease in physical activity during the transition from high school to college or university? Int. J. Behav. Med. 2015, 22, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilian, F.; Karami, B.; Ahmadpanah, M.; Ataee, M.; Ahmadi, T.; Eslami, A.A.; Mirzaei, M. Socio-demographic characteristics associated with cigarettes smoking, drug abuse and alcohol drinking among male medical university students in Iran. J. Res. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chacón, R.; Zurita, F.; Puertas, P.; Knox, E.; Cofré, C.; Viciana, V.; Muros, J.J. Relationship between Healthy Habits and Perceived Motivational Climate in Sport among University Students: A Structural Equation Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Costigan, S.A.; Williams, R.L.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Kennedy, S.G.; Robards, S.L.; Allen, J.; Collins, C.E.; Callister, R.; Germov, J. Effectiveness of interventions targeting physical activity, nutrition and healthy weight for university and college students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deliens, T.; Clarys, P.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Deforche, B. Determinants of eating behaviour in university students: A qualitative study using focus group discussions. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjimbei, E.; Botsaris, G.; Gekas, V.; Panayiotou, A.G. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and lifestyle characteristics of University students in Cyprus: A cross-sectional survey. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasa, A.; Miranda, J.; Bulló, M.; Casas, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Larretxi, I.; Estruch, R.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Portillo, M.P. Comparative effect of two Mediterranean diets versus a low-fat diet on glycaemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, F.; Macchi, C.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Mediterranean diet and health status: An updated meta-analysis and a proposal for a literature-based adherence score. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Valero, G.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Puertas-Molero, P.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Garcés, T.E.; Sánchez, M.C. Educación para la salud: Implementación del programa “Sportfruits” en escolares de Granada. SPORT TK 2017, 6, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Ros, E.; Predimed Investigators. Benefits of the Mediterranean diet: Insights from the PREDIMED study. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekelund, U.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Brown, W.J.; Fagerland, M.W.; Owen, N.; Powell, K.E.; Bauman, A.; Lee, I.-M. Does physical activity attenuate, or even eliminate, the detrimental association of sitting time with mortality? A harmonised meta-analysis of data from more than 1 million men and women. Lancet 2016, 388, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pageaux, B. Perception of effort in exercise science: Definition, measurement and perspectives. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2016, 16, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueto-Martín, M.B.; De la Cruz, J.C.; Morales-Ortíez, E.; Pérez-Díaz, C. Effect of joint physical activity on the physical condition of parents and children. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2018, 13, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, E.M.; Corcoran, P.; O’Regan, G.; Keeley, H.; Cannon, M.; Carli, V.; Wasserman, C.; Hadlaczky, G.; Sarchiapone, M.; Apter, A.; et al. Physical activity in European adolescents and associations with anxiety, depression and well-being. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health. Available online: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/factsheet_recommendations/en/ (accessed on 23 August 2018).
