Abstract
Carbon dots (CDs) have attracted significant research attention worldwide due to their unique properties and advantageous attributes, such as superior optical properties, biocompatibility, easy surface functionalization, and more. Moreover, biomass-derived CDs have attracted much attention because of their additional advantages related to more environmentally friendly and lower-cost synthesis. In this respect, chitosan has been recently explored for the preparation of CDs, which in comparison to other natural precursors exhibited additional advantages. Beyond the benefits related to the eco-friendly and abundant nature of chitosan, using it as a nanomaterial precursor offers additional benefits in terms of structure, morphology, and dopant elements. Furthermore, the high content of nitrogen in chitosan allows it to be used as a single carbon and nitrogen precursor for the preparation of N-doped CDs, significantly improving their fluorescent properties and, therefore, their performances. This review addresses the most recent advances in chitosan-based CDs with a special focus on synthesis methods, enhanced properties, and their applications in different fields, including biomedicine, the environment, and food packaging. Finally, this work also addresses the key challenges to be overcome to propose future perspectives and research to unlock their great potential for practical applications.
1. Introduction
Carbon dots (CDs) have attracted extensive attention due to their unique properties in UV fluorescence and their outstanding performances in uses such as cell-labeling materials and heavy metal sensors. CDs are described as zero-dimensional carbon nanoparticles with a particle size below 10 nm, quasi-spherical shaped, and optically active [1,2]. Furthermore, CDs stand out among most nanomaterials due to their unique properties. These are: biocompatibility, photoluminescence, chemical stability, enzyme mimicking, surface functionality, hydrophilicity, and simple synthesis methods, among others.
The development and understanding of CDs have significantly increased in recent times due to the research efforts of the scientific community, reflected by the increasing number of publications and growing interest in this type of nanomaterial [3]. Concurrently, their potential applications have been extended to different areas. For example, much literature has been published on the employment of CDs to detect toxic elements [4,5], remove emerging pollutants from water bodies [3], prepare energy storage devices [6], and act as artificial nanozymes for different catalytic applications [7], among other innovative applications. However, their synthesis through sustainable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly protocols remains challenging, as hydrothermal and microwave methods are the most common approaches [8,9]. Accordingly, natural, renewable, and economical carbon precursors play a crucial role since their utilization might increase the viability and competitiveness of the process providing sustainable alternatives and economical materials for the large-scale production of CDs [10]. In this manner, an inexpensive material can be converted into a precious product with great potential for biomedical and biotechnological applications. Recent studies have explored the synthesis of CDs from different natural and waste materials, including chitosan, an amino polysaccharide recovered from marine waste with remarkable advantages as a carbon precursor. Chitosan is extracted from chitin, an abundant nitrogenous biopolymer found in crustaceans or insects. It is the second most abundant natural polymer after cellulose; approximately 1010–1011 t of chitin are recovered annually and produced into chitosan [11,12].
In addition to its abundant, economical, and renewable nature, chitosan has additional benefits. For instance, it possesses high amounts of nitrogen [13], and multiple functional groups, including acetamido, amino, and hydroxyl groups [12]. This is highly relevant since chitosan can act as single carbon and nitrogen precursor to easily obtain N-doped carbon nanomaterials, which are advantageous for multiple applications [13]. The outstanding properties of chitosan have been documented in different studies reporting the synthesis of chitosan-based materials, including carbon spheres, porous carbon, nanoparticles, and, more recently, CDs [14,15,16,17]. A few reviews provide a broader perspective of carbon materials derived from chitosan [12,18,19]; however, none summarizes the most recent advances in chitosan-based CDs. Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of the preparation of chitosan-based CDs for several applications. This review addresses the structure and properties of chitosan-based CDs, their synthesis methods, and their applications in different fields, including biomedicine, the environment, and energy. Finally, current challenges are identified to propose further research directions to reach practical applicability.
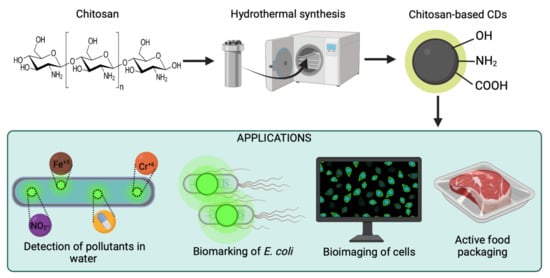
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the synthesis of chitosan-based carbon dots for applications such as the detection of pollutants, active food packaging, biosensing, and bioimaging. Created with BioRender.com and extracted under premium membership.
2. Chitosan as a Carbon Source for Nanomaterials
Chitin is a polymer derived from the exoskeleton of arthropods and mainly recovered for commercialization from shrimp, crabs, and other crustaceans (Figure 2). It is a linear polysaccharide built from beta-1,4 linked N-acetylglucosamine units, and it is highly insoluble in common solvents [20]. Chitosan is the biopolymer obtained from the deacetylation of chitin, and it can also be seen as a copolymer of d-glucosamine N-acetylglucosamine. Compared to chitin, chitosan is soluble in an acidic medium such as water acidified with acetic acid, with only low concentrations needed (commonly 1% v/v acetic acid is used). Its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and gel-forming properties make it easy to handle and manage as a polymeric matrix. However, chitin and chitosan have been used in tissue engineering for different applications, such as wound healing and cellular growth [21]. Chitin has shown highly hydrophobic properties caused by the N-acetylglucosamine polymeric structure, making it a rigid material. Still, it also has good electric properties when modified with maleic anhydride or reinforced with carbon nanotubes. This may be viable in biomedical applications requiring electrical conductivity [22]. These properties can be used for engineering scaffolds for neuron growth, nerves, and the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases [23]. Additionally, no reports of anti-inflammatory or allergic responses were observed in human subjects’ ingestion, injection, implantation, and topical application [24]. Amongst other important properties of chitosan, its degradation rate is influenced by the degree of deacetylation (d-glucosamine/N-acetylglucosamine ratio), which may be an essential factor for different biomedical and biotechnological applications [25].
