Marine Fungal Metabolites as Potential Antidiabetic Agents: A Comprehensive Review of Their Structures and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Compounds
2.1. Polyketides
2.2. Alkaloid
2.3. Terpenoids
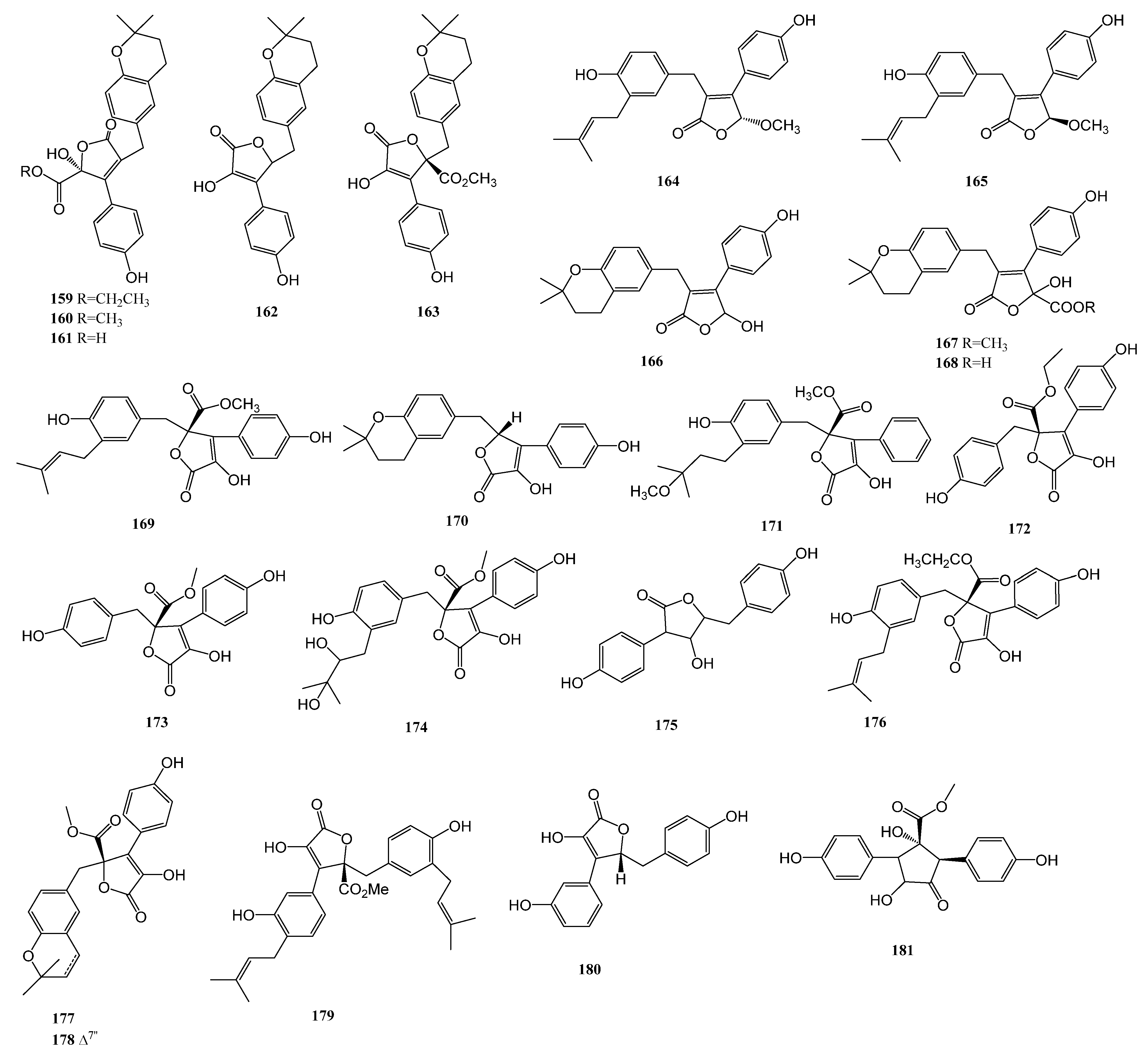
2.4. Lignan
| Compound Number | Derived Fungi | Sampling Source | Activity-Related Enzyme | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–5 | Aspergillus flavipes HN4-13 | Lianyungang coastal sediment sample | α-glucosidase | [13] |
| 159–163 | ||||
| 6–8 | Alternaria alternata LW37 | a deep-sea sediment sample collected at a depth of 2623 m in the Southwest Indian Ridge | α-glucosidase | [14] |
| 9–13 | Penicillium thomii YPGA3 | the sediments of the Yap Trench | α-glucosidase | [15] |
| 14–19 | Aspergillus insulicola | deep-sea sediments, which were collected from the South China Sea at a depth of 2500 m. | α-glucosidase | [16] |
| 20–26 | Penicillium sp. TW58-16 | hydrothermal vent sediment, collected from Kueishantao, Taiwan | α-glucosidase | [17] |
| 136 | ||||
| 27–29 | Aspergillus candidus HM5-4 | sponges from the South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [18] |
| 30–32 | Talaromyces indigoticus FS688 | the South China Sea (118°19.692′ N, 20°38.982′ E; depth 2372 m) | α-glucosidase | [19] |
| 33–37 | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | sediment samples from northern South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [20] |
| 38–39 | Meira sp. 1210CH-42 | a seawater sample collected at the Chuuk Islands, Federated States of Micronesia | α-glucosidase | [21] |
| 40–42 | Trichoderma sp. 307 | the stem bark of Clerodendrum inerme, which was collected from Zhanjiang Mangrove National Nature Reserve in Guangdong Province, China. | α-glucosidase | [22] |
| 43–45 | Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ004 | the mangrove Bruguiera sexangula var. Rhynchopetala collected in the South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [23] |
| 46 | Mycosphaerella sp. SYSU-DZG01 | the fruit of the marine mangrove plant Bruguiera collected in 2014 in Hainan Dongzhai Harbor Mangrove Reserve | α-glucosidase | [24] |
| 104–105 | ||||
| 47–49 | Aspergillus sp. 16-5B | the leaves of Sonneratia apetala, which was collected from Dongzhaigang Mangrove National Nature Reserve in Hainan Island, China | α-glucosidase | [25] |
| 50–52 | Penicillium pinophilum SCAU037 | the roots of a mangrove plant Rhizophora stylosa on the Techeng Isle, China | α-glucosidase | [26] |
| 53–56 | Aspergillus flavus QQSG-3 | a fresh branch of Kandelia obobata, which was collected from Huizhou city in the province of Guangdong, China | α-glucosidase | [27] |
| 57 | Penicillium strain M30 | the sediment that was collected at a depth of 14 m sea at the Co To island, Northern Vietnam | α-glucosidase | [28] |
| 58 | Aspergillus candidus | the gorgonian coral Anthogorgia ochracea collected from the South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [29] |
| 59–60 | Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ004 | the stem of mangrove Brguiera sexangula var. rhynchopetala, collected in the South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [30] |
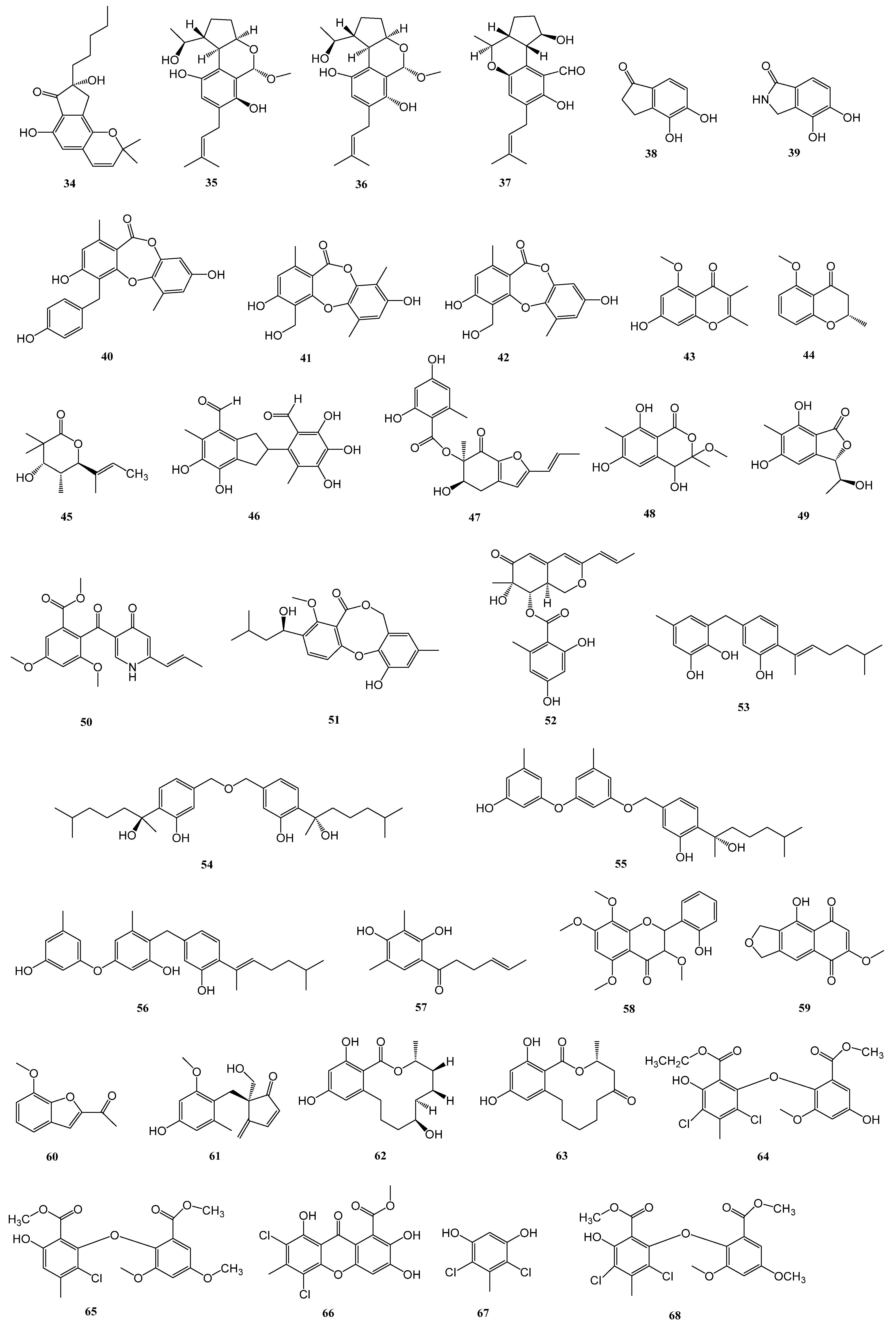
| 61 | Penicillium brefeldianum F4a | the roots of H. cordata | α-glucosidase and PTP1B | [31] |
| 109 | α-glucosidase | |||
| 110 | α-glucosidase and PTP1B | |||
| 62–63 | Trichoderma sp. 307 | the stem bark of Clerodendrum inerme, collected in Zhanjiang Mangrove National Nature Reserve in Guangdong Province, China | α-glucosidase | [32] |
| 64–72 | Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 41001 | the deep sea sediment of Indian Ocean (Lat: 10.00371667° N, long: 88.72803333° E) at a depth of 3386 m | α-glucosidase | [33] |
| 73 | Aspergillus sp. ZJ-68 | fresh leaves of the mangrove plant Kandelia candel, which were collected from the Zhanjiang Mangrove Nature Reserve in Guangdong Province, China | α-glucosidase | [34] |
