Antiviral Activity of Chlorophyll Extracts from Tetraselmis sp., a Marine Microalga, Against Zika Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Inhibitory Effects of Tetraselmis sp. Acetone Extracts on ZIKV
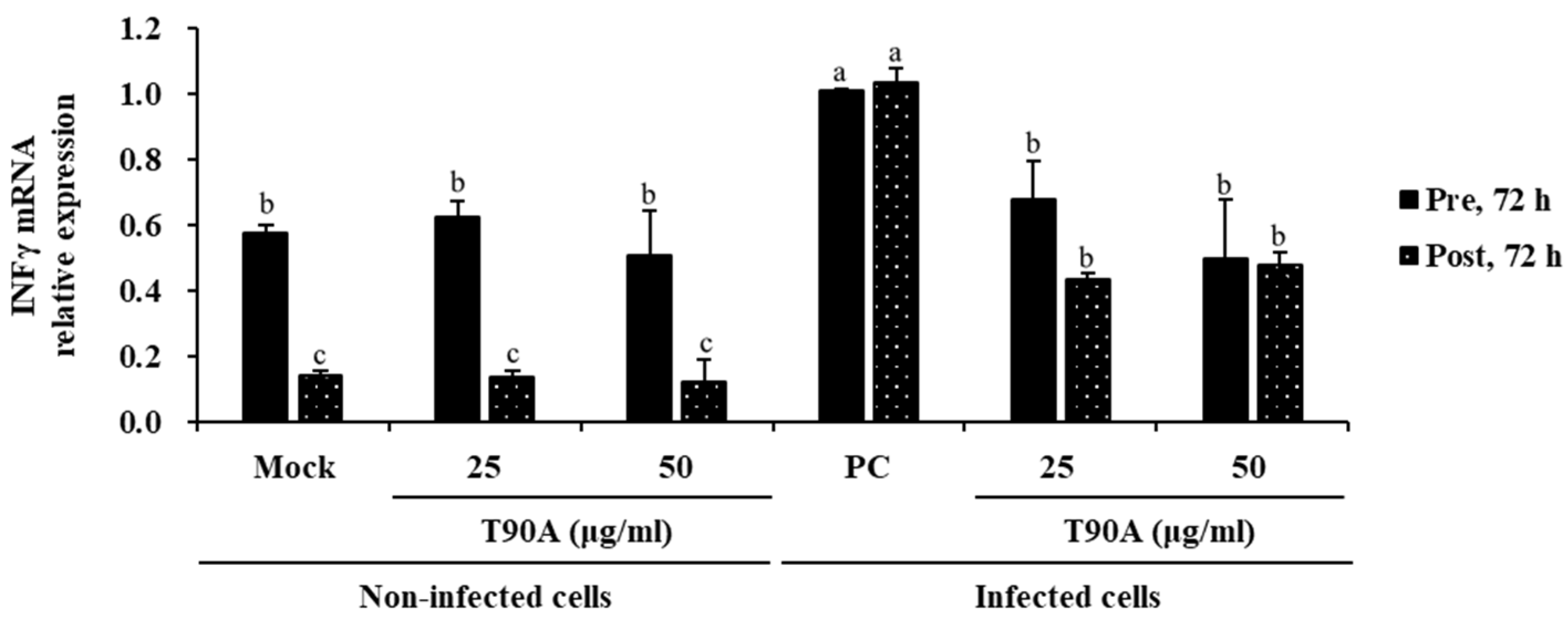
2.2. Effect of T90A on Interferon Response in ZIKV-Infected Cells
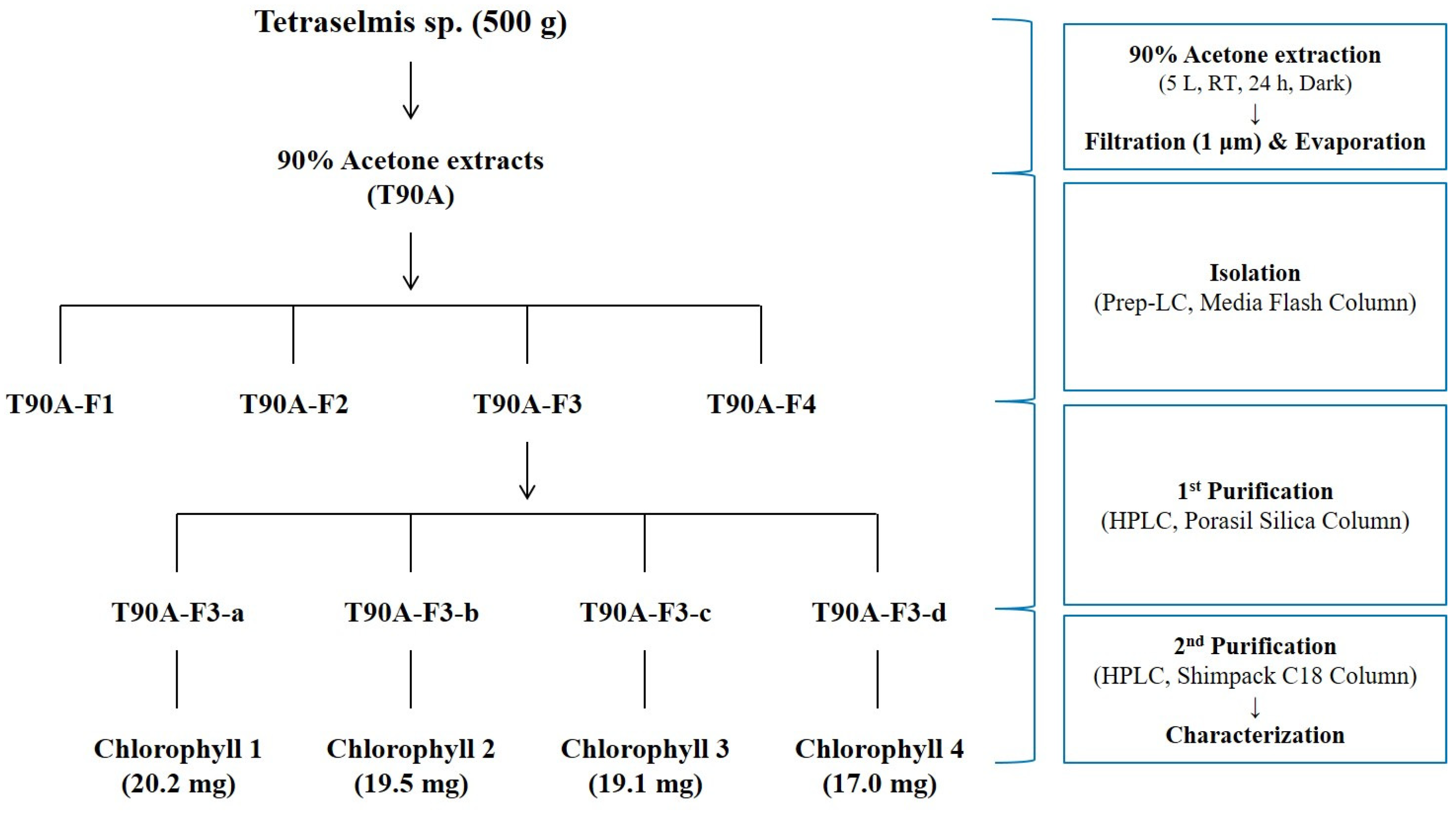
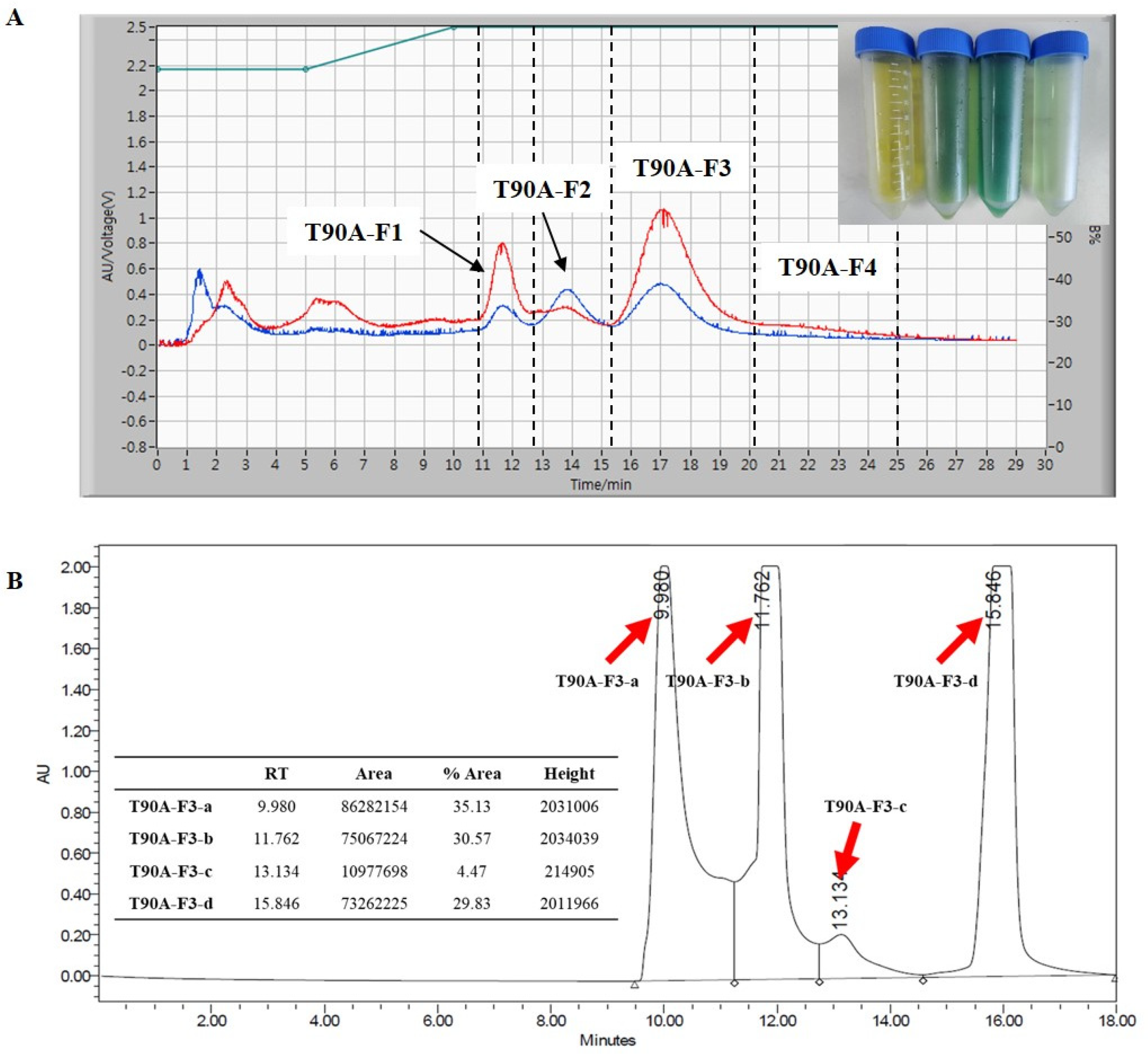
2.3. Isolation and Purification of Main Compounds from T90A
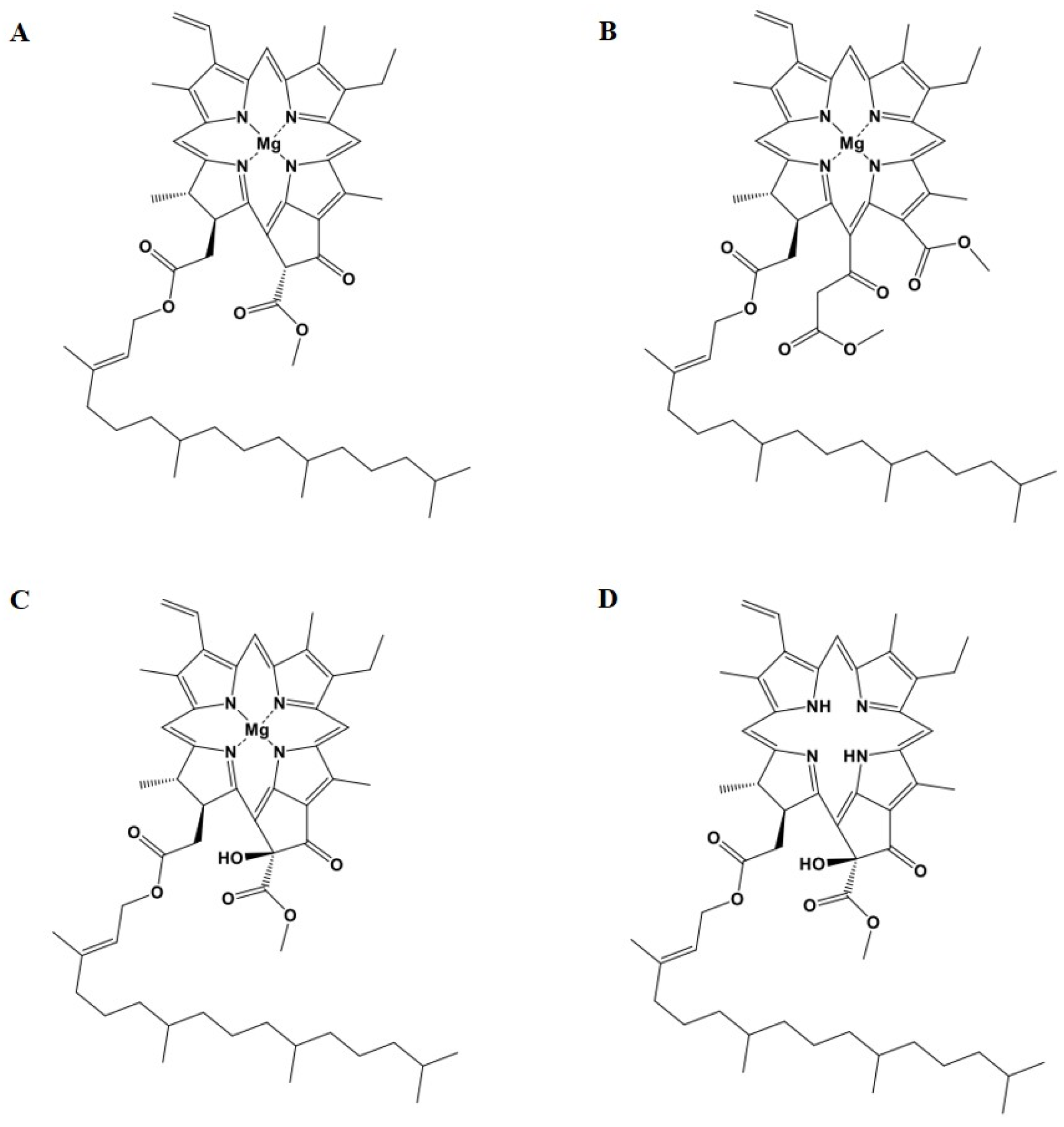
2.4. Characterization of Four Main Compounds from T90A
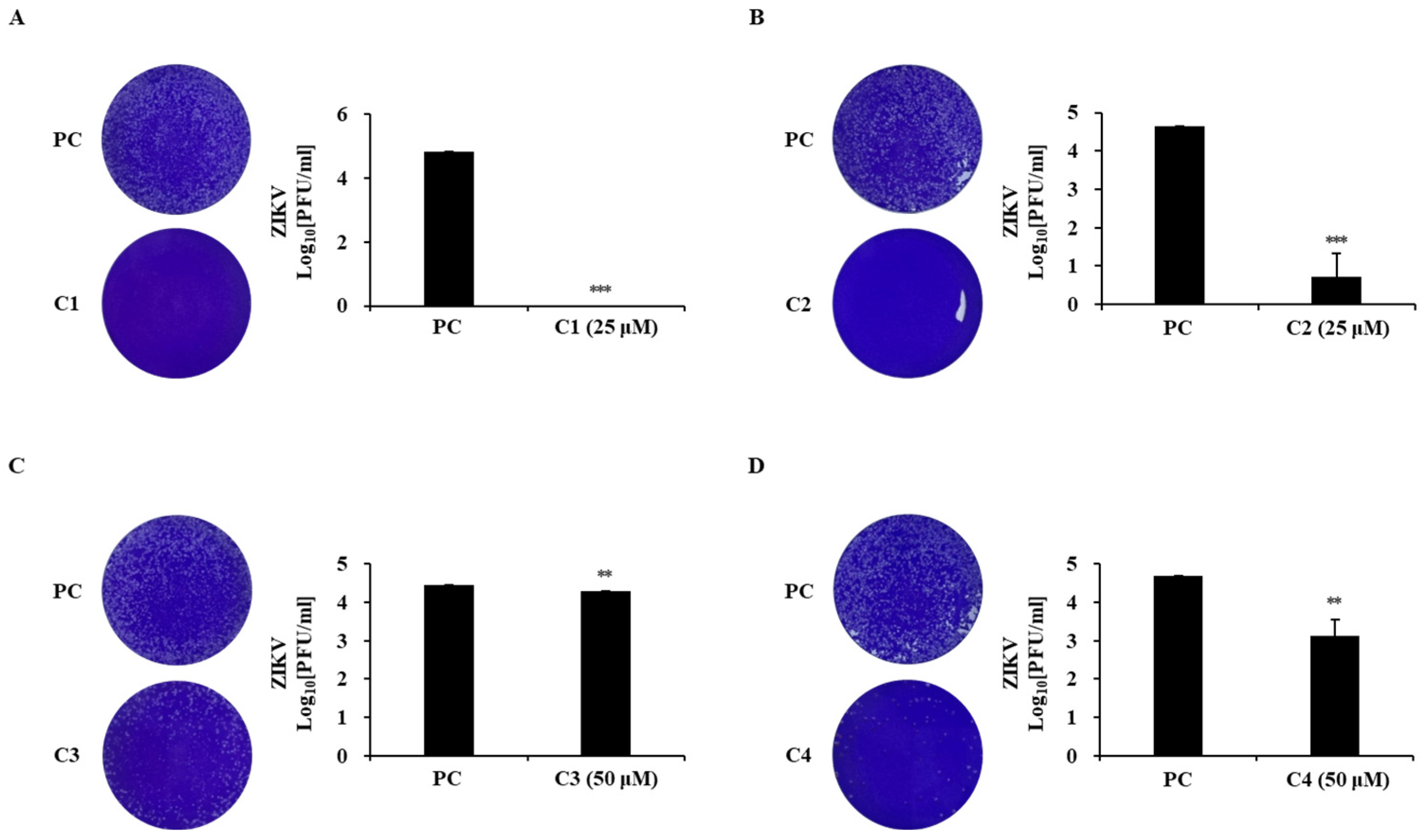
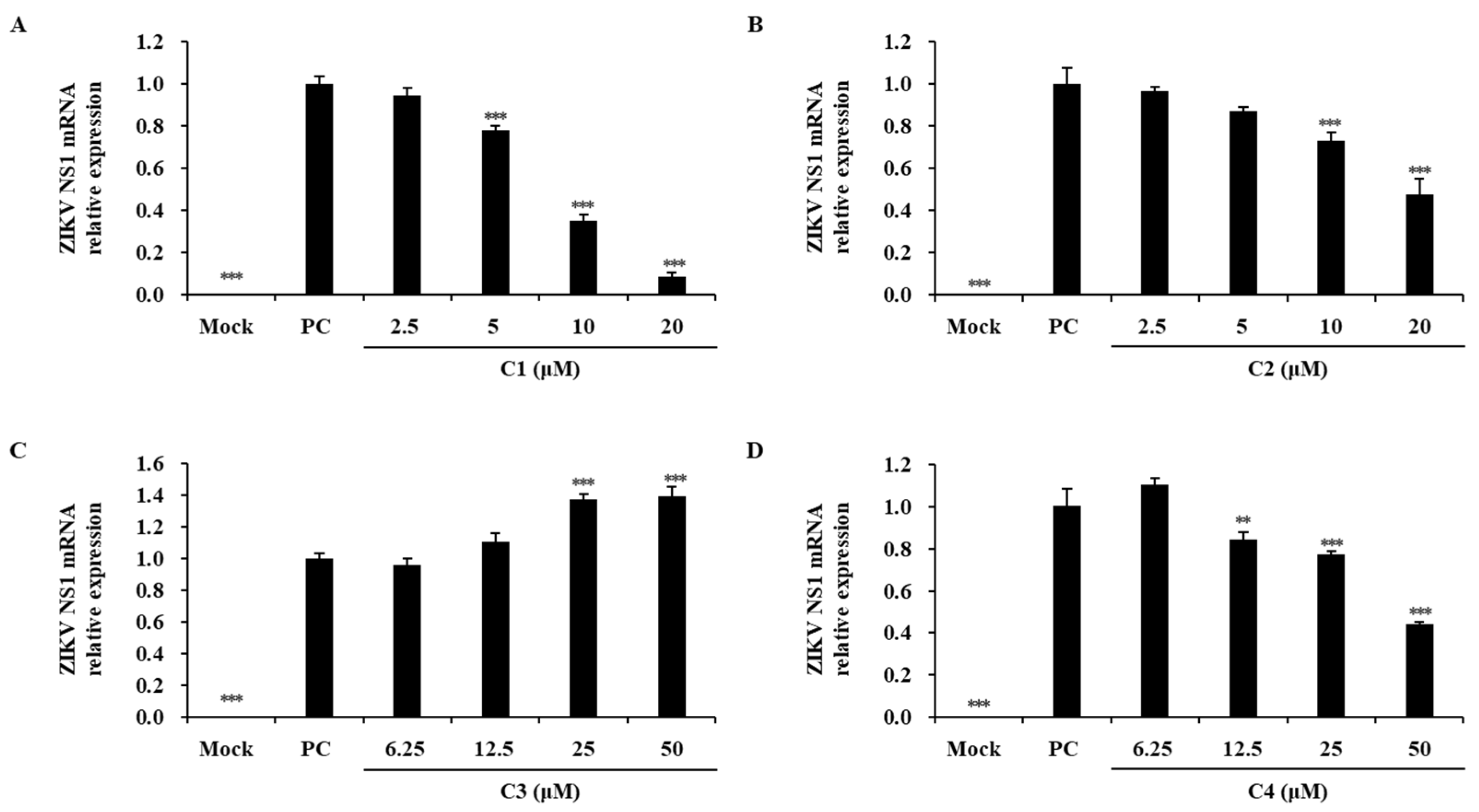
2.5. Inhibitory Effects of Chlorophylls from T90A on ZIKV Infection
2.6. Molecular Docking Analysis of Chlorophylls to ZIKV Proteins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mass Production of Tetraselmis sp.
3.2. Materials and Reagents
3.3. Preparation of Extracts and Purification of Main Compounds
3.4. Structural Identification of Compounds
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Measurement of Cytotoxicity and Calculation of SI
3.7. Measurement of Viral Plaque Formation Rate
3.8. Measurement of mRNA Expression Levels
3.9. Measurement of Virucidal Effect
3.10. Molecular Docking Analysis between Chlorophylls and ZIKV Proteins
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, W.; Ruan, R. Microalgae-based biomaterials for environmental remediation and functional use. In Biomass, Biofuels, and Biochemicals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, A.P.F.; Bragotto, A.P.A. Microalgae-based products: Food and public health. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.; Barros, A.N.; Rosa, E.; Antunes, L. Enhancing health benefits through chlorophylls and chlorophyll-rich agro-food: A comprehensive review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E.; Isambert, A. Commercial applications of microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramaniam, V.; Gunasegavan, R.D.-N.; Mustar, S.; Lee, J.C.; Mohd Noh, M.F. Isolation of industrial important bioactive compounds from microalgae. Molecules 2021, 26, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfer-Marquez, U.M.; Barros, R.M.C.; Sinnecker, P. Antioxidant activity of chlorophylls and their derivatives. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Böhm, V.; Courtney, P.D.; Schwartz, S.J. Antioxidant and antimutagenic activity of dietary chlorophyll derivatives determined by radical scavenging and bacterial reverse mutagenesis assays. J. Food Sci. 2006, 67, 2589–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombier, N.; Jauffrais, T.; Lebouvier, N. Antioxidant compounds from microalgae: A review. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramoniam, A.; Asha, V.V.; Nair, S.A.; Sasidharan, S.P.; Sureshkumar, P.K.; Rajendran, K.N.; Karunagaran, D.; Ramalingam, K. Chlorophyll revisited: Anti-inflammatory activities of chlorophyll a and inhibition of expression of TNF-α gene by the same. Inflammation 2012, 35, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.M.S.; Heimfarth, L.; Pereira, E.W.M.; Oliveira, F.S.; Menezes, I.R.A.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Picot, L.; Antoniolli, A.R.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. Phytol, a chlorophyll component, produces antihyperalgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antiarthritic effects: Possible NFκB pathway involvement and reduced levels of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Blakeslee, J. Digestion, absorption, and cancer preventative activity of dietary chlorophyll derivatives. Nutr. Res. 2007, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, W.M.; Hussin, W.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; AlFredan, M.A. The Conyza triloba extracts with high chlorophyll content and free radical scavenging activity had anticancer activity in cell lines. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 945638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hu, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Chlorophyll supplementation in early life prevents diet-induced obesity and modulates gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 63, 1801219. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Vaz, B.; Moreira, J.B.; de Morais, M.G.; Costa, J.A.V.C. Microalgae as a new source of bioactive compounds in food supplements. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lauritano, C.; Helland, K.; Riccio, G.; Andersen, J.H.; Ianora, A.; Hansen, E.H. Lysophosphatidylcholines and chlorophyll-derived molecules from the diatom Cylindrotheca Closterium with anti-inflammatory activity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T. Cultured microalgae and compounds derived thereof for food applications: Strain selection and cultivation, drying, and processing strategies. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 36, 559–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Sen, R. Sustainability of Microalgal Biorefinery: Scope, Challenges, and Opportunities. In Sustainable Energy Technology and Policies; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 335–351. [Google Scholar]
- Zittelli, G.C.; Rodolfi, L.; Bassi, N.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R. Photobioreactors for Microalgal Biofuel Production. In Algae for Biofuels and Energy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Yang, J.; Cui, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J. Comparative experiments of two novel tubular photobioreactors with an inner aerated tube for microalgal cultivation: Enhanced mass transfer and improved biomass yield. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, M.; Hadrich, B.; Miladi, R.; Barkallah, M.; Hentati, F.; Hachicha, R.; Laroche, C.; Michaud, P.; Fendri, I.; Abdelkafi, S. Effects of nutritional conditions on growth and biochemical composition of Tetraselmis sp. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondioli, P.; Della Bella, L.; Rivolta, G.; Zittelli, G.C.; Bassi, N.; Rodolfi, L.; Casini, D.; Prussi, M.; Chiaramonti, D.; Tredici, M.R. Oil production by the marine microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. F&M-M24 and Tetraselmis suecica F&M-M33. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, L.M.; Bombo, G.; Duarte, P.; Santos, T.F.; Maia, I.B.; Pinheiro, F.; Marques, J.; Jacinto, R.; Schulze, P.S.C.; Pereira, H.; et al. Carotenoid biosynthetic gene expression, pigment and n-3 fatty acid contents in carotenoid-rich Tetraselmis striata CTP4 strains under heat stress combined with high light. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Choi, W.-S.; Ye, B.-R.; Heo, S.-J.; Oh, D.; Kim, S.; Choi, K.-S.; Kang, D.-H.J. Cultivating spirulina maxima: Innovative approaches. Cyanobacteria 2018, 61, 61–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-K.; Ryu, Y.-K.; Choi, W.-Y.; Kim, T.; Park, A.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, C.