Functional Feed Assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei Using 100% Fish Meal Replacement by Soybean Meal, High Levels of Complex Carbohydrates and Bacillus Probiotic Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Feeds Preparation and Analysis
2.2. Shrimp Growth Conditions
2.3. Hemolymph Parameters Measurement
2.4. Stress Parameters Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Functional Feed Analysis
3.2. Shrimp Growth
3.3. Hemolymph Metabolites Quantification
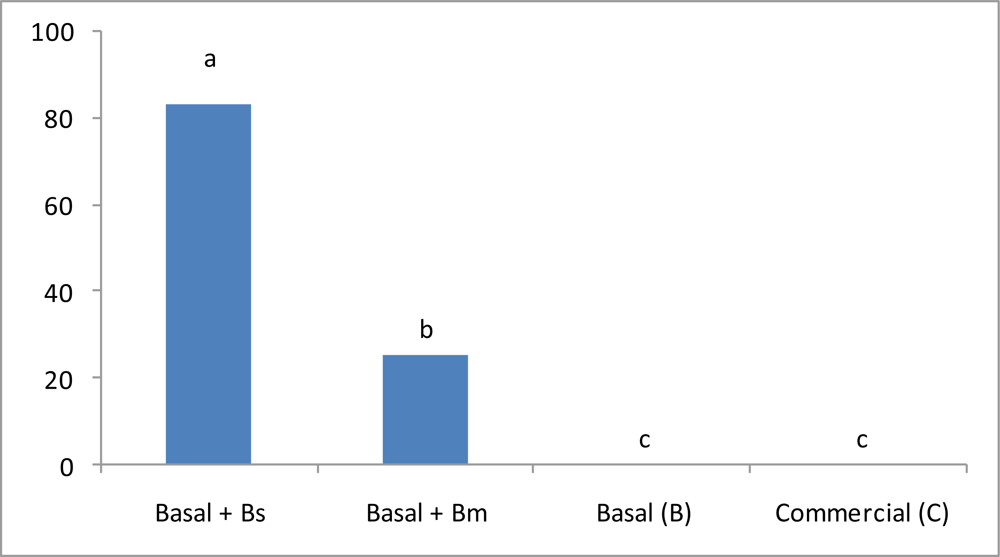
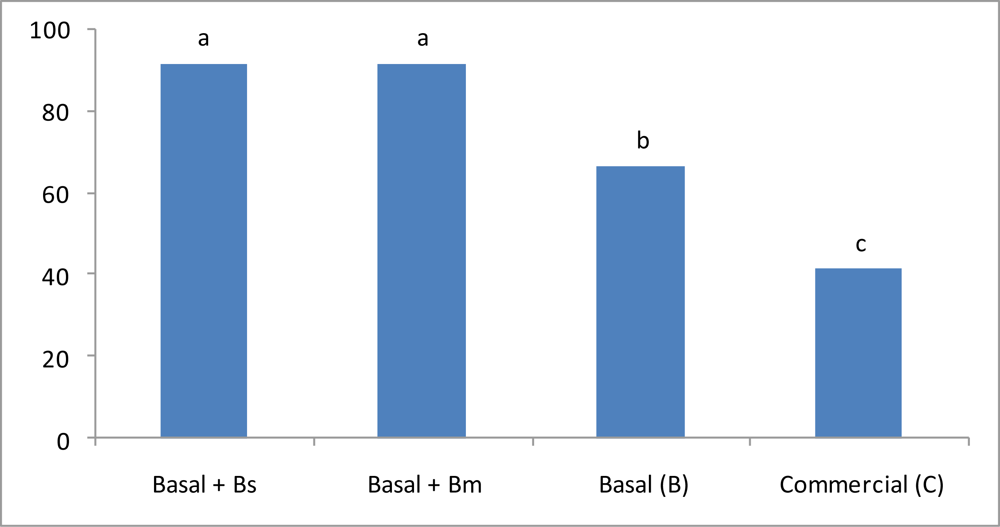
3.4. Stress Condition Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- FAO, The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO Fisheries Department: Rome, Italy, 2006; p. 159.
