Bioactivity of Fucoidan-Rich Extracts from Fucus vesiculosus against Rotavirus and Foodborne Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
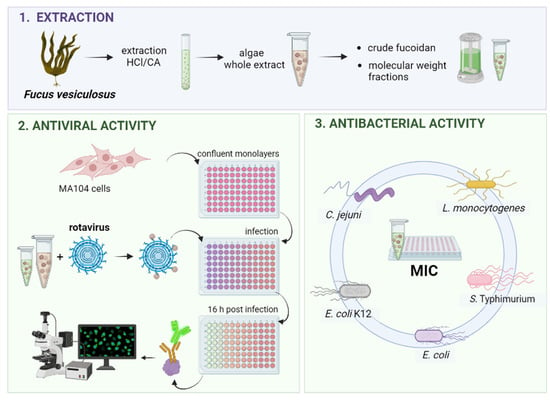
2.1. Extraction of Fucoidan from Seaweed
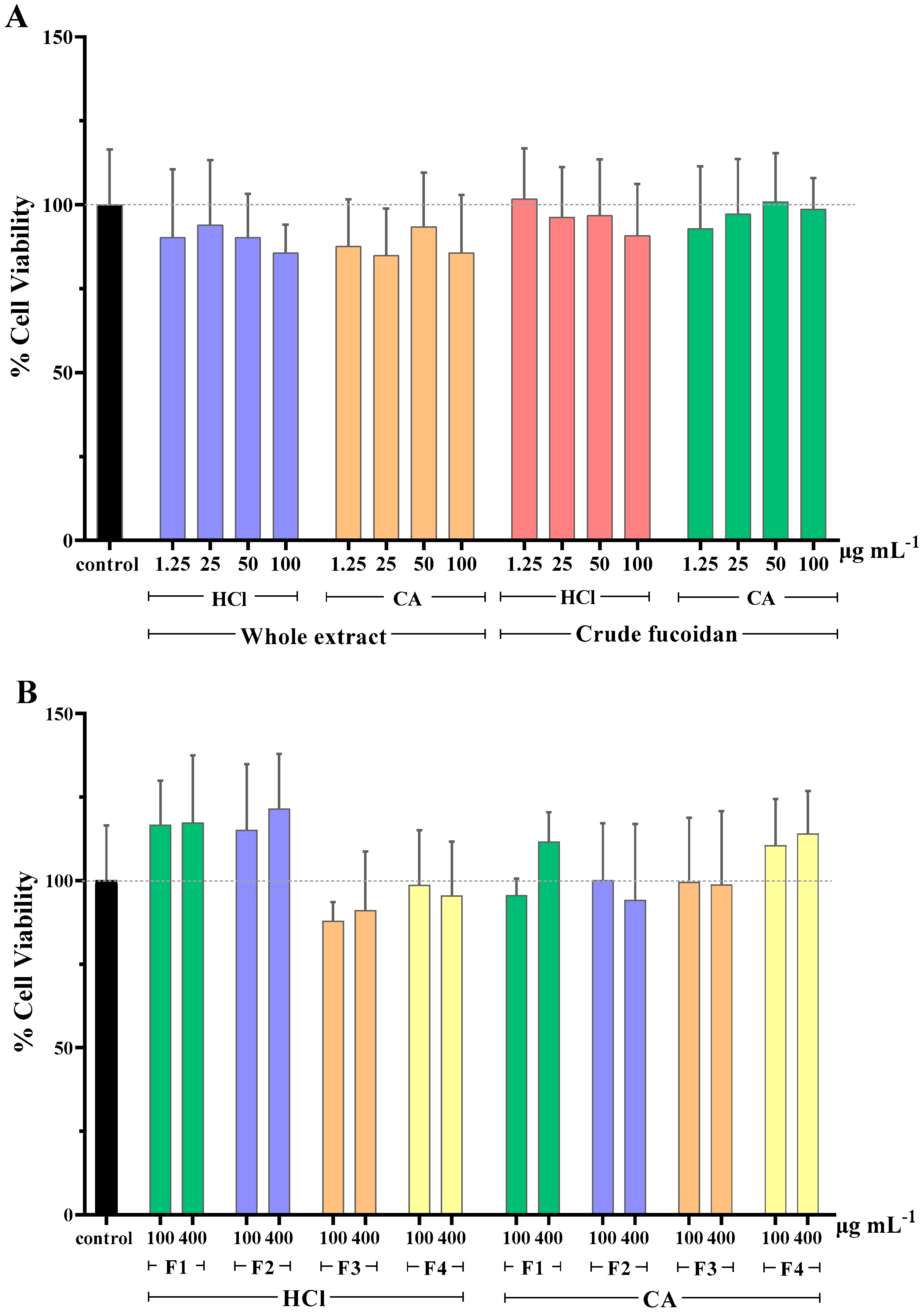
2.2. Cell Viability
2.3. Antirotaviral Activity
2.4. Antibacterial Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Samples
3.2. Seaweed Samples
3.3. Extraction of Fucoidan from Seaweed
3.4. Measurement of Fucoidan Content
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Algae Samples in the Vitro Assays
3.7. Cell Viability Assay
3.8. RV Propagation
3.9. RV Neutralization Assay
3.10. Cell Receptor Blocking Assay
3.11. Detection of RV Cell Infection by Indirect Immunofluorescence
3.12. MIC Method
3.13. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Troeger, C.; Forouzanfar, M.; Rao, P.C.; Khalil, I.; Brown, A.; Reiner, R.C., Jr.; Fullman, N.; Thompson, R.L.; Abajobir, A.; Ahmed, M.J.T.L.I.D. Estimates of global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoeal diseases: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 909–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troeger, C.; Khalil, I.A.; Rao, P.C.; Cao, S.; Blacker, B.F.; Ahmed, T.; Armah, G.; Bines, J.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; et al. Rotavirus vaccination and the global burden of rotavirus diarrhea among children younger than 5 years. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppong, T.; Yang, H.; Amponsem-Boateng, C.; Kyere, E.D.; Abdulai, T.; Duan, G.; Opolot, G.J. Enteric pathogens associated with gastroenteritis among children under 5 years in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallowell, B.D.; Tate, J.; Parashar, U. An overview of rotavirus vaccination programs in developing countries. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caddy, S.; Papa, G.; Borodavka, A.; Desselberger, U. Rotavirus research: 2014–2020. Virus Res. 2021, 304, 198499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, J.E.; Burton, A.H.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Parashar, U.D.; for the World Health Organization–Coordinated Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network; Agocs, M.; Serhan, F.; de Oliveira, L.; Mwenda, J.M.; Mihigo, R.; et al. Global, regional, and national estimates of rotavirus mortality in children< 5 years of age, 2000–2013. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, S96–S105. [Google Scholar]
- Desselberger, U. Reverse genetics of rotavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2106–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.F.; Gill, D. Rotavirus vaccine efficacy: Current status and areas for improvement. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 15, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.G.; Cadamuro, R.D.; Cabral, A.C.; Thaís da Silva, I.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Fongaro, G. Broad Spectrum Algae Compounds Against Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 809296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, K.K.; Renzette, N.; Kowalik, T.F.; Jensen, J.D. Antiviral drug resistance as an adaptive process. Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farthing, M. Diarrhoea: A significant worldwide problem. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 14, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourama, H. Foodborne pathogens. In Food Safety Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, L.; Zhu, M.-J. Practical in-storage interventions to control foodborne pathogens on fresh produce. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4584–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Maharana, S.; Bhakta, S.; Jena, M. Marine phytoplankton diversity of Odisha coast, India with special reference to new record of diatoms and dinoflagellates. Vegetos 2022, 35, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Fu, G.; Wang, K.