Enhancing Fucoxanthin Pickering Emulsion Stability and Encapsulation with Seaweed Cellulose Nanofibrils Using High-Pressure Homogenization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Polymerization Degree of Brown Seaweed Cellulose
2.2. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Crystalline Structure of Brown Seaweed Cellulose
2.3. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Chemical Construction of Brown Seaweed Cellulose
2.4. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Particle Size of Cellulose Nanofibers
2.5. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Zeta Potential of Cellulose Nanofibers
2.6. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Contact Angle of Cellulose Nanofibers
2.7. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Microstructure of Cellulose Nanofibers
2.8. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on Thermogravimetric Stability of Cellulose Nanofibers
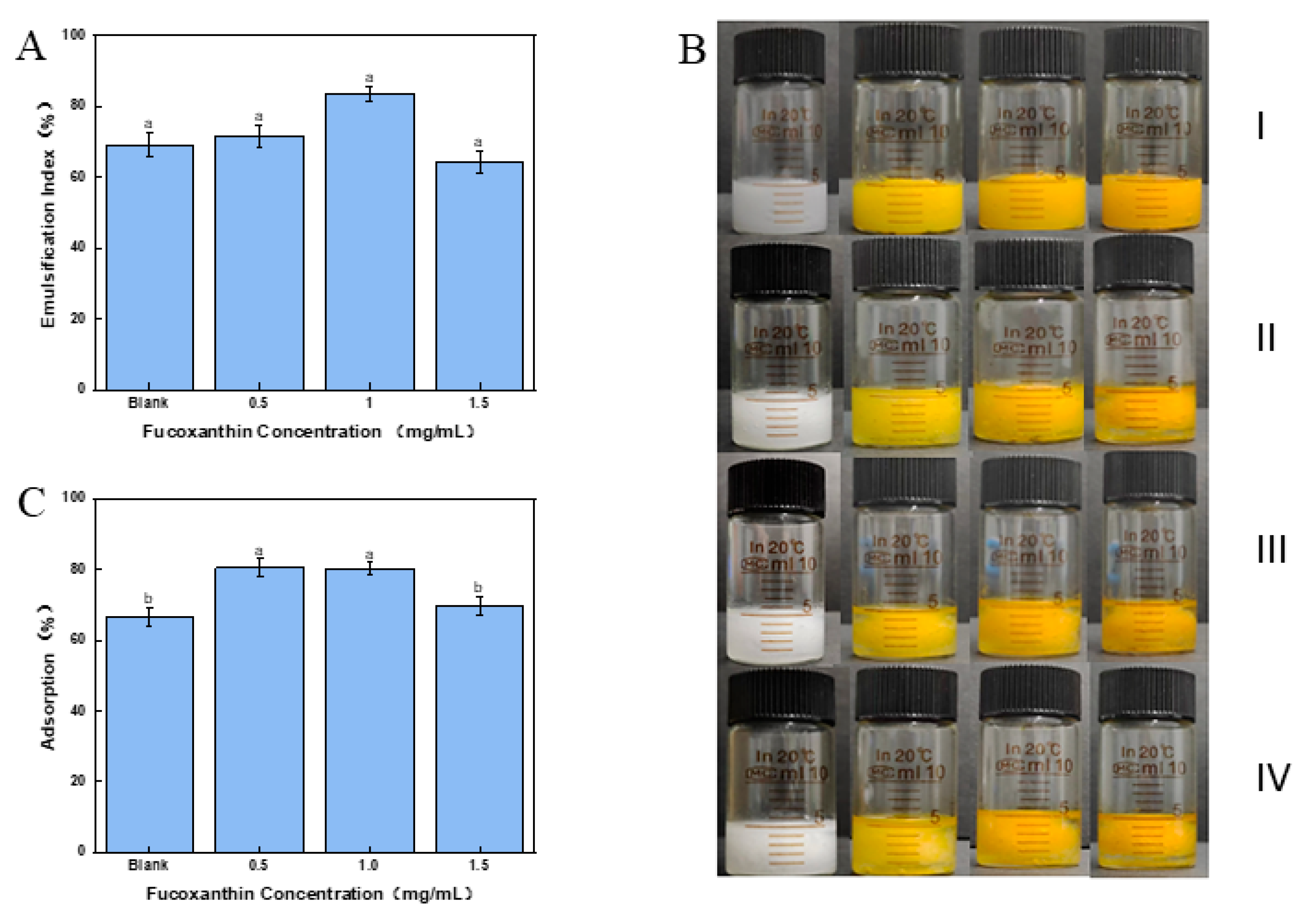
2.9. Encapsulation Efficiency of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsion
2.10. The Stability of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion
2.11. Interfacial Adsorption Amount of the Cellulose Nanofibers in Fucoxanthin Emulsion
2.12. Effect of pH Value on the Stability of Fucoxanthin Emulsion
2.13. Effect of Salinity on the Stability of Fucoxanthin Emulsion
2.14. Effect of Temperature on the Stability of Fucoxanthin Emulsion
2.15. Effect of UV Exposure on the Stability of Fucoxanthin Emulsion
2.16. Effect of Storage Time on the Stability of Fucoxanthin Emulsion
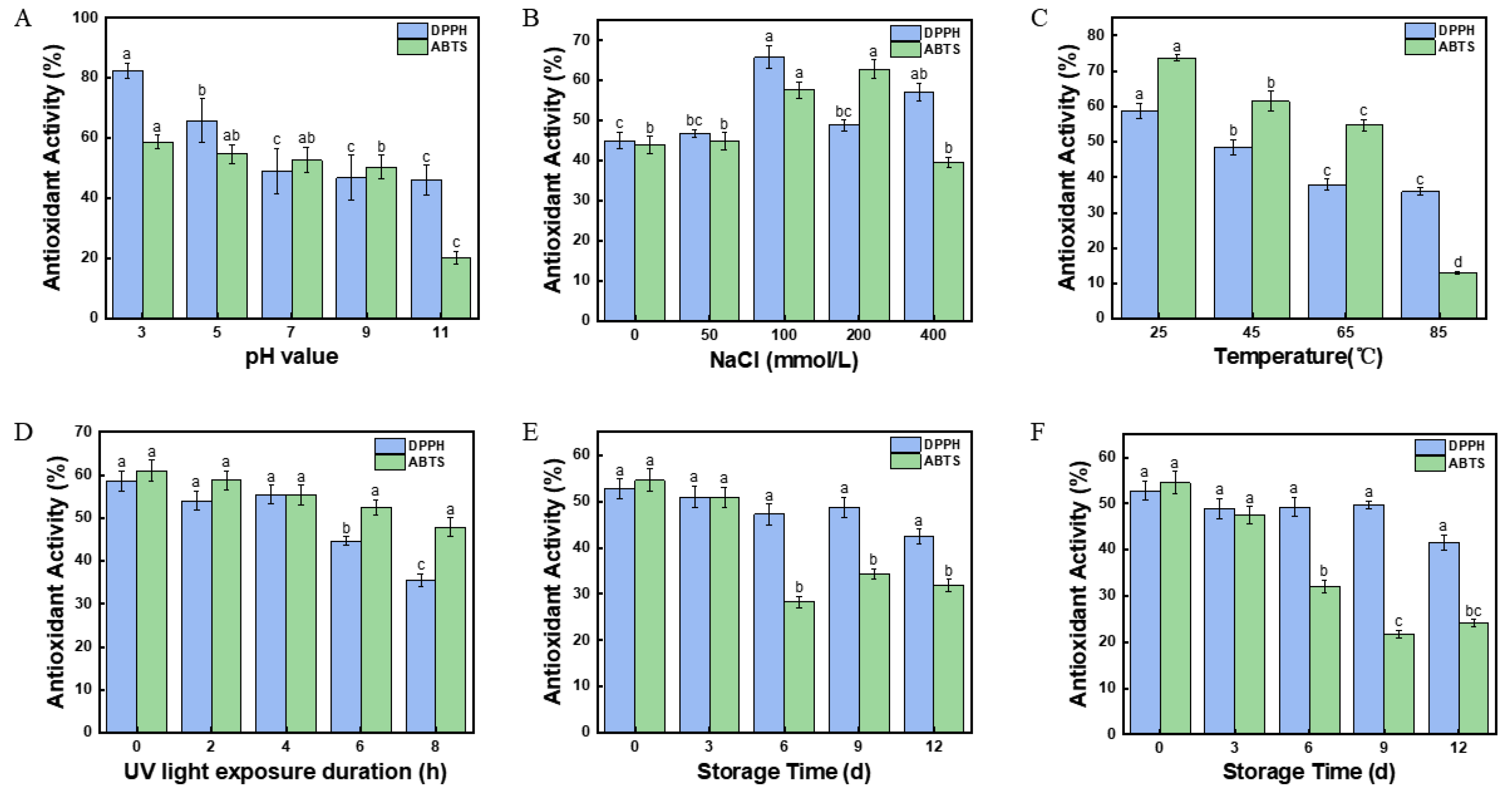
2.17. Effect of pH Value on the Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsions
2.18. Effect of Salinity on the Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsions
2.19. Effect of Temperature on the Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsions
2.20. Effect of UV Irradiation on the Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsions
2.21. Effect of Storage Time on the Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Isolation of Brown Seaweed Cellulose
3.3. Preparation of the Cellulose Nanofibrils (CNFs)
3.4. Determination on the Polymerization Degree of the CNFs
3.5. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of the CNFs
3.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis of the CNFs
3.7. Determination on Particle Size and Zeta Potential of the CNFs
3.8. Contact Angle Analysis of the CNFs
3.9. Morphology Observation of the CNFs
3.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis of the CNFs
3.11. Preparation of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion Stabilized by the CNFs