- Tacon, A; Nates, S; McNeil, R. Overview of farming systems for marine shrimp with particular reference to feeds and feeding. In Shrimp Culture: Economics, Market and Trade; Leung, P, Engle, C, Eds.; Blackwell Publishers: Ames, IA, USA, 2006; Chapter 20; pp. 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, A; Metian, M. Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: Trends and future prospects. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, M; Eusebio, P; Welsh, T. Utilization of feed pea, Pisum sativum, meal as a protein source in practical diets juvenile tiger shrimp. Penaeus monodon Aquaculture 2003, 225, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, RW. Alternate protein sources. Feed Management 1999, 50, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, RL; Goldburg, RJ; Primavera, JH; Kautsky, N; Beveridge, MCM; Clay, J; Folke, C; Lubchenco, J; Mooney, H; Troell, M. Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 2000, 405, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Amaya, E; Daves, D; Rouse, D. Replacement of fish meal in practical diets for the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vanname) reared under pond conditions. Aquaculture 1997a, 262, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Amaya, EA; Daves, DA; Rouse, DB. Alternative diets for the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 1997b, 262, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, I; Dominy, W; Tacon, A. The use of concentrates and other soy products in shrimp feeds. In Avances en Nutrición Acuícola VI; Cruz-Suárez, L, Ricque, D, Tapia, M, Gaxiola, M, Simoes, N, Eds.; Memorias del VI Simposium Internacional de Nutrición Acuícola: Cancún, Quintana Roo, México, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa, SJL; Olmos, SJ. The functional property of Bacillus for shrimp feeds. Food Microbiol 2006, 23, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, AGJ; Dominy, WG; Pruder, GD. Global trends and challenges in aquafeeds for marine shrimp. AquaFeed Int 1998, 4, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Swick, RA. Soybean meal quality: assessing the characteristics of a major aquatic feed ingredient. Glob Aquac Advocate 1998, 5, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Le Chevalier, P; Van Wormhoudt, A. Alpha-glucosidase from the hepatopancreas of the shrimp, Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea-Decapoda). J Exp Zool 1998, 280, 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano, CF; Olmos, SJ. Thermostable α-1,4- and α-1–6-glucosidase enzymes from Bacillus sp. isolated from a marine environment. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2002, 18, 791–795. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, C; Arena, L; Cuzon, G; Gaxiola, G; Tabeada, G; Valenzuela, M; Rosas, C. Effect of a size-based selection program on blood metabolites and immune response of Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles fed different dietary carbohydrate levels. Aquaculture 2004a, 230, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Gatesoupe, FJ. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 147–165. [Google Scholar]
