Bioactive Nitrogenous Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Haliclona
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bioactive Alkaloids from Haliclona Genus
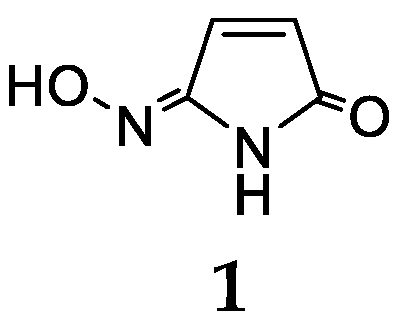
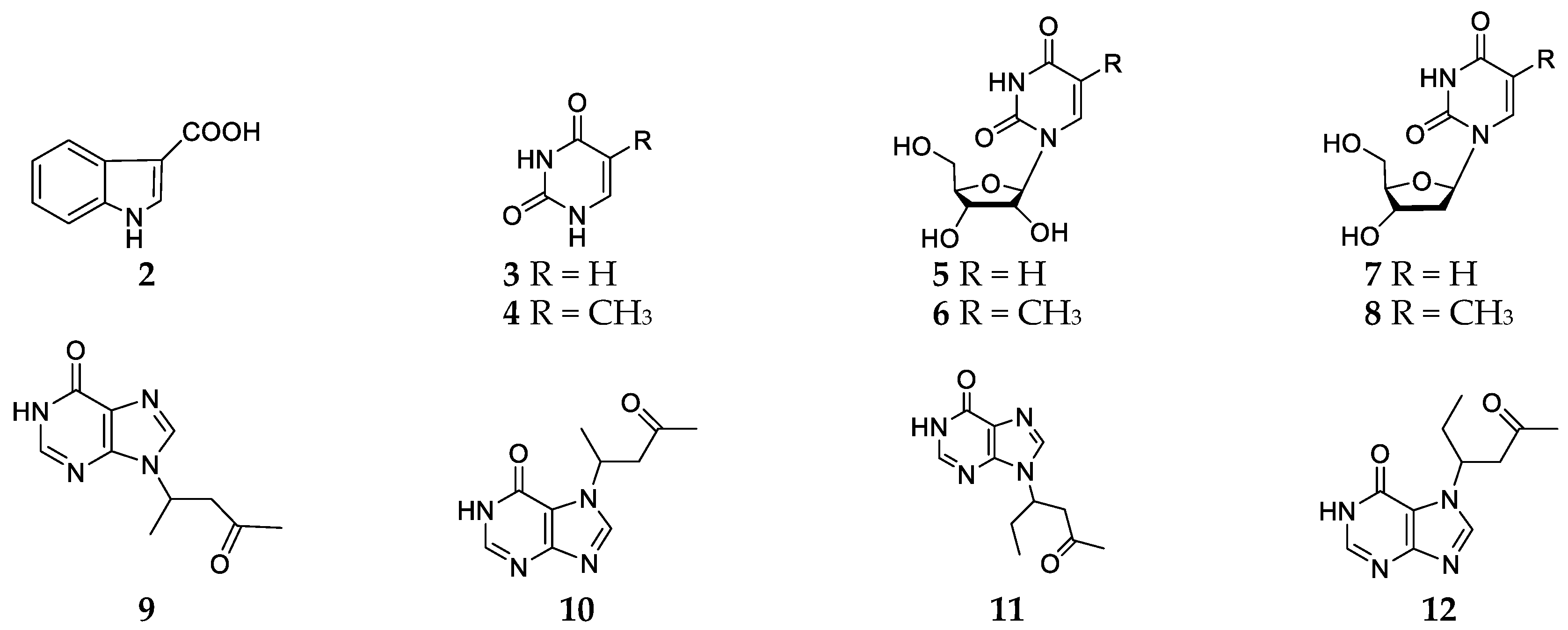
2.1. Haliclona Baeri
2.2. Haliclona Cymaeformis
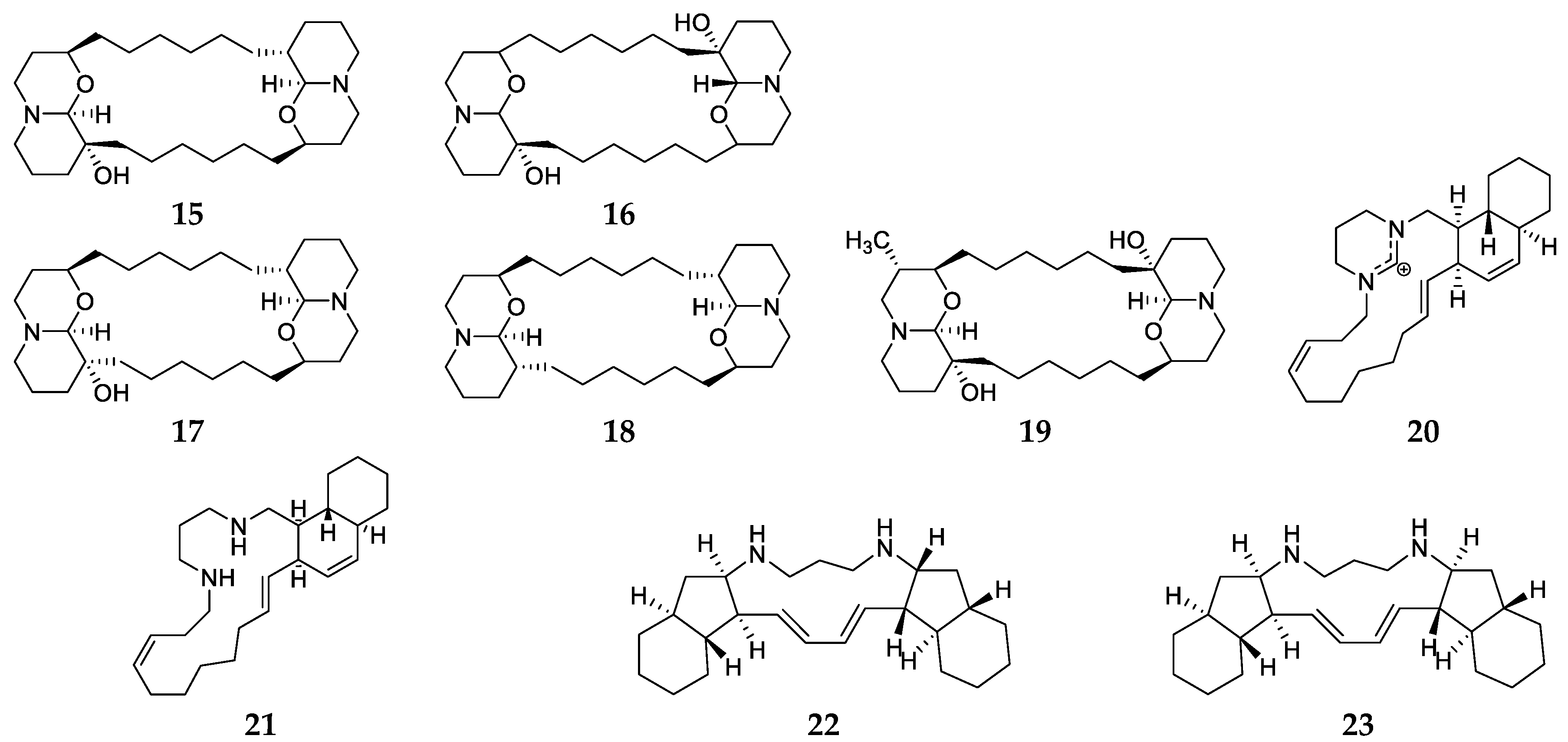
2.3. Haliclona Densaspicula
2.4. Haliclona Exigua
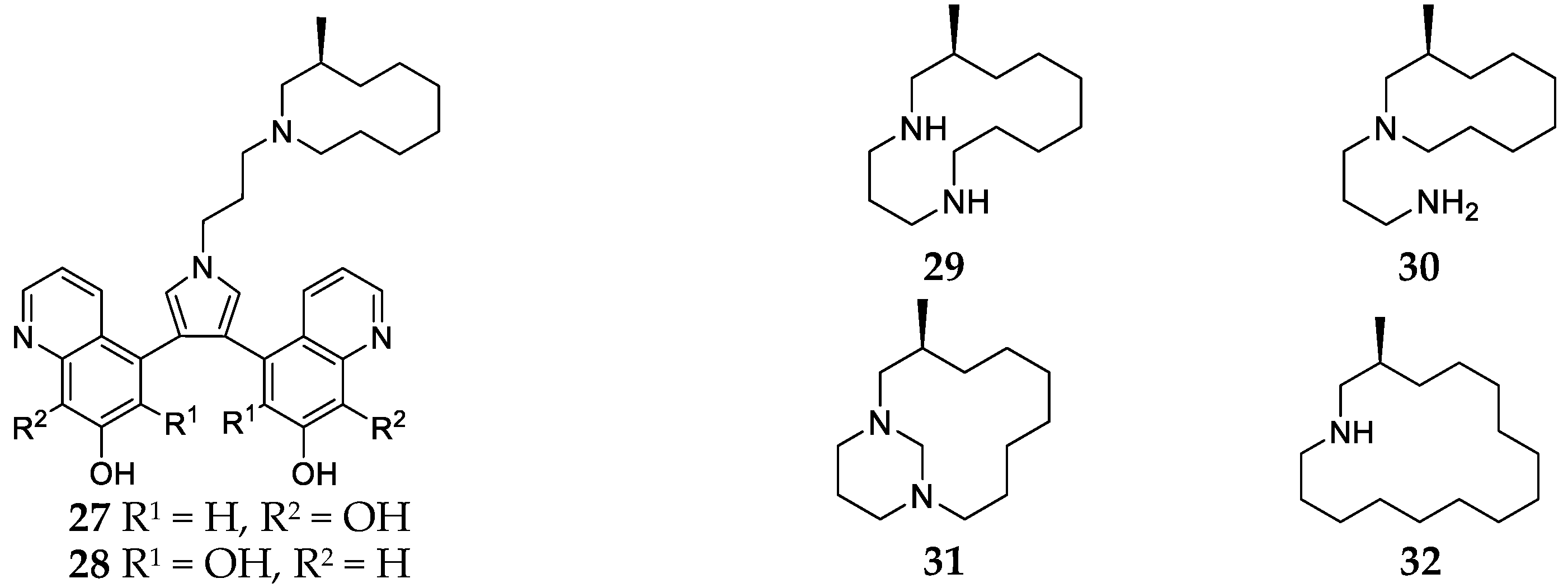
2.5. Haliclona Nigra
2.6. Haliclona Tulearensis
2.7. Other Haliclona Spps.
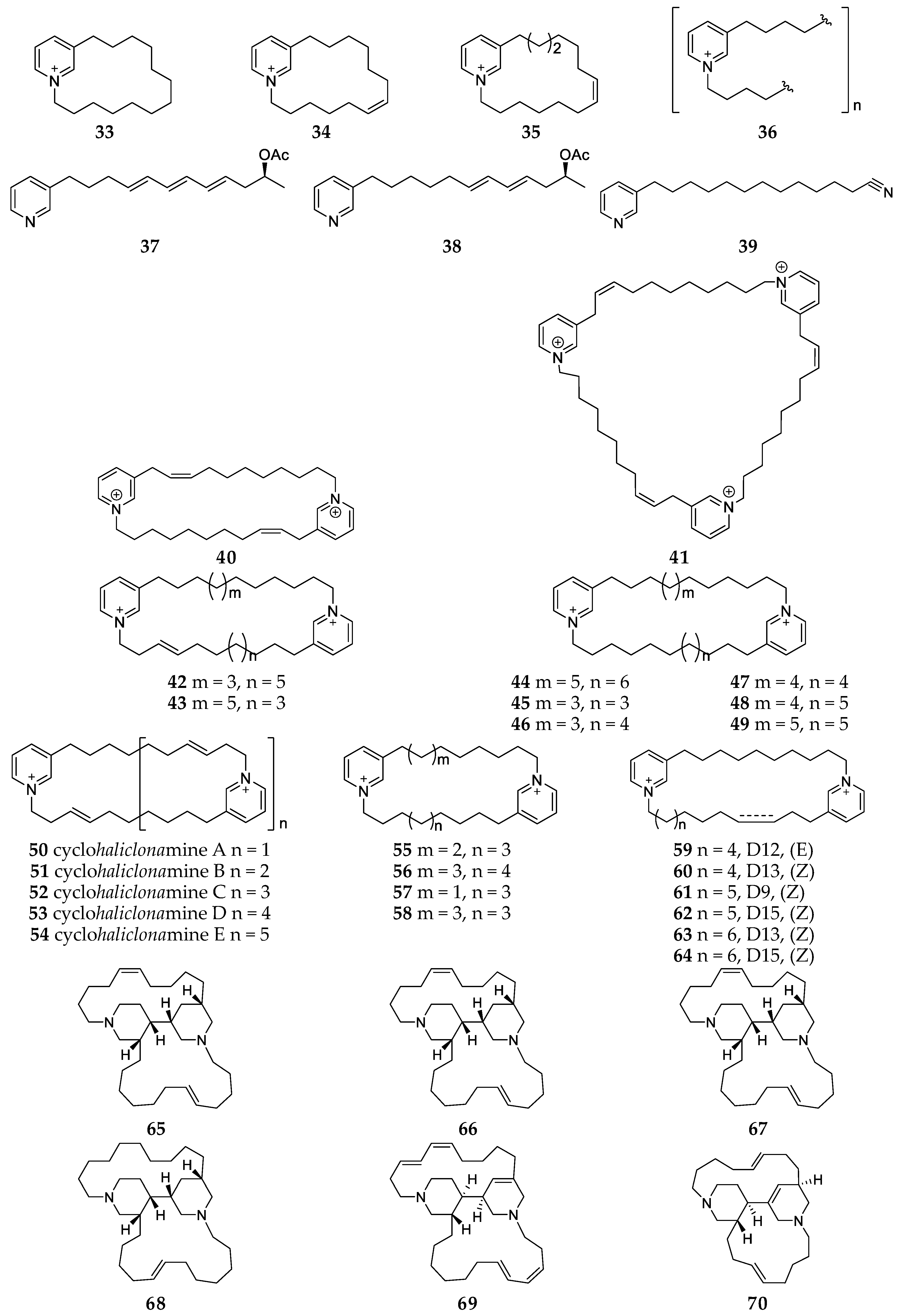
2.7.1. 3-Alkylpyridines
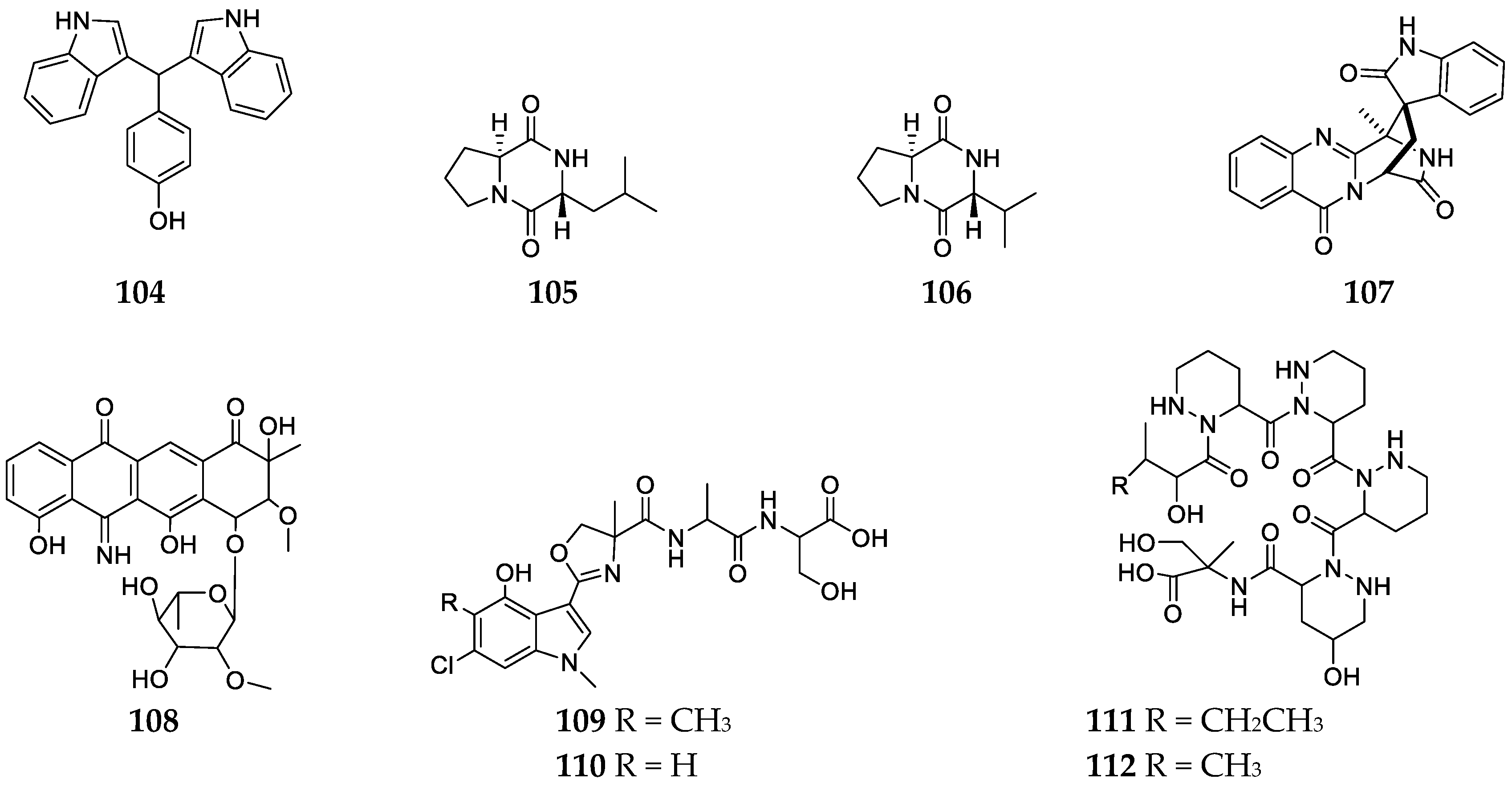
2.7.2. Amides and Depsipeptides
2.7.3. Miscellaneous Alkaloids
3. Bioactive Alkaloids from Haliclona-Derived Microbes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MarinLit-A Database of the Marine Natural Products Literature. Available online: http://pubs.rsc.org/marinlit/ (accessed on 3 November 2019).
- Tian, X.; He, S.; Ding, L. New research progress on chemical constituents and their bioactivities from marine sponges of genus Haliclona. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2018, 30, 1274–1279. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS-World Register of Marine Species. Available online: http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=131834 (accessed on 20 November 2019).
- Hwang, B.S.; Oh, J.S.; Jeong, E.J.; Sim, C.J.; Rho, J.R. Densanins A and B, new macrocyclic pyrrole alkaloids isolated from the marine sponge Haliclona densaspicula. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 6154–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkateswara Rao, J.; Desaiah, D.; Vig, P.J.S.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Marine biomolecules inhibit rat brain nitric oxide synthase activity. Toxicology 1998, 129, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.F.; de Melo, A.A.; de Almeida, A.S.; Moura, R.D.; Chaves, R.P.; de Sousa, B.L.; Nagano, C.S. H-3, a new lectin from the marine sponge Haliclona caerulea: Purification and mass spectrometric characterization. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2864–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, G.