3.12. Determination on Encapsulation Efficiency of Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsion
3.13. Analysis on Centrifugal Stability of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion
3.14. Analysis on Freeze–Thaw Stability of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion
3.15. Determination on Interfacial Adsorption Amount of the CNFs
3.16. Preparation of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion with Different pH Values
3.17. Preparation of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion with Different Salinities
3.18. Preparation of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion with Different Temperatures
3.19. Preparation of the Fucoxanthin Emulsion with Different UV Light Exposure Durations
3.20. Encapsulation Efficiency of Fucoxanthin in the Pickering Emulsion with Different Processing and Storage Factors
3.21. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Rate of the Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsion
3.22. ABTS Cation Radical Scavenging Rate of the Fucoxanthin in Pickering Emulsion
3.23. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kodai, N.; Naoki, T.; Fumiaki, B.; Aya, A.; Etsuko, T.; Tomohisa, F.; Makoto, O.; Masashi, H. Monocaprin Enhances Bioavailability of Fucoxanthin in Diabetic/Obese KK-Ay Mice. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohibbullah, M.; Haque, M.N.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Hossain, M.T.; Zahan, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Hannan, M.A.; Moon, I.S.; Choi, J.-S. A Systematic Review on Marine Algae-Derived Fucoxanthin: An Update of Pharmacological Insights. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, T.M.; Ożarowski, M.; Alam, R.; Łochyńska, M.; Stasiewicz, M. What Do We Know About Antimicrobial Activity of Astaxanthin and Fucoxanthin? Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food hydrocolloids: Application as Functional Ingredients to Control Lipid Digestion and Bioavailability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Ji, Y.; Yang, H.; Meng, X.; Liu, B. Soy Protein Isolate–Chitosan Nanoparticle-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions: Stability and in Vitro Digestion for DHA. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Q. Recent Advances in Pickering Double Emulsions and Potential Applications in Functional Foods: A Perspective Paper. Foods 2023, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zhao, S.; Guan, X.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Ngai, T. Polysaccharide-Based Pickering Emulsions: Formation, Stabilization and Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zaky, A.A.