Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates
Abstract
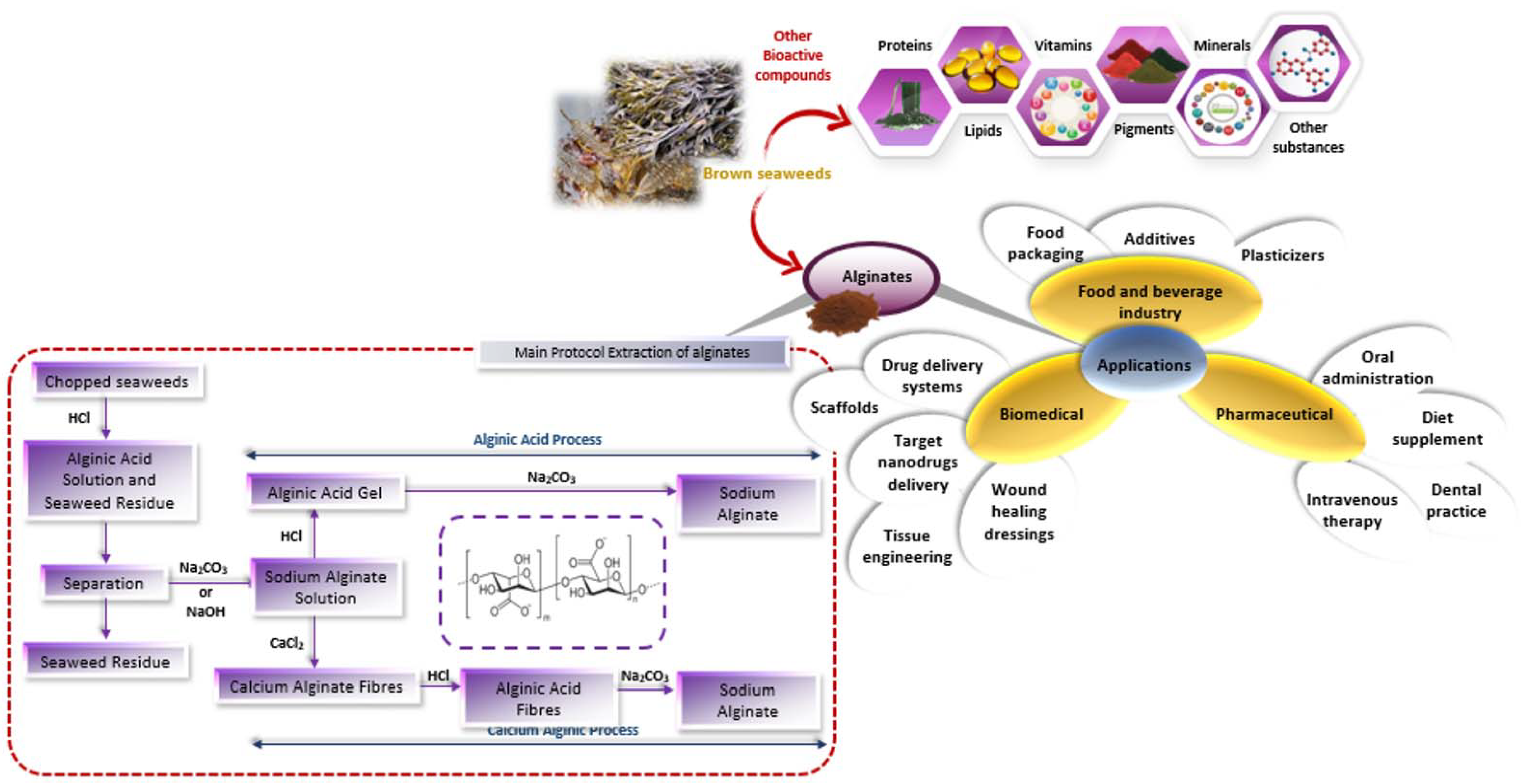
:1. Introduction
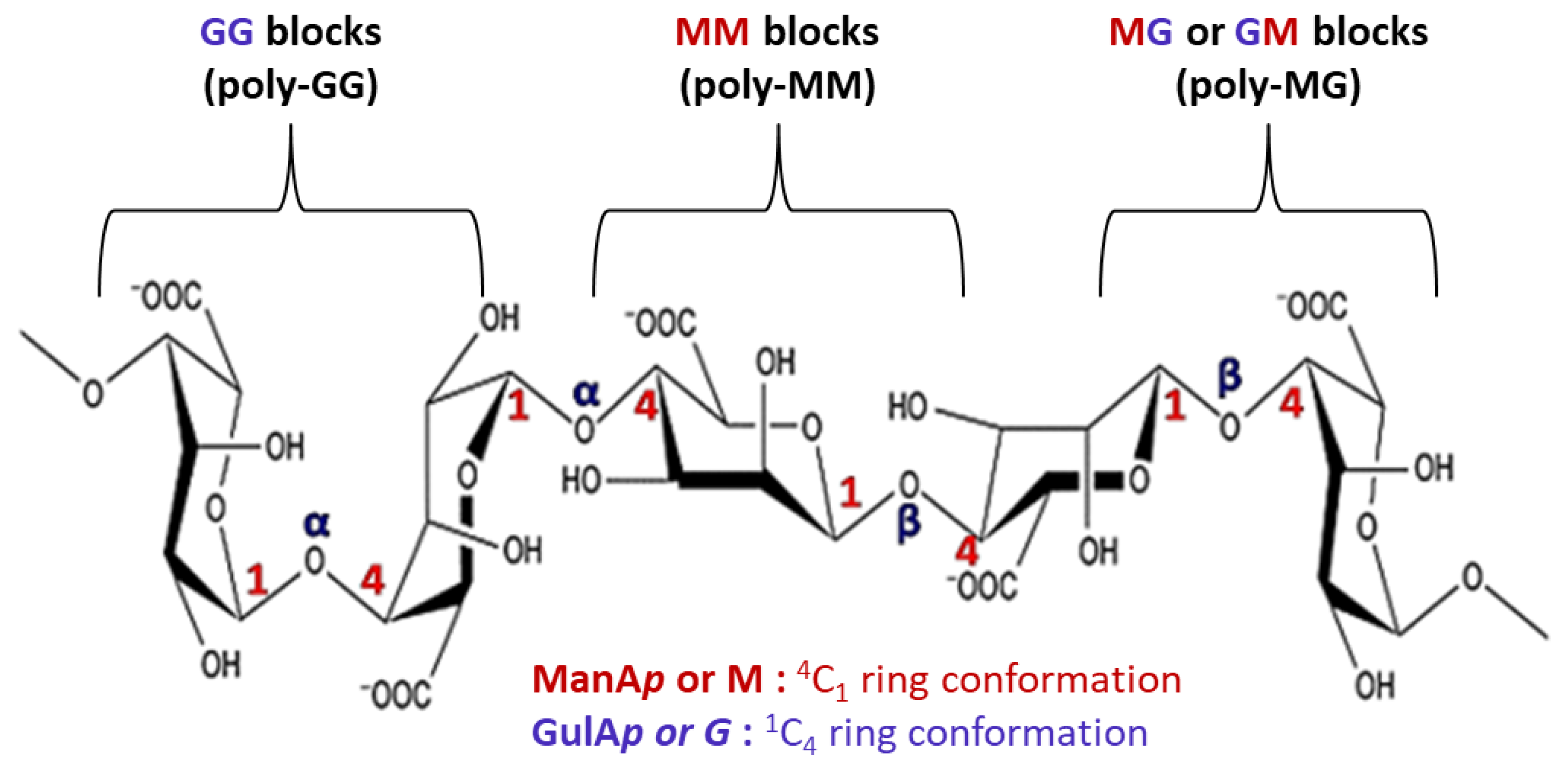
2. Molecular Structure of Alginate
3. Modification of Alginate by Processing Methods
4. Physical Properties of Alginate Gel
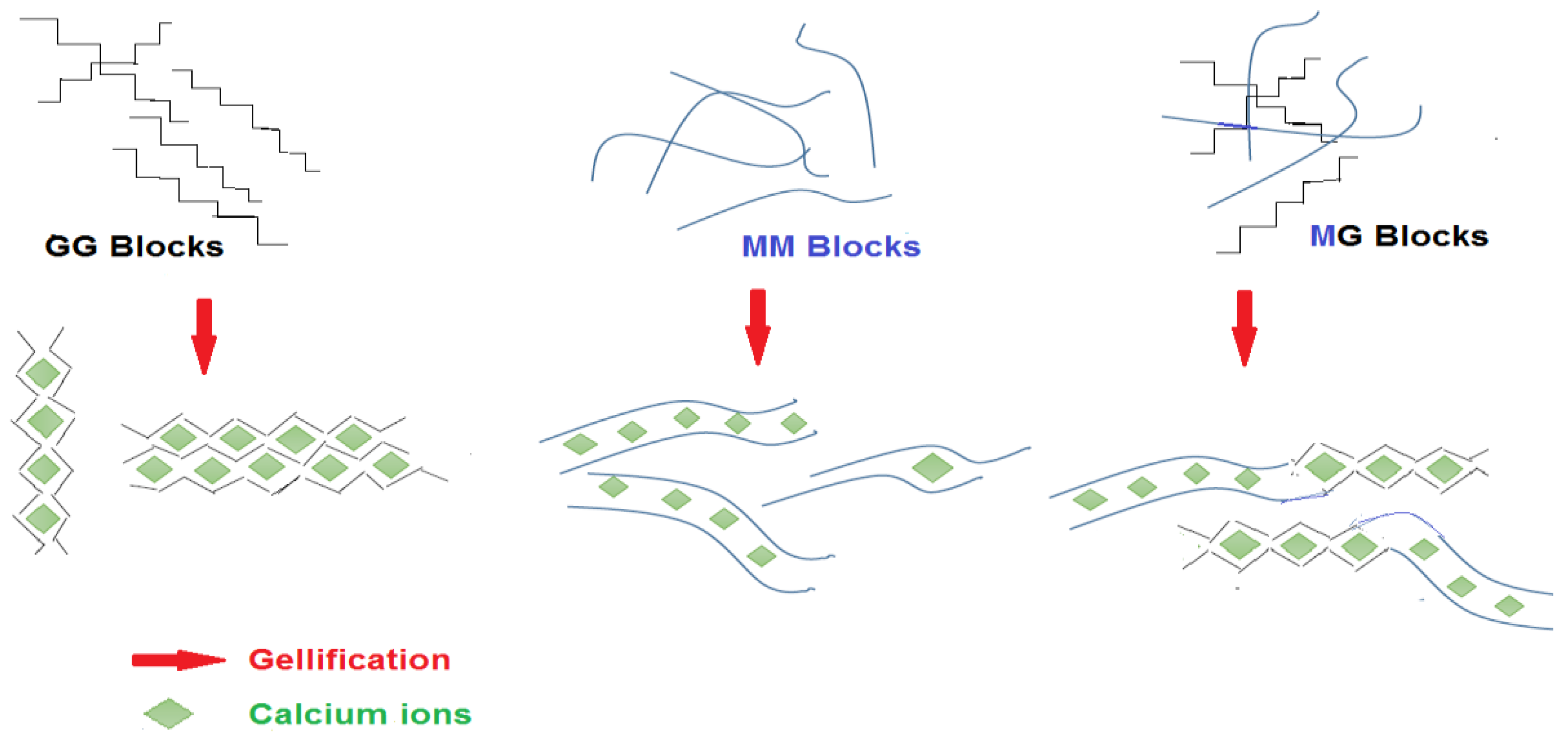
4.1. Gel Formation
4.2. Gel Power
4.3. Rheology of Alginate Gels
4.4. Porosity and Permeability
4.5. Release Characteristics
4.6. Syneresis and Swelling
4.7. Effects of pH
4.8. Rheology of Alginate Solutions
5. Applications
5.1. Food Applications
5.2. Non-Food Applications
5.3. Pharmaceutical Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirst, E.L.; Jones, J.K.N.; Jones, W.O. 389. The Structure of Alginic Acid. Part I. J. Chem. Soc. (Resumed) 1939, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, H.; Srebnik, S. Structural Characterization of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Alginate. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajouei, R.A.; Keramat, J.; Hamdami, N.; Ursu, A.-V.; Delattre, C.; Laroche, C.; Gardarin, C.; Lecerf, D.; Desbrières, J.; Djelveh, G.; et al. Extraction and Characterization of an Alginate from the Iranian Brown Seaweed Nizimuddinia zanardini. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, C.G.; Pérez Lambrecht, M.V.; Lozano, J.E.; Rinaudo, M.; Villar, M.A. Influence of the Extraction–Purification Conditions on Final Properties of Alginates Obtained from Brown Algae (Macrocystis Pyrifera). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutor Ale, M.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidans from Brown Seaweeds: An Update on Structures, Extraction Techniques and Use of Enzymes as Tools for Structural Elucidation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrinčić, A.; Balbino, S.; Zorić, Z.; Pedisić, S.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Elez Garofulić, I.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Advanced Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Brown Algal Polysaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponce, N.M.A.; Stortz, C.A. A Comprehensive and Comparative Analysis of the Fucoidan Compositional Data Across the Phaeophyceae. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 556312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Ursu, A.-V.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Trica, B.; Abdelkafi, S.; Djelveh, G.; Dobre, T.; Michaud, P. Production, Extraction and Characterization of Alginates from Seaweeds. In Handbook of Algal Technologies and Phytochemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, F.; Fantozzi, P.; Mancini, F.; Moresi, M. Optimal Conditions for Alginate Production by Azotobacter vinelandii. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1995, 17, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.; Han, E.J.; Ahn, G. Alginate-Based Nanomaterials: Fabrication Techniques, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertagnolli, C.; Espindola, A.P.D.M.; Kleinübing, S.J.; Tasic, L.; Da Silva, M.G.C. Sargassum filipendula Alginate from Brazil: Seasonal Influence and Characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Rivers, A.; Stuckey, D.C.; Ward, K. Alginate Extraction from Sargassum Seaweed in the Caribbean Region: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, B.H.A.; Valla, S. Bacterial Alginates: Biosynthesis and Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 48, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.S.M.D.; Kumar, N.S. Carbohydrate Constituents of the Marine Algae of Sri Lanka Part Ii. Composition and Sequence of Uronate Residues in Alginates from Some Brown Seaweeds. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 1984, 12, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari-Chmayssem, N.; Taha, S.; Mawlawi, H.; Guégan, J.