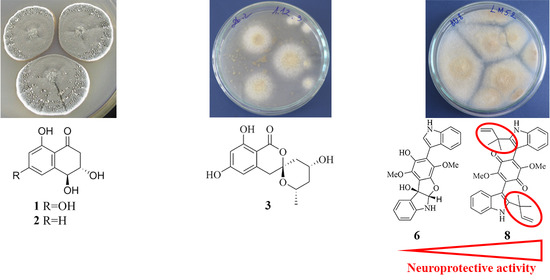
Neuroprotective Metabolites from Vietnamese Marine Derived Fungi of Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Compounds
2.2. Biological Activities of the Studied Compounds
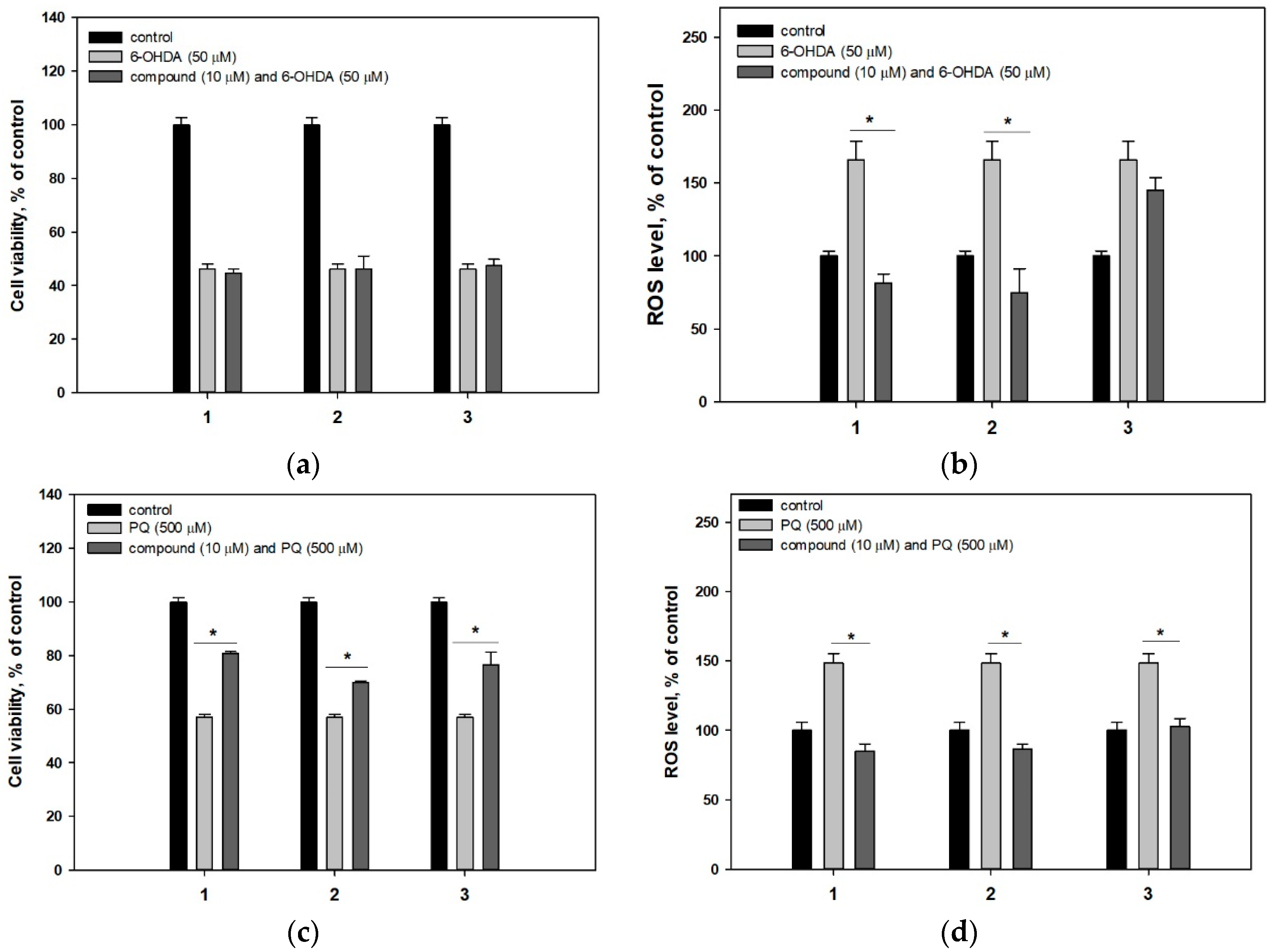
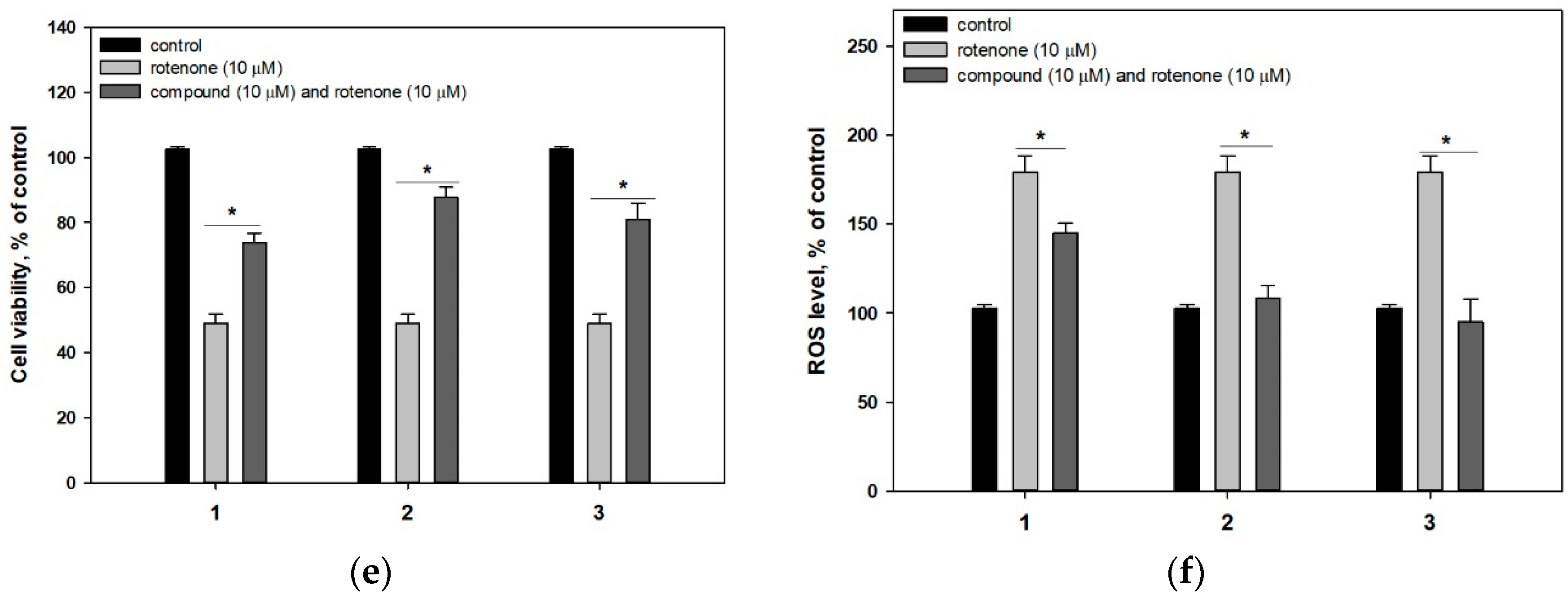
2.2.1. 4-Hydroxyscytalone (1), 4-Hydroxy-6-Dehydroxyscytalone (2) and Demethylcitreoviranol (3)
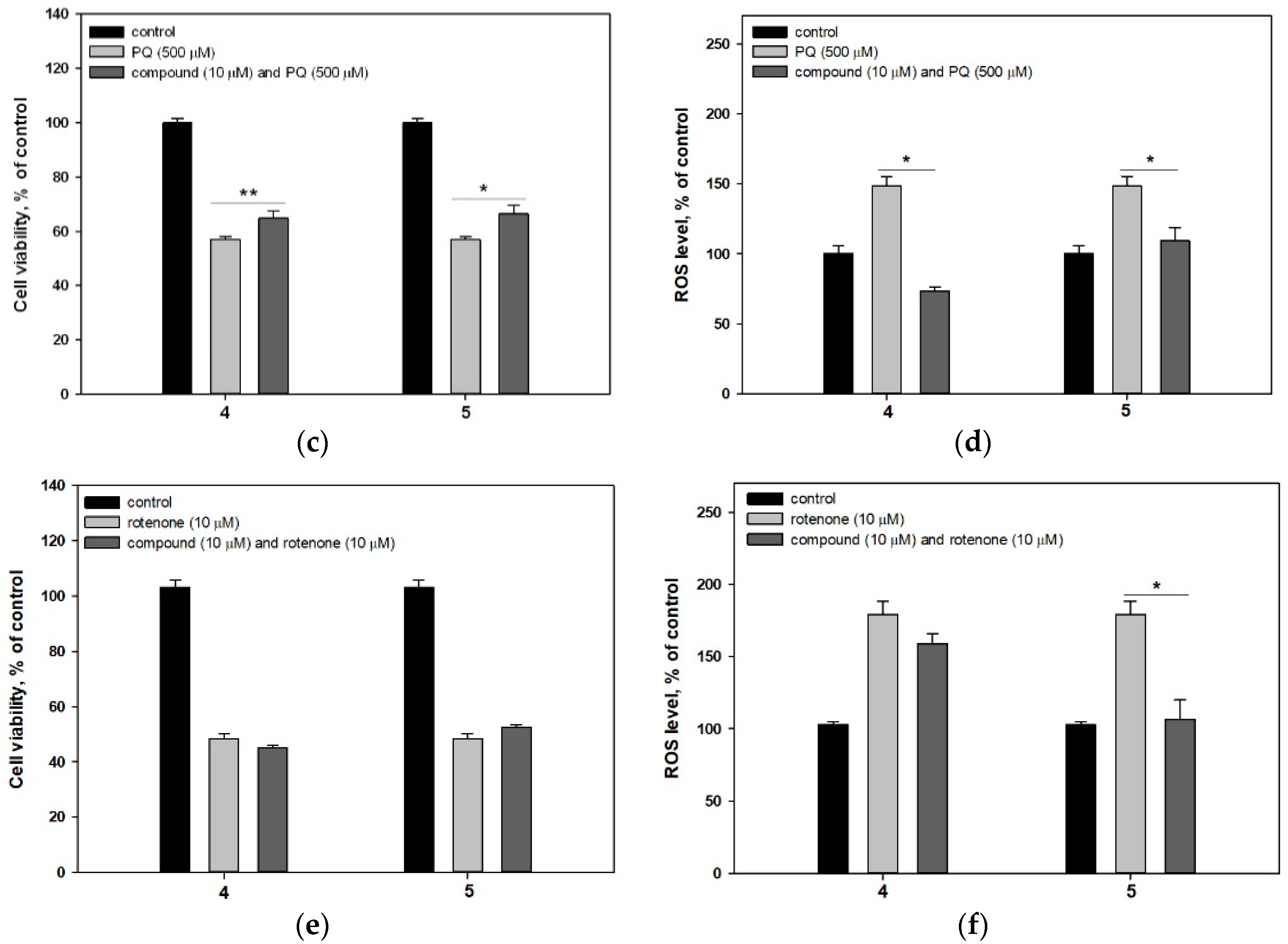
2.2.2. 4-Hydroxy-3,6-Dimethyl-2-Pyrone (4) and Dihydroaspyrone (5)
2.2.3. Asterriquinones (6–11) and Questin (12)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Fungal Strains
4.3. Cultivation of the Fungi
4.4. Extraction and Isolation
4.5. DPPH Radical Scavenger Assay
4.6. Bioassays
4.6.1. Cell Culture
4.6.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.6.3. Neurotoxin-Induced Cell Models of Parkinson’s Disease
4.6.4. ROS Level Studying in Neurotoxin-Treated Neuro-2a Cells
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, S.; Ansari, M.; Ahmad, A.; Mishra, M. Major bioactive metabolites from marine fungi: A Review. Bioinformation 2015, 11, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, K.R. Marine filamentous fungi: Diversity, distribution and bioprospecting. In Developments in Fungal Biology and Applied Mycology; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Langenfeld, A.; Blond, A.; Gueye, S.; Herson, P.; Nay, B.; Dupont, J.; Prado, S. Insecticidal cyclodepsipeptides from Beauveria felina. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, A.N.; Smetanina, O.F.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Pushilin, M.A.; Glazunov, V.P.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Kirichuk, N.N.; Ermakova, S.P.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Yurchenko, E.A.; et al. Oxirapentyns F-K from the Marine-Sediment-Derived Fungus Isaria felina KMM 4639. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladfelter, A.S.; James, T.Y.; Amend, A.S. Marine fungi. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R191–R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.T.M.; Ha, N.T.N.; Thanh, T.D. Position resources in the coastal area of Khanh Hoa province: Potential and prospects. Vietnam J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Savinkin, O.; Britayev, T.; Pavlov, D. Benthic fauna of the Bay of Nhatrang, Southern Vietnam; KMK Scientific Press: Moscow, Russia, 2007; Volume 2, p. 235. [Google Scholar]
- Dung, L.D. Nha Trang Bay marine protected area, Vietnam: Initial trends in coral structure and some preliminary linkages between these trends and human activities (2002–2005). Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2009, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypov, Y.Y. Scleractinian corals and reefs of Vietnam as a part of the Pacific reef ecosystem. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 1, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypov, Y.Y. Some Data on the Composition and Structure of Coral Communities in the Littoral and Sublittoral in the Province of Khanh Hoa, Vietnam. J. Mar. Sci. Res. Dev. 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanina, O.F.; Yurchenko, A.N.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Pushilin, M.A.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Slinkina, N.N.; Ermakova, S.P.; Yurchenko, E.A. Oxirapentyns B-D produced by a marine sediment-derived fungus Isaria felina (DC.) Fr. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanina, O.F.; Yurchenko, A.N.; Ivanets, E.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Von Amsberg, G.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Afiyatullov, S.S. Unique prostate cancer-toxic polyketides from marine sediment-derived fungus Isaria felina. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravleva, O.I.; Kirichuk, N.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Min’ko, E.M.; Ivanets, E.V.; Afiyatullov, S.S. New Diorcinol J Produced by Co-Cultivation of Marine Fungi Aspergillus sulphureus and Isaria felina. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, A.N.; Smetanina, O.F.; Kirichuk, N.N.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Afiyatullov, S.S. Biologically Active Metabolites of the Facultative Marine Fungus Aspergillus terreus. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 49, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, A.N.; Smetanina, O.F.; Ivanets, E.V.; Phan, T.T.H.; Ngo, N.T.D.; Zhuravleva, O.I.; Rasin, A.B.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; et al. Auroglaucin-related neuroprotective compounds from Vietnamese marine sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus niveoglaucus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanina, O.F.; Yurchenko, A.N.; Ivanets, E.V.G.; Trinh, P.T.; Antonov, A.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Von Amsberg, G.; Kim, N.Y.; Chingizova, E.A.; Pislyagin, E.A.; et al. Biologically active echinulin-related indolediketopiperazines from the marine sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus niveoglaucus. Molecules 2020, 25, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, E.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Ivanets, E.V.; Smetanina, O.F.; Yurchenko, A.N. Neuroprotective Activity of Some Marine Fungal Metabolites in the 6-Hydroxydopamin- and Paraquat-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, A.N.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Girich, E.V.; Smetanina, O.F.; Rasin, A.B.; Popov, R.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; von Amsberg, G.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Thanh Van, T.T.; et al. Biologically Active Metabolites from the Marine Sediment-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Choi, B.K.