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Su, W.; Wang, H.; Abd El-Aty, A.; Tan, M. High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Sea Bass Protein Microgel Particles: Food 3D Printing Application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ding, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Han, W. Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Spherical Cellulose Nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, S. Recent Advances in Delivery Systems of Fucoxanthin. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Delivery Systems for Fucoxanthin: Research Progress, Applications and Future Prospects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliyaei, N.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Tanideh, N. Preparation of Fucoxanthin Nanoemulsion Stabilized by Natural Emulsifiers: Fucoidan, Sodium Caseinate, and Gum Arabic. Molecules 2022, 27, 6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, Z.; Lim, V.; Khong, N.M.H.; Choo, W.S.; Foo, S.C. Unveiling Fucoxanthin’s Fate: In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Effects on Bioaccessibility, Antioxidant Potential, Colour Changes, and Metabolite Profiles. Food Chem. 2025, 463 Pt 2, 141209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, J. Light-Tuning Amphiphility of Host-Guest Alginate-Based Supramolecular Assemblies for Photo-Responsive Pickering Emulsions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 251, 117072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Fang, R.; Lei, C.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Pei, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, S. Application of Nanocellulose as Particle Stabilizer in Food Pickering Emulsion: Scope, Merits and Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Díaz, C.; Opazo-Navarrete, M.; Soto-Añual, M.; Leal-Calderón, F.; Bustamante, M. Food-Grade Pickering Emulsion as a Novel Astaxanthin Encapsulation System for Making Powder-Based Products: Evaluation of Astaxanthin Stability During Processing, Storage, and its Bioaccessibility. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Cao, A.; Cai, L.; Xiang, X.; Li, J.; Luan, Q. Preparation of Cellulose-Based Nanoparticles Via Electrostatic Self-Assembly for the pH-Responsive Delivery of Astaxanthin. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Ma, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhou, H.; He, Y.; Ren, D.; Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, L. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Fucoidan From Kjellmaniella Crassifolia Based on Kinetic Study of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Algal Cellulose. Algal Res. 2022, 66, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Mu, T.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Li, M. Preparation of Cellulose Nanofibers from Potato Residues by Ultrasonication Combined with High-Pressure Homogenization. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Mehandzhiyski, A.Y.; Zozoulenko, I. A computational Study of Cellulose Regeneration: Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanto, H.; Muhajir, M.; Susilo, B.D.; Aji Pradana, Y.R.; Wijaya, H.W.; Ansari, A.S.; Yanuhar, U. Nano Fibrillation of Bacterial Cellulose using High-Pressure Homogenization and its Films Characteristics. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Ou, Y.; Feng, X.; Lin, M.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Qi, H. Integrated Production of Cellulose Nanofibers and Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose through Controllable Eco-Carboxymethylation under Mild Conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3792–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulausks, A.; Kolisnyk, T.; Mohylyuk, V. The Increase in the Plasticity of Microcrystalline Cellulose Spheres’ when loaded with a Plasticizer. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelli, A.; Victor, R.; Vitalina, S. Raman and FT-IR Spectroscopy investigation the cellulose structural differences from bacteria Gluconacetobacter sucrofermentans during the different regimes of cultivation on a molasses media. AMB Express 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Parot, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Couillard, M.; Zou, S.; Hackley, V.A.; Johnston, L.J. Characterization of Size and Aggregation for Cellulose Nanocrystal Dispersions Separated by Asymmetrical-Flow Field-Flow Fractionation. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Production of Nanocellulose with Different Length from Ginkgo Seed Shells and Applications for Oil in Water Pickering Emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.-W.; Chong, W.-T.; Soo, Y.-T.; Tang, T.-K.; Ab Karim, N.A.; Phuah, E.-T.; Lee, Y.-Y. Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Palm-Pressed Fiber Cellulose Nanocrystal Extracted by Acid Hydrolysis-Assisted High Pressure Homogenization. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Jin, W.; Wen, H.; Xu, G.; Xu, P.; Cheng, H. Effects of High-Pressure Homogenization on the Structure and Functional Properties of Solenaia oleivora Proteins. Foods 2024, 13, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Chen, L.; Dai, H.; Zhu, J.Y. Effect of Fiber Drying on Properties of Lignin Containing Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanofibrils Produced through Maleic Acid Hydrolysis. Cellulose 2017, 24, 4205–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzawa, M.; Kanai, N.; Sakai, T.; Yamada, K.; Kumagai, S.; Mijiddorj, B.; Kawamura, I. Enhancing Emulsion Stability and Adsorption of Pickering Emulsions using Alkylated Cellulose Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 8, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, F.; Lanciotti, R. Applications of High and Ultra High Pressure Homogenization for Food Safety. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.-M.; Meng, R.; Chen, H.-Q.; Jin, Z.-Y. Preparation and Characterization of Emulsion Stabilized by Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Dextrin for Improving Storage Stability and Curcumin Encapsulation. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jin, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Nakamura, Y.; Qi, H. Royal Jelly Exosomes as a Stable and Bioavailable Carrier for Fucoxanthin: A Novel Approach for Antimelanoma Therapy. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Dehai, Y. Controlled Ibuprofen Release from Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by pH-Responsive Cellulose-Based Nanofibrils. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242 Pt 3, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z.; Fei, S.; Li, J.; Tan, M.; Su, W. Incorporation of Fucoxanthin into 3D Printed Pickering Emulsion Gels Stabilized by Salmon by-Product Protein/Pectin Complexes. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, L.; Zaky, A.A.; Tie, S.; Cui, G.; Liu, R.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Tan, M. High Internal phase Pickering Emulsion by Spanish Mackerel Proteins-Procyanidins: Application for Stabilizing Astaxanthin and Surimi. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Khalid, N.; Shu, G.; Neves, M.A.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Comparative Study of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Encapsulating Fucoxanthin Formulated by Microchannel Emulsification and High-Pressure Homogenization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, W.; Dou, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, X. Multiscale Combined Techniques for Evaluating Emulsion Stability: A Critical Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 311, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Dong, Y.; Si, J. Ovotransferrin Fibril—Gum Arabic Complexes as Stabilizers