-P.; Jeftić, J.; Benvegnu, T. Extracted and Depolymerized Alginates from Brown Algae Sargassum Vulgare of Lebanese Origin: Chemical, Rheological, and Antioxidant Properties. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1915–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedlock, D.J.; Fasihuddin, B.A.; Phillips, G.O. Characterisation of Alginates from Malaysia. In Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry; Phillips, G.O., Wedlock, D.J., Peter, A., Eds.; Williams: Venditch, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Minghou, J.; Yujun, W.; Zuhong, X.; Yucai, G. Studies on the M:G Ratios in Alginate. In Eleventh International Seaweed Symposium; Bird, C.J., Ragan, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 554–556. ISBN 978-94-009-6562-1. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, B.; Salem, D.M.S.A.; Sallam, M.A.E.; Mishrikey, M.M.; Beltagy, A.I. Characterization of the Alginates from Algae Harvested at the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behairy, A.K.A.; El-Sayed, M.M. Biochemical Composition of Some Marine Brown Algae from Jeddah Coast, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 1983, 12, 200–201. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T.A.; Ramirez, M.; Mucci, A.; Larsen, B. Extraction, Isolation and Cadmium Binding of Alginate from Sargassum spp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubia, M.; Payri, C.; Deslandes, E. Alginate, Mannitol, Phenolic Compounds and Biological Activities of Two Range-Extending Brown Algae, Sargassum Mangarevense and Turbinaria Ornata (Phaeophyta: Fucales), from Tahiti (French Polynesia). J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-N.; Chiang, Y.-M. Studies on Algin from Brown Algae of Taiwan, I. Estimation of the Yield and Quality of Algin. Acta Oceanogr. Taiwanica 1977, 6, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathi, S.J.; Babu, B.; Rengasamy, R. Seasonal Studies on the Alginate and Its Biochemical Composition I: Sargassum Polycystum (Fucales), Phaeophyceae. Phycol. Res 2003, 51, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, D. A Comprehensive Analysis of Alginate Content and Biochemical Composition of Leftover Pulp from Brown Seaweed Sargassum wightii. Algal Res. 2017, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.T.; Ajalloueian, F.; Meyer, A.S. Characterization of Alginates from Ghanaian Brown Seaweeds: Sargassum spp. and Padina spp. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamanantoanina, H.; Rinaudo, M. Characterization of the Alginates from Five Madagascan Brown Algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Delattre, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Desbrières, J.; Le Cerf, D.; Gardarin, C.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P.; Pierre, G. Structural Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from the Tunisian Brown Seaweed Cystoseira compressa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrid, R.; Bentiss, F.; Ali, R.A.B.; Belattmania, Z.; Zarrouk, A.; Eddaoui, A.; Reani, A.; Sabour, B. Potential uses of the brown seaweed Cystoseira humilis biomass: 1- Sodium alginate yield, FT-IR, 1H NMR and rheological analyses. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 613–620. [Google Scholar]
- Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M. Characterization of Polysaccharides Extracted from Brown Seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertah, M.; Belfkira, A.; Taourirte, M.; Brouillette, F. Extraction and Characterization of Sodium Alginate from Moroccan Laminaria Digitata Brown Seaweed. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3707–S3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgiou, S.K.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Katsaros, F.K. Calcium Alginate Beads from Laminaria Digitata for the Removal of Cu+2 and Cd+2 from Dilute Aqueous Metal Solutions. Desalination 2008, 224, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.R.; Sousa, A.P.A.; Silva Filho, E.A.T.; Melo, D.F.