Isolation and Characterization of a Heparin-Like Compound with Potent Anticoagulant and Fibrinolytic Activity from the Clam Coelomactra antiquata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
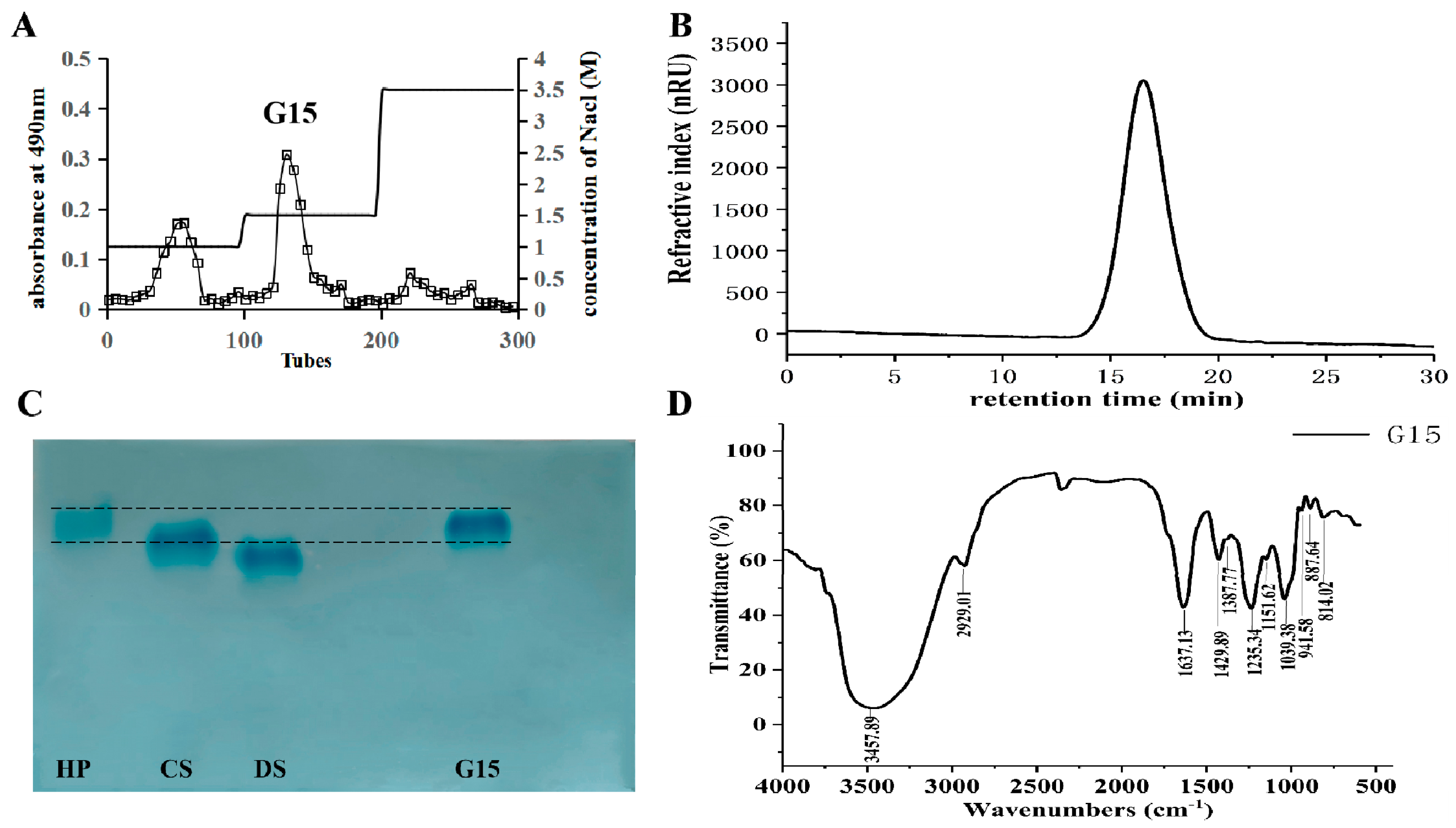
2.1. Heparinoid Purified from C. antiquata
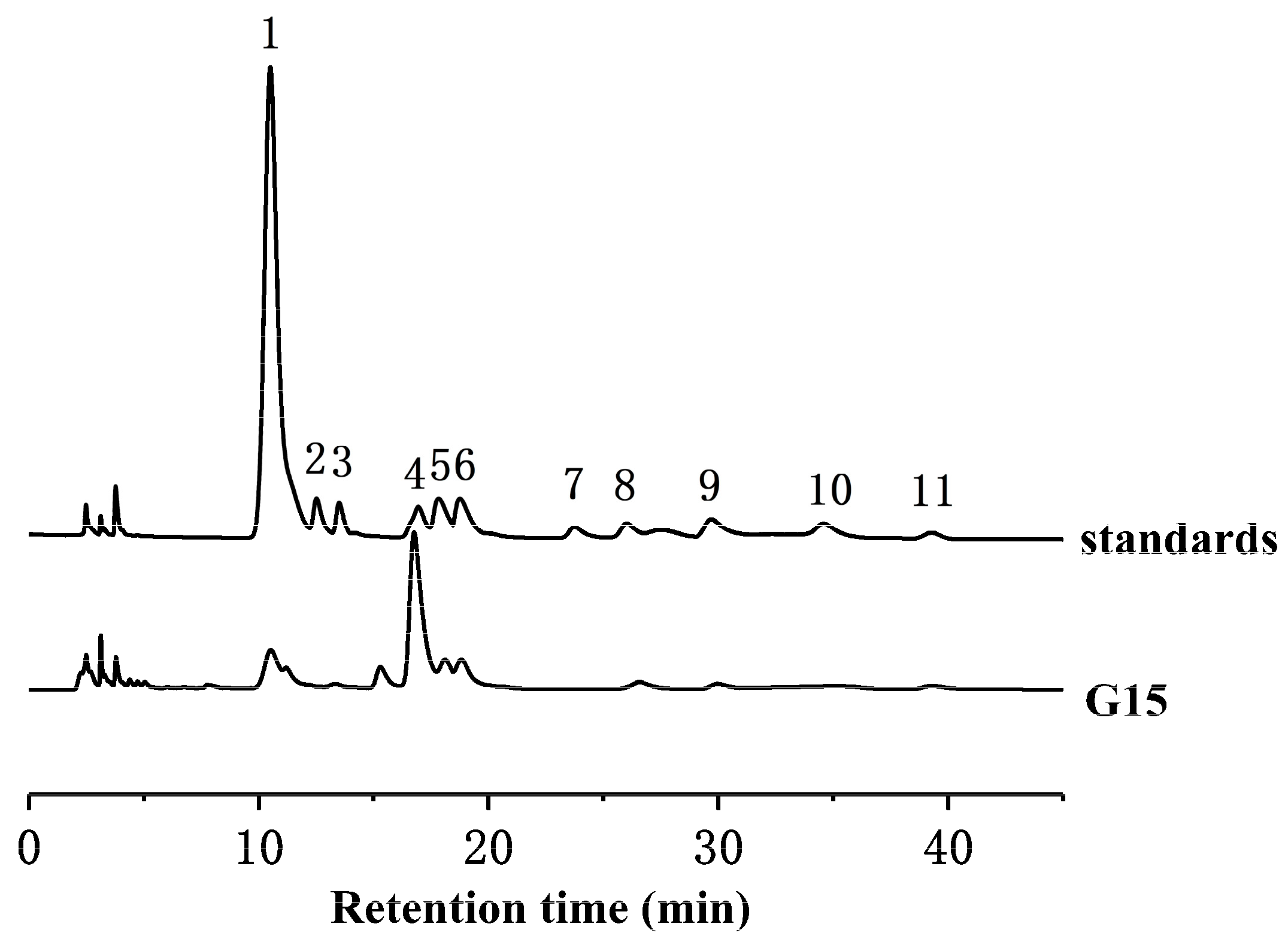
2.2. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
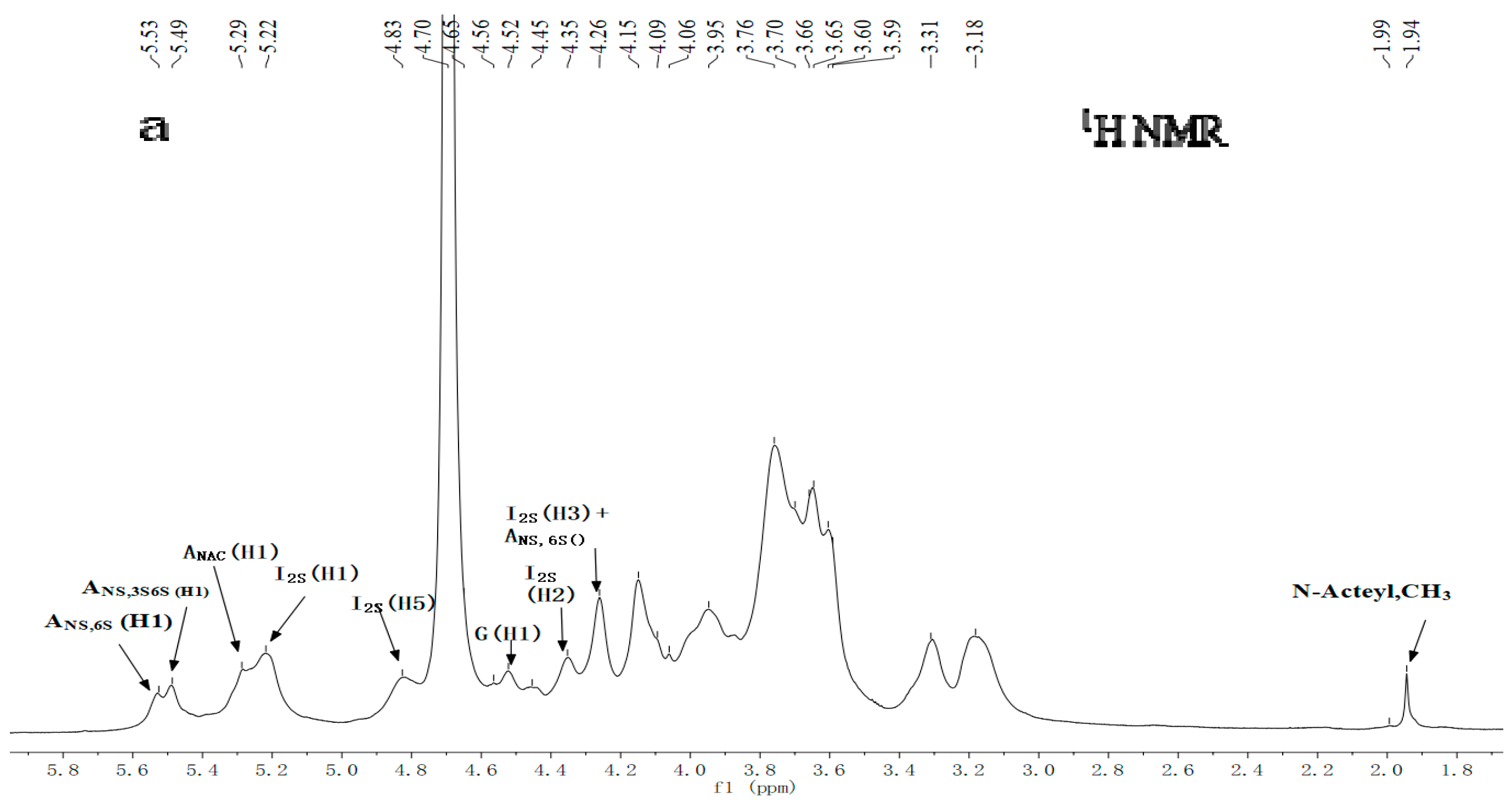
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
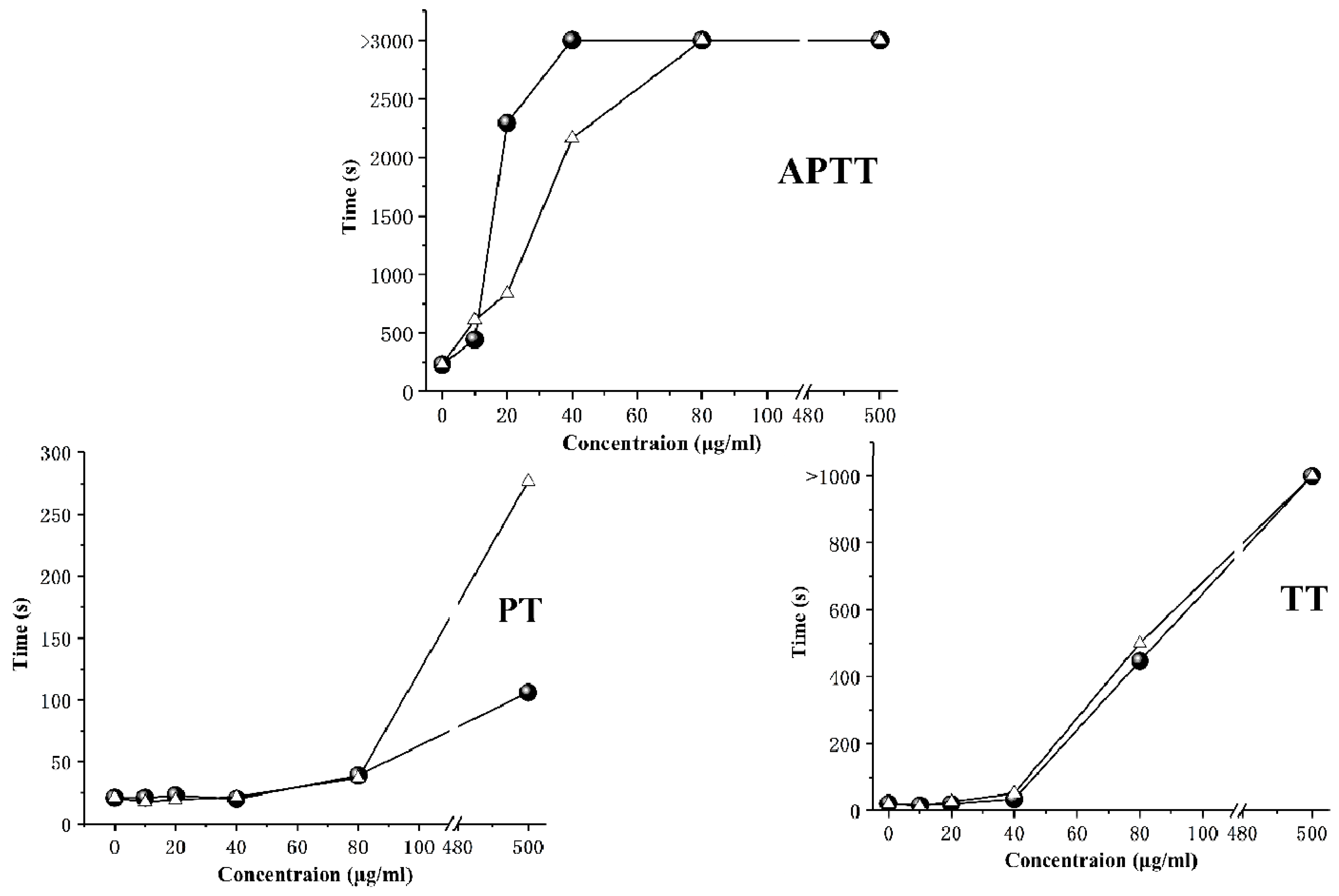
2.4. Anticoagulant Activity
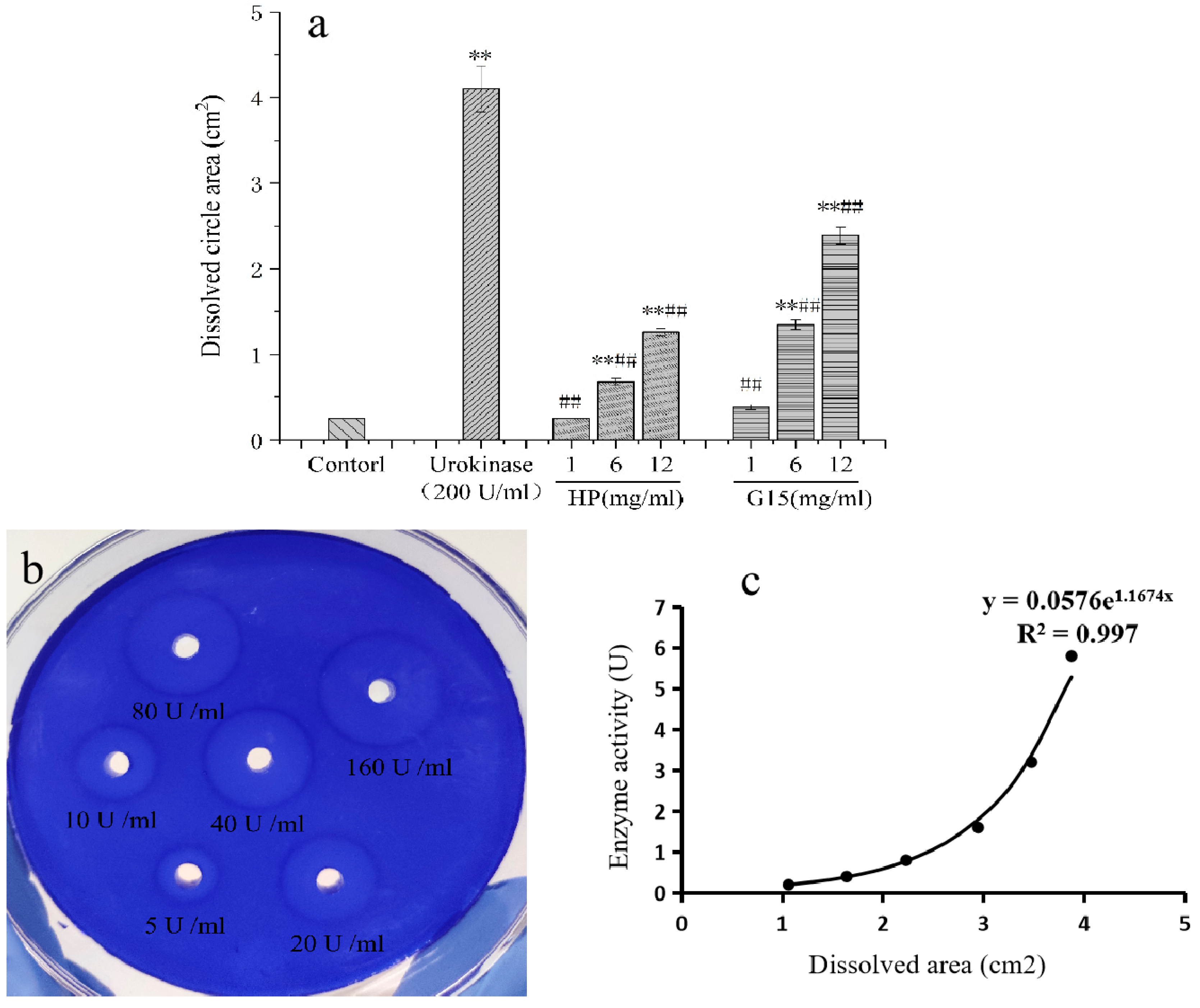
2.5. Fibrinolytic Activity
2.5.1. In Vitro Fibrinolytic Activity
2.5.2. In Vivo Fibrinolytic Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Animals
3.3. Isolation and Purification of C. antiquata Heparinoid
3.4. Cellulose Acetate Electrophoresis
3.5. Molecular Weight Analysis
3.6. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.7. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
3.8. NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.9. Anticoagulant Activity
3.10. Fibrinolytic Activity
3.10.1. In Vitro Fibrinolytic Activity
3.10.2. In Vivo Fibrinolytic Activity
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volpi, N. Occurrence and structural characterization of heparin from molluscs. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2005, 2, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.M.; Wan, R.J.; Xie, Y.H.; Luo, C.L.; Cheng, J. Influence of surf clam shell on blood lipid and antioxidant activity of diabetic mice. West. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 28, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.Q.; Wen, Y.M.; Lin, W.D.; Xie, Y.H.; Chen, C.M. Effect of polysaccharides from coelomactra antiquata on human carcinoma of esophagus cells transplanted in nude mice. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2015, 27, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt, R.J.; Claude, S. Hudson Award address in Carbohydrate Chemistry. Heparin Structure and Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2551–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamant, Z.; Timmers, M.C.; van der Veen, H.; Page, C.P.; van der Meer, F.J.; Sterk, P.J. Effect of inhaled heparin on allergen-induced early and late asthmatic responses in patients with atopic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariya, Y.; Kyogashima, M.; Suzuki, K.; Isomura, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Horie, K.; Hara, S. Preparation of completely 6-O-desulfated heparin and its ability to enhance activity of basic fibroblast growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25949–25958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulloy, B. The non-anticoagulant promise of heparin and its mimetics. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 46, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaretti, M.; Luppi, E.; Maccari, F.; Volpi, N. Isolation and characterization of a heparin with high anticoagulant activity from the clam Tapes phylippinarum: Evidence for the presence of a high content of antithrombin III binding site. Glycobiology 2004, 14, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcarcel, J.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Reis, R.L.; Vázquez, J.A. Glycosaminoglycans from marine sources as therapeutic agents. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyfuss, J.L.; Regatieri, C.V.; Lima, M.A.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Brito, A.S.; Chavante, S.F.; Nader, H.B. A heparin mimetic isolated from a marine shrimp suppresses neovascularization. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.M.; Kozlowski, E.O.; Borsig, L.; Teixeira, F.C.; Vlodavsky, I.; Pavão, M.S. Antitumor properties of a new non-anticoagulant heparin analog from the mollusk Nodipecten nodosus: Effect on P-selectin, heparanase, metastasis and cellular recruitment. Glycobiology 2014, 25, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Garg, H.; Ajithkumar, T.; Shanmugam, A. Antiproliferative heparin (glycosaminoglycans) isolated from giant clam (Tridacna maxima) and green mussel (Perna viridis). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 2394–2396. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, A.S.; Arimatéia, D.S.; Souza, L.R.; Lima, M.A.; Santos, V.O.; Medeiros, V.P.; Ferreira, P.A.; Silva, R.A.; Ferreira, C.V.; Justo, G.Z.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of a heparin-like glycosaminoglycan with reduced anti-coagulant activity isolated from a marine shrimp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9588–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandra, M.; Cavalcante, M.C.; Pavão, M.S. Anticoagulant sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the tissues of the primitive chordate Styela plicata (Tunicata). Glycobiology 2000, 10, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.P.; Lima, M.A.; de Souza Junior, A.A.; Fareed, J.; Hoppensteadt, D.A.; Santos, E.A. A heparin-like compound isolated from a marine crab rich in glucuronic acid 2-O-sulfate presents low anticoagulant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, G.F.; Mendes, A.; Castro, R.A.B.; Baú, E.C.; Nader, H.B.; Dietrich, C.P. Distribution of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the animal kingdom: Widespread occurrence of heparin-like compounds in invertebrates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1475, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Mesquita, J.M.F.; Belmiro, C.L.R.; da Silveira, C.B.M.; Viskov, C.; Mourier, P.A.; Pavão, M.S.G. Isolation and characterization of a heparin with low antithrombin activity from the body of Styela plicata (Chordata-Tunicata). Distinct effects on venous and arterial models of thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2007, 121, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SaravananIsolation, R. Isolation of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin/Heparan Sulfate from Marine Sources. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 72, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Colliec-Jouault, S.; Bavingon, C.; Delbarre-Ladrat, C. Heparin-like Entities from Marine Organisms. In Heparin-A Century of Progress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 423–443. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, A.S.; Cavalcante, R.S.; Palhares, L.C.; Hughes, A.J.; Andrade, G.P.; Yates, E.A.; Chavante, S.F. A non-hemorrhagic hybrid heparin/heparan sulfate with anticoagulant potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Di, L.Q.; Li, J.S.; Hu, L.H.; Cheng, J.M.; Wu, H. Elaboration in type, primary structure, and bioactivity of polysaccharides derived from mollusks. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1091–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.X.; Zhou, S.Y.; Zhong, S.Y.; Huang, F.J.; Chen, G.L.; Chen, J.; Hong, P.Z.; Zhang, C.H. Advance in the Study of Heparin-like Compounds from Marine Organisms. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2018, 4, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.X.; Zhou, S.Y.; Zhong, S.Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.L.; Chen, J.P.; Chen, S.H.; Hong, P.Z. Physicochemical Properties and Anticoagulant Activity of Heparin from Different Marine Organisms. Food Sci. 2019, 17, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Xia, Z. Structure and anticoagulant property of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green seaweed Monostroma angicava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J. Biochemical Research Technology of Sugar Complex; Zhejiang University Press: Zhejiang, China, 1999; ISBN 9787308021258. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, E.A.; Santini, F.; Guerrini, M.; Naggi, A.; Torri, G.; Casu, B. 1H and 13C NMR spectral assignments of the major sequences of twelve systematically modified heparin derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 294, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, G.; Yang, B.; Onishi, A.; Li, L.; Sun, P. Structural characterization of pharmaceutical heparins prepared from different animal tissues. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Diehl, B.W.; Fareed, J. Authentication of animal origin of heparin and low molecular weight heparin including ovine, porcine and bovine species using 1D NMR spectroscopy and chemometric tools. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palhares, L.C.; Brito, A.S.; de Lima, M.A.; Nader, H.B.; London, J.A.; Barsukov, I.L. A Further Unique Chondroitin Sulfate from the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei with Antithrombin Activity that Modulates Acute Inflammation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, B.; Guerrini, M.; Naggi, A.; Torri, G.; De-Ambrosi, L.; Boveri, G. Characterization of sulfation patterns of beef and pig mucosal heparins by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arzneim. Forsch. 1996, 46, 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Pomin, V.H. NMR chemical shifts in structural biology of glycosaminoglycans. Anal. Chem. 2013, 86, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.B.; Zhang, J.S.; Pan, Y.J. Application of the NMR techniques in structural analysis of polysaccharide from edible fungi. Acta Edulis Fungi 2007, 14, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chavante, S.F.; Brito, A.S.; Lima, M.; Yates, E.; Nader, H.; Guerrini, M.; Torri, G.; Bisio, A. A heparin-like glycosaminoglycan from shrimp containing high levels of 3-O-sulfated D-glucosamine groups in an unusual trisaccharide sequence. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 390, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.X.; He, Z.X.; Ji, S.L. Heparin; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015; ISBN 9787518403535. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar, A.M.; Capillé, N.V.; Santos, G.R.; Vairo, B.C.; Oliveira, S.N.M.; Fonseca, R.J.; Mourão, P.A. Heparin from bovine intestinal mucosa: Glycans with multiple sulfation patterns and anticoagulant effects. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.P.; Paiva, J.F.; Castro, R.A.; Chavante, S.F.; Jeske, W.; Fareed, J. Structural features and anticoagulant activities of a novel natural low molecular weight heparin from the shrimp Penaeus brasiliensis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1999, 1428, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, U.; Li, J.P.; Kusche-Gullberg, M.; Salmivirta, M.; Alaranta, S.; Veromaa, T. Generation of “neoheparin” from E. coli K5 capsular polysaccharide. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, H.P.; Grant, P.J. Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.L.; Zhang, P.P.; Liu, G.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, S. Study on effects of different molecular weight a postichopus japonicus glycosaminoglycans on the activity of fibrinolytic system in rats. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2018, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pavao, M.S.G.; Mourao, P.A.S. Challenges for heparin production: Artificial synthesis or alternative natural sources? Glycobiol. Insights 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, E.M. The quantitative spectrophotometric estimation of total sulfated glycosaminoglycan levels formation of soluble alcian blue complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1981, 673, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrowski, Y.; Maquart, F.X. Cellulose acetate electrophoresis of glycosaminoglycans. In Proteoglycan protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Domanig, R.; Jöbstl, W.; Gruber, S.; Freudemann, T. One-dimensional cellulose acetate plate electrophoresis-A feasible method for analysis of dermatan sulfate and other glycosaminoglycan impurities in pharmaceutical heparin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Lv, Z. Separation, purification, structures and anticoagulant activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from holothuria scabra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 108, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; You, S.G.; Lee, S.J. Antioxidative, hypolipidemic, and anti-inflammatory activities of sulfated polysaccharides frommonostroma nitidum. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichen, F.; Ghlissi, Z.; Amor, I.B.; Sayari, N.; Kallel, R.; Gargouri, J. In vitro and in vivo anti-coagulant activity and toxicological studies of marine sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 69, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.J.; He, X.X.; Qin, L.; He, M.