for Oleogel-in-Water Pickering Emulsions: Formation Mechanism, Physicochemical Properties, and Curcumin Delivery. Foods 2024, 13, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Weng, H.; Chen, F.; Xiao, A. A novel Pickering Emulsion Stabilized Solely by Hydrophobic Agar Microgels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 120035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jia, K.; Yu, L.; Li, H.; Xin, J.; Zheng, X.; Ning, J.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Wen, W. Robust pH-Switchable Pickering Emulsions Stabilized Solely by Organic Rosin-Based Particles with Adjustable Wettability. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 353, 118751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, K.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, S. Flexible Cellulose Nanofibrils as Novel Pickering Stabilizers: The Emulsifying Property and Packing Behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qi, W.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Z. Stability and pH-Dependent Mechanism of Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanoemulsions Stabilized by Almond Protein Isolate. Foods 2024, 13, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinaz, A.; Rasool, N.; Alice, T.; Tam, K.C. Effect of Oil Phase Transition on the Stability of Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Cellulose Nanocrystals. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2022, 38, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.D.; Loveday, S.M.; Singh, H.; Sarkar, A. Pickering Emulsions Stabilised by Hydrophobically Modified Cellulose nanocrystals: Responsiveness to pH and Ionic Strength. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. Exploring the Effects of Process Parameters During W/O/W Emulsion Preparation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction on the Protein Encapsulation and Release Properties of PLGA Microspheres. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, L.; Nomena, E.M.; Mathew, A.P.; Velikov, K.P. Biobased Cellulose Nanofibril–Oil Composite Films for Active Edible Barriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 16040–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, C.; Huang, Q. Kafirin nanoparticle-stabilized Pickering Emulsions as Oral Delivery Vehicles: Physicochemical Stability and in vitro Digestion Profile. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10263–10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Tarté, R.; Acevedo, N.C. Curcumin Encapsulation in Pickering Emulsions Co-Stabilized by Starch Nanoparticles and Chitin Nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16275–16284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Loya, J.; Lerma, M.