- Ding, D.; Lawson, K.D.; Kolbe-Alexander, T.L.; Finkelstein, E.A.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Van Mechelen, W.; Pratt, M. The economic burden of physical inactivity: A global analysis of major non-communicable diseases. Lancet 2016, 388, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muros, J.J.; Cofre-Bolados, C.; Salvador-Pérez, S.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Valdivia-Moral, P.; Pérez-Cortés, A.J. Relationship between physical activity level and body composition in school children in Santiago (Chile). J. Sport Health Res. 2016, 8, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, P.W.; Smeets, R.J. Interaction between pain, movement, and physical activity: Short-term benefits, long-term consequences, and targets for treatment. Clin. J. Pain 2015, 31, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubans, D.; Richards, J.; Hillman, C.; Faulkner, G.; Beauchamp, M.; Nilsson, M.; Kelly, P.; Smith, J.; Raine, L.; Biddle, S. Physical activity for cognitive and mental health in youth: A systematic review of mechanisms. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Cline, H.; Turkheimer, E.; Duncan, G.E. Access to green space, physical activity and mental health: A twin study. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 2015, 69, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, M.M.; Van Poppel, M.; Van Kamp, I.; Ruijsbroek, A.; Triguero-Mas, M.; Gidlow, C.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Gražulevičiene, R.; van Mechelen, W.; Kruize, H.; et al. Do Physical Activity, Social Cohesion, and Loneliness Mediate the Association Between Time Spent Visiting Green Space and Mental Health? Environ. Behav. 2017, 0013916517738563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Self-determination theory: A macrotheory of human motivation, development, and health. Can. Psychol. 2008, 49, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguer, I.; Duda, J.L.; Castillo, I. Motivational Antecedents of Well-Being and Health Related Behaviors in Adolescents. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 59, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babic, M.J.; Morgan, P.J.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Lonsdale, C.; White, R.L.; Lubans, D.R. Physical activity and physical self-concept in youth: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgian, B.; Lorand, B. The influence of leisure sports activities on social health in adults. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, M.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Force, E.C.; Petrie, T.A. Peers, parents, and coaches, oh my! The relation of the motivational climate to boys’ intention to continue in sport. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2015, 16, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, T.; Hill, A.P.; Hall, H.K.; Jowett, G.E. Relationships between the coach-created motivational climate and athlete engagement in youth sport. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2015, 37, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, T.; Ntoumanis, N.; Liukkonen, J. Motivational climate, goal orientation, perceived sport ability, and enjoyment within Finnish junior ice hockey players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, K.; Gucciardi, D.F. Antisocial and prosocial behavior in sport: The role of motivational climate, basic psychological needs, and moral disengagement. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2015, 37, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferriz, R.; González-Cutre, D.; Sicilia, Á.; Hagger, M.S. Predicting healthy and unhealthy behaviors through physical education: A self-determination theory-based longitudinal approach. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, S.J.; Hancox, J.; Hattar, A.; Maxwell-Smith, C.; Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C.; Hagger, M.S. Motivating the unmotivated: How can health behavior be changed in those unwilling to change? Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomfield, C.J.; Barber, B.L. Social networking site use: Linked to adolescents’ social self-concept, self-esteem, and depressed mood. Aust. J. Psychol. 2014, 66, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viholainen, H.; Aro, T.; Purtsi, J.; Tolvanen, A.; Cantell, M. Adolescents’ school-related self-concept mediates motor skills and psychosocial well-being. Brit. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 84, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muros, J.J.; Cofre-Bolados, C.; Arriscado, D.; Zurita, F.; Knox, E. Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with lifestyle, physical fitness, and mental wellness among 10-y-olds in Chile. Nutrition 2017, 35, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, O.; Vallier, J.M.; Nicol, C.; Mercier, C.S.; Maïano, C. Effects of combined vigorous interval training program and diet on body composition, Physical fitness, and physical self-perceptions among obese adolescent boys and girls. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 29, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino-Marban, R.; Mayorga-Vega, D.; Fernandez-Rodríguez, E.; Estrada, F.; Viciana, J. Effect of a physical education-based stretching programme on sit-andreach score and its posterior reduction in elementary schoolchildren. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2015, 21, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, M.; Duda, J.; Yin, Z. Examination of the psychometric properties of the Perceived Motivational Climate in Sport Questionnaire-2 in a sample of female athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2000, 18, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Cutre, D.; Sicilia, A.; Moreno, J.A. Social-cognitive model of goal motivation in Physical Education. Psicothema 2008, 20, 642–651. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, J.; Aasland, O.; Babor, T.; De la Fuente, J.; Grant, M. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): Who collaborative Project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-II. Addiction 1993, 88, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, G. Validation test for identifying disorders related to alcohol use (AUDIT) in primary care. Spec. Clin. J. 1998, 198, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, K.C.; Crocker, P.R.; Donen, R.M. The physical activity questionnaire for older children (PAQ-C) and adolescents (PAQ-A) manual. Coll. Kinesiol. 