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; de Paula, R.C.M.; Lima, M.G.S. Extraction and Physicochemical Characterization of Sargassum Vulgare Alginate from Brazil. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenoradosoa, T.A.; Ali, G.; Delattre, C.; Laroche, C.; Petit, E.; Wadouachi, A.; Michaud, P. Extraction and Characterization of an Alginate from the Brown Seaweed Sargassum Turbinarioides Grunow. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Llanes, F.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. Metal Selectivity of Sargassum Spp. and Their Alginates in Relation to Their α- l -Guluronic Acid Content and Conformation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate Gel Particles—A Review of Production Techniques and Physical Properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellimi, S.; Younes, I.; Ayed, H.B.; Maalej, H.; Montero, V.; Rinaudo, M.; Dahia, M.; Mechichi, T.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Structural, Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Sodium Alginate Isolated from a Tunisian Brown Seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benslima, A.; Sellimi, S.; Hamdi, M.; Nasri, R.; Jridi, M.; Cot, D.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Zouari, N. The Brown Seaweed Cystoseira Schiffneri as a Source of Sodium Alginate: Chemical and Structural Characterization, and Antioxidant Activities. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai-yu, Z.; Yan-xia, Z.; Xiao, F.; Li-jun, H. Effects of Composition and Structure of Alginates on Adsorption of Divalent Metals. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 1994, 12, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Yan, Q.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Jiang, Z. Alginate Oligosaccharides: Production, Biological Activities, and Potential Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1859–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawada, A.; Hiura, N.; Tajima, S.; Takahara, H. Alginate Oligosaccharides Stimulate VEGF-Mediated Growth and Migration of Human Endothelial Cells. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1999, 291, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, A.; Song, S. Advances in Research on the Bioactivity of Alginate Oligosaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokose, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Growth-Promoting Effect of Alginate Oligosaccharides on a Unicellular Marine Microalga, Nannochloropsis oculata. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Du, Y.; He, A.; Sun, K. The Promoting Effects of Alginate Oligosaccharides on Root Development in Oryza Sativa L. Mediated by Auxin Signaling. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Larsen, B.; Smidsrod, O.; Munch-Petersen, J. The Degradation of Alginates at Different PH Values. Acta Chem. Scand. 1963, 17, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Xie, Y.-J.; He, W. Research Progress on Chemical Modification of Alginate: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatbar, M.; Meena, R.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Microwave Assisted Rapid Method for Hydrolysis of Sodium Alginate for M/G Ratio Determination. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Molecular Weight Distribution, Rheological Property and Structural Changes of Sodium Alginate Induced by Ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Ahmed, E.; Ismaiel, A.; Ashokkumar, M.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Ultrasonic Emulsification: An Overview on the Preparation of Different Emulsifiers-Stabilized Emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abka Khajouei, R.; Keramat, J.; Hamdami, N.; Ursu, A.