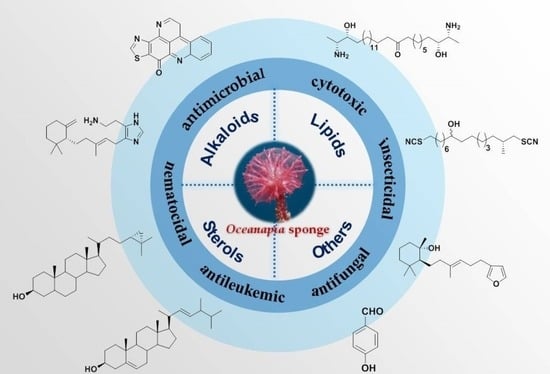
Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges of the Genus Oceanapia: Chemistry and Biological Activities
Abstract
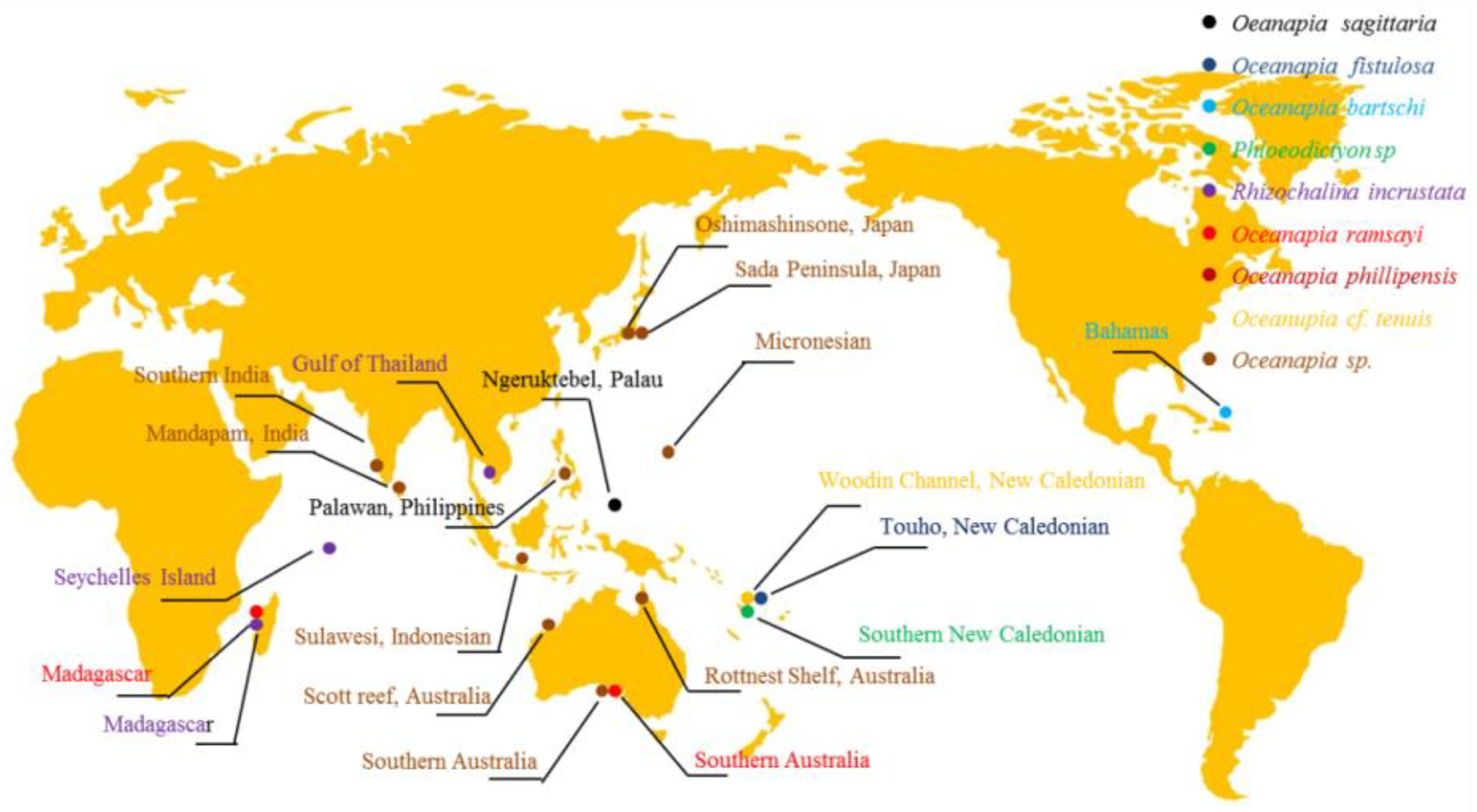
1. Introduction
2. Alkaloids
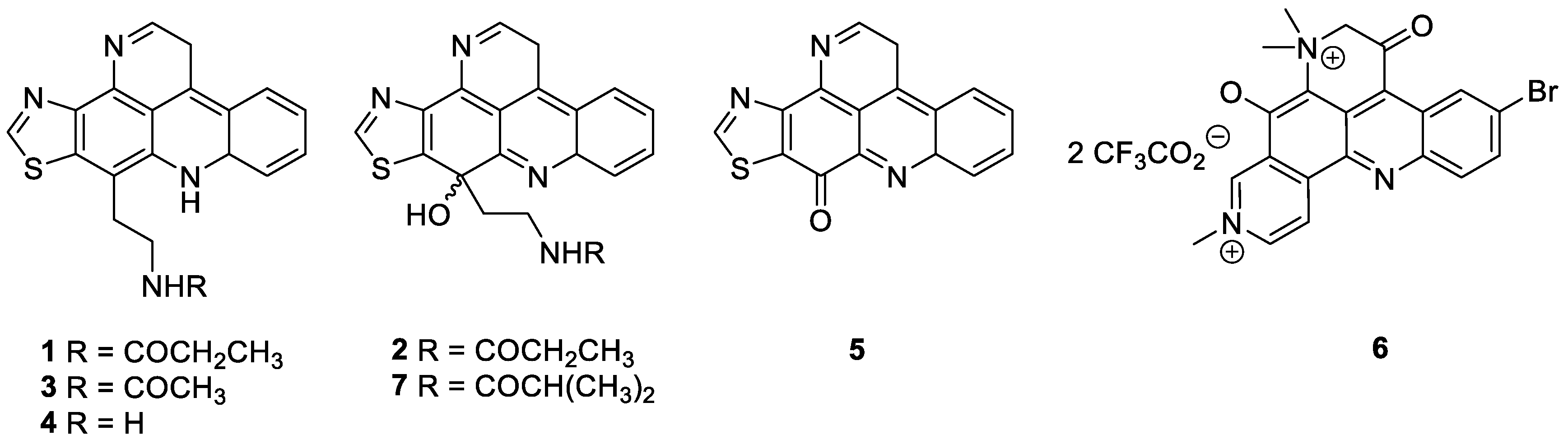
2.1. Pyridoacridine Alkaloids
2.2. Quinolizidine Alkaloids
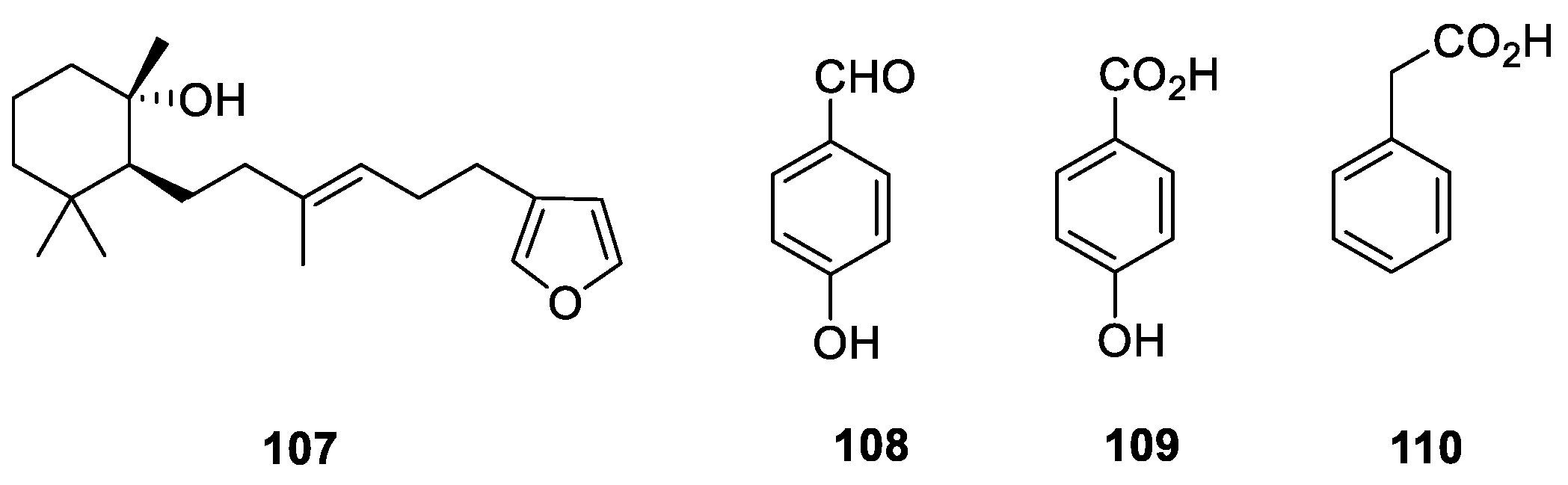
2.3. Sesquiterpene Alkaloid
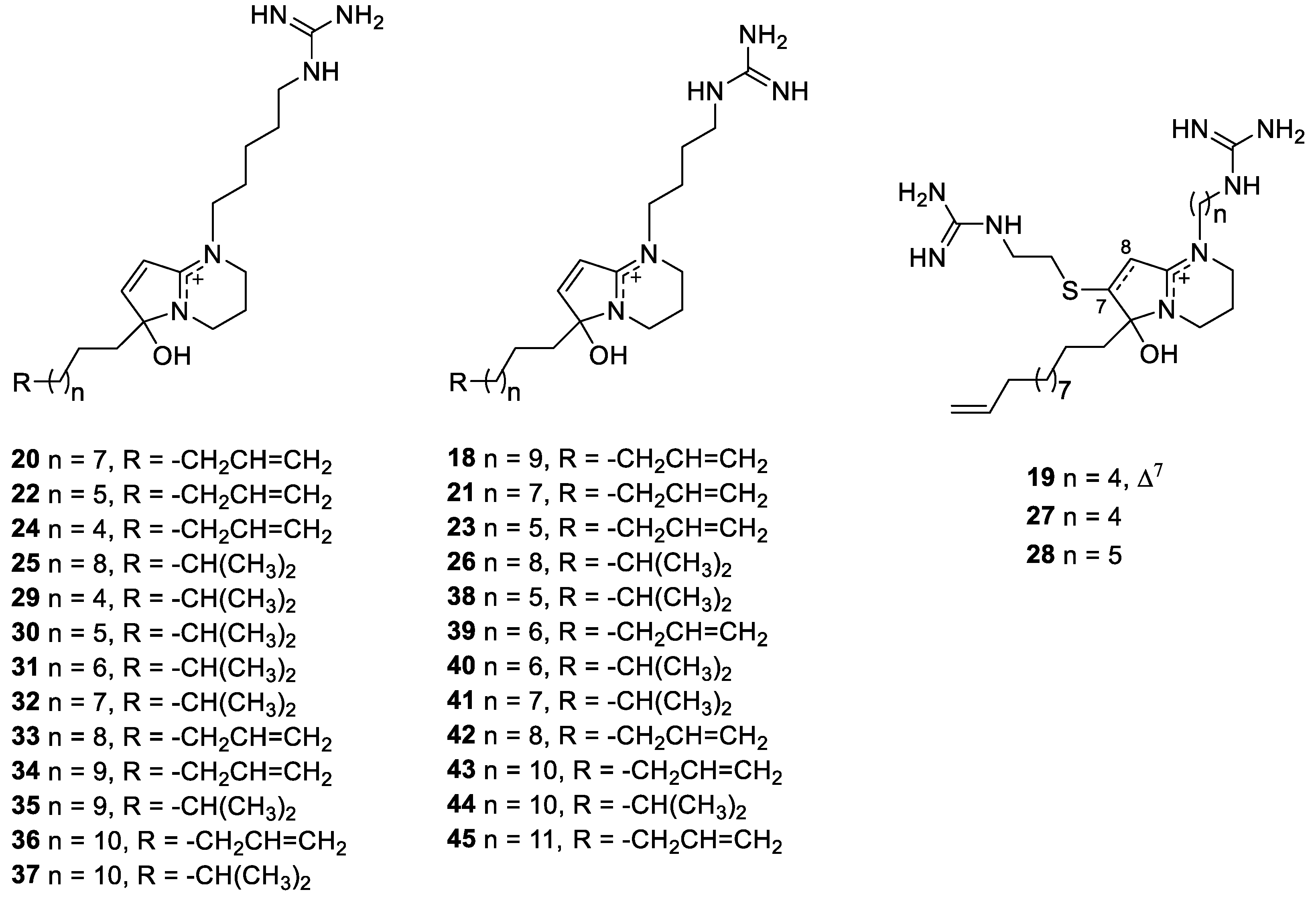
2.4. Phloeodictine Alkaloids
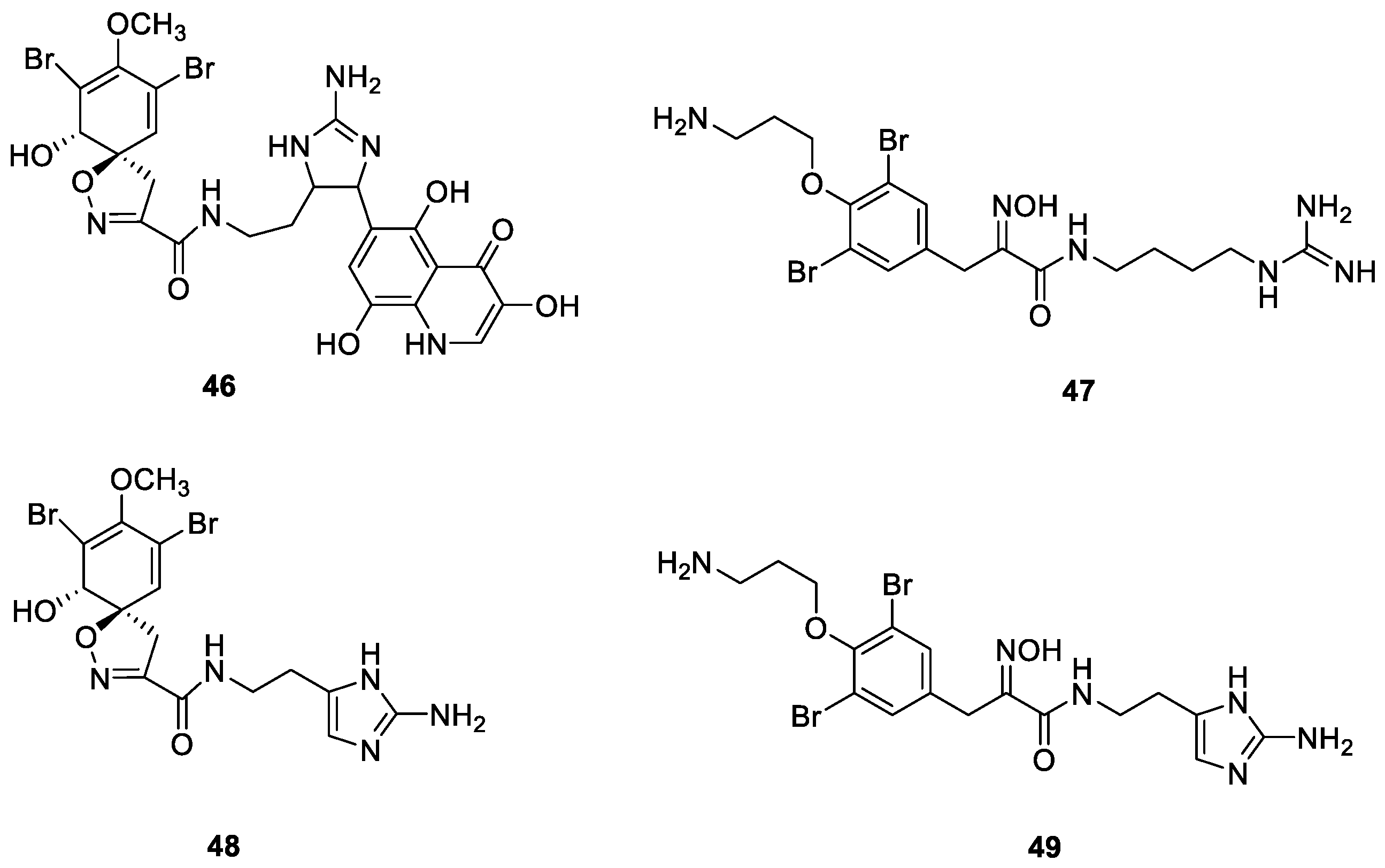
2.5. Bromotyrosine Alkaloids
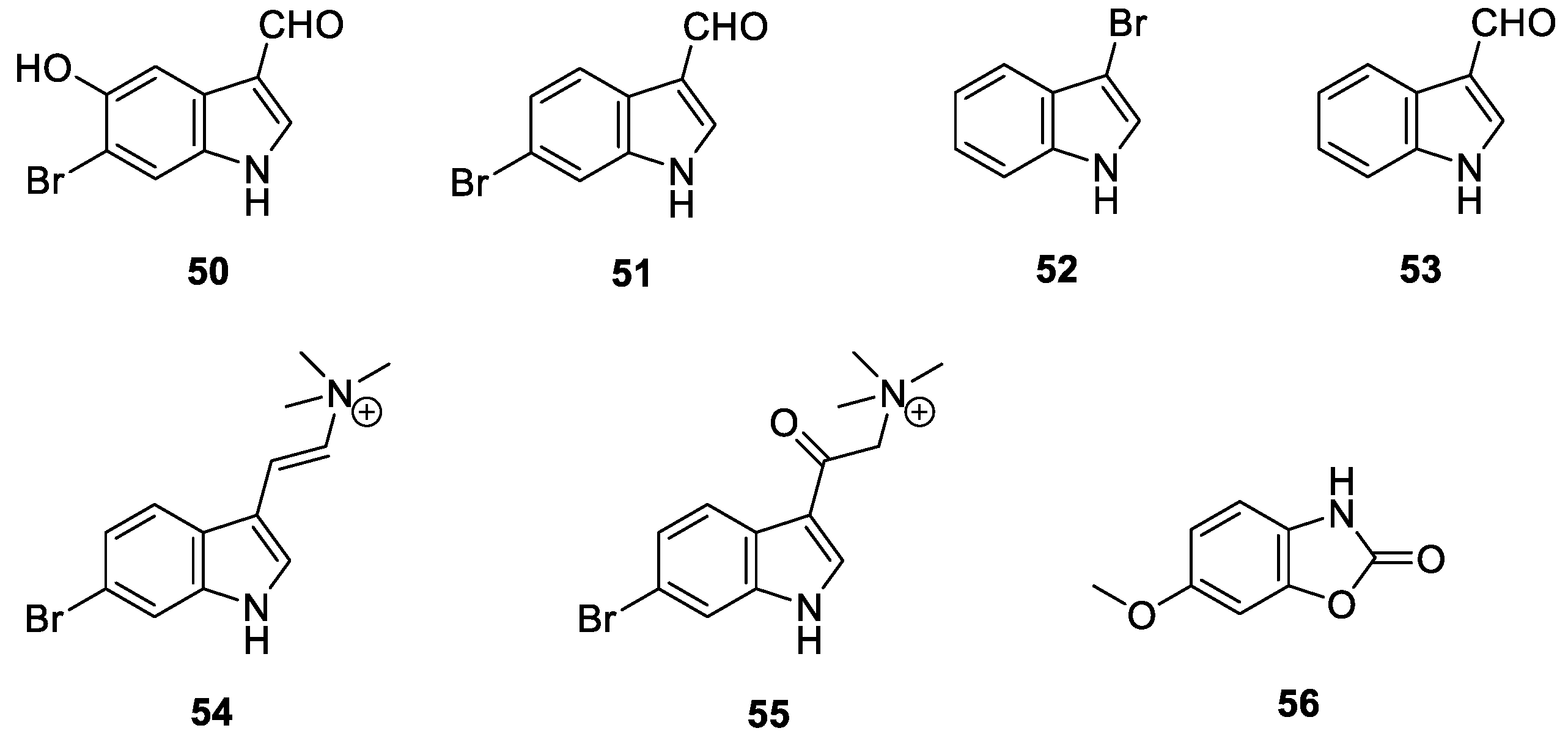
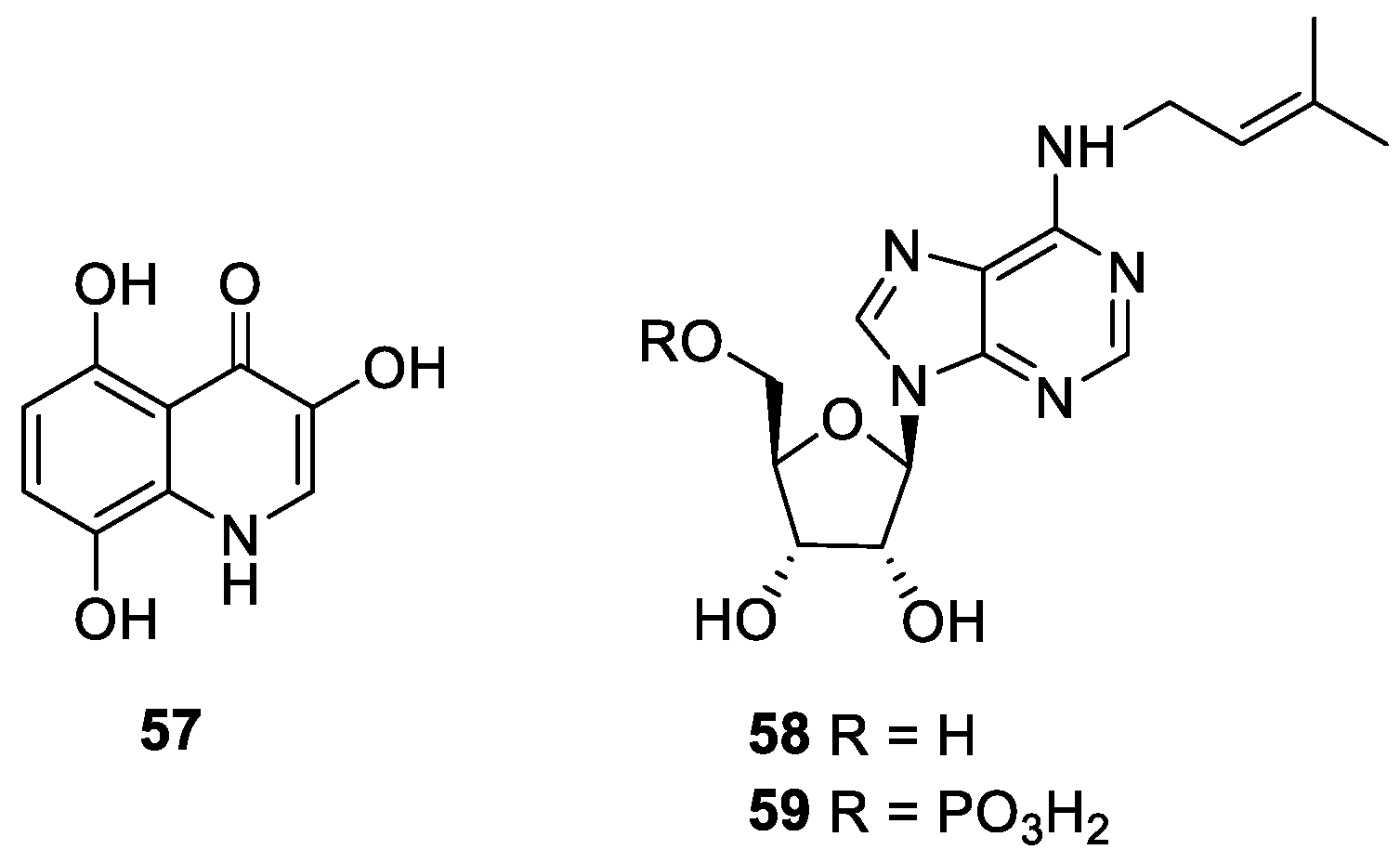
2.6. Indole Alkaloids
2.7. Nucleotide Alkaloids
3. Lipids
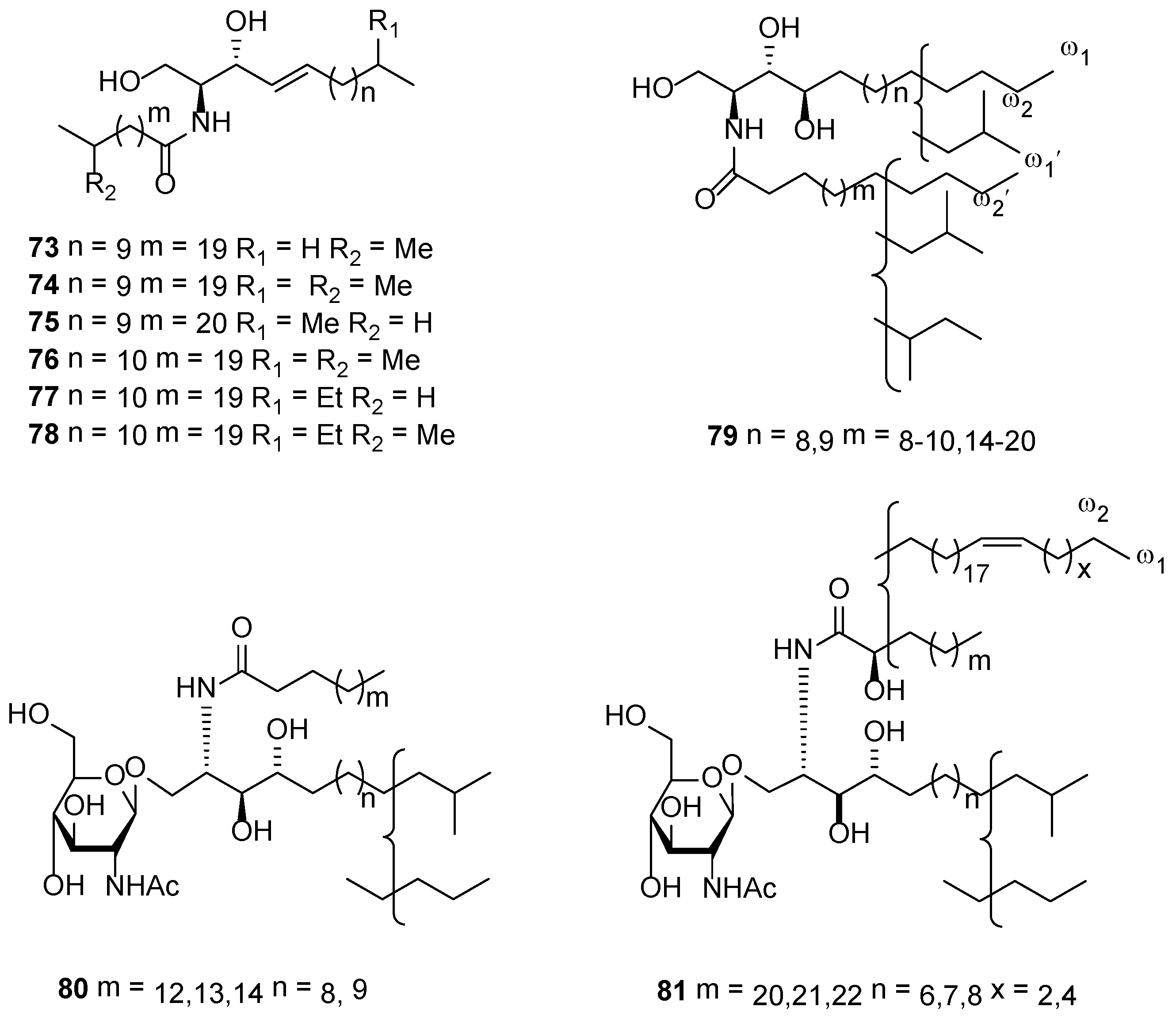
3.1. Sphingolipids
3.2. Ceramides and Cerebrosides
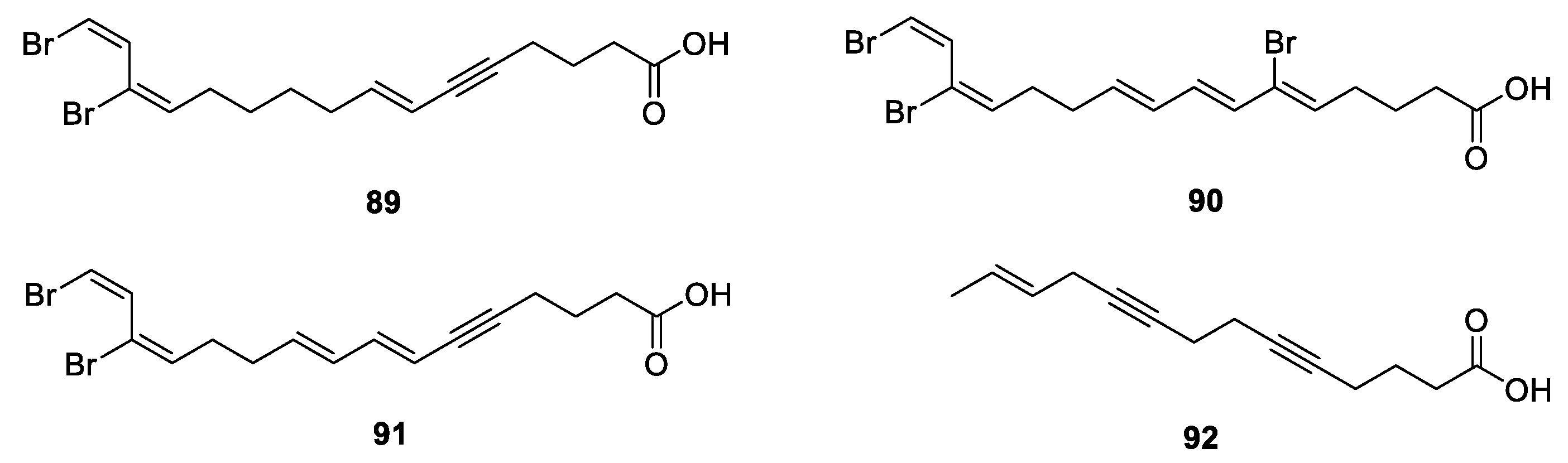
3.3. Dithiocyanates
3.4. Polyacetylenes
4. Sterols
5. Other Miscellaneous
6. Chemical Synthesis of Four Secondary Metabolites
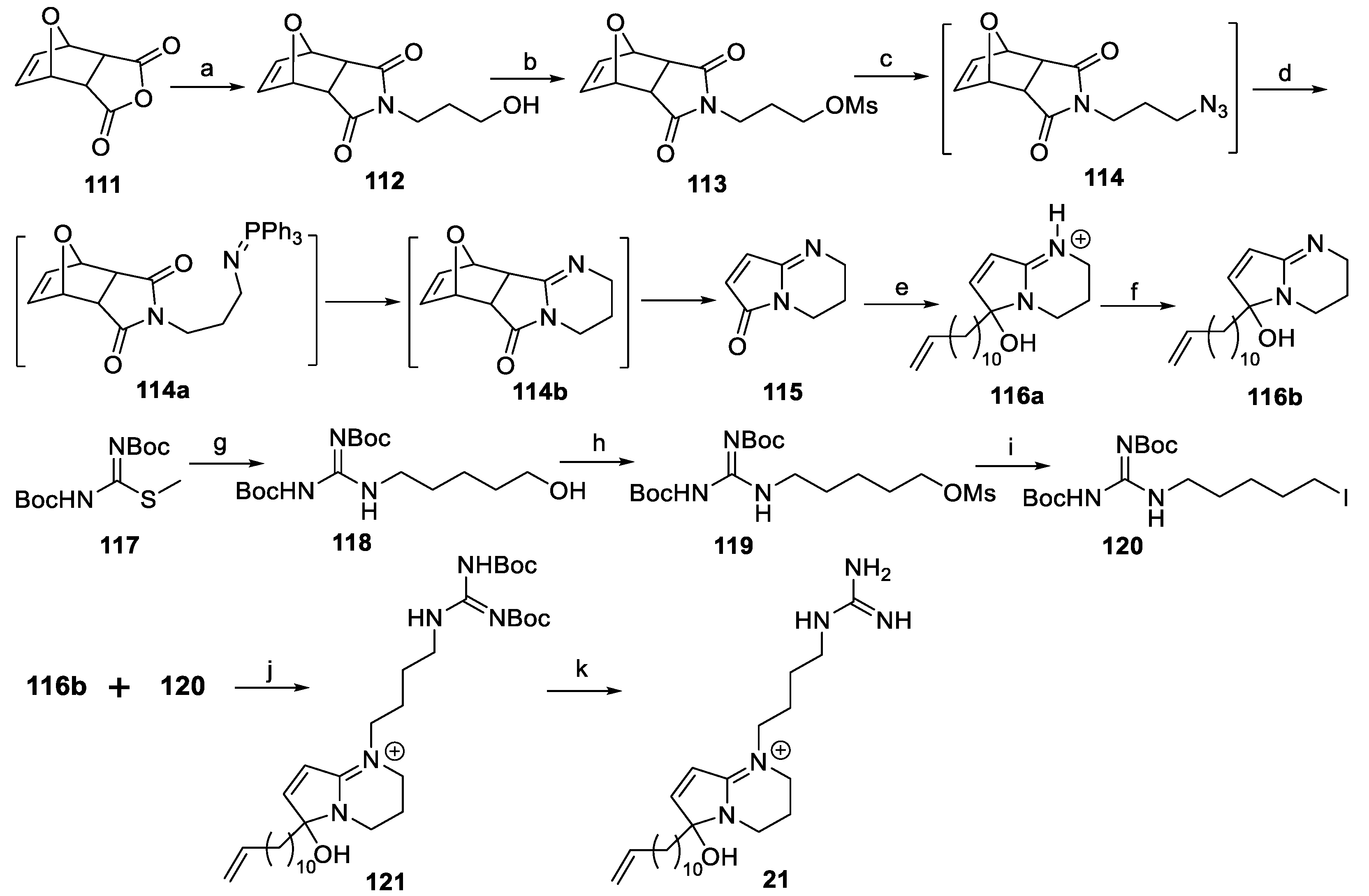
6.1. Synthesis of (±)-Phloeodictine A1 ((±)-21)
6.2. Synthesis of 6-Br-8-keto-conicamin A (55)
6.3. Synthesis of Rhizochalinin C (70)
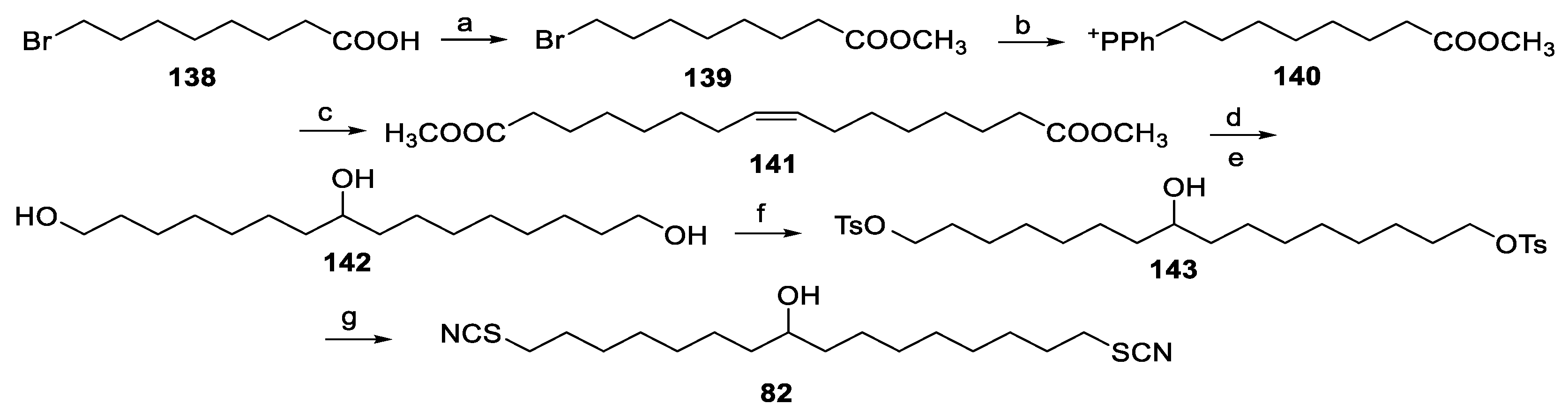
6.4. Synthesis of Thiocyanatin A (82)
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiménez, C. Marine natural products in medicinal chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desqueyroux-Faúndez, R.; Valentine, C. Family Phloeodictyidae Carter, 1882. In Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Willenz, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 893–905. [Google Scholar]