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.C.; Mao, W.J. Anticoagulant and Antithrombotic Properties in Vitro and in Vivo of a Novel Sulfated Polysaccharide from Marine Green Alga Monostroma nitidum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrien, A.; Bonnet, A.; Dufour, D.; Baudouin, S.; Maugard, T.; Bridiau, N. Anticoagulant Activity of Sulfated Ulvan Isolated from the Green Macroalga Ulva rigida. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrup, T.; Müllertz, S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1952, 40, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovati, J.I.; Delgado, O.D.; Figueroa, L.I.; Fariña, K.I. A novel source of fibrinolytic activity: Bionectria sp., an unconventional enzyme-producing fungus isolated from Las Yungas rainforest (Tucumán, Argentina). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
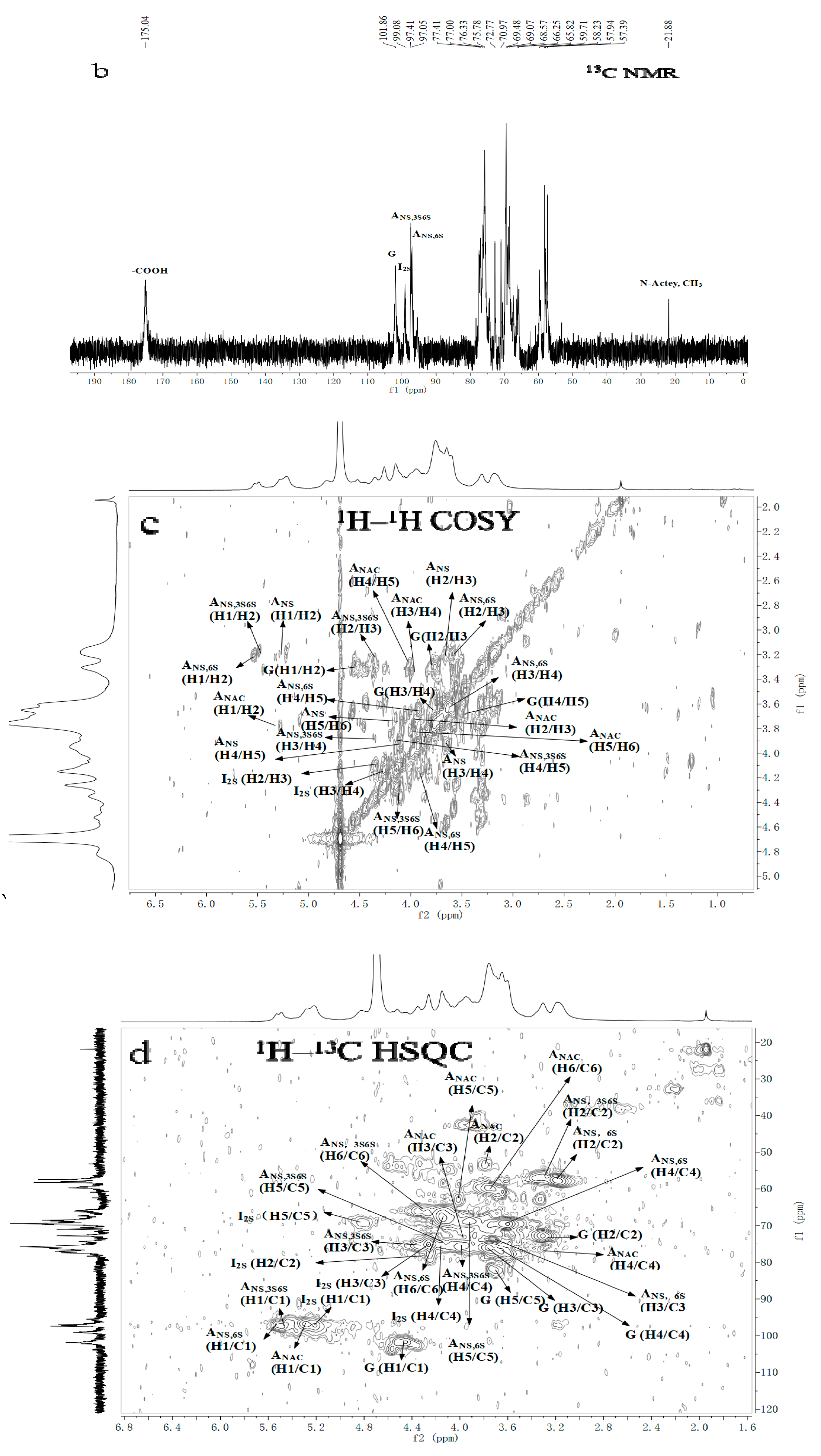
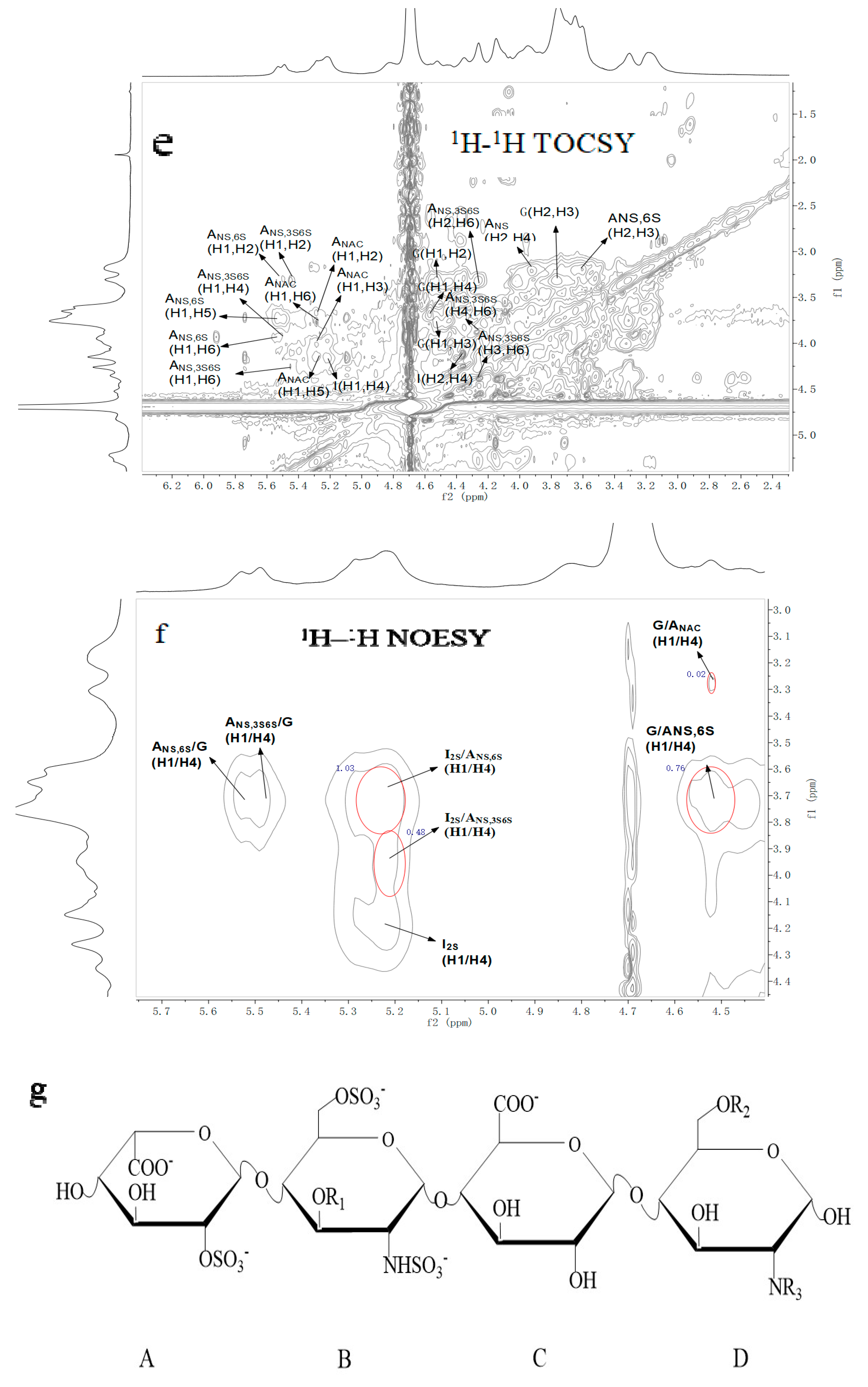
| Repetitive Units | Molar Ratio | Chemical Shifts | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uronic Acid | Glucosamine | |||||||||||
| H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | ||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | ||
| →4)-α-IdoA2S-(1→4)-α-GlcNS6S-(1→ | 1.03 | 5.20 | 4.34 | 4.25 | 4.14 | 4.83 | 5.53 | 3.21 | 3.60 | 3.65 | 3.92 | 4.17 |
| 99.08 | 78.13 | 75.46 | 75.63 | 71.15 | 97.61 | 57.53 | 73.00 | 69.61 | 69.05 | 67.30 | ||
| →4)-α-IdoA2S-(1→4)-α-GlcNS3S6S-(1→ | 0.48 | 5.20 | 4.34 | 4.25 | 4.14 | 4.83 | 5.49 | 3.2 | 4.35 | 4.00 | 4.13 | 4.27 |
| 99.08 | 78.13 | 75.46 | 75.63 | 71.15 | 97.38 | 55.05 | 78.61 | 74.90 | 72.59 | 66.74 | ||
| →4)-β-GlcA-(1→4)-α-GlcNS6S-(1→ | 0.76 | 4.56 | 3.31 | 3.76 | 3.67 | 3.71 | 5.53 | 3.21 | 3.60 | 3.65 | 3.92 | 4.17 |
| 101.77 | 73.15 | 76.36 | 76.53 | 81.12 | 97.61 | 57.53 | 73.00 | 69.61 | 69.05 | 67.30 | ||
| →4)-β-GlcA-(1→4)-α-GlcNAc(1→ | 0.02 | 4.56 | 3.31 | 3.76 | 3.67 | 3.71 | 5.29 | 3.81 | 3.96 | 3.34 | 4.03 | 3.84 |
