Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Their Potential to Treat Malarial Protozoan Parasites Infection: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study Selection and Analysis
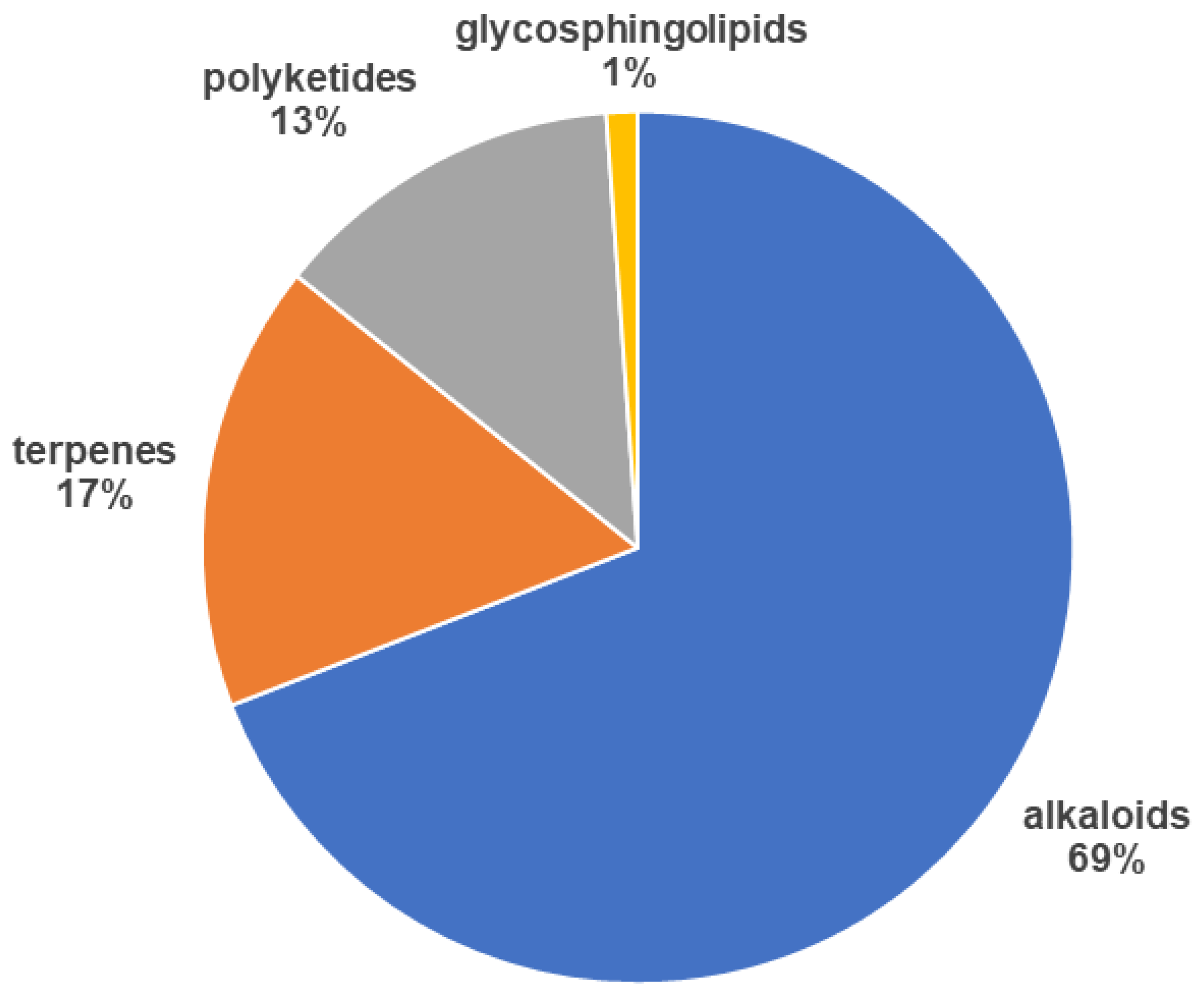
2.2. Classes of Compounds Found in Marine Sponge Extracts
2.2.1. Alkaloids
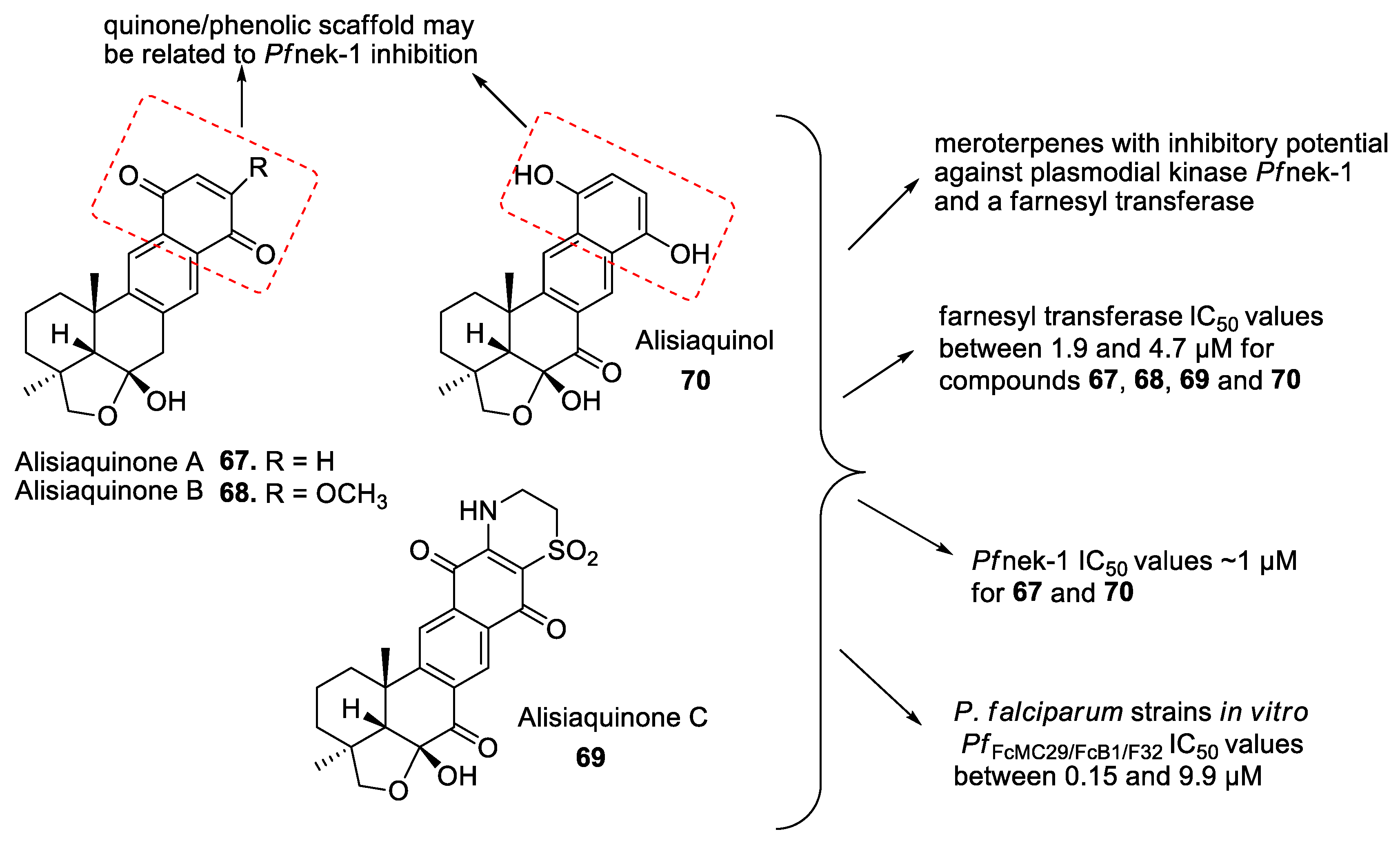
2.2.2. Terpenes
2.2.3. Polyketides
2.2.4. Glycosphingolipids
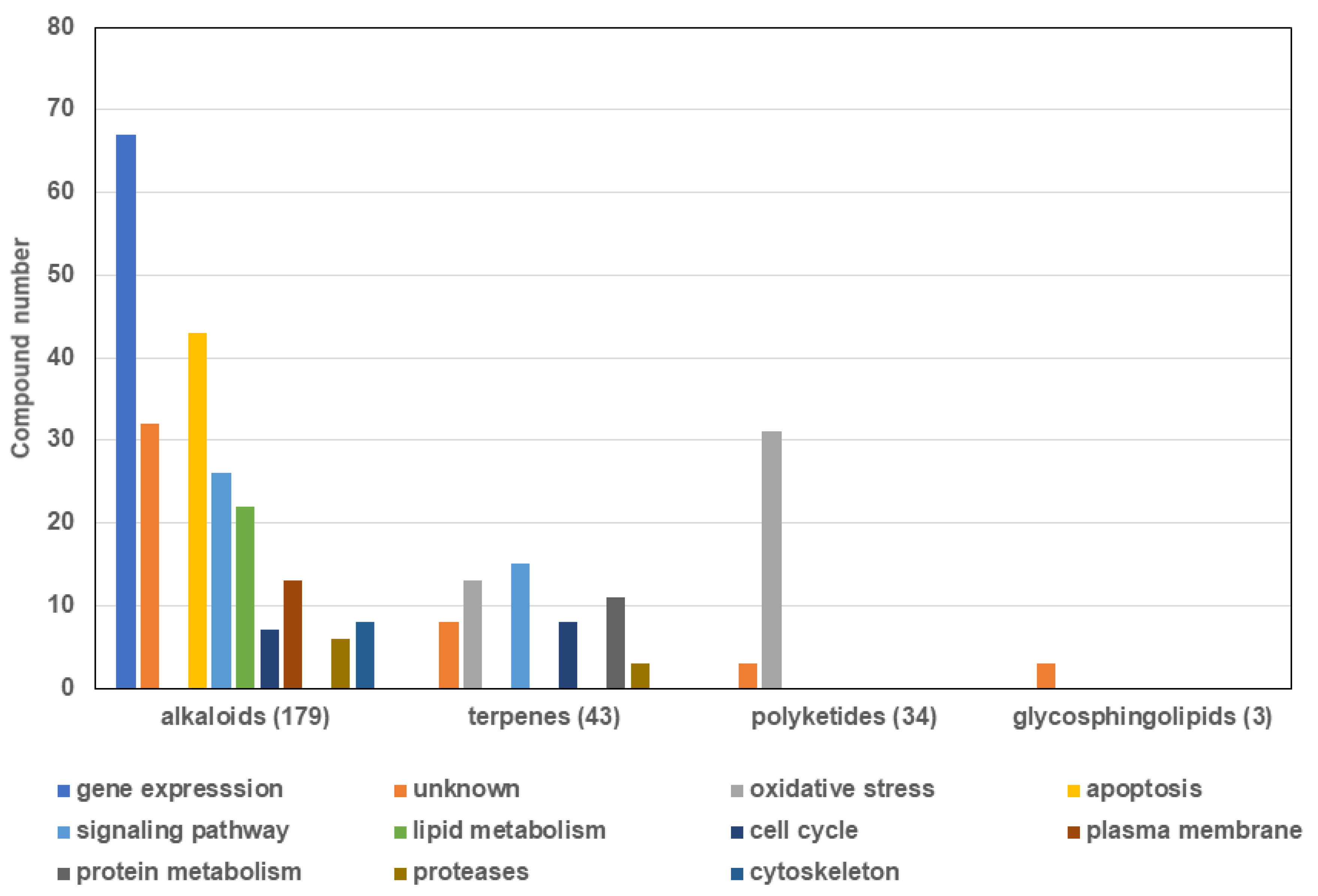
2.3. Mechanisms of Action of the New Compounds Found in Marine Sponge Extracts
3. Methodology
3.1. Review Protocol
3.2. Eligibility Criteria
3.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
3.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
3.3. Data Extraction
3.4. Types of Reported Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crompton, P.D.; Moebius, J.; Portugal, S.; Waisberg, M.; Hart, G.; Garver, L.S.; Miller, L.H.; Barillas, C.; Pierce, S.K. Malaria immunity in man and mosquito: Insights into unsolved mysteries of a deadly infectious disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Malaria Report 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wicht, K.J.; Mok, S.; Fidock, D.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Plasmodium falciparum Malaria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, C.; Caumes, E.; Thellier, M.; Ndour, P.A.; Buffet, P.A.; Jauréguiberry, S. Artesunate to treat severe malaria in travellers: Review of efficacy and safety and practical implications. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24, taw093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgford, J.L.; Xie, S.C.; Cobbold, S.A.; Pasaje, C.F.A.; Herrmann, S.; Yang, T.; Gillett, D.L.; Dick, L.R.; Ralph, S.A.; Dogovski, C.; et al. Artemisinin kills malaria parasites by damaging proteins and inhibiting the proteasome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves, K.; Prudhomme, J.; Le Roch, K.G.; Franzblau, S.G.; Rodríguez, A.D. Natural product-based synthesis of novel anti-infective isothiocyanate- and isoselenocyanate-functionalized amphilectane diterpenes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noedl, H.; Se, Y.; Schaecher, K.; Smith, B.L.; Socheat, D.; Fukuda, M.M. Evidence of Artemisinin-Resistant Malaria in Western Cambodia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2619–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariey, F.; Witkowski, B.; Amaratunga, C.; Beghain, J.; Langlois, A.C.; Khim, N.; Kim, S.; Duru, V.; Bouchier, C.; Ma, L.; et al. A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 2014, 505, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou Eleni, E. Therapeutic properties and uses of marine invertebrates in the ancient Greek world and early Byzantium. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Avilés, E.; Rodríguez, A.D. Marine sponge Hymeniacidon sp. amphilectane metabolites potently inhibit rat brain microglia thromboxane B 2 generation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Alencar, D.B.; Da Silva, S.R.; Pires-Cavalcante, K.M.S.; De Lima, R.L.; Pereira, F.N.; De Sousa, M.B.; Viana, F.A.; Nagano, C.S.; Do Nascimento, K.S.; Cavada, B.S.; et al. Antioxidant potential and cytotoxic activity of two red seaweed species, amansia multifida and meristiella echinocarpa, from the coast of Northeastern Brazil. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2014, 86, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leys, S.P.; Hill, A. The Physiology and Molecular Biology of Sponge Tissues. Adv. Marine Biol. 2012, 62, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amina, M.; Musayeib, N.M. Al Biological and Medicinal Importance of Sponge. In Biological Resources of Water; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feuda, R.; Dohrmann, M.; Pett, W.; Philippe, H.; Rota-Stabelli, O.; Lartillot, N.; Wörheide, G.; Pisani, D. Improved Modeling of Compositional Heterogeneity Supports Sponges as Sister to All Other Animals. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Lee, K.J. Nucleosides from the Marine Sponge Haliclona sp. Z. Fur Nat.-Sect. C J. Biosci. 2009, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zou, Y.; Wang, R.P.; Hamann, M.T.; Zhang, H.J.; Jiao, W.H.; Han, B.N.; Song, S.J.; Lin, H.W. Relative and absolute stereochemistry of diacarperoxides: Antimalarial norditerpene endoperoxides from marine sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4399–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniswamy, K.; Thamodaran, P. Genomic imprinting: A general overview. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Marine antimalarials. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.E.; Pichon, E.; Moriou, C.; Clerc, P.; Trépos, R.; Frederich, M.; De Voogd, N.; Hellio, C.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A.; Al-Mourabit, A. New antimalarial and antimicrobial tryptamine derivatives from the marine sponge fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Hamann, M.T.; Hashish, N.E.; Shier, W.T.; Kelly, M.; Khan, A.A. Antimalarial, antiviral, and antitoxoplasmosis norsesterterpene peroxide acids from the red sea sponge Diacarnus erythraeanus. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdemir, D.; Topaloglu, B.; Perozzo, R.; Brun, R.; O’Neill, R.; Carballeira, N.M.; Zhang, X.; Tonge, P.J.; Linden, A.; Rüedi, P. Marine natural products from the Turkish sponge Agelas oroides that inhibit the enoyl reductases from Plasmodium falciparum, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Escherichia coli. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6834–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gochfeld, D.J.; Hamann, M.T. Isolation and biological evaluation of filiformin, plakortide F, and plakortone G from the Caribbean sponge Plakortis sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Latif, A.; Kong, C.S.; Seo, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Dalal, S.R.; Cassera, M.B.; Kingston, D.G.I. Isolation and characterization of antiplasmodial constituents from the marine sponge Coscinoderma sp. Z. Fur Nat.-Sect. C J. Biosci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtihapsari, M.; Salam, S.; Kurnia, D.; Darwati, D.; Kadarusman, K.; Abdullah, F.F.; Herlina, T.; Husna, M.H.; Awang, K.; Shiono, Y.; et al. A new antiplasmodial sterol from Indonesian marine sponge, Xestospongia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, L.L.L.; Bertonha, A.F.; Severo, I.R.M.; Aguiar, A.C.C.; De Souza, G.E.; Oliva, G.; Guido, R.V.C.; Grazzia, N.; Costa, T.R.; Miguel, D.C.; et al. Isolation, Derivative Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationships of Antiparasitic Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Tedania brasiliensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.E.; Wolfender, J.L.; Queiroz, E.F.; Marcourt, L.; Al-Mourabit, A.; Frederich, M.; Bordignon, A.; De Voogd, N.; Illien, B.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A. Unguiculin A and Ptilomycalins E-H, Antimalarial Guanidine Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Monanchora unguiculata. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, R.P.; Xu, B.; Yu, H.B.; Ma, G.Y.; Wang, G.F.; Dai, S.W.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, W.H.; Song, S.J.; et al. New antimalarial norterpene cyclic peroxides from Xisha Islands sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2084–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gros, E.; Martin, M.T.; Sorres, J.; Moriou, C.; Vacelet, J.; Frederich, M.; Aknin, M.; Kashman, Y.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A.; Al-Mourabit, A. Netamines O-S, Five New Tricyclic Guanidine Alkaloids from the Madagascar Sponge Biemna laboutei, and Their Antimalarial Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, G.; Persico, M.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.W.; Guo, Y.W.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fattorusso, C. Endoperoxide polyketides from a Chinese Plakortis simplex: Further evidence of the impact of stereochemistry on antimalarial activity of simple 1,2-dioxanes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, E.; Al-Mourabit, A.; Martin, M.T.; Sorres, J.; Vacelet, J.; Frederich, M.; Aknin, M.; Kashman, Y.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A. Netamines H-N, tricyclic alkaloids from the marine sponge biemna laboutei and their antimalarial activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, S.; Roberts, B.F.; Wright, A.E.; Chakrabarti, D. The bis(Indolyl)imidazole alkaloid nortopsentin a exhibits antiplasmodial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.A.; Duffy, S.; Fletcher, S.; Avery, V.M.; Quinn, R.J. Thiaplakortones A-D: Antimalarial thiazine alkaloids from the Australian marine sponge plakortis lita. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhi, F.; Grellier, P.; Clément, M.; Roussakis, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Genin-Seward, E.; Kornprobst, J.M.; Barnathan, G.; Wielgosz-Collin, G. Antimalarial activity of axidjiferosides, new β-galactosylceramides from the African sponge Axinyssa djiferi. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirirak, T.; Brecker, L.; Plubrukarn, A. Kabiramide L, a new antiplasmodial trisoxazole macrolide from the sponge Pachastrissa nux. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanthathamrongsiri, N.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Wattanapiromsakul, C.; Plubrukarn, A. Bifunctionalized amphilectane diterpenes from the sponge Stylissa cf. massa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Buchanan, M.S.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Charman, S.A.; Charman, W.N.; White, K.L.; Shackleford, D.M.; Edstein, M.D.; Andrews, K.T.; et al. Antimalarial activity of pyrroloiminoquinones from the Australian marine sponge zyzzya sp. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Khan, S.I.; Jacob, M.R.; Tekwani, B.L.; Walker, L.A.; Samoylenko, V. Pentacyclic ingamine alkaloids, a new antiplasmodial pharmacophore from the marine sponge Petrosid Ng5 Sp5. Planta Med. 2012, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudianta, I.W.; Skinner-Adams, T.; Andrews, K.T.; Davis, R.A.; Hadi, T.A.; Hayes, P.Y.; Garson, M.J. Psammaplysin derivatives from the balinese marine sponge Aplysinella strongylata. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, E.; Thomas, O.P.; Robledo, S.; Munoz, D.; Martinez, A. Antiparasitic Bromotyrosine derivatives from the marine sponge Verongula rigida. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirirak, T.; Kittiwisut, S.; Janma, C.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Plubrukarn, A. Kabiramides J and K, trisoxazole macrolides from the sponge Pachastrissa nux. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Andrews, K.T.; Birrell, G.W.; Tran, T.L.; Camp, D.; Davis, R.A.; Quinn, R.J. Psammaplysin H, a new antimalarial bromotyrosine alkaloid from a marine sponge of the genus Pseudoceratina. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Romero, C.; Ortiz, I.; Vicente, J.; Vera, B.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Nam, S.; Jove, R. Bioactive cycloperoxides isolated from the Puerto Rican sponge Plakortis halichondrioides. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoylenko, V.; Khan, S.I.; Jacob, M.R.; Tekwani, B.L.; Walker, L.A.; Hufford, C.D.; Muhammad, I. Bioactive (+)-manzamine A and (+)-8-hydroxymanzamine A tertiary bases and salts from Acanthostrongylophora ingens and their preparations. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueoka, R.; Nakao, Y.; Kawatsu, S.; Yaegashi, J.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Furihata, K.; Van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Gracilioethers A-C, antimalarial metabolites from the marine sponge Agelas gracilis. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; Lang-Unnasch, N. Diterpene formamides from the tropical marine sponge cymbastela hooperi and their antimalarial activity in vitro. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller, J.; Mihci, G.; Martin, M.T.; Gallard, J.F.; Menou, J.L.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.; Petek, S.; Chevalley, S.; Valentin, A.; et al. Agelasines J, K, and L from the Solomon Islands marine sponge Agelas cf. mauritiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoubzdanne, D.; Marcourt, L.; Raux, R.; Chevalley, S.; Dorin, D.; Doerig, C.; Valentin, A.; Ausseil, F.; Debitus, C. Alisiaquinones and Alisiaquinol, dual inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum enzyme targets from a new caledonian deep water sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, D.; Jullian, V.; Parenty, A.; Knibiehler, M.; Dorin, D.; Schmitt, S.; Lozach, O.; Lebouvier, N.; Frostin, M.; Alby, F.; et al. Antimalarial potential of xestoquinone, a protein kinase inhibitor isolated from a Vanuatu marine sponge Xestospongia sp. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2006, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Sauvain, M.; Debitus, C.; Duigou, A.G.; Ausseil, F.; Menou, J.L.; Pietra, F. New 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrrolo [1,2-a]pyrimidinium alkaloids (phloeodictynes) from the New Caledonian shallow-water haplosclerid sponge Oceanapia fistulosa. Structural elucidation from mainly LC-tandem-MS-soft-ionization techniques and discovery of antiplasmodial activity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Parapini, S.; Campagnuolo, C.; Basilico, N.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Taramelli, D. Activity against Plasmodium falciparum of cycloperoxide compounds obtained from the sponge Plakortis simplex. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, G.; Köng, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Kaminsky, R. A new bioactive sesterterpene and antiplasmodial alkaloids from the marine sponge Hyrtios cf. erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerhofer, C.K.; Pezzuto, J.M.; König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Sticher, O. Antimalarial activity of sesquiterpenes from the marine sponge acanthella klethra. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Akl, E.A.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.; Brozek, J.; Norris, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Glasziou, P.; Debeer, H.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajuddeen, N.; Van Heerden, F.R. Antiplasmodial natural products: An update. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.H.; Holmes, M.J.; Higa, T.; Hamann, M.T.; Kara, U.A.K. In vivo antimalarial activity of the beta-carboline alkaloid manzamine A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, E.; Rodríguez, A.D. Monamphilectine A, a potent antimalarial β-lactam from marine sponge hymeniacidon sp: Isolation, structure, semisynthesis, and bioactivity. Org. Lett. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, R.F.; Keeling, P.J.; Donald, R.G.K.; Striepen, B.; Handman, E.; Lang-Unnasch, N.; Cowman, A.F.; Besra, G.S.; Roos, D.S.; Mcfadden, G.I. Nuclear-encoded proteins target to the plastid in Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.M.; Peng, J.; Fronczek, F.R.; Kelly, M.; Hamann, M.T. Crystallographic and NMR studies of antiinfective tricyclic guanidine alkaloids from the sponge Monanchora unguifera. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2004, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, E.; Latif, A.; Kong, C.S.; Seo, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Dalal, S.R.; Cassera, M.B.; Kingston, D.G.I. Antimalarial activity of the isolates from the marine sponge Hyrtios erectus against the chloroquine-resistant Dd2 strain of Plasmodium falciparum. Z. Fur Nat.-Sect. C J. Biosci. 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunjan, S.; Sharma, T.; Yadav, K.; Chauhan, B.S.; Singh, S.K.; Siddiqi, M.I.; Tripathi, R. Artemisinin Derivatives and Synthetic Trioxane Trigger Apoptotic Cell Death in Asexual Stages of Plasmodium. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, M.D.; Faulkner, D.J. Plakortin, an Antibiotic from Plakortis halichondrioides. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Xu, J.P.; Gingrich, D.E.; Williams, M.D.; Doubek, D.L.; Chapuis, J.C.; Schmidt, J.M. Antineoplastic agents, Part 395. Isolation and structure of agelagalastatin from the Papua New Guinea marine sponge Agelas sp. Chem. Commun. 1999, 10, 915–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, G.; Santamaría, G.; Cruz, P.G.; Fernández, R.; Pérez, M.; Martínez-Leal, J.F.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C.; Cuevas, C. Cytotoxic Anomoian B and Aplyzanzine B, New Bromotyrosine Alkaloids from Indonesian Sponges. ACS Omega 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goey, A.K.L.; Chau, C.H.; Sissung, T.M.; Cook, K.M.; Venzon, D.J.; Castro, A.; Ransom, T.R.; Henrich, C.J.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Screening and Biological Effects of Marine Pyrroloiminoquinone Alkaloids: Potential Inhibitors of the HIF-1α/p300 Interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Ma, W.; Fang, W.; Chen, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Bioactivities of six sterols isolated from marine invertebrates. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Blees, J.S.; Bayer, M.M.; Colburn, N.H.; Thomas, C.L.; Henrich, C.J.; Peach, M.L.; McMahon, J.B.; Schmid, T.; Gustafson, K.R. Tricyclic guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Acanthella cavernosa that stabilize the tumor suppressor PDCD4. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4593–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, J.; Ishizuka, E.; Nakao, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Isolation of 1-methylherbipoline salts of halisulfate-1 and of suvanine as serine protease inhibitors from a marine sponge, Coscinoderma mathewsi. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klenchin, V.A.; Allingham, J.S.; King, R.; Tanaka, J.; Marriott, G.; Rayment, I. Trisoxazole macrolide toxins mimic the binding of actin-capping proteins to actin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.; Ganesapandian, S.; Singh, M.; Kumaraguru, A.K. Anti-tumour activity of bromopyrrole alkaloids against human breast tumour (MCF-7) through apoptosis induction. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olkkonen, V.M.; Béaslas, O.; Nissilä, E. Oxysterols and their cellular effectors. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 76–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, M.G.J.; Leiser, T.; Haus, P.; Samlal, S.; Wong, A.C.; Wood, R.J.; Petrucci, V.; Gunaratnam, M.; Hughes, S.M.; Buluwela, L.; et al. Defining the mechanism of action and enzymatic selectivity of psammaplin A against its epigenetic targets. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.C.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, K.H.; Park, W.; Jeon, J.E.; Oh, H.; Shin, J.; Oh, K.B. Actin depolymerizing effect of trisoxazole-containing macrolides. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, A.; Salam, K.A.; Hermawan, I.; Akimitsu, N.; Tanaka, J.; Tani, H.; Yamashita, A.; Moriishi, K.; Nakakoshi, M.; Tsubuki, M.; et al. Identification and biochemical characterization of halisulfate 3 and suvanine as novel inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase from a marine sponge. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlinck, R.G.S.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Bruno, I.; Riccio, R.; Ferri, S.; Spampinato, S.; Speroni, E. Polycyclic guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge crambe crambe and Ca++ channel blocker activity of crambescidin 816. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawabteh, A.; Juma, S.; Bader, M.; Karaman, D.; Scrano, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Karaman, R. The biological activity of natural alkaloids against herbivores, cancerous cells and pathogens. Toxins 2019, 11, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Benedetti, R.; Pérez-Rodríguez, S.; Nebbioso, A.; García-Rodríguez, J.; Carafa, V.; Stuhldreier, M.; Conte, M.; Rodríguez-Barrios, F.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; et al. Indole-derived psammaplin a analogues as epigenetic modulators with multiple inhibitory activities. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senerovic, L.; Opsenica, D.; Moric, I.; Aleksic, I.; Spasić, M.; Vasiljevic, B. Quinolines and quinolones as antibacterial, antifungal, anti-virulence, antiviral and anti-parasitic agents. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Byler, K.G.; Wang, C.; Setzer, W.N. Quinoline alkaloids as intercalative topoisomerase inhibitors. J. Mol. Model. 2009, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.J.; Chia, W.N.; Loh, C.C.Y.; Li, Z.; Lee, Y.M.; He, Y.; Yuan, L.X.; Lim, T.K.; Liu, M.; et al. Haem-activated promiscuous targeting of artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangi, P.; Jain, R.; Mamidala, R.; Sharma, V.; Agarwal, S.; Bathula, C.; Thirumalachary, M.; Sen, S.; Singh, S. Natural Product Inspired Novel Indole based Chiral Scaffold Kills Human Malaria Parasites via Ionic Imbalance Mediated Cell Death. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheenpracha, S.; Park, E.J.; Rostama, B.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Chang, L.C. Inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells by the norsesterterpene peroxide, epimuqubilin A. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chokkalingam, U.; Hwang, T.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive Isoprenoid-Derived Natural Products from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sinularia erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, F.; Nuzzo, G.; Hamdy, N.A.; Fakhr, I.; Moreno, Y.; Banuls, L.; Van Goietsenoven, G.; Villani, G.; Mathieu, V.; Van Soest, R.; et al. In vitro pharmacological and toxicological effects of norterpene peroxides isolated from the red sea sponge diacarnus erythraeanus on normal and cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Scala, F.; Barone, V.; Cimino, P.; Stendardo, E.; Catalanotti, B.; Persico, M.; Fattorusso, C. Insight into the mechanism of action of plakortins, simple 1,2-dioxane antimalarials. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavishe, R.A.; Koenderink, J.B.; Alifrangis, M. Oxidative stress in malaria and artemisinin combination therapy: Pros and Cons. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, N.S.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: Love and other relationships. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.B.M.; Hooijmans, C.R.; Langendam, M.W.; van Luijk, J.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Wever, K.E. A protocol format for the preparation, registration and publication of systematic reviews of animal intervention studies. Evidence-Based Preclin. Med. 2015, 2, e00007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author | Sponge Genus | Material Collection Location | Extracted Material (P. falciparum Strain and IC50 Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Campos et al., (2019) [21] | Fascaplysinopsis reticulata | Mayotte (Indian Ocean) |  |
| Jeong., et al. (2019) [25] | Coscinoderma sp. | Chuuk Island, Federated States of Micronesia | 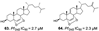 |
| Ju et al., (2019) [25] | Hyrtios erectus | Chuuk Island, Federated States of Micronesia |  |
| Murtihapsari. et al., (2019) [26] | Xestospongia sp | Kaimana, West Papua, Indonesia | 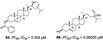 |
| Parra et al., (2018) [27] | Tedania Brasiliensis | Brazil |  |
| Campos et al., (2017) [28] | Monanchora unguiculata | Mitsio islands, Madagascar |  |
| Yang et al., (2016) [29] | Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa | SouthChina Sea Sponge |  |
| Gros et al., (2015) [30] | Biemna laboutei | Madagascar | 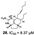 |
| Chianese et al., (2014) [31] | Plakortis simplexs | South China Sea | 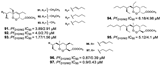 |
| Gros et al., (2014) [32] | Biemna laboutei | Madagascar at Salary Ba |  |
| Yang et al., (2014) [17] | Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa | South China Sea |  |
| Alvarado et al., (2013) [33] | Spongosorites sp | Not reported | 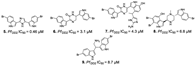 |
| Davis et al., (2013) [34] | Plakortis lita | Not reported | 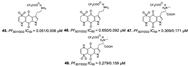 |
| Farokhi et al., (2013) [35] | Axinyssa djiferi | Senegalese coasts |  |
