Abstract
The sponge-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO41015 cultured on solid rice medium yielded twenty-one compounds (1–21), including two new alkaloids (1 and 2) and one new pyrone derivative (3). Their structures were elucidated by analysis of 1D/2D NMR data and HR–ESI–MS. Their absolute configurations were established by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis and comparison of the experimental with reported specific rotation values. Compound 16 exhibited selective cytotoxic activity against the human gastric cancer cells MGC803, with IC50 value of 5.19 μM. Compounds 9 and 18 showed weak antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii, respectively, both with MIC values of 57 μg/mL. Furthermore, compound 16 displayed potent antibacterial activity against S. aureus with an MIC value of 3.75 μg/mL.
1. Introduction
A considerable number of structurally unique secondary metabolites with biological and pharmacological activities have been isolated from the marine-derived fungi in recent years [1,2]. Marine-derived Penicillium and Aspergillus are reported to be the most ubiquitous genera [1]. Penicillium has become one of the most attractive fungal genera to search for bioactive molecules, since the advent of penicillin [3]. More than 400 new marine natural products, including half the number of polyketides and a quarter the number of nitrogen compounds have been isolated from marine-derived Penicillium fungi, and 58% of the new products have displayed bioactivities such as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-HIV, and anti-inflammatory properties [4]. As part of our continued searching for bioactive secondary metabolites from sponge-derived fungi [5,6,7], the fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO41015 was investigated. Three new compounds (1–3) and eighteen known ones (4–21) were isolated from the rice solid culture extract of the fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO41015 shown in Figure 1. Nearly all compounds were evaluated on their cytotoxic activities against six human cancer cells and their antibacterial activities against five pathogenic bacteria. Herein, we described the isolation, structure elucidation, and bioactivity evaluation of the twenty-one compounds, as well as the potential biosynthetic pathway of these alkaloids.

Figure 1.
Chemical structures of compounds 1–21.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structural Elucidation
Compound 1 was obtained as a colorless oil. Its molecular formula was established as C14H18N2O4, through high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (HR–ESI–MS) [M + H]+ peak at m/z 279.1336 (calculated forC14H19N2O4, 279.1339),indicating seven degrees of unsaturation. Its 1H NMR data (Table 1) showed four aromatic protons (δH 7.81, dd, J = 7.7, 1.4 Hz, H-6; 7.43, td, J = 7.7, 0.7 Hz, H-4; 6.74, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3; and 6.60, td, J = 7.7, 0.7 Hz, H-5), one methine (δH 4.76, td, J = 7.0, 5.6 Hz, H-9), one methylene (δH 3.44, dd, J = 17.5, 7.0 Hz, H-8a; 3.40, dd, J = 17.5, 5.6 Hz, H-8b), three methyls (δH 3.61, s, H3-14; 2.85, d, J = 4.9 Hz, H3-11; 1.82, s, H3-13), and two active hydrogen protons (δH 8.59, dd, J = 9.1, 4.2 Hz, NH-11; 8.23, d, J = 7.7 Hz, NH-9). Accordingly, the 13C NMR (DEPT) (Table 1) data also displayed fourteen carbon signals, including four sp2methines, a sp3methylene (δC 40.2, C-8), a sp3methine (δC 47.9, C-9), three methyls (δC 52.0, C-14; 29.0, C-11; 22.3, C-13), two sp2 non-protonated carbons, and three carbonyls (δC 198.1, C-7; 172.2, C-10; 169.2, C-12). Part of its NMR data were similar to N-acetyl-6-nitrotryptophanmethyl ester synthetized by R.R. King [8]. The obvious differences were that the signals of a nitro group and a double-bond were absentin compound 1, while an aromatic proton, and a methyl and a carbonyl group were observed. The changes indicated that the five-membered ring opened between C-2 and C-3 in N-acetyl-6-nitrotryptophanmethyl ester, which were confirmed by the 1H-1H correlation spectroscopy (COSY) of H-3/H-4/H-5/H-6, H3-11/NH-11, and the heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) spectrum of H2-8, H-9, and H-6, to C-7 (Figure 2). Thus, the planar structure of 1 was further ascertained by the HMBC spectrum (Figure 2). The potential biosynthetic pathway of 1 was speculated that 1 was synthesized from l-tryptophan as shown in Figure S1. Combining the comparison experimental specific rotation value (+58.1, CHCl3) of compound 1 with (+141, CHCl3) of the reported (2S)-methyl 2-acetamido-4-(2’-acetamidophenyl)-4-oxobutanoate [9], the absolute configuration of 1 was established to be S. Therefore, compound 1 was named (S)-methyl 2-acetamido-4-(2-(methylamino)phenyl)-4-oxobutanoate.

