Preparation and Vasodilation Mechanism of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Ulva prolifera Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
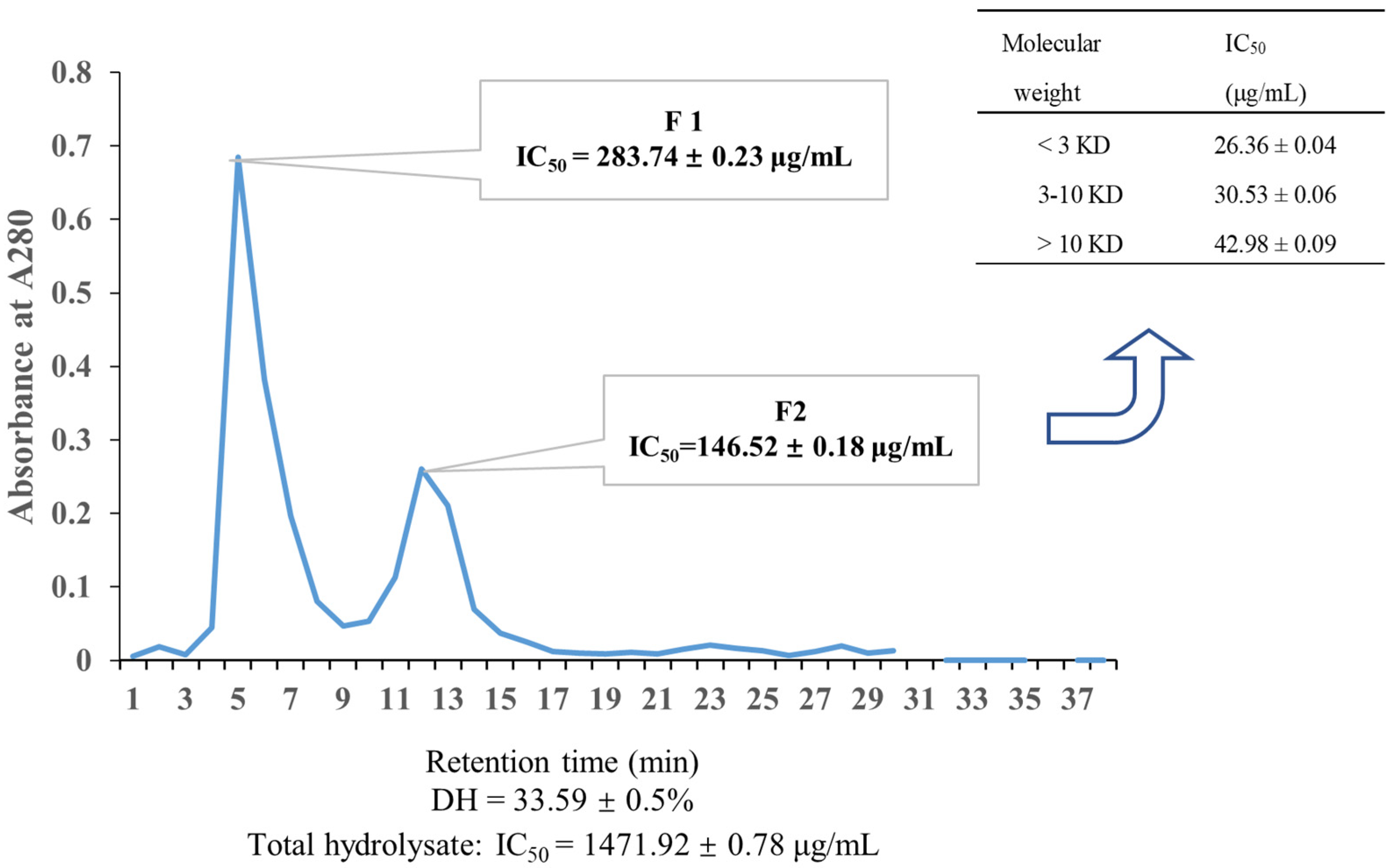
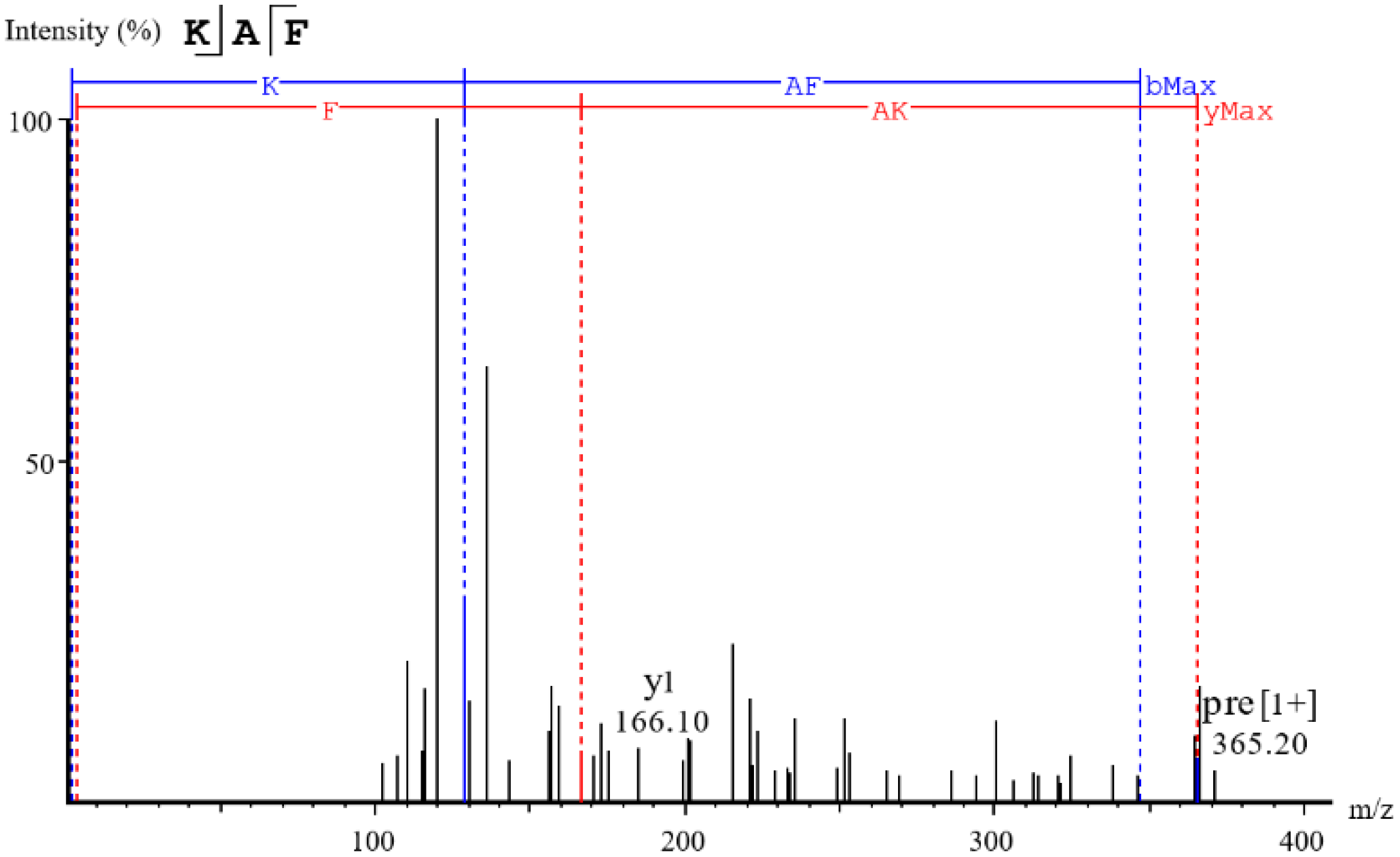
2.1. Purification and Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from U. prolifera Protein Hydrolysate
2.2. Screening of the Potential ACE Inhibitory Peptides
2.3. Inhibition Pattern of Peptide against ACE
2.4. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation
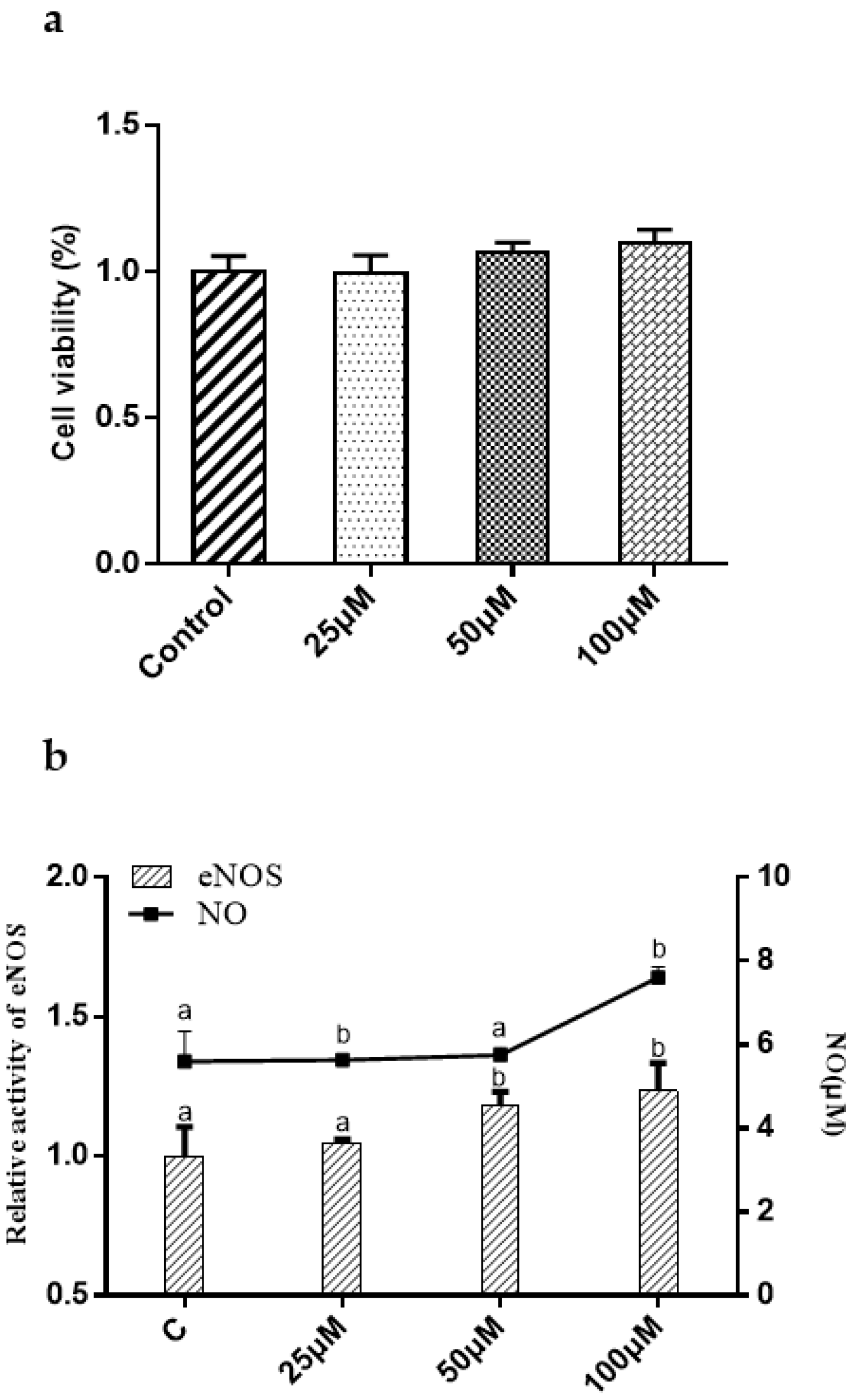
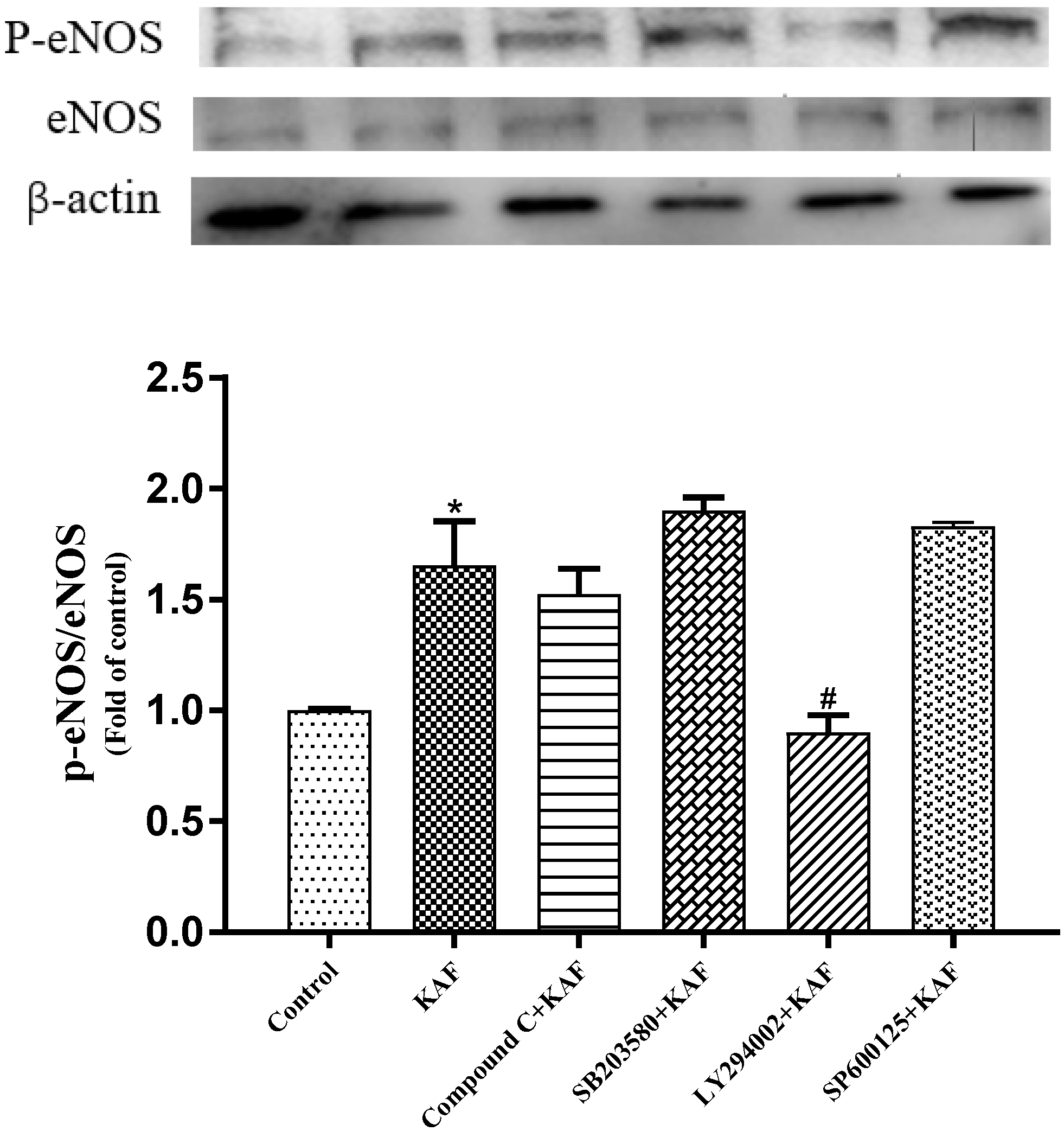
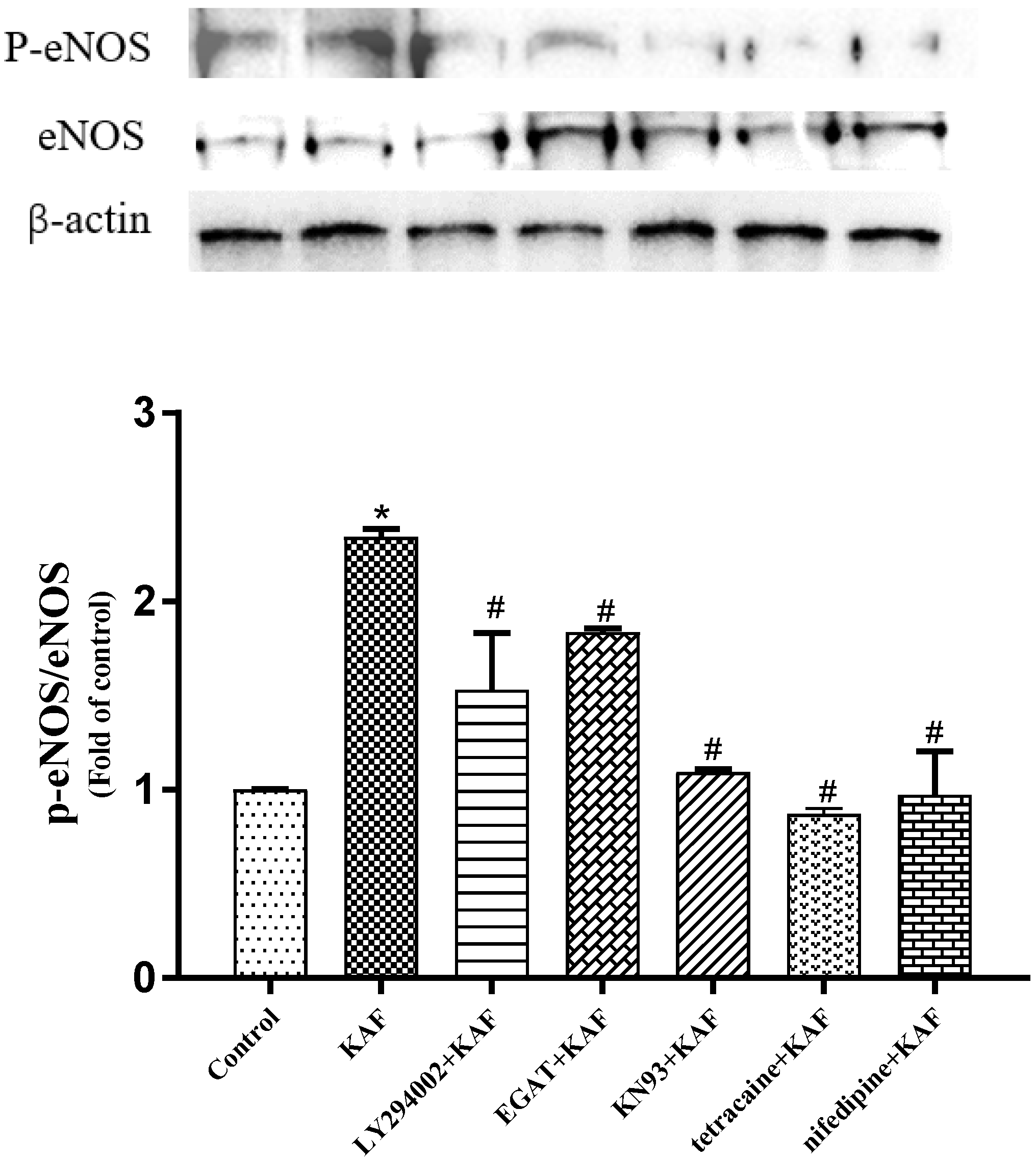
2.5. Effect of Synthetic Peptides on NO Production, eNOS Activity in HUVECs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of U. prolifera Protein Hydrolysate
3.3. Determination of ACE Inhibitory Activity
3.4. Purification and Identification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Hydrolysates
3.5. Screening and Synthesis of the Potential ACE Inhibitory Peptides
3.6. Inhibition Kinetics
3.7. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
3.8. Cell Culture of HUVEC
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rapsomaniki, E.; Timmis, A.; George, J.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Shah, A.D.; Denaxas, S.; White, I.R.; Caulfield, M.J.; Deanfield, J.E.; Smeeth, L.; et al. Blood pressure and incidence of twelve cardiovascular diseases: Lifetime risks, healthy life-years lost, and age-specific associations in 1.25 million people. Lancet 2014, 383, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azushima, K.; Morisawa, N.; Tamura, K.; Nishiyama, A. Recent Research Advances in Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Receptors. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.; Kristinsson, H.G. ACE-inhibitory activity of tilapia protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Q.; He, Q. Screening and mechanisms of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from rabbit meat proteins: A combined in silico and in vitro study. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, S.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-M.; Pan, X.-Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Seventeen novel angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from the protein hydrolysate of Mytilus edulis: Isolation, identification, molecular docking study, and protective function on HUVECs. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7831–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Pan, N.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z. Targeted Affinity Purification and Mechanism of Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-L.; Luo, Q.-B.; Suo, S.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Preparation, Identification, Molecular Docking Study and Protective Function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna Muscle. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, S.; Pan, N.; Su, J.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; et al. A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.-H.; Zhang, X.-W.; Mao, Y.-Z.; Liang, C.-W.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.-M.; Wang, Q.-Y. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Morales, M.; Casas-Valdez, M.; Carrillo-Domínguez, S.; González-Acosta, B.; Pérez-Gil, F. Chemical composition and microbiological assays of marine algae Enteromorpha spp. as a potential food source. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 18, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wang, S.; Jing, L.; Yao, D. Purification and characterisation of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptide derived from the enzymatic hydrolysate of Enteromorpha clathrata protein. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ilyas, I.; Little, P.J.; Li, H.; Kamato, D.; Zheng, X.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Han, J.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases and Beyond: From Mechanism to Pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 924–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Gao, Z.; Tayyab Rashid, M. An ACE-inhibitory peptide derived from maize germ antagonizes the Angiotensin II-induced dysfunction of HUVECs via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 112, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Pan, N.; Xu, M.; Su, Y.; Qiao, K.; Chen, B.; Zheng, B.; Xiao, M.; Liu, Z. ACE Inhibitory Peptide from Skin Collagen Hydrolysate of Takifugu bimaculatus as Potential for Protecting HUVECs Injury. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Peng, K.; Wang, X.L.; Ding, Z.; Liu, L.; Xu, P.; Liu, G.Q. Isolation and Characterization of Three Antihypertension Peptides from the Mycelia of Ganoderma lucidum (Agaricomycetes). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8149–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Tu, Z. Identification of novel angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Pacific saury: In vivo antihypertensive effect and transport route. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.-Q.; Luo, Q.-B.; Suo, S.-K.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Preparation, Characterization, and Cytoprotective Effects on HUVECs of Fourteen Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides From Protein Hydrolysate of Tuna Processing By-Products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 868681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, D.; Zhen, X.; Cao, J. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from bovine casein and identified by MALDI-TOF-MS/MS. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 93, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, S.; Rakib, M.A.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.O.; Ha, Y.L. Eritadenine from Edible Mushrooms Inhibits Activity of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiang, X.; Xu, L. A novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from oyster: Simulated gastro-intestinal digestion, molecular docking, inhibition kinetics and antihypertensive effects in rats. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 981163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esam, Z.; Akhavan, M.; Lotfi, M.; Bekhradnia, A. Molecular docking and dynamics studies of Nicotinamide Riboside as a potential multi-target nutraceutical against SARS-CoV-2 entry, replication, and transcription: A new insight. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1247, 131394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.Y.; Zhang, R.; Huang, G.D.; Wu, W.J. Studies on the conformations and hydrogen bonding of ACE inhibitory tripeptide VEF by all-atom molecular dynamics simulations and molecular docking. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2017, 36, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, S.; Siow, R.; Rowlands, D.; Becker, M.; Wyatt, A.; Aaronson, P.; Coen, C.; Kalló, I.; Jacob, R.; Mann, G. The isoflavone Equol mediates rapid vascular relaxation: Ca2+-independent activation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase/Hsp90 involving ERK1/2 and Akt phosphorylation in human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27335–27345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, F.; Yan, F.; Shen, S.; Zhu, M. TRPV1 agonism inhibits endothelial cell inflammation via activation of eNOS/NO pathway. Atherosclerosis 2017, 260, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.W.; Choi, C.Y.; Hwang, Y.P.