-V.; Delattre, C.; Gardarin, C.; Lecerf, D.; Desbrières, J.; Djelveh, G.; Michaud, P. Effect of High Voltage Electrode Discharge on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Alginate Extracted from an Iranian Brown Seaweed (Nizimuddinia Zanardini). Algal Res. 2021, 56, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villay, A.; Lakkis de Filippis, F.; Picton, L.; Le Cerf, D.; Vial, C.; Michaud, P. Comparison of Polysaccharide Degradations by Dynamic High-Pressure Homogenization. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresi, M.; Bruno, M.; Parente, E. Viscoelastic Properties of Microbial Alginate Gels by Oscillatory Dynamic Tests. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Chen, W.; Mei, Y.; Yun, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Effects of Molecular Weight and Guluronic Acid/Mannuronic Acid Ratio on the Rheological Behavior and Stabilizing Property of Sodium Alginate. Molecules 2019, 24, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belalia, F.; Djelali, N.-E. Rheological properties of sodium alginate solutions. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2014, 59, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bennacef, C.; Desobry-Banon, S.; Probst, L.; Desobry, S. Advances on Alginate Use for Spherification to Encapsulate Biomolecules. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.E.; Silva, P.; Alario, M.M.; Pastrana, L.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Effect of Alginate Molecular Weight and M/G Ratio in Beads Properties Foreseeing the Protection of Probiotics. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mørch, Ý.A.; Donati, I.; Strand, B.L.; Skjåk-Bræk, G. Effect of Ca2+, Ba2+, and Sr2+ on Alginate Microbeads. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wloka, M.; Rehage, H.; Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. Rheological Properties of Viscoelastic Biofilm Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Comparison to the Behavior of Calcium Alginate Gels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 282, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Thacker, A.; Sperger, D.M.; Boni, R.L.; Buckner, I.S.; Velankar, S.; Munson, E.J.; Block, L.H. Relevance of Rheological Properties of Sodium Alginate in Solution to Calcium Alginate Gel Properties. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, B.E.; Bjørnstad, J.; Pettersen, E.O.; Tønnesen, H.H.; Melvik, J.E. Rheological Characterization of an Injectable Alginate Gel System. BMC Biotechnol. 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donati, I.; Paoletti, S. Material Properties of Alginates. In Alginates: Biology and Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Microbiology Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–53. ISBN 978-3-540-92679-5. [Google Scholar]
- Draget, K.I.; Gåserød, O.; Aune, I.; Andersen, P.O.; Storbakken, B.; Stokke, B.T.; Smidsrød, O. Effects of Molecular Weight and Elastic Segment Flexibility on Syneresis in Ca-Alginate Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrabie, M.D.; Kendall, W.F.; Opara, E.C. Effect of Alginate Composition and Gelling Cation on Microbead Swelling. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, V.; Fassihi, R. In Vitro Release Modulation from Crosslinked Pellets for Site-Specific Drug Delivery to the Gastrointestinal Tract: I. Comparison of PH-Responsive Drug Release and Associated Kinetics. J. Control. Release 1999, 59, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, S.; Jain, P.; Kumar, D. Alginates: Properties and Applications. In Polysaccharides; Inamuddin, Ahamed, M.I., Boddula, R., Altalhi, T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 399–422. ISBN 978-1-119-71141-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Flow Behavior, Thixotropy and Dynamical Viscoelasticity of Sodium Alginate Aqueous Solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Phillips, G.O. Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 2—Production, Properties and Uses of Alginates. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/x5822e/x5822e04.htm (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Lapasin, R. Rheology of Industrial Polysaccharides: Theory and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J. Food Additives Databook. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, R.; Sanchez, C.C.; Pilosof, A.M.R.; Patino, J.M.R. Interfacial and Foaming Properties of Prolylenglycol Alginates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 36, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels: A Review of Patents and Commercial Products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, M.; Kelly, J. Pressure Ulcer Treatment in a Patient with Spina Bifida. Nurs. Stand. 2014, 28, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruigh, A.; Roman, S.; Chen, J.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Kahrilas, P.J. Gaviscon Double Action Liquid (Antacid & Alginate) Is More Effective than Antacid in Controlling Post-Prandial Oesophageal Acid Exposure in GERD Patients: A Double-Blind Crossover Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruskin, E.; Doll, B.A.; Futrell, F.W.; Schmitz, J.P.; Hollinger, J.O. Demineralized Bone Matrix in Bone Repair: History and Use. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, L.; Weyandt, G.H.; Havlickova, B.; Matsuda, Y.; Didelot, J.-M.; Rothhaar, A.; Sobrado, C.; Szabadi, A.; Vitalyos, T.; Wiesel, P. The Diagnosis and Management of Haemorrhoidal Disease from a Global Perspective. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegari, A.; Saei, A.A. An Update to Space Biomedical Research: Tissue Engineering in Microgravity Bioreactors. BioImpacts 2012, 2, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aziz, M.S.; Salama, H.E. Developing Multifunctional Edible Coatings Based on Alginate for Active Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, E.; Villalobos-Carvajal, R.; Reyes-Parra, J.; Jara-Quijada, E.; Ruiz, C.; Andrades, P.; Gacitúa, J.; Beldarraín-Iznaga, T. Preservation of Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus) by an Alginate-Based-Coating Containing a Cinnamaldehyde Essential Oil Nanoemulsion. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, S.-W. Enhancing Safety and Quality of Shrimp by Nanoparticles of Sodium Alginate-Based Edible Coating Containing Grapefruit Seed Extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemeini, H.; Azizian, A.; Adib, H. Inhibition of Listeria Monocytogenes Growth in Turkey Fillets by Alginate Edible Coating with Trachyspermum Ammi Essential Oil Nano-Emulsion. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 344, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molayi, R.; Ehsani, A.; Yousefi, M. The Antibacterial Effect of Whey Protein–Alginate Coating Incorporated with the Lactoperoxidase System on Chicken Thigh Meat. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Artiga-Artigas, M.; Acevedo-Fani, A.; Martín-Belloso, O. Improving the Shelf Life of Low-Fat Cut Cheese Using Nanoemulsion-Based Edible Coatings Containing Oregano Essential Oil and Mandarin Fiber. Food Control 2017, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senturk Parreidt, T.; Müller, K.; Schmid, M. Alginate-Based Edible Films and Coatings for Food Packaging Applications. Foods 2018, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brownlee, I.A.; Seal, C.J.; Wilcox, M.; Dettmar, P.W.; Pearson, J.P. Applications of Alginates in Food. In Alginates: Biology and Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Microbiology Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 211–228. ISBN 978-3-540-92679-5. [Google Scholar]