- Salomon, C.E.; Faulkner, D.J. Sagitol, a pyridoacridine alkaloid from the sponge Oceanapia sagittaria. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 9147–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, C.; Schupp, P.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Steube, K.; Müller, C.E.; Frobenius, W.; Herderich, A.M.; van Soest, R.W.M. Bioactive pyridoacridine alkaloids from the Micronesian sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardana, G.P.; Koehn, F.E.; Lee, A.Y.; Clardy, J.; He, H.Y.; Faulkner, D.J. Pyridoacridine alkaloids from deep-water marine sponges of the family Pachastrellidae: Structure revision of dercitin and related compounds and correlation with the kuanoniamines. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, P.; Eder, C.; Paul, V.; Proksch, P. Distribution of secondary metabolites in the sponge Oceanapia sp. and its ecological implications. Mar. Biol. 1999, 135, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijjoa, A.; Wattanadilok, R.; Campos, N.; Herz, W.; Nascimento, M.S.J.; Pinto, M. Anticancer activity evaluation of kuanoniamines A and C isolated from the marine sponge Oceanapia sagittaria, collected from the Gulf of Thailand. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Ngo, A.; Quinn, R.J.; Redburn, J.; Hooper, J.N.A. Petrosamine B, an inhibitor of the Helicobacter pylori enzyme aspartyl semialdehyde dehydrogenase from the Australian sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Fouad, M.A.; Proksch, P. Sagitol C, a new cytotoxic pyridoacridine alkaloid from the sponge Oceanapia sp. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2013, 51, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Das, B.; Naik, C.G. Quinolizidines alkaloids: Petrosin and xestospongins from the sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Chem. Sci. 2011, 123, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, K.G.; Harper, M.K.; Faulkner, D.J. Oceanapamine, a sesquiterpene alkaloid from the Philippine sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourany-Lefoll, E.; Pais, M.; Sevenet, T.; Guittet, E.; Montagnac, A.; Fontaine, C.; Guenard, D.; Adeline, M.T.; Debitus, C. Phloeodictines A and B: New antibacterial and cytotoxic bicyclic amidinium salts from the New Caledonian sponge, Phloeodictyon sp. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3832–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourany-Lefoll, E.; Laprévote, O.; Sévenet, T.; Montagnac, A.; Païs, M.; Debitus, C. Phloeodictines A1-A7 and C1-C2, antibiotic and cytotoxic guanidine alkaloids from the New Caledonian sponge, Phloeodictyon sp. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 3415–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, B.J.; Snider, B.B. Synthesis of (±)-phloeodictine A1. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Sauvain, M.; Debitus, C.; Duigou, A.-G.; Ausseil, F.; Menou, J.-L.; Pietra, F. New 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidinium alkaloids (phloeodictynes) from the New Caledonian shallow-water haplosclerid sponge Oceanapia fistulosa. Structural elucidation from mainly LC-tandem-MS-soft-ionization techniques and discovery of antiplasmodial activity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Newton, G.L.; Fahey, R.C.; Bewley, C.A. Novel bromotyrosine alkaloids: Inhibitors of mycothiol S-conjugate amidase. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1543–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Mahajnah, Y.; Mangoni, A. 6-Bromo-5-hydroxy-3-indolecarboxyaldehyde from the Caribbean sponge Oceanapia bartschi. Z. Naturforsch. B-J. Chem. Sci. 1993, 48, 1408–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig-Roach, N.; Hamkins-Indik, F.; Johnson, T.A.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. The potential of achiral sponge-derived and synthetic bromoindoles as selective cytotoxins against PANC-1 tumor cells. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, Y.; Reddy, N.S.; Ramesh, P.; Rao, J.V. Coixol: A bioactive principle from a marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1999, 27, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamukai, S.; Ise, Y.; Ohtsuka, S.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Isolation and identification of N6-isopentenyladenosine as the cytotoxic constituent of a marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Milgrom, Y.M.; Rashkes, Y.V. Rhizochalin, a novel secondary metabolite of mixed biosynthesis from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6581–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.M.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Membrane activity of rhizochalin isolated from Rhizochalina incrustata. Biofizika 1990, 35, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molinski, T.F.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. (-)-Rhizochalin is a dimeric enantiomorphic (2R)-sphingolipid: Absolute config-uration of pseudo-C2v-symmetric bis-2-amino-3-alkanols by CD. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 4076–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensemhoun, J.; Bombarda, I.; Aknin, M.; Faure, R.; Vacelet, J.; Gaydou, E.M. Marine bifunctional sphingolipids from the sponge Oceanapia ramsayi. Molecules 2008, 13, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Shubina, L.K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Stonik, V.A. Marine two-headed sphingolipid-like compound rhizochalin inhibits EGF-induced transformation of JB6 P+ Cl41 cells. Lipids 2009, 44, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-O.; Shastina, V.; Park, J.-I.; Han, J.-Y.; Makarieva, T.; Fedorov, S.; Rasskazov, V.; Stonik, V.; Kwak, J.-Y. Differential induction of apoptosis of leukemic cells by rhizochalin, two headed sphingolipids from sponge and its derivatives. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, P.; Kang, B.S.; Yun, H.J.; Cho, H.-G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Choi, H.S. Aglycon of rhizochalin from the Rhizochalina incrustata induces apoptosis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Hong, T.W.; Molinski, T.F.; Lerch, M.L.; Cancilla, M.T.; Lebrilla, C.B. Oceanapiside, an antifungal bis-α,ω-amino alcohol glycoside from the marine sponge Oceanapia phillipensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Molinski, T.F. Enantiodivergent biosynthesis of the dimeric sphingolipid oceanapiside from the marine sponge Oceanapia phillipensis. Determination of remote stereochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, G.M.; Li, R.; MacMillan, J.B.; Molinski, T.F. Antifungal activity of bifunctional sphingolipids. intramolecular synergism within long-chain α,ω-bis-aminoalcohols. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2159–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Guzii, A.G.; Li, R.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Rhizochalins C and D from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. A rare threo-sphingolipid and a facile method for determination of the carbonyl position in α,ω-bifunctionalized ketosphingolipids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Santalova, E.A.; Stonik, V.A.; MacMillan, J.B.; Molinski, T.F. Oceanalin A, a hybrid α,ω-bifunctionalized sphingoid tetrahydroisoquinoline β-glycoside from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 2897–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Santalova, E.A.; Pokanevich, E.V.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Rhizochalin A, a novel two-headed sphingolipid from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Shubina, L.K.; Kapustina, I.I.; Fedorov, S.N. Rhizochalinin A, a new antileukemic two-headed sphingolipid from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. New two-headed sphingolipid-like compounds from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2008, 57, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Molinski, T.F. D-Glucosamine-derived synthons for assembly of L-threo-sphingoid bases. Total synthesis of rhizochalinin C. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 78, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Savina, A.S.; Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F.; Stonik, V.A. Isorhizochalin: A minor unprecedented bipolar sphingolipid of stereodivergent biogenesis from the Rhizochalina incrustata. Lipids 2009, 44, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Pietra, F.; Debitus, C. Oceanapins A–F, unique branched ceramides isolated from the haplosclerid sponge Oceanapia cf. tenuis of the Coral Sea. Helv. Chim. Acta 1994, 77, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Svetashev, V.I.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Pokanevich, E.V.; Santalova, E.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Stonik, V.A. New ceramides from sea sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2006, 32, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Svetashev, V.I.; Rodkina, S.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Stonik, V.A. New cerebrosides from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2006, 55, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Liu, E.H.-T.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. The isolation and synthesis of novel nematocidal dithiocyanates from an Australian marine sponge, Oceanapia sp. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7765–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Liu, E.H.-T.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. Nematocidal thiocyanatins from a southern Australian marine sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiba, T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Sponge-derived polyunsaturated C16 di- and tribromocarboxylic acids. Helv. Chim. Acta 1993, 76, 2814–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Okada, Y.; Fusetani, N.; van Soest, R.W.M. An antimicrobial C14 acetylenic acid from a marine sponge Oceanapia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 690–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santalova, E.A.; Makarieva, T.N.