Table 1.
1H NMR and 13C NMR data for compounds 1–3.
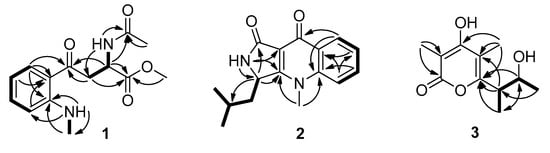
Figure 2.
Correlation spectroscopy (COSY) and key heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) correlations of compounds 1–3.
Compound 2 was isolated as a light-yellow powder that returned a HR–ESI–MS pseudomolecularion (m/z 293.1263, [M + Na]+), corresponding to a molecular formula (C16H18N2O2) requiring nine degrees of unsaturation. Analysis of its NMR data (Table 1) revealed that the structural features of 2 closely resembled those of quinolactacin D [10]. The only difference was a methine (δH 4.86, brd, J = 8.4 Hz, δC 52.5, CH-3) in 2 instead of the oxygenated non-protonated carbon in quinolactacin D, which was confirmed by the correlations of H-3 to C-1 (δC 167.9), C-3a (δC 165.6), C-10 (δC 42.3), C-11 (δC 24.7) in the HMBC spectrum and the COSY cross-peaks of H-3/H-10a/H-10b (Figure 2). Therefore, 2 was a N-methyl quinolone lactam, and the planar structure of 2 was determined as hydroxyl at C-3 reductive quinolactacin D, based on 2D NMR data (Figure 2). The deduction above was supported by the Cu Kα single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis (ORTEP, oak ridge thermal ellipsoid plot, drawing in Figure 3), while the X-ray data showed that the crystal of 2 existed as a pair of enantiomers. The chiral phase of HPLC analysis showed that were two conjoint peaks that could not separate well, also 2 dissolved in a solvent that was unstable and then changed to quinolactacin D, as speculated in the reference [10]. Compound 2 appeared to be synthesized from kynurenine and leucine, which was similar to the speculation reported by Nakagawa et al. [11]; shown in Figure S1. Thereby, 2 was elucidated as a pair of enantiomers and named quinolactacin E.

Figure 3.
ORTEP drawings of compounds 2 and 3.
The HR–ESI–MS data showed the molecular formula of compound 3 to be C11H16O4, which indicated four degrees of unsaturation in this molecular structure. The 1H NMR and 13C NMR data (Table 1) of 3 were quite similar with those of germicidin L [12], except for the absence of an aromatic proton signal, which was replaced by a non-protonated carbon (δC 110.0, C-5) and amore methyl group (δH 2.01, s, δC 10.0, CH3-8). The changes were confirmed by the HMBC correlations of H3-8 to C-4 (δC 168.0), C-5, C-6 (δC 161.6), indicating 3 was methyl-substituted germicidin L at position of C-5. The proposed structure was further verified by X-ray diffraction analysis of the single crystal of compound 3 (ORTEP drawing in Figure 3). Its single-crystal X-ray diffraction experiment with Cu Kα radiation and the value of the Flack parameter, 0.07(7), allowed the assignment of the absolute configuration of 3 as 9R, 10R. Thus, compound 3 was established as 4-hydroxy-6-((2R,3R)3-hydroxybutan-2-yl)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyran-2-one and named germicidin O.
