Antagonism of Quorum Sensing Phenotypes by Analogs of the Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolite 3-Methyl-N-(2′-Phenylethyl)-Butyramide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. N-Phenethyl Hexanamide from Vibrio neptunius RIP07-147
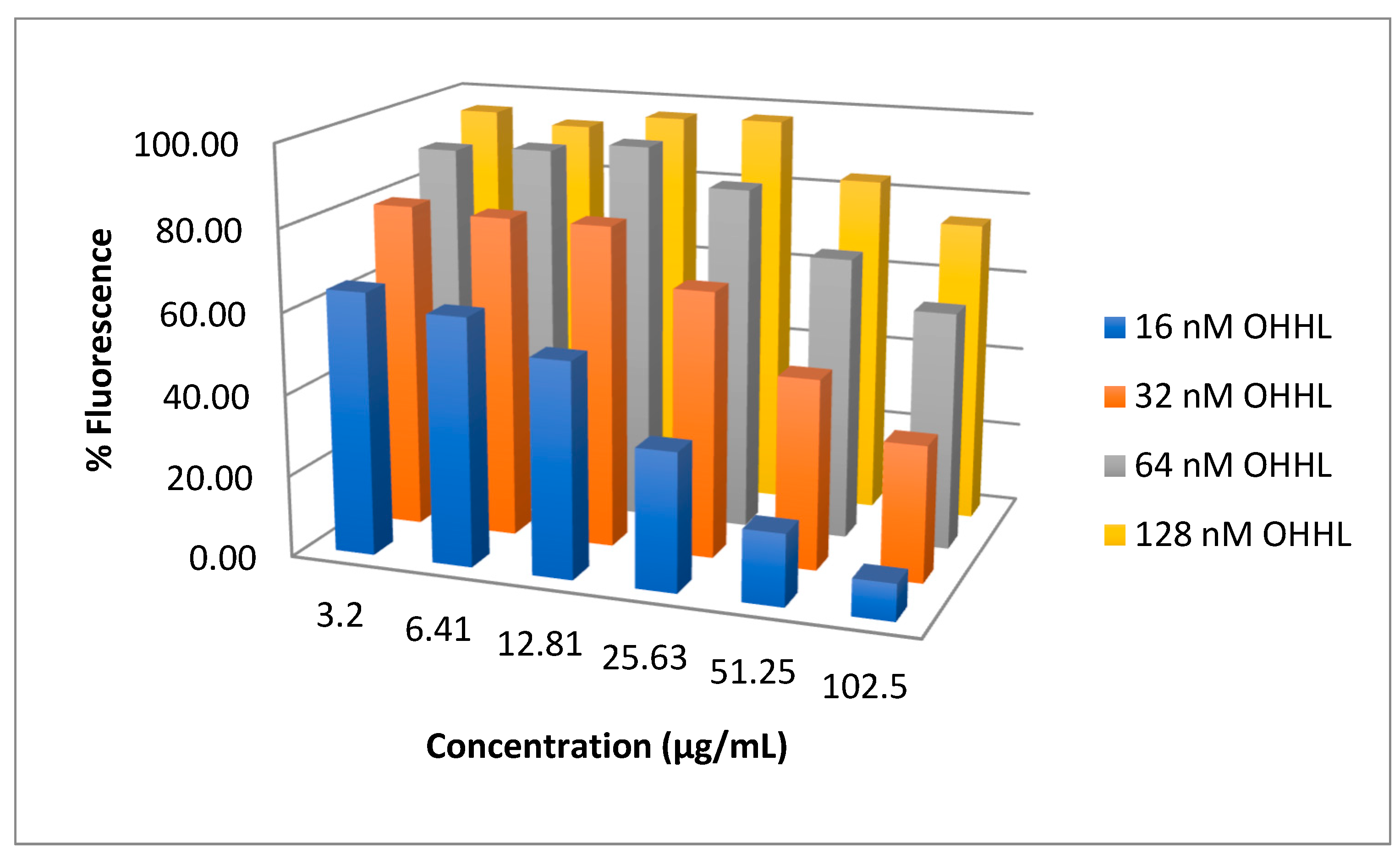
2.2. Bioassay Testing
2.3. Analog Design and Biological Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Media
4.2. Reporter Strains
4.3. Isolation and Sequencing RIP07-147
4.4. Co-Cultivation with V. harveyi BB120
4.5. Isolation of N-Phenethyl Hexanamide
4.6. Bioassays
4.6.1. V. harveyi BB120 Broth Dilution Assay
4.6.2. C. violaceum Disc Diffusion Assay
4.6.3. E. coli JB525 Bioassay
4.6.4. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Chemical Syntheses
4.7.1. General Procedure for Coupling Reactions
4.7.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Compounds 1–23
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001, 35, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Quadri, L.E.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M. Quorum sensing by peptide pheromones and two-component signal-transduction systems in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, B.L. Small talk. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Cell 2002, 109, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Christophersen, L.; Calum, H.; Hentzer, M.; Hougen, H.-P.; Rygaard, J.; Moser, C.; Eberl, L.; et al. Garlic blocks quorum sensing and promotes rapid clearing of pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3873–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilli, A.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial Small-Molecule Signaling Pathways. Science 2006, 311, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, L.; Winson, M.K.; Sternberg, C.; Stewart, G.S.; Christiansen, G.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.; Williams, P.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M. Involvement of N-acyl-L-hormoserine lactone autoinducers in controlling the multicellular behaviour of Serratia liquefaciens. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M. The role of quorum sensing in the pathogenicity of the cunning aggressor Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Pierson, E.; Hung, D.T. Targeting virulence: A new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.A.; Hoven, A.D.; Cook, A.M. Therapeutic frontiers: Preventing and treating infectious diseases by inhibiting bacterial quorum sensing. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T. Quorum-sensing systems as targets for antivirulence therapy. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busetti, A.; Shaw, G.; Megaw, J.; Gorman, S.P.; Maggs, C.A.; Gilmore, B.F. Marine-derived quorum-sensing inhibitory activities enhance the antibacterial efficacy of tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mar. Drugs 2014, 13, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackman, G.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Quorum sensing inhibitors increase the susceptibility of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givskov, M.; de Nys, R.; Manefield, M.; Gram, L.; Maximilien, R.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Steinberg, P.D.; Kjelleberg, S. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, L.; de Nys, R.; Maximilien, R.; Givskov, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Inhibitory Effects of Secondary metabolites from the red alga Delisea pulchra on swarming motility of Proteus mirabilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4284–4287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a quorum quenching agent from the Indonesian sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Donovan, K.A.; Forschner-Dancause, S.R.; Rowley, D.C. Gram-positive marine bacteria as a potential resource for the discovery of quorum sensing inhibitors. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Heydorn, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Parsek, M.R.; Rice, S.A.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Mascuch, S.J.; Villa, F.A.; Byrum, T.; Teasdale, M.E.; Smith, J.E.; Preskitt, L.B.; Rowley, D.C.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Honaucins A-C, potent inhibitors of inflammation and bacterial quorum sensing: Synthetic derivatives and structure-activity relationships. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: A signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8789–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Blackwell, H.E. N-Phenylacetanoyl-l-homoserine lactones can strongly antagonize or superagonize quorum sensing in Vibrio fischeri. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Miller, D.M.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Modulation of bacterial quorum sensing with synthetic ligands: Systematic evaluation of N-Acylated homoserine lactones in multiple species and new insights into their mechanisms of action. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13613–13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.M.; Bu, Y.; Suga, H. Induction and inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by synthetic autoinducer analogs. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, A.; Widrig, C.A.; McBath, P.; Schineller, J.B. Analogs of the autoinducer of bioluminescence in Vibrio fischeri. Arch. Microbiol. 1986, 146, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, M.E.; Combs, J.B.; Blackwell, H.E. N-Acyl l-homocysteine thiolactones are potent and stable synthetic modulators of the RhlR quorum sensing receptor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Beaber, J.W.; Moré, M.I.; Fuqua, C.; Eberhard, A.; Winans, S.C. Analogs of the autoinducer 3-oxooctanoyl-homoserine lactone strongly inhibit activity of the TraR protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5398–5405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Miller, D.M.; Wezeman, R.J.; Mattmann, M.E.; Lin, Q.; Blackwell, H.E. Comparative analyses of N-acylated homoserine lactones reveal unique structural features that dictate their ability to activate or inhibit quorum sensing. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Evaluation of a focused library of N-aryl L-homoserine lactones reveals a new set of potent quorum sensing modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5978–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, S.; Chantegrel, B.; Deshayes, C.; Doutheau, A.; Cotte-Pattat, N. New synthetic analogues of N-acyl homoserine lactones as agonists or antagonists of transcriptional regulators involved in bacterial quorum sensing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geske, G.D.; Wezeman, R.J.; Siegel, A.P.; Blackwell, H.E. Small molecule inhibitors of bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12762–12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Liu, J.; Wallace, J.; Akhlaghi, F.; Rowley, D.C. Secondary metabolites produced by the marine bacterium Halobacillus salinus that inhibit quorum sensing-controlled phenotypes in gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenhagen, A.; Tamura, S.Y.; Kenny, P.T.M.; Komura, H.; Naya, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Nishiyama, K.; Sugiura, M.; Kita, H. Andrimid, a new peptide antibiotic produced by an intracellular bacterial symbiont isolated from a brown planthopper. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 4409–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, R.P.; Asolkar, R.N.; Kapaun, E.; Wagner-Döbler, I.; Laatsch, H. Phytotoxic arylethylamides from limnic bacteria using a screening with microalgae. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, B.; Zhang, X.-H. Vibrio harveyi: A significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forschner-Dancause, S.; Poulin, E.; Meschwitz, S. Quorum sensing inhibition and structure-activity relationships of β-Keto Esters. Molecules 2016, 21, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manefield, M.; Harris, L.; Rice, S.A.; de Nys, R.; Kjelleberg, S. Inhibition of luminescence and virulence in the black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) pathogen Vibrio harveyi by intercellular signal antagonists. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching in Vibrio harveyi: Lessons learned from in vivo work. ISME J. 2008, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, J.M.; Bassler, B.L. Three parallel quorum-sensing systems regulate gene expression in Vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 6902–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143 Pt 12, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.B.; Heydorn, A.; Hentzer, M.; Eberl, L.; Geisenberger, O.; Christensen, B.B.