Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Characteristics of the Study Subjects
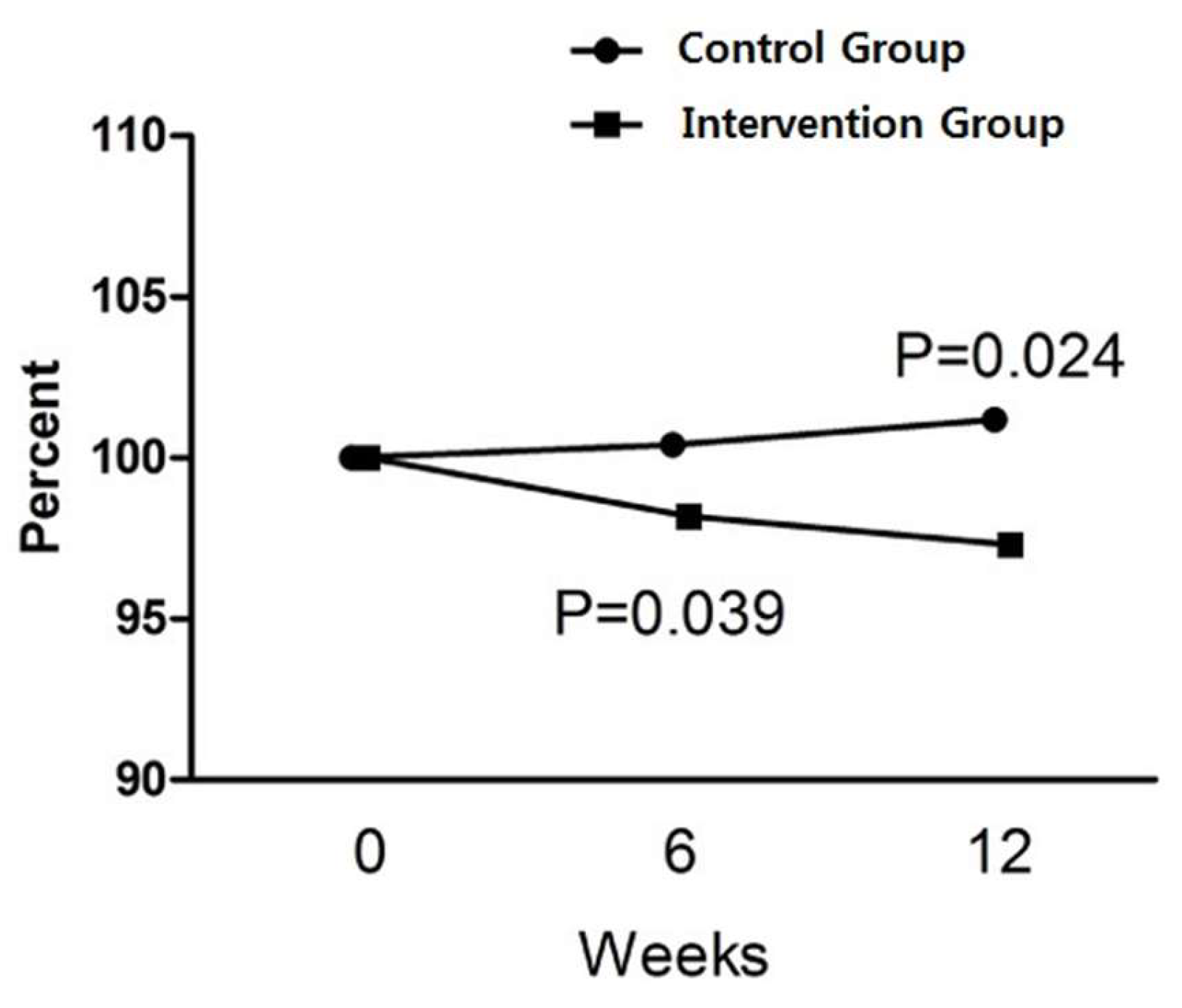
2.2. Changes inBody Composition
2.3. Changes in Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Safety
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Study Subjects
4.2. Randomization
4.3. Intervention
4.4. Evaluation of Dietary Intake and Physical Activities
4.5. Measurements
4.6. Statistical Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aminde, L.N.; Veerman, L. Interventions for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases: A protocol for a systematic review of economic evaluations in low-income and middle-income countries. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e013668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreidieh, D.; Itani, L.; El Masri, D.; Tannir, H.; Citarella, R.; El Ghoch, M. Association between Sarcopenic Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and Hypertension in Overweight and Obese Treatment-Seeking Adult Women. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; MacKenzie, R.G. Obesity Drug Update: The Lost Decade? Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 3494–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, N.P.; Kim, H.; Wells, A.M.; Kajkenova, O.; Evans, W.J. Effects of whey and fortified collagen hydrolysate protein supplements on nitrogen balance and body composition in older women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Baumstark, M.W.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, A.; Morimura, S.; Guo, H.-C.; Shigematsu, T.; Kida, K.; Uemura, Y. Production of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from sea bream scales. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-F.; Li, G.-Z.; Peng, H.-B.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Treatment with marine collagen peptides modulates glucose and lipid metabolism in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 35, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Koyama, Y.-I.; Nomura, Y. Effects of collagen peptide ingestion on UV-B-induced skin damage. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Pei, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. The lipid-lowering and antioxidative effects of marine collagen peptides. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2008, 42, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.M.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, J.S.; Jeong, K.S. Development of high functional collagen peptide materials using skate skins. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2016, 25, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Michael, L.; Eun, J.B. Nutritional composition and microflora of the fresh and fermented skate (Raja Kenojei) skins. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 55, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Deng, S.G. Two Novel Antioxidant Nonapeptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Skate (Raja porosa) muscle. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1993–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Anticancer Activity of a Hexapeptide from Skate (Raja porosa) Cartilage Protein Hydrolysate in HeLa Cells. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.O.; Kim, M.; Woo, M.; Baek, J.M.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Roh, S.S.; Park, C.H.; Jeong, K.S.; Noh, J.S. Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Damage in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshi, N.; Nobutaka, S. Isolation of collagen from fish waste material-skin, bone and fins. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 227–281. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.K.; Lee, M.K. Studies on the fatty acids and cholesterol level of Raja skate. J. Korean Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 12, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M.J.; Song, Y.O.; Kang, K.H.; Noh, J.S. Anti-Obesity Effects of Collagen Peptide Derived from Skate (Raja kenojei) Skin Through Regulation of Lipid Metabolism. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, O.-K.; Yoon, H.-G.; Park, J.; You, Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.-H.; Choi, K.-C.; Lee, J.; Jun, W. Anti-obesity effect of extract from fermented Curcuma longa L. through regulation of adipogenesis and lipolysis pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 30428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Cho, G.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, C.B.; et al. Appropriate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity in Korean adults. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Hur, J.W.; Ham, S.A.; Jo, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, M.J.; Seo, H.G. Fish collagen peptide inhibits the adipogenic differentiation of preadipocytes and ameliorates obesity in high fat diet-fed mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astre, G.; Deleruyelle, S.; Dortignac, A.; Bonnet, C.; Valet, P.; Dray, C. Diet-induced obesity and associated disorders are prevented by natural bioactive type 1 fish collagen peptides (Naticol®) treatment. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 74, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston-Banks, F.A. Gelatine. In Food Gels; Harris, P., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, R.; Diéguez, C.; Vidal-Puig, A.; López, M. AMPK: A metabolic gauge regulating whole-body energy homeostasis. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa Guerra, J.F.; Maciel, P.S.; de Abreu, I.C.M.E.; Pereira, R.R.; Silva, M.; de Morais Cardoso, L.; Pinheiro-Sant’Ana, H.M.; de Lima, W.G.; Silva, M.E.; Pedrosa, M.L. Dietary açai attenuates hepatic steatosis via adiponectin-mediated effects on lipid metabolism in high-fat diet mice. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toombs, R.J.; Ducher, G.; Shepherd, J.A.; De Souza, M.J. The impact of recent technological advances on the trueness and precision of DXA to assess body composition. Obesity 2012, 20, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, W.E.; Houmard, J.A.; Duscha, B.D.; Knetzger, K.J.; Wharton, M.B.; McCartney, J.S.; Bales, C.W.; Henes, S.; Samsa, G.P.; Otvos, J.D.; et al. Effects of the amount and intensity of exercise on plasma lipoproteins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, E.L.; Patnode, C.D.; Webber, E.M.; Redmond, N.; Rushkin, M.; O’Connor, E.A. Behavioral and Pharmacotherapy Weight Loss Interventions to Prevent Obesity-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Adults: An Updated Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2018, 320, 1172–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, R.; Murad, M.H.; Chandar, A.K.; Dulai, P.S.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Loomba, R.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S. Association of Pharmacological Treatments for Obesity with Weight Loss and Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2016, 315, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.R.; Weissman, N.J.; Anderson, C.M.; Sanchez, M.; Chuang, E.; Stubbe, S.; Bays, H.; Shanahan, W.R.; Behavioral Modification and Lorcaserin for Overweight and Obesity Management (BLOOM) Study Group. Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Lorcaserin for Weight Management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinert, R.E.; Christine, F.B.; Asarian, L.; Horowitz, M.; Beglinger, C.; Geary, N. Ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, and PYY(3–36): Secretory Controls and Physiological Roles in Eating and Glycemia in Health, Obesity, and After RYGB. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 411–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Dubey, V.; Ghosh, A.R. Obesity: An overview of possible role(s) of gut hormones, lipid sensing and gut microbiota. Metabolism 2016, 65, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Tartaglia, L.A. Medicinal strategies in the treatment of obesity. Nature 2000, 404, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, C.; Ho, J.C.Y.; Tay, Z.; Rebello, S.A.; Lu, Y.; Ong, C.N.; van Dam, R.M. Relative Validity and Reproducibility of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Assessing Dietary Intakes in a Multi-Ethnic Asian Population Using 24-h Dietary Recalls and Biomarkers. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothney, M.P.; Brychta, R.J.; Schaefer, E.V.; Chen, K.Y.; Skarulis, M.C. Body composition measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry half-body scans in obese adults. Obesity 2009, 17, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppini, L.Z.; Waitzberg, D.L.; Campos, A.C. Limitations and validation of bioelectrical impedance analysis in morbidly obese patients. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2005, 8, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Guidance for Industry Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers. July 2005; Pharmacology and Toxicology. APPENDIX B, Analysis of Body Weight Effects on HED Calculations; p. 19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/UCM078932.pdf%23search=%27guidekines+for+industry+sfe+starting%27 (accessed on 7 March 2019).
- Rural Development Administration, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences. Food Composition Table; Rural Development Administration, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences: Wanju, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.J.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, D.; Noh, H.; Song, S.; Kang, M. Development and feasibility of a web-based program ‘Diet Evaluation System (DES)’ in urban and community nutrition survey in Korea. Korean J. Health Promot. 2013, 13, 107–115. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Bradstock, K.; Forman, M.R.; Binkin, N.J.; Gentry, E.M.; Hogelin, G.C.; Williamson, D.F.; Trowbridge, F.L. Alcohol use and health behavior lifestyles among U.S. women: The behavioral risk factor surveys. Addict. Behav. 1988, 13, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, L.R.; Simões, E.J.; Assis, A.M.; Ramos, L.R. Validity and reliability of the sagittal abdominal diameter as a predictor of visceral abdominal fat. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2007, 51, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.S.; Han, D.S.; Kwon, S.O.; Yeo, K.M.; Kim, B.N.; Ly, S. The effect of Sargassum confusum on reduction of body fat in obese women. J. Nutr. Health 2014, 47, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Intention to Treat Analysis | Per Protocol Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG (n = 45) | IG (n = 45) | p * | CG (n = 41) | IG (n = 40) | p * | |
| Male (%) | 8 (17.8) | 9 (20.0) | 0.788 | 8 (19.5) | 8 (20.0) | 0.956 |
| Age (years) | 40.8 ± 11.1 | 41.7 ± 9.7 | 0.750 | 41.1 ± 11.2 | 41.8 ± 9.9 | 0.817 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.8 ± 1.9 | 25.5 ± 2.0 | 0.467 | 25.8 ± 1.9 | 25.4 ± 2.0 | 0.404 |
| Alcohol user (%) | 23 (51.1) | 18 (40.0) | 0.290 | 20 (48.8) | 17 (42.5) | 0.570 |
| Smoker (%) | 2 (4.4) | 1 (2.2) | 0.559 | 2 (4.9) | 1 (2.5) | 0.573 |
| Calorie intake (kcal/day) | 1660 ± 495 | 1594 ± 357 | 0.410 | 1667 ± 515 | 1601 ± 360 | 0.427 |
| IPAQ (METs) | 1151 (363–1726) | 740 (33–2170) | 0.813 | 1158 (396–1658) | 903 (33–2655) | 0.502 |
| Variable | Observed Values | Changes from Baseline | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG (n = 45) | IG (n = 45) | p * | CG (n = 45) | p ** | IG (n = 45) | p ** | p * | |
| Weight (kg) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 68.0 ± 8.5 | 66.6 ± 8.5 | 0.364 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 68.7 ± 8.8 | 66.8 ± 8.8 | 0.228 1 | 0.7 ± 1.9 | 0.018 4 | 0.2 ± 1.3 | 0.183 4 | 0.155 2 |