- Verschuere, L; Rombaut, G; Sorgeloos, P; Verstraete, W. Probiotic Bacteria as Biological Control Agents in Aquaculture. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar]
- Farzanfar, A. The use of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2006, 48, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, HZ; Guo, Z; Yang, Y; Zheng, W; Li, ZJ. Effect of dietay probiotics on apparent digestibility coefficients of nutrients of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Boone. Aquac Res 2004, 35, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, WY; Fu, LL; Li, WF; Zhu, YR. Effect of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis on the growth, performance, immune response and antioxidant activities of the shrimp. Aquac Res 2010, 41, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, YB. Effect of probiotics on growth performance and digestive enzyme activity of the shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, ZG; Olmos, SJ. Identification of bacterial diversity in the oyster Crassostrea gigas by fluorescent in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction. J Appl Microbiol 2006, 100, 664–672. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, TA; Olmos, SJ. Quantification by fluorescent in situ hybridization of bacteria associated with Litopenaeus vannamei larvae in Mexican shrimp hatchery. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, JH. Biostatistical Analysis, 2nd ed; Prentice-Hall Inc: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rosas, C; Cuzon, G; Gaxiola, G; Arena, L; Lemaire, P; Zoyez, C; van Wormhoudt, A. Influence of dietary carbohydrate on the metabolism of juvenile Litopenaeus stylirostris. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 2000, 249, 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Frischer, ME; Floriani, PJ; Nierzwicki-Bauer, SA. Differential sensitivity of 16S rRNA targeted oligonucleotide probes used for fluorescence in situ hybridization is a result of ribosomal higher order structure. Can J Microbiol 1996, 42, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, CE; Tucker, CS. Pond Aquaculture Water Quality Management; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; p. 700. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, C; Zenteno, E; Cuzon, G; Sanchez, A; Gaxiola, G; Taboada, G; Suarez, J; Maldonado, T; Rosas, C. Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles energetic balance and immunological response to dietary protein. Aquaculture 2004, 236, 431–450. [Google Scholar]
- Kureshy, N; Davis, DA. Protein requirement for maintenance and maximum weight gain for the Pacific white shrimp. Litopenaeus vannamei Aquaculture 2002, 204, 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, HA; Duc, H; Cutting, SM. The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2005, 29, 813–835. [Google Scholar]