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Dynamic Light Scattering and its Application to Control Nanoparticle Aggregation in Colloidal Systems: A Review. Micromachines 2023, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodharan, P.; Bakthavatsalam, A. Experimental Investigation on Thermophysical Properties of Coconut Oil and Lauryl Alcohol for Energy Recovery from Cold Condensate. J. Energy Storage 2020, 31, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.; Hamid, N.; Lu, J. Fucoxanthin Content and Antioxidant Properties of Undaria Pinnatifida. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravana, P.S.; Shanmugapriya, K.; Gereniu, C.R.N.; Chae, S.-J.; Kang, H.W.; Woo, H.-C.; Chun, B.-S. Ultrasound-Mediated Fucoxanthin rich oil Nanoemulsions Stabilized by κ-carrageenan: Process Optimization, Bio-accessibility and Cytotoxicity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Olszowy, M. Antioxidant properties of BHT estimated by ABTS assay in systems differing in pH or metal ion or water concentration. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 232, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, I.; Jose, N.M.; Mamatha, B.S. Oxidative Stability of Lutein on Exposure to Varied Extrinsic Factors. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Tian, Z.; Guan, Z.; Cai, Y.; Huang, L.; Van der Meeren, P. Formulation Effects on the Enhanced Structural and Anti-Oxidative Properties of Emulsions Stabilized by Complexes of Cellulose Nanofibrils (CNF) and Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG). LWT 2025, 223, 117758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, D.; Kim, M.; Gu, M.-Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Pan, C.-H.; Kim, G.-H.; Chung, D. Effects of Temperature, Light, and pH on the Stability of Fucoxanthin in an Oil-in-Water Emulsion. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.A.R.; Sánchez, C.L.D.T.; Vargas, G.L.; Lomelí, M.G.; Novoa, M.G.A.; Vargas, F.V.; Ruiz, B.V.; Mercado, A.T.B.; García, R.D.I.; Guzman, A.I.P.G.; et al. Development of Fucoxanthin-Enriched Yogurt Using Nanoliposomal Carriers: A Strategy for Functional Dairy Products with Antioxidant and Erythroprotective Benefits. Molecules 2025, 30, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajot, A.; Hao Huynh, G.; Picot, L.; Marchal, L.; Nicolau, E. Fucoxanthin From Algae to Human, an Extraordinary Bioresource: Insights and Advances in up and Downstream Processes. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Song, L.; Bi, A.; Wu, C.; Ma, Y.; Du, M.; Zhu, B. High Internal Phase Emulsion for Food-Grade 3D Printing Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45493–45503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhe, A.Y.; Peng, L.H.; Ee, L.L.; Kaur, S.S.C.; Seng, C.E.; Ti, T.B. Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC)-Stabilized Pickering Emulsion for Improved Curcumin SStorage Stability. LWT 2022, 159, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Huan, S.; Xiang, W.; Rojas, O.J. Pickering Emulsions by Combining Cellulose Nanofibrils and Nanocrystals: Phase Behavior and Depletion Stabilization. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhong, Q. Eugenol Improves Physical and Chemical Stabilities of Nanoemulsions loaded with β-carotene. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
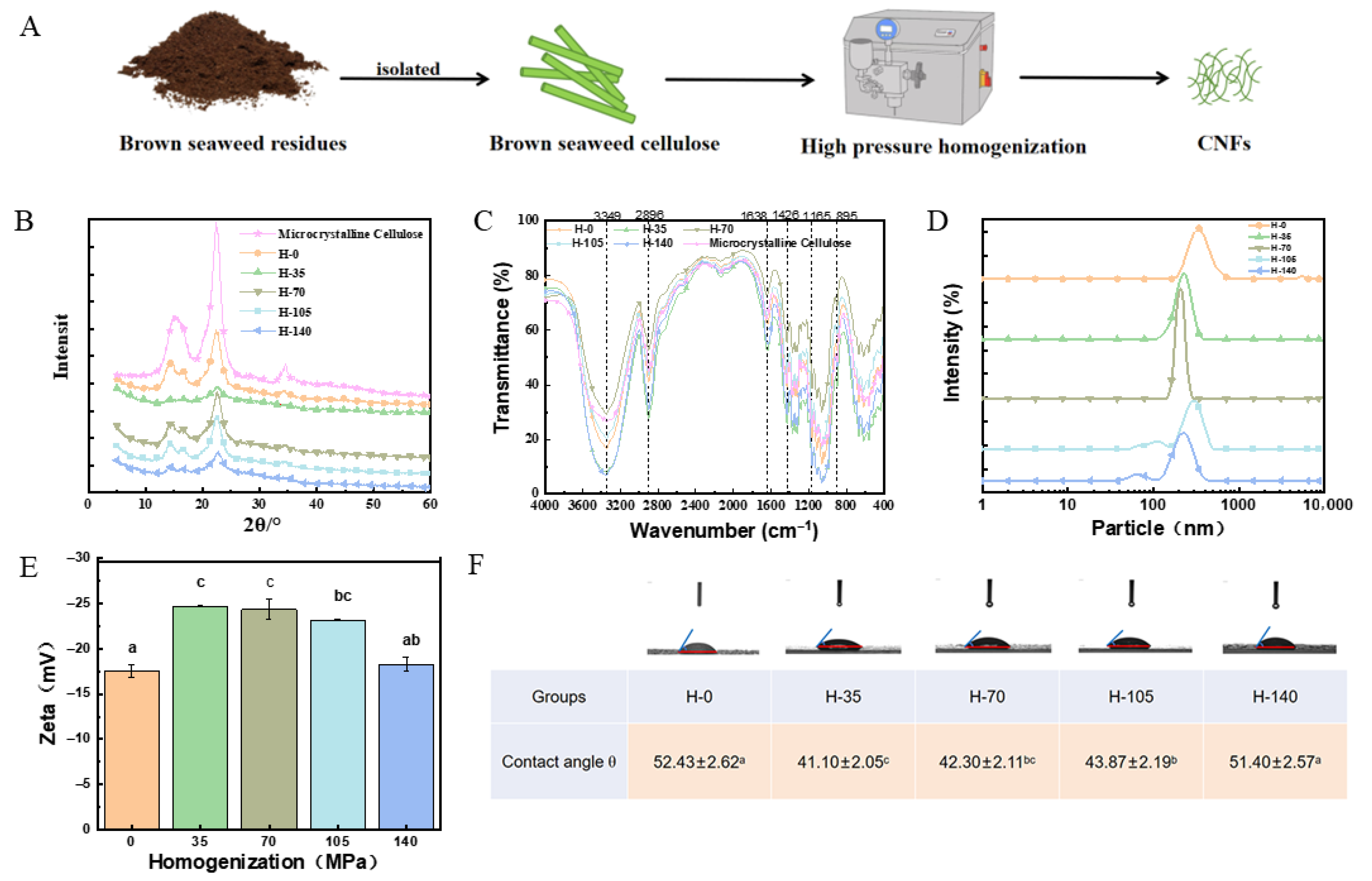
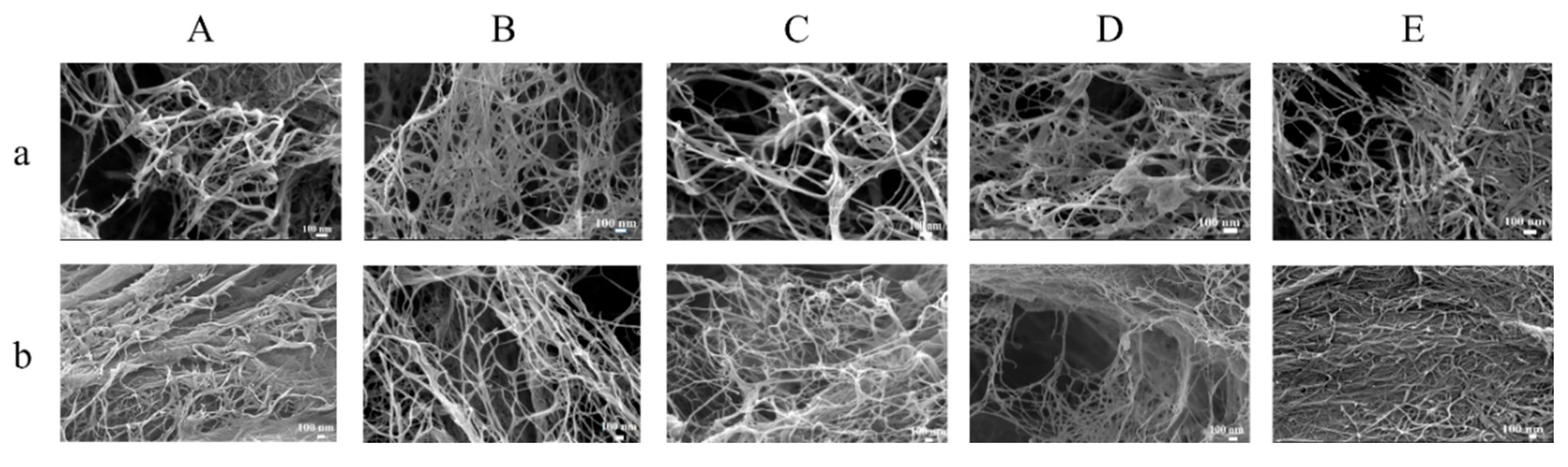
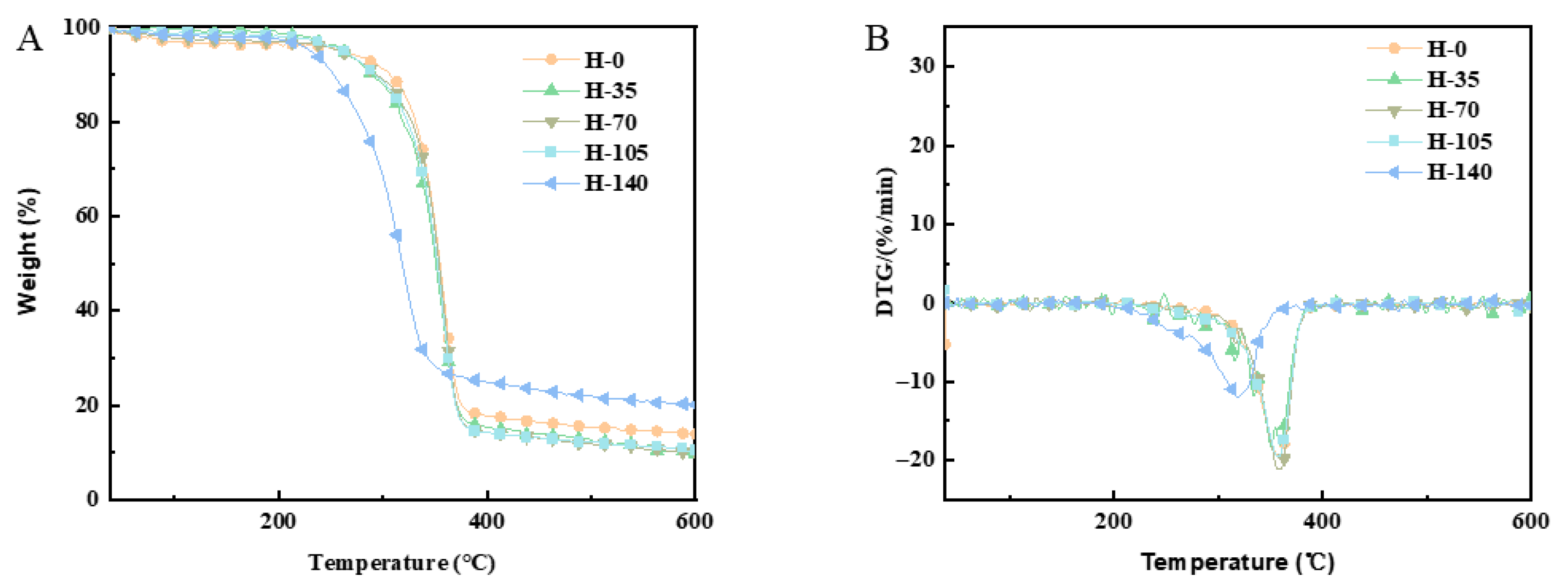
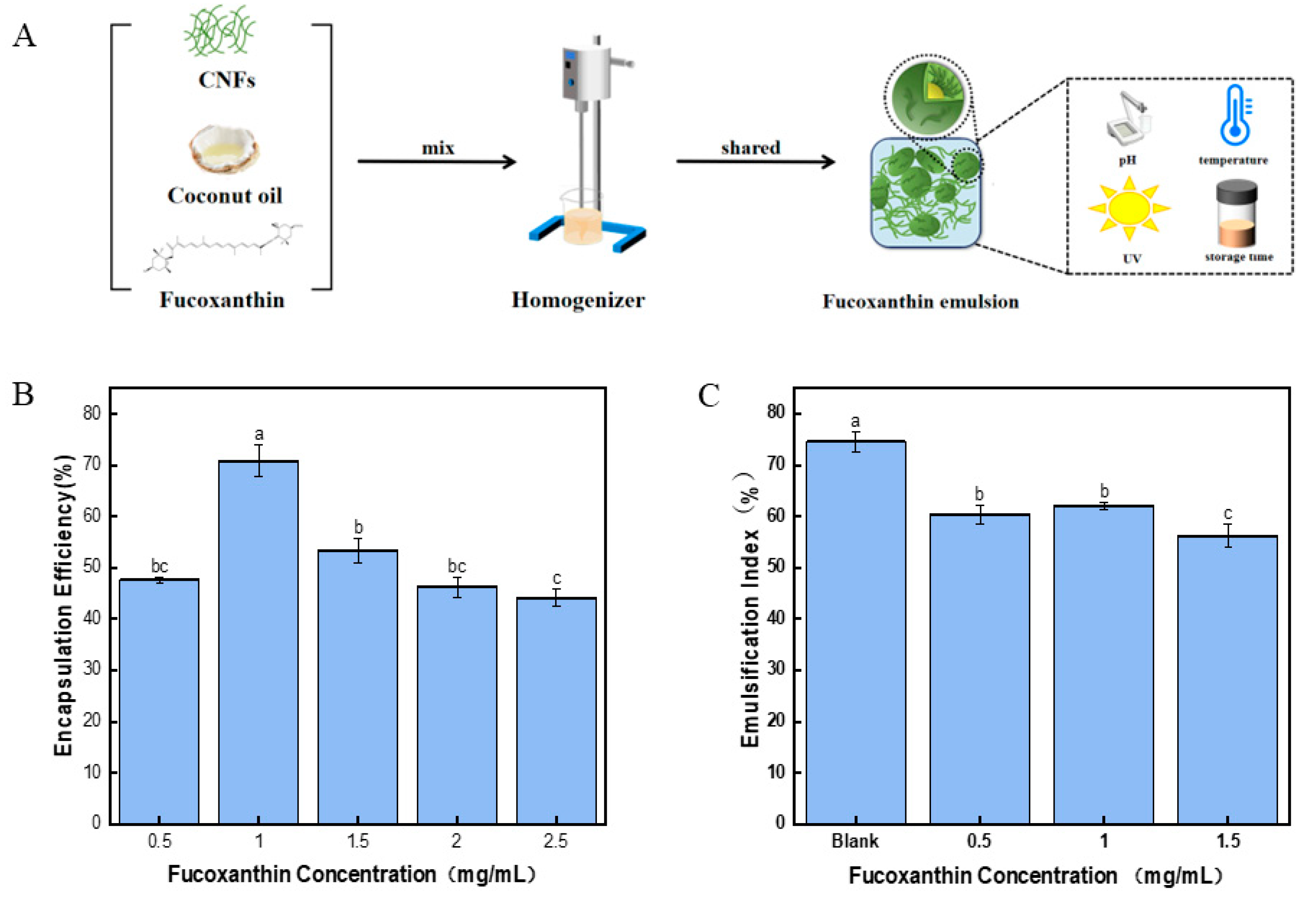

| Sample | Degree of Polymerization | CrI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Microcrystalline cellulose | 170.82 ± 4.1 c | 74.96 ± 0.74 a |
| H-0 | 331.24 ± 3.6 a | 65.23 ± 2.96 b |
| H-35 | 323.18 ± 15.3 a | 51.67 ± 1.14 c |
| H-70 | 312.78 ± 10.6 a | 65.13 ± 0.96 b |
| H-105 | 291.98 ± 11.1 ab | 59.82 ± 2.59 b |
| H-140 | 264.94 ± 10.5 b | 59.23 ± 2.66 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, X. Enhancing Fucoxanthin Pickering Emulsion Stability and Encapsulation with Seaweed Cellulose Nanofibrils Using High-Pressure Homogenization. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080311
Tuo Y, Wang M, Yu Y, Li Y, Hu X, Wu L, Zhang Z, Zhou H, Li X. Enhancing Fucoxanthin Pickering Emulsion Stability and Encapsulation with Seaweed Cellulose Nanofibrils Using High-Pressure Homogenization. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(8):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080311
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuo, Ying, Mingrui Wang, Yiwei Yu, Yixiao Li, Xingyuan Hu, Long Wu, Zongpei Zhang, Hui Zhou, and Xiang Li. 2025. "Enhancing Fucoxanthin Pickering Emulsion Stability and Encapsulation with Seaweed Cellulose Nanofibrils Using High-Pressure Homogenization" Marine Drugs 23, no. 8: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080311
APA StyleTuo, Y., Wang, M., Yu, Y., Li, Y., Hu, X., Wu, L., Zhang, Z., Zhou, H., & Li, X. (2025). Enhancing Fucoxanthin Pickering Emulsion Stability and Encapsulation with Seaweed Cellulose Nanofibrils Using High-Pressure Homogenization. Marine Drugs, 23(8), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080311