- Comaposada, J.; Gou, P.; Marcos, B.; Arnau, J. Physical Properties of Sodium Alginate Solutions and Edible Wet Calcium Alginate Coatings. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, G.; Rodríguez, A.; Valenzuela, R.; Moreno, J.; Mella, K. Chapter 12—Alginate as a Versatile Polymer Matrix with Biomedical and Food Applications. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering; Grumezescu, V., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 323–350. ISBN 978-0-12-818415-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghita Puscaselu, R.; Lobiuc, A.; Dimian, M.; Covasa, M. Alginate: From Food Industry to Biomedical Applications and Management of Metabolic Disorders. Polymers 2020, 12, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüero, L.; Zaldivar-Silva, D.; Peña, L.; Dias, M.L. Alginate Microparticles as Oral Colon Drug Delivery Device: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, P.; Kandasubramanian, B. Review of Alginate-Based Hydrogel Bioprinting for Application in Tissue Engineering. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reakasame, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Oxidized Alginate-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-González, A.C.; Téllez-Jurado, L.; Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.M. Alginate Hydrogels for Bone Tissue Engineering, from Injectables to Bioprinting: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Bhatnagar, I.; Manivasagan, P.; Kang, K.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Alginate Composites for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wróblewska-Krepsztul, J.; Rydzkowski, T.; Michalska-Pożoga, I.; Thakur, V.K. Biopolymers for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications: Recent Advances and Overview of Alginate Electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Fosse, H.K.; Li, K.; Chauton, M.S.; Vadstein, O.; Reitan, K.I. Influence of Nitrogen Limitation on Lipid Accumulation and EPA and DHA Content in Four Marine Microalgae for Possible Use in Aquafeed. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Puci, A.; Ciosek, P.; Winnicka, K. Alginate: Current Use and Future Perspectives in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 7697031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, M.; Abrahim, B.; Veiga, F.; Seiça, R.; Cabral, L.M.; Arnaud, P.; Andrade, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.J. Preparation Methods and Applications behind Alginate-Based Particles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K.; Kurakula, M.; Hoda, M.N. Chapter 6—Alginate Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. In Alginates in Drug Delivery; Nayak, A.K., Hasnain, M.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 129–152. ISBN 978-0-12-817640-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Li, B.; Gu, Q.; Fang, Y.; Xing, H. Preliminary Studies on the Chemical Characterization and Antihyperlipidemic Activity of Polysaccharide from the Brown Alga Sargassum fusiforme. In Proceedings of the Asian Pacific Phycology in the 21st Century: Prospects and Challenges, Hong Kong, China, 21–25 June 1999; Ang, P.O., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavendran, H.R.B.; Sathivel, A.; Devaki, T. Effect of Sargassum Polycystum (Phaeophyceae)-Sulphated Polysaccharide Extract against Acetaminophen-Induced Hyperlipidemia during Toxic Hepatitis in Experimental Rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 276, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, M.; Allahgholi, L.; Sardari, R.R.R.; Hreggviðsson, G.O.; Nordberg Karlsson, E. Extraction and Modification of Macroalgal Polysaccharides for Current and Next-Generation Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Król, Ż.; Marycz, K.; Kulig, D.; Marędziak, M.; Jarmoluk, A. Cytotoxicity, Bactericidal, and Antioxidant Activity of Sodium Alginate Hydrosols Treated with Direct Electric Current. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, E.A.; Mooney, D.J. Effects of VEGF Temporal and Spatial Presentation on Angiogenesis. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Seaweed Species | Place of Collection | Extraction Yield | M/G Ratio | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sargassum asperifolium | Egyptian Red Sea coast | 12.0 | 0.69 | [18] |