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, J.S.; Van, T.T.T.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J. Suppression of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by the metabolites from the marine fungus Aspergillus flocculosus isolated from a sponge Stylissa sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, P.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Mactanamide, a new fungistatic diketopiperazine produced by a marine Aspergillus sp. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1998, 12, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, D.Q.; Phan, T.T.T.; Nguyen, T.L.A.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Tran, T.T.V.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, H.J.; Choi, B.K. Insight into Antioxidant and Photoprotective Properties of Natural Compounds from Marine Fungus. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 1329–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanina, O.F.; Yurchenko, A.N.; Ivanets, E.V.; Gerasimenko, A.V.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Ly, B.M.; Nhut, N.D.; Van, T.T.T.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Afiyatullov, S.S. Aromatic Metabolites of Marine Fungus Penicillium sp. KMM 4672 Associated with a Brown Alga Padina sp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Muro, H.; Sasaki, K.; Nozoe, S.; Okuda, S.; Sato, Z. Isolations of phytotoxic substances produced by Pyricularia oryzae Cavara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Muro, H.; Nozoe, S.; Okuda, S.; Sato, Z. Isolation of 3,4-dihydro-3,4,8-trihydroxy-1(2H)-naphthalenone and tenuazonic acid from Pyricularia oryzae cavara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1972, 13, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizuri, Y.; Shigemori, H.; Sato, R.; Yamamura, S.; Kawai, K.; Furukawa, H. Four new metabolites produced by Penicillium citreo-viride B. on addition of NaBr. Chem. Lett. 1988, 17, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürki, N.; Michel, A.; Tabacchi, R. Naphthalenones and isocoumarins of the fungus Ceratocystis fimbriata f. sp. platani. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2003, 42, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Pittayakhajonwut, P.; Sohsomboon, P.; Dramae, A.; Suvannakad, R.; Lapanun, S.; Tantichareon, M. Antimycobacterial substances from Phaeosphaeria sp. BCC8292. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, R.; Furkert, D.P.; Brimble, M.A. Total Synthesis of the Resorcyclic Acid Lactone Spiroketal Citreoviranol. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 8343–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, X.M.; Mao, X.X.; Mandi, A.; Kurtan, T.; Wang, B.G. Varioloid A, a new indolyl-6,10b-dihydro-5aH-[1]benzofuro[2,3-b]indole derivative from the marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Paecilomyces variotii EN-291. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, X.M.; Mao, X.X.; Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T.; Wang, B.G. Correction: Varioloid A, a new indolyl-6,10b-dihydro-5aH-[1]benzofuro[2,3-b]indole derivative from the marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Paecilomyces variotii EN-291 (Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry (2016) 12 (2012–2018) doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.188). Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2394–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, K.; Shimizu, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Metabolic Products of Aspregillus terreus. VI. Metabolites of the Strain IFO 8835. (3). The Isolation and Chemical Structures of Colorless Metabolites. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Yamamoto, Y. Metabolic Products of Aspergillus terreus X: Biosynthesis of Asterriquinones. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2929–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Masuda, K.; Kiriyama, N.; Nitta, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shimizu, S. Metabolic Products of Aspergillus terreus. IV. Metabolites of the Strain IFO 8835. (2). The Isolation and Chemical Structure of Indolyl Benzoquinone Pigments. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodian, A.; Stickings, C.E. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms. 115. Metabolites of Penicillium frequentans Westling: Isolation of sulochrin, asterric acid, (+)-bisdechlorogeodin and two new substituted anthraquinones, questin and questinol. Biochem. J. 1964, 92, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamori, Y.; Kato, Y.; Kubo, M.; Kamiki, T.; Takemoto, T.; Nomoto, K. Studies on metabolites produced by Aspergillus terreus var. aureus. I. Chemical structures and antimicrobial activities of metabolites isolated from culture broth. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 4543–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.W.; Coller, D.R. Regioselective Synthesis of O-Methyl Derivatives of the Trihydroxy Anthraquinones Morindone and Nataloe-Emodin. Aust. J. Chem. 1999, 52, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, D.; Menkis, A.; Olson, K.; Stenlid, J.; Broberg, A.; Karlsson, M. Biosynthesis of fomannoxin in the root rotting pathogen Heterobasidion occidentale. Phytochemistry 2012, 84, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Li, X.M.; Yang, S.Q.; Meng, L.H.; Li, X.; Wang, B.G. Prenylated Phenol and Benzofuran Derivatives from Aspergillus terreus EN-539, an Endophytic Fungus Derived from Marine Red Alga Laurencia okamurai. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calton, G.J.; Ranieri, R.L.; Espenshade, M.A. Quadrone, a new antitumor substance produced by Aspergillus terreus. Production, isolation and properties. J. Antibiot. 