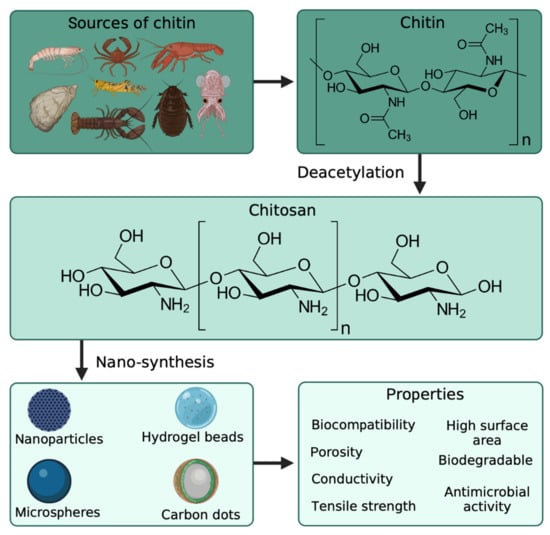
Figure 2.
Sources of chitosan for the preparation of chitosan-based nanomaterials with enhanced properties. Created with BioRender.com and extracted under premium membership.
The chemical structure of chitosan helps achieve cell adhesion and proliferation properties. Additionally, due to the highly hydrophilic surface it has, it promotes cell growth [24]. In addition, chitosan has shown antibacterial properties and can generate scaffolds with high porosity [26]. Although it has many advantages due to its properties, chitosan has poor mechanical strength, making it challenging to maintain a predefined shape for transplantation. However, this has been improved by cross-linking and copolymerizing this biomaterial with other polymers. Some attempts focused on reinforcement with nanoparticles [27], or incorporating hydroxyl-apatite, beta-tricalcium phosphate, alginate, and gelatin as copolymers. The cross-linkage of these polymers may result in better scaffolds that allow the construction of high mechanical strength tissues. In this manner, chitosan has prepared different nanomaterials, providing them with superior chemical, mechanical, and physical properties, including tensile strength, porosity, surface area, electrical conductivity, and thermal stability. The outstanding properties of chitosan-based nanoformulations have shown great potential in different research areas, such as drug delivery, bioimaging, sensing, gene delivery, diagnosis, and treatment of several diseases [28,29]. Different nanoformulations derived from chitosan can be found; however, the most commonly prepared are chitosan nanoparticles. Chitosan nanoparticles present low toxicity when studied in vivo and in vitro. Thus, it has been employed for biomedicine applications. Moreover, the surface of chitosan-based nanoparticles is typically positively charged, which, combined with their mucoadhesive properties, can adhere to mucus membranes for a sustained release of drugs [29].
Another attractive property of chitosan-based nanoparticles is their antibacterial activity. Thus, antimicrobial wound dressing applications have also been explored [30]. For instance, Babaee et al. [31] evaluated the effect of adding chitosan nanoparticles into a plasticized starch film for active packaging applications. Chitosan particles acted as a reinforcing and antimicrobial agent. Chitosan-based films presented excellent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria; they exhibited inhibition zones against S. aureus and E. coli with a complete reduction (100%) of S. aureus. Moreover, mechanical and barrier properties were enhanced at higher concentrations (4 wt.%) of chitosan nanoparticles [31]. Similarly, some research groups have enhanced antimicrobial activity by incorporating antibiotics, metallic particles, or other compounds with antimicrobial effects. For example, Yeamsuksawat et al. [32] prepared and characterized Fe3O4@Chitosan@Ag nanoparticles. Nanoparticles showed superior antibacterial performance against E. coli and S. cerevisiae, exhibiting a 100% inhibition rate. The authors concluded that the synthesized nanomaterial could be used in different applications, including food packaging, biological, textile, and medical applications [32]. Similar developments have been reported in which chitosan has played a key role in the antimicrobial performance of various hybrid materials for applications such as inhibiting bacterial growth in a food or preserving paper documents [33,34].
Chitosan nanospheres have also been recently developed. As a representative example, Zhao et al. [35] prepared nanospheres from N,N,N-Trimethyl chitosan to encapsulate hydrophobic curcumin and thus overcome the tissue barriers due to the positive charge of the surface. It reported an excellent encapsulation efficiency, higher than 90%, with no toxic effect on cells. Interestingly, at higher concentrations of chitosan, an extended release of curcumin was observed; therefore, adjusting the concentration of chitosan could represent a suitable strategy to achieve an extended release of drugs [35].
Among the carbon-based nanomaterials, CDs are outstanding due to their multiple advantageous features, such as chemical stability, biocompatibility, easy surface functionalization, fluorescence, and economical synthesis. In order to propose more sustainable synthesis protocols, natural and waste precursors have been explored to prepare such novel nanomaterials [2,4]. In this respect, the carbon atoms in the glucosamine chains of chitosan serve as a source for the preparation of CDs for applications in the biomedical and environmental fields [36,37].