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Denisenko, V.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G.; Stonik, V.A. Sterols and related metabolites from five species of sponges. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007, 35, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Kalinovsky, A.I. Isolation of (24R)-24,25-methylene-5α-cholestan-3β-ol, a new cyclopropane-containing sponge sterol. J. Chem. Res. 1996, 10, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


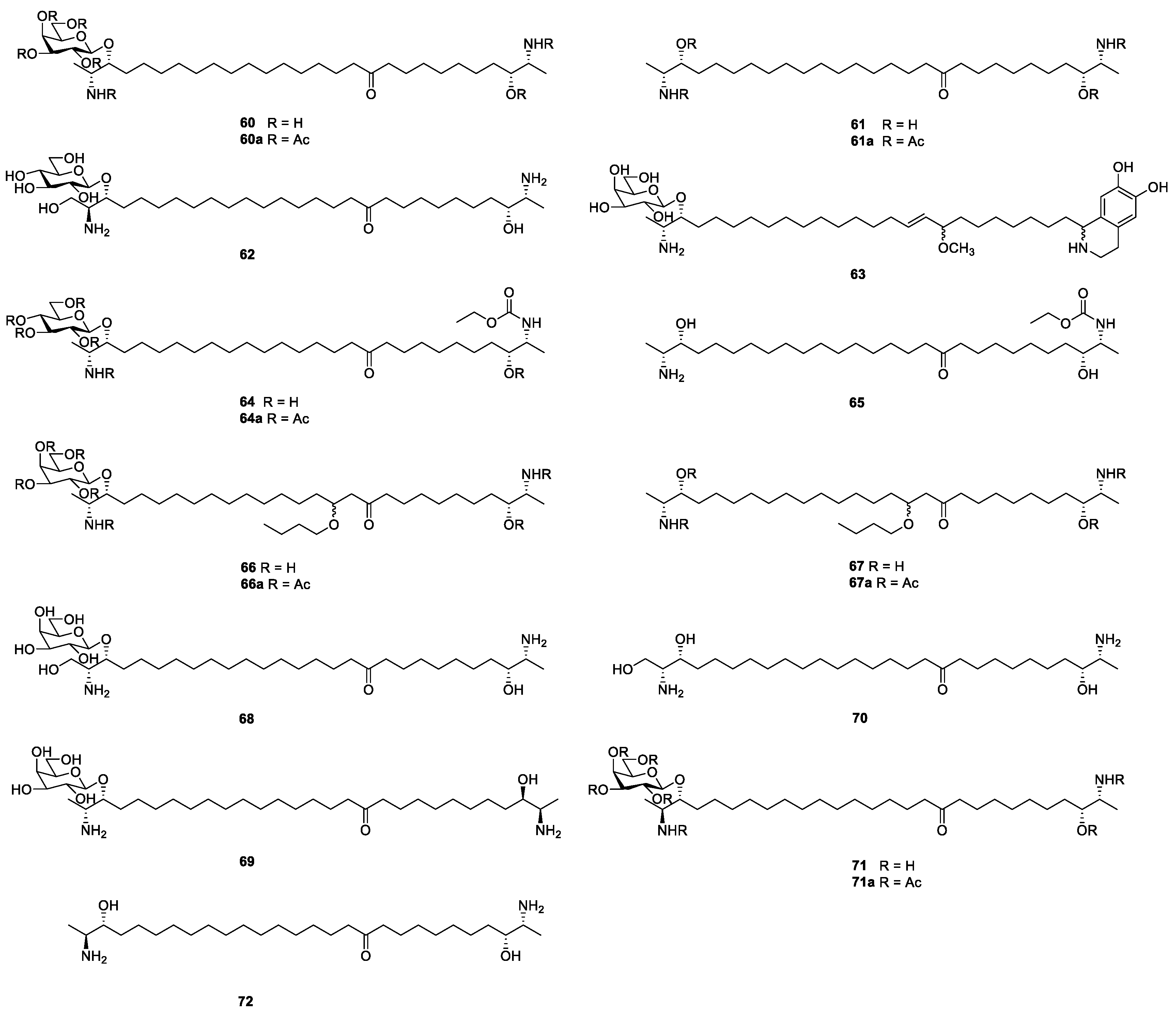




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.-J.; Zhong, L.-J.; Chen, J.-K.; Bu, Q.; Liang, L.-F. Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges of the Genus Oceanapia: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020144
Xu M-J, Zhong L-J, Chen J-K, Bu Q, Liang L-F. Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges of the Genus Oceanapia: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Meng-Juan, Lin-Jing Zhong, Jun-Kun Chen, Qing Bu, and Lin-Fu Liang. 2022. "Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges of the Genus Oceanapia: Chemistry and Biological Activities" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020144
APA StyleXu, M.-J., Zhong, L.-J., Chen, J.-K., Bu, Q., & Liang, L.-F. (2022). Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges of the Genus Oceanapia: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020144