Nanogels Derived from Fish Gelatin: Application to Drug Delivery System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Fish GelMA NGs
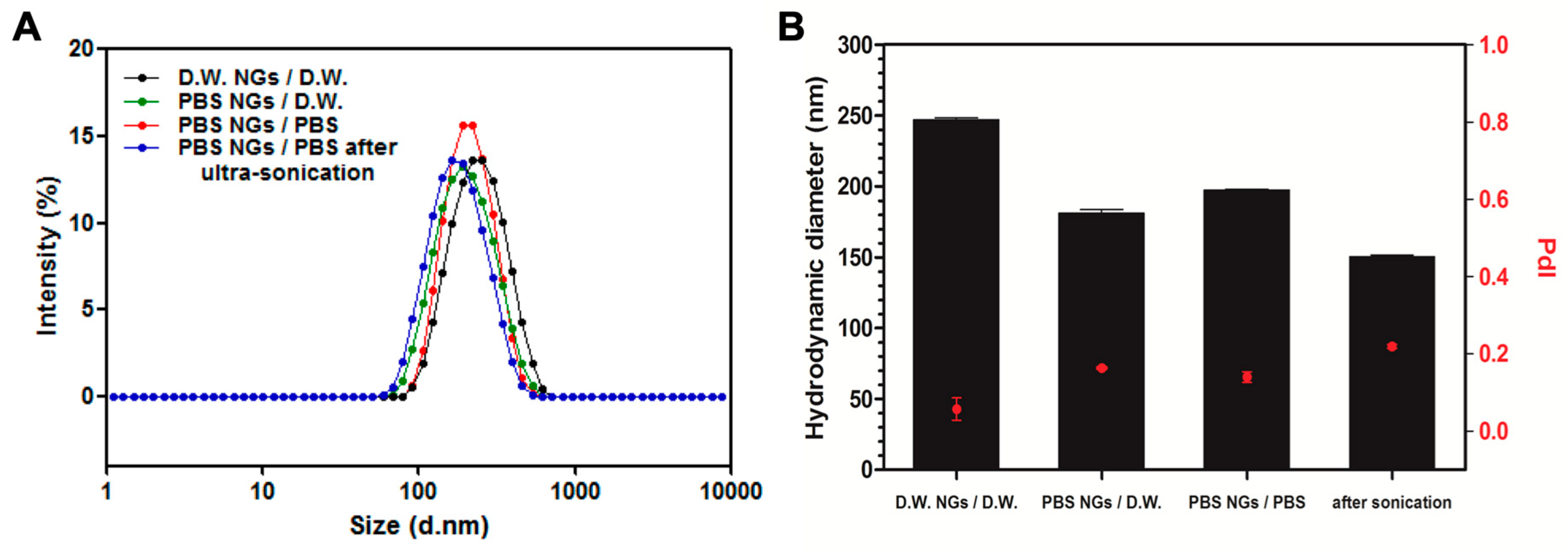
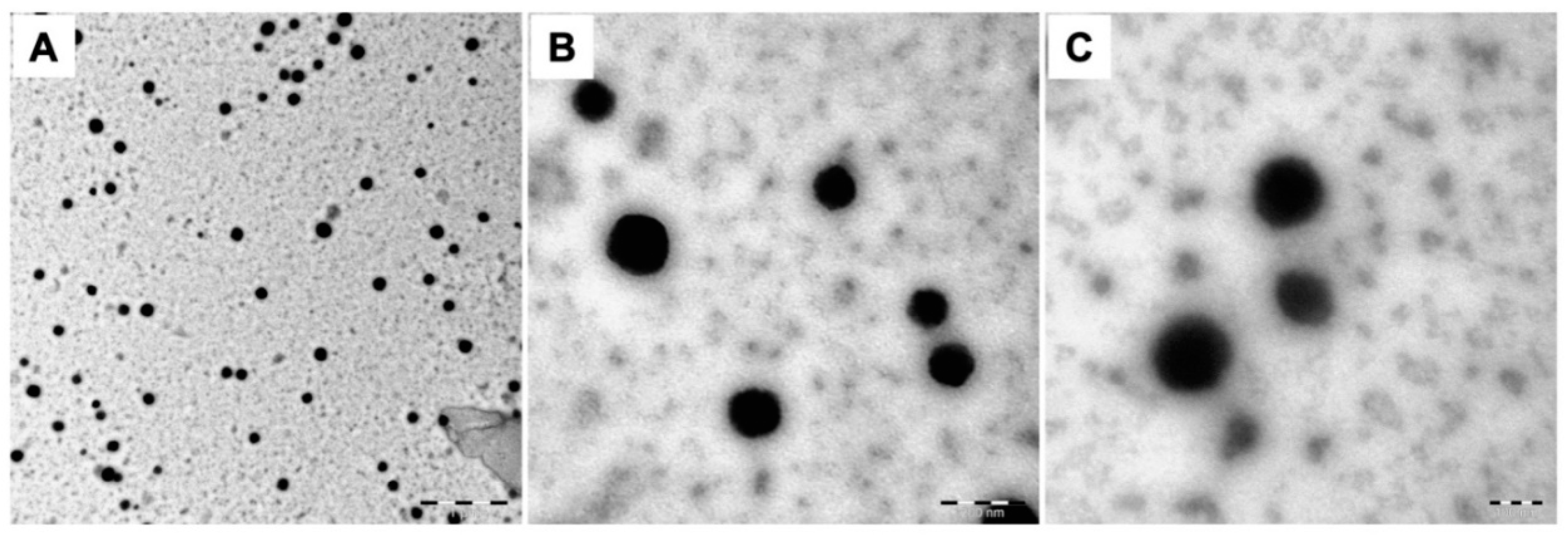
2.2. Characterization of Fish GelMA NGs
2.3. Characterization of Drug Loaded Fish GelMA NGs
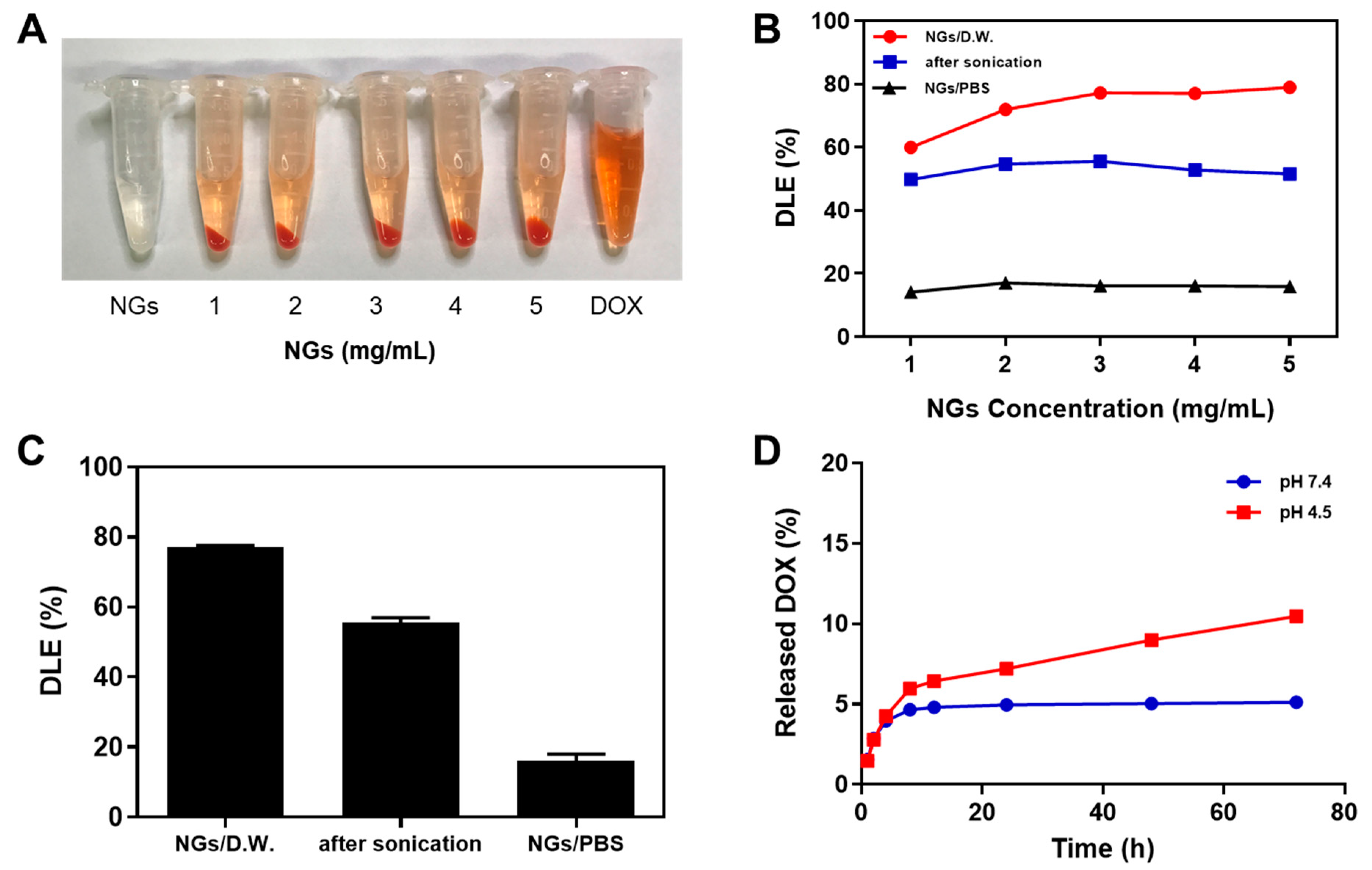
2.3.1. Drug Loading Efficiency
2.3.2. In Vitro DOX Release Studies
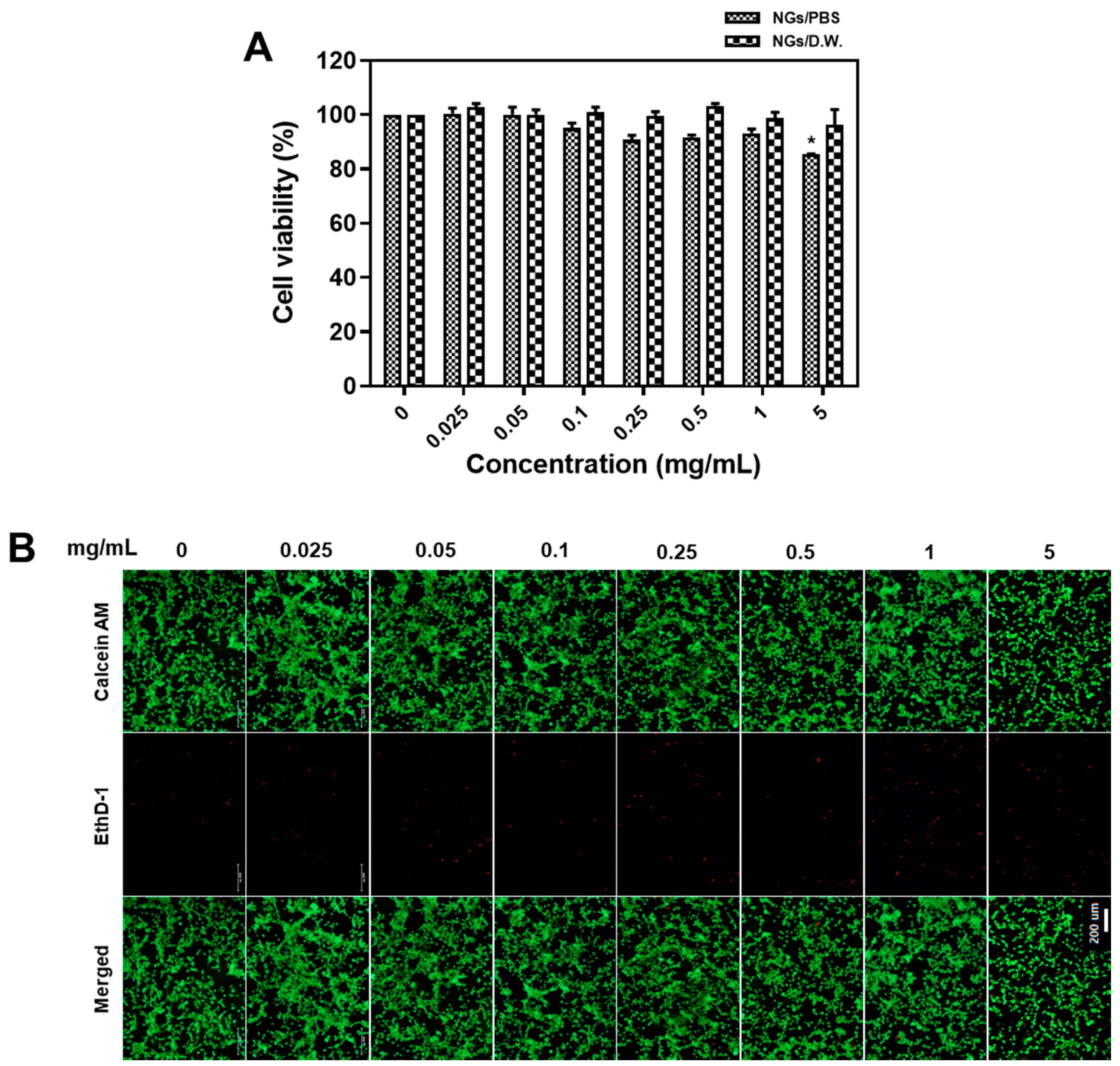
2.4. Biocompatibility Test of Fish GelMA NGs
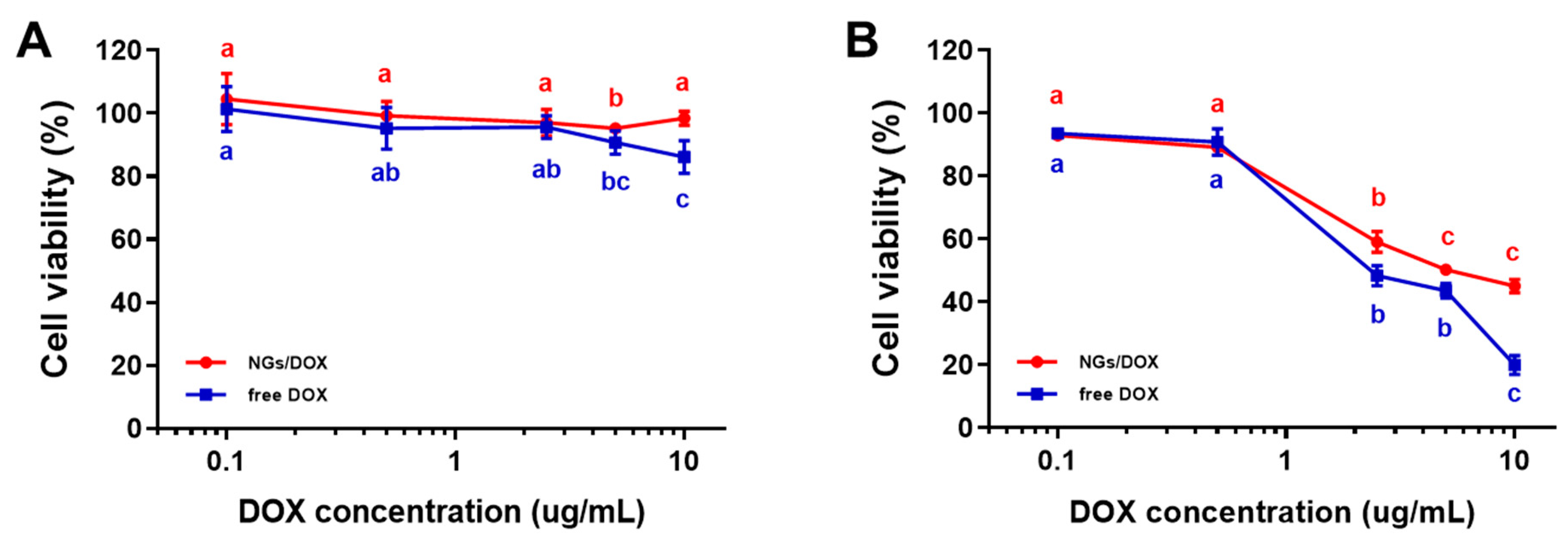
2.5. Cytotoxicity Test of DOX-GelMA NGs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of GelMA
3.3. Preparation of GelMA NGs
3.4. Preparation of DOX-loaded GelMA NGs
3.5. Size and PdI Measurements
3.6. Morphology of GelMA Nanogels
3.7. Drug Loading Efficiency
3.8. In Vitro Drug Release Test
3.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
3.9.1. Cell Culture
3.9.2. MTT Assay
3.9.3. Live/Dead Cell Assay
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santoro, M.; Tatara, A.M.; Mikos, A.G. Gelatin carriers for drug and cell delivery in tissue engineering. J. Control Release. 2014, 28, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Nikoo, M.; Boran, G.; Zhou, P.; Regenstein, J.M. Collagen and gelatin. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O. Gelatin-based nanoparticles as drug and gene delivery systems: Reviewing three decades of research. J. Control Release. 2013, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, M.H.; Piehl, M.D.; Burks, A.W. Near fatal anaphylaxis from orally administered gelatin capsule. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2013, 1, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, M.M.; Chandler, B.; Ho, K.M. Benefits and risks of using gelatin solution as a plasma expander for perioperative and critically ill patients: A meta–analysis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2012, 40, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Aizawa, C. Change in gelatin content of vaccines associated with reduction in reports of allergic reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foox, M.; Zilberman, M. Drug delivery from gelatin–based systems. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Sun, W.; Fang, J.; Lee, K.; Li, S.; Gu, Z.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Biodegradable Gelatin Methacryloyl Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.A.; da Silva Abreu, A.; Tedesco, A.C.; Junior, M.B.; Simioni, A.R. Functionalized Photosensitive Gelatin Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Application. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, N.; Godiny, M.; Moradi, S.; Hemati Azandaryani, A.; Shahlaei, M. Chitosan/gelatin as a new nano-carrier system for calcium hydroxide delivery in endodontic applications: Development, characterization and process optimization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 92, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterbrook, C.; Maddern, G. Porcine and bovine surgical products: Jewish, Muslim, and Hindu perspectives. Arch. Surg. 2008, 4, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakofski, J.; Brewer, M.S.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.; Killefer, J.; McCusker, R.H. Prion biology relevant to bovine spongiform encephalopathy. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1455–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, H.; Song, D.W.; Yang, Y.; Shin, B.S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Fabrication of an ultrafine fish gelatin nanofibrous web from an aqueous solution by electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, G.; Regenstein, J.M. Fish gelatin. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2010, 60, 119–143. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhmanova, A.; Khan, Z.A.; Sharif, R.; Lv, X. Meeting the requirements of halal gelatin: A mini review. MOJ Food Proc. Technol. 2018, 6, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Ninan, G.; Joseph, J.; Aliyamveettil, Z.A. A comparative study on the physical, chemical and functional properties of carp skin and mammalian gelatins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prommajak, T.; Raviyan, P. Physical properties of gelatin extracted from skin of Thai panga fish (Pangasius bocourti Sauvage). Food. Appl. Bio. J. 2013, 1, 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzapour Kouhdasht, A.; Moosavi–Nasab, M.; Aminlari, M. Gelatin production using fish wastes by extracted alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 5175–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamtu, I.; Rusu, A.G.; Diaconu, A.; Nita, L.E.; Chiriac, A.P. Basic concepts and recent advances in nanogels as carriers for medical applications. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, F.U.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.; Zeb, A. Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabuzu, D.; Cirja, A.; Puiu, R.; Grumezescu, A.M. Biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for stimuli–responsive controlled drug delivery: advances, challenges, and outlook. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingchoncharoen, P.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R. Lipid-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: What is available and what is yet to come. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 701–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Li, Z.; TieHong, Y.; Hong, W. Stimuli-responsive polymeric micelles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2921–2942. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Rizwan, A.; Jiang, L.; Bhujwalla, A.M.; Neoplasia, K.G. Molecular effects of doxorubicin on choline metabolism in breast cancer. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Kong, W.H.; Do, I.H.; Hahn, S.K. Nano graphene oxide-hyaluronic acid conjugate for target specific cancer drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14197–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetan, M.; Liu, Z.; Pumberger, M.; Giraldo, C.V.; Ruesink, T.; Lu, L.; Yaszemski, M.J. A stimuli–responsive hydrogel for doxorubicin delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8051–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.W.; Koshy, S.T.; Bae, H.; Hwang, C.M.; Yamanlar, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Gauvin, R.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kwon, S.-M.; Park, H.J.; Baek, S.H.; Cha, J.M.; Bae, H. Skin penetration–inducing gelatin methacryloyl nanogels for transdermal macromolecule delivery. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.G.; Lee, M.Y.; Cha, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, Y.-S.; Bae, H. Nanogels Derived from Fish Gelatin: Application to Drug Delivery System. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040246
Kang MG, Lee MY, Cha JM, Lee JK, Lee SC, Kim J, Hwang Y-S, Bae H. Nanogels Derived from Fish Gelatin: Application to Drug Delivery System. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(4):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040246
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Min Gyeong, Min Young Lee, Jae Min Cha, Jung Ki Lee, Sang Cheon Lee, Jeehye Kim, Yu-Shik Hwang, and Hojae Bae. 2019. "Nanogels Derived from Fish Gelatin: Application to Drug Delivery System" Marine Drugs 17, no. 4: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040246
APA StyleKang, M. G., Lee, M. Y., Cha, J. M., Lee, J. K., Lee, S. C., Kim, J., Hwang, Y.-S., & Bae, H. (2019). Nanogels Derived from Fish Gelatin: Application to Drug Delivery System. Marine Drugs, 17(4), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040246