2004, 87, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Gómez, D.; Martínez-de-Haro, V.; Pozo, T.; Welk, G.J.; Villagra, A.; Calle, M.E. Fiabilidad y validez del cuestionario de actividad física PAQ-A en adolescentes españoles. Span J. Public Health 2009, 83, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; Garcia, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean diet quality index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villareal-González, M.E. A Structural Model of Drug Use and Violent Behavior in School-Aged Adolescents. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, San Nicolás de los Garza, México, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heatherton, T.; Kozlowski, L.; Frecker, R.; Fagerström, K.O. The Fagerström Test of Nicotine Dependence: A revision of the Fagerström Tolerance Questionnaire. Br. J. Addict. 1991, 86, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, O.; Maïano, C.; Nicol, C.; Mercier, C.S.; Vallier, J.M. Psycho-Physiological Responses of Obese Adolescents to an Intermittent Run Test Compared with a 20-M Shuttle Run. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García, G.C.; Secchi, J.D. 20 meters’ shuttle run test with stages of one minute. An original idea that has lasted for 30 years. Apunts Med. Sport 2014, 49, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, L.A.; Lambert, J. A maximal multistage 20-m shuttle run test to predict V˙ O2 max. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1982, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, F.; Musitu, G. AF5: Self-Concept form 5; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, H.W. Handbook of Sport Psychology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Mato, V.; Cancela, J.M.; Ayan, C.; Martín, V.; Molina, A. Lifestyle and health among Spanish university students: Differences by gender and academic discipline. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2728–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganasegeran, K.; Al-Dubai, S.A.; Qureshi, A.M.; Al-Abed, A.A.; Rizal, A.M.; Aljunid, S.M. Social and psychological factors affecting eating habits among university students in a Malaysian medical school: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Muros, J.; Cachón-Zagalaz, J.; Zagalaz-Sánchez, M.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Zurita-Ortega, F. Physical activity, Mediterranean diet, maximal oxygen uptake and motivational climate towards sports in schoolchildren from the province of Granada: A structural equation model. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, R.J.; Harwood, C.G.; Spray, C.M.; Lavallee, D. A qualitative investigation of the motivational climate in elite sport. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogue, C.M.; Fry, M.D.; Fry, A.C. The differential impact of motivational climate on adolescents’ psychological and physiological stress responses. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2017, 30, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Valero, G.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Motivational and physical activity outlook in students: A systematic review. ESHPA Educ. Sport Health Phys. Act. 2017, 1, 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, D.; Borrego, C.C.; Silva, C.; Moutão, J.; Marinho, D.A.; Cid, L. Motivational Climate Sport Youth Scale: Measurement invariance across gender and five different sports. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 61, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyton, R.; García, M.; Fuentes, G.; Jiménez, C. Analysis of motivational variables and healthy lifestyles in sports center practitioners by gender. Rev. Retos. 2018, 34, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cabanas-Sánchez, V.; Martínez-Gómez, D.; Izquierdo-Gómez, R.; Segura-Jiménez, V.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Veiga, O.L. Association between Clustering of Lifestyle Behaviors and Health-Related Physical Fitness in Youth: The UP&DOWN Study. J. Pediatr. 2018, 199, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, S.; Wills, W.; Dickinson, A. The Mediterranean diet: Socio-cultural relevance for contemporary health promotion. Open Public Health J. 2015, 8, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Ortega, F.; San Román-Mata, S.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Muros, J.J. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with Physical Activity, Self-Concept and Sociodemographic Factors in University Student. Nutrients 2018, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoyne, J.; Valois, P.; Guay, F. Physical self-concept and participation in physical activity in college students. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motos, P.; Cortés, M.T.; Giménez, J.A.; Cadaveira, F. Predictors of weekly alcohol drinking and alcohol-related problems in binge-drinking undergraduates. Adicciones 2015, 27, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, R.; Zurita, F.; Castro, M.; Espejo, T.; Martínez, A.; Ruiz-Rico, G. The association of Self-concept with Substance Abuse and Problematic Use of Video Games in University Students: A Structural Equation Model. Adicciones 2018, 30, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, L.V.; Shrine, N.; Miller, S.; Jackson, V.E.; Ntalla, I.; Artigas, M.S.; Billington, C.K.; Kheirallah, A.K.; Allen, R.; Cook, J.P.; et al. Novel insights into the genetics of smoking behaviour, lung function, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (UK BiLEVE): A genetic association study in UK Biobank. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, K.P.; Neighbors, C.; Gasser, M.L.; Ramirez, J.J.; Cvencek, D. A review of implicit and explicit substance self-concept as a predictor of alcohol and tobacco use and misuse. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2017, 43, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, C.S.; Weber, R. Undisclosed flexibility in computing and reporting structural equation models in communication science. Commun. Methods Meas. 2015, 9, 208–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

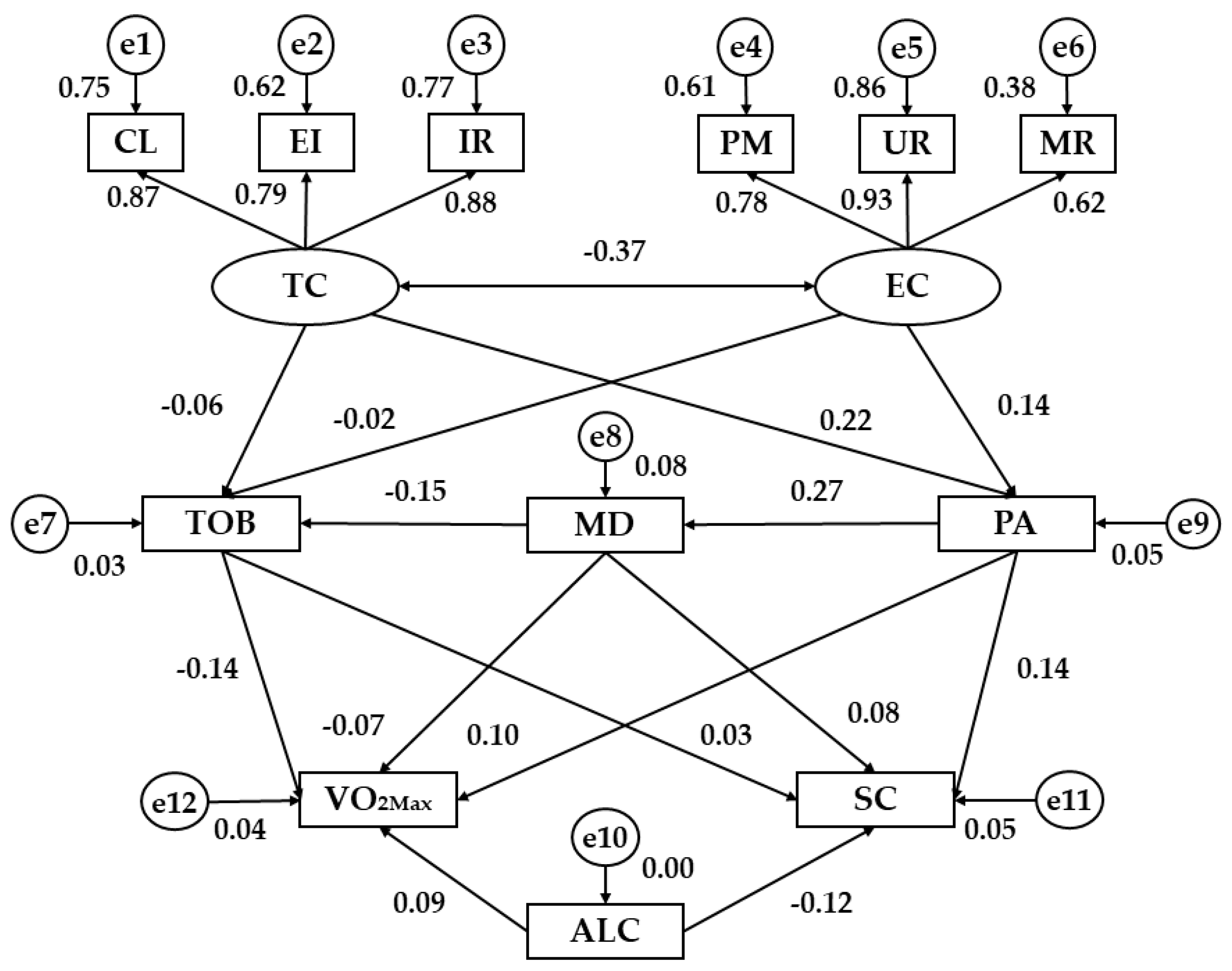
| Relationship between Variables | Regression Weights | S.R.W | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | p | Estimate | |||
| PA | ← | TC | 3.134 | 0.756 | 4.146 | *** | 0.22 |
| PA | ← | EC | 1.887 | 0.723 | 2.609 | ** | 0.14 |
| MD | ← | PA | 0.082 | 0.014 | 5.750 | *** | 0.27 |
| TOB | ← | TC | −0.288 | 0.281 | −1.025 | 0.305 | −0.06 |
| TOB | ← | EC | −0.076 | 0.271 | −0.279 | 0.780 | −0.02 |
| TOB | ← | MD | −0.184 | 0.057 | −3.258 | ** | −0.15 |
| VO2MAX | ← | MD | −21.522 | 14.720 | −1.462 | 0.144 | −0.07 |
| VO2MAX | ← | PA | 9.178 | 4.492 | 2.043 | * | 0.10 |