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M. gfp-Based N-Acyl Homoserine-lactone sensor systems for detection of bacterial communication. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.A.; Severinsen, R.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M.; Nielsen, J. Synthesis of new 3- and 4-substituted analogues of acyl homoserine lactone quorum sensing autoinducers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.J.C.; Pierson, L.S.; Fuqua, C. A simple screening protocol for the identification of quorum signal antagonists. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 58, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, P.; Desroches, J.; Paquin, J.-F. Organic fluorine as a hydrogen-bond acceptor: Recent examples and applications. Synthesis 2015, 47, 306–322. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Quorum sensing inhibitors from marine bacteria Oceanobacillus sp. XC22919. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, R.M.M.; Dobretsov, S.; Al-Fori, M.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Sudesh, K.; Paul, V.J. Quorum-sensing inhibitory compounds from extremophilic microorganisms isolated from a hypersaline cyanobacterial mat. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, F.L.; Hoste, B.; Vandemeulebroecke, K.; Swings, J. Genomic diversity amongst Vibrio isolates from different sources determined by fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 24, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Li, Y.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Thompson, C.C.; Hoste, B.; Vandemeulebroecke, K.; Rupp, G.S.; Pereira, A.; De Bem, M.M.; Sorgeloos, P.; et al. Vibrio neptunius sp. nov., Vibrio brasiliensis sp. nov. and Vibrio xuii sp. nov., isolated from the marine aquaculture environment (bivalves, fish, rotifers and shrimps). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | V. harveyi BB120 | E. coli JB525 | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | Std. Dev. | IC50 (μg/mL) | Std. Dev. | Zone of Inhibition a (mm) | |
| 1 | 110 | 12 | 11 | 3.5 | 20 |
| 2 | NA | NA | 12 | ||
| 3 | 99 | 5.9 | NA | 14 | |
| 4 | 89 | 13 | NA | NA | |
| 5 | NA | NA | 21 | ||
| 6 | 17 | 2.9 | NA | NA | |
| 7 | 94 | 7.0 | NA | NA | |
| 8 | 29 | 3.0 | NA | NA | |
| 9 | 6.2 | 0.40 | 5.2 | 1.0 | 11 |
| 10 | 15 | NA | NA | ||
| 11 | 48 | 7.6 | 1.1 | 0.36 | 22 |
| 12 | 3.3 | 1.9 | >200 | 12 | |
| 13 | 5.6 | 3.6 | 32 | 12 | 9 |
| 14 | 86 | 2.7 | >200 | NA | |
| 15 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 3.8 | 1.0 | NA |
| 16 | 1.1 | 0.60 | 25 | 13 | 9 |
| 17 | 3.0 | 0.37 | 69 | 14 | NA |
| 18 | 6.0 | 2.0 | NA | NA | |
| 19 | 12 | 8.1 | >150 | NA | |
| 20 | NA | NA | NA | ||
| 21 | >200 | NA | NA | ||
| 22 | 19 | 1.2 | 56 | 2.2 | 13 b |
| 23 | 82 | 17 | 13 | 4.0 | 11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meschwitz, S.M.; Teasdale, M.E.; Mozzer, A.; Martin, N.; Liu, J.; Forschner-Dancause, S.; Rowley, D.C. Antagonism of Quorum Sensing Phenotypes by Analogs of the Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolite 3-Methyl-N-(2′-Phenylethyl)-Butyramide. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070389
Meschwitz SM, Teasdale ME, Mozzer A, Martin N, Liu J, Forschner-Dancause S, Rowley DC. Antagonism of Quorum Sensing Phenotypes by Analogs of the Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolite 3-Methyl-N-(2′-Phenylethyl)-Butyramide. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(7):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070389
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeschwitz, Susan M., Margaret E. Teasdale, Ann Mozzer, Nicole Martin, Jiayuan Liu, Stephanie Forschner-Dancause, and David C. Rowley. 2019. "Antagonism of Quorum Sensing Phenotypes by Analogs of the Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolite 3-Methyl-N-(2′-Phenylethyl)-Butyramide" Marine Drugs 17, no. 7: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070389
APA StyleMeschwitz, S. M., Teasdale, M. E., Mozzer, A., Martin, N., Liu, J., Forschner-Dancause, S., & Rowley, D. C. (2019). Antagonism of Quorum Sensing Phenotypes by Analogs of the Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolite 3-Methyl-N-(2′-Phenylethyl)-Butyramide. Marine Drugs, 17(7), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070389





