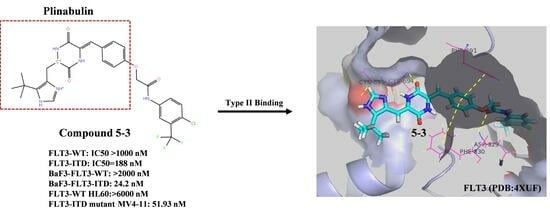
The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells
Abstract
Share and Cite
Bi, S.; Cao, Y.; Fang, S.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Yu, R.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, P. The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289
Bi S, Cao Y, Fang S, Chu Y, Zhang Z, Li M, Yu R, Yang J, Tang Y, Qiu P. The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Shijie, Yating Cao, Shiyuan Fang, Yanyan Chu, Zixuan Zhang, Meng Li, Rilei Yu, Jinbo Yang, Yu Tang, and Peiju Qiu. 2025. "The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289
APA StyleBi, S., Cao, Y., Fang, S., Chu, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, M., Yu, R., Yang, J., Tang, Y., & Qiu, P. (2025). The Novel Diketopiperazine Derivative, Compound 5-3, Selectively Inhibited the Proliferation of FLT3-ITD Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells. Marine Drugs, 23(7), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070289