Effect of Conformational Diversity on the Bioactivity of µ-Conotoxin PIIIA Disulfide Isomers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
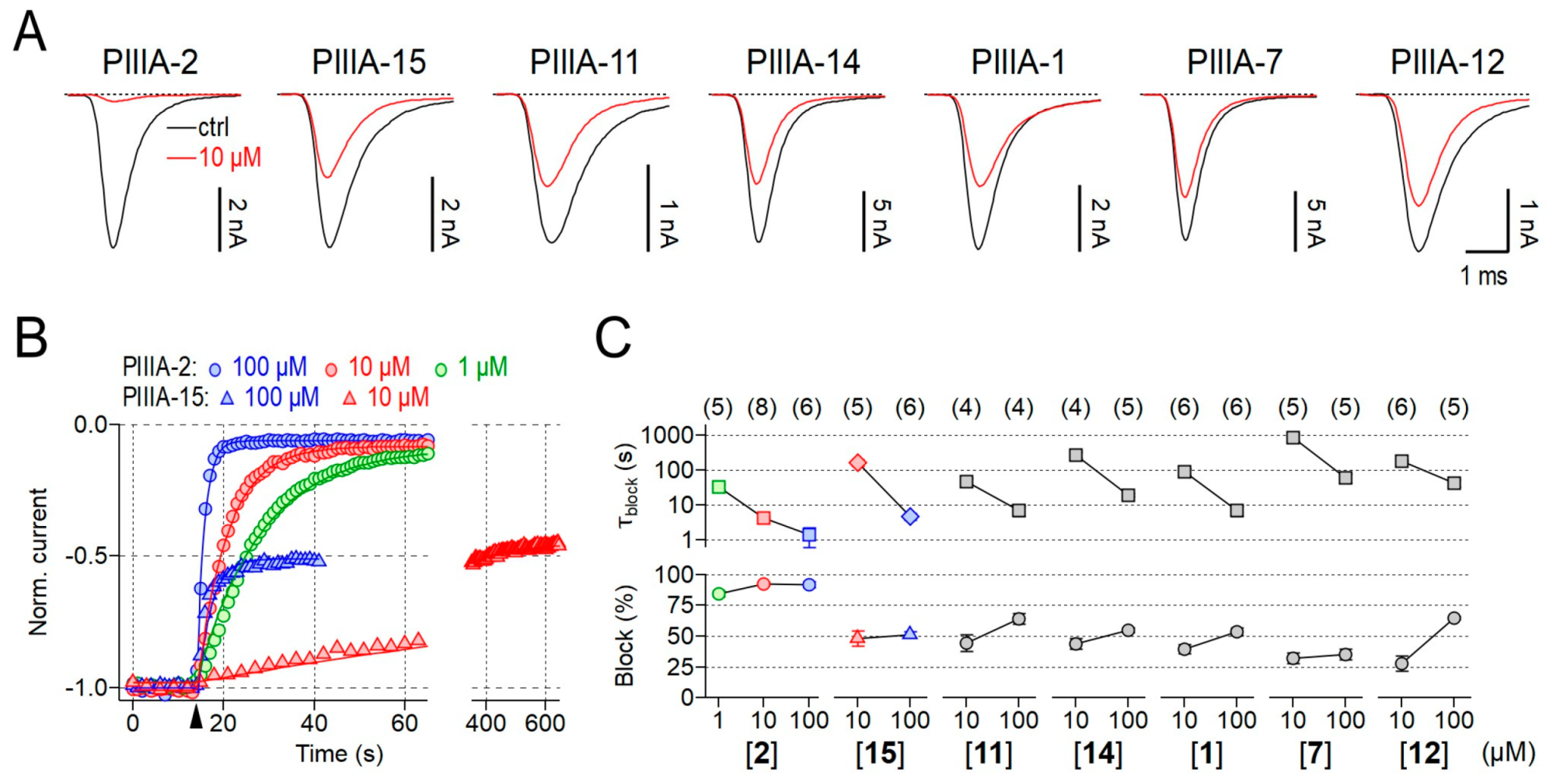
2.1. Bioactivity of 3- and 2-Disulfide-bonded µ-PIIIA Analogs at Nav1.4
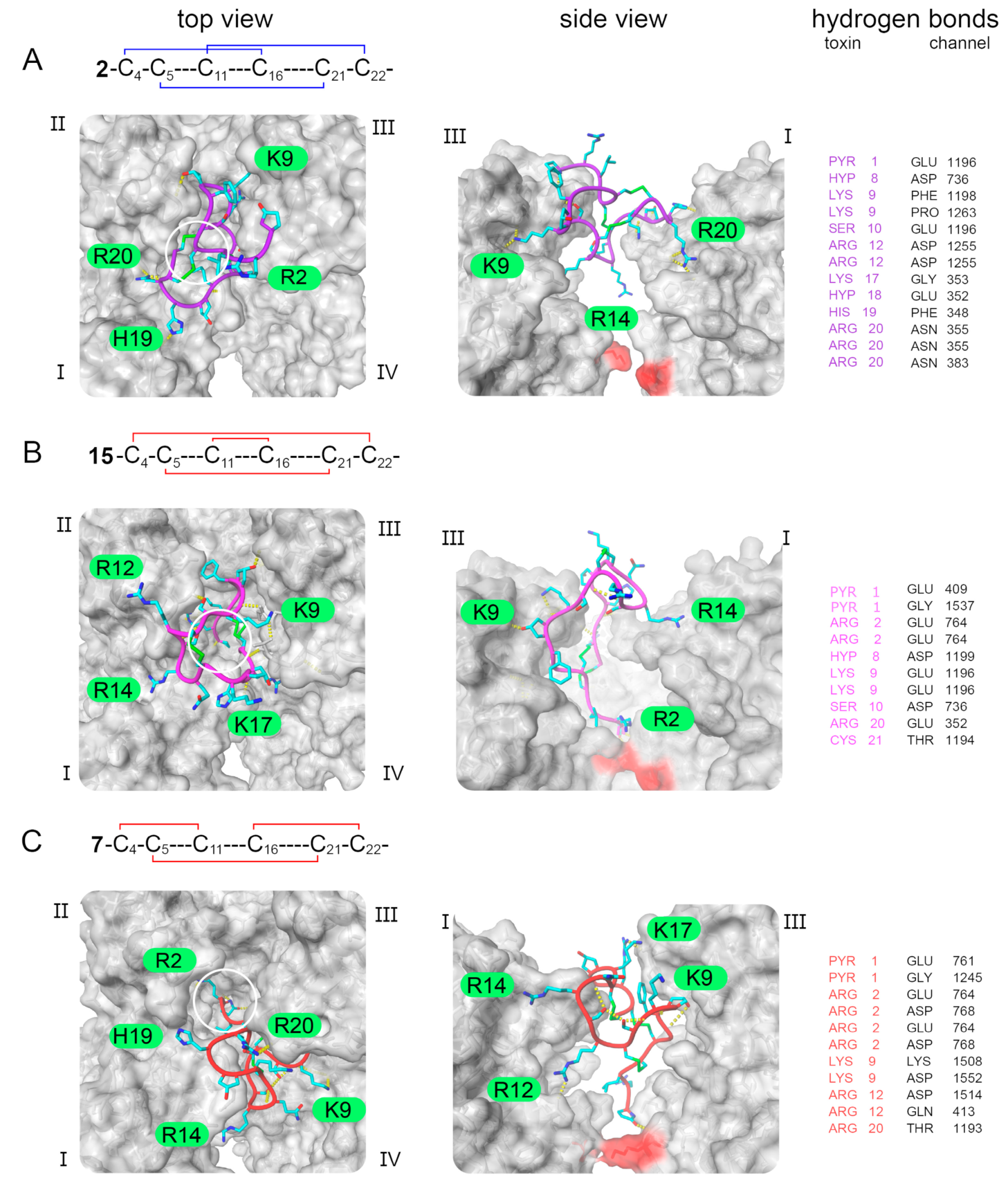
2.2. In Silico Toxin Binding Studies of the 3-Disulfide-Bonded µ-PIIIA Analogs at Nav1.4
2.3. MD- and Molecular Electrostatic Potential (MEP)-Based Analysis
2.3.1. Analysis of 3-Disulfide-bonded µ-PIIIA Isomers 1–15
2.3.2. Analysis of 2-Disulfide-bonded µ-PIIIA Isomers 16–18
2.3.3. Analysis of 2-Disulfide-bonded µ-PIIIA Isomers Δ(C5-C21)2, Δ(C11-C21)4, and Δ(C5-C22)10
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis and Purification
4.2. Electrophysiological Experiments
4.3. Molecular Modeling and Docking Simulations
4.4. MD Simulations of the µ-PIIIA Isomers and Analogs
4.5. MD Simulations of the µ-PIIIA Isomer-Channel Complexes
4.6. MEP Calculations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weissman, J.S.; Kim, P.S. Response. Science 2006, 256, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, W.J.; Welker, E.; Narayan, M.; Scheraga, H.A. Disulfide bonds and protein folding. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 4207–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemazar, M.; Zahariev, S.; Lopez, J.J.; Carugo, O.; Jones, J.A.; Hore, P.J.; Pongor, S. Oxidative folding intermediates with nonnative disulfide bridges between adjacent cysteine residues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 5754–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, J.E.; Jimenez, E.C.; Kranski, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Buczek, O.; Goodsell, I.; Nielsen, J.S. Efficient oxidative folding of conotoxins and the radiation of venomous cone snails. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 14562–14568. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Yang, J.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q. Cone snails: A big store of conotoxins for novel drug discovery. Toxins (Basel). 2017, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y. Diverse pathways of oxidative folding of disulfide proteins: Underlying causes and folding models. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3414–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, M.; Yoshikami, D.; Balaram, P.; Khoo, K.K.; Norton, R.S.; Olivera, B.M.; Zhang, M.-M.; Gupta, K.; Green, B.R.; Bulaj, G. Distinct Disulfide Isomers of μ-Conotoxins KIIIA and KIIIB Block Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9826–9835. [Google Scholar]
- Paul George, A.A.; Heimer, P.; Maaß, A.; Hamaekers, J.; Hofmann-Apitius, M.; Biswas, A.; Imhof, D. Insights into the Folding of Disulfide-Rich μ-Conotoxins. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12330–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutton, J.L.; Hogg, R.C.; Bansal, P.S.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. A New Level of Conotoxin Diversity, a Non-native Disulfide Bond Connectivity in α-Conotoxin AuIB Reduces Structural Definition but Increases Biological Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48849–48857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, A.A.; Tietze, D.; Ohlenschläger, O.; Leipold, E.; Ullrich, F.; Kühl, T.; Mischo, A.; Buntkowsky, G.; Görlach, M.; Heinemann, S.H.; et al. Structurally diverse μ-conotoxin PIIIA isomers block sodium channel Na V1.4. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4058–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Carstens, B.B.; O’Donnell, T.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Berecki, G.; Tae, H.-S.; Sadeghi, M.; Daniel, J.T.; Deiteren, A.; et al. Structure-Activity Studies of Cysteine-Rich α-Conotoxins that Inhibit High-Voltage-Activated Calcium Channels via GABA B Receptor Activation Reveal a Minimal Functional Motif. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4692–4696. [Google Scholar]
- Corpuz, G.P.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Jimenez, E.C.; Watkins, M.; Walker, C.; Colledge, C.; Garrett, J.E.; McDougal, O.; Li, W.; Gray, W.R.; et al. Definition of the M-conotoxin superfamily: Characterization of novel peptides from molluscivorous Conus venoms. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8176–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munasinghe, N.R.; Christie, M.J. Conotoxins that could provide analgesia through voltage gated sodium channel inhibition. Toxins (Basel). 2015, 7, 5386–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosti, E.; Boni, R.; Gallo, A. µ-Conotoxins modulating sodium currents in pain perception and transmission: A therapeutic potential. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipold, E.; Ullrich, F.; Thiele, M.; Tietze, A.A.; Terlau, H.; Imhof, D.; Heinemann, S.H. Subtype-specific block of voltage-gated K+ channels by μ-conopeptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimer, P.; Tietze, A.A.; Bäuml, C.A.; Resemann, A.; Mayer, F.J.; Suckau, D.; Ohlenschläger, O.; Tietze, D.; Imhof, D. Conformational μ-Conotoxin PIIIA Isomers Revisited: Impact of Cysteine Pairing on Disulfide-Bond Assignment and Structure Elucidation. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3321–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, Synthesis, and Structure–Activity Relationships of Conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Huang, W.; Jiang, T.; Yu, R. Determination of the µ-conotoxin PIIIA specificity against voltage-gated sodium channels from binding energy calculations. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroumov, V.; McMaster, D.; Al-Sabi, A.; French, R.J.; McArthur, J.R. Multiple, Distributed Interactions of μ-Conotoxin PIIIA Associated with Broad Targeting among Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Biochemistry 2010, 50, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, H.; Wu, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; et al. Structure of the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.4 in complex with β1. Science 2018, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Mclachlan, A.D. Solvation energy in protein folding and binding. Nature 1986, 319, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotný, J.; Bruccoleri, R.; Karplus, M. An analysis of incorrectly folded protein models. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 177, 787–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Q.; Chen, F.