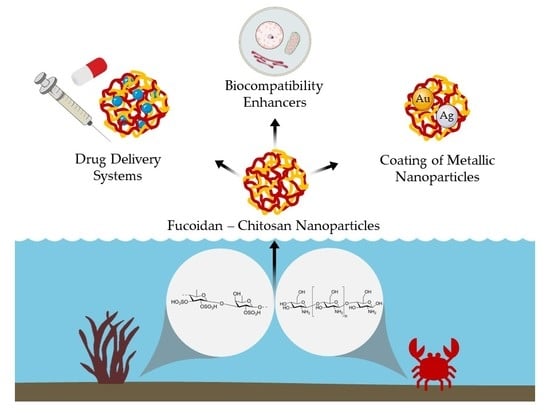
Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biomaterials as Drug Delivery Systems
3. Marine Polysaccharides as Drug Delivery Systems
- I
- Undergo chemical and enzymatic reactions to produce different materials [24];
- II
- Are biocompatible, biodegradable, and have low immunogenic properties [22];
- III
- Can be produced, conjugated, and complexed with proteins or other bioactive molecules [25];
- IV
- V
- Can be modified as gels or give rise to interpenetrated polymeric networks [28].
3.1. Marine Algae
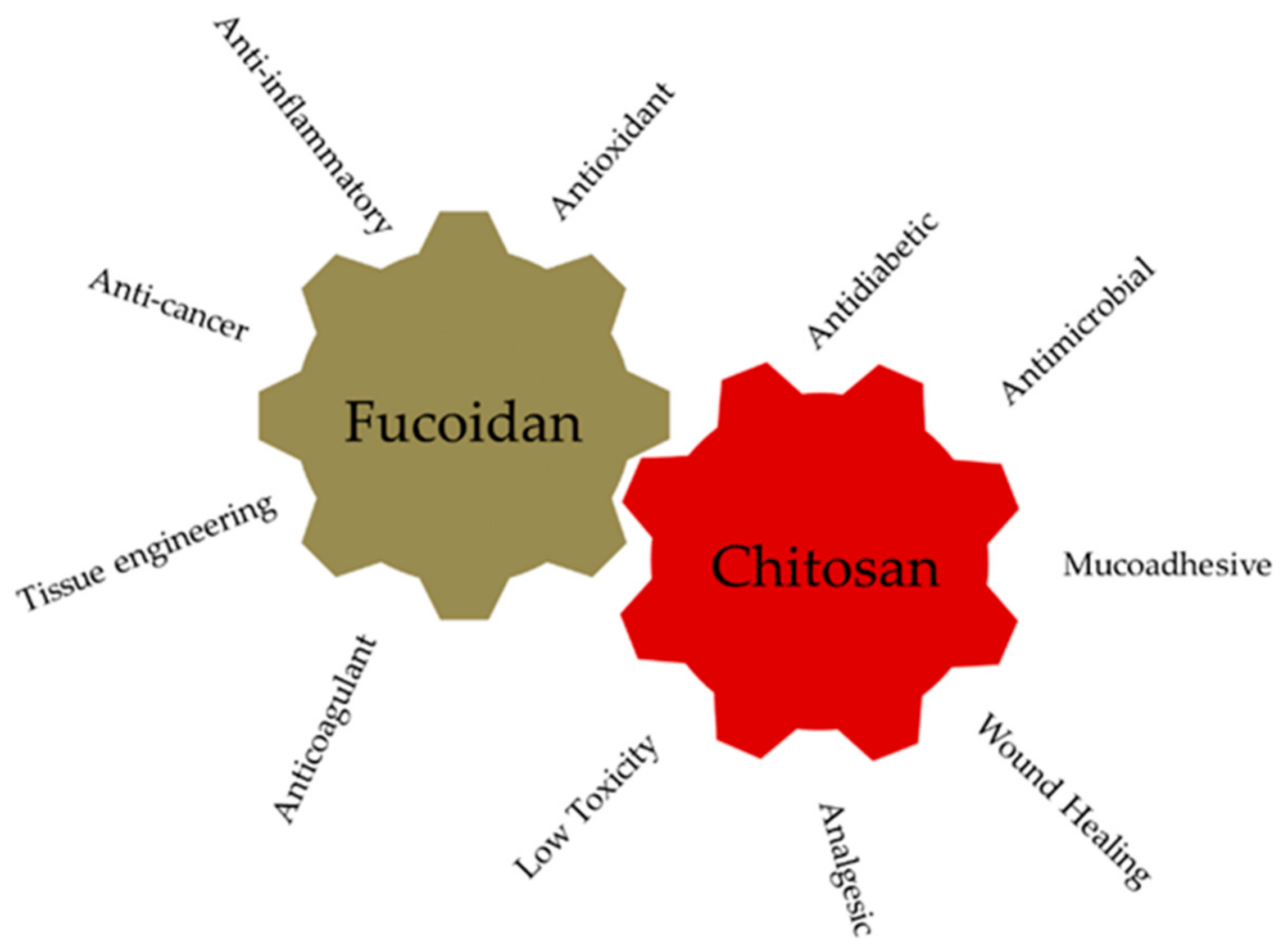
3.1.1. Fucoidan: Sources, Chemical Structure, Biological Properties
3.1.2. Fucoidan-Based Nanoparticles and Their Applications
3.2. Marine Crustaceans
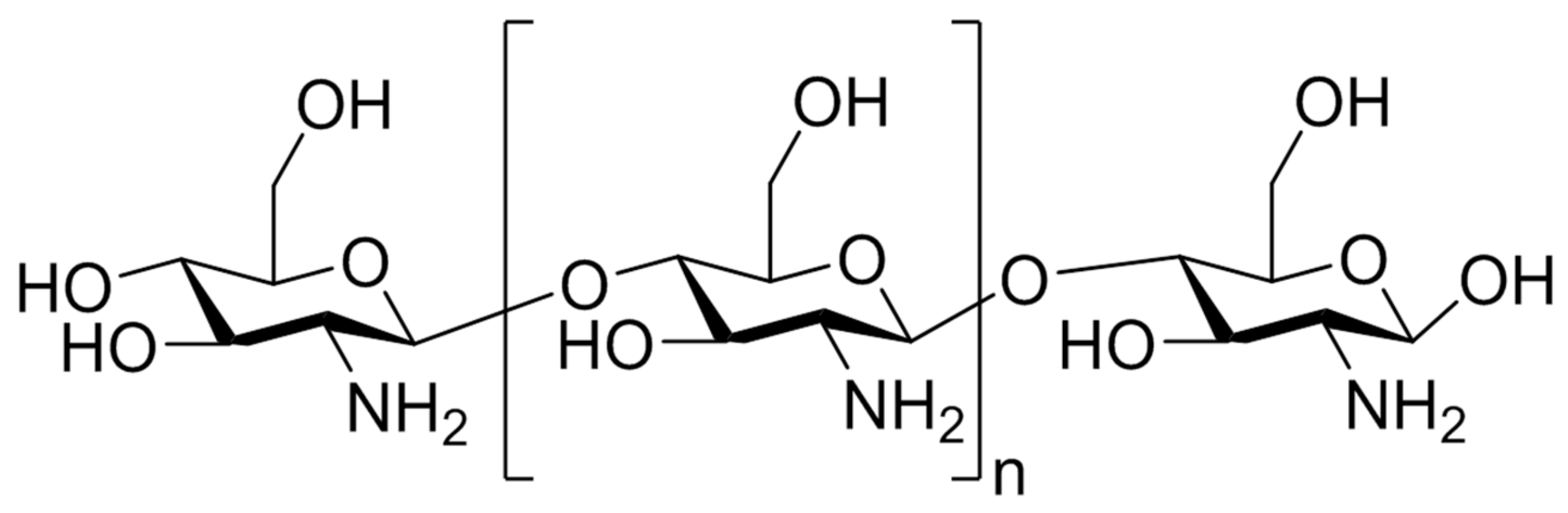
3.2.1. Chitosan: Sources, Chemical Structure, Biological Properties
3.2.2. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles and Their Applications
4. Fucoidan–Chitosan Nanoparticles
4.1. Preparation Methods of Fucoidan–Chitosan Nanoparticles
4.2. Nanomedicine Applications of Fucoidan–Chitosan Nanoparticles
4.2.1. Polyphenolic Compounds Delivery
4.2.2. Antibacterial Agents Delivery
4.2.3. Tissue Engineering Applications
4.2.4. Anticancer Compounds Delivery
4.2.5. Coating of Metallic Nanoparticles
4.2.6. Other Applications
4.3. Biomedical Applications of Fucoidan and Chitosan
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Appeltans, W.; Ahyong, S.T.; Anderson, G.; Angel, M.V.; Artois, T.; Bailly, N.; Bamber, R.; Barber, A.; Bartsch, I.; Berta, A. The magnitude of global marine species diversity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Advanced tools in marine natural drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 42, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.X.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Marine natural products as sources of novel scaffolds: Achievement and concern. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Vieira, H.; Gaspar, H.; Santos, S. Marketed marine natural products in the pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries: Tips for success. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1066–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Costa, R.R.; Mano, J.F. Marine Origin Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Daniel, R. Achievements and new knowledge unraveled by metagenomic approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.-Q.; Wang, J.-F.; Hao, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y. Recent Advances in the Discovery and Development of Marine Microbial Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashforth, E.J.; Fu, C.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Song, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. Bioprospecting for antituberculosis leads from microbial metabolites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpicco, S.; Battaglia, L.; Brusa, P.; Cavalli, R.; Chirio, D.; Dosio, F.; Gallarate, M.; Milla, P.; Peira, E.; Rocco, F.; et al. Recent studies on the delivery of hydrophilic drugs in nanoparticulate systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.M.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Nano-and microdelivery systems for marine bioactive lipids. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6014–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.K. Drug delivery systems—An overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 437, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freeman, A.I.; Mayhew, E. Targeted drug delivery. Cancer 1986, 58 (Suppl. 2), 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Seog, J.H.; Graham, L.M.; Lee, S.B. Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus Raposo, M.F.; De Morais, A.M.B.; De Morais, R.M.S.C. Marine polysaccharides from algae with potential biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2967–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raemdonck, K.; Martens, T.F.; Braeckmans, K.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.C. Polysaccharide-based nucleic acid nanoformulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1123–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, R.E. Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility, 2nd ed.; Dumitriu, S., Dekker, M., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, N.; Varshochian, R.; Kamalinia, G.