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, K.; Song, S. Advances in research on antiviral activities of sulfated polysaccharides from seaweeds. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Poonia, A.K.; Choure, K.; Yadav, A.N.; Pandey, A. Antimicrobial therapeutics isolated from algal source: Retrospect and prospect. Biologia 2022, 78, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, H.; Xue, K.; Xu, S.; Tian, Z. The anti-cancer effects of fucoidan: A review of both in vivo and in vitro investigations. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.; Federico, S.; Glaviano, F.; Somma, E.; Zupo, V.; Costantini, M. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges and Algae: Effects on Cancer Cell Metabolome and Chemical Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Amarante, S.J.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Brown Algae Phlorotannins: A Marine Alternative to Break the Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cancer Network. Foods 2021, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.; Sørensen, A.M.; Holdt, S.L.; Akoh, C.C.; Hermund, D.B. Source, Extraction, Characterization, and Applications of Novel Antioxidants from Seaweed. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Nikolova, M.; Iliev, I.; Peychev, L.; Trica, B.; Oancea, F.; Delattre, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Shabaan, M.T.; Hassan, L.; Morsi, H.H. Antiviral activity of algae biosynthesized silver and gold nanoparticles against Herps Simplex (HSV-1) virus in vitro using cell-line culture technique. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, I.; Özogul, F.; Özogul, Y.; Regenstein, J.M. Marine bioactive compounds and their health benefits: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Nayak, R.; Patra, S.; Bhuyan, P.P.; Dash, S.R.; Ki, J.-S.; Adhikary, S.P.; Ragusa, A.; Jena, M. Cyanobacteria and Algae-Derived Bioactive Metabolites as Antiviral Agents: Evidence, Mode of Action, and Scope for Further Expansion; A Comprehensive Review in Light of the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumar, J.; Chidambaram, R.; Sukumaran, S.J. Sulfated polysaccharides and its commercial applications in food industries—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2453–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisuwan, W.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Chaiyaso, T.; Techapun, C.; Leksawasdi, N.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Rachtanapun, P.; Wangtueai, S.; Sommano, S.R.; You, S. The antiviral activity of bacterial, fungal, and algal polysaccharides as bioactive ingredients: Potential uses for enhancing immune systems and preventing viruses. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 772033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.A.; Kang, N.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y.; Kim, Y.-T.; Jeon, Y.-J.J.F.H. Bioactive potentials of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from brown seaweed Sargassum spp in related to human health applications: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Yi, Y.-L.; Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H.; Zhan, Z.-L.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, J.-A. Isolation, structural characterization and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Laminaria japonica: A review. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, N.; Malik, A.; Naik, S. Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae and its application in combating COVID-19: Mini review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 13, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.-X.; Guan, H.-S. The antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2795–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Silva, S.A.; Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Carpena, M.; Gullón, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Domingues, V.F.; Barroso, M.F.; Simal-Gandara, J.; et al. Antibacterial Use of Macroalgae Compounds against Foodborne Pathogens. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, E.M.; Oliveira, M.; Mondala, J.R.; Curtin, J.; Tiwari, B.K.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Antimicrobials from seaweeds for food applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajauria, G.; Ravindran, R.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Rai, D.K.; Sweeney, T.; O’Doherty, J. Purification and molecular characterization of fucoidan isolated from Ascophyllum nodosum brown seaweed grown in Ireland. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauziee, N.A.M.; Chang, L.S.; Mustapha, W.A.W.; Nor, A.R.M.; Lim, S.J. Functional polysaccharides of fucoidan, laminaran and alginate from Malaysian brown seaweeds (Sargassum polycystum, Turbinaria ornata and Padina boryana). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.J.; You, D.-J.; Lee, K.-W. Characterization and immunomodulatory effects of high molecular weight fucoidan fraction from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, E.M.; Mondala, J.R.M.; Oliveira, M.; Przyborska, J.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Rai, D.K.; Sivagnanam, S.P.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; O’Shea, D.; Devereux, M. Influence of molecular weight fractionation on the antimicrobial and anticancer properties of a fucoidan rich-extract from the macroalgae Fucus vesiculosus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.; Beaulieu, M. Characterization of polysaccharides extracted from brown seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vaquero, M.; Rajauria, G.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Sweeney, T. Polysaccharides from macroalgae: Recent advances, innovative technologies and challenges in extraction and purification. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, H.; Biller, P.; Ross, A.; Adams, J. The seasonal variation of fucoidan within three species of brown macroalgae. Algal Res. 2017, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men’shova, R.; Ermakova, S.; Rachidi, S.; Al-Hajje, A.; Zvyagintseva, T.; Kanaan, H. Seasonal variations of the composition, structural features, and antitumor properties of polysaccharides from Padina pavonica (Lebanon) as a function of composition. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 47, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Monagail, M.; Cornish, L.; Morrison, L.; Araújo, R.; Critchley, A.T. Sustainable harvesting of wild seaweed resources. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Meaney, S.; Tiwari, B.K. Bioactive peptides from algae: Traditional and novel generation strategies, structure-function relationships, and bioinformatics as predictive tools for bioactivity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, N.M.; Flores, M.L.; Pujol, C.A.; Becerra, M.B.; Navarro, D.A.; Córdoba, O.; Damonte, E.B.; Stortz, C.A. Fucoidans from the phaeophyta Scytosiphon lomentaria: Chemical analysis and antiviral activity of the galactofucan component. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 478, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokofjeva, M.M.; Imbs, T.I.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Spirin, P.V.; Horn, S.; Fehse, B.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Prassolov, V.S. Fucoidans as potential inhibitors of HIV-1. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3000–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, S.; Menon, T.; Hanna, L.E.; Suresh, V.; Sathuvan, M.; Manikannan, M. In vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of fucoidan from Sargassum swartzii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo-Gonzalez, R.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Mendoza-Gamboa, E.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. In vitro characterization of the antiviral activity of fucoidan from Cladosiphon okamuranus against Newcastle Disease Virus. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Nakano, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Kanekiyo, K.; Hayashi, T. Defensive effects of a fucoidan from brown alga Undaria pinnatifida against herpes simplex virus infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-B.; Hayashi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T. Novel antiviral fucoidan from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida (Mekabu). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, E.A.; Falshaw, R.; Carnachan, S.M.; Kern, E.R.; Prichard, M.N. Virucidal activity of polysaccharide extracts from four algal species against herpes simplex virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 83, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidari, K.I.; Takahashi, N.; Arihara, M.; Nagaoka, M.; Morita, K.; Suzuki, T. Structure and anti-denguevirus activity of sulfated polysaccharide from a marine alga. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hao, C.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, G.; Shan, X.; Tai, W.; Yu, G. Inhibition of influenza A virus infection by fucoidan targeting viral neuraminidase and cellular EGFR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanniyasi, E.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Anbalagan, M.M.; Raj, P.P.; Gopal, R.K. In vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of the bioactive compound extracted and purified from two different marine macroalgae (seaweeds) (Dictyota bartayesiana J.V.Lamouroux and Turbinaria decurrens Bory). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofeed, J.; Deyab, M.; Mohamed, A.; Moustafa, M.; Negm, S.; El-Bilawy, E. Antimicrobial activities of three seaweeds extract against some human viral and bacterial pathogens. Biocell 2022, 46, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, M.; Mahmoud, R.; El-Senousy, W.; Ibrahim, M.; El-Taweel, G.; Ali, G. Antiviral and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A.; Cravotto, G. Green extraction of natural products: Concept and principles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green chemistry. Frontiers 1998, 640, 850. [Google Scholar]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.; Cardoso, S.M. Phycochemical constituents and biological activities of Fucus spp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important determinants for fucoidan bioactivity: A critical review of structure-function relations and extraction methods for fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, K.; Medeiros, V.; Queiroz, L.; Abreu, L.; Rocha, H.; Ferreira, C.; Jucá, M.; Aoyama, H.; Leite, E. Inhibition of reverse transcriptase activity of HIV by polysaccharides of brown algae. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2008, 62, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; Muffler, K.; Hahn, T.; Rupp, S.; Finkelmeier, D.; Burger-Kentischer, A.; Ulber, R. Physicochemical and biological characterization of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus purified by dye affinity chromatography. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliyaei, N.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Mazloomi, S.M. Therapeutic activity of fucoidan and carrageenan as marine algal polysaccharides against viruses. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Lavrov, V.F.; Leneva, I.A.; Kompanets, G.G.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Nosik, M.N.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Falynskova, I.N.; Silchenko, A.S. The comparative analysis of antiviral activity of native and modified fucoidans from brown algae Fucus evanescens in vitro and in vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, J.B.; Crawford, S.E.; Estes, M.K.; Venkataram Prasad, B.V. Rotavirus Proteins: Structure and Assembly. In Reoviruses: Entry, Assembly and Morphogenesis; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Roy, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 189–219. [Google Scholar]