3. Methods for the Synthesis of Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots
Chitosan is an excellent precursor for preparing carbon nanoparticles, as it is an abundant and inexpensive renewable biomass source with high nitrogen content [12,38]. In the literature can be found many studies of CDs prepared through different processes and using a vast variety of precursors, in which citric acid stands out as a popular selection [39,40]. However, citric acid-based CDs usually require the simultaneous addition of nitrogen-rich co-precursors such as urea, ethylenediamine, and phenylalanine, among others, to provide nitrogen elements to the CDs’ structures and thus enhance their overall properties and performances [41,42,43].
In this context, the employment of chitosan as a precursor for CDs represents additional advantages since it is a single carbon and nitrogen source; thus, chitosan provides amino functional groups in addition to hydroxyl groups on the CDs’ surface. Several methods of chitosan-based CDs are summarized in Table 1 [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70], for different applications in the biomedical and environmental fields. Generally, the presence of nitrogen elements on the CDs’ surface is highly desired, since nitrogen plays a fundamental role in maximizing the quantum yield [38]. In this manner, chitosan-based CDs present self-doped nitrogen elements that increase the surface-state defects resulting in enhanced optical and electronic properties, including photoluminescence and tailored electron properties due to the strong electron-donating capacity of nitrogen [17]. The most common functional groups on the surface of chitosan-based CDs include -NH2, -OH, and COOH [12,64].

Table 1.
Overview of chitosan-based carbon dots: synthesis methods and applications.
Chitosan has been widely used to prepare novel CDs with excellent properties and great potential in different applications. The transformation of chitosan into such CDs can be achieved through different synthetic procedures, including hydrothermal, microwave-assisted, and pyrolysis, among others (Figure 3a). The relevance of the synthesis method is widely demonstrated in the literature; preparation methods have considerable effects on the electronic and optical properties of the CDs. For instance, Zattar et al. [38] compared chitosan CDs prepared by two methods: hydrothermal and acid dehydration. Interestingly, several differences were reported, including particle size distribution, nitrogen content, and quantum yield. Regarding particle size distribution, hydrothermally prepared CDs presented an average diameter of 2.4 nm. In comparison, CDs from acid dehydration showed a smaller average size of 1.5 nm with a narrower distribution attributed to the stronger acid attack during that method. This difference in diameter can be impactful depending on the type of application, as long as there is a consistent size average, which indicates a good synthesis protocol. Moreover, CDs prepared by the hydrothermal method exhibited a greater content of nitrogen-containing functional groups and, thus, a higher quantum yield (9.3%) than CDs prepared by acid dehydration with a quantum yield of 3.3% [38]. In this manner, synthesis methods directly impact the properties of the obtained CDs and their further applications.
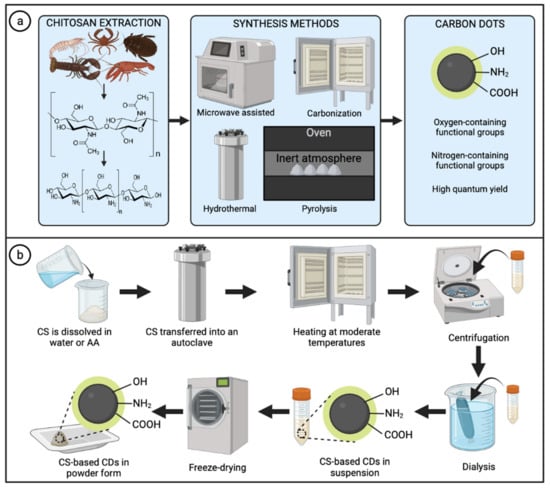
Figure 3.
Synthesis methods for the preparation of chitosan-based carbon dots. (a) Chitosan extraction and most common synthesis methods to obtain carbon dots. (b) Typical methodology for the preparation of chitosan-based carbon dots through the hydrothermal method. Abbreviations: CS (chitosan); AA (acetic acid); CDs (carbon dots). Created with BioRender.com and extracted under premium membership.
The hydrothermal method is considered one of the most applied methods to obtain CDs due to its low cost, eco-friendliness, and facile control of parameters such as temperature and time of reaction [71,72,73,74]. Chitosan–alone or combined with other co-precursors–is typically dissolved in water or acetic acid solution and transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave. Subsequently, the stainless-steel reactor must be adequately sealed and heated at moderate temperatures (below 220 °C) under autogenous pressure. After reactions occur and room temperature is reached, the obtained product is collected and separated/purified. Researchers have reported different purification methods, including filtration, centrifugation, and dialysis, among others, or a combination of some [64,75]. Then, CDs in solution are stored in refrigeration or freeze-dried to obtain solid samples for further applications or to meet requirements for some characterization techniques (Figure 3b) [76].
In this context, chitosan-based CDs reported by Ni et al. [17] were prepared from an ultrasonically dispersed suspension of chitosan in water, which was transferred into an autoclave and heated at 200 °C for 10 h. After room temperature was reached, the collected solution was centrifuged and filtered to remove larger particles. Finally, the supernatant was dialyzed and freeze-dried to obtain CDs in powder form [17].
A similar approach was followed by Xu et al. [77]; however, they used chitosan in combination with p-phenylenediamine as the source of carbon and nitrogen, which were dispersed in acetic acid. Moreover, higher temperatures and longer reaction times were used (220 °C for 18 h); in contrast, purification required only centrifugation and filtration to finally obtain CDs in suspension [77].