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. A review of polysaccharide cytotoxic drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahy, S.; Peer, D. Polysaccharides as building blocks for nanotherapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2623–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Polysaccharides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaraju, S.L. Colon targeted delivery systems: Review of polysaccharides for encapsulation and delivery. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Puga, A.M.; Concheiro, A. Crosslinked ionic polysaccharides for stimuli-sensitive drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1148–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, M.D.; Merzouki, A.; Lavertu, M.; Thibault, M.; Jean, M.; Darras, V. Chitosans for delivery of nucleic acids. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1234–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Hou, D.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Sun, S.; Ping, Q.; Xu, Y. Effects and molecular mechanism of chitosan-coated levodopa nanoliposomes on behavior of dyskinesia rats. Biol. Res. 2016, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, K.; Chaturvedi, K.; More, U.A.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Polysaccharide-based micro/nanohydrogels for delivering macromolecular therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Teng, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Hou, L.; Zou, X. Fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berteau, O.; Mulloy, B. Sulfated fucans, fresh perspectives: Structures, functions, and biological properties of sulfated fucans and an overview of enzymes active toward this class of polysaccharide. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 29R–40R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastyuk, S.D.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Structural analysis of a fucoidan from the brown alga Fucus evanescens by MALDI-TOF and tandem ESI mass spectrometry. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Lam, U.I. Chitosan/Fucoidan pH Sensitive Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery System. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2011, 58, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, E.M.; Conde, E.; Moure, A.; Falque, E.; Dominguez, H. In vitro antioxidant properties of crude extracts and compounds from brown algae. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1764–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Yokoyama, G.; Dobashi, K.; Fujihara, M.; Nagumo, T. Isolation, purification, and characterization of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome and their blood-anticoagulant activities. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 186, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Besednova, N.N.; Mamaev, A.N.; Momot, A.P.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Anticoagulant activity of fucoidan from brown algae Fucus evanescens of the Okhotsk Sea. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 136, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.D.; Yao, C.J.; Chow, J.M.; Chang, C.L.; Hwang, P.A.; Chuang, S.E.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lai, G.M. Fucoidan Elevates MicroRNA-29b to Regulate DNMT3B-MTSS1 Axis and Inhibit EMT in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6099–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Shukla, S.K.; Bhanu, S.; Kankane, S. Responsive polymers in controlled drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1088–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, P.; Pillay, V.; Choonara, Y.E.; Du Toit, L.C. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications in drug delivery. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha de Souza, M.C.; Marques, C.T.; Guerra Dore, C.M.; Ferreira da Silva, F.R.; Oliveira Rocha, H.A.; Leite, E.L. Antioxidant activities of sulfated polysaccharides from brown and red seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.A.P.; Dewar, E.T.; Woodward, F.N. Manufacture of algal chemicals. IV—Laboratory-scale isolation of fucoidin from brown marine algae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1952, 3, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitoshi, K.; Miki, Y.; Kimura, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Kawamukai, M.; Matsuda, H. Effects of Fucoidan from Mozuku on Human stomach cell lines. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2006, 12, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma, K.; Ishihara, T.; Nakamoto, H.; Amaha, T.; Osaki, T.; Tsuka, T.; Imagawa, T.; Minami, S.; Takashima, O.; Ifuku, S.; et al. Effects of oral administration of fucoidan extracted from Cladosiphon okamuranus on tumor growth and survival time in a tumor-bearing mouse model. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeguchi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Arai, Y.; Maeta, Y.; Ashida, K.; Katano, K.; Miki, Y.; Kimura, T. Fucoidan reduces the toxicities of chemotherapy for patients with unresectable advanced or recurrent colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Tomimori, K.; Kimura, R.; Ishikawa, C.; Nowling, T.K.; Mori, N. Anti-tumor activity of fucoidan is mediated by nitric oxide released from macrophages. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomori, M.; Nagamine, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Iha, M. Evaluation of the immunomodulatory effects of fucoidan derived from cladosiphon okamuranus tokida in mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermakova, S.; Sokolova, R.; Kim, S.M.; Um, B.H.; Isakov, V.; Zvyagintseva, T. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds Sargassum hornery, Eclonia cava, Costaria costata: Structural characteristics and anticancer activity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.K.; Lee, M.; Kwon, H.O.; Lee, D.; Park, J.; Kim, E.; You, Y.; Lim, Y.T.; Jun, W.; Lee, J. Costaria costata extract suppresses development of atopic dermatitis in chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene-treated NC/Nga Mice. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, C.I.; Jee, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, S.; Men’shova, R.; Vishchuk, O.; Kim, S.M.; Um, B.H.; Isakov, V.; Zvyagintseva, T. Water-soluble polysaccharides from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis: Structural characteristics and antitumor activity. Algal Res. 2013, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.J.; Chung, H.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of fucoidan with blocking NF-κB and STAT1 in human keratinocytes cells. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2015, 21, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Vishchuk, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. The fucoidans from brown algae of Far-Eastern seas: Anti-tumor activity and structure–function relationship. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philchenkov, A.; Zavelevich, M.; Imbs, T.; Zvyagintseva, T.; Zaporozhets, T. Sensitization of human malignant lymphoid cells to etoposide by fucoidan, a brown seaweed polysaccharide. Exp. Oncol. 2007, 29, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alekseyenko, T.V.; Zhanayeva, S.Y.; Venediktova, A.A.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Besednova, N.N.; Korolenko, T.A. Antitumor and antimetastatic activity of fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the Okhotsk sea Fucus evanescens brown alga. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 143, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Ivanushko, L.A.; Persiyanova, E.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Besednova, N.N. Markers of Systemic Inflammation in Experimental Dyslipidemia Induced by P-407: Modulation with Fucoidan from Brown Alga Fucus evanescens. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 166, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Xu, W.; Liang, J.-W.; Wang, C.-S.; Kang, Y. Effect Of Fucoidan On B16 Murine Melanoma Cell Melanin Formation And Apoptosis. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 14, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Pan, H.F.; Shao, S.L.; Xu, X.M. Anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects of Fucoidan on prostate cancer: Possible JAK-STAT3 pathway. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, Y.; Miyakawa, Y.; Nakazato, T.; Shibata, H.; Saito, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kizaki, M. Fucoidan induces apoptosis of human HS-Sultan cells accompanied by activation of caspase-3 and down-regulation of ERK pathways. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 78, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; González-Muñoz, M.J.; Domínguez, H. Potential of intensification techniques for the extraction and depolymerization of fucoidan. Algal Res. 2018, 30, 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.