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, Y.; Wan, S.; Jiang, T.; Yu, R. Role of the disulfide bond on the structure and activity of μ-conotoxin PIIIA in the inhibition of Na V 1.4. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schulten, K.; Gruebele, M.; Bansal, P.S.; Wilson, D.; Daly, N.L. Disulfide bridges: Bringing together frustrated structure in a bioactive peptide. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; Wang, W.; Thirumalai, D. Protein folding guides disulfide bond formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 11241–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombkowski, A.A.; Sultana, K.Z.; Craig, D.B. Protein disulfide engineering. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góngora-Benítez, M.; Tulla-Puche, J.; Albericio, F. Multifaceted roles of disulfide bonds. peptides as therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 901–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Robinson, A.; Chung, S.H. Mechanism of μ-conotoxin PIIIA binding to the voltage-gated Na+channel NaV1.4. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, P.J. Disulfide bonds as switches for protein function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, D.J.; Yu, R.; Kaas, Q.; Adams, D.J.; Berecki, G.; Jia, X.; Seymour, V.A.L.; Akcan, M. Less is More: Design of a Highly Stable Disulfide-Deleted Mutant of Analgesic Cyclic α-Conotoxin Vc1.1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13264. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, C.; Boelens, R.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J. HADDOCK: A protein-protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zundert, G.C.P.; Rodrigues, J.P.G.L.M.; Trellet, M.; Schmitz, C.; Kastritis, P.L.; Karaca, E.; Melquiond, A.S.J.; Van Dijk, M.; De Vries, S.J.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J. The HADDOCK2.2 Web Server: User-Friendly Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. YASARA View - molecular graphics for all devices - from smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. New ways to boost molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G.; Essmann, U.; Darden, T.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E.; Van Der Spoel, D.; Mark, A.E.; Groenhof, G. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepeis, J.L.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Shaw, D.E.; Palmo, K.; Dror, R.O.; Maragakis, P.; Piana, S. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Argos, P.; Eisenhaber, F.; Lijnzaad, P.; Scharf, M.; Sander, C. The double cubic lattice method: Efficient approaches to numerical integration of surface area and volume and to dot surface contouring of molecular assemblies. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- William Humphrey; Andrew Dalke; Klaus Schulten VMD – Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38.