Hydrothermal synthesis is a very convenient method for preparing CDs derived from chitosan since the mild operating conditions in combination with water and the composition of the precursor lead to CDs with oxygen-containing and nitrogen-containing functional groups. Moreover, some molecules can be produced during the decomposition of the chitosan, such as CH3COOH and NH3, which persist in the reaction medium and cause the addition of heteroatoms into the structure of CDs through different chemical reactions. The introduction of heteroatoms in the structure of CDs represents significant improvements in quantum yield; in addition, the presence of nitrogen- and oxygen-containing surface functional groups improve the solubility and photoluminescence of the hydrothermally synthesized CDs [38].
The hydrothermally synthesized CDs derived from chitosan are obtained due to different transformation pathways; however, they might present significant variations in their properties, particle size, structure, and yields. The notable variability is due to the many factors involved, such as operational conditions (e.g., temperature, reaction time, heating rate), composition, properties, and structures of precursors. Further efforts should be directed to fully understand the formation mechanisms to optimize CDs’ yields and properties. Other methods have been employed for preparing chitosan-based CDs, such as the microwave-assisted method. This approach uses chitosan under microwave irradiation, receiving homogeneous heating directly to the target molecules. This is a notable difference since other synthesis methods heat the precursors convectively or conductively. One of the main advantages of this method is the reaction time, which is significantly shorter compared to the hydrothermal methods, which require a longer reaction time, usually around 5 h to 24 h. For instance, Pawar et al. [53] prepared passivated CDs using chitosan gel as the carbon precursor and poly(ethylene glycol) as the passivating agent. Their methodology consisted of microwave heating at 600 W at 100 °C within 3 min. Their CDs presented a particle size of 2.3–7.6 nm and a quantum yield of 25%, showing great potential for detecting trace amounts of water in organic solvents [53]. However, this synthesis method has challenges, such as low synthetic yield. In this manner, Liu et al. [78] proposed a microwave-hydrothermal carbonization method to reduce the reaction time and increase the synthesis yield; chitosan-based CDs were prepared within 30 min of the reaction with a high synthetic yield of 45.9%. Their method has the advantage of better controlling parameters, including temperature and pressure, which avoids side reactions and improves the overall synthetic yield. Moreover, CDs exhibited a quantum yield of 12.17% and the capacity to sensitively detect Fe2+ [78].
Pyrolysis, as a classical and simple thermal method, has also been employed for the preparation of CDs, including chitosan-based ones. This approach converts the carbon precursor into CDs via degradation and carbonization under an inert atmosphere and high temperatures. Typically, carbon precursors are placed inside the reactor, which is heated at a certain temperature with a controlled heating rate. The inert atmosphere is usually achieved by the introduction of nitrogen or argon gas. Inert gases should be introduced before heating to remove the oxygen in the system and avoid the combustion of the precursors. The main advantage of the pyrolysis method relies on its simplicity; however, it might require high temperatures and the obtained CDs can present broad particle size distribution and low values of quantum yield [73,79].
In addition, some properties of the CDs obtained by this method can be tuned by modifying the parameters of the process, such as the temperature, reaction time, heating rate, etc. [74]. As a representative example, Horo et al. [80] prepared CDs from low molecular weight chitosan and silk-fibroin blends under an inert atmosphere by introducing nitrogen flow. The pyrolysis was performed at 230 °C for 3 h. Then, a fine powder product was obtained after grinding, which was later dissolved in water. After filtration, CD samples were freeze-dried and stored for further analyses and applications [80]. Similarly, other research groups have applied pyrolysis under an inert atmosphere to prepare chitosan-based CDs [81,82]. The tailored photoluminescent properties of chitosan-based CDs prepared by the hydrothermal method have led researchers to employ them mainly for the sensitive and selective detection of several emerging pollutants in water samples (Table 2) [17,52,68,72,75,77,83,84,85,86,87].

Table 2.
Overview of hydrothermally prepared carbon dots derived from chitosan: synthesis, properties, and applications.
4. Applications
4.1. Biomedicine
Being zero-dimensional (0D), quantum dots (QDs) are a nanomaterial from the carbon family. QDs have shown promising biomedical applications due to their size on the nanoscale. Carbon quantum dots are particularly useful in applications of the biomedical field, such as bioimaging, cell labeling, and biosensing. Chitosan-based CDs were applied for imaging human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVAC), which were exposed to low concentrations (50 µg/mL) of water-dispersed CDs. These CDs were synthesized through a simple one-pot hydrothermal method from a mixture of gum tragacanth and chitosan, which showed good detection of the cells by fluorescence microscopy due to the luminescence of the CDs intracellularly [45].
The same hydrothermal approach was used for synthesizing CDs from chitosan and applied for the bioimaging of A549 epithelial cells, which showed low cytotoxicity and good biocompatibility [58]. While CDs are commonly synthesized using the hydrothermal autoclave, another technique often used is pyrolysis through microwaves. The common one-pot method has the dissolved chitosan put under a microwave for several minutes until carbonized, as explained in the previous section. This technique has been used to synthesize CDs implemented in cellular labeling, bioimaging, and drug delivery [64,88]. Not only are the biocompatibility and non-toxicity of CDs properties relevant for the application of this nanomaterial in the biomedical field for bioimaging, biosensing, and drug delivery, but also the surface area to volume ratio which allows these materials to enter the extracellular matrix. The most important aspect is the photoluminescence, which provides for tunability of the color reflected by such material and the functionalization of the surface, depending on what type of application will be given to the final product.