| SAD (cm) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 19.6 ± 2.0 | 19.3 ± 1.6 | 0.226 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 19.5 ± 2.2 | 19.2 ± 1.8 | 0.433 2 | −0.1 ± 1.1 | 0.489 3 | −0.1 ± 1.0 | 0.701 4 | 0.840 4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 25.8 ± 1.9 | 25.5 ± 2.0 | 0.467 2 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 26.1 ± 2.2 | 25.6 ± 2.0 | 0.274 2 | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 0.015 3 | 0.1 ± 0.5 | 0.265 3 | 0.153 1 |
| Body fat (%) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 40.5 ± 4.7 | 41.2 ± 5.5 | 0.255 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 40.3 ± 4.4 | 40.6 ± 5.3 | 0.455 1 | −0.2 ± 1.4 | 0.364 3 | −0.6 ± 1.5 | 0.017 4 | 0.226 1 |
| Fat mass (kg) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 27.4 ± 4.0 | 28.2 ± 7.0 | 0.744 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 27.7 ± 4.0 | 27.0 ± 4.3 | 0.458 2 | 0.3 ±1.4 | 0.154 3 | −1.2 ± 4.8 | 0.072 4 | 0.025 1 |
| Lean mass (kg) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 40.5 ± 7.0 | 39.8 ± 8.2 | 0.260 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 41.1 ± 7.0 | 39.8 ± 7.5 | 0.139 1 | 0.6 ± 1.4 | 0.154 3 | −0.1 ± 4.0 | 0.011 4 | 0.762 1 |
| Adiponectin (ug/mL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 3.95 ± 2.0 | 4.36 ± 2.1 | 0.314 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 4.23 ± 1.8 | 4.79 ± 2.3 | 0.456 1 | 0.28 ± 0.7 | 0.003 4 | 0.43 ± 1.48 | 0.007 4 | 0.762 1 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 199.4 ± 28.9 | 203.0 ± 33.6 | 0.592 2 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 200.6 ± 32.7 | 205.8 ± 32.6 | 0.448 2 | 1.2 ± 24.5 | 0.753 3 | 2.8 ± 17.9 | 0.292 3 | 0.288 1 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 128.3 ± 114.3 | 124.2 ± 88.4 | 0.741 1 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 138.0 ± 85.9 | 136.8 ± 102.1 | 0.710 1 | 9.7 ± 95.0 | 0.009 4 | 12.6 ± 51.2 | 0.095 4 | 0.301 1 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 55.0 ± 10.5 | 57.7 ± 13.7 | 0.290 2 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 54.6 ± 11.2 | 55.6 ± 12.8 | 0.490 1 | −0.4 ± 8.9 | 0.141 4 | −2.1 ± 5.9 | 0.020 3 | 0.665 1 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 118.8 ± 28.1 | 120.9 ± 26.9 | 0.711 2 | |||||
| At 12 weeks | 119.1 ± 26.8 | 122.8 ± 27.5 | 0.529 2 | 0.4 ± 23.8 | 0.739 3 | 1.8 ± 17.1 | 0.474 3 | 0.355 1 |
| Variable | Control (n = 45) | Collagen (n = 45) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | Week 12 | p | Week 0 | Week 12 | p | |
| AST (IU/L) | 24.51 ± 7.9 | 20.93 ± 5.8 | 0.003 | 23.84 ± 10.0 | 24.87 ± 11.8 | 0.066 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 22.31 ± 13.3 | 20.76 ± 9.5 | 0.876 | 24.02 ± 19.7 | 25.44 ± 20.1 | 0.932 |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 0.69 ± 0.14 | 0.66 ± 0.1 | 0.016 | 0.71 ± 0.1 | 0.69 ± 0.1 | 0.812 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 91.67 ± 11.8 | 88.6 ± 9.7 | 0.033 | 90.07 ± 10.5 | 89.58 ± 12.6 | 0.244 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tak, Y.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.G.; Yi, Y.-H.; Cho, Y.H.; Kang, G.H.; Lee, S.Y. Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030157
Tak YJ, Kim YJ, Lee JG, Yi Y-H, Cho YH, Kang GH, Lee SY. Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(3):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030157
Chicago/Turabian StyleTak, Young Jin, Yun Jin Kim, Jeong Gyu Lee, Yu-Hyun Yi, Young Hye Cho, Geun Hee Kang, and Sang Yeoup Lee. 2019. "Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Marine Drugs 17, no. 3: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030157
APA StyleTak, Y. J., Kim, Y. J., Lee, J. G., Yi, Y.-H., Cho, Y. H., Kang, G. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2019). Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Marine Drugs, 17(3), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17030157