- Olmos, SJ; Bolaños, V; Causey, S; Ferrari, E; Bolivar, F; Valle, F. A functional SpoOA is required for maximal aprE expresión in Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett 1996, 381, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Olmos, SJ; DeAnda, R. Regulations of the aprE (subtilisin) gene in abrB mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Asia Pac J Mol Biol Biotechnol 1998, 6, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bechard, J; Eastwell, K; Sholberg, P; Mazza, G; SkuraI, B. Isolation and Partial Chemical Characterization of an Antimicrobial Peptide Produced by a Strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Agric Food Chem 1998, 46, 5355–5361. [Google Scholar]
- Olmos, SJ; Contreras, FR. Genetic system constructed to overproduce and secrete proinsulin in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2003, 62, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Cheon, J; Seong, B; Seong, W; Jong, K; Kim, P. Characterization of L-Arabinose in Bacillus, a GRAS Host, for the Production of Edible Tagatose. Food Biotechnol 2009, 23, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C; Dominy, W. Evaluation of soybean meal as a replacement for marine animal protein in diets for shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 1990, 87, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, LE; Ricque, MD; Pinal, JD; Wesche, P. Effect of different carbohydrate sources on the growth of P. vannamei: Economical impact. Aquaculture 1994, 123, 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Le Chevalier, P; Sellos, D; van Wormhoudt, A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding alpha-glucosidase in the digestive gland of the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Cell Mol Life Sci 2000, 57, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Dersjant-Li, Y. The use of soy protein in aquafeeds. In Avances en Nutrición Acuícola VI; Cruz-Suárez, L, Ricque, D, Tapia, M, Gaxiola, M, Simoes, N, Eds.; Memorias del VI Simposium Internacional de Nutrición Acuícola: Cancún, Quintana Roo, México, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hochachka, PW. The organization and control of metabolism in the crustaccean gill. Comp Biochem Physiol 1970, 33, 529–548. [Google Scholar]
- Huggins, AK. Intermediary metabolism in Carcinus maenas. Comp Biochem Physiol 1966, 18, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, EA; Keller, R. Crustacean hyperglicemic hormona (CHH) and the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism: current perspectivas. Comp Biochem Physiol 1993, 106a, 105–411. [Google Scholar]
- Frias, MG; Harfush, M; Paez, F. Effects of ammonia on mortality and feeding of postlarvae shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2000, 65, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Colt, J; Amstrong, D. Nitrogen toxicity to fish, crustaceans and mollusks. In Proceedings of the Bioengineering Symposium for Fish Culture; American Fisheries Society, Fish Culture Section: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1981; pp. 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dall, W; Hill, B; Rothlisberg, P; Sharples, D. The biology of the Penaeidae. In Advances in Marine Biology; Blaxter, JHS, Southward, AJ, Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, JC; Liu, PC; Lei, SC. Toxicity of ammonia and nitrite to Penaeus monodon adolescents. Aquaculture 1990, 89, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