-G.; Kang, D.-H. Year-round cultivation of Tetraselmis sp. for essential lipid production in a semi-open raceway system. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-A.; Kang, N.; Heo, S.-Y.; Oh, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Cha, S.-H.; Kim, W.-K.; Heo, S.-J. Antioxidant, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities of lutein-enriched extract of Tetraselmis species. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielnaa, P.; Al-Saadawe, M.; Saro, A.; Dama, M.F.; Zhou, M.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xia, Z. Zika virus-spread, epidemiology, genome, transmission cycle, clinical manifestation, associated challenges, vaccine and antiviral drug development. Virology 2020, 543, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sales-Neto, J.M.; Carvalho, D.C.M.; Magalhaes, D.W.A.; Medeiros, A.B.A.; Soares, M.M.; Rodrigues-Mascarenhas, S. Zika virus: Antiviral immune response, inflammation, and cardiotonic steroids as antiviral agents. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marban-Castro, E.; Gonce, A.; Fumado, V.; Pomero-Acevedo, L.; Bardaji, A. Zika virus infection in pregnant women and their children: A review. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 265, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Shi, W.F.; Qin, C.F. The evolution of Zika virus from Asia to the Americas. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lao, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Long, H.; Li, D.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, W.; et al. Antiviral activity of lycorine against Zika virus in vivo and in vitro. Viorology 2020, 546, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcareggi Morcelli, A.; da Silva Andrade, W.; Frankenberg, C.L.C.; Rech, R.; Marcílio, N.R. Extraction of chlorophylls and carotenoids from microalgae: Cosmo-sac-assisted solvent screening. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2021, 44, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, N.J.; Baker, A.; Quinnell, R.J.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. A simple and non-destructive method for chlorophyll quantification of Chlamydomonas cultures using digital image analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngcobo, S.; Bada, S.O.; Ukpong, A.M.; Risenga, I. Optimal chlorophyll extraction conditions and postharvest stability in Moringa (M. oleifera) leaves. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 1611–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiji, S.; Rokni, Y.; Benayad, O.; Laaraj, N.; Asehraou, A.; Mimouni, M. Chemical Composition related to antimicrobial activity of Moroccan Nigella sativa L. extracts and isolated fractions. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 1, 8308050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabti, I.; Albert, Q.; Philippot, S.; Dupire, F.; Westerhuis, B.; Fontanay, S.; Risler, A.; Kassab, T.; Elfalleh, W.; Aferchichi, A.; et al. Advances on antiviral activity of Morus spp. plant extracts: Human coronavirus and virus-related respiratory tract infections in the spotlight. Molecules 2020, 25, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.C.C.; Silva, B.M.; de Moura, H.M.M.; Pereira, G.R.; Brandão, G.C. Anti-Zika virus activity and chemical characterization by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography (UPLC-DAD-UV-MS) of ethanol extracts in Tecoma species. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobrinho, A.C.N.; de Morais, S.M.; Marinho, M.M.; de Souza, N.V.; Lima, D.M. Antiviral activity on the Zika virus and larvicidal activity on the Aedes spp. of Lippia alba essential oil and β-caryophyllene. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2021, 162, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katze, M.G.; He, Y.; Gale, M.G., Jr. Viruses and interferon: A fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S.; Farzan, M. The broad-spectrum antiviral functions of IFIT and IFITM proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Brown, H.M.; Hwang, S. Direct Antiviral Mechanisms of Interferon-Gamma. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, P.A.S.; Assone, T.; Prates, G.; Tedeschi, M.R.M.; Fonseca, L.A.M.; Casseb, J. The role of IFN-γ production during retroviral infections: An important cytokine involved in chronic inflammation and pathogenesis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao. Paulo. 