1978, 31, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.-d.; Zheng, J.-j.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.-y. Cytochalasins from the Gorgonian-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. XS-2009-0B15. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnkar, S.; Goswami, P.; Kamat, P.K.; Gupta, S.; Patro, I.K.; Singh, S.; Nath, C. Rotenone-induced apoptosis and role of calcium: A study on Neuro-2a cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantiya, P.; Thonusin, C.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Mitochondrial abnormalities in neurodegenerative models and possible interventions: Focus on Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease. Mitochondrion 2020, 55, 14–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, A.; Nemoto, A.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Hojo, H.; Abe, N. Isolation of a 2-pyrone compound as an antioxidant from a fungus and its new reaction product with 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. Natural anthraquinone derivatives from a marine mangrove plant-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium rubrum: Structural elucidation and DPPH radical scavenging activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenblatt, G.A.; Wheeler, M.H. HPLC Analysis of Fungal Melanin Intermediates and Related Metabolites. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1986, 9, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hu, H.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y. Chemical constituents of Penicillium oxalicum, an endophytic fungus isolated from Bletilla striata (Thunb.) Reichb. f. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2019, 25, 438–444. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, R.P.; Araujo, A.R.; Andersen, R.J.; Soares, M.A.; Silva, F.A.; Silva, D.H.S. Aromatic compounds produced by endophytic fungi isolated from red alga Asparagopsis taxiformis—Falkenbergia stage. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, A.A.; Upadhyay, R.; Hershenhorn, J.; Strobel, G.A.; Molina, G. The phytotoxins of Mycosphaerella fijiensis, the causative agent of Black Sigatoka disease of bananas and plantains. Experientia 1991, 47, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Maddau, L.; Masi, M.; Evidente, M.; Linaldeddu, B.T.; Evidente, A. Further secondary metabolites produced by Diplodia corticola, a fungal pathogen involved in cork oak decline. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 6788–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, L.; He, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K. Screening and isolation of antinematodal metabolites against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus produced by fungi. Ann. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Sun, Z.H.; Li, H.H.; Li, S.N.; Yan, M.L.; Zhang, W.M. Two new metabolites from the endophytic fungus Alternaria sp. A744 derived from Morinda officinalis. Molecules 2017, 22, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, R.; Chagas, F.O.; Caraballo-Rodriguez, A.M.; Melo, W.G.D.P.; do Nascimento, A.M.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; de Moraes, M.O.; Pessoa, C.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Krogh, R.; et al. Endophytic Actinobacteria from the Brazilian Medicinal Plant Lychnophora ericoides Mart. and the Biological Potential of Their Secondary Metabolites. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, T.; Xie, X.S.; Ma, K.X.; Fang, X.W.; Wu, S.H. Secondary Metabolites from an Endophytic Fungus Nigrospora sp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Yu, S.; Lin, W. Isocoumarin Derivatives from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Peyronellaea glomerata with Antioxidant Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Peng, S.; Yang, J.; Cong, Z.; Lin, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structurally diverse sesquiterpenoids and polyketides from a sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus sydowii SCSIO41301. Fitoterapia 2019, 135, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfali, R.S.; Aly, A.H.; Ebrahim, W.; Proksch, P. Isochroman and isocoumarin derivatives from hypersaline lake sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Nemoto, A.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Hojo, H.; Hirota, A. Studies on the 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Radical Scavenging Mechanism for a 2-Pyrone Compound. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Li, C.W.; Cui, C.B.; Hua, W.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q. Nine new and five known polyketides derived from a deep sea-sourced Aspergillus sp. 16-02-1. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3116–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kito, K.; Ookura, R.; Yoshida, S.; Namikoshi, M.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Pentaketides relating to aspinonene and dihydroaspyrone from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus ostianus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfike, A.F.; Romli, M.; Clements, C.; Abbott, G.; Young, L.; Schumacher, M.; Diederich, M.; Farag, M.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Isolation of anticancer and anti-trypanosome secondary metabolites from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus flocculus via bioactivity guided isolation and MS based metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1106–1107, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.M.; Meng, L.H.; Wang, B.G. Polyketides from the marine mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus MA-15 and their activity against aquatic pathogenic bacteria. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Pirrung, M.C.; Deng, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Webster, N.J.G. Neuroprotection by small molecule activators of the nerve growth factor receptor. J. Pharm. Exp. 2007, 322, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.J.G.; Pirrung, M.C. Small molecule activators of the Trk receptors for neuroprotection. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.H.; Ou-Yang, H.; Yan, X.; Tang, B.W.; Fang, M.J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.W.; Qiu, Y.K. Open-Ring Butenolides from a Marine-Derived Anti-Neuroinflammatory Fungus Aspergillus terreus Y10. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.B.; Lei, X.L.; Qian, Z.J. Butyrolactone-i from coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus attenuates neuro-inflammatory response via suppression of NF-κB pathway in BV-2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.P. Butenolide derivatives from the fungus Aspergillus terreus and their radical scavenging activity and protective activity against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agamy, D.S.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Ahmed, N.; Khoshhal, S.; Abo-Haded, H.M.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Aljuhani, N.; Mohamed, G.A. Aspernolide F, as a new cardioprotective butyrolactone against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, D. Marine microbial diversity as a source of bioactive natural products. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, A.; Smetanina, O.; Ivanets, E.; Kalinovsky, A.; Khudyakova, Y.; Kirichuk, N.; Popov, R.; Bokemeyer, C.; von Amsberg, G.; Chingizova, E.; et al. Pretrichodermamides D–F from a Marine Algicolous Fungus Penicillium sp. KMM 4672. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutou, A.S.; Yun, K.; Son, B.W. Induced production of 6,9-dibromoflavasperone, a new radical scavenging naphthopyranone in the marine-mudflat-derived fungus Aspergillus niger. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2016, 39, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyakhova, E.G.; Kolesnikova, S.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Popov, R.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Lissodendoric acids A and B, manzamine-related alkaloids from the far eastern sponge Lissodendoryx florida. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5320–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

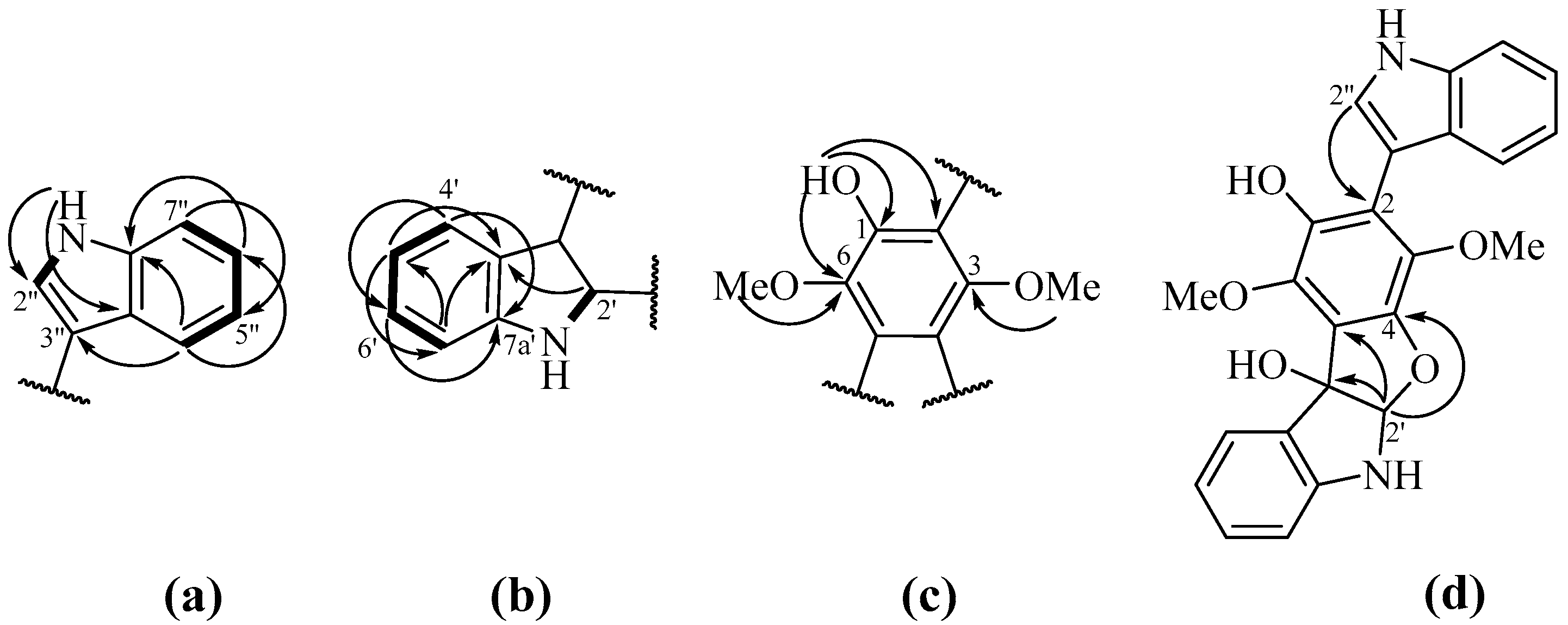


| Pos. | δC, mult | δH, (J in Hz) | HMBC | COSY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 141.3, C | |||
| 2 | 116.7, C | |||
| 3 | 138.4, C | |||
| 4 | 144.9, C | |||
| 5 | 121.6, C | |||
| 6 | 139.1, C | |||
| 6-OMe | 61.5, CH3 | 4.12, s | 6 | |
| 3-OMe | 60.4, CH3 | 3.58, s | 3 | |
| 2’ | 104.6, CH | 6.24, s | 4, 5, 3’, 3a’, 7a’ | |