| 74 | Penicillium sp. S-1-18 | the Antarctic seabed sediments (47.09° W, 62.05° S, the depth of 1393 m) | PTP1B | [35] |
| 75–77 | Aspergillus sp. SF5929 | marine-derived | PTP1B | [36] |
| 118 | ||||
| 181 | ||||
| 78 | Aspergillus candidus LDJ-5 | the root of Rhizophora apiculata Blume in the Sanya Bailu Park of Hainan Province, China | PTP1B | [37] |
| 79 | Penicillium sp. SF-5203 | an intertidal sediment sample collected from Wan Island, Korea | PTP1B | [38] |
| 119–122 | ||||
| 80–81 | Penicillium sp. JF-55 | an unidentified sponge that was manually collected using scuba equipment off the shores of Jeju Island | PTP1B | [39] |
| 82–83 | Penicillium glabrum SF-7123 | sediments that were collected using a dredge at the Ross Sea (77°34.397′ N, 166°10.865′ W) | PTP1B | [40] |
| 84–85 | Penicillium sp. SF-6013 | the sea urchin Brisaster latifrons collected from the Sea of Okhotsk (N 53°22.626′ E 144°24.200′) | PTP1B | [41] |
| 86 | Cladosporium sp. TPU1507 | an unidentified marine sponge collected at Manado, Indonesia | PTP1B | [42] |
| 123 | ||||
| 87 | Cosmospora sp. SF-5060 | an inter-tidal sediment collected at Gejae Island | PTP1B | [43] |
| 88–89 | Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 07007 | deep-sea hydrothermal vent environment sample collected from the Western Atlantic | PTP1B | [44] |
| 90 | Fusarium sp. Hungcl | the soil, collected from the Futian Mangrove Reserve in Shenzhen, Guangdong Province | PTP1B | [45] |
| 91 | Eutypella sp. F0219 | a marine sediment sample collected in the northern part of the South China Sea (GPS 114.6609° E, 21.5942° N) at a water depth of 75 m | FABP4 | [46] |
| 92 | Meira sp. 1210CH-42 | a seawater sample collected at Chuuk Islands, Federated States of Micronesia | α-glucosidase | [48] |
| 132–133 | ||||
| 93 | Aspergillus aculeatus CRI323-04 | the marine sponge Xestospongia testudinaria (specimen no. CRI323) | α-glucosidase | [49] |
| 94–95 | Aspergillus sp. HNMF114 | the bivalve mollusk Sanguinolaria chinensis | α-glucosidase | [50] |
| 96–100 | Talaromyces sp. CY-3 | the fresh leaves of the semimangrove Hibiscus tiliaceus | α-glucosidase | [51] |
| 101 | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41029 | a deep-sea sediment sample of South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [52] |
| 172–175 | ||||
| 102 | Penicillium sp. ZYX-Z-143 | an arthropod, Dardanus scutellatus, collected from Yinyu Island, one of the Paracel Islands in South China Sea, Hainan province (16°35′03″ N, 111°42′39″ E) | PTP1B | [53] |
| 103 | α-glucosidase | |||
| 106–108 | Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025 | the root of A. marina (Forsk.) Vierh. (Acanthaceae) collected from the mangrove wetland in Zhanjiang, Guangdong province, China (coordinates 21.235° N, 110.451° E) | α-glucosidase | [54] |
| 111–112 | Penicillium sp. KFD28 | Meretrix lusoria, collected from Haikou Bay, China | PTP1B | [55] |
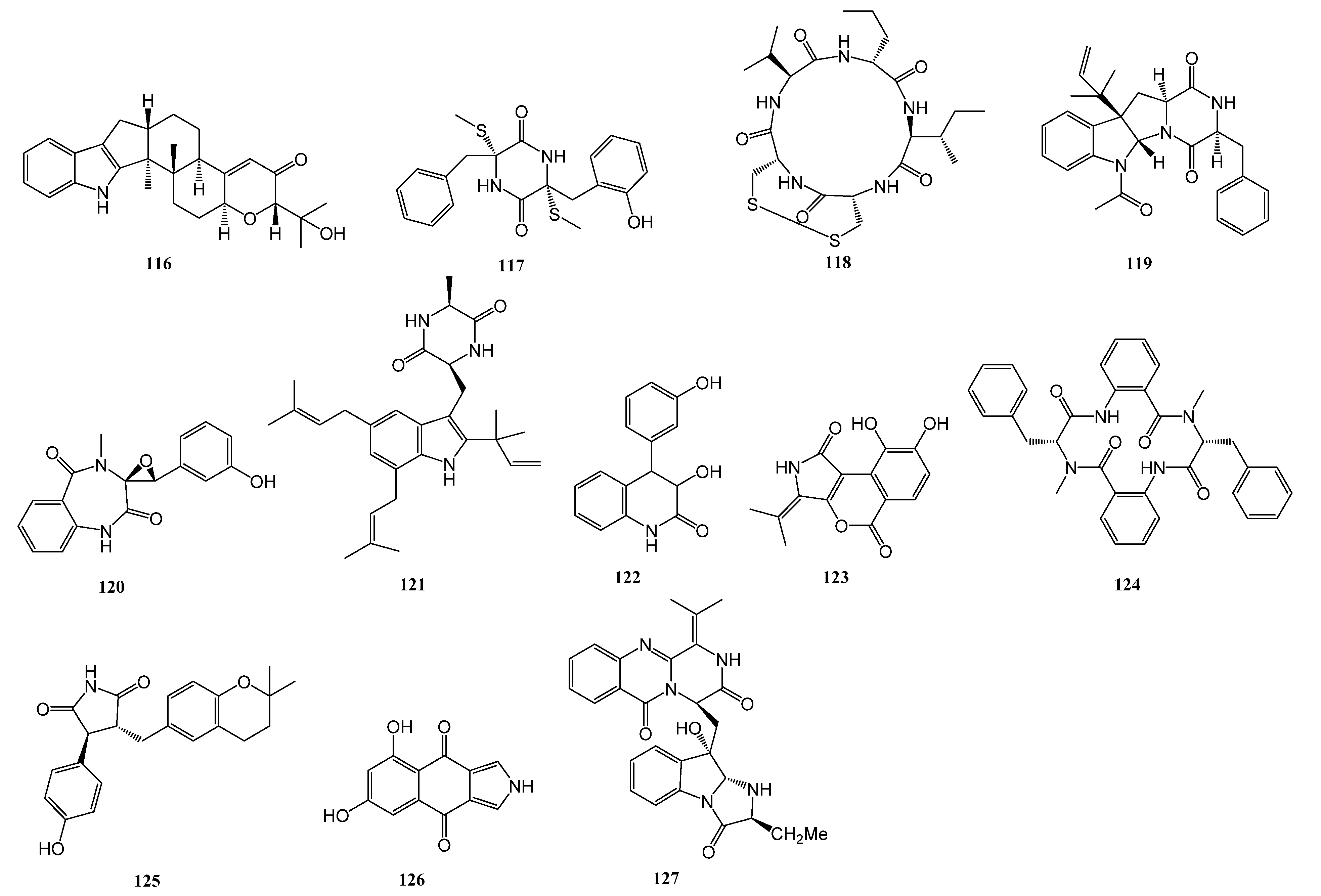
| 113–116 | Aspergillus sp. ZF-104 | a marine soft coral in Haikou Bay, Hainan province, China | PTP1B | [56] |
| 117 | Aspergillus terreus RA2905 | a piece of fresh tissue from the inner part of the sea hare Aplysia pulmonica, collected from the Weizhou coral reefs in the South China Sea | PTP1B | [57] |
| 124 | Penicillium solitum MCCC 3A00215 | deep-sea-derived | GSK-3β | [58] |
| 125 | Aspergillus terreus EGF7-0-1 | soft coral in the South China Sea | GSK-3β | [59] |
| 126 | Biscogniauxia | the sediment of the Herodotes Basin (2800 m water depth) | GSK-3β | [60] |
| 127 | Scedosporium apiospermum F41-1 | the inner tissue of the soft coral Lobophytum crassum collected from Hainan Sanya National Coral Reef Reserve, People’s Republic of China | FABP4 | [61] |
| 128–131 | Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD09 | a marine worm, Sipunculusnudus, from Haikou Bay, China | PTP1B | [63] |
| 134–135 | Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16 | an unidentified sea snail collected from Silver Island, Xisha, South Sea, China | α-glucosidase | [64] |