2022, 64, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, J.C.M.; Vidal, T.; Decker, E.R.; Santurio, J.M.; Mello, C.F.; Pillat, M.M. Use of recombinant S1 protein with hFc for analysis of SARS-CoV-2 adsorption and evaluation of drugs that inhibit entry into VERO E6 cells. Immunol. Lett. 2023, 263, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Nam, H.G.; Zare, R.N. Microdroplet fusion mass spectrometry: Accelerated kinetics of acid-induced chlorophyll demetallation. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2017, 50, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gliszczyńska, A.; Dancewicz, K.; Gabryś, B.; Świtalska, M.; Wietrzyk, J.; Maciejewska, G. Synthesis of novel phytol-derived γ-butyrolactones and evaluation of their biological activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Aleman, G.H.; Castro, V.; Londaitsbehere, A.; Gutierrez-Rodríguez, M.; Garaigorta, U.; Solano, R.; Gastaminza, P. SARS-CoV-2 fears green: The chlorophyll catabolite pheophorbide a is a potent antiviral. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, T.; Desmarets, L.; Bordage, S.; Bamba, M.; Hervouet, K.; Rouillé, Y.; François, N.; Decossas, M.; Sencio, V.; Trottein, F.; et al. A photoactivable natural product with broad antiviral activity against enveloped viruses, including highly pathogenic coronaviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e01581-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnoglik, S.L.; Aoki, C.; Sudarmono, P.; Komoto, M.; Deng, L.; Shoji, I.; Fuchino, H.; Kawahara, N.; Hotta, H. Antiviral activity of extracts from Morinda citrifolia leaves and chlorophyll catabolites, pheophorbide a and pyropheophorbide a, against hepatitis C virus. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2014, 58, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, Y.; Aoki, M. A chlorophyll c2 analogue from the marine brown alga Eisenia bicyclis inactivates the infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus, a fish rhabdovirus. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorshkov, K.; Shiryaev, S.A.; Fertel, S.; Lin, Y.W.; Huang, C.T.; Pinto, A.; Farhy, C.; Strongin, A.Y.; Zheng, W.; Tershikh, A.V. Zika Virus: Origins, Pathological Action, and Treatment Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.S.; Nascimento, T.C.; Pinheiro, P.N.; de Rosso, V.V.; de Menezes, C.R.; Jacob-Lopes, E.; Zepka, L.Q. Insights on the intestinal absorption of chlorophyll series from microalgae. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kim, E.-A.; Park, A.; Heo, S.-Y.; Heo, J.-H.; Heo, S.-J. Antiviral potential of fucoxanthin, an edible carotenoid purified from Sargassum siliquastrum, against Zika virus. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction: Twenty-something years on. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Rajoriya, S.; Kim, B.; Natasha, A.; Im, H.; Shim, H.S.; Yoo, J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, E.-W.; Shin, H.J.; et al. In vitro broad-spectrum antiviral activity of MIT-001, a mitochondria-targeted reactive oxygen species scavenger, against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and multiple zoonotic viruses. Virus Res. 2024, 342, 199325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki-Utsubo, C.; Chen, M.; Hotta, H. Virucidal and Neutralizing Activity Tests for Antiviral Substances and Antibodies. Bio Protoc. 2018, 8, e2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, N.; Heo, S.-Y.; Kim, E.-A.; Cha, S.-H.; Ryu, B.; Heo, S.-J. Antiviral effect of fucoxanthin obtained from Sargassum siliquastrum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Algae 2023, 38, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kim, E.-A.; Heo, S.-Y.; Heo, S.-J. Structure-based in silico screening of marine phlorotannins for potential walrus calicivirus inhibitor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Antiviral Activity | Virucidal activity | Cytotoxicity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | |||||
| EC50 (μg/mL) | SI | EC50 (μg/mL) | SI | EC50 (μg/mL) | SI | CC50 (μg/mL) |
| 36.4 ± 0.5 | 21.1 | 31.3 ± 0.8 | 24.6 | 34.1 ± 0.2 | 22.6 | 769.6 ± 6.9 |
| Chlorophyll | Protein | Binding energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a | Envelope protein | −276.459 |
| NS2B/NS3 | −767.837 | |
| RdRp | −692.708 | |
| Chlorin e6-131-152-dimethyl-173-phytyl ester | Envelope protein | −374.144 |
| NS2B/NS3 | −779.602 | |
| RdRp | −727.470 |
| Chlorophyll | Protein | Non-Bond Interaction in Active Site |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a (C1) | Envelope protein | Mg2+-TRP101, Mg2+-GLY102, C1-LEU107 (2), C1-TRP101 (2) |
| NS2B/NS3 | Mg2+-ASN1152, Mg2+- GLY1153, Mg2+-VAL1154, Mg2+-VAL1162, C1-VAL1036, C1-HIS1051 (3), C1-ALA1132 (3), C1-SER1135 (2), C1-TYR1150, C1-GLY1151, C1-ASN1152 (2), C1-TYR1161 (4) | |