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Villani, G.; Manzo, E.; Zanfardino, A.; Varcamonti, M.; Gavagnin, M. Fulvynes, antimicrobial polyoxygenated acetylenes from the Mediterranean sponge Haliclona fulva. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanadilok, R.; Sawangwong, P.; Rodrigues, C.; Cidade, H.; Pinto, M.; Pinto, E.; Kijjoa, A. Antifungal activity evaluation of the constituents of Haliclona baeri and Haliclona cymaeformis, collected from the gulf of Thailand. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Massarani, S.M.; El-Gamal, A.A.; Al-Said, M.S.; Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Ashour, A.E.; Kumar, A.; Fun, H.K. Studies on the red sea sponge Haliclona sp. for its chemical and cytotoxic properties. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2012, 12, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Mei, W.; Shao, C.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Dai, H. Studies on the chemical constituents of sponge Haliclona cymaeformis from the South China Sea. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2011, 30, 12–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Shen, N.; Wang, C. Four new 6-oxy purine alkaloids from the South China Sea sponge, Haliclona cymaeformis. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 16, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.R.; Jung, E.J.; Hwang, B.S. Hexacyclic Diamine Alkaloid Derivatives for Treating and Preventing Neurodegenerative Disease; Semantic Scholar: Seattle, WA, USA, 2014. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswarlu, Y.; Reddy, M.V.R.; Rao, J.V. Bis-1-oxaquinolizidines from the sponge Haliclona exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Sulzmaier, F.J.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly, M.; Ramos, J.W.; Williams, P.G. Neopetrocyclamines A and B, polycyclic diamine alkaloids from the sponge Neopetrosia cf exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, V.; Srivastava, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Misra, S.; Verma, M.; Misra-Bhattacharya, S. In vitro and in vivo antifilarial potential of marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick), against human lymphatic filarial parasite Brugia malayi: Antifilarial activity of H. exigua. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, A.; Singh, N.; Saxena, A.; Lakshmi, V. Antileishmanial potential of a marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick) against experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limna Mol, V.P.; Raveendran, T.V.; Parameswaran, P.S. Antifouling activity exhibited by secondary metabolites of the marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Ardianti, R.; Ahmadi, P.; Setiawan, A.; Mohamad, K.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J. Ichthyotoxic principles against zebrafish embryos from the Indonesian marine sponge Neopetrosia chaliniformis. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yagia, A.; Yamazakia, H.; Kirikoshia, R.; Takahashia, O.; Namikoshib, M.; Uchida, R. Anti-mycobacterial haliclonadiamine alkaloids from the Okinawan marine sponge Haliclona sp. collected at Iriomote Island. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 26, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kanno, S.-I.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Haliclonadiamine derivatives and 6-epi-monanchorin from the marine sponge Halichondria panicea collected at Iriomote Island. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Boswell, J.L.; Boyd, M.R. Haligramides A and B, two new cytotoxic hexapeptides from the marine sponge Haliclona nigra. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorek, H.; Rudi, A.; Aknin, M.; Gaydou, E.M.; Kashman, Y. Isohalitulin and haliclorensins B and C, three marine alkaloids from Haliclona tulearensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren-Goldshlager, G.; Kashman, Y.; Schleyer, M. Haliclorensin, a novel diamino alkaloid from the marine sponge Haliclona tulearensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Koren-Goldshlager, G.; Gravalos, M.D.G.; Schleyer, M. Halitulin, A new-cytotoxic alkaloid from the marine sponge Haliclona tulearensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Suenaga, K.; Kigoshi, H. Cyclohaliclonamines A-E: Dimeric, trimeric, tetrameric, pentameric, and hexameric 3-alkyl Pyridinium alkaloids from a marine sponge Haliclona sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, V.; Ryan, J.L.; Keyzers, R.A. Cyclic 3-alkyl pyridinium alkaloid monomers from a ew Zealand Haliclona sp. marine sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blihoghe, D.; Manzo, E.; Villela, A.; Cutignano, A.; Picariello, G.; Faimali, M.; Fontana, A. Evaluation of the antifouling properties of 3-alyklpyridine compounds. Biofouling 2011, 27, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casapullo, A.; Pinto, O.C.; Marzocco, S.; Autore, G.; Riccio, R. 3-Alkylpyridinium alkaloids from the Pacific sponge Haliclona sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarisit, W.; Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kirikoshi, R.; Takahashi, O.; Namikoshi, M.; Uchida, R. Anti-mycobacterial alkaloids, cyclic 3-alkyl pyridinium dimers, from the Indonesian marine sponge Haliclona sp. Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3503–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, T.; Sepcic, K.; Mancini, I.; Guella, G. 3-akylpyridinium and 3-alkylpyridine compounds from marine sponges, their synthesis, biological activities and potential use. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2008, 35, 355–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Jang, K.H.; Jeon, J.-E.; Yang, W.-Y.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Cyclic bis-1,3-dialkylpyridiniums from the sponge Haliclona sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; Garson, M.J.; Brereton, I.M.; Willis, A.C.; Hooper, J.N.A. Haliclonacyclamines A and B, cytotoxic alkaloids from the tropical marine sponge Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 9111–9120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.J.; Field, K.L.; Charan, R.D.; Garson, M.G.; Brereton, I.M.; Willis, A.C. The Haliclonacyclamines, cytotoxic tertiary alkaloids from the tropical marine sponge Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 8811–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Liu, L.; Fujimoto, T.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. DedA protein relates to action-mechanism of Halicyclamine A, a marine spongean macrocyclic alkaloid, as an anti-dormant mycobacterial substance. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Takeishi, Y.; Nehira, T.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Tsukamoto, S. Tetradehydrohalicyclamine B, a new proteasome inhibitor from the marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Lee, K.J.; Zhang, S.; Jung, J.H.; Liu, Y. 2-Palmitamidoethanesulfonic acid, a taurine derivative from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2009, 45, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Gao, C.; Huang, R. Two new phthalate derivatives from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2018, 54, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.H.; Kang, G.W.; Jeon, J.-E.; Lim, C.; Lee, H.-S.; Sim, C.J.; Shin, J. Haliclonin A, a new macrocyclic diamide from the sponge Haliclona sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.L.; Beutler, J.A.; Cardellina, J.H., II; Boyd, M.R. Salicylihalamides A and B, novel cytotoxic macrolides from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 8188–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, A.; Debitus, C.; Gomez-Paloma, L. Haliclamide, a novel cyclic metabolite from the Vanuatu marine sponge Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 4443–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, A.; Bifulco, G.; Giannini, C.; Bucci, M.; Debitus, C.; Cirino, G.; Gomez-Paloma, L. Halipeptins A and B: Two novel potent anti-inflammatory cyclic depsipeptides from the Vanuatu marine sponge Haliclona species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 10870–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Lizos, D.E.; Kim, D.W.; Schlawe, D.; de Noronha, R.G.; Longbottom, D.A.; Cirino, G. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of Halipeptins A and D and analogues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 138, 4460–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Cao, L.; Matsui, K.; Rachmat, R.; Akiyama, S.-I.; Kobayashi, M. Kendarimide A, a novel peptide reversing P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in tumor cells, from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7053–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sera, Y.; Adachi, K.; Fujii, K.; Shizuri, Y. A new antifouling hexapeptide from a Palauan sponge, Haliclona sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.L.; Sera, Y.; Adachi, K.; Nishida, F.; Shizuri, Y. Isolation and evaluation of nonsiderophore cyclic peptides from marine sponges. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sera, Y.; Adachi, K.; Fujii, K.; Shizuri, Y. Isolation of haliclonamides: New peptides as antifouling substances from a marine sponge species, Haliclona. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 3, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urda, C.; Péreza, M.; Rodríguez, J.; Fernández, R.; Jiménez, C.; Cuevas, C. Njaoamine I, a cytotoxic polycyclic alkaloid from the Haplosclerida sponge Haliclona (Reniera) sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 2577–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Boyd, M.R. A New isoquinoline alkaloid from the marine sponge Haliclona species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1249–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plubrukarn, A.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Thammasaroj, T.; Jitsue, A. Cytotoxic isoquinoline quinones from the Thai sponge Cribrochalina. Pharm. Biol. 2003, 41, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Chen, Y.; Aoki, S.; In, Y.; Ishida, T.; Kitagawa, I. Four new β-carboline alkaloids isolated from two Okinawan marine sponges of Xestospongia sp. and Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Higa, T.; Jefford, C.W.; Bernardinelli, G. Manzamine A, a novel antitumor alkaloid from a sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6404–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.J.; Garson, M.J.; Hooper, J.N.A. Antifungal alkyl amino alcohols from the tropical marine sponge Haliclona n. sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1568–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yao, L.; Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Xin, G.; Guo, Y. New polyunsaturated amino ketones from a Guangxi sponge Haliclona sp. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cao, L.; Su, J. Study on the chemical constituents of Hainan island sponge Haliclona sp. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 1998, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H. Cytotoxic natural products from marine sponge-derived microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuong, P.V.; Cuc, N.T.K.; Quyen, V.T.; Binh, P.T.; Kiem, P.V.; Nam, N.H.; Nguyen, T.D. Antimicrobial constituents from the bacillus megaterium lc isolated from marine sponge Haliclona oculata. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2014, 20, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Oclarit, J.M.; Ohta, S.; Kamimura, K.; Yamaoka, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Ikegami, S. A novel antimicrobial substance from a strain of the bacterium, Vibrio sp. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1994, 4, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ting, G.; Ping, Z. The bioactive metabolites of Aspergillus versicolor F62 isolated from Haliclona simulans. Mycosystema 2011, 30, 636–643. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.T.; Komaki, H.; Motohashi, K.; Kozone, I.; Mukai, A.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. Streptomyces associated with a marine sponge Haliclona sp.; biosynthetic genes for secondary metabolites and productsemi. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Bioactive Nitrogenous Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Haliclona. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120682
Zhu J, Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang H, Zhang H. Bioactive Nitrogenous Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Haliclona. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(12):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120682
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiaying, Yang Liu, Zijun Liu, Hao Wang, and Huawei Zhang. 2019. "Bioactive Nitrogenous Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Haliclona" Marine Drugs 17, no. 12: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120682
APA StyleZhu, J., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, H., & Zhang, H. (2019). Bioactive Nitrogenous Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Haliclona. Marine Drugs, 17(12), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120682