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, Y.C.; Lee, K.J.; Jeong, T.C.; Jeong, H.G. Betulinic Acid Increases eNOS Phosphorylation and NO Synthesis via the Calcium-Signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.W.; Pham, H.T.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, G.H.; Han, E.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Chung, Y.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, H.G. Impressic Acid, a Lupane-Type Triterpenoid from Acanthopanax koreanum, Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction via Activation of eNOS/NO Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, T.; Kimura, J.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Naito, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases as potential targets of nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide 2011, 25, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinkamp-Fenske, K.; Bollinger, L.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Horke, S.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Reciprocal regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase and NADPH oxidase by betulinic acid in human endothelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.-C.; Kebir, D.E.; Chéreau, C.; Lanone, S.; Huang, X.-L.; Roessingh, A.S.D.B.; Mercier, J.-C.; Dall’Ava-Santucci, J.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T. Involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in endothelial NO production and endothelium-dependent relaxation. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H2311–H2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; He, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Lu, A.; Che, T.; Shen, S. Purification identification and function analysis of ACE inhibitory peptide from Ulva prolifera protein. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, S.B.; Ekhteiari Salmas, R.; Fatmi, M.Q.; Durdagi, S. Discovery of Klotho peptide antagonists against Wnt3 and Wnt3a target proteins using combination of protein engineering, protein–protein docking, peptide docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 32, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-D.; Xi, Q.-H.; Kong, J.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from the Collagens of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Swim Bladders: Isolation, Characterization, Molecular Docking Analysis and Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Peptide | Peptide Ranker | WS | Toxin | HIA | BBB | -C Dock Energy | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRW | 0.88931 | GOOD | NO | 0.7047 | −0.8101 | fail | |
| GMR | 0.884249 | GOOD | NO | 0.6327 | −0.6948 | fail | |
| MGR | 0.860347 | GOOD | NO | 0.6327 | −0.6948 | fail | |
| RYFR | 0.846704 | GOOD | NO | 0.4488 | 0.8791 | fail | |
| KWY | 0.794787 | GOOD | NO | 0.9434 | −0.8790 | fail | |
| RWK | 0.774831 | GOOD | NO | 0.8444 | −0.8040 | fail | |
| LGSFR | 0.737369 | GOOD | NO | 0.8291 | −0.7994 | fail | |
| EGRW | 0.734044 | GOOD | NO | 0.8291 | −0.7994 | fail | |
| WRAA | 0.702731 | GOOD | NO | 0.9124 | −0.8063 | fail | |
| KAF | 0.682106 | GOOD | NO | 0.7042 | −0.8181 | 88.967 | 0.63 ± 0.26 |
| DFT | 0.600067 | GOOD | NO | 0.4747 | −0.8839 | fail | |
| ERFY | 0.464208 | GOOD | NO | 0.6018 | −0.8872 | fail | |
| PAMK | 0.419096 | GOOD | NO | 0.774 | −0.7314 | fail | |
| Captopril | 46.94 | 0.017 [19] |
| Candidates | Bond Position | Distance(Å) | Type | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KAF | A: ASP415:OD2-KAF:H22 A: ARG522:NH1-KAF: O44 A: ZN701: ZN-KAF: O44 | 2.16146 4.49144 2.24177 | Attractive Charge | 3 |
| A: ASP415:OD1-KAF: H21 A: ALA354:O-KAF: H36 | 2.26404 2.3907 | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | 2 | |