| RdRp | Mg2+-GLU707 (2), Mg2+-TRP848, C1-VAL708, C1-HIS713, C1-HIS732 (2), C1-CYS849, | |
| Chlorin e6-131-152-dimethyl-173-phytyl ester (C2) | Envelope protein | Mg2+-GLY104, Mg2+-Cys105, Mg2+-GLY106 C2-TRP101(5), C2-GLY104, C2-GLY106, C2-LEU107 |
| NS2B/NS3 | Mg2+-ASP1129 (2), Mg2+-ASN1152, Mg2+-GLY1153, Mg2+-VAL1162, C2-HIS1051, C2-ALA1132, C2-VAL1154, C2-TYR1161 (2) | |
| RdRp | Mg2+-GLU707, C2-TRP702 (2), C2-VAL708 (2), C2-TRP848 (2) |
| Gene | Sequence | Primer |
|---|---|---|
| ZIKV NS1 | 5’-CRA CTA CTG CAA GYG GAA GG-3’ | F |
| 5’-GCC TTA TCT CCA TTC CAT ACC-3’ | R | |
| Monkey GAPDH | 5’-GCA AAT TCC ATG GCA CCG T-3’ | F |
| 5’-TCG CCC CAC TTG ATT TTG G-3’ | R | |
| Monkey IFNγ | 5’-CGA ATG TCC AAC GCA AAG CAG TAC-3’ | F |
| 5’-TGC TCT TCG ACC TCG AAA CAT CTG-3’ | R | |
| Monkey IFIT1 | 5’- GGA TTC TGT ACA ATA CAC TAG AAA CCA-3’ | F |
| 5’- CTT TTG GTT ACT TTT CCC CTA TCC-3 ‘ | R | |
| Monkey IFIT2 | 5’- ATC CCC CAT CGC TTA TCT CT-3’ | F |
| 5’- CCACCTCAATTAATCAGGCACT-3’ | R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, N.; Kim, E.-A.; Park, A.; Heo, S.-Y.; Heo, J.-H.; Lee, W.-K.; Ryu, Y.-K.; Heo, S.-J. Antiviral Activity of Chlorophyll Extracts from Tetraselmis sp., a Marine Microalga, Against Zika Virus Infection. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090397
Kang N, Kim E-A, Park A, Heo S-Y, Heo J-H, Lee W-K, Ryu Y-K, Heo S-J. Antiviral Activity of Chlorophyll Extracts from Tetraselmis sp., a Marine Microalga, Against Zika Virus Infection. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(9):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090397
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Nalae, Eun-A Kim, Areumi Park, Seong-Yeong Heo, Jun-Ho Heo, Won-Kyu Lee, Yong-Kyun Ryu, and Soo-Jin Heo. 2024. "Antiviral Activity of Chlorophyll Extracts from Tetraselmis sp., a Marine Microalga, Against Zika Virus Infection" Marine Drugs 22, no. 9: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090397
APA StyleKang, N., Kim, E.-A., Park, A., Heo, S.-Y., Heo, J.-H., Lee, W.-K., Ryu, Y.-K., & Heo, S.-J. (2024). Antiviral Activity of Chlorophyll Extracts from Tetraselmis sp., a Marine Microalga, Against Zika Virus Infection. Marine Drugs, 22(9), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090397