| Sargassum dentifolium | Egyptian Red Sea coast | 3.3 | 0.52 | [18] |
| Sargassum duplicatum | Saudi Arabia | 32.5 | 0.86 | [19] |
| Sargassum fluitans | Sargasso Sea of the north-west Atlantic Ocean | 21.1–24.5 | 0.52–0.57 | [20] |
| Sargassum hemiphyllum | Guangdong Province | 23.0 | 1.06 | [17] |
| Sargassum henslowianum | Guangdong Province | 17.8 | 0.82 | [17] |
| Sargassum horneri | Dalian | 11.5 | 0.64 | [17] |
| Sargassum ilicifolium | Egyptian Red Sea coast | 4.3–17.2 | 0.25–0.82 | [18] |
| Sargassum mangarevense | Tahiti, French Polynesia | 9.3 ± 1.7 | 1.42 ± 0.24 | [21] |
| Turbinaria ornata | Tahiti, French Polynesia | 19.2 ± 1.3 | 1.25 ± 0.20 | [21] |
| Turbinaria ornata | Hainan Island | 20.6 | 0.89 | [17] |
| Sargassum mcclurei | Guangdong Province | 23.6 | 1.4 | [17] |
| Sargassum microphyllum | Taiwan | 20.3–23.5 | - | [22] |
| Sargassum miyabei | Qingdao | 10.5–18.1 | 0.62–1.10 | [17] |
| Sargassum oligocystum | Australia | 16.3–20.5 | 0.49–0.62 | [20] |
| Sargassum pallidum | Qingdao | 10.4 | 1.26 | [17] |
| Sargassum patens | Guangdong Province | 16.0 | 1.59 | [17] |
| Sargassum polycystum | South India | 17.1–27.6 | 0.56–0.74 | [23] |
| Sargassum siliquastrum | Guangdong Province | 18.1 | 1.13 | [17] |
| Sargassum thunbergii | Qingdao | 12.8 | 0.78 | [17] |
| Sargassum vulgare | Saudi Arabia | 30.2 | 0.71 | [19] |
| Turbinaria murrayana | Saudi Arabia | 40.1 | 1.09 | [19] |
| Sargassum wightii | India | 21.1–33.1 | - | [24] |
| Sargassum natans | Ghana | 23 ± 1.6 | 0.6 | [25] |
| Sargassum vulgare | Ghana | 17 ± 4.4 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | [25] |
| Padina gymnospora | Ghana | 16 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | [25] |
| Padina antillarum | Ghana | 22 ± 1.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | [25] |
| Zonaria sp. | Madagascar | 10.2–30.0 | 0.41 | [26] |
| Chnoospora sp. | Madagascar | 9.2- 50.8 | 0.51 | [26] |
| Spatoglossum sp. | Madagascar | 9.7–17.4 | 0.75 | [26] |
| Spatoglossum sp. | Madagascar | 22.0–30.5 | 0.68–1.09 | [26] |
| Cystoseira compressa | Tunisia | 21.65 ± 1.5 | 0.77 | [27] |
| Cystoseira humilis | Morocco | 5.43–19.21 | 1.46 | [28] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | Quebec | 16.2 ± 3.2 | 1.17 | [29] |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Quebec | 24.0 ± 0.3 | 0.61 | [29] |
| Saccharina longicruris | Quebec | 20.0 ± 1.1 | 0.79 | [29] |
| Laminaria digitata | Morocco | 35.2 − 51.8 | 1.12 | [30] |
| Macrocystis pyrifera | Argentina | 33 | 1.17 | [4] |
| Laminaria digitata | France Atlantic ocean | - | 1.5 | [31] |
| Sargassum vulgare | Brazil | - | 1.27 | [32] |
| Sargassum turbinarioides Grunow | Madagascar | 10 | 0.94 | [33] |
| Sargassum thunbergii | Korea | - | 0.53 | [34] |
| Source | 1 FG | 2 FM | 3 M/G | 4 FGG | 5 FMM | 6 FMG | 6 FGM | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. natans | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.09 | [12] |
| C. schiffneri | 0.91 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.88 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | [37] |
| C. compressa | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.77 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | [27] |
| N. zanardini | 0.47 | 0.53 | 1.11 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.06 | [3] |
| L. digitata | 0.47 | 0.53 | 1.12 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.06 | [30] |
| C. humilis | 0.41 | 0.59 | 1.46 | 0.21 | 0.40 | 0.19 | 0.19 | [28] |
| F. vesiculosus | 0.46 | 0.54 | 1.17 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.21 | [29] |