- Fogolari, F.; Brigo, A.; Molinari, H. The Poisson-Boltzmann equation for biomolecular electrostatics: A tool for structural biology. J. Mol. Recognit. 2002, 15, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, N.A. Poisson-Boltzmann Methods for Biomolecular Electrostatics. Methods Enzymol. 2004, 383, 94–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holst, M.J.; McCammon, J.A.; Sept, D.; Baker, N.A.; Joseph, S. Electrostatics of nanosystems: Application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002, 98, 10037–10041. [Google Scholar]
| Isomer Nomenclature | Number of Disulfides | Disulfide Connectivity | Type of Structure | Source Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16], Tietze et al. [10]. |
| 2 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16], Tietze et al. [10]. |
| 3 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16], Tietze et al. [10]. |
| 4 | 3 | 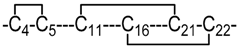 | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 5 | 3 | 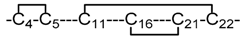 | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 6 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 7 | 3 |  | In silico model | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 8 | 3 | 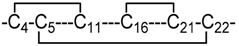 | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 9 | 3 | 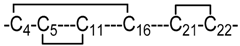 | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 10 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 11 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 12 | 3 |  | In silico model | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 13 | 3 |  | In silico model | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 14 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 15 | 3 |  | NMR | Heimer et al. [16]. |
| 16* | 2 | 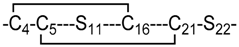 | In silico model | Current study |
| 17* | 2 |  | In silico model | Current study |
| 18* | 2 |  | In silico model | Current study |
| Δ(C5-C21)2# | 2 |  | In silico model | Current study |
| Δ(C11-C21)4# | 2 |  | In silico model | Current study |
| Δ(C5-C22)10# | 2 |  | In silico model | Current study |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul George, A.A.; Heimer, P.; Leipold, E.; Schmitz, T.; Kaufmann, D.; Tietze, D.; Heinemann, S.H.; Imhof, D. Effect of Conformational Diversity on the Bioactivity of µ-Conotoxin PIIIA Disulfide Isomers. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070390
Paul George AA, Heimer P, Leipold E, Schmitz T, Kaufmann D, Tietze D, Heinemann SH, Imhof D. Effect of Conformational Diversity on the Bioactivity of µ-Conotoxin PIIIA Disulfide Isomers. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(7):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070390
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul George, Ajay Abisheck, Pascal Heimer, Enrico Leipold, Thomas Schmitz, Desiree Kaufmann, Daniel Tietze, Stefan H. Heinemann, and Diana Imhof. 2019. "Effect of Conformational Diversity on the Bioactivity of µ-Conotoxin PIIIA Disulfide Isomers" Marine Drugs 17, no. 7: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070390
APA StylePaul George, A. A., Heimer, P., Leipold, E., Schmitz, T., Kaufmann, D., Tietze, D., Heinemann, S. H., & Imhof, D. (2019). Effect of Conformational Diversity on the Bioactivity of µ-Conotoxin PIIIA Disulfide Isomers. Marine Drugs, 17(7), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17070390