-H.; Kim, S.-C.; Kang, J.-I.; Kim, M.-K.; Boo, H.-J.; Kwon, J.-M.; Koh, Y.-S.; Hyun, J.-W.; Park, D.-B.; Yoo, E.-S.; et al. Apoptosis Inducing Activity of Fucoidan in HCT-15 Colon Carcinoma Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Kwon, M.J.; Nam, T.J. Differences in cell death and cell cycle following fucoidan treatment in high-density HT-29 colon cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4116–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Yoon, D.; Han, M.H.; Lee, D.S.; Choi, G.; Yim, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest by fucoidan in HCT116 human colorectal carcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, Q. Anticancer properties and mechanisms of fucoidan on mouse breast cancer in vitro and in Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-H.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Chan, Y.-L.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Wang, H.; Huang, K.-C.; Li, T.-L.; Hsu, K.-H.; Wu, C.-J. Prophylactic Administration of Fucoidan Represses Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Lewis Tumor-Bearing Mice. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.O.; Zhang, W.; Du, J.Y.; Wong, K.W.; Oda, T.; Yu, Q. Fucoidan can function as an adjuvant in vivo to enhance dendritic cell maturation and function and promote antigen-specific T cell immune responses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Tsao, S.M.; Hwang, P.A.; Shih, Y.W.; Hsu, J. Fucoidan inhibition of lung cancer in vivo and in vitro: Role of the Smurf2-dependent ubiquitin proteasome pathway in TGFβ receptor degradation. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7870–7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.P.; O’Connor, J.; Fitton, J.H.; Brooks, L.; Rolfe, M.; Connellan, P.; Wohlmuth, H.; Cheras, P.A.; Morris, C. A combined Phase I and II open-label study on the Immunomodulatory effects of seaweed extract nutrient complex. Biol. Targets Ther. 2011, 5, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.P.; O’Connor, J.; Fitton, J.H.; Brooks, L.; Rolfe, M.; Connellan, P.; Wohlmuth, H.; Cheras, P.A.; Morris, C. A combined phase I and II open label study on the effects of a seaweed extract nutrient complex on osteoarthritis. Biol. Targets Ther. 2010, 4, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.; Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A. Fucoidan from Sargassum sp and Fucus vesiculosus reduces cell viability of lung carcinoma and melanoma cells in vitro and activates natural killer cells in mice in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phycochemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Fucus spp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, J.; Xu, X. Bioactivity of fucoidan extracted from Laminaria japonica using a novel procedure with high yield. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Oda, T.; Yu, Q.; Jin, J.O. Fucoidan from Macrocystis pyrifera has powerful immune-modulatory effects compared to three other fucoidans. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Ahn, G.; Kim, J.; Jeon, Y.J. Fucoidan isolated from invasive Sargassum horneri inhibit LPS-induced inflammation via blocking NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Algal Res. 2019, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishchuk, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds Saccharina japonica and Undaria pinnatifida: Isolation, structural characteristics, and antitumor activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ge, K.; Tian, Q.; Zhao, P.; Guo, Y. Anti-inflammatory effect of low molecular weight fucoidan from Saccharina japonica on atherosclerosis in apoE-knockout mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marudhupandi, T.; Ajith Kumar, T.T.; Lakshmana Senthil, S.; Nanthini Devi, K. In vitro antioxidant properties of fucoidan fractions from Sargassum tenerrimum. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 17, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Joseph, D.; Raola, V.K. Anti-Inflammatory Concentrate Enriched with Substituted Oligofucans Derived from Brown Seaweed Turbinaria conoides (J. Agardh) Kützing and Its Safety Assessment on Wistar Rats. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synytsya, A.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, S.