| A: HIS387:HD2-KAF: O44 A: TYR423: OH-KAF: H38 | 3.01083 2.3496 | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | 2 | |
| A: VAL418-KAF | 4.90944 | Pi-Alkyl | 1 | |
| A: ZN701: ZN-KAF: O34 | 3.0144 | Metal-Acceptor | 1 | |
| Captopril (Cap) | A: ARG522:NH1-Cap: O11 A: ZN701: ZN-Cap: O11 | 4.49391 2.27274 | Attractive Charge | 2 |
| A: ALA356:HN-Cap: O1 | 2.89368 | Conventional Hydrogen Bond | 1 | |
| A: ALA354:O-Cap: H22 | 2.91634 | Carbon Hydrogen Bond | 1 | |
| A: HIS387-Cap:H18 | 2.76629 | Pi-Donor Hydrogen Bond; Pi-Sulfur | 1 | |
| A: VAL518-Cap | 4.64702 | Alkyl | 1 | |
| A: PHE391-Cap: S4 A: HIS410-Cap: S4 | 4.77799 4.40347 | Pi-Sulfur | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; He, H.; Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Fu, C.; Zeb, A.; Che, T.; Shen, S. Preparation and Vasodilation Mechanism of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Ulva prolifera Protein. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090398
Li Z, He H, Liu J, Gu H, Fu C, Zeb A, Che T, Shen S. Preparation and Vasodilation Mechanism of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Ulva prolifera Protein. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(9):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090398
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhiyong, Hongyan He, Jiasi Liu, Huiyue Gu, Caiwei Fu, Aurang Zeb, Tuanjie Che, and Songdong Shen. 2024. "Preparation and Vasodilation Mechanism of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Ulva prolifera Protein" Marine Drugs 22, no. 9: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090398
APA StyleLi, Z., He, H., Liu, J., Gu, H., Fu, C., Zeb, A., Che, T., & Shen, S. (2024). Preparation and Vasodilation Mechanism of Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Ulva prolifera Protein. Marine Drugs, 22(9), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090398