Polyketides and alkaloids are two major secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungi, and the same polyketides or alkaloids were often isolated from different fungi. According to the detailed spectroscopic analysis and comparison to the reported literature data, the known compounds (4–21) were identified as quinolactacin B (4) [10], quinolonimide (5) [10], quinolonic acid (6) [10], 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2(1H)-quinolinone (7) [13], sydowinin A (8) [14], pinselin (9) [15], β-diversonolic ester (10) [16], coniochaetone J (11) [17], dihydrocitrinone (12) [18], stoloniferol A (13) [18], 6,8-dihydroxy-3,4,5-trimethylisochroman (14) [19], moniliphenone (15) [20], frangula-emodin (16) [21], methyl-2-(2-acetyl-3,5-dihydroxy-4,6-dimethylphenyl) acetate (17) [22], phenol A (18) [23], latifolicinin C (19) [24], penicitrinone A (20) [25], and 22-acetylisocyclocitrinol A (21) [26], respectively.
2.2. Biological Activity
Compounds 1–21, excepting 2 (since it was unstable in solvent and its quality was poor after the second preparation) were evaluated on their cytotoxic activities against human gastric cancer cells MGC803, human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231, human prostate cancer cells C4-2B, human osteosarcoma 143B, and human hung cancer cells A549, using the CCK-8 method. Compound 16 selectively exhibited cytotoxic activity against MGC803 with IC50 value of 5.19 μM. The antibacterial activities of all compounds, except 2, were estimated against A.baumannii (ATCC 19606), Klebsiella pneumonia (ATCC 13883), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), S.aureus (ATCC 29213) and Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212). Compounds 9, 16, 18, and 21 with 100 μg/disc showed an inhibition zone against S. aureus with a diameter of about 9, 12, 21, and 7 mm, respectively. Compounds 18 and 13 with 100 μg/disc displayed an inhibition zone against A. baumannii both with a diameter of about 8 mm (Figure S2). Further, their minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were tested. The MIC values of compounds 9 and 16 against S. aureus were 57 and 3.75 μg/mL, respectively, and the MIC value of compound 18 against A. baumannii was 57 μg/mL, while the other compounds showed more than 100 μg/mL. Ampicillin and gentamicin were used as positive control against S. aureus and A. baumannii, respectively, with the MIC values of 0.45 and 0.9 μg/mL (Table S1).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
UV spectra were recorded on a UV-2600 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan). Optical rotations were measured using a MCP-500 polarimeter (Anton, Austria). 1D and 2D NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker Avance 500 MHz or 700 MHz NMR spectrometer (Fällanden, Switzerland) with TMS as an internal standard. HR–ESI–MS data were recorded on a maXis Q-TOF mass spectrometer in the positive ion mode (Bruker, Fällanden, Switzerland). X-ray diffraction intensity data were collected on XtalLAB PRO single-crystal diffractometer, using Cu Kα radiation (Rigaku, Japan). The data were corrected for absorption, using CrysAlisPro 1.171.39.33c (Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, 2017). The structures were solved by the direct methods (SHELXS 97), expanded using difference Fourier techniques, and refined by full-matrix least-squares calculation. All H atoms were fixed at the calculated positions and the non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. HPLC was performed on the Hitachi Primaide with the YMC ODS SERIES column (YMC-Pack ODS-A, YMC Co. Ltd., Kyoto, 250 × 10 mm I.D., S-5 μm, 12 nm). Column chromatography (CC) was carried out on silica gel (200–300 mesh, Jiangyou Silica Gel Development Co., Yantai, China), YMC Gel ODS-A (12 nm, S-50 μm YMC, MA, USA), and Sephadex LH-20 (40–70 μm, Amersham Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden). Spots on the thin-layer chromatography (TLC) plates were analyzed under UV light, or through heating, after spraying with amixed solvent of saturated vanillin and 5% H2SO4 in H2O. The TLC plates with silica gel GF254 (0.4–0.5 mm, Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China) were used for the analyses and preparations.