4.2. Environmental
In terms of environmental applications of chitosan-based CDs, there have been many studies showing the capability of such nanomaterial for the detection of heavy metals in water such as Fe (III), Cu (II), and Cr (VI) [49,60,76], and some other specific applications as antibacterial agents in food packaging [72], detection of nitrite and enrofloxacin in water [76,81], algal growth enhancement, etc., [47]. In a recent study done by Wu et al. [71] CDs were obtained from the carbonization of chitosan and doped with nitrogen and phosphorus, using phosphoric acid as a medium. The carbon quantum dots showed luminescence from blue to green and orange, allowing for the tunability of the colors emitted from the material at different wavelengths depending on the type of application required and the desired emission. It was shown through this study that the addition of phosphoric acid as a solvent allowed for faster reaction times in the synthesis process, which, in this case, was a parallel hydrothermal microwave reaction.
The application scope of CDs in visible-light photocatalysis at longer wavelengths can be extended through this approach while allowing multi-color-emissive. The synthesis reaction can be shortened to only 5 min, and the fluorescence of the nanomaterial from blue to green to orange can be tailored by adjusting the acid concentrations. This can open up new possibilities in environmental and biotechnological applications for detecting microorganisms, heavy metal ions, microalgal growth, and many more [71].
4.3. Food Packaging
Antimicrobial properties are an important aspect of coating materials for applications such as food packaging to increase the shelf life of foods. With the help of nanotechnology, nanoparticles and nanocomposites can be synthesized to open a broader scope of novel options to tackle this problem in the global market. Thus, incorporating carbon quantum dots and other nanoparticles into these materials, particularly those obtained from natural sources such as chitosan, have been demonstrated to have antibacterial properties. These are mainly attributed to its polycationic nature, which interacts with the negatively charged surface of bacteria, altering cell permeability [89].
The incorporation of chitosan-based carbon quantum dots on carboxymethyl cellulose films for food packaging applications was performed by Riahi et al. [72], with average sizes around 7.2 nm, demonstrated not only an improvement in the mechanical properties of the film, but also a strong antibacterial effect on E. coli and L. monocytogenes, as well as considerable antioxidant activity, and antifungal activity on A. niger and P. chrysogenum. Additionally, the films showed almost null cytotoxicity against L929 cells at concentrations up to 500 μg/mL. Furthermore, mechanically, the addition of the chitosan-based quantum dots increased the tensile strength of the carboxymethyl cellulose film by up to 27.6% and its elastic modulus by approximately 61.5% [72]. Another approach is not using chitosan directly as the carbon source for quantum dots, but instead using it as the polymeric matrix in the form of thin films or fibers reinforced with CDs from other sources, such as kelp, allowing the CDs to do their antibacterial activity combined with that of the chitosan-based matrix and their respective biocompatibility/biodegradability properties [90]. In this context, CDs are good candidates for antibacterial and antifungal functions, whether using chitosan as the carbon source or as the polymeric matrix.
5. Current Challenges and Recommendations
Research on CDs has shown great progress in recent times, thus providing useful information and data for a better understanding of CDs’ properties, structures, and applications. However, there are still many key issues to be addressed. For instance, many synthesis methods have been reported for preparing chitosan-based CDs; however, scalable synthesis methodologies to produce high-quality CDs at high production yields remain unreported. In addition, the unclear effects of parameters, reaction conditions, and characteristics of the initial precursor make it difficult to control precisely the properties obtained in the CDs. In this respect, further efforts should be directed to understand the formation mechanisms in detail to get higher yields of CDs with controllable and enhanced properties.
Chitosan-based CDs have been employed for multiple applications, such as detecting toxic elements, active food packaging, and nanozymes for catalytic applications. Despite the efforts and progress in such applications, there is still investigation work to be done to achieve practical application in real scenarios. For example, the precise exploration of the role of CDs in each reaction and their interaction with other components or media is highly required. In addition, further examination of their toxicity and metabolic pathways on different organisms is extremely relevant for some applications such as biomedicine.