| 137–138 | Penicillium levitum N33.2 | the leaf of seagrass Enhalus acoroides (Hydrocharitaceae, Alismatales) obtained at Nhatrang bay, Khanhhoa, Vietnam (N 12°59.243′, E 109°21.965′) and symbolized as N33.2. | α-glucosidase | [65] |
| 139 | Aspergillus hiratsukae SCSIO 5Bn1003 | a coral sample collected from the South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [65] |
| 140–141 | Penicillium thomii YPGA3 | deep sea water at a depth of 4500 m in the Yap Trench (West Pacific Ocean) | α-glucosidase | [67] |
| 142 | Penicillium sp. SCSIO 41512 | a soft coral of the South China Sea | PTP1B | [68] |
| 143–146 | Microascus sp. SCSIO 41821 | a gorgonian Melitodes squamata collected from the South China Sea, Sanya (18°11′ N, 109°25′ E), Hainan, China | PTP1B | [69] |
| 147 | Penicillium chrysogenum | Plakortis simplex collected in Xisha islands, China | PTP1B | [70] |
| 148–149 | Penicillium sp. SF-5497 | a sample of sea sand collected at Gijang-gun, Busan (35°22.2257′ N; 129°23.9238′ E) | PTP1B | [71] |
| 150–153 | Penicillium sp. KFD28 | a bivalve mollusk, Meretrix lusoria, collected from Haikou Bay, China | PTP1B | [72] |
| 154–155 | Penicillium sp. KFD28 | a bivalve mollusk, Meretrix lusoria, collected from Haikou Bay, China | PTP1B | [73] |
| 156–158 | Penicillium verruculosum TPU1311 | an ascidian Polycarpa aurata collected in Indonesia | PTP1B | [74] |
| 164–170 | Aspergillus terreus | marine-derived | α-glucosidase | [76] |
| 171 | Aspergillus terreus | the coral Sarcophyton subviride, which was collected from the coast of Xisha Island in the South China Sea | α-glucosidase | [77] |
| 176–178 | Aspergillus terreus YPGA10 | the deep-sea water at a depth of 4159 m in the Yap Trench (West Pacific Ocean) | α-glucosidase | [78] |
| 179–180 | Aspergillus terreus SCAU011 | the rhizosphere sediment of a mangrove plant Rhizophora stylosa collected on the Techeng Isle, China | α-glucosidase | [79] |
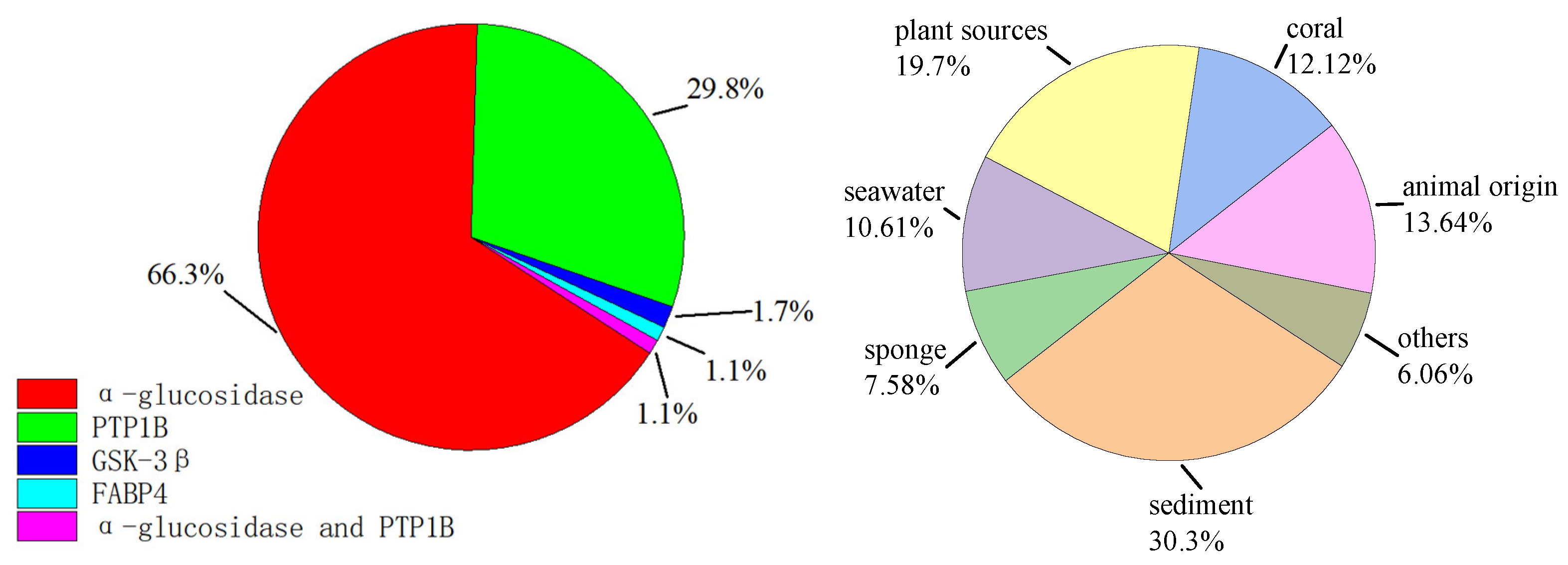
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, M.J.; Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.R. Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: Early detection should be focused. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habegger, K.M.; Heppner, K.M.; Geary, N.; Bartness, T.J.; DiMarchi, R.; Tschöp, M.H. The metabolic actions of glucagon revisited. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olokoba, A.B.; Obateru, O.A.; Olokoba, L.B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of current trends. Oman Med. J. 2012, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, A.M.; Calsolaro, V.; Rogani, S.; Okoye, C.; Caraccio, N.; Monzani, F. Optimal Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management and Active Ageing. Endocrines 2021, 2, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Mu, Y.M. Progress of type 2 diabetes in the past decade. Chin. J. Int. Med. 2024, 63, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, M.; Nesi, I.; Caselli, A.; Paoli, P. Natural α-Glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors: A Source of Scaffold Molecules for Synthesis of New Multitarget Antidiabetic Drugs. Molecules 2021, 26, 4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patridge, E.; Gareiss, P.; Kinch, M.S.; Hoyer, D. An analysis of FDA-approved drugs: Natural products and their derivatives. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar]