3.2. Fungal Material
The fungal strain SCSIO41015 was obtained from a Callyspongia sp. sponge, which was collected from the sea area near Xuwen County, Guangdong Province, China. The strain SCSIO41015 was stored on MB agar (malt extract 15 g, agar 16 g, sea salt 10 g, water 1 L, pH 7.4–7.8) slants at 4 °C and deposited at the Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-Resources and Ecology, Chinese Academy of Science. The ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 sequence region (508 base pairs, GenBank accession No. MK813890) of strain SCSIO41015 was amplified by PCR, and DNA sequencing showed that it shared significant homology with several species of Penicillium. The 508 base pair ITS sequence had 99% sequence identity to that of the Penicillium citrinum strain SCSGAF0167 (GenBank accession No. JN851046.1). Then, it was designated as a member of Penicillium sp. and named Penicillium sp. SCSIO41015.
3.3. Fermentation and Extraction
The mass fermentation of this fungus was carried out at 25 °C for 30 days, using a rice medium in a 1 L flask (×45) and every flask contained 200 g of rice, 2.5 g of sea salt, and 200 mL of tap H2O. The flasks were cultivated statically at 25 °C, under normal day–night cycle. After 30 days, the cultures were soaked in acetone (500 mL/flask) and mashed into small pieces and sonicated for 20 min. Then, the acetone was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain an aqueous solution, which was extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc), for three times. The rice residue was also extracted with EtOAc. Both of the EtOAc solutions were concentrated under reduced pressure to gain a crude extract. The crude extract was suspended in MeOH and then partitioned with an equal volume of petroleum ether to remove the oil. Lastly, the MeOH solution was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford a brown extract (77.0 g).
3.4. Isolation and Purification
The brown extract was subjected to silica gel CC, which was eluted with CH2Cl2 and MeOH mixed solvent in a step gradient (100:0–5:1, v/v) and separated into eight fractions (Fr-1–Fr-8). Fr-1 (1.4 g) was applied to a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH and reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v) to gain four sub-fractions (Fr-1-1–Fr-1-4). Fr-1-1 was further purified with semi-preparative HPLC (60% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to afford 8 (8.3 mg, tR = 10.0 min), 9 (6.4 mg, tR = 14.5 min), and 16 (3.8 mg, tR = 22.4 min). Fr-1-3 was further separated with semi-preparative HPLC (60% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to yield 20 (26.1 mg, tR = 10.8 min). Fr-1-4 was further purified with semi-preparative HPLC (27% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to gain 12 (18.3 mg, tR = 19 min). Fr-2 (8.5 g) was subjected to silica gel CC eluted with PE and an acetone mixed solvent in a step gradient (10:1–0:1, v/v), to get three sub-fractions (Fr-2-1–Fr-2-3). Fr-2-2 was applied to a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH and reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v), and was further purified with a semi-preparative HPLC to obtain five sub-fractions (Fr-2-2-1–Fr-2-2-5). Fr-2-2-1 was separated with semi-preparative HPLC (24% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to afford 10 (7.6 mg, tR = 46.0 min), 14 (42.4 mg, tR = 37.0 min), and 15 (23.0 mg, tR = 59.0 min). Fr-2-2-4 was further isolated by semi-preparative HPLC (45% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to obtain 21 (8.5 mg, tR = 27.0 min). Fr-3 (3.9 g) was subjected to a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH, and reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v) to get two sub-fractions (Fr-3-1–Fr-3-2). Fr-3-1 was further purified with semi-preparative HPLC (35% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to obtain 13 (7.4 mg, tR = 16.0 min). Compound 7 (21.0 mg, tR = 13.4 min) was obtained from Fr-3-2 with semi-preparative HPLC (30% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min). Fr-4 (3.1 g) was subjected to a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH to get three sub-fractions (Fr-4-1–Fr-4-3). Fr-4-1 was applied to reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v) and semi-preparative HPLC (30% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to afford 1 (5.5 mg, tR = 18.5 min) and 17 (20.2 mg, tR = 17.0 min). Compound 11 (3.8 mg, tR = 36 min) was gained from Fr-4-2 with semi-preparative HPLC (40% MeOH/H2O, 2 mL/min). Fr-6 (1.8 g) was separated by a Sephadex LH-20 column, eluted with MeOH and reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v), to get two sub-fractions. This sub-fraction was further isolated by semi-preparative HPLC (42% MeOH/H2O, 2 mL/min) to obtain 3 (15.5 mg, tR = 17.8 min). The other sub-fraction was also purified by semi-preparative HPLC (17% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to gain 19 (5.1 mg, tR = 17 min). Fr-7 (2.1 g) was separated by a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH, reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v) and further isolated using semi-preparative HPLC (22% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to yield 2 (3.1 mg, tR = 45.0 min), 4 (6.4 mg, tR = 18.0 min ), and 6 (2.7 mg, tR = 15.0 min). Fr-8 (1.8 g) was separated by a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH, reversed-phase C-18 MPLC with MeOH/H2O (10:90–100:0, v/v), and further purified with semi-preparative HPLC (18% CH3CN/H2O, 2 mL/min) to yield 5 (3.6 mg, tR = 11.6 min) and 18 (64.3 mg, tR = 14.2 min).