-M.; Pohl, R.; Synytsya, A.; Kvasnička, F.; Čopíková, J.; Il Park, Y. Structure and antitumour activity of fucoidan isolated from sporophyll of Korean brown seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H. Topical application of fucoidan improves atopic dermatitis symptoms in NC/Nga mice. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ayala, G.G.; Malinconico, M.; Laurienzo, P. Marine derived polysaccharides for biomedical applications: Chemical modification approaches. Molecules 2008, 13, 2069–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T.; Kitahara, T.; Kawakami, S.; Nishida, K.; Nakamura, J.; Teshima, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Kodama, Y.; To, H.; Sasaki, H. The development of a gene vector electrostatically assembled with a polysaccharide capsule. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4427–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.A.; Grenha, A. Polysaccharide nanoparticles for protein and Peptide delivery: Exploring less-known materials. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2015, 98, 223–261. [Google Scholar]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Bui, N.Q.; Jang, B.; Oh, Y.O.; Lim, I.J.; Oh, J. Doxorubicin-loaded fucoidan capped gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and photoacoustic imaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lira, M.C.B.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S.; Nicolas, V.; Marsaud, V.; Silva, M.P.C.; Ponchel, G.; Vauthier, C. Cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of newly synthesized fucoidan-coated nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, T.C.Y.; Wong, C.K.; Xie, Y. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using biopolymers, carboxymethylated-curdlan and fucoidan. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mano, J.F. Stimuli-responsive polymeric systems for biomedical applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneja, A.; Nehate, C.; Alam, N.; Gupta, P.N. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Nanomedicines for Cancer Chemotherapy; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkaš, V. Fungal cell walls: Their structure, biosynthesis and biotechnological aspects. Acta Biotechnol. 1990, 10, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, P.; Li, Y.M.; Wei, Q.; Tian, L.H. A pH-sensitive chitosan-tripolyphosphate hydrogel beads for controlled glipizide delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 97, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Lv, P.; Wang, L.; Ma, G. Preparation and evaluation of alginate-chitosan microspheres for oral delivery of insulin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prego, C.; Garcia, M.; Torres, D.; Alonso, M.J. Transmucosal macromolecular drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 101, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prego, C.; Fabre, M.; Torres, D.; Alonso, M.J. Efficacy and mechanism of action of chitosan nanocapsules for oral peptide delivery. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranaldi, G.; Marigliano, I.; Vespignani, I.; Perozzi, G.; Sambuy, Y. The effect of chitosan and other polycations on tight junction permeability in the human intestinal Caco-2 cell line(1). J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.H.; Hsu, L.W.; Tseng, M.T.; Lee, P.L.; Sonjae, K.; Ho, Y.C.; Sung, H.W. Mechanism and consequence of chitosan-mediated reversible epithelial tight junction opening. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6164–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaje, K.; Lin, K.J.; Tseng, M.T.; Wey, S.P.; Su, F.Y.; Chuang, E.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, C.T.; Sung, H.W. Effects of chitosan-nanoparticle-mediated tight junction opening on the oral absorption of endotoxins. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8712–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senel, S.; Kremer, M.J.; Kas, S.; Wertz, P.W.; Hincal, A.A.; Squier, C.A. Enhancing effect of chitosan on peptide drug delivery across buccal mucosa. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.M.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Watts, P.; Castile, J.; Jabbal-Gill, I.; Nankervis, R.; Smith, A.; Illum, L. Nasal delivery of insulin using novel chitosan based formulations: A comparative study in two animal models between simple chitosan formulations and chitosan nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan—A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.F.; Xu, Z.R.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Han, X.Y. In vitro effects of chitosan nanoparticles on proliferation of human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 5136–5141. [Google Scholar]