| 101.77 | 73.15 | 76.36 | 76.53 | 81.12 | 97.44 | 53.31 | 73.5 | 75.85 | 63.93 | 20.22 | ||
| Index | Injection | a Concentration (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 6 | 12 | ||
| t-PA (ng/mL) | HP | 23.86 ± 3.80 | 46.97 ± 5.07 | 65.24 ± 10.75 | 65.72 ± 4.23 |
| G15 | 23.86 ± 3.80 | 35.64 ± 4.66 | 41.22 ± 8.16 | 62.73 ± 2.66 | |
| u-PA (ng/mL) | HP | 1.12 ± 0.06 | 1.01 ± 0.07 | 1.23 ± 0.09 | 1.41 ± 0.14 |
| G15 | 1.12 ± 0.64 | 1.22 ± 0.11 | 1.39 ± 0.24 | 1.58 ± 0.17 | |
| PAI-1 (ng/mL) | HP | 12.80 ± 1.57 | 37.50 ± 17.56 | 33.21 ± 11.95 | 24.05 ± 5.93 |
| G15 | 12.80 ± 1.57 | 25.63 ± 6.46 | 9.46 ± 0.52 | 6.03 ± 1.74 | |
| t-PA/PAI-1 | HP | 1.86 ± 0.07 | 1.25 ± 0.68 | 1.96 ± 0.39 | 2.73 ± 0.31 |
| G15 | 1.86 ± 0.07 | 1.39 ± 0.44 | 4.35 ± 0.62 | 10.40 ± 1.26 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Z.; Jia, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhong, S.; Hong, P. Isolation and Characterization of a Heparin-Like Compound with Potent Anticoagulant and Fibrinolytic Activity from the Clam Coelomactra antiquata. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010006
Du Z, Jia X, Chen J, Zhou S, Chen J, Liu X, Cao X, Zhong S, Hong P. Isolation and Characterization of a Heparin-Like Compound with Potent Anticoagulant and Fibrinolytic Activity from the Clam Coelomactra antiquata. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, ZhenXing, XueJing Jia, Jing Chen, SiYi Zhou, JianPing Chen, XiaoFei Liu, XiaoHuang Cao, SaiYi Zhong, and PengZhi Hong. 2020. "Isolation and Characterization of a Heparin-Like Compound with Potent Anticoagulant and Fibrinolytic Activity from the Clam Coelomactra antiquata" Marine Drugs 18, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010006
APA StyleDu, Z., Jia, X., Chen, J., Zhou, S., Chen, J., Liu, X., Cao, X., Zhong, S., & Hong, P. (2020). Isolation and Characterization of a Heparin-Like Compound with Potent Anticoagulant and Fibrinolytic Activity from the Clam Coelomactra antiquata. Marine Drugs, 18(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010006