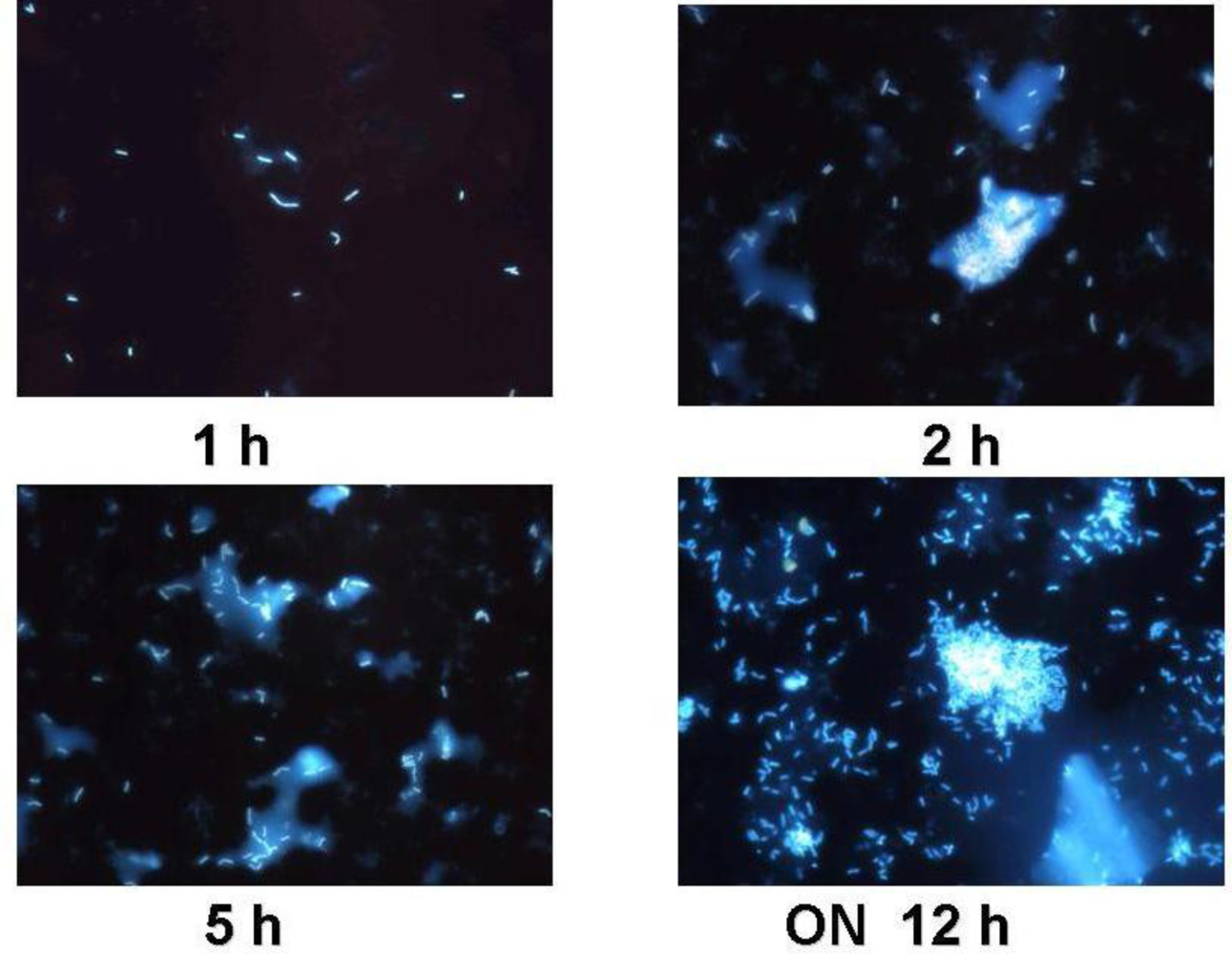
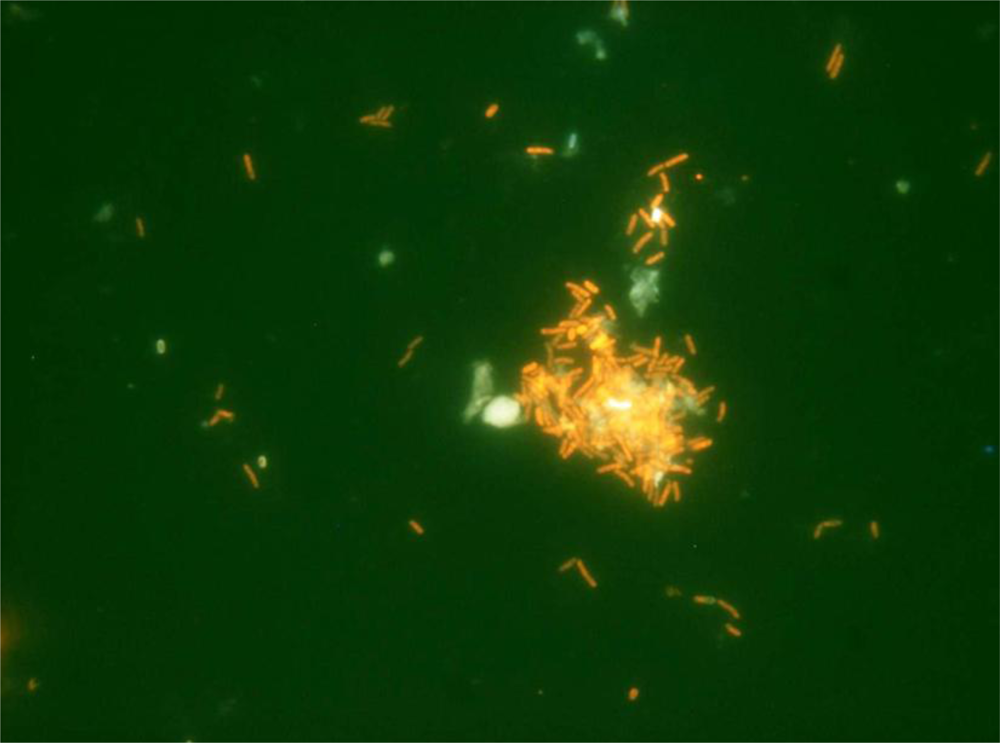
| Treatments (amount%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Items | Basal diet (B) | Commercial diet (C) |
| Crude Protein | 27.41 | 36.39 |
| Total Lipid | 6.46 | 3.98 |
| Carbohydrates | 49.50 | 38.42 |
| Moisture | 11.34 | 9.88 |
| Ash | 5.29 | 11.33 |
| Items | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Basal + Bs | 2 Basal + Bm | 3 Basal (B) | 4 Commercial (C) | |
| Initial weight (g) | 5.96 ± 0.20 a | 5.81 ± 0.15 a | 5.98 ± 0.22 a | 6.06 ± 0.18 a |
| Final weight (g) | 10.71 ± 0.11 a | 9.69 ± 0.10 c | 9.48 ± 0.13 c | 10.38 ± 0.16 b |
| Daily Weight Gain (DWG; g/day) | 0.169 ± 0.003 a | 0.138 ± 0.004 b | 0.125 ± 0.003 c | 0.154 ± 0.001 b |
| Food conversion ratio (FCR) | 1.54 ± 0.07 a | 2.02 ± 0.18 b | 2.49 ± 0.15 c | 2.06 ± 0.22 b |
| Survival (%) | 100 a | 96.67 ± 3.87 a | 96.67 ± 3.87 a | 96.67 ± 3.87 a |
| Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | Basal + Bs | Basal + Bm | Basal [B] | Commercial [C] |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 0.675 ± 0.02 a | 0.483 ± 0.03 b | 0.470 ± 0.02 b | 0.452 ± 0.03 b |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 0.385 a ± 0.03 a | 0.273 ± 0.03 b | 0.261 ± 0.02 b | 0.249 ± 0.03 b |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 0.323 ± 0.08 a | 0.159 ± 0.01 b | 0.134 ± 0.07 b | 0.163 ± 0.03 b |
| Hemocytes (cell/mL) | 2.02 × 107 ± 0.08 a | 9.83 × 106 ± 0.18 b | 9.41 × 106 ± 0.15 b | 9.63 × 106 ± 0.12 b |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Olmos, J.; Ochoa, L.; Paniagua-Michel, J.; Contreras, R. Functional Feed Assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei Using 100% Fish Meal Replacement by Soybean Meal, High Levels of Complex Carbohydrates and Bacillus Probiotic Strains. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1119-1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9061119
Olmos J, Ochoa L, Paniagua-Michel J, Contreras R. Functional Feed Assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei Using 100% Fish Meal Replacement by Soybean Meal, High Levels of Complex Carbohydrates and Bacillus Probiotic Strains. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(6):1119-1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9061119
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlmos, Jorge, Leonel Ochoa, Jesus Paniagua-Michel, and Rosalia Contreras. 2011. "Functional Feed Assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei Using 100% Fish Meal Replacement by Soybean Meal, High Levels of Complex Carbohydrates and Bacillus Probiotic Strains" Marine Drugs 9, no. 6: 1119-1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9061119
APA StyleOlmos, J., Ochoa, L., Paniagua-Michel, J., & Contreras, R. (2011). Functional Feed Assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei Using 100% Fish Meal Replacement by Soybean Meal, High Levels of Complex Carbohydrates and Bacillus Probiotic Strains. Marine Drugs, 9(6), 1119-1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9061119