- Ponchel, G.; Irache, J. Specific and non-specific bioadhesive particulate systems for oral delivery to the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 34, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Thiomers: A new generation of mucoadhesive polymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.H. Biochemistry of Antimicrobial Action. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1977, 50, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sudarshan, N.R.; Hoover, D.G.; Knorr, D. Antibacterial action of chitosan. Food Biotechnol. 1992, 6, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuba, J.L.; Stossel, P. Chitosan and Other Polyamines: Antifungal Activity and Interaction with Biological Membranes. In Chitin in Nature and Technology; Muzzarelli, R., Jeuniaux, C., Gooday, G.W., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Park, P.J.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Free radical scavenging activity of chitooligosaccharides by electron spin resonance spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4624–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divya, K.; Jisha, M.S. Chitosan nanoparticles preparation and applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ikram, S. Chitosan Based Scaffolds and Their Applications in Wound Healing. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Khan, S.A.; Lim, K.H. Chitosan-nanoparticle preparation by polyelectrolyte complexation. World J. Eng. 2009, 6, 541–542. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, S.; Geng, D.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, A. Preparation and characterization of fucoidan-chitosan nanospheres by the sonification method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 3844–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chen, J.K.; Lam, U.I.; Chen, S.Y. Preparing, characterizing, and evaluating chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles as oral delivery carriers. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Li, R.Y. Preparation and characterization of antioxidant nanoparticles composed of chitosan and fucoidan for antibiotics delivery. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4379–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Don, T.M.; Lin, C.W.; Mi, F.L. Delivery of berberine using chitosan/fucoidan-taurine conjugate nanoparticles for treatment of defective intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5677–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Lim, K.H. Polyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan self-assembled with fucoidan: An optimum condition to prepare their nanoparticles and their characteristics. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Lim, K.H. Relative charge density model on chitosan-fucoidan electrostatic interaction: Qualitative approach with element analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Lim, K.H. Formation of chitosan-fucoidan nanoparticles and their electrostatic interactions: Quantitative analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbi, S.; Nimal, T.R.; Rajan, V.K.; Baranwal, G.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R.; Sathianarayanan, S. Fucoidan coated ciprofloxacin loaded chitosan nanoparticles for the treatment of intracellular and biofilm infections of Salmonella. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Kuo, T.H. O-carboxymethyl chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles increase cellular curcumin uptake. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Liu, T.J. Mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells by stromal cell-derived factor-1 released from chitosan/tripolyphosphate/fucoidan nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Li, R.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, J.K. Biphasic release of gentamicin from chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles for pulmonary delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 138, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Yang, Y.T. Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor released from chitosan-fucoidan nanoparticles on neurite extension. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasan, S.A.; Pietrasczkiwicz, H.; Alonso, M.D.; Ensley, J.; Sarkar, F.H. Genistein-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 34, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Tang, D.W.