6. Conclusions
Chitosan-based CDs have demonstrated great potential in many research fields, including biomedicine, the environment, and energy. They possess enhanced fluorescence and optical properties owing to their precursor’s characteristics and benefits due to the eco-friendly and abundant nature of chitosan. In this review, we have discussed the enhanced properties of chitosan-based CDs directly associated with the precursor. Moreover, we have analyzed the most recent applications, highlighting the detection of different pollutants in environmental samples as the most common. However, other novel applications have been reported, such as the fabrication of active food packaging and their use as nanozymes. Current challenges that need to be addressed and some key insights regarding synthesis protocols, properties, and applications of chitosan-based CDs for future guidance have also been identified. The optimized synthesis methods capable of producing chitosan-based CDs on a large scale with precise control of their properties will considerably expand the spectrum of applications for chitosan-based CDs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.V.-R., R.B.G.-G. and H.M.N.I.; investigation, A.M.V.-R., R.B.G.-G., M.M.-R. and E.A.F.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.V.-R., R.B.G.-G., M.M.-R., E.A.F.-C. and M.F.C.-A.; writing—review and editing, H.M.N.I. and R.P.-S.; visualization, H.M.N.I.; supervision, H.M.N.I. and R.P.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) Mexico and Tecnologico de Monterrey, Mexico are thankfully acknowledged for supporting this work under Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (SNI) program awarded to Hafiz M. N. Iqbal (CVU: 735340) and Roberto Parra-Saldivar (CVU: 35753).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Das, S.; Ngashangva, L.; Goswami, P. Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; González, L.T.; Madou, M.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Mendoza, A. Synthesis, Purification, and Characterization of Carbon Dots from Non-Activated and Activated Pyrolytic Carbon Black. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; Sharma, A.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Decontamination of Emerging Pharmaceutical Pollutants Using Carbon-Dots as Robust Materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Carbon Dots as a New Fluorescent Nanomaterial with Switchable Sensing Potential and Its Sustainable Deployment for Metal Sensing Applications. Mater. Lett. 2022, 309, 131372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; Morales-Murillo, M.B.; Martínez-Prado, M.A.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Ahmed, I.; Bilal, M.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Carbon Dots-Based Nanomaterials for Fluorescent Sensing of Toxic Elements in Environmental Samples: Strategies for Enhanced Performance. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Goswami, M.; Singh, N.; Sathish, N.; Reddy, M.V.; Kumar, S. Exploring Carbon Quantum Dots as an Aqueous Electrolyte for Energy Storage Devices. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Cantu, D.O.; González-González, R.B.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Martínez, S.A.H.; Araújo, R.G.; Parra-Arroyo, L.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Enzyme-Mimicking Capacities of Carbon-Dots Nanozymes: Properties, Catalytic Mechanism, and Applications—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.C.; Hassan, M.; Gomes, V.G. Coal Derived Carbon Nanomaterials–Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; González, L.T.; Iglesias-González, S.; González-González, E.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Madou, M.; Alvarez, M.M.; Mendoza, A. Characterization of Chemically Activated Pyrolytic Carbon Black Derived from Waste Tires as a Candidate for Nanomaterial Precursor. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, D.P. Natural and Waste Hydrocarbon Precursors for the Synthesis of Carbon Based Nanomaterials: Graphene and CNTs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 976–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, J.; Delattre, C.; Michaud, P.; de Baynast, H. Optimization of Chitosan Properties with the Aim of a Water Resistant Adhesive Development. Polymers 2021, 13, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammi, N.; Chen, S.; Dumeignil, F.; Royer, S.; el Kadib, A. Chitosan as a Sustainable Precursor for Nitrogen-Containing Carbon Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Uses. Mater. Today Sustain. 2020, 10, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Goepel, M.; Colmenares, J.C.; Gläser, R. Chitosan-Based N-Doped Carbon Materials for Electrocatalytic and Photocatalytic Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 4708–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ding, Y.; Qin, C.; Song, W.; Sun, S.; Fang, K.; Li, W.; Du, J.; Wang, F. Anchoring Mn3O4 Nanoparticles onto Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Spheres Derived from Carboxymethyl Chitosan as Superior Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhamurthy, K.; Udayashankar, A.C.; de Britto, S.; Lavanya, S.N.; Abdelrahman, M.; Soumya, K.; Shetty, H.S.; Srinivas, C.; Jogaiah, S. Chitosan and Chitosan-Derived Nanoparticles Modulate Enhanced Immune Response in Tomato against Bacterial Wilt Disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Lv, H.; Sun, H.; Zhai, S.; An, Q. Construction of CuO/Cu-Nanoflowers Loaded on Chitosan-Derived Porous Carbon for High Energy Density Supercapacitors. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2023, 630, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Jing, Y. Room-Temperature Phosphorescence Based on Chitosan Carbon Dots for Trace Water Detection in Organic Solvents and Anti-Counterfeiting Application. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 197, 109923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, H.; Hameed, B.H. Chitosan-Derived Hydrothermally Carbonized Materials and Its Applications: A Review of Recent Literature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Chitosan-Based Materials: Preparation, Modification and Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Rodriguez, A.M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Ahmed, I.; Karthik, K.; Malik, Y.S.; Dhama, K.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Bio-Inspired Biomaterials and Their Drug Delivery Perspectives—A Review. Curr. Drug Metab. 2017, 18, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertmen, A.; Dziedzic, I.; Ehrlich, H. Patentology of chitinous biomaterials. Part II: Chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 301, 120224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, I.; Celik, O. Physicochemical Characterization and the Comparison of Chitin and Chitin Modified with Maleic Anhydride. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Chen, J.; Koziol, K.K.; Hallam, K.R.; Janas, D.; Patil, A.J.; Strachan, A.; Hanley, J.G.; Rahatekar, S.S. Chitin and Carbon Nanotube Composites as Biocompatible Scaffolds for Neuron Growth. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8288–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandapani, G.; Supriya Prasad, P.; Sudha, P.N.; Sukumaran, A. Size Optimization and in Vitro Biocompatibility Studies of Chitosan Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámiz-González, M.A.; Correia, D.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Sencadas, V.; Gómez Ribelles, J.L.; Vidaurre, A. Kinetic Study of Thermal Degradation of Chitosan as a Function of Deacetylation Degree. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Zheng, H.; Du, Y.; Xiang, W.; Deng, H. Applications of Chitin and Chitosan Nanofibers in Bone Regenerative Engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; van Hai, L.; Kim, H.C.; Zhai, L.; Kim, J. Preparation and Characterization of Synthetic Melanin-like Nanoparticles Reinforced Chitosan Nanocomposite Films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Arotiba, O.A.; Mamba, B.B. Chitosan-Based Nanomaterials: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravanja, G.; Primožič, M.; Knez, Ž.; Leitgeb, M. Chitosan-Based (Nano)Materials for Novel Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaee, M.; Garavand, F.; Rehman, A.; Jafarazadeh, S.; Amini, E.; Cacciotti, I. Biodegradability, Physical, Mechanical and Antimicrobial Attributes of Starch Nanocomposites Containing Chitosan Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeamsuksawat, T.; Zhao, H.; Liang, J. Characterization and Antimicrobial Performance of Magnetic Fe3O4@Chitosan@Ag Nanoparticles Synthesized via Suspension Technique. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egil, A.C.; Ozdemir, B.; Gunduz, S.K.; Altıkatoglu-Yapaoz, M.; Budama-Kilinc, Y.; Mostafavi, E. Chitosan/Calcium Nanoparticles as Advanced Antimicrobial Coating for Paper Documents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.G.R.; Picone, C.S.F. Antimicrobial Activity of Lactoferrin-Chitosan-Gellan Nanoparticles and Their Influence on Strawberry Preservation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; She, J.; Manoj, D.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, F. Functionalized Graphene Fiber Modified by Dual Nanoenzyme: Towards High-Performance Flexible Nanohybrid Microelectrode for Electrochemical Sensing in Live Cancer Cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Green Synthesis, Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications of Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots. A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedian, L.; Villalba-Rodríguez, A.M.; Hernández-Vargas, G.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Bio-Based Materials with Novel Characteristics for Tissue Engineering Applications—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zattar, A.P.P.; Fajardo, G.L.; de Mesquita, J.P.; Pereira, F.V. Luminescent Carbon Dots Obtained from Chitosan: A Comparison between Different Methods to Enhance the Quantum Yield. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2021, 29, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludmerczki, R.; Mura, S.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Mandity, I.M.; Carraro, M.; Senes, N.; Garroni, S.; Granozzi, G.; Calvillo, L.; Marras, S.; et al. Carbon Dots from Citric Acid and Its Intermediates Formed by Thermal Decomposition. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 11963–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, K.J.; Zhou, Y.; Leblanc, R.M. Recent Development of Carbon Quantum Dots Regarding Their Optical Properties, Photoluminescence Mechanism, and Core Structure. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4634–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, N. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as Fluorescent Probes for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Nitrite. Molecules 2017, 22, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahal, S.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N. Green Synthesis of High Quantum Yield Carbon Dots from Phenylalanine and Citric Acid: Role of Stoichiometry and Nitrogen Doping. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5566–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowska, J.D.; Murphy, A.; Mellor, C.; Fernandes, D.; Gibbons, E.N.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Burgaz, E.; Moore, J.; Yeates, S.G. A Rich Gallery of Carbon Dots Based Photoluminescent Suspensions and Powders Derived by Citric Acid/Urea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, L.; Pang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W.F.; Yan, R. Chitosan-Based Carbon Nanoparticles as a Heavy Metal Indicator and for Wastewater Treatment. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 12015–12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Sadrjavadi, K.; Farhadian, N.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Shahlaei, M. Easy Synthesis, Characterization and Cell Cytotoxicity of Green Nano Carbon Dots Using Hydrothermal Carbonization of Gum Tragacanth and Chitosan Bio-Polymers for Bioimaging. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 259, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Huang, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, B.; Han, Y.; Han, S.; Xu, T.; Si, C.; Zhang, C. Resistance to Aggregation-Caused Quenching: Chitosan-Based Solid Carbon Dots for White Light-Emitting Diode and 3D Printing. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Influence of Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots on Astaxanthin Production of Green Alga Tetraselmis sp. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Ghosh, T.; Kumar, H.; Jain, T.; Singh, Y. Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Synthesis of Carbon Dots from Chitosan-Ethanol System. Asian Chitin J. 2015, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yang, X.; Yao, C. High Quantum Yield Fluorescent Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots for the Turn-On-Off-On Detection of Cr(VI) and H2O2. Nano 2021, 16, 2150103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, N.; Barooah, M.; Majumdar, G.; Chowdhury, D. Carbon Dots Rooted Agarose Hydrogel Hybrid Platform for Optical Detection and Separation of Heavy Metal Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarbeygi, Z.; Farhadian, N.; Ansari, M.; Shahlaei, M.; Moradi, S. An Innovative Green Sensing Strategy Based on Cu-Doped Tragacanth/Chitosan Nano Carbon Dots for Isoniazid Detection. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 228, 117848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y. Chitosan-Derived N-Doped Carbon Dots for Fluorescent Determination of Nitrite and Bacteria Imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 251, 119468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.; Togiti, U.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Nag, A. Functionalized Chitosan-Carbon Dots: A Fluorescent Probe for Detecting Trace Amount of Water in Organic Solvents. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11301–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Dai, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Lv, M.; Yin, X. Dansyl-Modified Carbon Dots with Dual-Emission for PH Sensing, Fe3+ Ion Detection and Fluorescent Ink. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 36971–36979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.F. Selective Biosensing of Staphylococcus Aureus Using Chitosan Quantum Dots. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 188, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; El-Bery, H.M.; Metwally, A.A.; Elshazly, M.; Hathout, R.M. Synthesis of CdS-Modified Chitosan Quantum Dots for the Drug Delivery of Sesamol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q. Carbon Quantum Dots Prepared with Chitosan for Synthesis of CQDs/AuNPs for Iodine Ions Detection. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zheng, M.; Hu, C.; Tan, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y. One-Step Synthesis of Amino-Functionalized Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Chitosan. Chem. Commun. 