- Uras, I.S.; Ebada, S.S.; Korinek, M.; Albohy, A.; Abdulrazik, B.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, B.H.; Horng, J.T.; Lin, W.; Hwang, T.L.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory, Antiallergic, and COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) Inhibitory Activities of Butenolides from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus. Molecules 2021, 26, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Ianora, A. Marine Organisms with Anti-Diabetes Properties. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Xu, M.; Feng, C.; Hu, C.H. Progress in fungal polyketide biosynthesis. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Hao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, W. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavipes HN4-13. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Cai, L.; Liu, L. New Dibenzo-α-pyrone Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities from the Marine-Derived Fungus Alternaria alternata. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhao, F.; Xu, W.; Cheng, Z. Chromone Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Fungus Penicillium thomii Maire. Molecules 2021, 26, 5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zeng, Y.; Chang, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Dai, H.; Lv, F. Potential α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from the Deep-Sea Sediment-Derived Fungus Aspergillus insulicola. Mar. Drugs. 2023, 21, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, X.; Tian, D.; Wei, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Ding, W.; Wu, B.; Tang, J. New Drimane Sesquiterpenes and Polyketides from Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. TW58-16 and Their Anti-Inflammatory and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effects. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, S.; Peng, H.; Zhao, W.; Chang, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Dai, H. p-Terphenyl and Diphenyl Ether Derivatives from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus candidus HM5-4. Mar. Drugs 2023, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W. Thioester-Containing Benzoate Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Talaromyces indigoticus FS688. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.M.; Wei, X.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, J.F.; Shi, X.F.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, S. Structurally Diverse Polycyclic Salicylaldehyde Derivative Enantiomers from a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A.; Kang, J.S.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, H.S.; Heo, C.S.; Park, S.J.; Shin, H.J. Meirols A-C: Bioactive Catecholic Compounds from the Marine-Derived Fungus Meira sp. 1210CH-42. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Niaz, S.I.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L. α-Glucosidase inhibitory and cytotoxic botryorhodines from mangrove endophytic fungus Trichoderma sp. 307. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.X.; Zheng, C.J.; Huang, G.L.; Mei, R.Q.; Nong, X.H.; Shao, T.M.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive Polyketide Derivatives from the Mangrove-Derived Fungus Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ004. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, R.; Chen, G.; She, Z. Secondary Metabolites with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from the Mangrove Fungus Mycosphaerella sp. SYSU-DZG01. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Xia, G.; Liu, H.; He, L.; She, Z. Bioactive Metabolites from Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus sp. 16-5B. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Li, X.; Yu, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Chen, G.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Bao, J.; Zhang, H. Secondary metabolites from the mangrove sediment-derived fungus Penicillium pinophilum SCAU037. Fitoterapia 2019, 136, 104177. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, T.; Cao, W.; She, Z. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors: Diphenyl Ethers and Phenolic Bisabolane Sesquiterpenoids from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus flavus QQSG-3. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.M.T.; Do, Q.T.; Doan, M.H.T.; Vu, Q.T.; Nguyen, M.A.; Vu, T.H.T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Duong, N.T.T.; Tran, M.H.; Chau, V.M.; et al. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Metabolites from the Marine Fungi Penicillium sp. Isolated from Sediments of Co To Island, Vietnam. Molecules 2019, 24, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Aspergivones A and B, two new flavones isolated from a gorgonian-derived Aspergillus candidus fungus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.X.; Shao, T.M.; Mei, R.Q.; Huang, G.L.; Zhou, X.M.; Zheng, C.J.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from the Culture of the Mangrove-Derived Fungus Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ004. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yi, P.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Pan, H. Novel Antioxidants and α-Glycosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors from an Endophytic Fungus Penicillium brefeldianum F4a. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Niaz, S.I.; Khan, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Induction of Diverse Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Trichoderma sp. (Strain 307) by Co-Cultivation with Acinetobacter johnsonii (Strain B2). Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhou, L.M.; Chen, S.T.; Yang, B.; Liao, S.R.; Kong, F.D.; Lin, X.P.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.H. New chlorinated diphenyl ethers and xanthones from a deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 41001. Fitoterapia 2018, 125, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Jiang, H.; Zang, Z.; Li, C.; She, Z. New Benzofuranoids and Phenylpropanoids from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus, Aspergillus sp. ZJ-68. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Yu, H.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Lu, X.L.; Jiao, B.H. Furanone derivative and sesquiterpene from Antarctic marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. S-1-18. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 20, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.C.; Ha, T.M.; Sohn, J.H.; Yim, J.H.; Oh, H. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from a marine-derived fungal strain aspergillus sp. SF-5929. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, X.; Shah, M.; Che, Q.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Polyhydroxy p-Terphenyls from a Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus candidus LDJ-5. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. PTP1B inhibitory secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungal strains Penicillium spp. and Eurotium sp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Jang, J.H.; Ko, W.; Kim, K.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Kang, M.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. PTP1B inhibitory and anti-inflammatory effects of secondary metabolites isolated from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. JF-55. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.M.; Kim, D.C.; Sohn, J.H.; Yim, J.H.; Oh, H. Anti-Inflammatory and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Metabolites from the Antarctic Marine-Derived Fungal Strain Penicillium glabrum SF-7123. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, T.H.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Ko, W.; Kim, D.C.; Yoon, C.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. Tanzawaic acid derivatives from a marine isolate of Penicillium sp. (SF-6013) with anti-inflammatory and PTP1B inhibitory activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5787–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotinsulu, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Sugai, S.; Iwakura, N.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Namikoshi, M. Cladosporamide A, a new protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor, produced by an Indonesian marine sponge-derived Cladosporium sp. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.; Sohn, J.H.; Oh, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Ahn, J.S. Isolation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory metabolite from the marine-derived fungus Cosmospora sp. SF-5060. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6095–6097. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Cai, J.; Zhong, W.; Xu, G.; Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitorsfrom the deep-sea fungus Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 07007. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103646. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Chen, C.; Mo, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zang, Y.; Li, H.; Chai, C.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Z.; et al. Fusaresters A-E, new γ-pyrone-containing polyketides from fungus Fusarium sp. Hungcl and structure revision of fusariumin D. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 5526–5532. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.T.; Fu, T.T.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.F.; Xu, C.J.; Li, W.S.; Li, B.L.; Jiang, Z.P.; et al. Natural linoleic acid from marine fungus Eutypella sp. F0219 blocks KEAP1/NRF2 interaction and ameliorates MASLD by targeting FABP4. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 224, 630–643. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P.; López-Martínez, L.X.; Contreras-Angulo, L.A.; Elizalde-Romero, C.A.; Heredia, J.B. Plant Alkaloids: Structures and Bioactive Properties; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 85, p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.J.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.S.; Heo, C.S. Thiolactones and Δ8,9-Pregnene Steroids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Meira sp. 1210CH-42 and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingavat, N.; Dobereiner, J.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Aspergillusol A, an α-glucosidase inhibitor from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2049–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.S.; Yang, L.; Kong, F.D.; Zhao, J.H.; Yao, L.; Yuchi, Z.G.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Guo, M.F.; et al. Three New Quinazoline-Containing Indole Alkaloids From the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. HNMF114. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 680879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Tan, Q.; Yin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, B.; She, Z. Secondary Metabolites with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Talaromyces sp. CY-3. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, C.; Long, J.; Lan, S.; Lin, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Bioactive secondary metabolites from the deep-sea derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41029. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.T.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.C.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.F.; Dai, H.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory indole diterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. ZYX-Z-143. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 145, 107205. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.M.; Chen, W.H.; Pang, X.Y.; Liao, S.R.; Wang, J.F.; Lin, X.P.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.F.; Luo, X.W.; Liu, Y.H. Pyrrolyl 4-quinolone alkaloids from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium steckii SCSIO 41025: Chiral resolution, configurational assignment, and enzyme inhibitory activities. Phytochemistry 2021, 186, 112730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; Wu, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.X. Two new indole-diterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 23, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, L.; Xie, Q.Y.; Guo, J.C.; Ma, Q.Y.; Dai, L.T.; Zhou, L.M.; Dai, H.F.; Kong, F.D.; Luo, D.Q.; et al. Diverse indole-diterpenoids with protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory activities from the marine coral-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. ZF-104. Phytochemistry 2023, 216, 113888. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.S.; Shi, X.H.; Yao, G.S.; Shao, C.L.; Fu, X.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Guan, H.S.; Wang, C.Y. New Thiodiketopiperazine and 3,4-Dihydroisocoumarin Derivatives from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.L.; Yue, Y.T.; Xu, J.P.; Li, N.; Lin, T.; Ji, G.R.; Yang, X.W.; Xu, R. Penicopeptide A (PPA) from the deep-sea-derived fungus promotes osteoblast-mediated bone formation and alleviates ovariectomy-induced bone loss by activating the AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 197, 106968. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.K.; Wu, P.P.; He, Y.P.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Bioactive Aspergteroids G-J from Soft-Coral-Associated Symbiotic and Epiphytic Fungus Aspergillus terreus EGF7-0-1. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wiese, J.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Biscogniauxone, a New Isopyrrolonaphthoquinone Compound from the Fungus Biscogniauxia mediterranea Isolated from Deep-Sea Sediments. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Chen, P.N.; Li, H.J.; Mahmud, T.; Wu, D.L.; Xu, J.; Lan, W.J. Potential Antidiabetic Fumiquinazoline Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Scedosporium apiospermum F41-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Masyita, A.; Mustika Sari, R.; Dwi Astuti, A.; Yasir, B.; Rahma Rumata, N.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Simal-Gandara, J. Terpenes and terpenoids as main bioactive compounds of essential oils, their roles in human health and potential application as natural food preservatives. Food. Chem. X 2022, 13, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.D.; Zhang, R.S.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, P.W.; Zhou, L.M.; Dai, H.F.; Luo, D.Q.; Zhao, Y.X. Chrodrimanins O-S from the fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD09 isolated from a marine worm, Sipunculusnudus. Fitoterapia 2017, 122, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Yang, L.; Ma, Q.; Xie, Q.; Dai, H.; Sun, K.; Zhao, Y. Meroterpenoids and Steroids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Trametes sp. ZYX-Z-16. Molecules 2022, 27, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, C.K.; Le, C.H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Tran, H.T.N.; Luu, C.V.; Le, H.M.; Tran, H.T.H. Steroid Components of Marine-Derived Fungal Strain Penicillium levitum N33.2 and Their Biological Activities. Mycobiology 2023, 51, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Che, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, W.; Wei, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Diverse Secondary Metabolites from the Coral-Derived Fungus Aspergillus hiratsukae SCSIO 5Bn1003. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, W.; Fan, R.; Han, S.; Li, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Terpenoids from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Penicilliumthomii YPGA3 and Their Bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.H.; Liang, X.; Lu, X.H.; Cheng, X.; Luo, L.X.; Qi, S.H. Pyrrospirones K-Q, Decahydrofluorene-Class Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO 41512. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.H.; Liang, X.; Shen, W.B.; Lu, X.H.; Li, G.C.; Qi, S.H. Microascones, Decahydrofluorene-Class Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Microascus sp. SCSIO 41821. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, P.; Luo, X.; Qiao, D.; Tang, X.; Li, G. Two new compounds from the marine sponge derived fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2926–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Quang, T.H.; Thi Thanh Ngan, N.; Sohn, J.H.; Oh, H. New preaustinoids from a marine-derived fungal strain Penicillium sp. SF-5497 and their inhibitory effects against PTP1B activity. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.M.; Kong, F.D.; Fan, P.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Li, J.H.; Zheng, H.Z.; Zheng, Z.H.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; et al. Indole-Diterpenoids with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitory Activities from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2638–2644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.D.; Fan, P.; Zhou, L.M.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xie, Q.Y.; Zheng, H.Z.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhang, R.S.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F.; et al. Penerpenes A-D, Four Indole Terpenoids with Potent Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitory Activity from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. KFD28. Org Lett. 2019, 21, 4864–4867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Nakayama, W.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Izumikawa, Y.; Iwasaki, K.; Toraiwa, K.; Ukai, K.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; et al. Verruculides A and B, two new protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from an Indonesian ascidian-derived Penicillium verruculosum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3087–3090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.S. Lignans, neolignans, and related compounds. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1995, 12, 183–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Gong, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Hua, H.; Lin, H. New butenolide derivatives from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Qi, C.; Zhu, H.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Bioactive secondary metabolites from the marine-associated fungus Aspergillus terreus. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, W.; Luo, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Q. Butenolide Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitions from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, X.X.; Zhu, K.; He, F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Bioactive aromatic butenolides from a mangrove sediment originated fungal species, Aspergillus terreus SCAU011. Fitoterapia 2021, 150, 104856. [Google Scholar]

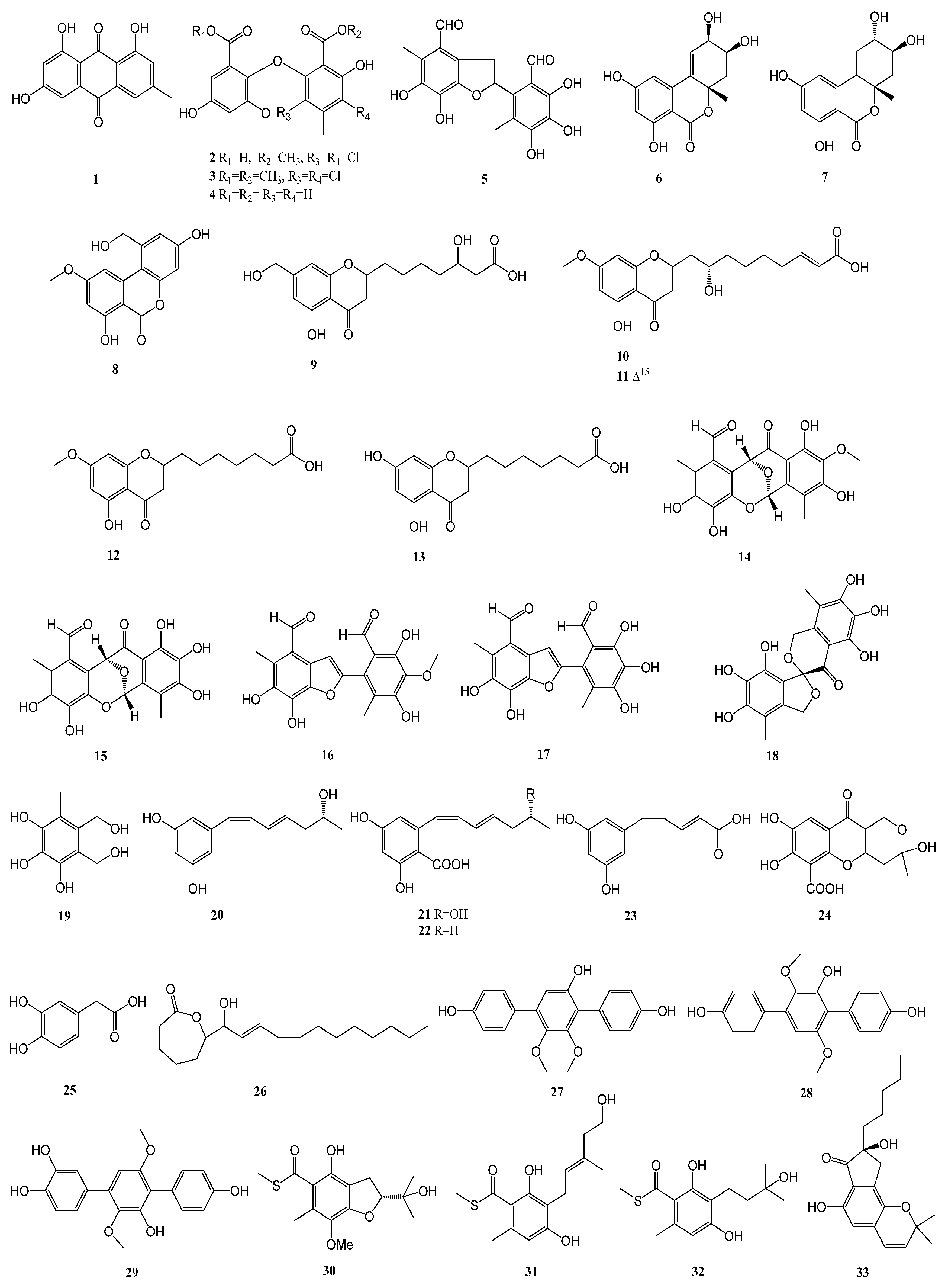
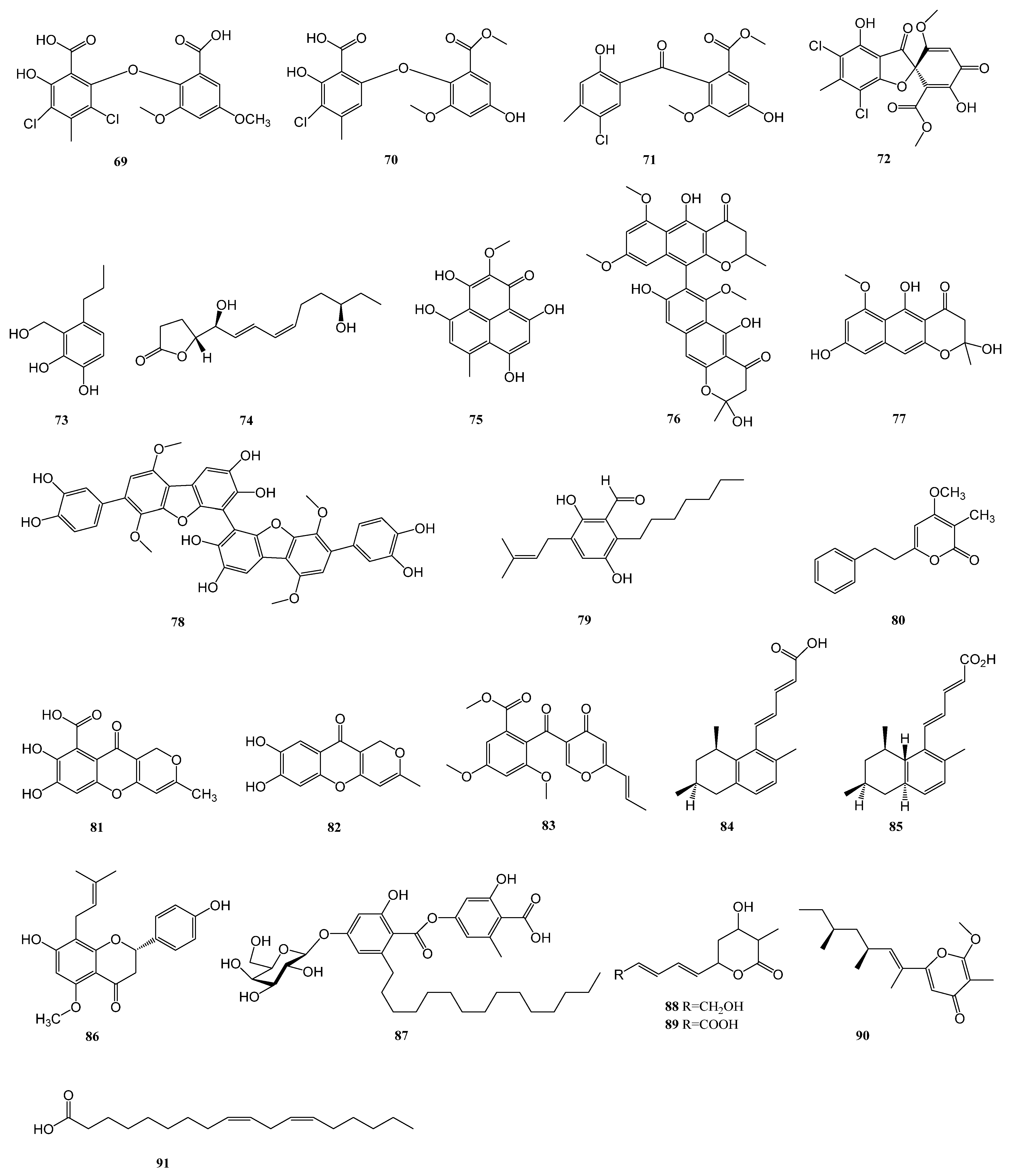


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F.; Lin, N.; Wang, Q. Marine Fungal Metabolites as Potential Antidiabetic Agents: A Comprehensive Review of Their Structures and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040142
Wang Z, Zhao M, Yu Y, Kong F, Lin N, Wang Q. Marine Fungal Metabolites as Potential Antidiabetic Agents: A Comprehensive Review of Their Structures and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(4):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040142
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zimin, Meirong Zhao, Yunxia Yu, Fandong Kong, Nanxin Lin, and Qi Wang. 2025. "Marine Fungal Metabolites as Potential Antidiabetic Agents: A Comprehensive Review of Their Structures and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities" Marine Drugs 23, no. 4: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040142
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhao, M., Yu, Y., Kong, F., Lin, N., & Wang, Q. (2025). Marine Fungal Metabolites as Potential Antidiabetic Agents: A Comprehensive Review of Their Structures and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities. Marine Drugs, 23(4), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040142