3.5. Spectral Data
(S)-methyl 2-acetamido-4-(2-(methylamino)phenyl)-4-oxobutanoate (1)—white powder; +58.1 (c 0.1, CHCl3); UV (MeOH) λmax(log ε) 383 (3.16), 259 (3.31), 228 (3.79), 202 (3.69) nm, 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 700 MHz), and 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 175 MHz), Table 1; HR–ESI–MS m/z 301.1155 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C14H18N2NaO4, 301.1159) and 279.1336 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C14H19N2O4, 279.1339).
Quinolactacin E (2)—light yellow crystal; +1.4 (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax(log ε) 327 (3.86), 314 (3.90), 256 (4.13), 248 (4.15), 217 (4.29) nm; 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 700 MHz), and 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 175 MHz), Table 1;HR–ESI–MS m/z 293.1263 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C16H18N2NaO2, 293.1260).
Germicidin O (3)—colorless oil; −58.9 (c 0.1, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax(log ε) 292 (3.74), 208 (4.03) nm; 1H NMR (CD3OD, 500 MHz), and 13C NMR (CD3OD, 125 MHz), Table 1; HR–ESI–MS m/z 235.0952 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C11H16NaO4, 235.0941).
3.6. X-ray Crystal Structure Analysis
Crystal data (CCDC No.1912523) for 2 (moiety formula)—C16H18N2O2 (MW = 270.32), clear yellowish yellow needle, crystal size = 0.4 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm3, monoclinic, space group P21/n; unit cell dimensions: a = 12.8540(2) Å, b = 8.79200(10) Å, c = 13.6987(2) Å, V = 1502.38(4) Å3, Z = 4, ρcalcd = 1.195 g cm−3, and T = 102(4) K, μ(Cu Kα) = 0.640 mm−1. A total of 7071 reflections were measured with 2945 independent reflections (Rint= 0.0264, Rsigma = 0.0315). Final R indices [I>2σ (I)]: R1 = 0.0428, wR2 = 0.1199. Final R indices [all date]: R1 = 0.0514, wR2 = 0.1257. Largest diff. peak and hole = 0.20 and −0.24eÅ−3.
Crystal data (CCDC No.1912525) for 3 (moiety formula)—C11H16O4 (MW = 212.24), clear light colorless block, crystal size = 0.2 × 0.15× 0.1 mm3, monoclinic, space group P21; unit cell dimensions: a = 7.61640 (10) Å, b = 8.58280 (10) Å, c = 8.15540 (10) Å, V = 530.633(11) Å3, Z = 2, ρcalcd = 1.328 g cm−3, and T = 99.9(5) K, μ(Cu Kα) = 0.835 mm−1. A total of 5131 reflections were measured with 2206 independent reflections (Rint = 0.0188, Rsigma = 0.0215). Final R indices [I>2σ (I)]: R1 = 0.0310, wR2 = 0.0860. Final R indices [all date]: R1 = 0.0314, wR2 = 0.0863, Flack parameter = 0.07(7). Largest diff. peak and hole = 0.17 and −0.20eÅ−3.