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Wu, W.S.; Lin, B.X.; Chuang, E.Y.; Sung, H.W.; Mi, F.L. Nanoparticle-induced tight-junction opening for the transport of an anti-angiogenic sulfated polysaccharide across Caco-2 cell monolayers. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7449–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, S.J.; Mi, F.L. Mutlifunctional nanoparticles prepared from arginine-modified chitosan and thiolated fucoidan for oral delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, L.C.R.P.; Todaro, V.; Do Carmo, F.A.; Frattani, F.S.; De Sousa, V.P.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Sathler, P.C.; Cabral, L.M. A promising oral fucoidan-based antithrombotic nanosystem: Development, activity and safety. Nanotechnology 2018, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Neves, N.M.; Reis, R.L.; Martins, A.; Silva, T.H. Gemcitabine delivered by fucoidan/chitosan nanoparticles presents increased toxicity over human breast cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2037–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Application of pH-responsive fucoidan/chitosan nanoparticles to improve oral quercetin delivery. Molecules 2019, 24, E346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Huang, Y.C. Soluble eggshell membrane protein-loaded chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles for treatment of defective intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, C.; Trapani, G.; Ponchel, G.; Trapani, A.; Vauthier, C. Mucoadhesive properties of low molecular weight chitosan-or glycol chitosan-and corresponding thiomer-coated poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate) core-shell nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Encapsulation of curcumin in alginate-chitosan-pluronic composite nanoparticles for delivery to cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.G. Nanoencapsulation of Red Ginseng Extracts Using Chitosan with Polyglutamic Acid or Fucoidan for Improving Antithrombotic Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4765–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, B.; Wydro, P.; Janczyk, A. Probing the Modes of Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan. Effects of pH and Molecular Weight on Chitosan Interactions with Membrane Lipids in Langmuir Films. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4144–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Hashemi, M.; Hosseini, S.M. Effect of chitosan molecular weight as micro and nanoparticles on antibacterial activity against some soft rot pathogenic bacteria. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.I.; Kim, H.J. Preparation of low molecular weight fucoidan by gamma-irradiation and its anticancer activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Lu, K.Y.; Mi, F.L. Synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial and anti-oxidant activity of small molecular chitosan–fucoidan conjugate nanoparticles. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4855–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.G.; Venkatesan, J.; Shim, M.S. Selective Anticancer Therapy Using Pro-Oxidant Drug-Loaded Chitosan-Fucoidan Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Singh, S.K.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.K.; Shim, M.S. Preparation, characterization and biological applications of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles with chitosan-fucoidan coating. Molecules 2018, 23, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Hoang, G.; Santha Moorthy, M.; Mondal, S.; Minh Doan, V.H.; Kim, H.; Vy Phan, T.T.; Nguyen, T.P.; Oh, J. Chitosan/fucoidan multilayer coating of gold nanorods as highly efficient near-infrared photothermal agents for cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Development of methotrexate loaded fucoidan/chitosan nanoparticles with anti-inflammatory potential and enhanced skin permeation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.C.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Ho, Y.C.; Mi, F.L. Development of mutlifunctional nanoparticles self-assembled from trimethyl chitosan and fucoidan for enhanced oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvaneswary, S.; Talebian, S.; Raghavendran, H.B.; Murali, M.R.; Mehrali, M.; Afifi, A.M.; Kasim, N.H.B.A.; Kamarul, T. Fabrication and in vitro biological activity of βTCP-Chitosan-Fucoidan composite for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, B.; Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Shim, M.S.; Kim, S.K. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-natural nano hydroxyapatite-fucoidan nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvaneswary, S.; Raghavendran, H.B.; Talebian, S.; Murali, M.R.; Mahmod, S.A.; Singh, S.; Kamarul, T. Incorporation of Fucoidan in β-Tricalcium phosphate-Chitosan scaffold prompts the differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells into osteogenic lineage. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ran, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Yu, S. Electrospinning of fucoidan/chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Y.; Huang, Y.C. Basic fibroblast growth factor released from fucoidan-modified chitosan/alginate scaffolds for promoting fibroblasts migration. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Lu, T.W.; Chen, C.H.; Mi, F.L. Development of genipin-crosslinked and fucoidan-adsorbed nano-hydroxyapatite/hydroxypropyl chitosan composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Nambu, M.; Ishizuka, T.; Hattori, H.; Kanatani, Y.; Takase, B.; Kishimoto, S.; Amano, Y.; Aoki, H.; Kiyosawa, T.; et al. Effect of controlled release of fibroblast growth factor-2 from chitosan/fucoidan micro complex-hydrogel on in vitro and in vivo vascularization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 85, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Cevher, E.; Hatipoǧlu, F.; Oǧurtan, Z.; Baş, A.L.; Akbuǧa, J. Preparation of fucoidan-chitosan hydrogel and its application as burn healing accelerator on rabbits. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Ishihara, M.; Aoki, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, S.I.; Yanagibayashi, S.; Takikawa, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Yokoe, H.; Kiyosawa, T.; et al. Enhanced healing of mitomycin C-treated healing-impaired wounds in rats with hydrosheets composed of chitin/chitosan, fucoidan, and alginate as wound dressings. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indest, T.; Laine, J.; Johansson, L.S.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Strnad, S.; Dworczak, R.; Ribitsch, V. Adsorption of fucoidan and chitosan sulfate on chitosan modified PET films monitored by QCM-D. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucard, N.; Viton, C.; Agay, D.; Mari, E.; Roger, T.; Chancerelle, Y.; Domard, A. The use of physical hydrogels of chitosan for skin regeneration following third-degree burns. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3478–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Mulloy, B.; Mourao, P.A.S. Structure and anticoagulant activity of sulfated fucans. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7656–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fucoidan Source | Biological Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| Anticancer | Anti-Inflammatory | |
| Cladosiphon okamuranus | [41,42] | [43] |
| Cladosiphon okamuranus Tokida | [44] | [45] |
| Costaria costata | [46] | [47] |
| Ecklonia cava | [46] | [48] |
| Eisenia bicyclis | [49] | [50] |
| Fucus evanescens | [51,52,53] | [54] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | [41,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] | [64,65,66,67] |
| Fucus sp. | [68] | [69] |
| Laminaria japonica | [70] | [66,67] |
| Macrocystis pyrifera | [71] | [66,67] |
| Sargassum sp. | [68] | [72] |
| Saccharina japonica | [73] | [74] |
| Turbinaria conoides | [75] | [76] |
| Undaria pinnatifida | [51,73,77] | [78] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, A.I.; Coutinho, A.J.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120654
Barbosa AI, Coutinho AJ, Costa Lima SA, Reis S. Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(12):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120654
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Ana Isabel, Ana Joyce Coutinho, Sofia A. Costa Lima, and Salette Reis. 2019. "Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field" Marine Drugs 17, no. 12: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120654
APA StyleBarbosa, A. I., Coutinho, A. J., Costa Lima, S. A., & Reis, S. (2019). Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field. Marine Drugs, 17(12), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120654