- Isa, P.; Arias, C.F.; López, S. Role of sialic acids in rotavirus infection. Glycoconj. J. 2006, 23, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.; Kumar, S. Lectins from plants and algae act as anti-viral against HIV, influenza and coronaviruses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 12239–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C. Griffithsin, a highly potent broad-spectrum antiviral lectin from red algae: From discovery to clinical application. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fakharany, E.M.; Saad, M.H.; Salem, M.S.; Sidkey, N.M. Biochemical characterization and application of a novel lectin from the cyanobacterium Lyngabya confervoides MK012409 as an antiviral and anticancer agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, N.; Smyth, T.; Soler-Villa, A.; Fitzgerald, R.; Brunton, N. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of fractions obtained from selected Irish macroalgae species (Laminaria digitata, Fucus serratus, Gracilaria gracilis and Codium fragile). J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besednova, N.N.; Andryukov, B.G.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Fedyanina, L.N.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Shchelkanov, M.Y. Antiviral effects of polyphenols from marine algae. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzi, E.; Trybala, E.; Bergström, T.; Lindahl, U.; Spillmann, D. Structural requirement of heparan sulfate for interaction with herpes simplex virus type 1 virions and isolated glycoprotein C. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24850–24857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekblad, M. Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus Activities of Sulfomannan Oligosaccharide PI-88 and Disulfated Cyclitols. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Clinical Virology, Göteborg University, Göteborg, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Marschall, M.; Karmakar, P.; Mandal, P.; Ray, B. Focus on antivirally active sulfated polysaccharides: From structure–activity analysis to clinical evaluation. Glycobiology 2008, 19, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.-J.; Liu, G.-M.; Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, H. Antibacterial activity and mechanisms of depolymerized fucoidans isolated from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-i.; Kim, H.-J. Preparation of low molecular weight fucoidan by gamma-irradiation and its anticancer activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Ushakova, N.A.; Usov, A.I.; Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Nifantiev, N.E. Fucoidans: Pro-or antiangiogenic agents? Glycobiology 2014, 24, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-Y.; Moon, S.-Y.; Joo, H.-G. Differential effects of fucoidans with low and high molecular weight on the viability and function of spleen cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, J.A.; Jaime, L.; Santoyo, S.; Reglero, G.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibañez, E.; Señoráns, F.J. Screening of functional compounds in supercritical fluid extracts from Spirulina platensis. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Rajauria, G.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Study of the microbial diversity and antimicrobial properties of Irish edible brown seaweeds. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, F.; Cirlini, M.; Lazzi, C.; Neviani, E.; Bernini, V. Edible seaweeds and spirulina extracts for food application: In vitro and in situ evaluation of antimicrobial activity towards foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Foods 2020, 9, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornsey, I.S.; Hide, D. The production of antimicrobial compounds by British marine algae I. Antibiotic-producing marine algae. Br. Phycol. J. 1974, 9, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins Hoare, A.; Tan, S.P.; McLoughlin, P.; Mulhare, P.; Hughes, H. The screening and evaluation of Fucus serratus and Fucus vesiculosus extracts against current strains of MRSA isolated from a clinical hospital setting. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.-Y.; Jung, M.-J.; Jeong, I.-H.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawai, Y.; Kim, B.-M. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae against dental plaque bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dische, Z.; Shettles, L.B. A specific color reaction of methylpentoses and a spectrophotometric micromethod for their determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 175, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barltrop, J.A.; Owen, T.C.; Cory, A.H.; Cory, J.G. 5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4, 5-dimethylthiazolyl)-3-(4-sulfophenyl) tetrazolium, inner salt (MTS) and related analogs of 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazolyl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reducing to purple water-soluble formazans as cell-viability indicators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1991, 1, 611–614. [Google Scholar]
- Parrón, J.A.; Ripollés, D.; Navarro, F.; Ramos, S.J.; Pérez, M.D.; Calvo, M.; Sánchez, L. Effect of high pressure treatment on the antirotaviral activity of bovine and ovine dairy by-products and bioactive milk proteins. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 48, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Patton, J.T.; McDonald, S.M. Culturing, storage, and quantification of rotaviruses. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2009, 15, 15C.3.1–15C.3.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Cox, S.; Rajauria, G.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Growth inhibition of common food spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in the presence of brown seaweed extracts. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2012, 5, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fraction | Extraction Solvent | Fucoidan Content |
|---|---|---|
| (g fucoidan/100 g Extract) | ||
| Whole extract | HCl | 25.69 ± 0.91 |
| CA | 12.70 ± 0.10 | |
| Crude fucoidan | HCl | 55.08 ± 0.89 |
| CA | 47.30 ± 0.96 |
| Extraction Solvent | Fraction | Fucoidan Content |
|---|---|---|
| (g fucoidan/100 g Extract) | ||
| HCl | F1 (>300 KDa) | 63.59 ± 1.01 |
| F2 (<300 KDa) | 3.78 ± 0.31 | |
| F3 (<100 KDa) | 2.16 ± 0.03 | |
| F4 (<10 KDa) | 2.18 ± 0.02 | |
| CA | F1 (>300 KDa) | 42.74 ± 0.27 |
| F2 (<300 KDa) | 1.12 ± 0.03 | |
| F3 (<100 KDa) | 0.73 ± 0.00 | |
| F4 (<10 KDa) | 0.73 ± 0.01 |
| Bacteria | Concentration (mg mL−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 3.13 | 6.25 | |
| E. coli | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| E. coli K12 | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| S. Typhimurium | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| L. monocytogenes | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| C. jejuni | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graikini, D.; Soro, A.B.; Sivagnanam, S.P.; Tiwari, B.K.; Sánchez, L. Bioactivity of Fucoidan-Rich Extracts from Fucus vesiculosus against Rotavirus and Foodborne Pathogens. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090478
Graikini D, Soro AB, Sivagnanam SP, Tiwari BK, Sánchez L. Bioactivity of Fucoidan-Rich Extracts from Fucus vesiculosus against Rotavirus and Foodborne Pathogens. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(9):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090478
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraikini, Dimitra, Arturo B. Soro, Saravana P. Sivagnanam, Brijesh K. Tiwari, and Lourdes Sánchez. 2023. "Bioactivity of Fucoidan-Rich Extracts from Fucus vesiculosus against Rotavirus and Foodborne Pathogens" Marine Drugs 21, no. 9: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090478
APA StyleGraikini, D., Soro, A. B., Sivagnanam, S. P., Tiwari, B. K., & Sánchez, L. (2023). Bioactivity of Fucoidan-Rich Extracts from Fucus vesiculosus against Rotavirus and Foodborne Pathogens. Marine Drugs, 21(9), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090478