| S. longicruris | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.79 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.33 | [29] |
| A. nodosum | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.61 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.30 | [29] |
| S. vulgare | 0.44 | 0.56 | 1.27 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.02 | [32] |
| S. fluitans | 0.46 | 0.54 | 1.18 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | [20] |
| S. oligocystum | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.14 | [20] |
| C. myrica | 0.69 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.59 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.10 | [18] |
| C. trinode | 0.63 | 0.37 | 0.59 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.13 | [18] |
| S. latifolium | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.82 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.04 | [18] |
| S. polycystum | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.10 | [34] |
| S. filipendula | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.76 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.16 | [33] |
| L. japonica | 0.35 | 0.65 | 1.86 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.14 | [38] |
| Product | Company | Route of Administration | Main Ingredients | Description | Indications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purilon Gel® gel | Coloplast | Dermal | Calcium alginate and sodium carboxymethylcellulose | Provides moist environment at wound surface | Indicated in conjunction with a secondary dressing for necrotic and sloughy wounds and first and second degree burns | [71] |
| Algivon® dressing | Advancis Medical | Dermal | Calcium alginate dressing impregnated with Manuka honey | Binds of exudate, regeneration | Sloughy, necrotic, and malodorous wounds | [72] |
| Gaviscon® Double Action Liquid | Reckitt Benckiser Healthcare Hull, UK | Oral | 0.25 g sodium alginate, 162.5 mg calcium carbonate, and 106.5 mg sodium bicarbonate per 5 mL | Creates a mechanical barrier between the stomach and the esophagus; regenerates mucous membranes of the esophagus and ensures its protection; accelerates gastric movement | Adult reflux treatment | [73] |
| Progenix putty® | Medtronic Spinal & Biologics | Periodontal | Demineralised bone matrix in type-1 bovine collagen and sodium alginate | Regeneration, complementation of bone losses; periodontal diseases | Gaps or bony voids of the skeletal system | [74] |
| Natalsid® suppositories | STADA | Rectal | Sodium alginate | Anti-inflammatory local action | Chronic haemorrhoids, proctosigmoiditis, and chronic anal fissures after surgical interventions in the area of the rectum | [75] |
| ChondroArt 3D® injection | Arkopharma | Arthroscopic | Autologous chondrocytes situated on a hydrogel scaffold built from connection of alginate and agarose | Increase production and growth of cartilage | Degenerative diseases of joints and backbones (osteochondrosis, osteoarthrosis) | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abka-khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060364
Abka-khajouei R, Tounsi L, Shahabi N, Patel AK, Abdelkafi S, Michaud P. Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(6):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060364
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbka-khajouei, Roya, Latifa Tounsi, Nasim Shahabi, Anil Kumar Patel, Slim Abdelkafi, and Philippe Michaud. 2022. "Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates" Marine Drugs 20, no. 6: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060364
APA StyleAbka-khajouei, R., Tounsi, L., Shahabi, N., Patel, A. K., Abdelkafi, S., & Michaud, P. (2022). Structures, Properties and Applications of Alginates. Marine Drugs, 20(6), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060364