| Sirirak et al., (2013) [36] | Pachastrissa nuxs | Thailand | 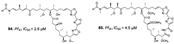 |
| Chanthathamrongsiri et al., (2012) [37] | Stylissacf. massa | Not reported | 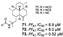 |
| Davis et al., (2012) [38] | Zyzzya sp | Not reported |  |
| Ilias et al., (2012) [39] | Petrosia | Eastern Fields north of Australia | 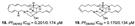 |
| Mudianta et al., (2012) [40] | Aplysinella strongylata | Tulamben, Bali, Indonesia |  |
| El Sayed et al., (2011) [22] | Diacarnus erythraeanus | Red Sea |  |
| Galeano et al., (2011) [41] | Verongula rigida | Urabá Gulf is located in the Southwestern Caribbean |  |
| Sirirak et al., (2011) [42] | Pachastrissa nux | Koh-Tao, Surat-Thani ProvinceChumphon IslandsNational Park, Chumphon Province, |  |
| Xu et al., (2011) [43] | Pseudoceratina sp | Australian biota |  |
| Jiménez-Romero et al., (2010) [44] | Plakortis halichondrioides | Puerto Rico | 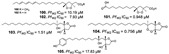 |
| Samoylenko et al., (2009) [45] | Acanthostrongylophora ingens | Pacific |  |
| Ueoka et al., (2009) [46] | Agelas gracilis | southern Japan |  |
| Wright et al., (2009) [47] | Cymbastela hooperi | Not reported |  |
| Appenzeller et al., (2008) [48] | Agelas cf. mauritiana | Solomon Islands |  |
| Desoubzdanne et al., (2008) [49] | New Caledonian | Norfolk Rise (New Caledonia) |  |
| Tasdemir et al., (2007) [23] | Agelas oroides | Northern Aegean Sea, Turkey | - fractions: fatty acid mixtures FAME (3.4 μg/mL) and FAMF (8.7 μg/mL)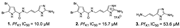 |
| Laurent et al., (2006) [50] | Xestospongia | Vanuatu |  |
| Mancini et al., (2004) [51] | Oceanapia fistulosa | New Caledonia Main Island | -crude mixture (0.98 μM) -N-methyl derivatives from the crude mixture (8 μM) |
| Fattorusso et al., (2002) [52] | Plakortis simplex | Berry Island (Bahamas) |  |
| Gochfeld et al., (2001) [24] | Plakortis sp. | Jamaica |  |
| Kirsch et al., (2000) [53] | Hyrtios cf. erecta | Fiji |  |
| Angerhofer et al., (1992) [54] | Acanthella klethra | Australia | 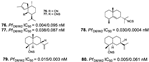 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguiar, A.C.C.; Parisi, J.R.; Granito, R.N.; de Sousa, L.R.F.; Renno, A.C.M.; Gazarini, M.L. Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Their Potential to Treat Malarial Protozoan Parasites Infection: A Systematic Review. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030134
Aguiar ACC, Parisi JR, Granito RN, de Sousa LRF, Renno ACM, Gazarini ML. Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Their Potential to Treat Malarial Protozoan Parasites Infection: A Systematic Review. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(3):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030134
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguiar, Anna Caroline Campos, Julia Risso Parisi, Renata Neves Granito, Lorena Ramos Freitas de Sousa, Ana Cláudia Muniz Renno, and Marcos Leoni Gazarini. 2021. "Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Their Potential to Treat Malarial Protozoan Parasites Infection: A Systematic Review" Marine Drugs 19, no. 3: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030134
APA StyleAguiar, A. C. C., Parisi, J. R., Granito, R. N., de Sousa, L. R. F., Renno, A. C. M., & Gazarini, M. L. (2021). Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Their Potential to Treat Malarial Protozoan Parasites Infection: A Systematic Review. Marine Drugs, 19(3), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030134