3.7. Antibacterial Activity Assay
Compounds 1–21, excepting 2, were tested for their antibacterial activities against five pathogenic bacteria, using the method of agar filter paper diffusion. Those compounds which had an inhibition zone were tested in 96-well plates using a modification of the broth microdilution method [5]. Ampicillin and gentamicin were used as a positive control for the gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, respectively.
3.8. Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytotoxic activities of compounds 1–21, excepting 2, against human gastric cancer cells MGC803, human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231, human prostate cancer cells C4-2B, human osteosarcoma 143B, and human hung cancer cells A549 were evaluated using the CCK-8 method [27].
4. Conclusions
Two new alkaloids (1 and 2) and one new pyrone derivative (3), along with eighteen known compounds (4–21) were isolated from the rice cultures of sponge-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO41015. The new structures were elucidated by analysis of their NMR data and HR-ESI-MS. Their absolute configurations were established by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis or a comparison of the experimental with the reported specific rotation values.The biosynthetic pathway of quinolactacin A has been studied, andspeculated that it is synthesized from tryptophan and isoleucine [11]. Based on the current investigation, possible biosynthetic pathways of alkaloids 1, 2, and 4–6 were speculated.Compound 2 appeared to be synthesized from tryptophan and leucine, whereas compound 4 was made from tryptophan and valine. Compounds 1–21, excepting 2, were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities againstsix humancancer cells and their antibacterial activities against five pathogenic bacteria. Only compound 16 exhibited selective inhibitory activity against the MGC803 cells with an IC50 value of 5.19 μM. Other compounds showed no inhibitory activities at concentrations of 5 μM in the preliminary screening. While compounds 9 and 16 displayed an antibacterial ability against S. aureus with MIC values of 57 and 3.75 μg/mL, respectively. Compound 18 exhibited a weak antibacterial ability against A. baumannii, with an MIC value of 57 μg/mL.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/17/7/398/s1, The ITS sequences data of Penicillium sp. SCSIO41015, the 1D and 2D NMR spectra, HR–ESI–MS for the new compounds 1–3, and X-ray crystallographic files of compounds 2 and 3 (in CIF format).
Author Contributions
X.P., J.W. (Junfeng Wang), S.X., and Y.L. contributed to the conception and design of the study. X.P. performed experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript, X.L. did the isolation and identification of the fungus. J.W. (Junjian Wang) and G.C. performed the cytotoxicity assay. All authors contributed to the manuscript revision, and read and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC0310900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21172230, 21502204, 21672084, 21772210, 31270402, 41476135, 41776169 and 41876145), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA11030403), the Guangdong Province Public Welfare Research and Capacity Building Project (No. 2016A020222010), and Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (No. 201710010136).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jin, L.M.; Quan, C.S.; Hou, X.Y.; Fan, S.D. Potential pharmacological resources: Natural bioactive compounds from marine-derived fungi. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, M.Z.; Song, S.J.; Jung, J.H. Marine-derived Penicillium species as producers of cytotoxic metabolites. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.G.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, G.L.; Liu, H.S.; Zhu, W.M. Marine natural products sourced from marine-derived Penicillium fungi. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 92–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.Y.; Lin, X.P.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.F.; Liu, Y.H. Spiro-phthalides and isocoumarins isolated from the marine-sponge-derived fungus Setosphaeria sp. SCSIO41009. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.Y.; Lin, X.P.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.F.; Liu, Y.H. Perylenequione derivatives with anticancer activities isolated from the marine sponge-derived fungus, Alternaria sp. SCSIO41014. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.Y.; Lin, X.P.; Wang, J.; Liang, R.; Tian, Y.Q.; Salendra, L.; Luo, X.W.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, B.; Tu, Z.C.; et al. Three new highly oxygenated sterols and one new dihydroisocoumarin from the marine sponge-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. SCSIO41007. Steroids 2018, 129, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.R.; Calhoun, L.A. Synthesis and NMR characteristics of N-acetyl-4-nitro, N-acetyl-5-nitro, N-acetyl-6-nitro and N-acetyl-7-nitrotryptophan methyl esters. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, C.; Anderson, J.; Phillips, R.S. Differential effects of bromination on substrates and inhibitors of kynureninase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.; Capon, R.J.; Lacey, E.; Tennant, S.; Gill, J.H. Quinolactacins revisited: From lactams to imide and beyond. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Takahashi, S.; Uchida, K.; Funayama, S.; Kainosho, M.; Nakagawa, A. Biosynthesis of Quinolactacin A, a TNF production inhibitor. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.Q.; Sun, J.; Gong, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Zhu, W.M. New alpha-pyridones with quorum-sensing inhibitory activity from diversity-enhanced extracts of a Streptomyces sp. derived from marine algae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.M.; Qi, S.H.; Yin, H.; Gao, C.H.; Zhang, S. Alkaloids from the stem bark of Micromelum falcatum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, M.L.; Mottier, N.; Jeanneret-Gris, J.; Christen, D.; Tabacchi, R.; Abou-Mansour, E. Differential production of phytotoxins from Phomopsis sp. from grapevine plants showing esca symptoms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8602–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.Q.; Zhu, G.L.; Liu, H.S.; Jiang, G.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.M. Diversity and function of the Antarctic krill microorganisms from Euphausia superba. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Li, A. Total syntheses and structural revision of alpha- and beta-diversonolic esters and total syntheses of diversonol and blennolide C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 6579–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Dong, J.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Nong, X.H.; Qi, S.H. Cyclopentane-condensed chromones from marine-derived fungus Penicillium oxalicum. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 837–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.H.; Tian, L.; Zhu, T.J.; Wang, W.L.; Du, L.; Fang, Y.C.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Isocoumarin derivatives from the sea squirt-derived fungus Penicillium stoloniferum QY2-10 and the halotolerant fungus Penicillium notatum B-52. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.X.; Xue, J.H.; Xu, H.H.; Liu, X.Z.; Ma, W.Z.; Wei, X.Y. Three new isochromans from the mycelial culture of a Cylindrocarpon fungus. Heterocycles 2006, 68, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Ronsberg, D.; Debbab, A.; Mandi, A.; Vasylyeva, V.; Bohler, P.; Stork, B.; Engelke, L.; Hamacher, A.; Sawadogo, R.; Diederich, M.; et al. Pro-apoptotic and immunostimulatory tetrahydroxanthone dimers from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis longicolla. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 12409–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meselhy, M.R. Constituents from moghat, the roots of Glossostemon bruguieri (Desf.). Molecules 2003, 8, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, K.; Zhong, P.; Hu, X.; Fang, Z.X.; Wu, J.L.; Zhang, Q.Q. Tumonoic acids K and L, novel metabolites from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium citrinum. Heterocycles 2012, 85, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Mei, W.L.; Zhao, Y.X.; Deng, Y.Y.; Dai, H.F. A new cytotoxic isocoumarin from endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. 091402 of the mangrove plant Bruguiera sexangula. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2009, 45, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Gai, C.J.; Guo, Z.K.; Dai, H.F.; Mei, W.L. Studyon the secondary metabolites from the endophytic fungus Coriolopsis sp. J5 of Ceriops tagal and their biological activities. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2016, 35, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.L.; Lu, C.H.; Xu, Q.Y.; Song, S.Y.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zheng, Z.H. Four new citrinin derivatives from a marine-derived Penicillium sp. fungal strain. Molecules 2013, 18, 5723–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Amagata, A.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J.; Crews, P. Unusual C25 steroids produced by a sponge-derived Penicillium citrinum. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 4393–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Qin, X.C.; Tian, X.P.; Liao, L.; Li, K.M.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, X.W.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, T.Y.; et al. Antiviral merosesquiterpenoids produced by the antarctic fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).