| VO2MAX | ← | TOB | −34.737 | 11.763 | −2.953 | ** | −0.14 |
| VO2MAX | ← | ALC | 17.114 | 8.771 | 1.951 | * | 0.09 |
| CL | ← | TC | 1.000 | - | - | *** | 0.87 |
| EI | ← | TC | 0.760 | 0.039 | 19.344 | *** | 0.79 |
| IR | ← | TC | 1.019 | 0.047 | 21.582 | *** | 0.88 |
| PM | ← | EC | 1.000 | - | - | *** | 0.78 |
| UR | ← | EC | 1.316 | 0.082 | 16.040 | *** | 0.93 |
| MR | ← | EC | 0.930 | 0.070 | 13.228 | *** | 0.62 |
| SC | ← | TOB | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.730 | 0.466 | 0.03 |
| SC | ← | ALC | −0.011 | 0.004 | −2.681 | ** | −0.12 |
| SC | ← | PA | 0.006 | 0.002 | 2.901 | ** | 0.14 |
| SC | ← | MD | 0.012 | 0.007 | 1.687 | * | 0.08 |
| EC | ↔ | TC | −0.145 | 0.023 | −6.286 | *** | −0.37 |
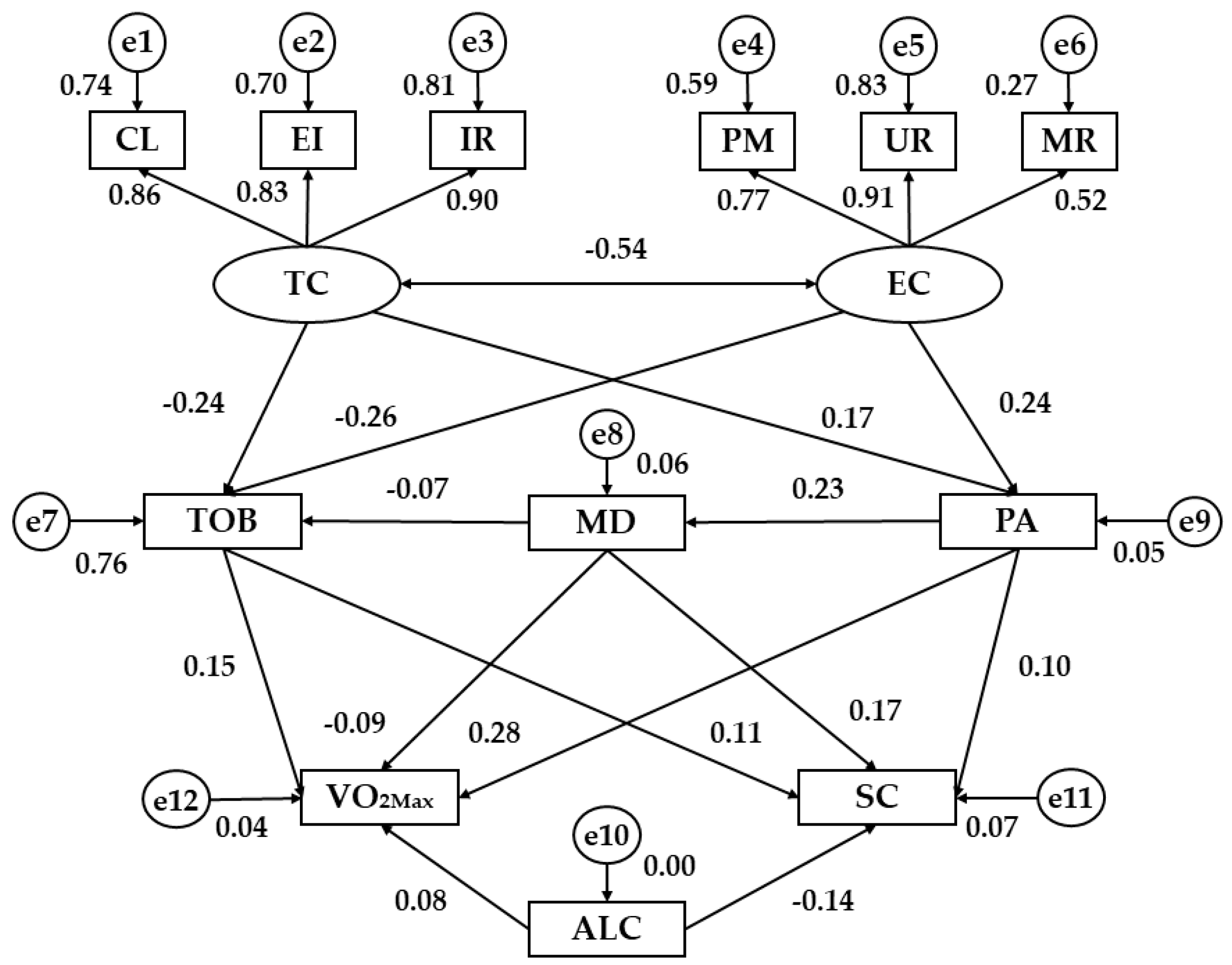
| Relationship between Variables | Regression Weights | S.R.W | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | p | Estimate | |||
| PA | ← | TC | 2.053 | 0.900 | 2.280 | * | 0.17 |
| PA | ← | EC | 3.208 | 0.987 | 3.249 | ** | 0.24 |
| MD | ← | PA | 0.069 | 0.017 | 4.083 | *** | 0.23 |
| TOB | ← | TC | −1.158 | 0.351 | −3.295 | *** | −0.24 |
| TOB | ← | EC | −1.364 | 0.385 | −3.542 | *** | −0.26 |
| TOB | ← | MD | −0.086 | 0.071 | −1.213 | 0.225 | −0.07 |
| VO2MAX | ← | MD | −19.462 | 11.317 | −1.720 | 0.085 | −0.09 |
| VO2MAX | ← | PA | 17.183 | 3.421 | 5.022 | *** | 0.28 |
| VO2MAX | ← | TOB | 24.550 | 8.539 | 2.875 | ** | 0.15 |
| VO2MAX | ← | ALC | 10.496 | 7.272 | 1.443 | 0.149 | 0.08 |
| CL | ← | TC | 1.000 | - | - | *** | 0.86 |
| EI | ← | TC | 0.878 | 0.048 | 18.377 | *** | 0.83 |
| IR | ← | TC | 1.072 | 0.053 | 20.123 | *** | 0.90 |
| PM | ← | EC | 1.000 | - | - | *** | 0.77 |
| UR | ← | EC | 1.294 | 0.099 | 13.082 | *** | 0.91 |
| MR | ← | EC | 0.769 | 0.086 | 8.974 | *** | 0.52 |
| SC | ← | TOB | 0.014 | 0.007 | 2.027 | * | 0.11 |
| SC | ← | ALC | −0.016 | 0.006 | −2.670 | ** | −0.14 |
| SC | ← | PA | 0.005 | 0.003 | 1.608 | 0.108 | 0.10 |
| SC | ← | MD | 0.029 | 0.009 | 3.125 | ** | 0.17 |
| EC | ↔ | TC | −0.217 | 0.031 | −6.902 | *** | −0.54 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Olmedo-Moreno, E.M.; Padial-Ruz, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M. An Exploratory Model of Psychosocial Factors and Healthy Habits in University Students of Physical Education Depending on Gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112430
Chacón-Cuberos R, Zurita-Ortega F, Olmedo-Moreno EM, Padial-Ruz R, Castro-Sánchez M. An Exploratory Model of Psychosocial Factors and Healthy Habits in University Students of Physical Education Depending on Gender. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(11):2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112430
Chicago/Turabian StyleChacón-Cuberos, Ramón, Félix Zurita-Ortega, Eva María Olmedo-Moreno, Rosario Padial-Ruz, and Manuel Castro-Sánchez. 2018. "An Exploratory Model of Psychosocial Factors and Healthy Habits in University Students of Physical Education Depending on Gender" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 11: 2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112430
APA StyleChacón-Cuberos, R., Zurita-Ortega, F., Olmedo-Moreno, E. M., Padial-Ruz, R., & Castro-Sánchez, M. (2018). An Exploratory Model of Psychosocial Factors and Healthy Habits in University Students of Physical Education Depending on Gender. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(11), 2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112430