2011, 48, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Peng, R.; Wei, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Xiao, B. Ethanol-Precipitation-Assisted Highly Efficient Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots from Chitosan. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22574–22580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, F.; Tajfar, N.; Mohammadnejad, M. The Synthesis and Efficiency Investigation of a Boronic Acid-Modified Magnetic Chitosan Quantum Dot Nanocomposite in the Detection of Cu2+ Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, J.A.O.; Crispim, G.O.; Pinto, B.P.; San Gil, R.A.S.; Mota, C.J.A. Synthesis, Characterization, and CO2 Uptake of Adsorbents Prepared by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Chitosan. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29520–29529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Kang, M.; Payne, G.F.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Probing Energy and Electron Transfer Mechanisms in Fluorescence Quenching of Biomass Carbon Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17478–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keerthana, A.K.; Ashraf, P.M. Carbon Nanodots Synthesized from Chitosan and Its Application as a Corrosion Inhibitor in Boat-Building Carbon Steel BIS2062. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, Ł.; Piatkowski˛, M.; Radwan-Pragłowska, J.; Bogdał, D.; Matysek, D. Chitosan-Based Carbon Quantum Dots for Biomedical Applications: Synthesis and Characterization. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Shuang, S.; Li, C.; Dong, C. Carbon Nano-Dots as a Fluorescent and Colorimetric Dual-Readout Probe for the Detection of Arginine and Cu2+ and Its Logic Gate Operation. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11545–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Jing, Y.; Ni, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhou, P. Potentiality of Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Chitin as a Fluorescent Sensor for Detection of ClO−. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Yuan, D.; He, H.; Lu, J. Microwave-Assisted One-Step Green Synthesis of Amino-Functionalized Fluorescent Carbon Nitride Dots from Chitosan. Luminescence 2013, 28, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Deng, Y.; Xia, Y. Facile Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots with Chitosan for Fluorescent Detection of Fe3+. Polymers 2019, 11, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Pathan, S.H.; Mitra, S.; Modha, B.H.; Goswami, A.; Pramanik, P. Tuning of Photoluminescence on Different Surface Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 3602–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hakkarainen, M.; Grützmacher, H.; Chiappone, A.; Sangermano, M. Photocrosslinked Chitosan Hydrogels Reinforced with Chitosan-Derived Nano-Graphene Oxide. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Yan, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, R.; Huang, L. Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots with Multi-Color-Emissive Tunable Fluorescence and Visible Light Catalytic Enhancement Properties. Nano Res. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Z.; Rhim, J.W.; Bagheri, R.; Pircheraghi, G.; Lotfali, E. Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Functional Film Integrated with Chitosan-Based Carbon Quantum Dots for Active Food Packaging Applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 166, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, Q. Carbon Dots Based on Natural Resources: Synthesis and Applications in Sensors. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.F.; Chen, Z.P. A Review of Carbon Dots Produced from Biomass Wastes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, P.; Duan, C. Non-Toxic Carbon Dots Fluorescence Sensor Based on Chitosan for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Cr (VI) in Water. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Jebakumar Immanuel Edison, T.N.; Shanmugam, M.; Perumal, S.; Somanathan, T.; Lee, Y.R. Sustainable Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from Banana Peel Waste Using Hydrothermal Process for in Vivo Bioimaging. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 126, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qi, Q.; Sun, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. Green Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Chitosan as Selective and Sensitive “off-on” Probes for Nitrite and “on-off-on” Probes for Enrofloxacin Detection. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 908, 164519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Rapid and High Yield Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Chelating Ability Derived from Acrylamide/Chitosan for Selective Detection of Ferrous Ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Lee, Y.R. Sustainable Synthesis of Multifunctional Carbon Dots Using Biomass and Their Applications: A Mini-Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horo, H.; Saha, M.; Das, H.; Mandal, B.; Kundu, L.M. Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent, Amine-Functionalized Carbon Dots from Biotin-Modified Chitosan and Silk-Fibroin Blend for Target-Specific Delivery of Antitumor Agents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X. Simple Approach to Synthesize Amino-Functionalized Carbon Dots by Carbonization of Chitosan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, L.G.; Subedi, S.; Dahal, B.; Truong, P.L.; Gwag, J.S.; Tran, N.T.; Nguyen, M.K. Highly Efficient Fluorescent Probes from Chitosan-Based Amino-Functional Carbon Dots for the Selective Detection of Cu2+ Traces. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; Wu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Shen, Y. Engineering Efficient Artificial Nanozyme Based on Chitosan Grafted Fe-Doped-Carbon Dots for Bacteria Biofilm Eradication. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Qi, Q.; Zhao, X. Chitosan and κ-Carrageenan-Derived Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-Doped Carbon Dots “on-off-on” Fluorescent Probe for Sequential Detection of Fe3+ and Ascorbic Acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Rao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, C.; Shan, Z.; Ren, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, X. Green and High-Yield Synthesis of Carbon Dots for Ratiometric Fluorescent Determination of PH and Enzyme Reactions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Man, H.; Dong, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, X. Preparation of Highly Crystalline Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application in Sequential Fluorescent Detection of Fe3+ and Ascorbic Acid. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Chen, M.; Hu, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Growth and Stabilization of Silver Nanoparticles on Carbon Dots and Sensing Application. Langmuir 2013, 29, 16135–16140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.R.; He, G.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Carpio-Perochena, A.; Bramante, C.M.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Moura, M.R.d.; Aouada, F.A.; Kishen, A. Chelating and Antibacterial Properties of Chitosan Nanoparticles on Dentin. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2015, 40, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, M.; Guo, C.; Dan, W.; Devahastin, S. Laser-Induced Microporous Modified Atmosphere Packaging and Chitosan Carbon-Dot Coating as a Novel Combined Preservation Method for Fresh-Cut Cucumber. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).