| 3’ | 90.3, C | |||
| 3a’ | 129.7, C | |||
| 4’ | 125.0, CH | 7.78, d (7.5) | 3’, 6’, 7’, 7a’ | 5’ |
| 5’ | 120.1, CH | 6.88, t (7.5) | 3a’, 4’, 7’ | 4’, 6’ |
| 6’ | 130.1, CH | 7.18, t (7.8) | 3a’, 4’, 7’, 7a’ | 5’, 7’ |
| 7’ | 109.9, CH | 6.70, d (8.0) | 3a’, 5’ | 6’ |
| 7a’ | 148.6, C | |||
| 1” | (NH) | 8.44, brs | 3” | 2” |
| 2” | 124.8, CH | 7.29, d (2.4) | 2, 3”, 3a’’, 7a’’ | 3’’ |
| 3” | 106.7, C | |||
| 3a’’ | 126.5, C | |||
| 4” | 120.3, CH | 7.47, d (8.1) | 3”, 3a’’, 5”, 6”, 7”, 7a’’ | 5’’ |
| 5” | 120.4, CH | 7.14, t (7.5) | 3a’’, 7” | 4’’, 6’’ |
| 6” | 122.7, CH | 7.24, t (7.8) | 4”, 7a’’ | 5’’, 7’’ |
| 7” | 111.4, CH | 7.43, d (8.1) | 3a’’, 5”, 6” | 6’’ |
| 7a’’ | 136.2, C | |||
| 1-OH | 5.06, brs | 1, 2, 6 |
| Compounds | Cytotoxicity | DPPH Radical Scavenging | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50, µM | 100 µM % of MeOH | EC50, µM | |
| 1 | >100 | 83.4 ± 1.2 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 | 84.8 ± 3.2 | >100 |
| 3 | >100 | 91.2 ± 1.8 | >100 |
| 4 | >100 | 87.2 ± 1.4 | 500 [43] |
| 5 | >100 | 95.2 ± 1.0 | >100 |
| 6 | >100 | 67.3 ± 3.9 | >100 |
| 7 | >100 | 88.9 ± 1.6 | >100 |
| 8 | 91.45 ± 1.87 | 89.5 ± 0.9 | >100 |
| 9 | 42.32 ± 1.45 | 82.4 ± 1.7 | >100 |
| 10 | >100 | 91.3 ± 1.1 | >100 |
| 11 | >100 | 85.6 ± 1.3 | >100 |
| 12 | >100 | 87.7 ± 2.4 | >100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Girich, E.V.; Yurchenko, A.N.; Smetanina, O.F.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Ngoc, N.T.D.; Pivkin, M.V.; Popov, R.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; et al. Neuroprotective Metabolites from Vietnamese Marine Derived Fungi of Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120608
Girich EV, Yurchenko AN, Smetanina OF, Trinh PTH, Ngoc NTD, Pivkin MV, Popov RS, Pislyagin EA, Menchinskaya ES, Chingizova EA, et al. Neuroprotective Metabolites from Vietnamese Marine Derived Fungi of Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(12):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120608
Chicago/Turabian StyleGirich, Elena V., Anton N. Yurchenko, Olga F. Smetanina, Phan Thi Hoai Trinh, Ngo Thi Duy Ngoc, Mikhail V. Pivkin, Roman S. Popov, Evgeny A. Pislyagin, Ekaterina S. Menchinskaya, Ekaterina A. Chingizova, and et al. 2020. "Neuroprotective Metabolites from Vietnamese Marine Derived Fungi of Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera" Marine Drugs 18, no. 12: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120608
APA StyleGirich, E. V., Yurchenko, A. N., Smetanina, O. F., Trinh, P. T. H., Ngoc, N. T. D., Pivkin, M. V., Popov, R. S., Pislyagin, E. A., Menchinskaya, E. S., Chingizova, E. A., Afiyatullov, S. S., & Yurchenko, E. A. (2020). Neuroprotective Metabolites from Vietnamese Marine Derived Fungi of Aspergillus and Penicillium Genera. Marine Drugs, 18(12), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120608